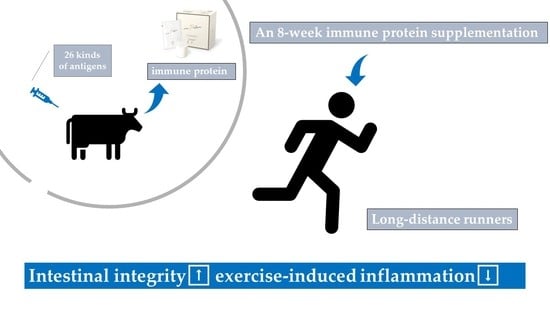
Effects of an 8-Week Protein Supplementation Regimen with Hyperimmunized Cow Milk on Exercise-Induced Organ Damage and Inflammation in Male Runners: A Randomized, Placebo Controlled, Cross-Over Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Immune Protein Supplementation
2.4. Experimental Protocol
2.5. Urine Sampling and Analysis
2.6. Assays for Urine Biochemistry, Inflammatory Substances, and Organ Damage Markers
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
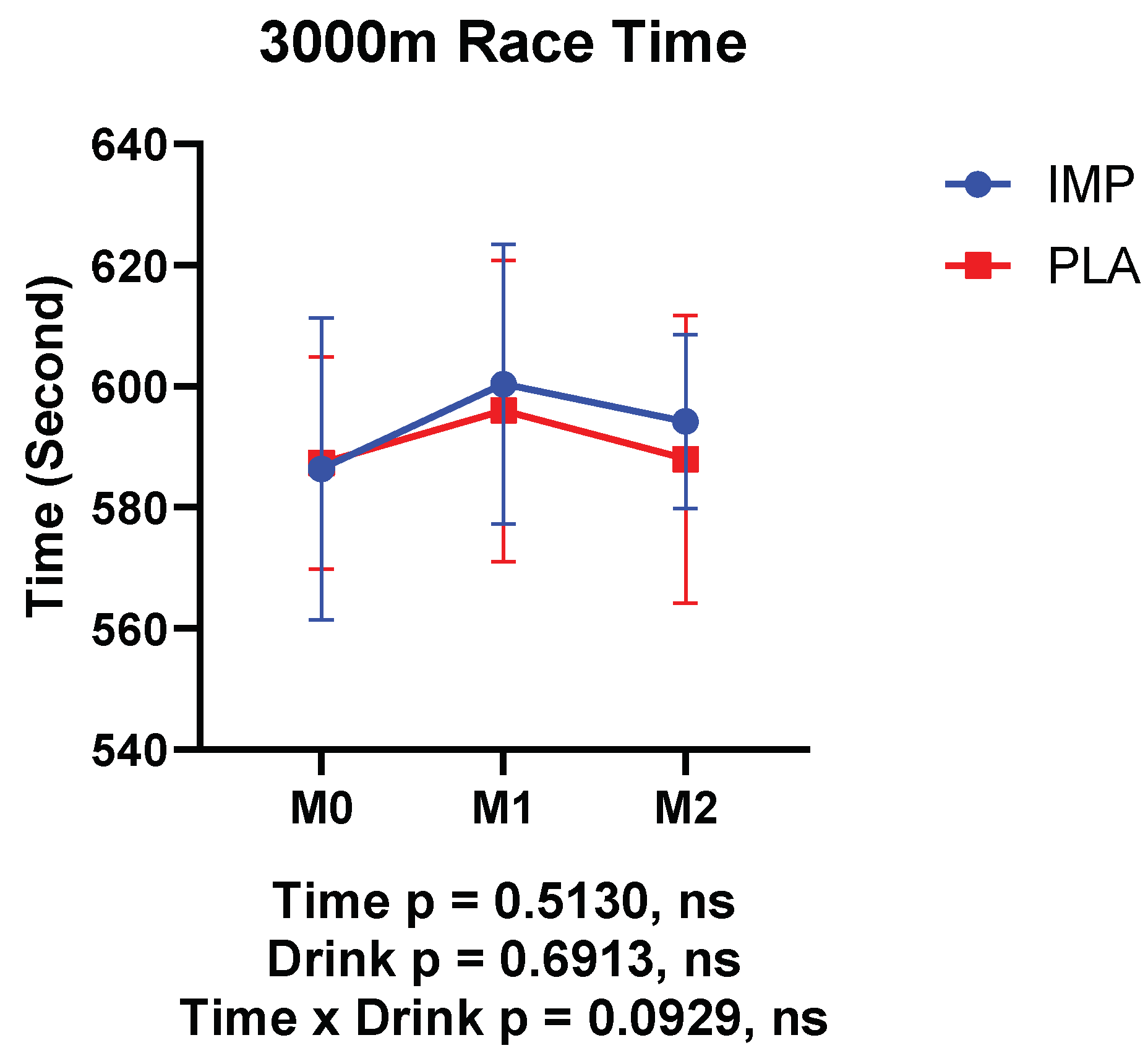
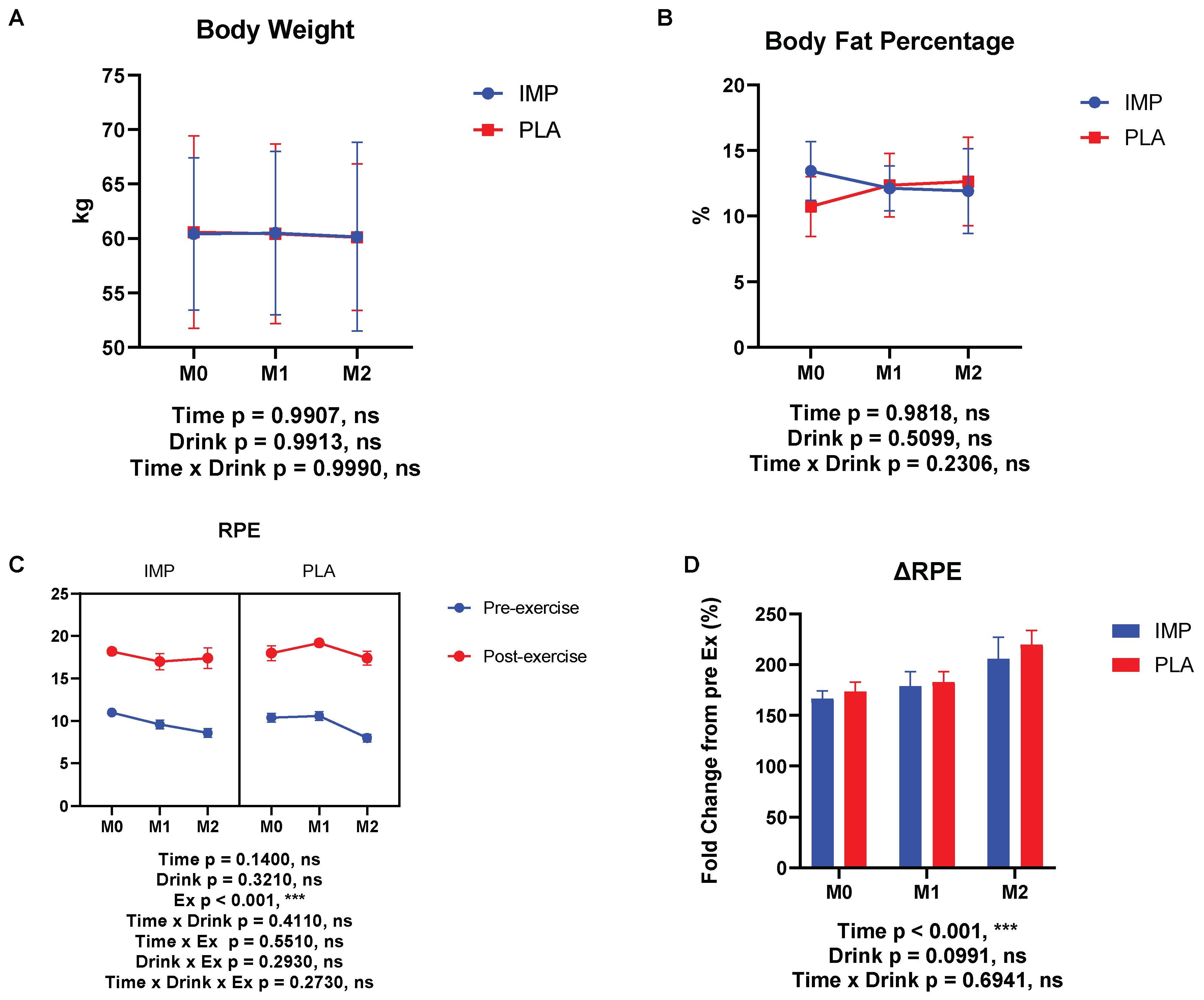
3.1. Body Composition, RPE, and 3000 m Time Trial Results
3.2. Renal Function Markers
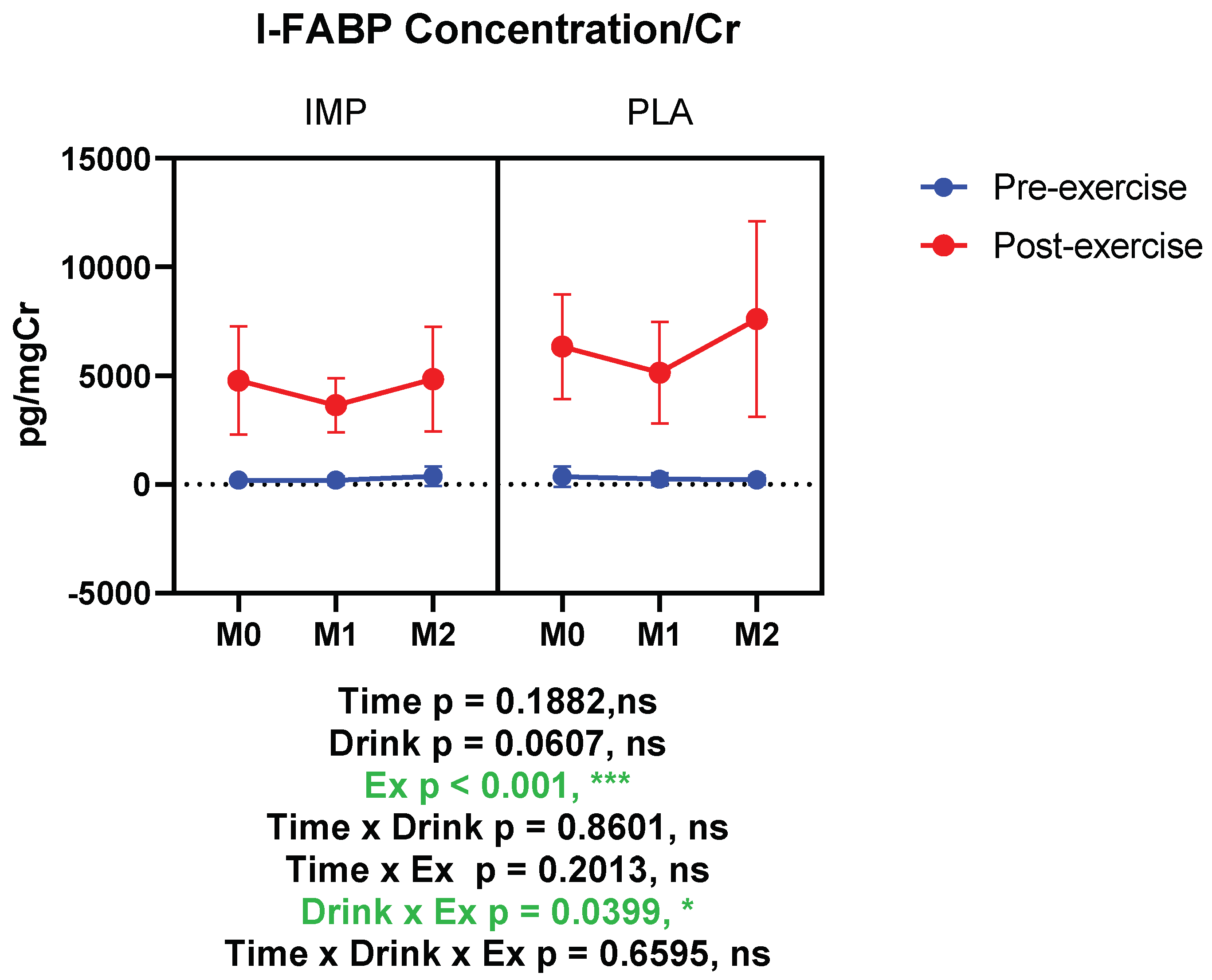
3.3. Intestine Damage Marker
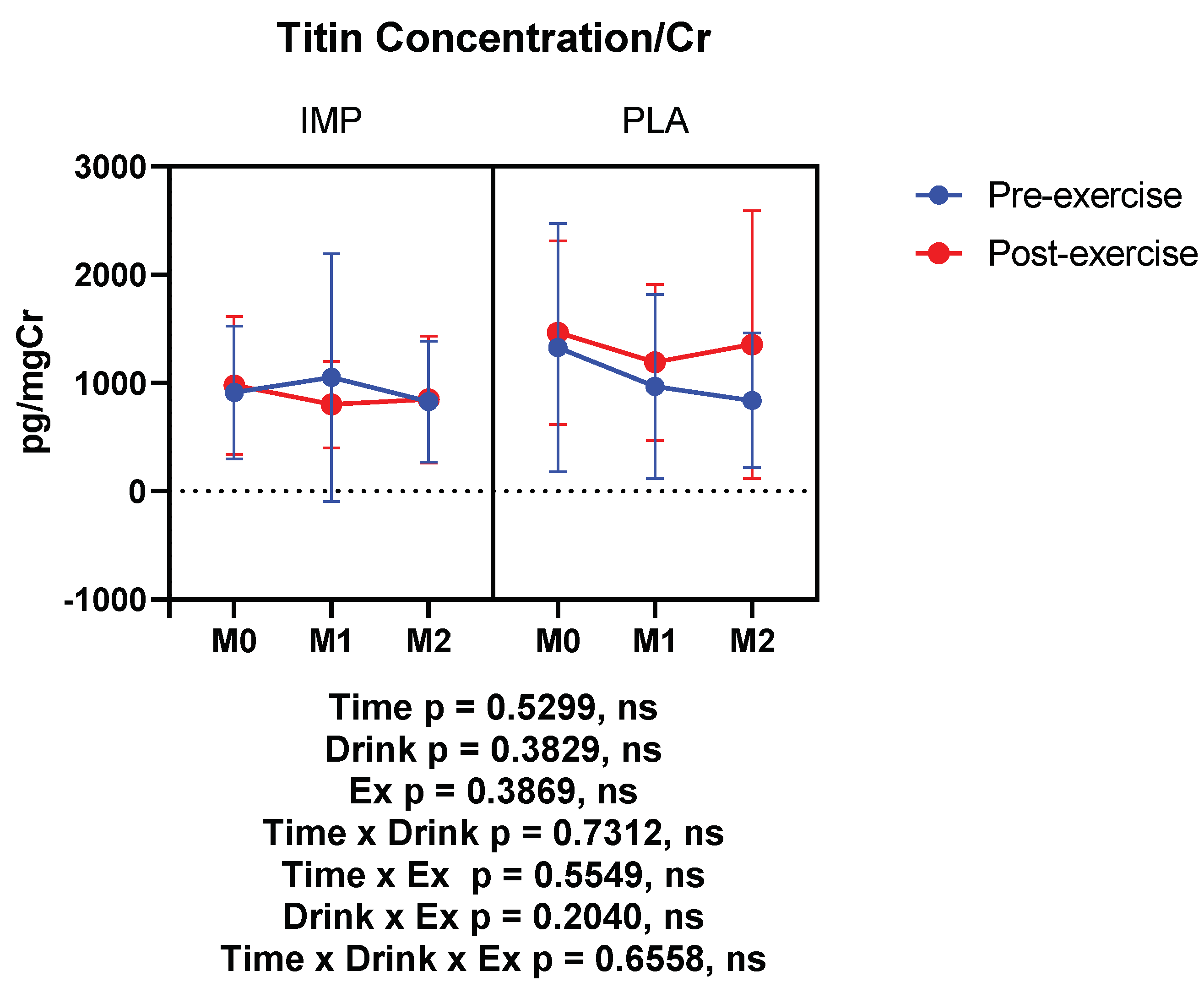
3.4. Muscle Damage Marker
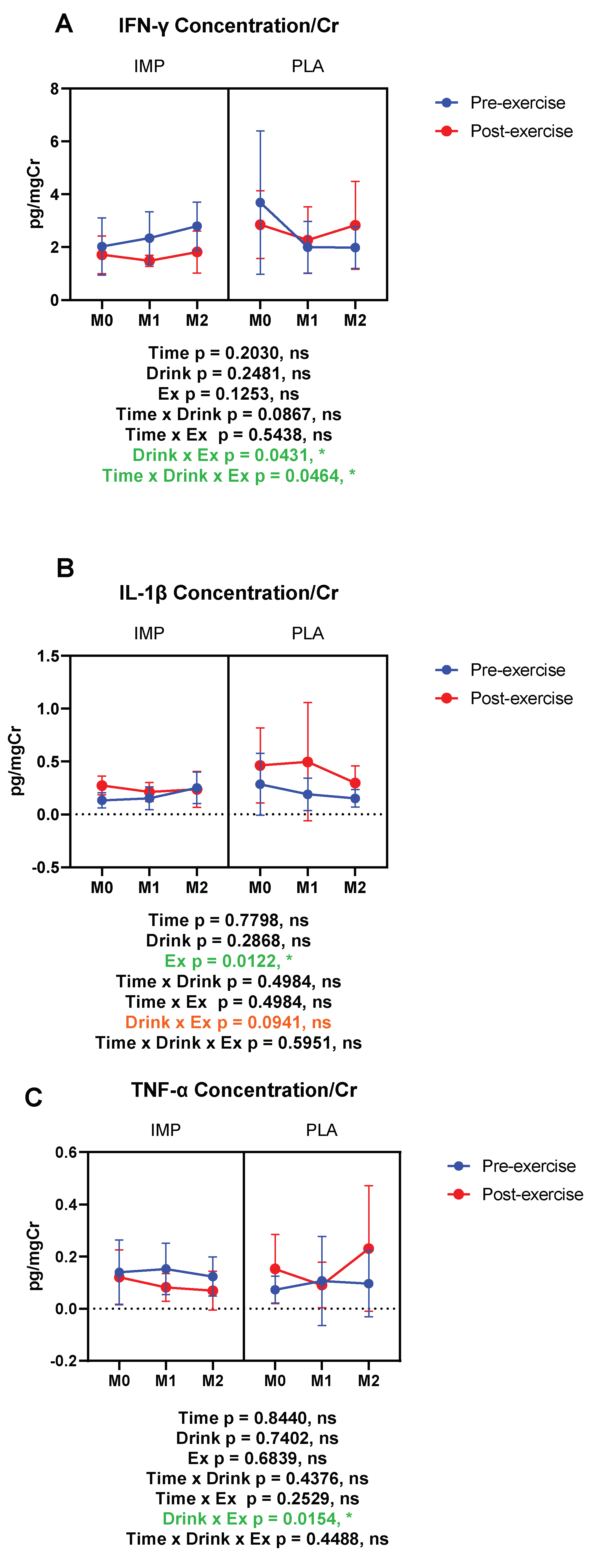
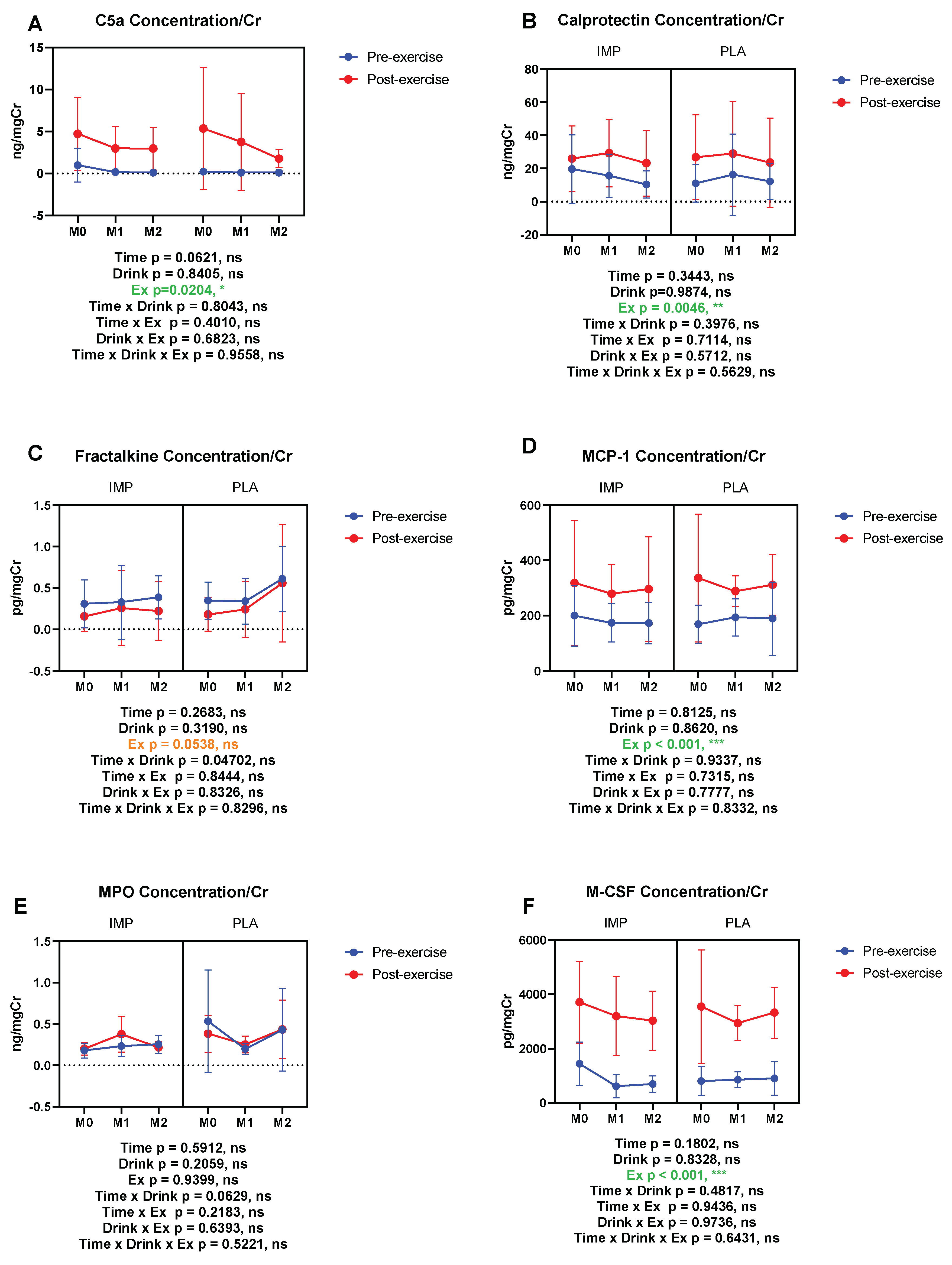
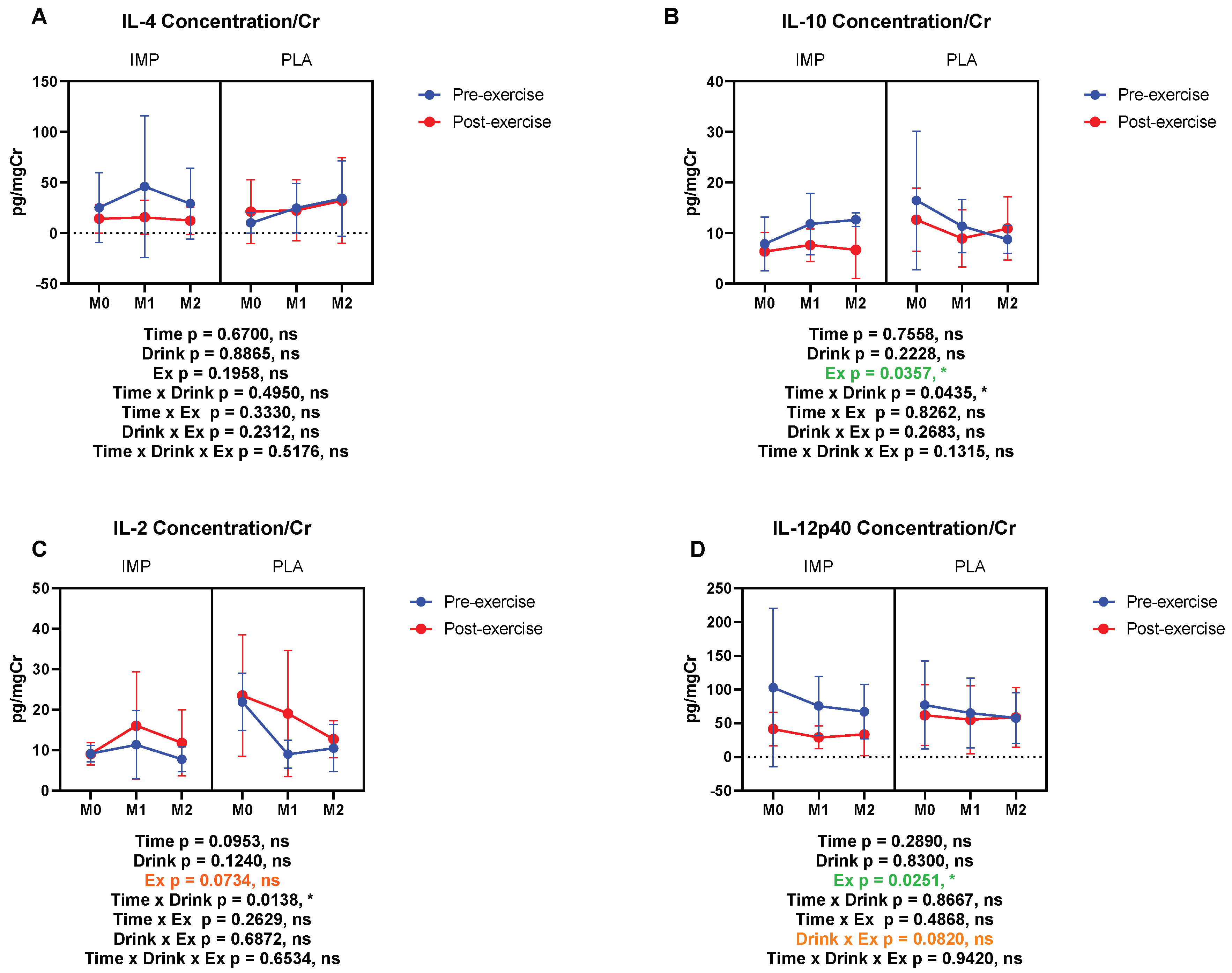
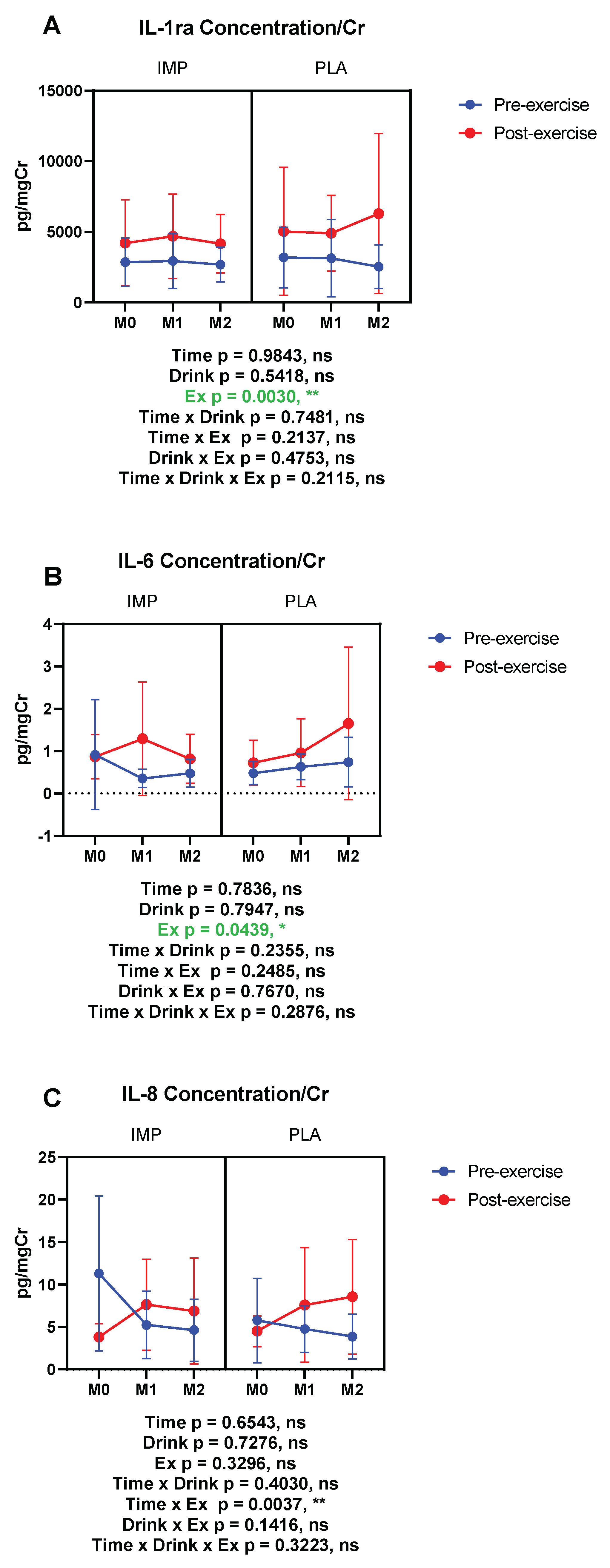
3.5. Inflammatory Substance Profile
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suzuki, K. Chronic Inflammation as an Immunological Abnormality and Effectiveness of Exercise. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K. Cytokine Response to Exercise and Its Modulation. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, J.; Lim, C.L.; Suzuki, K. Effects of Endurance-, Strength-, and Concurrent Training on Cytokines and Inflammation. In Concurrent Aerobic and Strength Training: Scientific Basics and Practical Applications; Schumann, M., Rønnestad, B.R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 125–138. ISBN 978-3-319-75547-2. [Google Scholar]
- van Wijck, K.; Lenaerts, K.; van Loon, L.J.C.; Peters, W.H.M.; Buurman, W.A.; Dejong, C.H.C. Exercise-Induced Splanchnic Hypoperfusion Results in Gut Dysfunction in Healthy Men. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lis, D.; Ahuja, K.D.; Stellingwerff, T.; Kitic, C.M.; Fell, J. Case study: Utilizing a low FODMAP diet to combat exercise-induced gastrointestinal symptoms. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2016, 26, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, R.J.S.; Snipe, R.M.J.; Kitic, C.M.; Gibson, P.R. Systematic review: Exercise-induced gastrointestinal syndrome—Implications for health and intestinal disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 46, 246–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, T.; Suzuki, K.; Takahashi, M.; Tomari, M.; Hara, R.; Gando, Y.; Muraoka, I. Involvement of Neutrophil Dynamics and Function in Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage and Delayed-Onset Muscle Soreness: Effect of Hydrogen Bath. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Suzuki, K. Keto-Adaptation and Endurance Exercise Capacity, Fatigue Recovery, and Exercise-Induced Muscle and Organ Damage Prevention: A Narrative Review. Sports 2019, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peake, J.; Suzuki, K. Neutrophil activation, antioxidant supplements and exercise-induced oxidative stress. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 10, 129–141. [Google Scholar]
- Peake, J.; Neubauer, O.; Walsh, N.P.; Simpson, R.J. Recovery of the immune system after exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 122, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.P.; Turner, J.E. Debunking the Myth of Exercise-Induced Immune Suppression: Redefining the Impact of Exercise on Immunological Health Across the Lifespan. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuhara, D.; Kurashima, Y.; Kamioka, M.; Nakayama, T.; Ernst, P.; Kiyono, H. A comprehensive understanding of the gut mucosal immune system in allergic inflammation. Allergol. Int. 2019, 68, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Zhang, J. Role of intestinal microbiota and metabolites on gut homeostasis and human diseases. BMC Immunol. 2017, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, A.E.; Maughan, R.J.; Whiting, P.H. Effects of ibuprofen on exercise-induced muscle soreness and indices of muscle damage. Br. J. Sports Med. 1990, 24, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, G.P.; Boylan, M.; Laventure, J.P.; Bull, A.; Lanspa, S. Effect of aspirin and ibuprofen on GI permeability during exercise. Int. J. Sports Med. 2007, 28, 722–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunser, O.; Espinoza, J.; Figueroa, G.; Araya, M.; Spencer, E.; Hilpert, H.; Link-Amster, H.; Brüssow, H. Field trial of an infant formula containing anti-rotavirus and anti-Escherichia coli milk antibodies from hyperimmunized cows. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1992, 15, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormrod, D.J.; Miller, T.E. Milk from hyperimmunized dairy cows as a source of a novel biological response modifier. Agents Actions 1993, 38, C146–C149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordle, C.T.; Duska-McEwen, G.; Janas, L.M.; Malone, W.T.; Hirsch, M.A. Evaluation of the immunogenicity of protein hydrolysate formulas using laboratory animal hyperimmunization. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 1994, 5, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenblatt, H.C.; Adalsteinsson, O.; Brodie, D.A.; Fitzpatrick-McElligott, S.G. Method of Preventing, Countering, or Reducing NSAID-Induced Gastrointestinal Damage by Administering Milk or Egg Products from Hyperimmunized Animals 1998. U.S. Patent No. 5,772,999, 30 June 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kisic, J.A.; Shipp, T.E. Combination of Plasma and Hyperimmunized Products for Increased Performance 2003. U.S. Patent No. 6,569,447, 27 May 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, L.; Yin, C.; Othtani, S.; Aoyama, K.; Lu, C.; Sun, X.; Yoshikai, Y. Oral administration of bovine milk from cows hyperimmunized with intestinal bacterin stimulates lamina propria T lymphocytes to produce Th1-biased cytokines in mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 5458–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, A.; Yoshikai, Y.; Murosaki, S.; Hidaka, Y.; Nomoto, K. Administration of milk from cows immunized with intestinal bacteria protects mice from radiation-induced lethality. Biotherapy 1992, 5, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Ohmori, T.; Yanai, M.; Kawanishi, G.; Yoshikai, Y.; Nomoto, K. Protective Effect of Orally Administering Immune Milk on Endogenous Infection in X-Irradiated Mice. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1991, 55, 2265–2272. [Google Scholar]
- Kravets, S.; Kravets, A.; Jacobson, M. Medical Food Composition and Methods Management of Inflammatory Processes in Mammals 2011. U.S. Patent Application No. 12,885,530, 11 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, W.E.; Nickerson, S.C. Evaluation of an Anti-Inflammatory Factor Derived from Hyperimmunized Cows. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1989, 190, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayer, R.; Andrews, C.; Ungar, B.L.P.; Blagburn, B. Efficacy of hyperimmune bovine colostrum for prophylaxis of cryptosporidiosis in neonatal calves. J. Parasitol. 1989, 75, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, L.H.; Wu, C.H.; Lin, B.F.; Hwang, L.S. Hyperimmune colostrum alleviates rheumatoid arthritis in a collagen-induced arthritis murine model. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3778–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bähr, M.; Fechner, A.; Krämer, J.; Kiehntopf, M.; Jahreis, G. Lupin protein positively affects plasma LDL cholesterol and LDL: HDL cholesterol ratio in hypercholesterolemic adults after four weeks of supplementation: A randomized, controlled crossover study. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, D.J.; Kendall, C.W.; Garsetti, M.; Rosenberg-Zand, R.S.; Jackson, C.J.; Agarwal, S.; Rao, A.V.; Diamandis, E.P.; Parker, T.; Faulkner, D.; et al. Effect of soy protein foods on low-density lipoprotein oxidation and ex vivo sex hormone receptor activity—A controlled crossover trial. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2000, 49, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, L.A.; Lipscomb, E.R.; Cadogan, J.; Martin, B.; Wastney, M.E.; Peacock, M.; Weaver, C.M. The effect of soy protein and soy isoflavones on calcium metabolism in postmenopausal women: A randomized crossover study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, K.; Sakuma, J.; Akimoto, T.; Kawakami, Y.; Suzuki, K. Detection of titin fragments in urine in response to exercise-induced muscle damage. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.G.; Buchner, A. G*power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinert, R.; Kohl, L.; Rainone, T.; Scalea, T. Exercise-Induced Rhabdomyolysis. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1994, 23, 1301–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yada, K.; Suzuki, K.; Oginome, N.; Ma, S.; Fukuda, Y.; Iida, A.; Radak, Z. Single Dose Administration of Taheebo Polyphenol Enhances Endurance Capacity in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konrad, M.; Nieman, D.C.; Henson, D.A.; Kennerly, K.M.; Jin, F.; Wallner-Liebmann, S.J. The Acute Effect of Ingesting a Quercetin-Based Supplement on Exercise-Induced Inflammation and Immune Changes in Runners. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2011, 21, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Suzuki, K. Toll-like Receptor 4: Target of Lipotoxicity and Exercise-Induced Anti-inflammatory Effect? Annu. Nutr. Food Sci. 2018, 2, 1027. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Huang, Q.; Yada, K.; Liu, C.; Suzuki, K. An 8-Week Ketogenic Low Carbohydrate, High Fat Diet Enhanced Exhaustive Exercise Capacity in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegenfuss, T.N.; Kerksick, C.M.; Kedia, A.W.; Sandrock, J.; Raub, B.; Lopez, H.L. Proprietary Milk Protein Concentrate Reduces Joint Discomfort While Improving Exercise Performance in Non-Osteoarthritic Individuals. Nutrients 2019, 11, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, J.N.; Impey, S.G.; Doran, D.A.; Fleming, S.C.; Morton, J.P.; Close, G.L. Acute high-intensity interval running increases markers of gastrointestinal damage and permeability but not gastrointestinal symptoms. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 42, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.L.; Suzuki, K. Systemic inflammation mediates the effects of endotoxemia in the mechanisms of heat stroke. Biol. Med. 2017, 9, 376–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, G.P.; Broussard, L.J.; Mason, B.L.; Mauermann, W.J.; Gisolfi, C.V. Gastrointestinal permeability during exercise: Effects of aspirin and energy-containing beverages. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 90, 2075–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuhl, M.; Dokladny, K.; Mermier, C.; Schneider, S.; Salgado, R.; Moseley, P. The effects of acute oral glutamine supplementation on exercise-induced gastrointestinal permeability and heat shock protein expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Cell Stress Chaperones 2015, 20, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchbank, T.; Limdi, J.K.; Mahmood, A.; Elia, G.; Playford, R.J. Clinical trial: Protective effect of a commercial fish protein hydrolysate against indomethacin (NSAID)-induced small intestinal injury. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 28, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shing, C.M.; Peake, J.M.; Lim, C.L.; Briskey, D.; Walsh, N.P.; Fortes, M.B.; Ahuja, K.D.K.; Vitetta, L. Effects of probiotics supplementation on gastrointestinal permeability, inflammation and exercise performance in the heat. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 114, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, S.A.; Casswall, T.H.; Juneja, L.R.; Hoq, E.; Hossain, I.; Fuchs, G.J.; Hammarström, L. Randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial of hyperimmunized chicken egg yolk immunoglobulin in children with rotavirus diarrhea. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2001, 32, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K. Inflammatory responses to exercise and its prevention. Curr. Top. Biochem. Res. 2018, 19, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sugama, K.; Suzuki, K.; Yoshitani, K.; Shiraishi, K.; Kometani, T. Urinary excretion of cytokines versus their plasma levels after endurance exercise. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 19, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sugama, K.; Suzuki, K.; Yoshitani, K.; Shiraishi, K.; Kometani, T. IL-17, neutrophil activation and muscle damage following endurance exercise. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 18, 116–127. [Google Scholar]
- Sugama, K.; Suzuki, K.; Yoshitani, K.; Shiraishi, K.; Miura, S.; Yoshioka, H.; Mori, Y.; Kometani, T. Changes of thioredoxin, oxidative stress markers, inflammation and muscle/renal damage following intensive endurance exercise. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 21, 130–142. [Google Scholar]
- Peake, J.; Della Gatta, P.; Suzuki, K.; Nieman, D. Cytokine expression and secretion by skeletal muscle cells: Regulatory mechanisms and exercise effects. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 21, 8–25. [Google Scholar]
- Okhuysen, P.C.; Chappell, C.L.; Crabb, J.; Valdez, L.M.; Douglass, E.T.; DuPont, H.L. Prophylactic Effect of Bovine Anti-Cryptosporidium Hyperimmune Colostrum Immunoglobulin in Healthy Volunteers Challenged with Cryptosporidium parvum. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 26, 1324–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shing, C.M.; Peake, J.M.; Suzuki, K.; Jenkins, D.G.; Coombes, J.S. Bovine Colostrum Modulates Cytokine Production in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Stimulated with Lipopolysaccharide and Phytohemagglutinin. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009, 29, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shing, C.M.; Peake, J.M.; Suzuki, K.; Okutsu, M.; Pereira, R.; Stevenson, L.; Jenkins, D.G.; Coombes, J. Effects of bovine colostrum supplementation on immune variables in highly trained cyclists. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 102, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, G.; Marchbank, T.; March, D.S.; Thatcher, R.; Playford, R.J. Zinc carnosine works with bovine colostrum in truncating heavy exercise–induced increase in gut permeability in healthy volunteers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Playford, R.J.; Macdonald, C.E.; Calnan, D.P.; Floyd, D.N.; Podas, T.; Johnson, W.; Wicks, A.C.; Bashir, O.; Marchbank, T. Co-administration of the health food supplement, bovine colostrum, reduces the acute non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced increase in intestinal permeability. Clin. Sci. 2001, 100, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, M.J.; Cheon, J.H.; Kim, S.W.; Park, J.J.; Moon, C.M.; Han, S.Y.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, T.I.; Kim, W.H. Bovine colostrum inhibits nuclear factor κB–mediated proinflammatory cytokine expression in intestinal epithelial cells. Nutr. Res. 2009, 29, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, R.; Angolkar, T.; Kaur, G.; S Buttar, H. Antibacterial and Anti-inflammatory Properties of Bovine Colostrum. Recent Pat. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Discov. 2016, 10, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Name | Trial | M0 | M1 | M2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMP | PLA | IMP | PLA | IMP | PLA | ||
|
NAG> (IU/L) | Pre Post | 2.729 ± 1.438 8.543 ± 2.540 | 1.714 ± 1.182 7.257 ± 4.712 | 2.729 ± 0.991 10.457 ± 5.369 | 2.943 ± 1.258 5.629 ± 1.847 | 2.500 ± 1.956 11.971 ± 8.136 | 2.471 ± 1.423 9.029 ± 7.692 |
|
UOP mOSm/L | Pre Post | 878.7 ± 205.1 785.8 ± 130.2 | 642.5 ± 275.9 580.3 ± 179.7 | 869.4 ± 284.2 867.3 ± 86.36 | 906.2 ± 193.6 676.0 ± 169.4 | 672.7 ± 205.5 729.0 ± 63.38 | 879.7 ± 188.6 670.7 ± 211.8 |
| SPG | Pre Post | 1.026 ± 0.006 1.024 ± 0.003 | 1.019 ± 0.008 1.018 ± 0.006 | 1.025 ± 0.008 1.027 ± 0.004 | 1.025 ± 0.006 1.018 ± 0.009 | 1.019 ± 0.004 1.022 ± 0.003 | 1.024 ± 0.006 1.020 ± 0.006 |
|
I-FABP (pg/mgCr) | Pre Post | 196.8 ± 52.90 4783 ± 2491 | 354.0 ± 473.5 6335 ± 2411 | 183.7 ± 195.1 3635 ± 1249 | 232.0 ± 283.4 5139 ± 2331 | 370.0 ± 450.9 4845 ± 2402 | 205.9 ± 206.8 7609 ± 4507 |
|
Titin (pg/mgCr) | Pre Post | 912.0 ± 613.6 978.1 ± 637.1 | 1329 ± 1147 1466 ± 846.7 | 1050 ± 1146 802.1 ± 400.1 | 968.5 ± 849.9 11901 ± 720.4 | 828.6 ± 561.3 848.5 ± 586.2 | 838.8 ± 621.9 1355 ± 1238 |
|
IFN-γ (pg/mgCr) | Pre Post | 2.030 ± 1.089 1.716 ± 0.710 | 3.694 ± 2.713 2.273 ± 1.261 | 2.351 ± 0.998 1.488 ± 0.206 | 2.004 ± 0.971 2.273 ± 1.261 | 2.801 ± 0.908 1.821 ± 0.797 | 1.990 ± 0.785 2.834 ± 1.665 |
|
IL-1β (pg/mgCr) | Pre Post | 0.132 ± 0.073 0.272 ± 0.089 | 0.285 ± 0.292 0.462 ± 0.355 | 0.152 ± 0.107 0.210 ± 0.088 | 0.189 ± 0.153 0.496 ± 0.559 | 0.251 ± 0.148 0.235 ± 0.169 | 0.150 ± 0.084 0.297 ± 0.161 |
|
TNF-α (pg/mgCr) | Pre Post | 0.139 ± 0.123 0.121 ± 0.104 | 0.073 ± 0.051 0.153 ± 0.132 | 0.153 ± 0.098 0.082 ± 0.053 | 0.107 ± 0.170 0.091 ± 0.087 | 0.124 ± 0.074 0.069 ± 0.074 | 0.096 ± 0.127 0/231 ± 0.240 |
|
C5a (ng/mgCr) | Pre Post | 0.991 ± 1.998 4.726 ± 4.349 | 0.232 ± 0.219 5.362 ± 7.272 | 0.181 ± 0.079 2.992 ± 2.598 | 0.125 ± 0.068 3.766 ± 5.757 | 0.125 ± 0.058 2.967 ± 2.559 | 0.125 ± 0.057 1.782 ± 1.073 |
|
Calprotectin (ng/mgCr) | Pre Post | 21.18 ± 22.26 27.31 ± 21.49 | 12.25 ± 11.94 29.43 ± 27.06 | 15.47 ± 14.25 25.68 ± 19.60 | 17.19 ± 26.81 31.23 ± 34.14 | 10.40 ± 9.010 23.56 ± 21.63 | 13.30 ± 11.63 26.53 ± 29.17 |
|
Fractalkine (pg/mgCr) | Pre Post | 0.241 ± 0.251 0.104 ± 0.200 | 0.398 ± 0.200 0.276 ± 0.357 | 0.329 ± 0.488 0.295 ± 0.484 | 0.385 ± 0.274 2.276 ± 0.357 | 0.323 ± 0.214 0.252 ± 0.380 | 0.579 ± 0.422 0.356 ± 0.507 |
|
MCP-1 (pg/mgCr) | Pre Post | 175.6 ± 96.93 341.7 ± 238.7 | 166.4 ± 75.83 364.7 ± 241.2 | 151.8 ± 40.74 257.2 ± 97.94 | 208.3 ± 60.27 294.3 ± 58.86 | 183.8 ± 75.61 320.48 ± 195.4 | 202.8 ± 139.8 325.4 ± 113.7 |
|
MPO (ng/mgCr) | Pre Post | 0.181 ± 0.090 0.202 ± 0.076 | 0.535 ± 0.620 0.384 ± 0.224 | 0.234 ± 0.126 0.377 ± 0.216 | 0.199 ± 0.063 0.254 ± 0.102 | 0.256 ± 0.109 0.219 ± 0.075 | 0.432 ± 0.500 0.436 ± 0.354 |
|
M-CSF (pg/mgCr) | Pre Post | 1206 ± 501.5 3904 ± 1550 | 831.9 ± 596.4 3766 ± 2213 | 706.1 ± 395.9 3100 ± 1563 | 875.2 ± 311.3 2987 ± 688.3 | 714.5 ± 324.1 3274 ± 977.6 | 714.8 ± 389.8 3375 ± 1041 |
|
IL-4 (pg/mgCr) | Pre Post | 12.76 ± 17.64 14.78 ± 15.49 | 5.900 ± 3.816 21.63 ± 24.64 | 20.34 ± 18.00 10.50 ± 9.960 | 24.65 ± 26.71 23.54 ± 32.92 | 17.95 ± 19.85 10.87 ± 14.31 | 30.44 ± 39.17 36.49 ± 44.67 |
|
IL-10 (pg/mgCr) | Pre Post | 7.875 ± 5.324 6.883 ± 3.913 | 18.55 ± 13.73 13.31 ± 6.581 | 11.12 ± 6.290 8.265 ± 3.075 | 11.46 ± 5.722 9.332 ± 6.126 | 12.88 ± 1.372 7.371 ± 5.916 | 9.478 ± 2.233 12.28 ± 5.593 |
|
IL-2 (pg/mgCr) | Pre Post | 9.136 ± 2.035 9.079 ± 2.721 | 21.94 ± 7.037 23.51 ± 15.03 | 11.34 ± 8.41 16.08 ± 13.32 | 9.022 ± 3.647 19.07 ± 15.58 | 7.782 ± 3.061 11.80 ± 8.148 | 10.49 ± 5.818 12.74 ± 4.582 |
|
IL-12p40 (pg/mgCr) | Pre Post | 72.08 ± 92.78 41.16 ± 27.32 | 82.30 ± 69.99 66.71 ± 47.09 | 61.79 ± 26.67 24.63 ± 13.15 | 64.49 ± 56.61 53.56 ± 55.21 | 56.42 ± 31.53 35.61 ± 33.74 | 49.23 ± 33.20 59.48 ± 48.20 |
|
IL-1ra (pg/mgCr) | Pre Post | 2660 ± 1798 4340 ± 3328 | 3221 ± 2392 5053 ± 4958 | 2382 ± 1412 4522 ± 3244 | 3314 ± 2953 4690 ± 2889 | 2501 ± 1237 4172 ± 2276 | 2262 ± 1490 4211 ± 2819 |
|
IL-6 (pg/mgCr) | Pre Post | 0.445 ± 0.392 0.798 ± 0.530 | 0.527 ± 0.267 0.780 ± 0.557 | 0.397 ± 0.212 1.418 ± 1.423 | 0.676 ± 0.302 1.021 ± 0.861 | 0.484 ± 0.359 0.907 ± 0.579 | 0.794 ± 0.619 1.839 ± 1.897 |
|
IL-8 (pg/mgCr) | Pre Post | 9.168 ± 7.782 3.786 ± 1.791 | 6.491 ± 5.077 4.969 ± 1.629 | 5.460 ± 4.316 8.400 ± 5.455 | 5.112 ± 2.853 8.615 ± 6.825 | 4.541 ± 3.988 7.604 ± 6.530 | 3.935 ± 2.887 9.366 ± 7.042 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, S.; Tominaga, T.; Kanda, K.; Sugama, K.; Omae, C.; Hashimoto, S.; Aoyama, K.; Yoshikai, Y.; Suzuki, K. Effects of an 8-Week Protein Supplementation Regimen with Hyperimmunized Cow Milk on Exercise-Induced Organ Damage and Inflammation in Male Runners: A Randomized, Placebo Controlled, Cross-Over Study. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8030051
Ma S, Tominaga T, Kanda K, Sugama K, Omae C, Hashimoto S, Aoyama K, Yoshikai Y, Suzuki K. Effects of an 8-Week Protein Supplementation Regimen with Hyperimmunized Cow Milk on Exercise-Induced Organ Damage and Inflammation in Male Runners: A Randomized, Placebo Controlled, Cross-Over Study. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(3):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8030051
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Sihui, Takaki Tominaga, Kazue Kanda, Kaoru Sugama, Chiaki Omae, Shunsuke Hashimoto, Katsuhiko Aoyama, Yasunobu Yoshikai, and Katsuhiko Suzuki. 2020. "Effects of an 8-Week Protein Supplementation Regimen with Hyperimmunized Cow Milk on Exercise-Induced Organ Damage and Inflammation in Male Runners: A Randomized, Placebo Controlled, Cross-Over Study" Biomedicines 8, no. 3: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8030051
APA StyleMa, S., Tominaga, T., Kanda, K., Sugama, K., Omae, C., Hashimoto, S., Aoyama, K., Yoshikai, Y., & Suzuki, K. (2020). Effects of an 8-Week Protein Supplementation Regimen with Hyperimmunized Cow Milk on Exercise-Induced Organ Damage and Inflammation in Male Runners: A Randomized, Placebo Controlled, Cross-Over Study. Biomedicines, 8(3), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8030051