Long-Term Exposure to Temozolomide Affects Locomotor Activity and Cartilage Structure of Elderly Experimental Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Animals
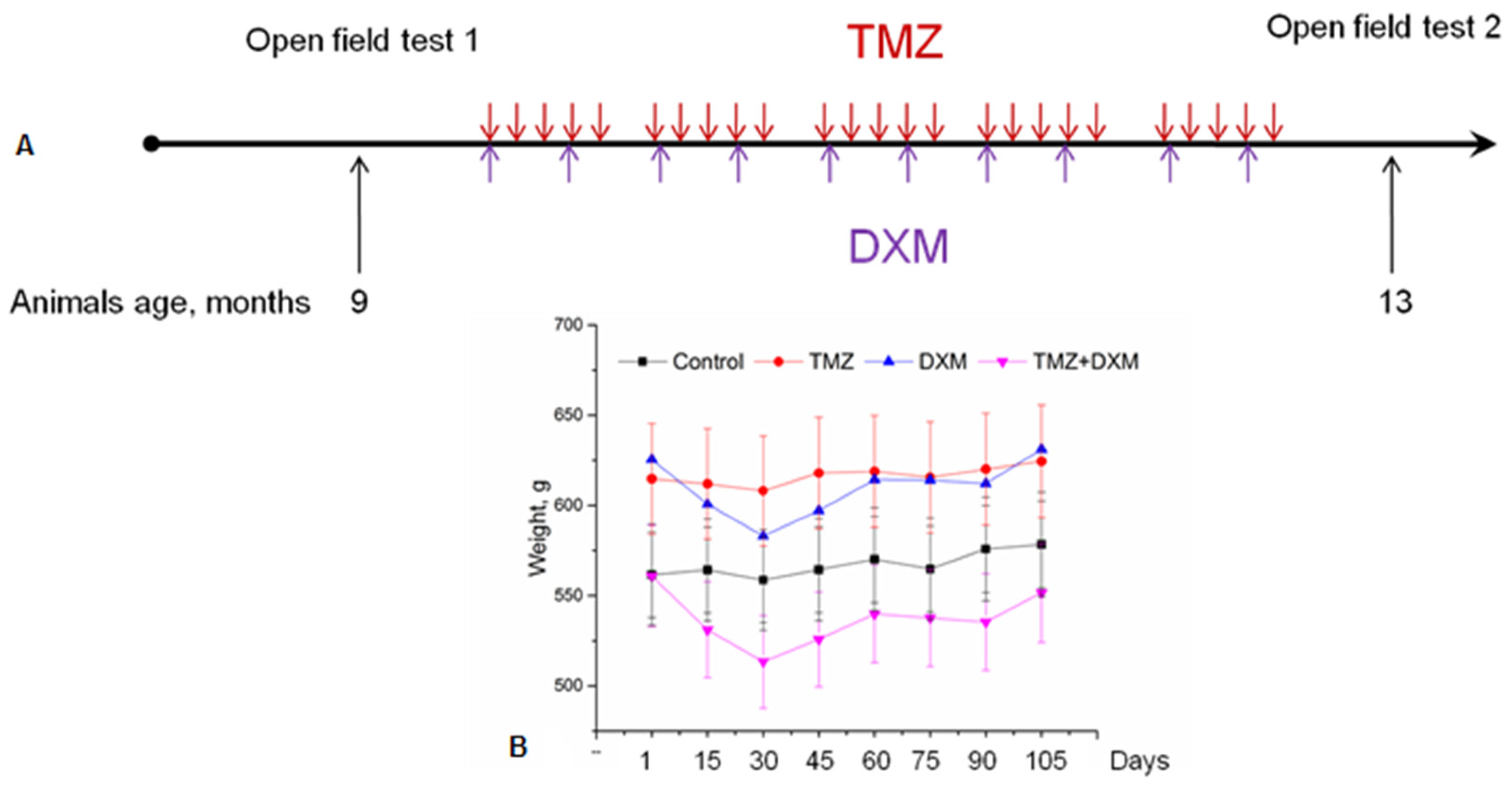
2.2. TMZ and DXM Administration
2.3. Open Field Test
2.4. Histological Analysis
2.5. Staining for Total and Sulfated Glycosaminoglycans
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Long-Term Administration of TMZ and DXM Affects Locomotor Activity of Wistar Rats
3.2. TMZ Affects Epiphyseal Cartilage Morphology in Rat Knee Joints
3.3. TMZ and DXM Affect on the Length and Ratio of Epiphyseal Cartilage Zones Knee Joint
3.4. TMZ and DXM Affect on the Length and Ratio of Epiphyseal Cartilage Zones of Knee Joint
3.5. TMZ and DXM Affect the Content and Localisation of GAGs in Rat Knee Joint Cartilage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, R.H.; Hou, X.Y.; Yang, C.S.; Liu, W.L.; Tang, J.Q.; Liu, Y.Q.; Jiang, G. Temozolomide for Treating Malignant Melanoma. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2015, 25, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cosentini, D.; Badalamenti, G.; Grisanti, S.; Basile, V.; Rapa, I.; Cerri, S.; Spallanzani, A.; Perotti, P.; Musso, E.; Laganà, M.; et al. Activity and safety of temozolomide in advanced adrenocortical carcinoma patients. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 181, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almalki, M.H.; Aljoaib, N.N.; Alotaibi, M.J.; Aldabas, B.S.; Wahedi, T.S.; Ahmad, M.M.; Alshahrani, F. Temozolomide therapy for resistant prolactin-secreting pituitary adenomas and carcinomas: A systematic review. Hormones (Athens) 2017, 16, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumor and Radiotherapy Groups; National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobel, H.; Baisch, T.; Fitzel, R.; Schilberg, K.; Siegelin, M.D.; Karpel-Massler, G.; Debatin, K.-M.; Westhoff, M.A. Temozolomide and Other Alkylating Agents in Glioblastoma Therapy. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreck, K.C.; Grossman, S.A. Role of Temozolomide in the Treatment of Cancers Involving the Central Nervous System. Oncology (Williston Park.) 2018, 32, 555–560. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Zhou, L.; Qian, J.Q.; Qiu, T.Z.; Shu, Y.Q.; Liu, P. Temozolomide for treatment of brain metastases: A review of 21 clinical trials. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 5, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Fu, L.; Jing, W.; Guo, D.; Kong, L.; Yu, J. Effectiveness of temozolomide combined with whole brain radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanenko, A.A.; Chekhonin, V.P. On the Critical Issues in Temozolomide Research in Glioblastoma: Clinically Relevant Concentrations and MGMT-independent Resistance. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker-Schiebe, M.E.; Wetzel, M.; Wetzel, F.; Christansen, H.; Hoffmann, W. Hematologic toxicity of temozolomide and radiation in glioblastoma patients—Correlation with clinicopathological factors. J. Clin. Med. 2015, 1, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Stepanovic, A.; Nikitovic, M. Severe hematologic temozolomide-related toxicity and lifethreatening infections. JBUON 2018, 23, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dario, A.; Tomei, G. The safety of the temozolomide in patients with malignant glioma. Curr. Drug Saf. 2006, 1, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaringi, C.; De Sanctis, V.; Minniti, G.; Enrici, R.M. Temozolomide-related hematologic toxicity. Onkologie 2013, 36, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minniti, G.; Scringi, C.; Baldoni, A.; Lanzetta, G.; De Sanctis, V.; Esposito, V.; Enrici, R.M. Health-related quality of life in elderly patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma treated with short-course radiation therapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 86, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, G.; Bergo, E.; Del Bianco, P.; Bellu, L.; Pambuku, A.; Caccese, M.; Trentin, L.; Zagonel, V. Quality of Life Perception, Cognitive Function, and Psychological Status in a Real-world Population of Glioblastoma Patients Treated with Radiotherapy and Temozolomide: A Single-center Prospective Study. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 41, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Qi, F.; Song, X.; Di, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, X.; Chang, J.; Yu, Y. A prospective longitudinal evaluation of cognition and depression in postoperative patients with high-grade glioma following radiotherapy and chemotherapy. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2018, 14 (Supplement), S1048–S1051. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, D.; Parihar, V.K.; Szabo, G.G.; Klein, P.M.; Tran, J.; Moayyad, J.; Ahmed, F.; Nguyen, Q.A.; Murry, A.; Merriott, D.; et al. Neurological Impairments in Mice Subjected to Irradiation and Chemotherapy. Radiat. Res. 2020, 193, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeland, M.; Guinaudie, C.; Du Preez, A.; Musaelyan, K.; Zunszain, P.A.; Fernandes, C.; Pariante, C.M.; Thuret, S. Depletion of adult neurogenesis using the chemotherapy drug temozolomide in mice induces behavioural and biological changes relevant to depression. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Caixeta, A.R.; Guarnieri, L.O.; Medeiros, D.C.; Mendes, E.M.A.M.; Ladeira, L.C.D.; Pereira, M.T.; Moraes, M.F.D.; Pereira, G.S. Inhibiting constitutive neurogenesis compromises long-term social recognition memory. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2018, 155, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, M.D.; Puduvalli, V.K.; Hess, K.R.; Jaeckle, K.A.; Peterson, P.; Yung, W.K.A.; Levin, V.A. Phase II trial of temozolomide plus the matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, marimastat, in recurrent and progressive glioblastoma multiforme. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempen, C.; Weiss, E.; Hess, C.F. Dexamethasone treatment in patients with brain metastases and primary brain tumors: Do the benefits outweigh the side-effects? Support. Care Cancer 2002, 10, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostaras, X.; Cusano, F.; Kline, G.A.; Roa, W.; Easaw, J. Use of dexamethasone in patients with high-grade glioma: A clinical practice guideline. Curr. Oncol. 2014, 21, e493–e503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitter, K.L.; Tamagno, I.; Alikhanyan, K.; Hosni-Ahmed, A.; Pattwell, S.S.; Donnola, S.; Dai, C.; Ozawa, T.; Chang, M.; Chan, T.A.; et al. Hambardzumyan D17. Corticosteroids compromise survival in glioblastoma. Brain 2016, 139 Pt 5, 1458–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polderman, J.A.; Farhang-Razi, V.; Van Dieren, S.; Kranke, P.; DeVries, J.H.; Hollmann, M.W.; Preckel, B.; Hermanides, J. Adverse side effects of dexamethasone in surgical patients. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 8, CD011940. [Google Scholar]
- Lajic, S.; Nordenström, A.; Hirvikoski, T. Long-term outcome of prenatal dexamethasone treatment of 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Endocr. Dev. 2011, 20, 96–105. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson, L.; Nordenström, A.; Hirvikoski, T.; Lajic, S. Prenatal dexamethasone treatment in the context of at risk CAH pregnancies: Long-term behavioral and cognitive outcome. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 91, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skupio, U.; Tertil, M.; Sikora, M.; Golda, S.; Wawrzczak-Bargiela, A.; Przewlocki, R. Behavioral and molecular alterations in mice resulting from chronic treatment with dexamethasone: Relevance to depression. Neuroscience 2015, 286, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafaei, A.A.; Rashidy-Pour, A.; Taherian, A.A. Peripheral injection of dexamethasone modulates anxiety related behaviors in mice: An interaction with opioidergic neurons. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 21, 285–289. [Google Scholar]
- Menshanov, P.N.; Bannova, A.V.; Dygalo, N.N. Dexamethasone suppresses the locomotor response of neonatal rats to novel environment. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 271, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, T.; Gedikli, Ö.; Yildirim, M. Evaluation of spatial memory and locomotor activity during hypercortisolism induced by the administration of dexamethasone in adult male rats. Brain Res. 2015, 1595, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Jiang, J.; Yang, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, B.; Kong, B.; Lu, P.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Timing of glucocorticoid administration determines severity of lipid metabolism and behavioral effects in rats. Chronobiol. Int. 2017, 34, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydincak, O.; Yilmaz, M.B.; Emmez, H.; Kurt, G.; Sepici, A.; Memis, L.; Baykaner, K. The effect of temozolomide on the prevention of epidural fibrosis developing after lumbar laminectomy in rats. Turk. Neurosurg. 2012, 22, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glade, M.J.; Krook, L.; Schryver, H.F.; Hintz, H.F. Morphologic and biochemical changes in cartilage of foals treated with dexamethasone. Cornell Vet. 1983, 73, 170–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Podbielski, A.; Raiss, R. Dose related effects of dexamethasone treatment on the ultrastructure of articular cartilage in rats. Agents Actions 1985, 17, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annefeld, M.; Erne, B. The mode of action of a glycosaminoglycan-peptide-complex (Rumalon) on articular cartilage of the rat in vivo. Clin. Rheumatol. 1987, 6, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, R.; Grodzinsky, A.J. Dexamethasone: Chondroprotective corticosteroid or catabolic killer? Eur. Cells Mater. 2019, 38, 246–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsidulko, A.Y.; Bezier, C.; de La Bourdonnaye, G.; Suhovskih, A.V.; Pankova, T.M.; Kazanskaya, G.M.; Aidagulova, S.V.; Grigorieva, E.V. Conventional Anti-glioblastoma Chemotherapy Affects Proteoglycan Composition of Brain Extracellular Matrix in Rat Experimental Model in vivo. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankin, H.J.; Zarins, A.; Jaffe, W.L. The effect of systemic corticosteroids on rabbit articular cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 1972, 15, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Group | Distal Femoral Epiphysis | Proximal Tibial Epiphysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epiphyseal Cartilage, Maturation Zone | Epiphyseal Plate | Epiphyseal Cartilage, Maturation Zone | Epiphyseal Plate | |
| Control | 20.35 ± 4.43 | 15.91 ± 1.11 | 22.17 ± 0.24 | 20.93 ± 2.88 |
| TMZ | 24.12 ± 2.37 | 1332 ± 1.56 | 22.98 ± 1.07 | 18.54 ± 1.21 |
| DXM | 20.05 ± 3.02 | 13.14 ± 0.72 | 23.09 ± 3.19 | 17.37 ± 1.45 |
| TMZ + DXM | 23.61 ± 1.3 | 17.82 ± 2.66 | 24.11 ± 2.92 | 25.18 ± 1.17 |
| Group | Femur Bone | Tibia Bone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Ossification Center (Diaphysis) | Secondary Ossification Center (Epiphysis) | Primary Ossification Center (Diaphysis) | Secondary Ossification Center (Epiphysis) | |
| Control | 78.52 ± 4.13 | 64.05 ± 8.75 | 86.96 ± 2.71 | 68.64 ± 5.54 |
| TMZ | 76.21 ± 4.49 | 58.64 ± 5.97 | 75.96 ± 5.13 | 62.00 ± 5.44 |
| DXM | 86.19 ± 1.97 | 62.12 ± 1.41 | 81.65 ± 1.27 | 71.71 ± 1.90 |
| TMZ + DXM | 83.11 ± 6.05 | 65.93 ± 3.68 | 80.35 ± 3.32 | 60.23 ± 5.86 |
| Group | Distal Femoral Epiphysis | Proximal Tibial Epiphysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length of Proliferation Zone/Maturation Zone, % | Length of Maturation Zone/Epiphyseal Cartilage, % | Mean Thickness of Epiphyseal Cartilage, µM | Mean Thickness of Epiphyseal Cartilage Proliferative Zone, µM | Length of Proliferation Zone/Maturation Zone, % | Length of Maturation Zone/Epiphyseal Cartilage, % | Mean Thickness of Epiphyseal Cartilage, µM | Mean Thickness of Epiphyseal Cartilage Proliferative Zone, µM | |
| Control | 18.03 ± 2.86 | 36.44 ± 1.68 | 195.83 ± 37.65 | 12.23 ± 1.23 | 6.86 ± 0.13 | 65.68 ± 0.07 | 349.08 ± 14.90 | 15.71 ± 0.35 |
| TMZ | 18.58 ± 2.33 | 37.25 ± 1.47 | 198.39 ± 33.81 | 13.63 ± 2.92 | 25.40 ± 4.91 ** | 43.92 ± 4.56 ** | 161.63 ± 40.26 *** | 17.07 ± 2.04 |
| DXM | 21.34 ± 4.99 | 37.77 ± 5.84 | 210.73 ± 11.48 | 15.82 ± 2.24 | 10.29 ± 1.18 | 56.01 ± 3.48 | 266.37 ± 29.30 * | 14.70 ± 1.65 |
| TMZ + DXM | 17.24 ± 4.88 | 38.69 ± 4.30 | 228.39 ± 31.91 | 13.54 ± 0.72 | 15.51 ± 1.50 ** | 36.73 ± 5.77 ** | 208.53 ± 28.67 *** | 11.32 ± 0.87 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suhovskih, A.V.; Molodykh, O.P.; Ushakov, V.S.; Politko, M.O.; Sokolov, D.K.; Koldysheva, E.V.; Grigorieva, E.V. Long-Term Exposure to Temozolomide Affects Locomotor Activity and Cartilage Structure of Elderly Experimental Rats. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120541
Suhovskih AV, Molodykh OP, Ushakov VS, Politko MO, Sokolov DK, Koldysheva EV, Grigorieva EV. Long-Term Exposure to Temozolomide Affects Locomotor Activity and Cartilage Structure of Elderly Experimental Rats. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(12):541. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120541
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuhovskih, Anastasia V., Olga P. Molodykh, Victor S. Ushakov, Maxim O. Politko, Dmitry K. Sokolov, Elena V. Koldysheva, and Elvira V. Grigorieva. 2020. "Long-Term Exposure to Temozolomide Affects Locomotor Activity and Cartilage Structure of Elderly Experimental Rats" Biomedicines 8, no. 12: 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120541
APA StyleSuhovskih, A. V., Molodykh, O. P., Ushakov, V. S., Politko, M. O., Sokolov, D. K., Koldysheva, E. V., & Grigorieva, E. V. (2020). Long-Term Exposure to Temozolomide Affects Locomotor Activity and Cartilage Structure of Elderly Experimental Rats. Biomedicines, 8(12), 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120541





