Development and Evaluation of Quality Metrics for Bioinformatics Analysis of Viral Insertion Site Data Generated Using High Throughput Sequencing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
| Clones | Ratio | Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| K562 clone 3 + K562 clone 6 | 100:0 | LM, LAM, nrLAM |
| K562 clone 3 + K562 clone 6 | 99.9:0.1 | LM, LAM, nrLAM |
| K562 clone 3 + K562 clone 6 | 99:1 | LM, LAM, nrLAM |
| K562 clone 3 + K562 clone 6 | 90:10 | LM, LAM, nrLAM |
| K562 clone 3 + K562 clone 6 | 75:25 | LM, LAM, nrLAM |
| K562 clone 3 + K562 clone 6 | 50:50 | LAM, nrLAM |
| K562 clone 3 + K562 clone 6 | 25:75 | LAM, nrLAM |
| K562 clone 3 + K562 clone 6 | 10:90 | LM, LAM, nrLAM |
| K562 clone 3 + K562 clone 6 | 1:99 | LM, LAM, nrLAM |
| K562 clone 3 + K562 clone 6 | 0.1:99.9 | LM, LAM, nrLAM |
| K562 clone 3 + K562 clone 6 | 0:100 | LM, LAM, nrLAM |
2.1. Theoretical Yield

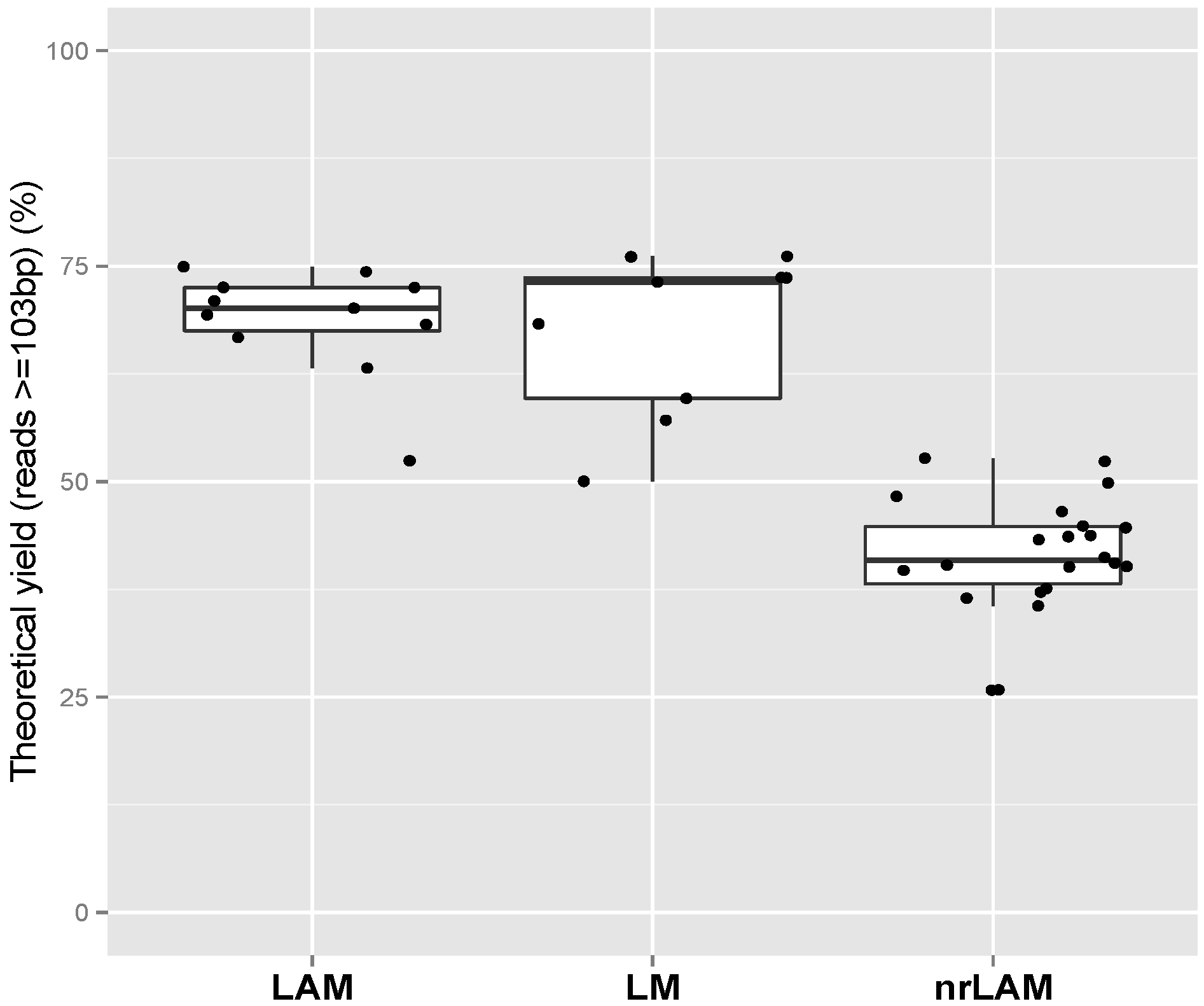
2.2. Vector Specificity
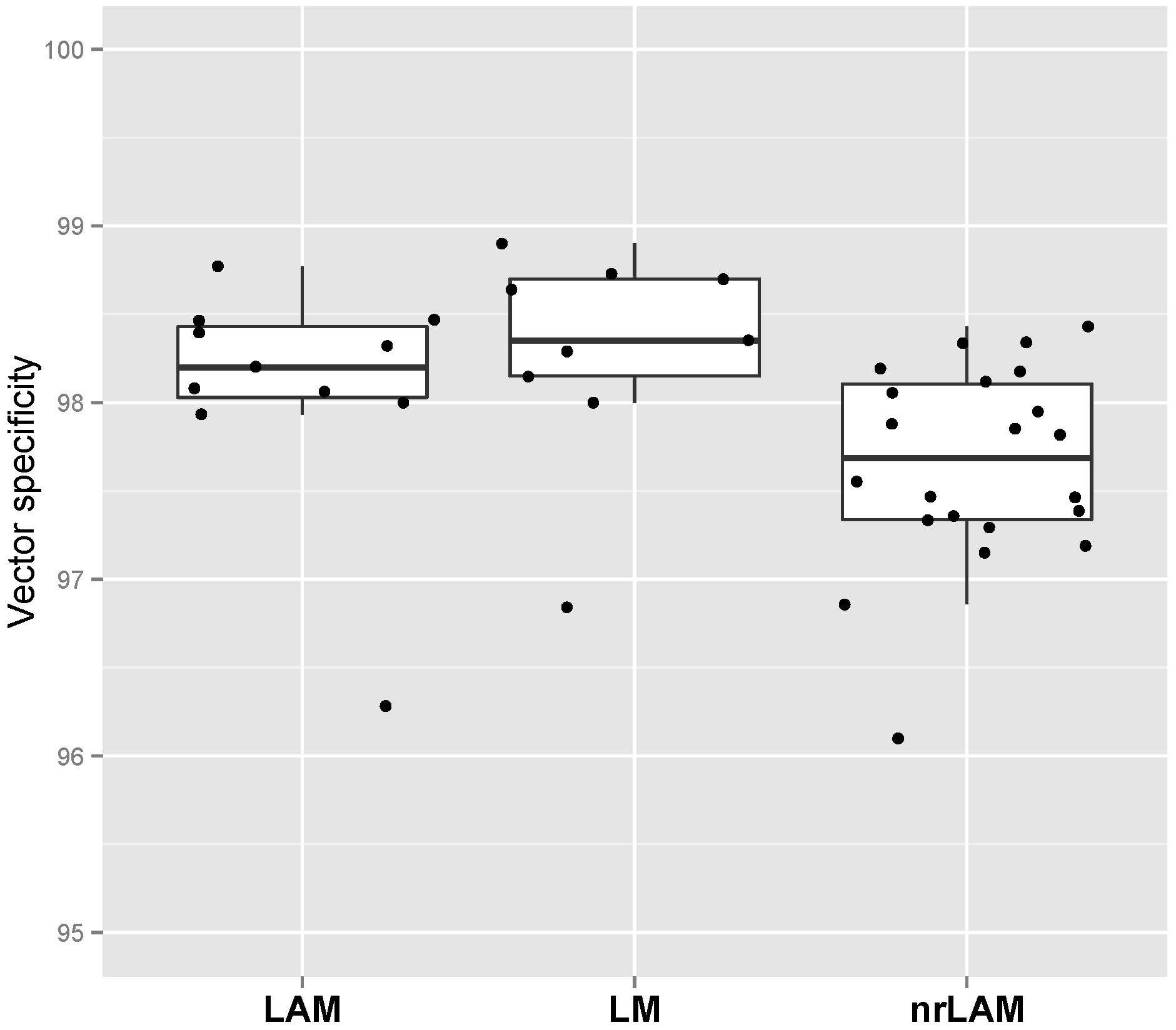
2.3. Internal Control and Genomic Specificity
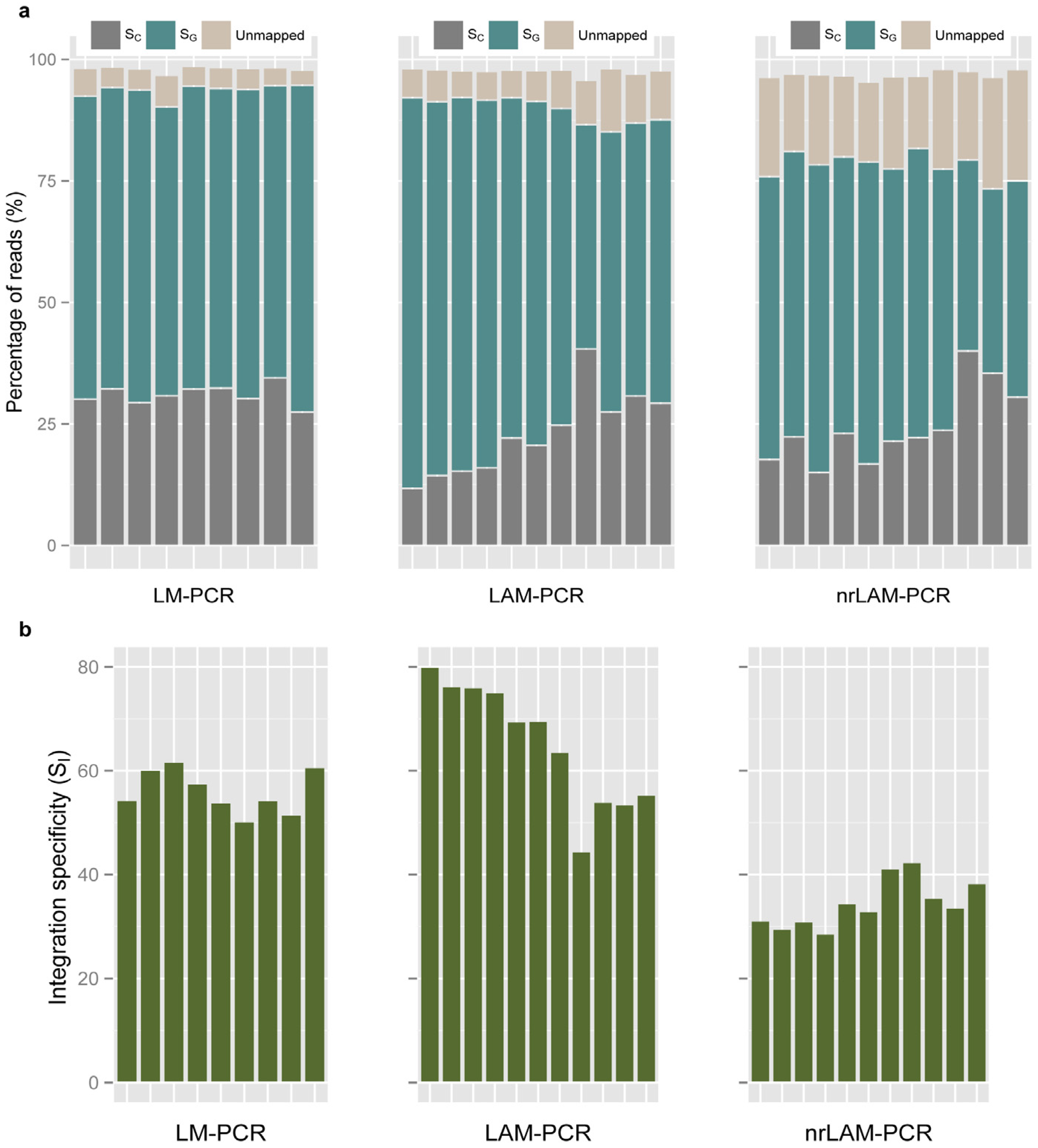
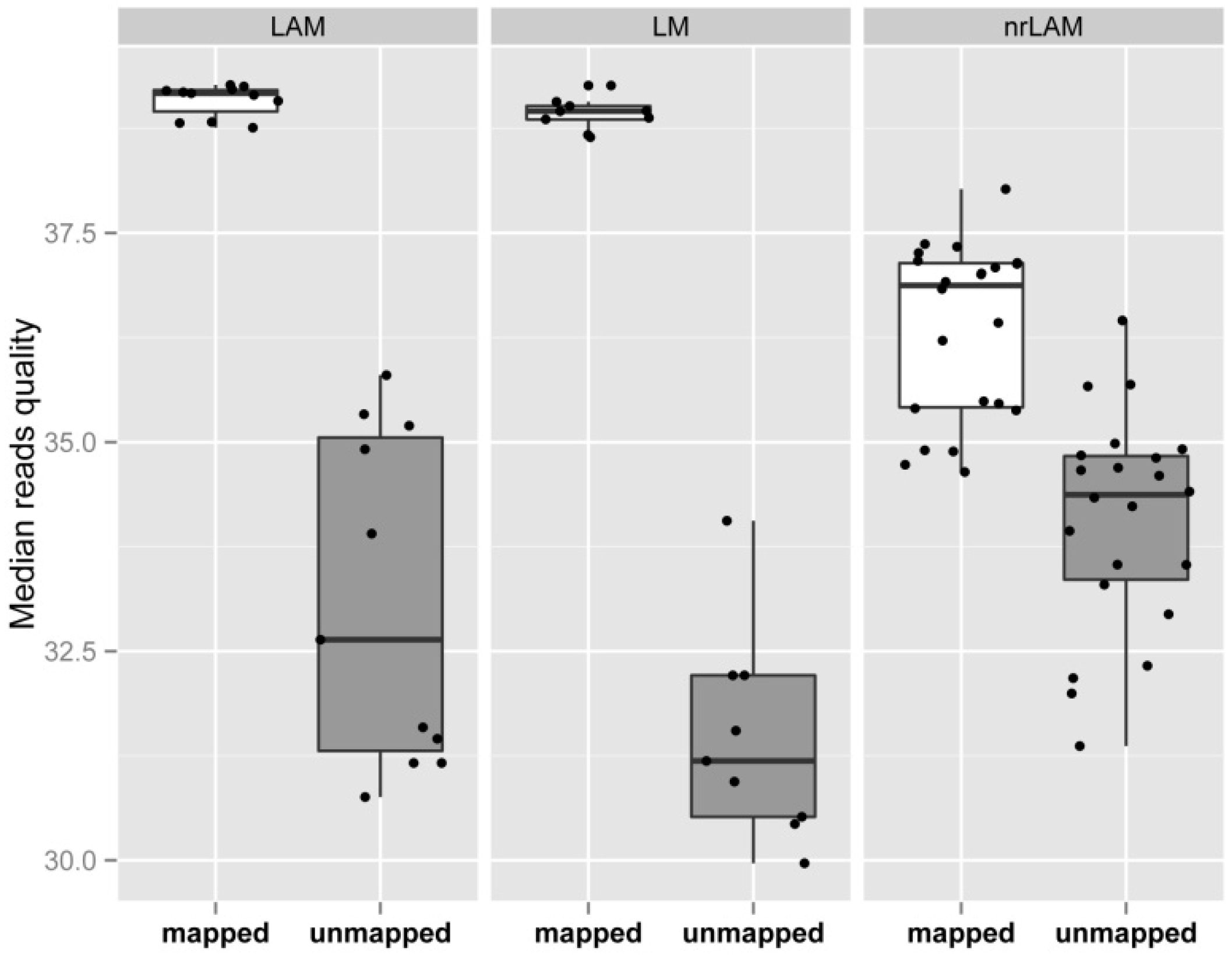
2.4. Integration Specificity
2.5. Assaying Lower Limit Sensitivity of the IS-PCR Methods
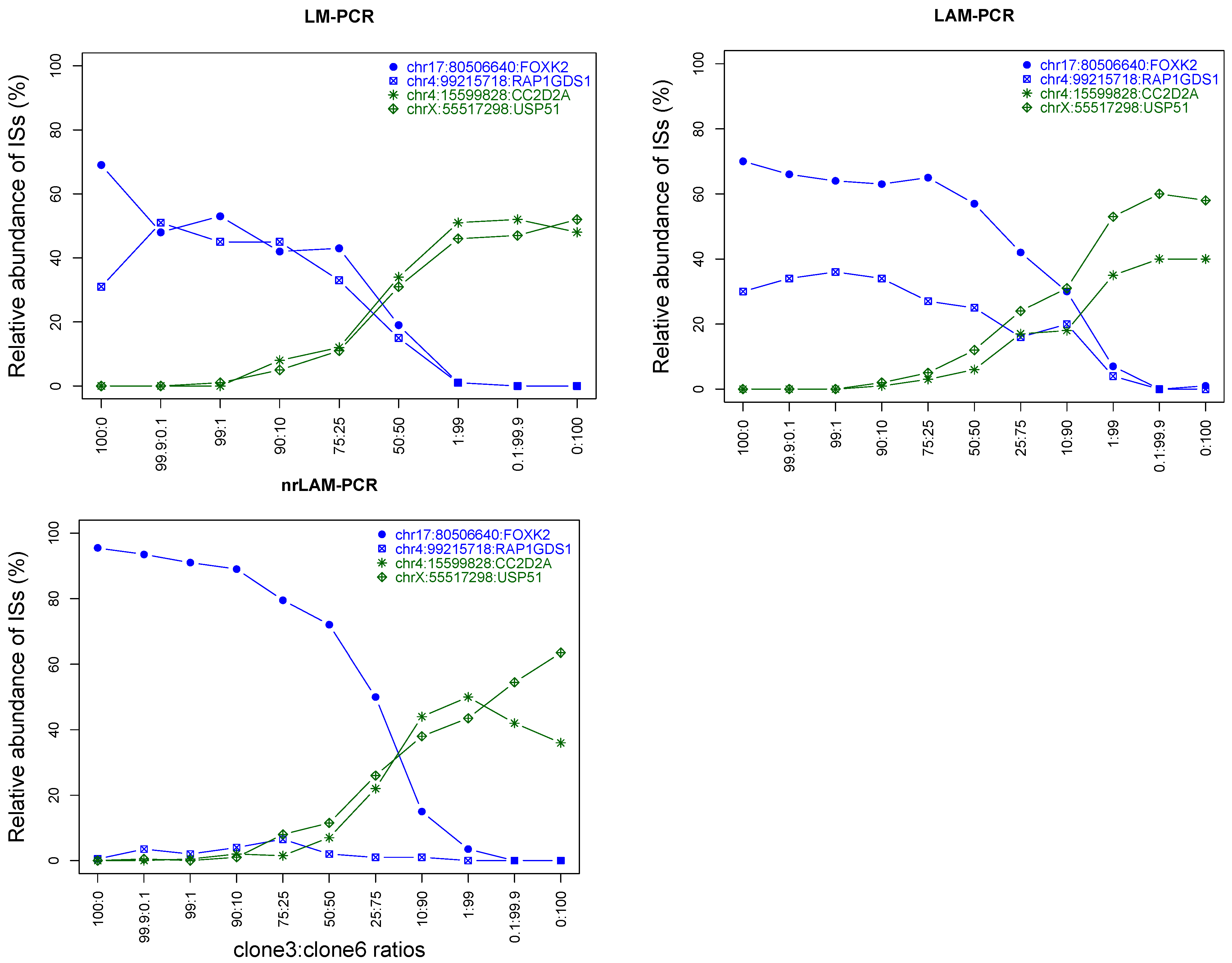
2.6. Application of Various Metrics Developed
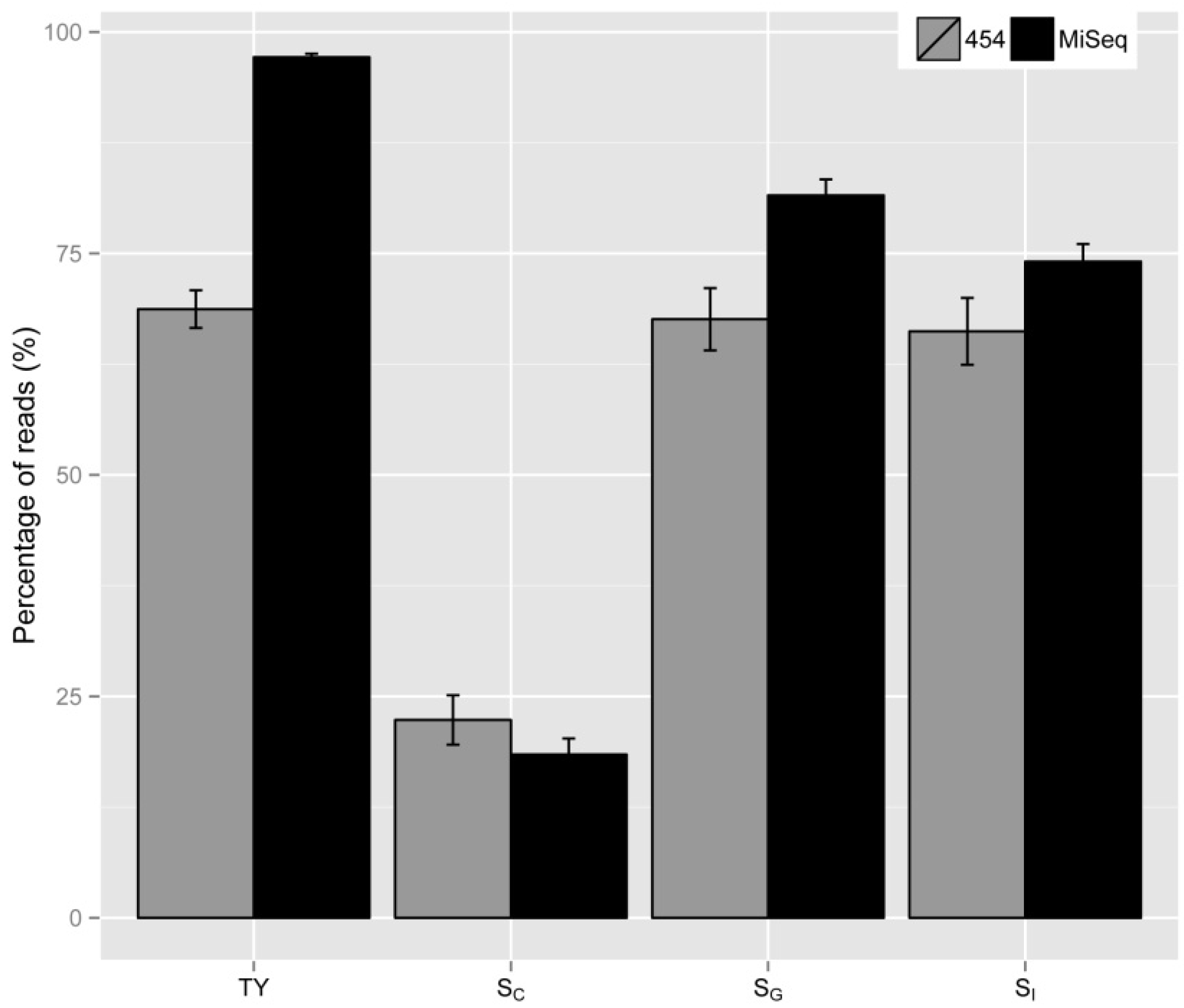
| Samples # | Number of Insertion Sites * | TY | SV | SC | SG | SI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 bone marrow | 57 | 70.5 ± 0.68 | 97.73 ± 0.44 | 44.82 ± 0.96 | 52.49 ± 0.69 | 47.25 ± 0.26 |
| Sample 1 spleen | 58 | 64.25 ± 0.57 | 99.27 ± 0.04 | 47.32 ± 1.11 | 50.36 ± 1.06 | 47.39 ± 0.91 |
| Sample 2 bone marrow | 7 | 79.6 ± 0.32 | 98.72 ± 0.17 | 57.75 ± 1.11 | 40.65 ± 1.03 | 39 ± 1.03 |
| Sample 2 spleen | 24 | 73.87 ± 0.05 | 99.22 ± 0.14 | 50.67 ± 0.24 | 48.08 ± 0.15 | 46.74 ± 0.18 |
| Sample 3 bone marrow | 33 | 54.9 ± 0.56 | 93.54 ± 0.21 | 49.5 ± 1.19 | 45.34 ± 1.24 | 33.1 ± 1.14 |
| Sample 3 spleen | 53 | 65.72 ± 0.71 | 94.67 ± 0.38 | 49.69 ± 0.93 | 44.75 ± 1.04 | 36.06 ± 0.83 |
| Sample 4 bone marrow | 28 | 67.72 ± 0.68 | 99.49 ± 0.11 | 55.48 ± 0.84 | 42.92 ± 0.65 | 39.19 ± 0.82 |
| Sample 4 spleen | 37 | 68.83 ± 0.84 | 99.23 ± 0.12 | 61.43 ± 0.23 | 36.68 ± 0.13 | 32.44 ± 0.33 |
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Metrics Calculation
3.3. LTR Insertions Site Analysis by LM-PCR, LAM-PCR and nrLAM-PCR
3.4. 454 Library Preparation
3.5. MiSeq Sequencing
3.6. Data Processing and Integration Loci Identification
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hacein-Bey-Abina, S.; von Kalle, C.; Schmidt, M.; le Deist, F.; Wulffraat, N.; McIntyre, E.; Radford, I.; Villeval, J.L.; Fraser, C.C.; Cavazzana-Calvo, M.; et al. A serious adverse event after successful gene therapy for X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 255–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, S.; Ott, M.G.; Schultze-Strasser, S.; Jauch, A.; Burwinkel, B.; Kinner, A.; Schmidt, M.; Kramer, A.; Schwable, J.; Glimm, H.; et al. Genomic instability and myelodysplasia with monosomy 7 consequent to evi1 activation after gene therapy for chronic granulomatous disease. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 198–204. [Google Scholar]
- Cavazzana-Calvo, M.; Payen, E.; Negre, O.; Wang, G.; Hehir, K.; Fusil, F.; Down, J.; Denaro, M.; Brady, T.; Westerman, K.; et al. Transfusion independence and hmga2 activation after gene therapy of human beta-thalassaemia. Nature 2010, 467, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasco, L.; Baricordi, C.; Aiuti, A. Retroviral integrations in gene therapy trials. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, P.R.; Wold, B. In vivo footprinting of a muscle specific enhancer by ligation mediated pcr. Science 1989, 246, 780–786. [Google Scholar]
- Steigerwald, S.D.; Pfeifer, G.P.; Riggs, A.D. Ligation-mediated pcr improves the sensitivity of methylation analysis by restriction enzymes and detection of specific DNA strand breaks. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 1435–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R. Ligation-mediated pcr of restriction fragments from large DNA molecules. PCR Methods Appl. 1992, 2, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Hoffmann, G.; Wissler, M.; Lemke, N.; Mussig, A.; Glimm, H.; Williams, D.A.; Ragg, S.; Hesemann, C.U.; von Kalle, C. Detection and direct genomic sequencing of multiple rare unknown flanking DNA in highly complex samples. Hum. Gene Ther. 2001, 12, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Zickler, P.; Hoffmann, G.; Haas, S.; Wissler, M.; Muessig, A.; Tisdale, J.F.; Kuramoto, K.; Andrews, R.G.; Wu, T.; et al. Polyclonal long-term repopulating stem cell clones in a primate model. Blood 2002, 100, 2737–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Schwarzwaelder, K.; Bartholomae, C.; Zaoui, K.; Ball, C.; Pilz, I.; Braun, S.; Glimm, H.; von Kalle, C. High-resolution insertion-site analysis by linear amplification-mediated pcr (lam-pcr). Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Jares, A.; Winkler, T.; Xie, J.; Metais, J.Y.; Dunbar, C.E. High efficiency restriction enzyme-free linear amplification-mediated polymerase chain reaction approach for tracking lentiviral integration sites does not abrogate retrieval bias. Hum. Gene Ther. 2013, 24, 38–47. [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel, R.; Eckenberg, R.; Paruzynski, A.; Bartholomae, C.C.; Nowrouzi, A.; Arens, A.; Howe, S.J.; Recchia, A.; Cattoglio, C.; Wang, W.; et al. Comprehensive genomic access to vector integration in clinical gene therapy. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1431–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paruzynski, A.; Arens, A.; Gabriel, R.; Bartholomae, C.C.; Scholz, S.; Wang, W.; Wolf, S.; Glimm, H.; Schmidt, M.; von Kalle, C. Genome-wide high-throughput integrome analyses by nrlam-pcr and next-generation sequencing. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1379–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustikova, O.; Fehse, B.; Modlich, U.; Yang, M.; Dullmann, J.; Kamino, K.; von Neuhoff, N.; Schlegelberger, B.; Li, Z.; Baum, C. Clonal dominance of hematopoietic stem cells triggered by retroviral gene marking. Science 2005, 308, 1171–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.P.; Garrigue, A.; Ciuffi, A.; Ronen, K.; Leipzig, J.; Berry, C.; Lagresle-Peyrou, C.; Benjelloun, F.; Hacein-Bey-Abina, S.; Fischer, A.; et al. DNA bar coding and pyrosequencing to analyze adverse events in therapeutic gene transfer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornils, K.; Bartholomae, C.C.; Thielecke, L.; Lange, C.; Arens, A.; Glauche, I.; Mock, U.; Riecken, K.; Gerdes, S.; von Kalle, C.; et al. Comparative clonal analysis of reconstitution kinetics after transplantation of hematopoietic stem cells gene marked with a lentiviral sin or a gamma-retroviral ltr vector. Exp. Hematol. 2013, 41, 28–38.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaeppel, C.; Beattie, S.G.; Fronza, R.; van Logtenstein, R.; Salmon, F.; Schmidt, S.; Wolf, S.; Nowrouzi, A.; Glimm, H.; von Kalle, C.; et al. A largely random aav integration profile after lpld gene therapy. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 889–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiuti, A.; Biasco, L.; Scaramuzza, S.; Ferrua, F.; Cicalese, M.P.; Baricordi, C.; Dionisio, F.; Calabria, A.; Giannelli, S.; Castiello, M.C.; et al. Lentiviral hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy in patients with wiskott-aldrich syndrome. Science 2013, 341, 1233151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffi, A.; Montini, E.; Lorioli, L.; Cesani, M.; Fumagalli, F.; Plati, T.; Baldoli, C.; Martino, S.; Calabria, A.; Canale, S.; et al. Lentiviral hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy benefits metachromatic leukodystrophy. Science 2013, 341, 1233158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelt, J.U.; Giordano, F.A.; Ecker, M.; Roeder, I.; Grund, N.; Hotz-Wagenblatt, A.; Opelz, G.; Zeller, W.J.; Allgayer, H.; Fruehauf, S.; et al. Quickmap: A public tool for large-scale gene therapy vector insertion site mapping and analysis. Gene Ther. 2009, 16, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, T.B.; Dantzer, J.; Peters, B.; Dinauer, M.; Mockaitis, K.; Mooney, S.; Cornetta, K. Identifying viral integration sites using seqmap 2.0. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 720–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arens, A.; Appelt, J.U.; Bartholomae, C.C.; Gabriel, R.; Paruzynski, A.; Gustafson, D.; Cartier, N.; Aubourg, P.; Deichmann, A.; Glimm, H.; et al. Bioinformatic clonality analysis of next-generation sequencing-derived viral vector integration sites. Hum. Gene Ther. Methods 2012, 23, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarver, A.L.; Erdman, J.; Starr, T.; Largaespada, D.A.; Silverstein, K.A. Tapdance: An automated tool to identify and annotate transposon insertion ciss and associations between ciss from next generation sequence data. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huston, M.W.; Brugman, M.H.; Horsman, S.; Stubbs, A.; van der Spek, P.; Wagemaker, G. Comprehensive investigation of parameter choice in viral integration site analysis and its effects on the gene annotations produced. Hum. Gene Ther. 2012, 23, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Pech, N.K.; Shelley, W.C.; Srour, E.F.; Yoder, M.C.; Dinauer, M.C. Antibody targeting kit as pretransplantation conditioning in immunocompetent mice. Blood 2010, 116, 5419–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. Bioinform. Action 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Development Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, H.; Hawkins, T.; Jasti, A.; Chen, Y.-H.; Mockaitis, K.; Dinauer, M.; Cornetta, K. Development and Evaluation of Quality Metrics for Bioinformatics Analysis of Viral Insertion Site Data Generated Using High Throughput Sequencing. Biomedicines 2014, 2, 195-210. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines2020195
Gao H, Hawkins T, Jasti A, Chen Y-H, Mockaitis K, Dinauer M, Cornetta K. Development and Evaluation of Quality Metrics for Bioinformatics Analysis of Viral Insertion Site Data Generated Using High Throughput Sequencing. Biomedicines. 2014; 2(2):195-210. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines2020195
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Hongyu, Troy Hawkins, Aparna Jasti, Yu-Hsiang Chen, Keithanne Mockaitis, Mary Dinauer, and Kenneth Cornetta. 2014. "Development and Evaluation of Quality Metrics for Bioinformatics Analysis of Viral Insertion Site Data Generated Using High Throughput Sequencing" Biomedicines 2, no. 2: 195-210. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines2020195
APA StyleGao, H., Hawkins, T., Jasti, A., Chen, Y.-H., Mockaitis, K., Dinauer, M., & Cornetta, K. (2014). Development and Evaluation of Quality Metrics for Bioinformatics Analysis of Viral Insertion Site Data Generated Using High Throughput Sequencing. Biomedicines, 2(2), 195-210. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines2020195





