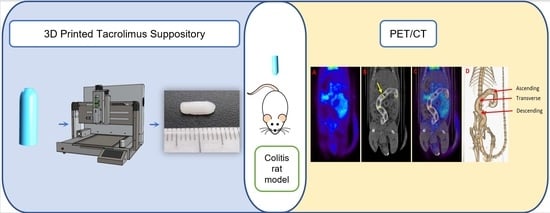
3D Printed Tacrolimus Rectal Formulations Ameliorate Colitis in an Experimental Animal Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
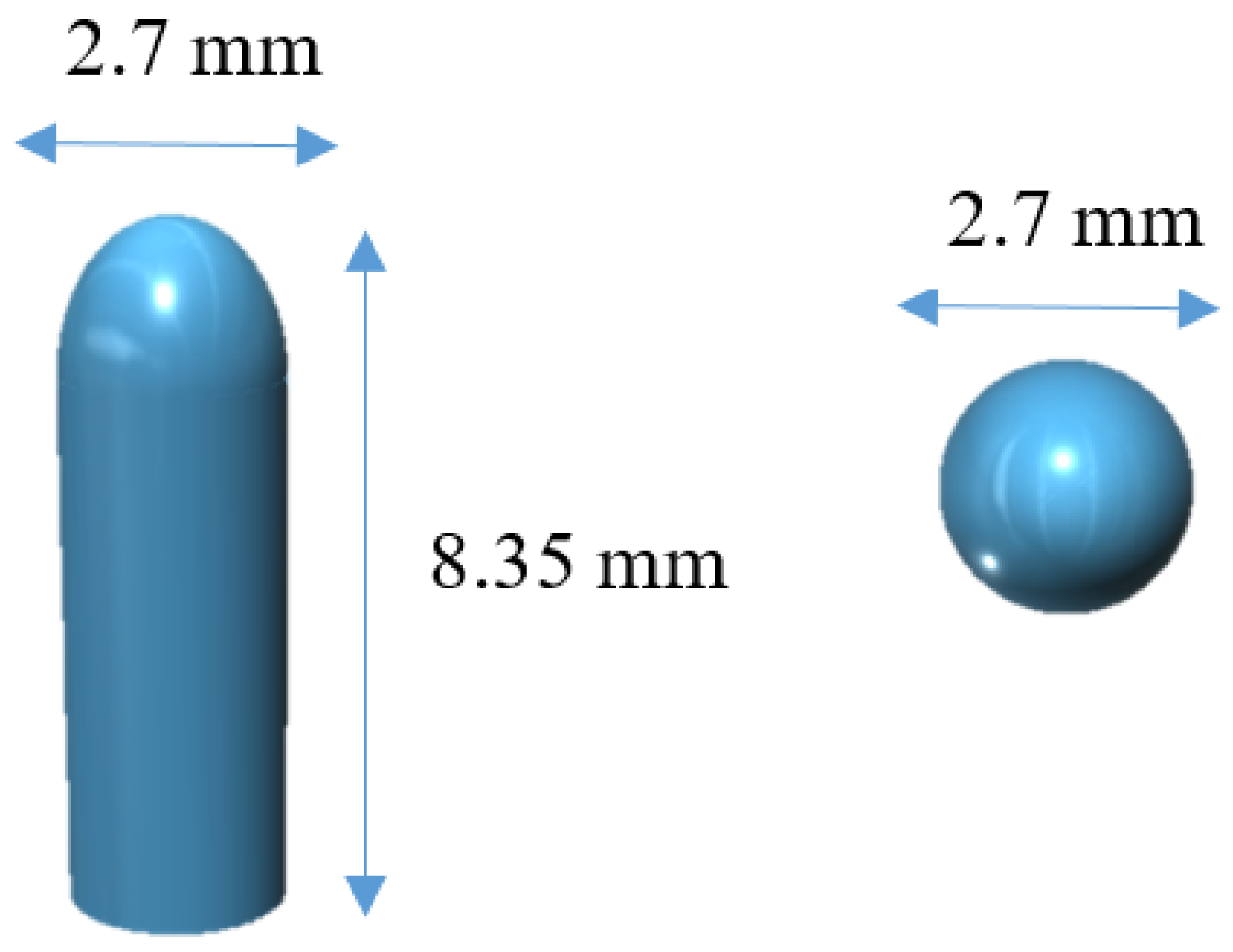
2.2.1. 3D Design
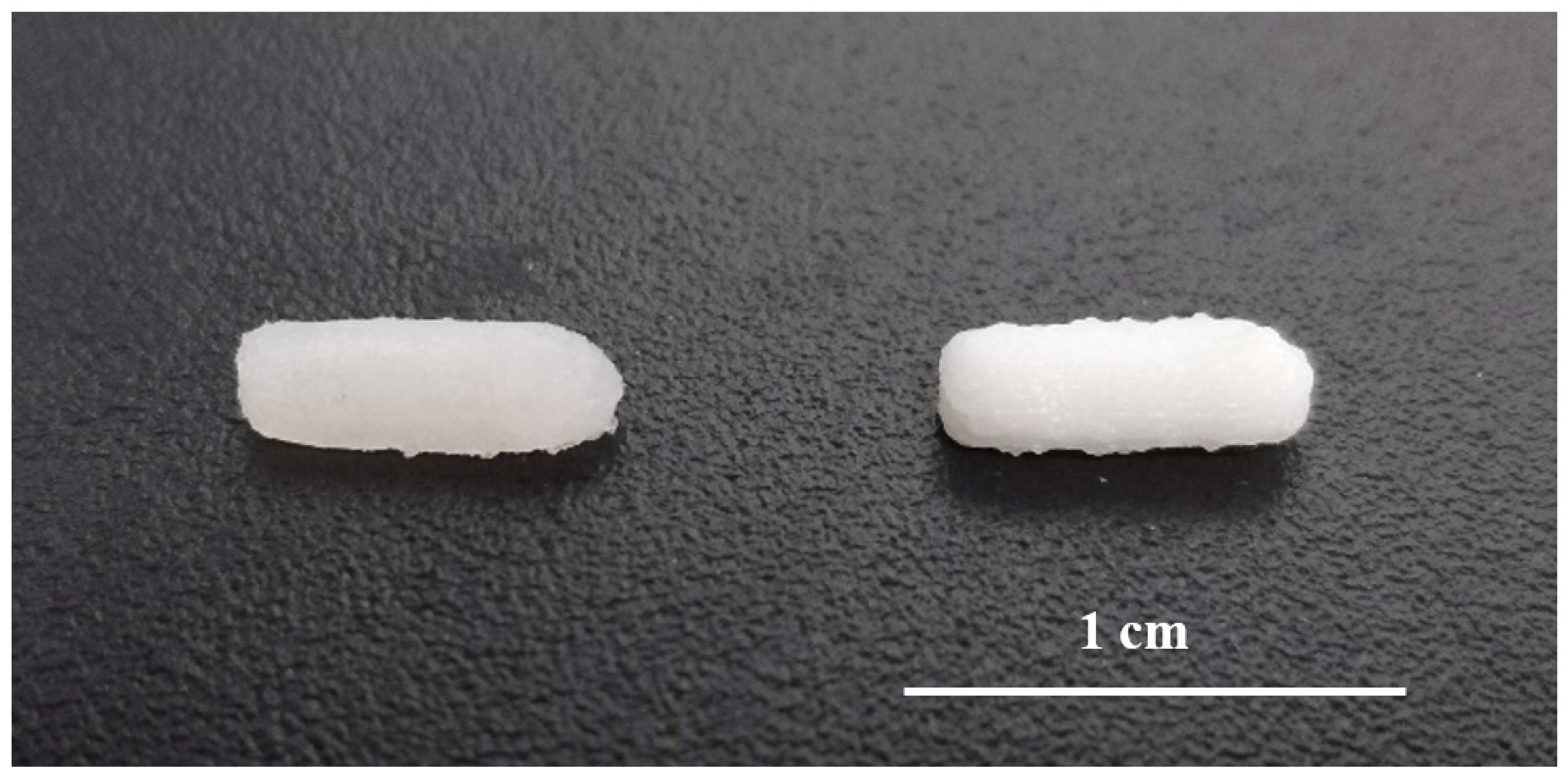
2.2.2. Semisolid Extrusion 3D Printing
2.2.3. Characterization of the 3D Printed Suppositories
Drug Loading
In Vitro Disintegration Time of 3D Printed Suppositories
In Vitro Drug Release
In Vivo Disintegration Time of 3D Printed Suppositories
2.2.4. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Animal Model
2.2.5. Experimental Design
Assessment of the Efficacy of Tacrolimus Treatment
PET/CT Acquisition and Evaluation
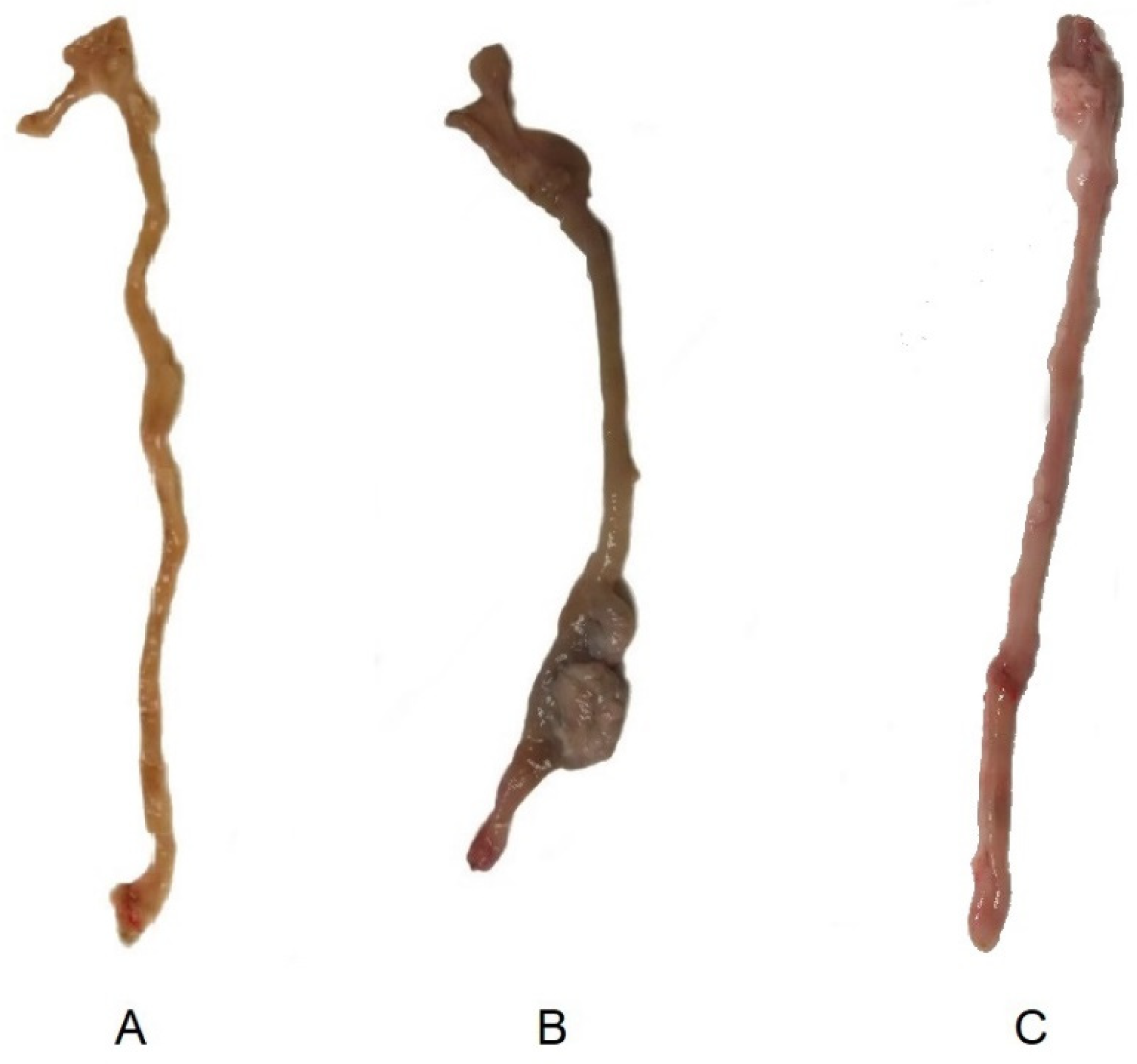
Macroscopic Evaluation and Histopathology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of 3D Printed Suppositories
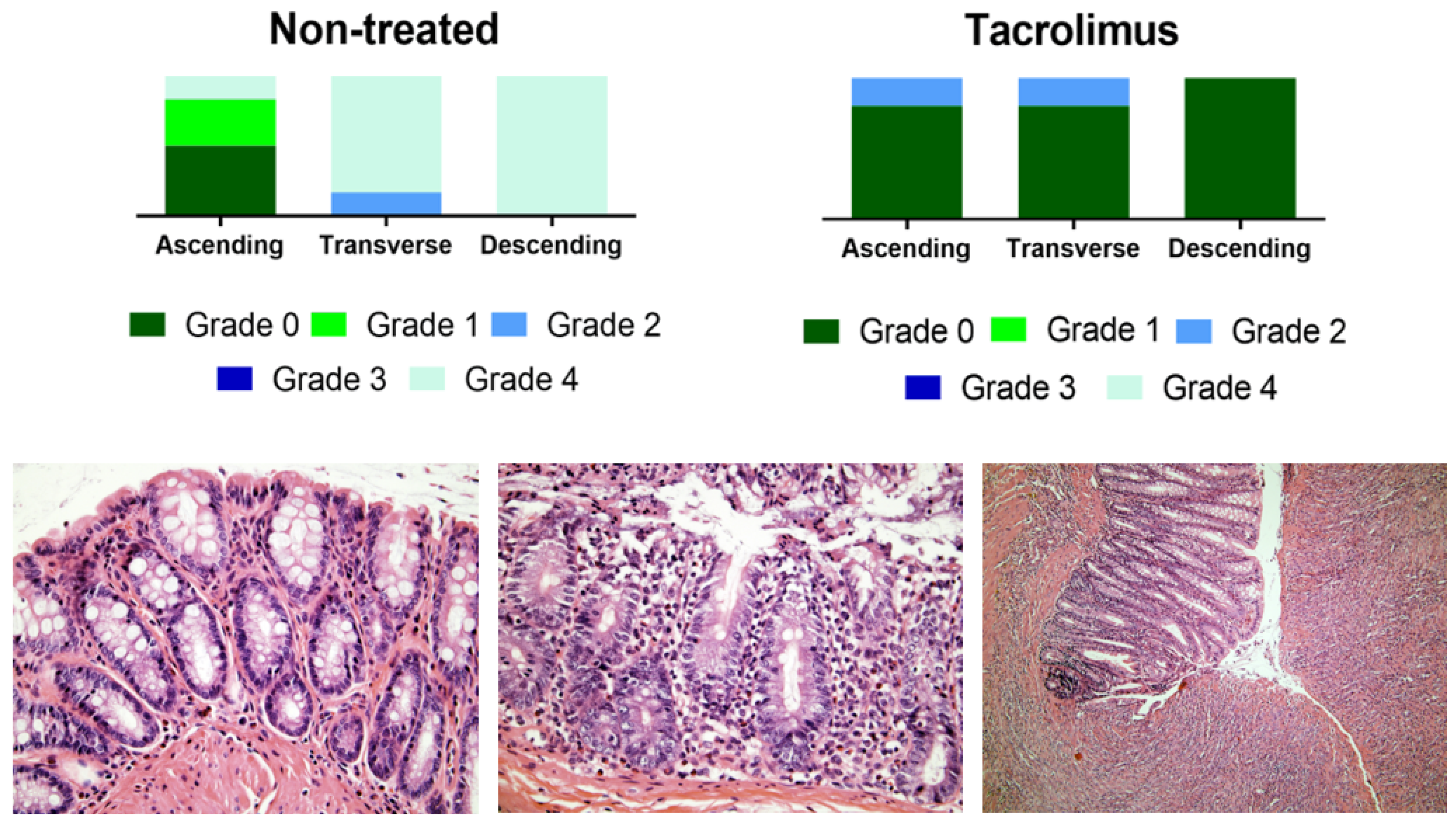
3.2. Assessment of the Efficacy of Tacrolimus Treatment by PET/CT Imaging and Histopathological Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yadav, V.; Varum, F.; Bravo, R.; Furrer, E.; Bojic, D.; Basit, A.W. Inflammatory bowel disease: Exploring gut pathophysiology for novel therapeutic targets. Transl. Res. 2016, 176, 38–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, H.S.P.; Fiocchi, C.; Iliopoulos, D. The IBD interactome: An integrated view of aetiology, pathogenesis and therapy. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazel, K.; O’Connor, A. Emerging treatments for inflammatory bowel disease. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argollo, M.; Kotze, P.G.; Kakkadasam, P.; D’Haens, G. Optimizing biologic therapy in IBD: How essential is therapeutic drug monitoring? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrance, I.C.; Copeland, T.S. Rectal tacrolimus in the treatment of resistant ulcerative proctitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 28, 1214–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, S.U.; Klag, T.; Hoeger, K.; Klumpp, S.; Escher, M.; Malek, N.; Stange, E.; Wehkamp, J. Tacrolimus Suppositories in Therapy-Resistant Ulcerative Proctitis. Inflamm. Intest. Dis. 2018, 3, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, P.; Wehling, C.; Krisam, J.; Pfeiffenberger, J.; Belling, N.; Gauss, A. Performance of tacrolimus in hospitalized patients with steroid-refractory acute severe ulcerative colitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 1603–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talley, N.J.; Abreu, M.T.; Achkar, J.P.; Bernstein, C.N.; Dubinsky, M.C.; Hanauer, S.B.; Kane, S.V.; Sandborn, W.J.; Ullman, T.A.; Moayyedi, P. An evidence-based systematic review on medical therapies for inflammatory bowel disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106 (Suppl. 1), S2–S25, quiz S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Tong, J.; Ran, Z. Tacrolimus Therapy in Steroid-Refractory Ulcerative Colitis: A Review. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 26, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, K.; Saito, E.; Fujii, T.; Takenaka, K.; Kimura, M.; Nagahori, M.; Ohtsuka, K.; Watanabe, M. Tacrolimus for the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis. Intest. Res. 2015, 13, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S. Physiological and Pharmaceutical Considerations for Rectal Drug Formulations. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, A.L.; Plamondon, S.; Kamm, M.A. Topical tacrolimus in the treatment of perianal Crohn’s disease: Exploratory randomized controlled trial. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2007, 13, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seoane-Viano, I.; Gomez-Lado, N.; Lazare-Iglesias, H.; Barreiro-de Acosta, M.; Silva-Rodriguez, J.; Luzardo-Alvarez, A.; Herranz, M.; Otero-Espinar, F.; Antunez-Lopez, J.R.; Lamas, M.J.; et al. Longitudinal PET/CT evaluation of TNBS-induced inflammatory bowel disease rat model. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 549, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmochowska, N.; Tieu, W.; Keller, M.D.; Wardill, H.R.; Mavrangelos, C.; Campaniello, M.A.; Takhar, P.; Hughes, P.A. Immuno-PET of Innate Immune Markers CD11b and IL-1beta Detects Inflammation in Murine Colitis. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoane-Viaño, I.; Gómez-Lado, N.; Lázare-Iglesias, H.; Rey-Bretal, D.; Lamela-Gómez, I.; Otero-Espinar, F.; Blanco-Méndez, J.; Ramón Antúnez-López, J.; Pombo-Pasín, M.; Aguiar, P.; et al. Evaluation of the therapeutic activity of Melatonin and Resveratrol in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A longitudinal PET/CT study in an animal model. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 118713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takizawa, H.; Shintani, N.; Natsui, M.; Sasakawa, T.; Nakakubo, H.; Nakajima, T.; Asakura, H. Activated Immunocompetent Cells in Rat Colitis Mucosa Induced by Dextran Sulfate Sodium and Not Complete but Partial Suppression of Colitis by FK506. Digestion 1995, 56, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamprecht, A.; Yamamoto, H.; Takeuchi, H.; Kawashima, Y. Nanoparticles enhance therapeutic efficiency by selectively increased local drug dose in experimental colitis in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 315, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, T.; Nakase, H.; Honzawa, Y.; Matsumura, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Takeda, Y.; Ueno, S.; Uza, N.; Masuda, S.; Inui, K.; et al. Immunosuppressive effects of tacrolimus on macrophages ameliorate experimental colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 16, 2022–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatton, G.B.; Yadav, V.; Basit, A.W.; Merchant, H.A. Animal Farm: Considerations in Animal Gastrointestinal Physiology and Relevance to Drug Delivery in Humans. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 2747–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettenworth, D.; Reuter, S.; Hermann, S.; Weckesser, M.; Kerstiens, L.; Stratis, A.; Nowacki, T.M.; Ross, M.; Lenze, F.; Edemir, B.; et al. Translational 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging to monitor lesion activity in intestinal inflammation. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pio, B.S.; Byrne, F.R.; Aranda, R.; Boulay, G.; Spicher, K.; Song, M.H.; Birnbaumer, L.; Phelps, M.E.; Czernin, J.; Silverman, D.H. Noninvasive quantification of bowel inflammation through positron emission tomography imaging of 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-D-glucose-labeled white blood cells. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2003, 5, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Lado, N.; Seoane-Viaño, I.; Matiz, S.; Madla, M.C.; Yadav, V.; Aguiar, P.; Basit, W.A.; Goyanes, A. Gastrointestinal Tracking and Gastric Emptying of Coated Capsules in Rats with or without Sedation Using CT imaging. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, S.; Sun, H.; Gao, S.; Xin, J.; Lu, Z. Metabolic parameters with different thresholds for evaluating tumor recurrence and their correlations with hematological parameters in locally advanced squamous cell cervical carcinoma: An observational 18F-FDG PET/CT study. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2019, 9, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaaru, E.; Bianchi, A.; Wunder, A.; Rasche, V.; Stiller, D. Molecular Imaging in Preclinical Models of IBD with Nuclear Imaging Techniques: State-of-the-Art and Perspectives. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 2491–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Seoane-Viaño, I.; Ong, J.J.; Luzardo-Álvarez, A.; González-Barcia, M.; Basit, A.W.; Otero-Espinar, F.J.; Goyanes, A. 3D printed tacrolimus suppositories for the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.; Fina, F.; Trenfield, S.J.; Patel, P.; Goyanes, A.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. 3D Printed Pellets (Miniprintlets): A Novel, Multi-Drug, Controlled Release Platform Technology. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithani, K.; Goyanes, A.; Jannin, V.; Basit, A.W.; Gaisford, S.; Boyd, B.J. An Overview of 3D Printing Technologies for Soft Materials and Potential Opportunities for Lipid-based Drug Delivery Systems. Pharm. Res. 2018, 36, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaled, S.A.; Burley, J.C.; Alexander, M.R.; Yang, J.; Roberts, C.J. 3D printing of tablets containing multiple drugs with defined release profiles. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 494, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haring, A.P.; Tong, Y.; Halper, J.; Johnson, B.N. Programming of Multicomponent Temporal Release Profiles in 3D Printed Polypills via Core–Shell, Multilayer, and Gradient Concentration Profiles. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1800213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyanes, A.; Madla, C.M.; Umerji, A.; Duran Piñeiro, G.; Giraldez Montero, J.M.; Lamas Diaz, M.J.; Gonzalez Barcia, M.; Taherali, F.; Sánchez-Pintos, P.; Couce, M.L.; et al. Automated therapy preparation of isoleucine formulations using 3D printing for the treatment of MSUD: First single-centre, prospective, crossover study in patients. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 567, 118497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithani, K.; Goyanes, A.; Jannin, V.; Basit, A.W.; Gaisford, S.; Boyd, B.J. A Proof of Concept for 3D Printing of Solid Lipid-Based Formulations of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs to Control Formulation Dispersion Kinetics. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J.; Faham, A.; Clas, S.-D.; Boyd, B.J.; Jannin, V.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Zhao, H.; Lecommandoux, S.; Evans, J.C.; Allen, C.; et al. Lipids and polymers in pharmaceutical technology: Lifelong companions. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 558, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, B.J.; Bergström, C.A.S.; Vinarov, Z.; Kuentz, M.; Brouwers, J.; Augustijns, P.; Brandl, M.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Shrestha, N.; Préat, V.; et al. Successful oral delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs both depends on the intraluminal behavior of drugs and of appropriate advanced drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 137, 104967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.R.; Ho, M.J.; Jung, H.J.; Cho, H.R.; Park, J.S.; Yoon, S.-H.; Choi, Y.S.; Choi, Y.W.; Oh, C.-H.; Kang, M.J. Enhanced dissolution and oral absorption of tacrolimus by supersaturable self-emulsifying drug delivery system. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, M.; Hobara, N.; Hokama, N.; Kameya, H.; Ohshiro, S.; Sakanashi, M.; Saitoh, H. Increased bioavailability of tacrolimus after rectal administration in rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 1480–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Disintegration of suppositories and pessaries. In European Pharmacopoeia 8.0; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2005.
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Animal research: Reporting in vivo experiments: The ARRIVE guidelines. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1577–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.P.; Beck, P.L.; Herridge, M.S.; Depew, W.T.; Szewczuk, M.R.; Wallace, J.L. Hapten-induced model of chronic inflammation and ulceration in the rat colon. Gastroenterology 1989, 96, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, D.M.; Vicini, P. Non-Compartmental and Compartmental Approaches to Pharmacokinetic Data Analysis. In Principles of Clinical Pharmacology, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Marchal-Bressenot, A.; Scherl, A.; Salleron, J.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. A practical guide to assess the Nancy histological index for UC. Gut 2016, 65, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchal-Bressenot, A.; Salleron, J.; Boulagnon-Rombi, C.; Bastien, C.; Cahn, V.; Cadiot, G.; Diebold, M.D.; Danese, S.; Reinisch, W.; Schreiber, S.; et al. Development and validation of the Nancy histological index for UC. Gut 2017, 66, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzardo-Álvarez, A.; Lamela-Gómez, I.; Otero-Espinar, F.; Blanco-Méndez, J. Development, Characterization, and In Vitro Evaluation of Resveratrol-Loaded Poly-(ε-caprolactone) Microcapsules Prepared by Ultrasonic Atomization for Intra-Articular Administration. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, F.A.; de Andrade, K.Q.; Dos Santos, J.C.F.; Araújo, O.R.P.; Goulart, M.O.F. Antioxidant therapy for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: Does it work? Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 617–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamprecht, A.; Yamamoto, H.; Ubrich, N.; Takeuchi, H.; Maincent, P.; Kawashima, Y. FK506 microparticles mitigate experimental colitis with minor renal calcineurin suppression. Pharm. Res. 2005, 22, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.S.; Altayari, A.A.; Khan, L.M.; Alharthi, S.E.; Ahmed, O.A.; El-Shitany, N.A.; Ali, S.S.; Saadah, O.I. Colon-Targeted Therapy of Tacrolimus (FK506) in the Treatment of Experimentally Induced Colitis. Pharmacology 2020, 105, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Awad, A.; Martinez, P.R.; Gaisford, S.; Goyanes, A.; Basit, A.W. Vat photopolymerization 3D printing for advanced drug delivery and medical device applications. J. Control. Release 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyanes, A.; Wang, J.; Buanz, A.; Martínez-Pacheco, R.; Telford, R.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. 3D Printing of Medicines: Engineering Novel Oral Devices with Unique Design and Drug Release Characteristics. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 4077–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbadawi, M.; Muñiz Castro, B.; Gavins, F.K.H.; Ong, J.J.; Gaisford, S.; Pérez, G.; Basit, A.W.; Cabalar, P.; Goyanes, A. M3DISEEN: A novel machine learning approach for predicting the 3D printability of medicines. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 590, 119837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genina, N.; Boetker, J.P.; Colombo, S.; Harmankaya, N.; Rantanen, J.; Bohr, A. Anti-tuberculosis drug combination for controlled oral delivery using 3D printed compartmental dosage forms: From drug product design to in vivo testing. J. Control. Release 2017, 268, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafat, B.; Qinna, N.; Cieszynska, M.; Forbes, R.T.; Alhnan, M.A. Tailored on demand anti-coagulant dosing: An in vitro and in vivo evaluation of 3D printed purpose-designed oral dosage forms. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 128, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.; Kapoor, Y.; Hermans, A.; Nofsinger, R.; Kesisoglou, F.; Gustafson, T.P.; Procopio, A. 3D printed capsules for quantitative regional absorption studies in the GI tract. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 550, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Kim, T.H.; Jeong, S.W.; Chung, S.E.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, D.-H.; Shin, B.S. Development of a gastroretentive delivery system for acyclovir by 3D printing technology and its in vivo pharmacokinetic evaluation in Beagle dogs. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.L.; Zou, X.; McCandler, C.A.; Kirtane, A.R.; Ning, S.; Zhou, J.; Abid, A.; Jafari, M.; Rogner, J.; Minahan, D.; et al. 3D-Printed Gastric Resident Electronics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Non-Treated | Tacrolimus | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRRT (days) | tmax (days) | MRRT (days) | tmax (days) | |||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Ascending | 9.76 | 2.62 | 10.00 | 3.00 | 4.78 | 0.81 | 4.00 | 2.00 |
| Transverse | 8.37 | 1.01 | 10.75 | 2.87 | 4.68 | 1.37 | 3.50 | 2.52 |
| Descending | 9.54 | 1.06 | 10.75 | 1.50 | 5.74 | 1.86 | 1.80 | 1.10 |
| Mean ± SD | 9.22 | 0.61 | 10.50 | 0.35 | 5.07 | 0.48 | 3.10 | 0.94 |
| Methylprednisolone | Resveratrol | Melatonin | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| MRRT (days) | Ascending | 4.57 | 1.5 | 4.17 | 1.97 | 6.36 | 1.53 |
| Transverse | 5.37 | 1.12 | 4.49 | 1.79 | 7.42 | 2.27 | |
| Descending | 4.29 | 1.53 | 3.72 | 2.49 | 6.37 | 1.5 | |
| Mean ± SD | 4.74 | 0.56 | 4.13 | 0.39 | 6.72 | 0.61 | |
| tmax (days) | Ascending | 3.00 | 2.83 | 1.83 | 1.03 | 5.92 | 4.10 |
| Transverse | 3.25 | 1.26 | 1.92 | 1.00 | 4.75 | 3.49 | |
| Descending | 3.00 | 0.01 | 1.50 | 0.90 | 4.50 | 3.06 | |
| Mean ± SD | 3.08 | 0.14 | 1.75 | 0.22 | 5.06 | 0.76 | |
| Data obtained from | [13] | [15] | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seoane-Viaño, I.; Gómez-Lado, N.; Lázare-Iglesias, H.; García-Otero, X.; Antúnez-López, J.R.; Ruibal, Á.; Varela-Correa, J.J.; Aguiar, P.; Basit, A.W.; Otero-Espinar, F.J.; et al. 3D Printed Tacrolimus Rectal Formulations Ameliorate Colitis in an Experimental Animal Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120563
Seoane-Viaño I, Gómez-Lado N, Lázare-Iglesias H, García-Otero X, Antúnez-López JR, Ruibal Á, Varela-Correa JJ, Aguiar P, Basit AW, Otero-Espinar FJ, et al. 3D Printed Tacrolimus Rectal Formulations Ameliorate Colitis in an Experimental Animal Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(12):563. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120563
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeoane-Viaño, Iria, Noemí Gómez-Lado, Héctor Lázare-Iglesias, Xurxo García-Otero, José Ramón Antúnez-López, Álvaro Ruibal, Juan Jesús Varela-Correa, Pablo Aguiar, Abdul W. Basit, Francisco J. Otero-Espinar, and et al. 2020. "3D Printed Tacrolimus Rectal Formulations Ameliorate Colitis in an Experimental Animal Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease" Biomedicines 8, no. 12: 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120563
APA StyleSeoane-Viaño, I., Gómez-Lado, N., Lázare-Iglesias, H., García-Otero, X., Antúnez-López, J. R., Ruibal, Á., Varela-Correa, J. J., Aguiar, P., Basit, A. W., Otero-Espinar, F. J., González-Barcia, M., Goyanes, A., Luzardo-Álvarez, A., & Fernández-Ferreiro, A. (2020). 3D Printed Tacrolimus Rectal Formulations Ameliorate Colitis in an Experimental Animal Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Biomedicines, 8(12), 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120563