Involvement of Secondary Induced Thrombus on Hemorrhage Induced by Both Delayed Recanalization and Delayed t-PA Treatment in Murine Ischemic Stroke Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Whole Experimental Setup and Ischemic Stroke Models
2.3. Blood Flow Measurement
2.4. Visualization of SIT, Glycocalyx, and Vascular Permeability Following Cerebral Infarction
2.5. Administration of t-PA, Heparin, and Aprotinin
2.6. Measurement of the Amount of SIT and TL Negative Area
2.7. Quantification of Damage Size and Bleeding Volume
2.8. MMP Activity
2.9. Immunohistochemistry
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
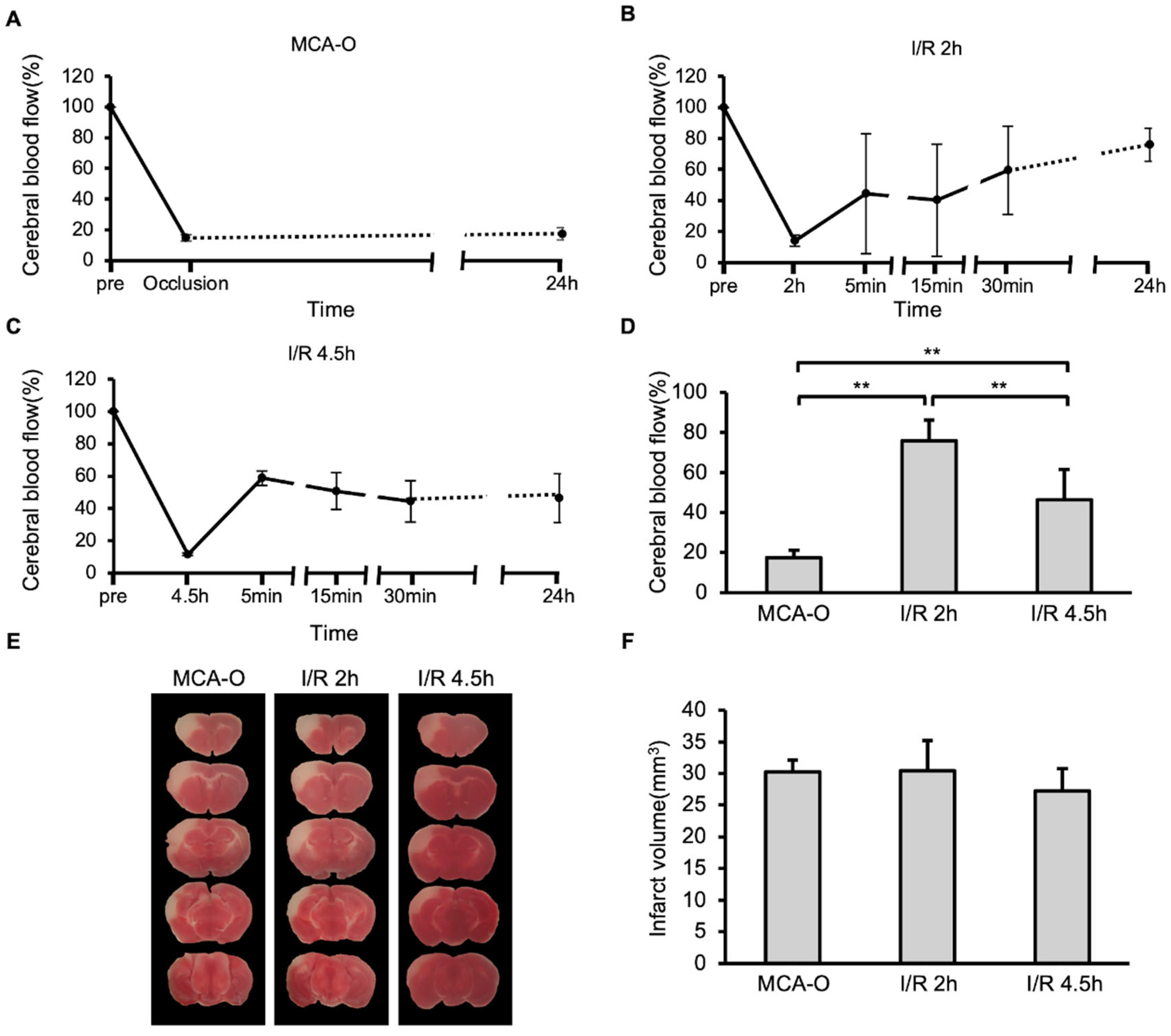
3.1. Blood Flow and Lesion Size in MCA-O and I/R Models
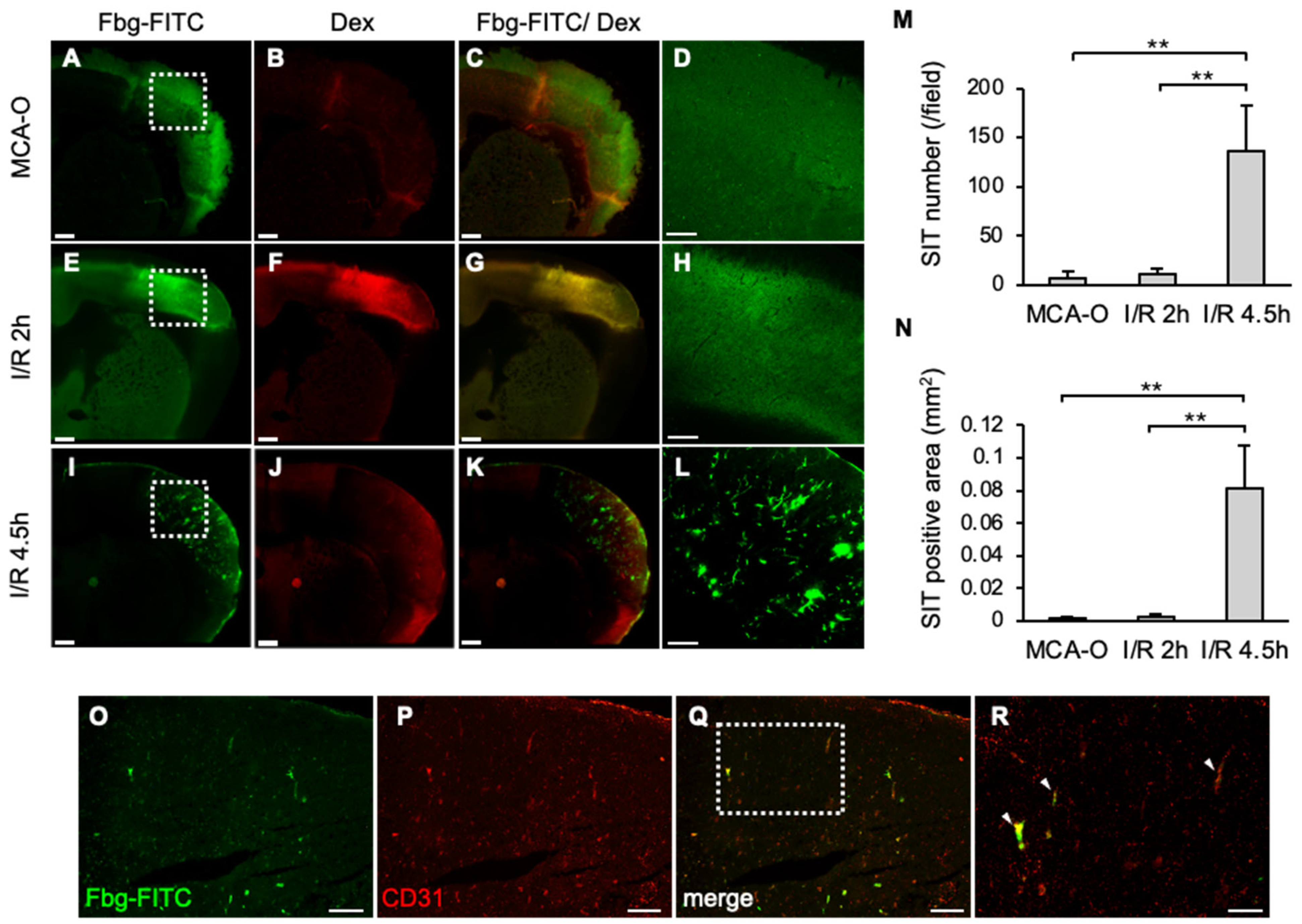
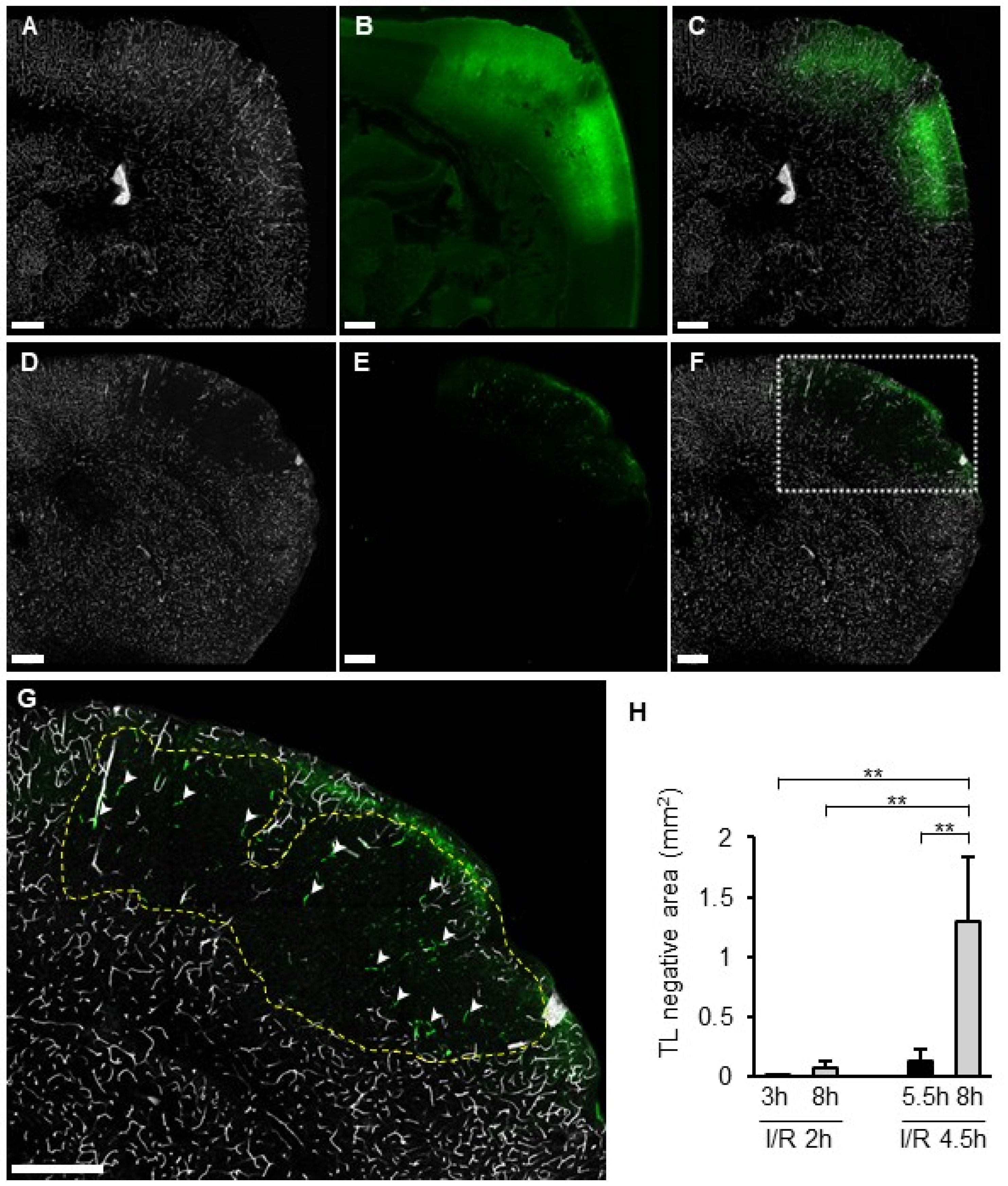
3.2. SIT and Vascular Permeability
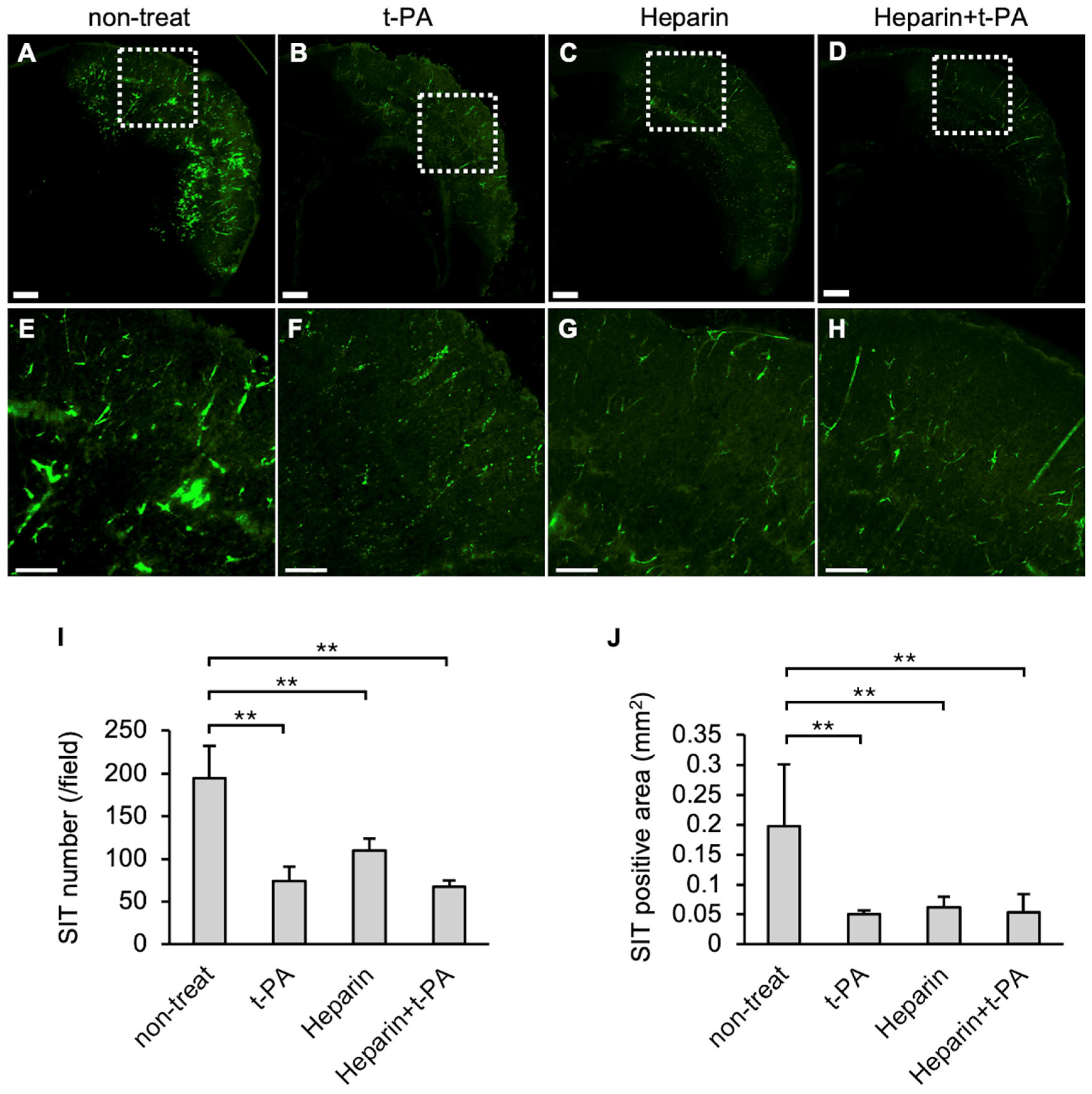
3.3. Effects of t-PA and Heparin Administration on SIT Formation
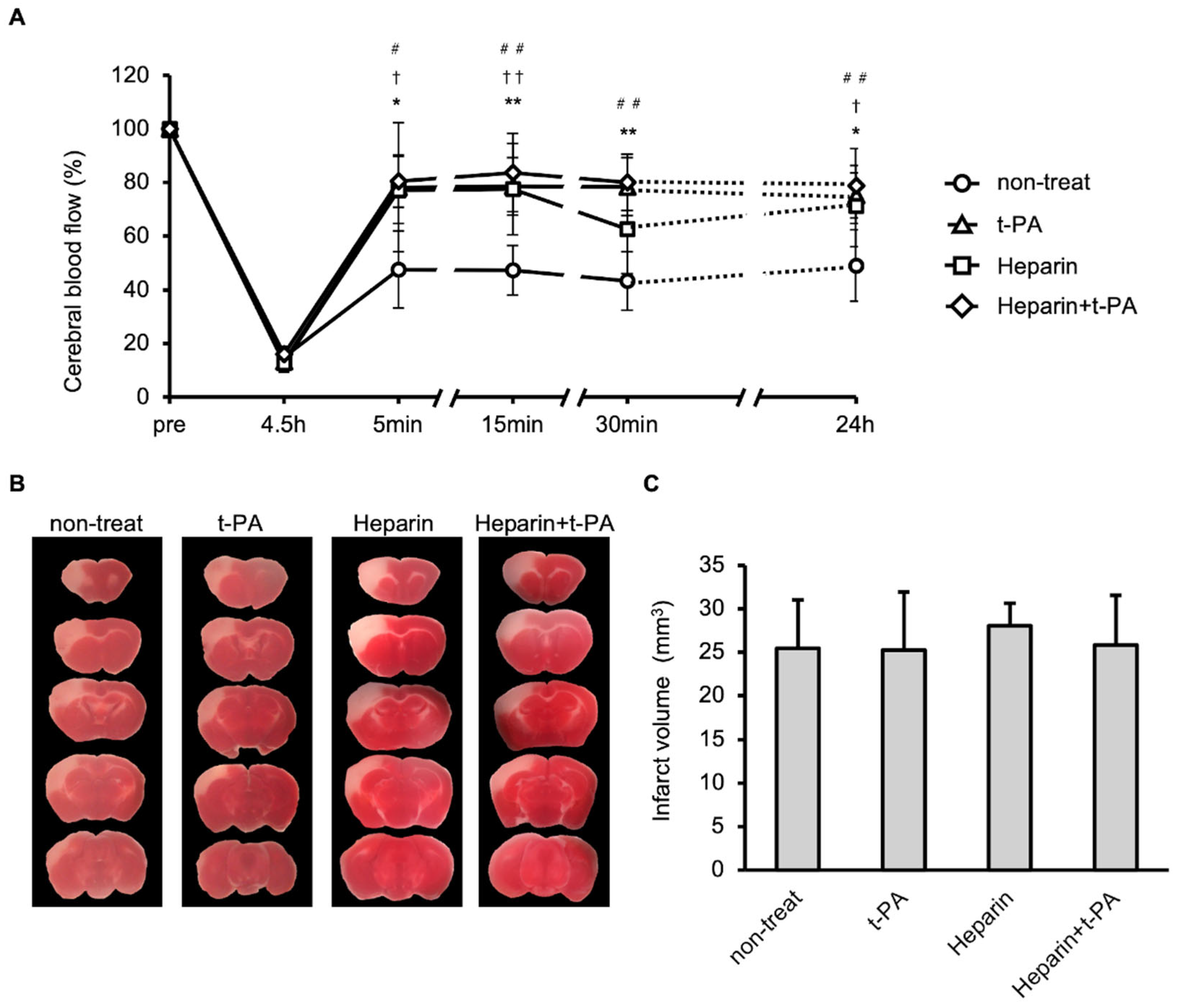
3.4. Blood Flow and Infarct Size Following Administration of t-PA and/or Heparin in an I/R 4.5 h Model
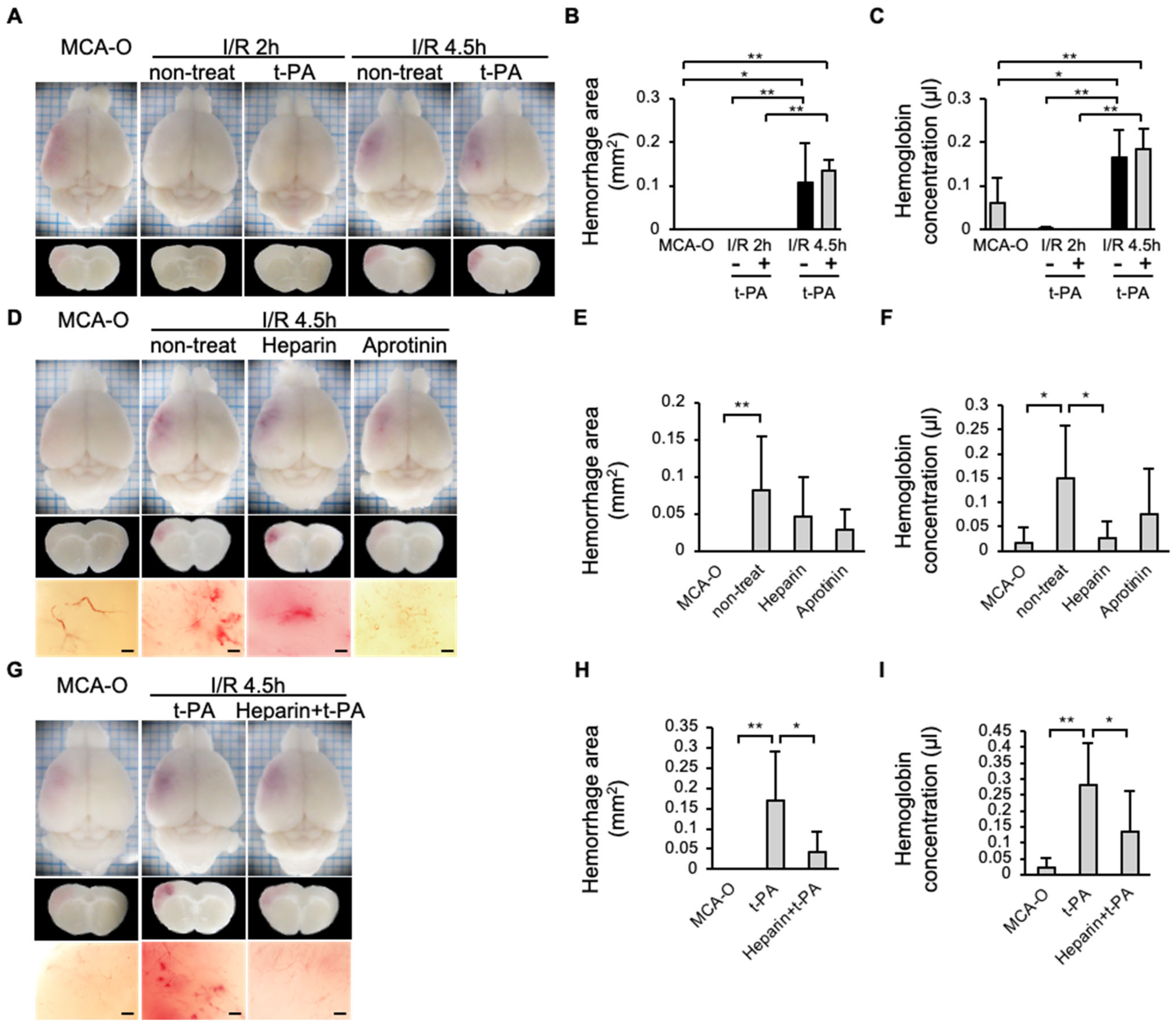
3.5. Hemorrhage
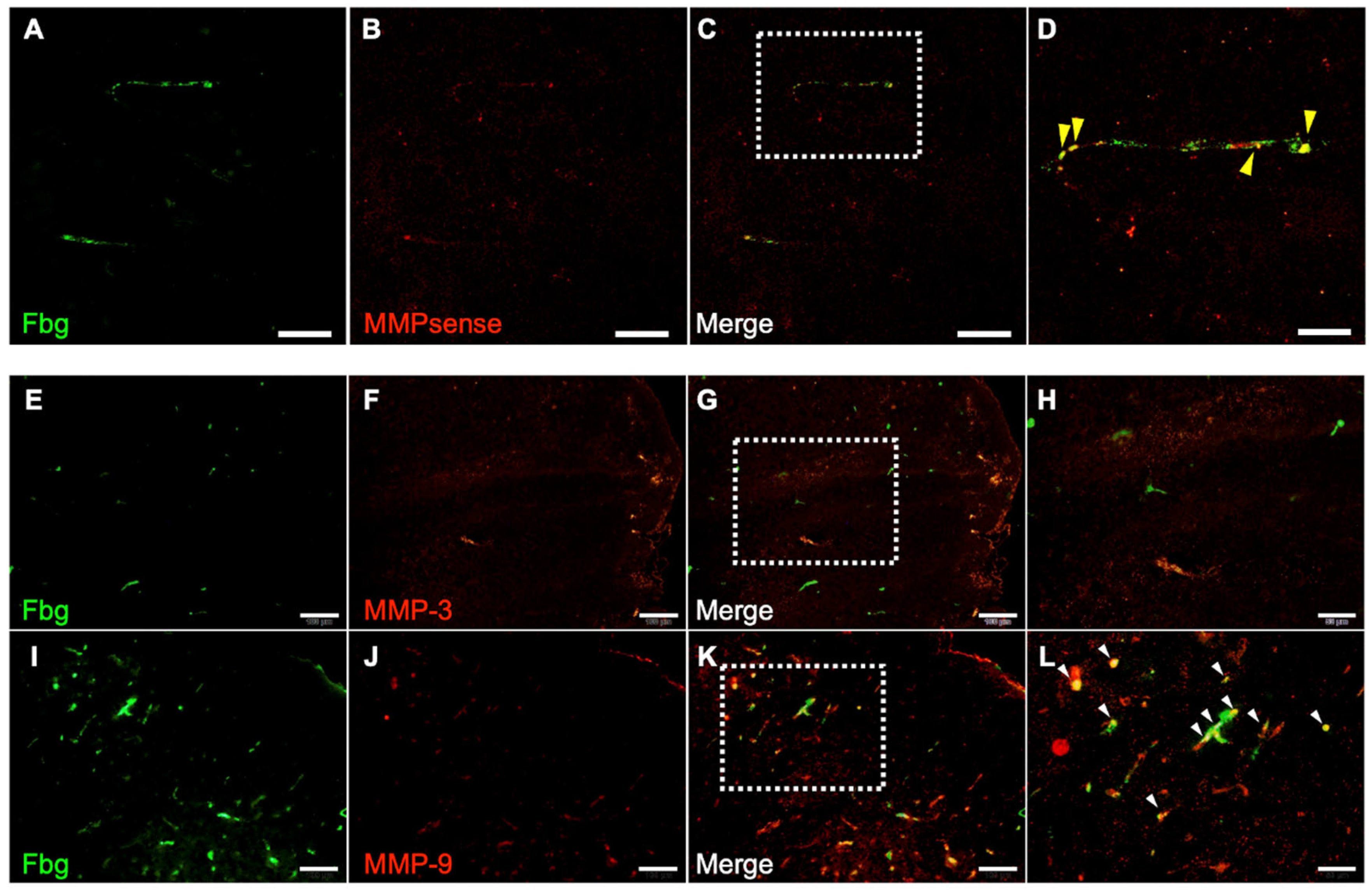
3.6. MMP Activity and Immunohistochemistry of MMP-3 and MMP-9
3.7. TL Treatment and the SIT
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, Q.; Liu, S.; Yao, Y.; Liu, H.; Cai, T.; Han, L. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Ischemic Stroke, 1990–2019. Neurology 2022, 98, e279–e290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, W.M.; Wissman, S.; Albers, G.W.; Jhamandas, J.H.; Madden, K.P.; Hamilton, S.; ATLANTIS Study Investigators. Recombinant Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator (Alteplase) for Ischemic Stroke 3 to 5 Hours After Symptom Onset: The ATLANTIS Study: A Randomized Controlled Trial. JAMA 1999, 282, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacke, W.; Kaste, M.; Bluhmki, E.; Brozman, M.; Dávalos, A.; Guidetti, D.; Larrue, V.; Lees, K.R.; Medeghri, Z.; Machnig, T.; et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1317–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Nagai, N.; Umemura, K.; Collen, D.; Lijnen, H.R. Stromelysin-1 (MMP-3) is critical for intracranial bleeding after t-PA treatment of stroke in mice. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 1732–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, G.A.; Estrada, E.Y.; Dencoff, J.E.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced gelatinase B causes delayed opening of the blood-brain barrier: An expanded therapeutic window. Brain Res. 1995, 703, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Ye, Z.; Dai, Q.; Liu, X.; Xu, G. Risk of Intracranial Hemorrhage after Endovascular Treatment for Acute Ischemic Stroke: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Interv. Neurol. 2017, 6, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelderblom, M.; Leypoldt, F.; Steinbach, K.; Behrens, D.; Choe, C.-U.; Siler, D.A.; Arumugam, T.V.; Orthey, E.; Gerloff, C.; Tolosa, E.; et al. Temporal and spatial dynamics of cerebral immune cell accumulation in stroke. Stroke 2009, 40, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Cooper, D.; Arumugam, T.V.; Zhang, J.H.; Nanda, A.; Granger, D.N. Platelet-leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions after middle cerebral artery occlusion and reperfusion. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2004, 24, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, H.; Yuki, S.; Sugimoto, J.; Tamao, Y. Effects of a thrombin inhibitor, argatroban, on ischemic brain damage in the rat distal middle cerebral artery occlusion model. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1996, 278, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göb, V.; Voll, M.G.; Zimmermann, L.; Hemmen, K.; Stoll, G.; Nieswandt, B.; Schuhmann, M.K.; Heinze, K.G.; Stegner, D. Infarct growth precedes cerebral thrombosis following experimental stroke in mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhri, T.F.; Hoh, B.L.; Zerwes, H.G.; Prestigiacomo, C.J.; Kim, S.C.; Connolly, E.S.; Kottirsch, G.; Pinsky, D.J. Reduced microvascular thrombosis and improved outcome in acute murine stroke by inhibiting GP IIb/IIIa receptor-mediated platelet aggregation. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Rosa, X.; Cervera, A.; Kristoffersen, A.K.; Valdés, C.P.; Varma, H.M.; Justicia, C.; Durduran, T.; Chamorro, Á.; Planas, A.M. Mannose-binding lectin promotes local microvascular thrombosis after transient brain ischemia in mice. Stroke 2014, 45, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, N.; De Mol, M.; Lijnen, H.R.; Carmeliet, P.; Collen, D. Role of plasminogen system components in focal cerebral ischemic infarction: A gene targeting and gene transfer study in mice. Circulation 1999, 99, 2440–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matano, Y.; Nojiri, Y.; Nomura, M.; Masuda, A.; Moriike, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Umemura, K.; Nagai, N. Repair of brain damage size and recovery of neurological dysfunction after ischemic stroke are different between strains in mice: Evaluation using a novel ischemic stroke model. Exp. Anim. 2021, 70, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ding, S.-L.; Li, Y.; Royall, J.; Feng, D.; Lesnar, P.; Graddis, N.; Naeemi, M.; Facer, B.; Ho, A.; et al. The Allen Mouse Brain Common Coordinate Framework: A 3D Reference Atlas. Cell 2020, 181, 936–953.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Nagai, N.; Collen, D. Comparative effects of microplasmin and tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) on cerebral hemorrhage in a middle cerebral artery occlusion model in mice. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 2, 1617–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Hata, R.; Hossmann, K.A. Regional metabolic disturbances and cerebrovascular anatomy after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in C57black/6 and SV129 mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 1999, 6, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Tang, Y.; Lin, X.; Xi, Y.; Guan, Y.; Xiao, T.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, G.-Y.; Wang, Y. Optimizing suture middle cerebral artery occlusion model in C57BL/6 mice circumvents posterior communicating artery dysplasia. J. Neurotrauma 2012, 29, 1499–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.; Clark, J.F.; Broderick, J.P.; Pyne-Geithman, G.J.; Wagner, K.R.; Khatri, P.; Tomsick, T.; Sharp, F.R. Mechanical reperfusion is associated with post-ischemic hemorrhage in rat brain. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 216, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, G.A.; Cunningham, L.A.; Wallace, J.; Alexander, S.; Estrada, E.Y.; Grossetete, M.; Razhagi, A.; Miller, K.; Gearing, A. Immunohistochemistry of matrix metalloproteinases in reperfusion injury to rat brain: Activation of MMP-9 linked to stromelysin-1 and microglia in cell cultures. Brain Res. 2001, 893, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, R.H.P.; Caradoc-Davies, T.; Cowieson, N.; Horvath, A.J.; Quek, A.J.; Encarnacao, J.A.; Steer, D.; Cowan, A.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, B.G.C.; et al. The X-ray crystal structure of full-length human plasminogen. Cell Rep. 2012, 1, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Bodin, C.; Olsson, K. Crystal structure of the native plasminogen reveals an activation-resistant compact conformation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 1385–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, J.R.; Fong, T.H.; Liu, C.M.; Shen, M.Y.; Chen, T.L.; Chang, Y.; Lu, M.S.; Hsiao, G. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in human platelets: Regulation of platelet activation in in vitro and in vivo studies. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 143, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.H.; Sakamoto, H.; Xu, E.C.; Lee, R.T. Biomechanical regulation of human monocyte/macrophage molecular function. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Zee, J.M.; Patel, K.D. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in TNF-stimulated neutrophils: Novel pathways for tertiary granule release. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 79, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Huesing, J.E.; Shade, R.E.; Bressan, R.A.; Hasegawa, P.M.; Murdock, L.L. An insecticidal N-acetylglucosamine-specific lectin gene from Griffonia simplicifolia (Leguminosae). Plant Physiol. 1996, 110, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermert, K.; Buhl, E.M.; Klinkhammer, B.M.; Floege, J.; Boor, P. Reduction of Endothelial Glycocalyx on Peritubular Capillaries in Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2023, 193, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dane, M.J.C.; Khairoun, M.; Lee, D.H.; van den Berg, B.M.; Eskens, B.J.M.; Boels, M.G.S.; van Teeffelen, J.W.G.E.; Rops, A.L.W.M.M.; van der Vlag, J.; van Zonneveld, A.J.; et al. Association of kidney function with changes in the endothelial surface layer. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Kimura, S.; Nishinaga, M.; Takeuchi, K.; Ozawa, T. Anticoagulant heparin-like glycosaminoglycans on endothelial cell surface. Jpn. Circ. J. 1991, 55, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiler, H.; Isermann, B.H. Thrombomodulin. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 1, 1515–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H. Regulation of functions of vascular wall cells by tissue factor pathway inhibitor: Basic and clinical aspects. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, K.; Suzuki, T.; Ishikawa, R.; Hattori, N.; Ito, R.; Umehara, K.; Furihata, T.; Dohmae, N.; Linhardt, R.J.; Igarashi, K.; et al. Ischemic stroke disrupts the endothelial glycocalyx through activation of proHPSE via acrolein exposure. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 18614–18624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.N.; Reynell, C.; Gesslein, B.; Hamilton, N.B.; Mishra, A.; Sutherland, B.A.; O’Farrell, F.M.; Buchan, A.M.; Lauritzen, M.; Attwell, D. Capillary pericytes regulate cerebral blood flow in health and disease. Nature 2014, 508, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorov, M.I.; Paetzold, J.C.; Schoppe, O.; Tetteh, G.; Shit, S.; Efremov, V.; Todorov-Völgyi, K.; Düring, M.; Dichgans, M.; Piraud, M.; et al. Machine learning analysis of whole mouse brain vasculature. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Moriike, Y.; Nakano, Y.; Matano, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Umemura, K.; Nagai, N. Involvement of Secondary Induced Thrombus on Hemorrhage Induced by Both Delayed Recanalization and Delayed t-PA Treatment in Murine Ischemic Stroke Models. Biomedicines 2026, 14, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines14020308
Moriike Y, Nakano Y, Matano Y, Suzuki Y, Umemura K, Nagai N. Involvement of Secondary Induced Thrombus on Hemorrhage Induced by Both Delayed Recanalization and Delayed t-PA Treatment in Murine Ischemic Stroke Models. Biomedicines. 2026; 14(2):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines14020308
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoriike, Yuhki, Yumeta Nakano, Yasuki Matano, Yasuhiro Suzuki, Kazuo Umemura, and Nobuo Nagai. 2026. "Involvement of Secondary Induced Thrombus on Hemorrhage Induced by Both Delayed Recanalization and Delayed t-PA Treatment in Murine Ischemic Stroke Models" Biomedicines 14, no. 2: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines14020308
APA StyleMoriike, Y., Nakano, Y., Matano, Y., Suzuki, Y., Umemura, K., & Nagai, N. (2026). Involvement of Secondary Induced Thrombus on Hemorrhage Induced by Both Delayed Recanalization and Delayed t-PA Treatment in Murine Ischemic Stroke Models. Biomedicines, 14(2), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines14020308





