Targeting Brain Tumors with Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Experimental Model of the Orthotopic Glioblastoma in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation, In Vitro Culture
2.2. In Vitro Rat MSCs Labeling with SPIONs
2.3. In Vitro Assessment of Rat MSCs Glioma Tropism
2.3.1. Impedance-Based xCelligence System
2.3.2. High-Content Quantitative Image Cytometer CQ1
2.4. Animals
2.5. Model of Intracranial C6 Glioblastoma and Administration of the SPION-Labeled MSCs
2.6. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
2.7. Histological Analysis
2.8. In Vivo Analysis of the SPIONs-Labeled MSCs by NLR-M2
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
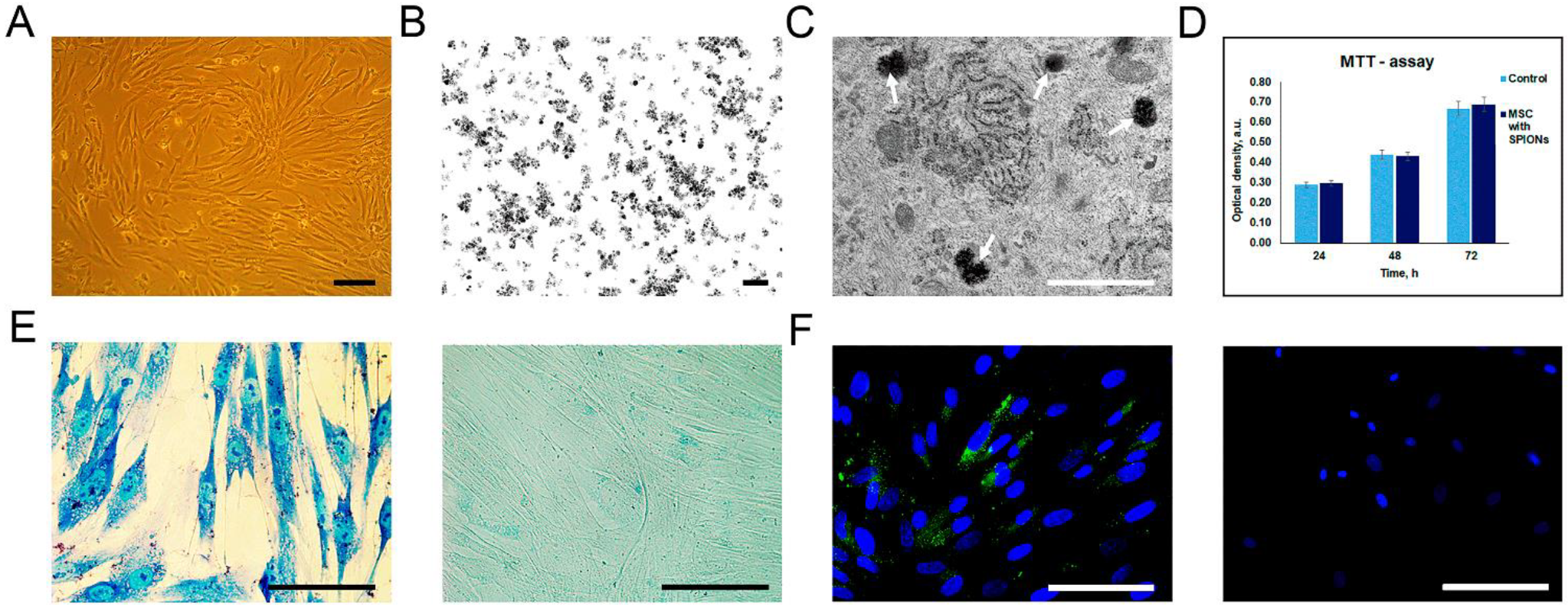
3.1. Detection of Cellular Internalization of Nanoparticles
3.2. Assessment of Rat MSCs Tropism to Glioma C6 Cells In Vitro
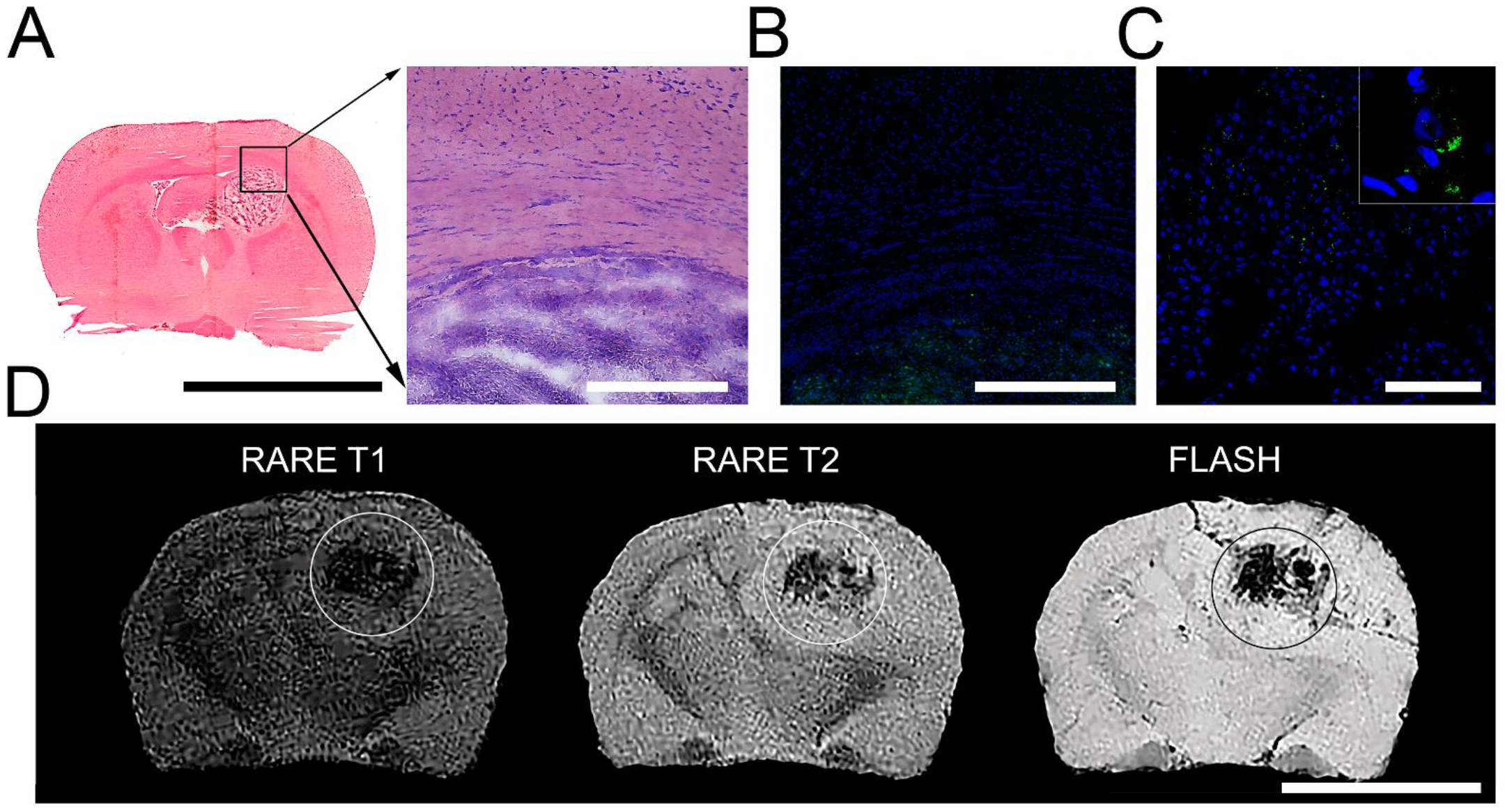
3.3. Detection of SPION-Labeled Rat MSCs
3.4. Biodistribution Analysis of SPIONs-Labeled Rat MSCs by NLR-M2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bagley, S.J.; Kothari, S.; Rahman, R.; Lee, E.Q.; Dunn, G.P.; Galanis, E.; Chang, S.M.; Nabors, L.B.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Stupp, R.; et al. Glioblastoma Clinical Trials: Current Landscape and Opportunities for Improvement. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Taillibert, S.; Kanner, A.A.; Read, W.; Steinberg, D.M.; Lhermitte, B.; Toms, S.; Idbaih, A.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Fink, K.; et al. Effect of Tumor-Treating Fields Plus Maintenance Temozolomide vs Maintenance Temozolomide Alone on Survival in Patients with Glioblastoma. JAMA 2017, 318, 2306–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Tao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Mediated Drug Delivery in Tumor-Targeted Therapy. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2020, 18, 864–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboody, K.S.; Brown, A.; Rainov, N.G.; Bower, K.A.; Liu, S.; Yang, W.; Small, J.E.; Herrlinger, U.; Ourednik, V.; Black, P.M.; et al. Neural stem cells display extensive tropism for pathology in adult brain: Evidence from intracranial gliomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12846–12851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovenberg, M.S.S.; Degeling, M.H.; Tannous, B.A. Advances in stem cell therapy against gliomas. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K. Stem cell-based therapies for tumors in the brain: Are we there yet? Neuro-Oncology 2016, 18, 1066–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Álvarez, B.; López-Vázquez, A.; López-Larrea, C. Mobilization and Homing of Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Stem Cell Transplant. 2012, 741, 152–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flier, J.S.; Underhill, L.H.; Dvorak, H.F. Tumors: Wounds That Do Not Heal. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 315, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prockop, D.J. The exciting prospects of new therapies with mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy 2016, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuckey, D.W.; Shah, K. Stem cell-based therapies for cancer treatment: Separating hope from hype. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhuang, X.; Lin, L.; Liangyu, L.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Hu, G.; Sun, Y. New horizons in tumor microenvironment biology: Challenges and opportunities. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.V.; Laux, P.; Luch, A.; Sudrik, C.; Wiehr, S.; Wild, A.-M.; Santomauro, G.; Bill, J.; Sitti, M. Review of emerging concepts in nanotoxicology: Opportunities and challenges for safer nanomaterial design. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2019, 29, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavreul, A.; Lautram, N.; Franconi, F.; Passirani, C.; Montero-Menei, C.; Menei, P.; Tetaud, C.; Montagu, A.; Laine, A.-L.; Vessieres, A. Targeting and treatment of glioblastomas with human mesenchymal stem cells carrying ferrociphenol lipid nanocapsules. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shevtsov, M.; Nikolaev, B.P.; Ryzhov, V.A.; Yakovleva, L.Y.; Dobrodumov, A.V.; Marchenko, Y.Y.; Margulis, B.A.; Pitkin, E.; Guzhova, I.V. Brain tumor magnetic targeting and biodistribution of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles linked with 70-kDa heat shock protein study by nonlinear longitudinal response. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 388, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, T.E.G.; Thorek, D.L.J.; Denmeade, S.R.; Isaacs, J.T.; Brennen, W.N. Concise Review: Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Drug Delivery: The Good, the Bad, the Ugly, and the Promise. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2018, 7, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, M.; Thompson, K.; Zafar, H.; Alexandrov, S.; Foley, M.; O’Flatharta, C.; Dockery, P. Functional imaging for regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudintceva, N.; Mikhailova, N.; Bobkov, D.; Yakovleva, L.; Nikolaev, B.; Krasavina, D.; Muraviov, A.; Vinogradova, T.; Yablonskiy, P.; Samusenko, I.; et al. Evaluation of the Biodistribution of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a Pre-clinical Renal Tuberculosis Model by Non-linear Magnetic Response Measurements. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevtsov, M.A.; Nikolaev, B.P.; Ryzhov, V.A.; Yakovleva, L.Y.; Marchenko, Y.Y.; Parr, M.A.; Rolich, V.I.; Mikhrina, A.L.; Dobrodumov, A.V.; Pitkin, E.; et al. Ionizing radiation improves glioma-specific targeting of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles conjugated with cmHsp70.1 monoclonal antibodies (SPION–cmHsp70.1). Nanoscale 2015, 7, 20652–20664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Nejadnik, H.; Daldrup-Link, H.E. Next-generation superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for cancer theranostics. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevtsov, M.; Stangl, S.; Nikolaev, B.; Yakovleva, L.; Marchenko, Y.; Tagaeva, R.; Sievert, W.; Pitkin, E.; Mazur, A.; Tolstoy, P.; et al. Granzyme B Functionalized Nanoparticles Targeting Membrane Hsp70-Positive Tumors for Multimodal Cancer Theranostics. Small 2019, 15, e1900205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhov, V.A.; Multhoff, G.; Shevtsov, M.A. Detection of Magnetosome-Like Structures in Eukaryotic Cells Using Nonlinear Longitudinal Response to ac Field. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2019, 50, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, G. Evaluation of isolation methods and culture conditions for rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Cytotechnology 2012, 65, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozhokin, M.S.; Vcherashnii, D.B.; Yastrebov, S.G.; Beilinson, L.L.; Zherebtsova, J.V.; Khotin, M.G. Low-intensity photobiomodulation at 632.8 nm increases tgfβ3, col2a1, and sox9 gene expression in rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Lasers Med. Sci. 2021, 146, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevtsov, M.A.; Komarova, E.Y.; Meshalkina, D.A.; Bychkova, N.V.; Aksenov, N.D.; Abkin, S.V.; Margulis, B.A.; Guzhova, I.V. Exogenously delivered heat shock protein 70 displaces its endogenous analogue and sensitizes cancer cells to lymphocytes-mediated cytotoxicity. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 3101–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagalievska, M.; Sabadashka, M.; Hachkova, H.; Sybirna, N. Galega officinalis extract regulate the diabetes mellitus related violations of proliferation, functions and apoptosis of leukocytes. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, P.T.; Wu, C.-C.; Chiang, Y.-H.; Hu, C.-J.; Chen, K.-Y. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell Therapy in Blood–Brain Barrier Preservation Following Ischemia: Molecular Mechanisms and Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjmand, B.; Abedi, M.; Arabi, M.; Alavi-Moghadam, S.; Rezaei-Tavirani, M.; Hadavandkhani, M.; Tayanloo-Beik, A.; Kordi, R.; Roudsari, P.P.; Larijani, B. Regenerative Medicine for the Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease; Status and Future Perspectives. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 704903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galderisi, U.; Peluso, G.; Di Bernardo, G. Clinical Trials Based on Mesenchymal Stromal Cells are Exponentially Increasing: Where are We in Recent Years? Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Wang, L.; Zou, X.; Huang, S. Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Regenerative Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Opportunities and Challenges. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 3927–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanshahi, G.; Roohi, M.A.; Esmaeili, S.-A.; Pourghadamyari, H.; Nosratabadi, R. Involvement of various chemokine/chemokine receptor axes in trafficking and oriented locomotion of mesenchymal stem cells in multiple sclerosis patients. Cytokine 2021, 148, 155706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, O.Y.-J.; Chen, Y.-F.; Xu, H.-T.; Lee, C.-W. The Efficacy of Naïve versus Modified Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Improving Muscle Function in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: A Systematic Review. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razeghian, E.; Margiana, R.; Chupradit, S.; Bokov, D.O.; Abdelbasset, W.K.; Marofi, F.; Shariatzadeh, S.; Tosan, F.; Jarahian, M. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells as a Vehicle for Cytokine Delivery: An Emerging Approach for Tumor Immunotherapy. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W.-Z.; Lin, Y.-H.; Su, L.-J.; Wu, M.-S.; Jeng, H.-Y.; Chang, H.-C.; Huang, Y.-H.; Ling, T.-Y. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-based therapy: Mechanism, systemic safety and biodistribution for precision clinical applications. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-H.; Fan, W.-S.; Wang, M.-M.; Wang, Y.-H.; Ren, Z.-G. Effects of mesenchymal stem cells on solid tumor metastasis in experimental cancer models: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, B.; Ahmadi-Zeidabadi, M.; Dini, L.; Vergallo, C. Stem cell-based therapy treating glioblastoma multiform. Hematol. Stem Cell Ther. 2020, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Gumin, J.; Gao, F.; Hossain, A.; Shpall, E.J.; Kondo, A.; Kerrigan, B.C.P.; Yang, J.; Ledbetter, D.; Fueyo, J.; et al. Characterization of patient-derived bone marrow human mesenchymal stem cells as oncolytic virus carriers for the treatment of glioblastoma. J. Neurosurg. 2021, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Xia, Q.; Muhammad, T.; Liu, L.; Meng, X.; Bars-Cortina, D.; Khan, A.A.; Huang, Y.; Dong, L. Glioblastoma Therapy: Rationale for a Mesenchymal Stem Cell-based Vehicle to Carry Recombinant Viruses. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaei, A.; Soleimanjahi, H.; Soleimani, M.; Arefian, E. Mesenchymal stem cells loaded with oncolytic reovirus enhances antitumor activity in mice models of colorectal cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 190, 114644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyed-Khorrami, S.-M.; Soleimanjahi, H.; Soudi, S.; Habibian, A. MSCs loaded with oncolytic reovirus: Migration and in vivo virus delivery potential for evaluating anti-cancer effect in tumor-bearing C57BL/6 mice. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavon, L.F.; Sibov, T.T.; De Souza, A.V.; da Cruz, E.F.; Malheiros, S.M.F.; Cabral, F.R.; De Souza, J.G.; Boufleur, P.; Oliveira, D.; De Toledo, S.R.C.; et al. Tropism of mesenchymal stem cell toward CD133+ stem cell of glioblastoma in vitro and promote tumor proliferation in vivo. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kharboosh, R.; ReFaey, K.; Lara-Velazquez, M.; Grewal, S.S.; Imitola, J.; Quiñones-Hinojosa, A. Inflammatory Mediators in Glioma Microenvironment Play a Dual Role in Gliomagenesis and Mesenchymal Stem Cell Homing: Implication for Cellular Therapy. Mayo Clin. Proc. Innov. Qual. Outcomes 2020, 4, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Xiang, W.; Tian, J.; Wang, H.; Hu, S.; Wang, K.; Chen, L.; Huang, C.; Zhou, J. Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Differentially Affect Glioblastoma Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion: A 2D-DIGE Proteomic Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, J.; Huang, S.; Li, Y.; Sheng, F.; Yu, S.; Yu, S.; Liu, X. Mesenchymal stem cells show little tropism for the resting and differentiated cancer stem cell-like glioma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mishra, P.J.; Mishra, P.J.; Humeniuk, R.; Medina, D.J.; Alexe, G.; Mesirov, J.P.; Ganesan, S.; Glod, J.W.; Banerjee, D. Carcinoma-Associated Fibroblast–Like Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4331–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoto, K.; Ito, K.; Aoki, S. Complex formation between platelet-derived growth factor receptor β and transforming growth factor β receptor regulates the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into cancer-associated fibroblasts. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 34090–34102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jotzu, C.; Alt, E.; Welte, G.; Li, J.; Hennessy, B.T.; Devarajan, E.; Krishnappa, S.; Pinilla, S.; Droll, L.; Song, Y.-H. Adipose tissue derived stem cells differentiate into carcinoma-associated fibroblast-like cells under the influence of tumor derived factors. Cell. Oncol. 2011, 34, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcellos-De-Souza, P.; Comito, G.; Pons-Segura, C.; Taddei, M.L.; Gori, V.; Becherucci, V.; Bambi, F.; Margheri, F.; Laurenzana, A.; Del Rosso, M.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells are Recruited and Activated into Carcinoma-Associated Fibroblasts by Prostate Cancer Microenvironment-Derived TGF-β1. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 2536–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapproth, A.P.; Shevtsov, M.; Stangl, S.; Li, W.B.; Multhoff, G. A New Pharmacokinetic Model Describing the Biodistribution of Intravenously and Intratumorally Administered Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (SPIONs) in a GL261 Xenograft Glioblastoma Model. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 4677–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheets, K.T.; Bago, J.R.; Hingtgen, S.D. Delivery of Cytotoxic Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Biodegradable Scaffolds for Treatment of Postoperative Brain Cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1831, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliperta, R.; Welzel, P.B.; Bergmann, R.; Freudenberg, U.; Berndt, N.; Feldmann, A.; Arndt, C.; Koristka, S.; Stanzione, M.; Cartellieri, M.; et al. Cryogel-supported stem cell factory for customized sustained release of bispecific antibodies for cancer immunotherapy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep42855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.; Oudin, A.; Tiemann, K.; Bernard, A.; Golebiewska, A.; Keunen, O.; Fack, F.; Stieber, D.; Wang, B.; Hedman, H.; et al. The soluble form of the tumor suppressor Lrig1 potently inhibits in vivo glioma growth irrespective of EGF receptor status. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 1200–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



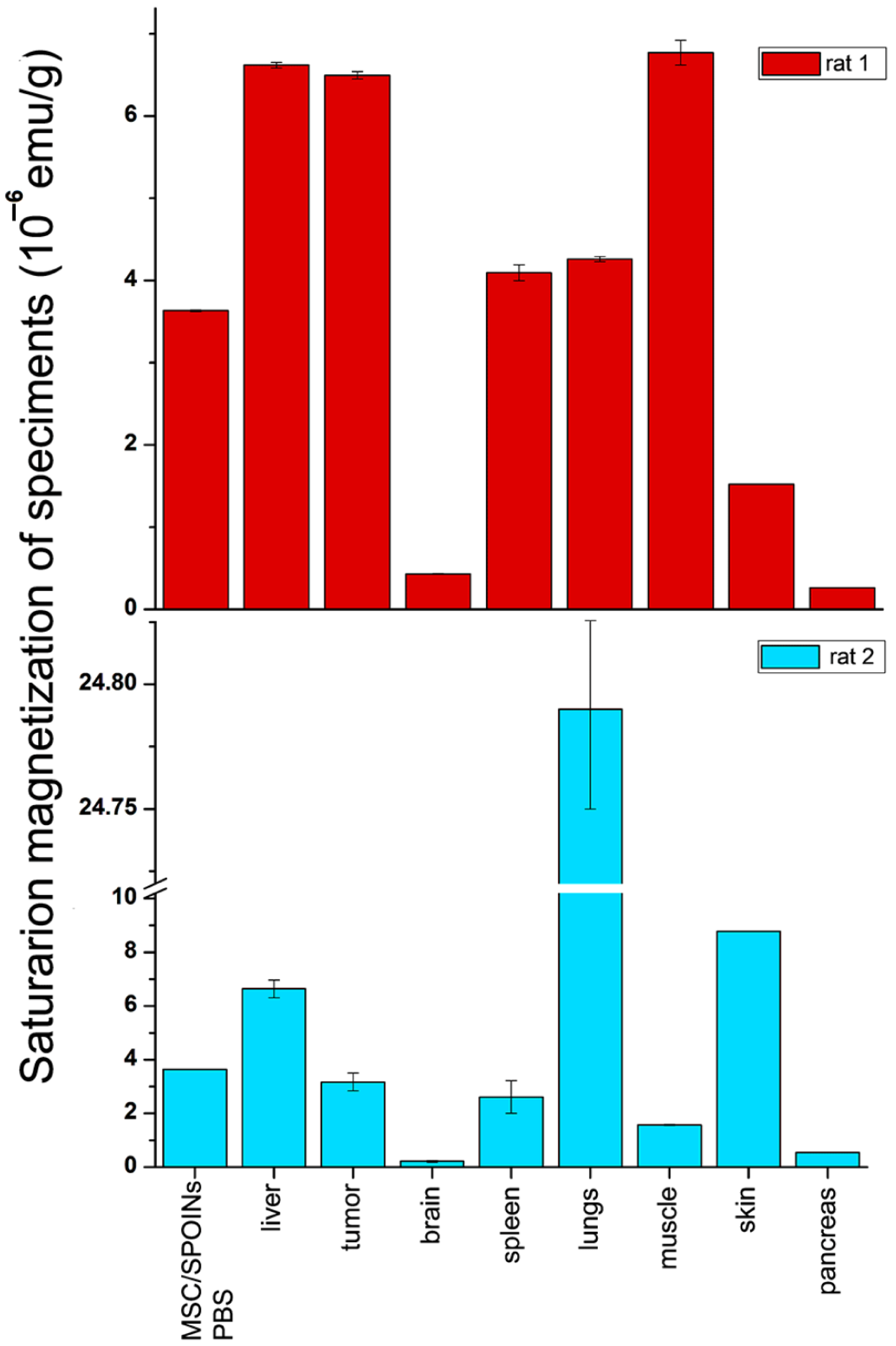
| Organ | , emu/g | NP, g−1 | NMSC, g−1 | MC, μB | σ | α | τN, ns | EA, K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSC-SPIONs in PBS | 3.633(5) × 10−6 | 1.24(4) × 1010 | 1.5 × 105 | 31,580(30) | 0.734(1) | 0.2057(6) | 1.020(3) | 8.3(1.0) |
| Tumor (rat 1) | 6.495(45) × 10−6 | 2.65(8) × 1010 | 3.2 × 105 | 26,400(100) | 0.485(5) | 0.287 (9) | 0.651(21) | 0(15) |
| Brain (rat 1) | 4.303(57) × 10−7 | 1.18(2) × 109 | 1.4 × 104 | 39,400(300) | 0.241(17) | 0.207 (8) | 1.29(5) | 0(29) |
| Lungs (rat 1) | 4.26(3) × 10−6 | 1.74(5) × 1010 | 2.1 × 105 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Spleen (rat 1) | 4.093(96) × 10−6 | 1.578(51) × 1010 | 1.9 × 105 | 28,000(600) | 0.758(8) | 0.2374(13) | 0.810(18) | 17.4(9) |
| Muscle (rat 1) | 6.77(15) × 10−6 | 2.85(47) × 1010 | 3.4 × 105 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Liver (rat 1) | 6.618(33) × 10−6 | 3.24(24) × 1010 | 3.9 × 105 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Skin (rat 1) | ~1.52 × 10−6 | ~4.17 × 109 | ~5.0 × 104 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Pancreas (rat 1) | ~2.64 × 10−7 | ~0.72(9) × 109 | ~8.7 × 103 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Tumor (rat 2) | 3.17(33) × 10−6 | 1.29(20) × 1010 | 1.6 × 105 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Brain (rat 2) | 2.17(3) × 10−7 | 0.59(2) × 109 | 7.1 × 103 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Lungs (rat 2) | 2.479(57) × 10−5 | 1.01(3) × 1011 | 1.2 × 106 | 26,700(600) | 0.786(8) | 0.2421(12) | 0.759(17) | 13.3(1.2) |
| Spleen (rat 2) | 2.61(61) × 10−6 | 1.01(32) × 1010 | 1.2 × 105 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Muscle (rat 2) | 1.572(23) × 10−6 | 0.662(11) × 1010 | 8.0 × 104 | 25,700(0) | 0.283(0) | 1.036 (0) | 0.332(0) | 8.22(0) |
| Liver (rat 2) | 6.64(33) × 10−6 | 3.48(24) × 1010 | 4.2 × 105 | 20,600(1000) | 0.862(15) | 0.291 (2) | 0.502(24) | 0(12) |
| Skin (rat 2) | ~8.78 × 10−6 | ~2.41 × 1010 | ~2.9 × 105 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Pancreas (rat 2) | ~5.44×10−7 | ~1.49 × 109 | ~1.8 × 104 | - | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yudintceva, N.; Lomert, E.; Mikhailova, N.; Tolkunova, E.; Agadzhanian, N.; Samochernych, K.; Multhoff, G.; Timin, G.; Ryzhov, V.; Deriglazov, V.; et al. Targeting Brain Tumors with Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Experimental Model of the Orthotopic Glioblastoma in Rats. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111592
Yudintceva N, Lomert E, Mikhailova N, Tolkunova E, Agadzhanian N, Samochernych K, Multhoff G, Timin G, Ryzhov V, Deriglazov V, et al. Targeting Brain Tumors with Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Experimental Model of the Orthotopic Glioblastoma in Rats. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(11):1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111592
Chicago/Turabian StyleYudintceva, Natalia, Ekaterina Lomert, Natalia Mikhailova, Elena Tolkunova, Nikol Agadzhanian, Konstantin Samochernych, Gabriele Multhoff, Grigoriy Timin, Vyacheslav Ryzhov, Vladimir Deriglazov, and et al. 2021. "Targeting Brain Tumors with Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Experimental Model of the Orthotopic Glioblastoma in Rats" Biomedicines 9, no. 11: 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111592
APA StyleYudintceva, N., Lomert, E., Mikhailova, N., Tolkunova, E., Agadzhanian, N., Samochernych, K., Multhoff, G., Timin, G., Ryzhov, V., Deriglazov, V., Mazur, A., & Shevtsov, M. (2021). Targeting Brain Tumors with Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Experimental Model of the Orthotopic Glioblastoma in Rats. Biomedicines, 9(11), 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111592









