The Phenotypic Spectrum of PRRT2-Associated Paroxysmal Neurologic Disorders in Childhood
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Analysis
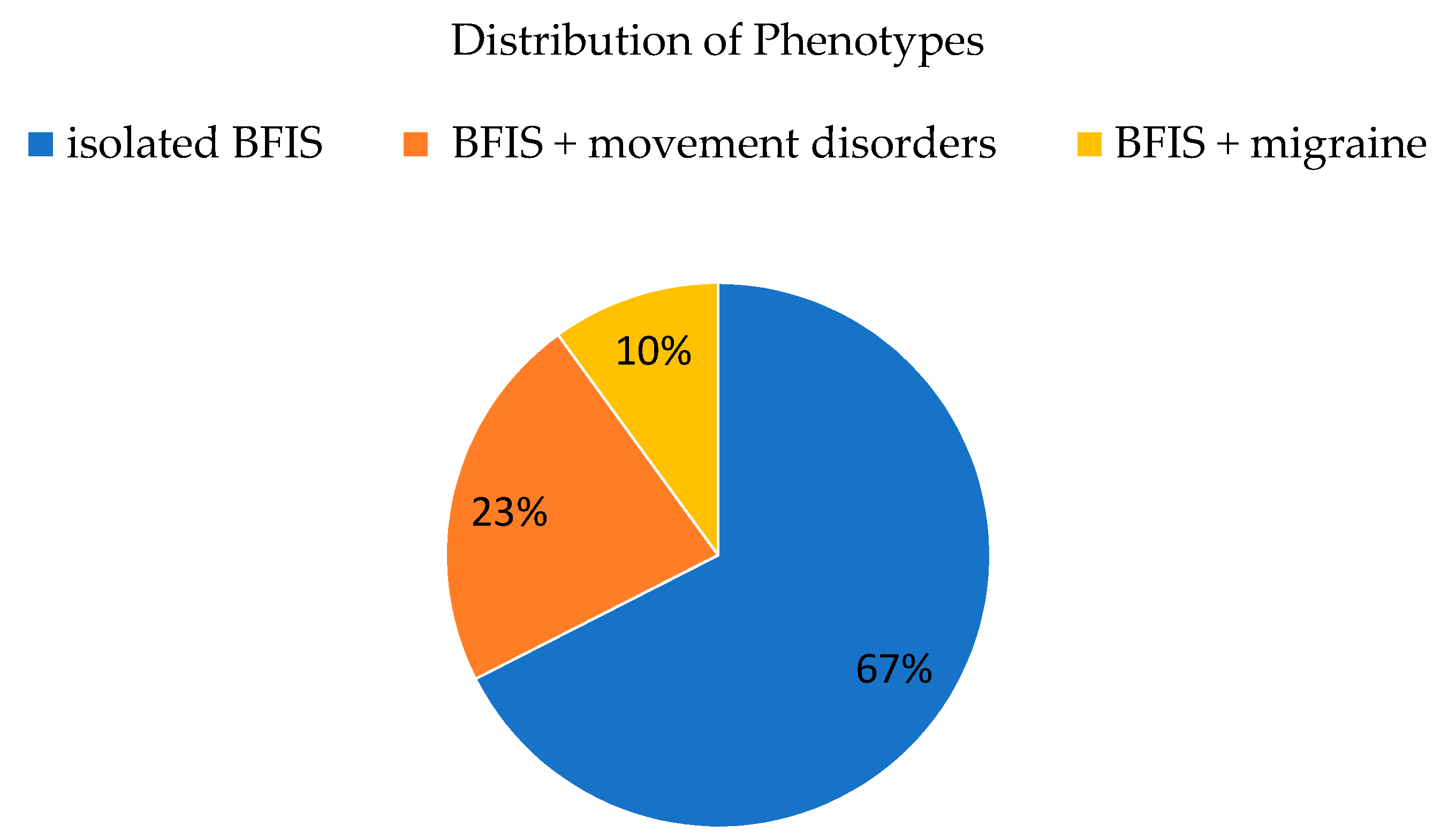
3.2. Phenotypic Spectrum
3.3. Epilepsy
3.4. BFIS Evolving to Acquired Aphasia with Epilepsy (Landau-Kleffner Syndrome)
3.5. Non-Epileptic Cyanotic Breath Holding Spells
3.6. Movement Disorders
3.7. Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia with Infantile Onset
3.8. Benign Myoclonus of Infancy
3.9. Episodic Ataxia with Myoclonus after Minor Head Trauma
3.10. Migraine
3.11. Development
3.12. Associated Morbidity and Mortality
3.13. Brain Imaging
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, W.-J.; Lin, Y.; Xiong, Z.-Q.; Wei, W.; Ni, W.; Tan, G.-H.; Guo, S.-L.; He, J.; Chen, Y.-F.; Zhang, Q.-J.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies truncating mutations in PRRT2 that cause paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesia. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1252–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, S.; Yoshiura, K.-I.; Kinoshita, A.; Kikuchi, T.; Nakane, Y.; Kato, N.; Sadamatsu, M.; Konishi, T.; Nagamitsu, S.; Matsuura, M.; et al. Mutations in PRRT2 responsible for paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesias also cause benign familial infantile convulsions. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 57, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heron, S.E.; Grinton, B.E.; Kivity, S.; Afawi, Z.; Zuberi, S.M.; Hughes, J.N.; Pridmore, C.; Hodgson, B.L.; Iona, X.; Sadleir, L.G.; et al. PRRT2 Mutations Cause Benign Familial Infantile Epilepsy and Infantile Convulsions with Choreoathetosis Syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-Y.; Huang, Y.; Bruneau, N.; Roll, P.; Roberson, E.D.O.; Hermann, M.; Quinn, E.; Maas, J.; Edwards, R.; Ashizawa, T.; et al. Mutations in the Gene PRRT2 Cause Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia with Infantile Convulsions. Cell Rep. 2012, 1, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi-Fakhari, D.; Saffari, A.; Westenberger, A.; Klein, C. The evolving spectrum ofPRRT2-associated paroxysmal diseases. Brain 2015, 138, 3476–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi-Fakhari, D.; El Achkar, C.M.; Klein, C. PRRT2-Associated Paroxysmal Movement Disorders; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2018. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK475803/ (accessed on 28 October 2020).
- Dale, R.C.; Gardiner, A.; Antony, J.; Houlden, H. Familial PRRT2 mutation with heterogeneous paroxysmal disorders including paroxysmal torticollis and hemiplegic migraine. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2012, 54, 958–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, A.R.; Bhatia, K.P.; Stamelou, M.; Dale, R.C.; Kurian, M.A.; Schneider, S.A.; Wali, G.M.; Counihan, T.; Schapira, A.H.; Spacey, S.D.; et al. PRRT2 gene mutations: From paroxysmal dyskinesia to episodic ataxia and hemiplegic migraine. Neurology 2012, 79, 2115–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riant, F.; Roze, E.; Barbance, C.; Méneret, A.; Guyant-Marechal, L.; Lucas, C.; Sabouraud, P.; Trébuchon, A.; Depienne, C.; Tournier-Lasserve, E. PRRT2 mutations cause hemiplegic migraine. Neurology 2012, 79, 2122–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labate, A.; Tarantino, P.; Viri, M.; Mumoli, L.; Gagliardi, M.; Romeo, A.; Zara, F.; Annesi, G.; Gambardella, A. Homozygous c.649dupC mutation inPRRT2worsens the BFIS/PKD phenotype with mental retardation, episodic ataxia, and absences. Epilepsia 2012, 53, e196–e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, I.E.; Grinton, B.E.; Heron, S.E.; Kivity, S.; Afawi, Z.; Iona, X.; Goldberg-Stern, H.; Kinali, M.; Andrews, I.; Guerrini, R.; et al. PRRT2 phenotypic spectrum includes sporadic and fever-related infantile seizures. Neurology 2012, 79, 2104–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maini, I.; Iodice, A.; Spagnoli, C.; Salerno, G.G.; Bertani, G.; Frattini, D.; Fusco, C. Expanding phenotype of PRRT2 gene mutations: A new case with epilepsy and benign myoclonus of early infancy. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2016, 20, 454–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, P.; Castroflorio, E.; Rossi, P.; Fadda, M.; Sterlini, B.; Cervigni, R.I.; Prestigio, C.; Giovedi, S.; Onofri, F.; Mura, E.; et al. PRRT2 Is a Key Component of the Ca(2+)-Dependent Neurotransmitter Release Machinery. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Oksvold, P.; Kampf, C.; Djureinovic, D.; Odeberg, J.; Habuka, M.; Tahmasebpoor, S.; Danielsson, A.; Edlund, K.; et al. Analysis of the human tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 13, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, P.; Romei, A.; Fadda, M.; Sterlini, B.; Lonardoni, D.; Forte, N.; Fruscione, F.; Castroflorio, E.; Michetti, C.; Giansante, G.; et al. Constitutive Inactivation of the PRRT2 Gene Alters Short-Term Synaptic Plasticity and Promotes Network Hyperexcitability in Hippocampal Neurons. Cereb. Cortex 2018, 29, 2010–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardiles, Á.O.; Grabrucker, A.M.; Scholl, F.; Rudenko, G.; Borsello, T. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Synaptopathies. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 2643943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, S.G.N. Synaptopathies: Diseases of the synaptome. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2012, 22, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtorta, F.; Benfenati, F.; Zara, F.; Meldolesi, J. PRRT2: From Paroxysmal Disorders to Regulation of Synaptic Function. Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méneret, A.; Gaudebout, C.; Riant, F.; Vidailhet, M.; Depienne, C.; Roze, E. PRRT2mutations and paroxysmal disorders. Eur. J. Neurol. 2013, 20, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcourt, M.; Riant, F.; Mancini, J.; Milh, M.; Navarro, V.; Roze, E.; Humbertclaude, V.; Korff, C.; Portes, V.D.; Szepetowski, P.; et al. Severe phenotypic spectrum of biallelic mutations in PRRT2 gene. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 86, 782–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockmann, K. Erhebung Seltener Neurologischer Erkrankungen im Kindesalter. Neuropediatrics 2014, 45, fp036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; ACMG Laboratory Quality Assurance Committee; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassinari, C.A.; Rubboli, G.; Volpi, L.; Meletti, S.; D’Orsi, G.; Franca, M.; Sabetta, A.R.; Riguzzi, P.; Gardella, E.; Zaniboni, A.; et al. Encephalopathy with electrical status epilepticus during slow sleep or ESES syndrome including the acquired aphasia. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2000, 111, S94–S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Sun, W.; Feng, B.; Du, T.; Sun, B.; Niu, F.; Wei, H.; Wu, X.; et al. Targeted genomic sequencing identifies PRRT2 mutations as a cause of paroxysmal kinesigenic choreoathetosis. J. Med. Genet. 2011, 49, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlaskamp, D.R.; Callenbach, P.M.C.; Rump, P.; Giannini, L.A.A.; Brilstra, E.H.; Dijkhuizen, T.; Vos, Y.J.; Van Der Kevie-Kersemaekers, A.-M.F.; Knijnenburg, J.; De Leeuw, N.; et al. PRRT2-related phenotypes in patients with a 16p11.2 deletion. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2019, 62, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Qin, X.; Nong, Y.; Zou, D.; Wu, Y. The genetic relationship between epilepsy and hemiplegic migraine. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2017, 13, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraballo, R.; Pavlidis, E.; Nikanorova, M.; Loddenkemper, T. Encephalopathy with continuous spike-waves during slow-wave sleep: Evolution and prognosis. Epileptic Disord. 2019, 21, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Lemke, J.R.; Lal, D.; Reinthaler, E.M.; Steiner, I.; Nothnagel, M.; Alber, M.; Geider, K.; Laube, B.; Schwake, M.; Finsterwalder, K.; et al. Mutations in GRIN2A cause idiopathic focal epilepsy with rolandic spikes. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvill, G.L.; Regan, B.M.; Yendle, S.C.; O’Roak, B.J.; Lozovaya, N.; Bruneau, N.; Burnashev, N.; Khan, A.; Cook, J.; Geraghty, E.; et al. GRIN2A mutations cause epilepsy-aphasia spectrum disorders. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, A.; Ng-Cordell, E.; Hanna, N.; Brkic, D.; Baker, K. The Neurodevelopmental Spectrum of Synaptic Vesicle Cycling Disorders. J. Neurochem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labate, A.; Tarantino, P.; Palamara, G.; Gagliardi, M.; Cavalcanti, F.; Ferlazzo, E.; Sturniolo, M.; Incorpora, G.; Annesi, G.; Aguglia, U.; et al. Mutations in PRRT2 result in familial infantile seizures with heterogeneous phenotypes including febrile convulsions and probable SUDEP. Epilepsy Res. 2013, 104, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMario, F.J. Prospective study of children with cyanotic and pallid breath-holding spells. Pediatrics 2001, 107, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.K.C.; Leung, A.A.; Wong, A.H.; Hon, K.L. Breath-Holding Spells in Pediatrics: A Narrative Review of the Current Evidence. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2019, 15, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, J.; Martinez, J.; Maertens, P. Atypical Cyanotic Breath-Holding Spells in an Infant with 16p11.2 Microdeletion Syndrome. Clin. Pediatr. 2017, 57, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, R.B.; Bigal, M.E.; Diamond, M.; Freitag, F.; Reed, M.L.; Stewart, W.F. Migraine prevalence, disease burden, and the need for preventive therapy. Neurology 2007, 68, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, L.L.; Eriksen, M.K.; Roemer, S.F.; Andersen, I.; Olesen, J.; Russell, M.B. A population-based study of familial hemiplegic migraine suggests revised diagnostic criteria. Brain 2002, 125, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poethko-Mueller, C.; Thamm, R.; Heidemann, C.; Busch, M.; Neuhauser, H. Febrile seizures, epilepsy, migraine, diabetes, and heart disease as well as measles, chicken pox, and whooping cough in children and adolescents in Germany: Results from KiGGS Wave 2. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundh. Gesundh. 2019, 62, 1162–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Legris, N.; Chassin, O.; Nasser, G.; Riant, F.; Tournier-Lasserve, E.; Denier, C. Acute-Onset Ataxia and Transient Cerebellar Diffusion Restriction Associated with a PRRT2 Mutation. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2019, 28, e3–e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| n | Mean | Minimum | Maximum | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at inclusion (years) | 40 | 6.6 | 1 | 26 | 5.46 |
| Age at first reported seizure (months) | 40 | 5.7 | 1 | 15 | 2.67 |
| Age at seizure freedom (months) | 33 | 14.4 | 1 | 132 | 22.24 |
| Age at diagnosis (months) | 40 | 6.1 | 1 | 15 | 2.85 |
| Age at genetic diagnosis (months) | 40 | 45.3 | 3 | 216 | 60.85 |
| Index (n) | Family (n) | Gene (Coding DNA) | Protein | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heterozygous Variants in PRRT2 | ||||
| 1 | 0 | c.323_324del | p.(Thr108Serfs*25) | |
| 1 | 1 | c.341_342del | p.(Val114Glufs*19) | |
| 1 | 1 | c.593_594del | p.(Pro198Argfs*26) | |
| 30 | 31 | c.649dupC | p.(Arg217Profs*8) | |
| 0 | 1 # | c.836C>T | p.(Pro279Leu) | |
| 1 | 1 | c.843G>T | p.(Trp281Cys) | |
| 1 | 0 | c.(?-65)_(1243-?)del | exon 2-4 del | |
| 2 | 0 | 16p11.2del | 16p11.2 del | |
| Biallelic Variants in PRRT2 | ||||
| Compound heterozygous | 1 | 0 | c.649dupC 16p11.2del | p.(Arg217Profs*8) 16p11.2 del |
| Compound heterozygous | 1 | 0 | c.836C>T 16p11.2del | p.(Pro279Leu) 16p11.2 del |
| Homozygous | 1 | 0 | c.649dupC c.649dupC | p.(Arg217Profs*8) p.(Arg217Profs*8) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Döring, J.H.; Saffari, A.; Bast, T.; Brockmann, K.; Ehrhardt, L.; Fazeli, W.; Janzarik, W.G.; Kluger, G.; Muhle, H.; Møller, R.S.; et al. The Phenotypic Spectrum of PRRT2-Associated Paroxysmal Neurologic Disorders in Childhood. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8110456
Döring JH, Saffari A, Bast T, Brockmann K, Ehrhardt L, Fazeli W, Janzarik WG, Kluger G, Muhle H, Møller RS, et al. The Phenotypic Spectrum of PRRT2-Associated Paroxysmal Neurologic Disorders in Childhood. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(11):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8110456
Chicago/Turabian StyleDöring, Jan Henje, Afshin Saffari, Thomas Bast, Knut Brockmann, Laura Ehrhardt, Walid Fazeli, Wibke G. Janzarik, Gerhard Kluger, Hiltrud Muhle, Rikke S. Møller, and et al. 2020. "The Phenotypic Spectrum of PRRT2-Associated Paroxysmal Neurologic Disorders in Childhood" Biomedicines 8, no. 11: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8110456
APA StyleDöring, J. H., Saffari, A., Bast, T., Brockmann, K., Ehrhardt, L., Fazeli, W., Janzarik, W. G., Kluger, G., Muhle, H., Møller, R. S., Platzer, K., Santos, J. L., Bache, I., Bertsche, A., Bonfert, M., Borggräfe, I., Broser, P. J., Datta, A. N., Hammer, T. B., ... Syrbe, S. (2020). The Phenotypic Spectrum of PRRT2-Associated Paroxysmal Neurologic Disorders in Childhood. Biomedicines, 8(11), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8110456






