The Assessment of the Autonomic Polyneuropathy Through Sudoscan and Vitamin B12 in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and High Cardiovascular Risk or Established Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
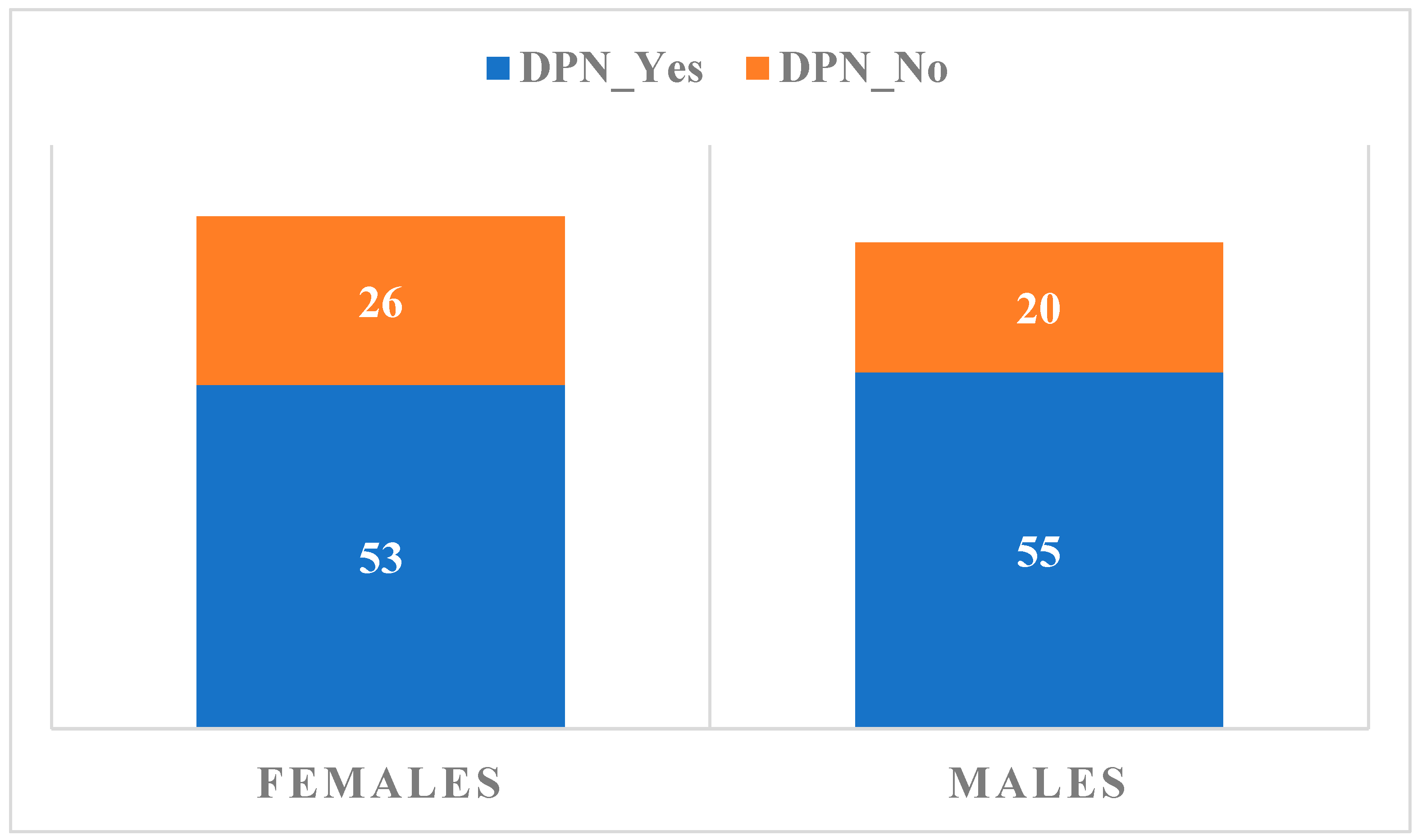
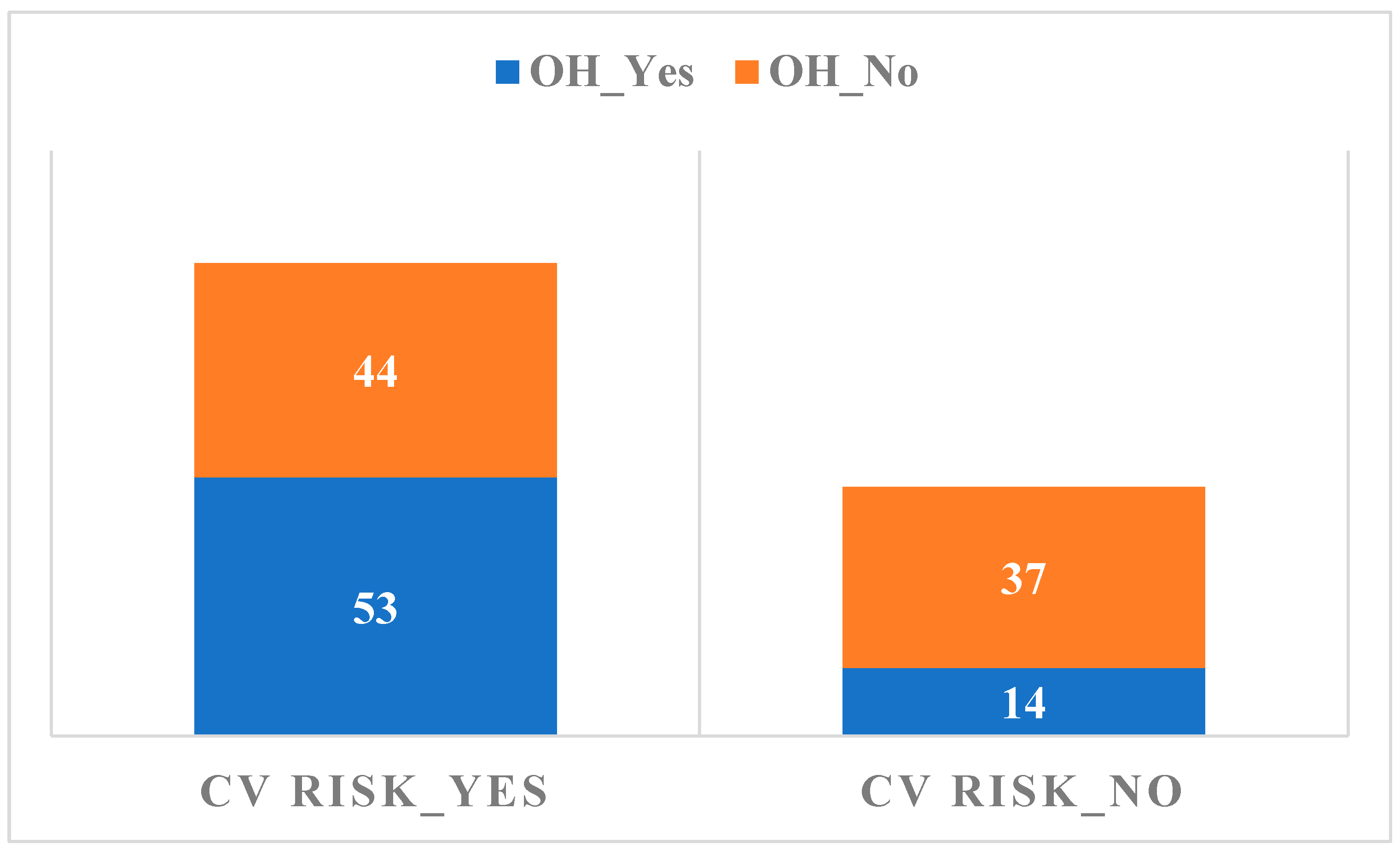
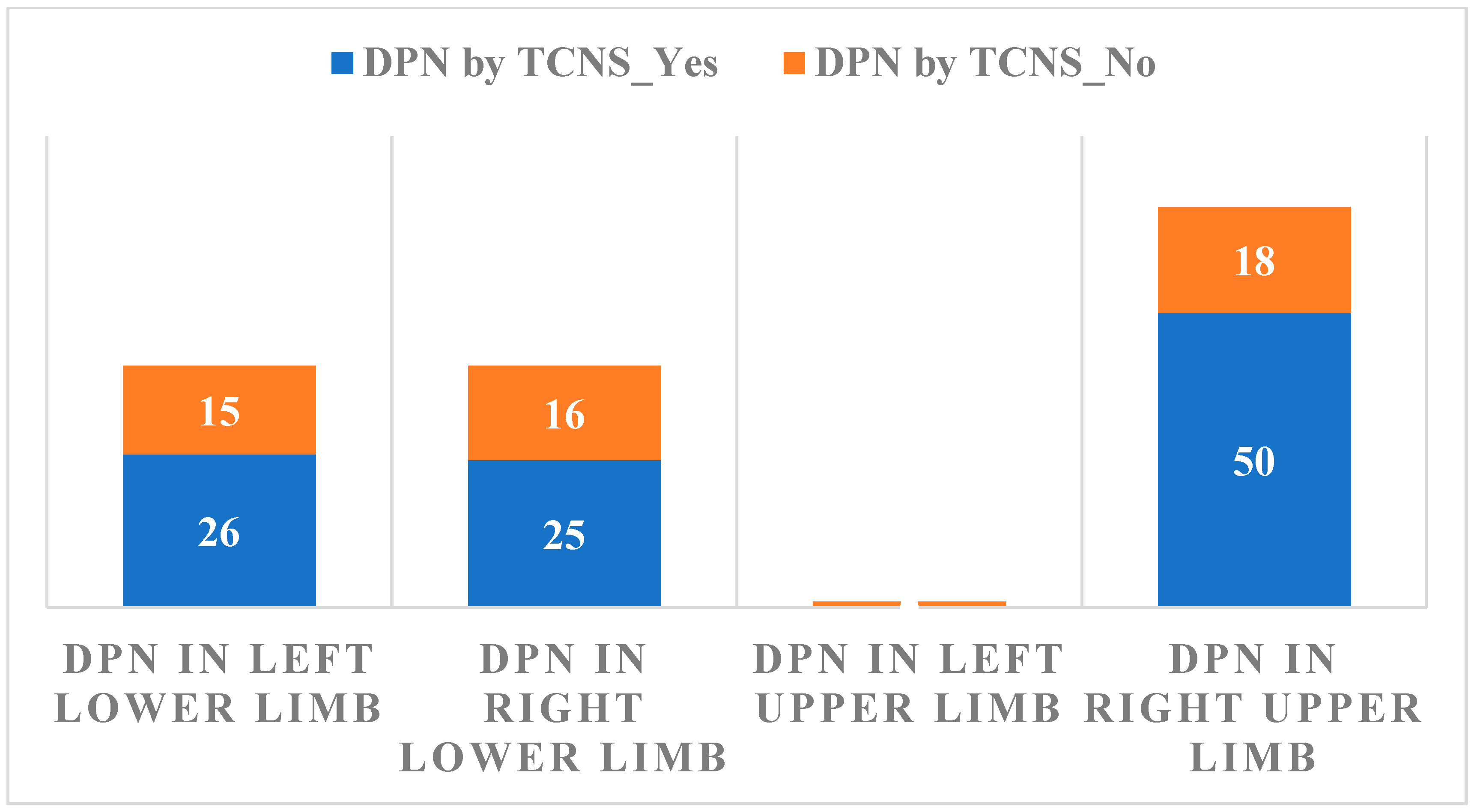
3.2. Neuropathy Findings
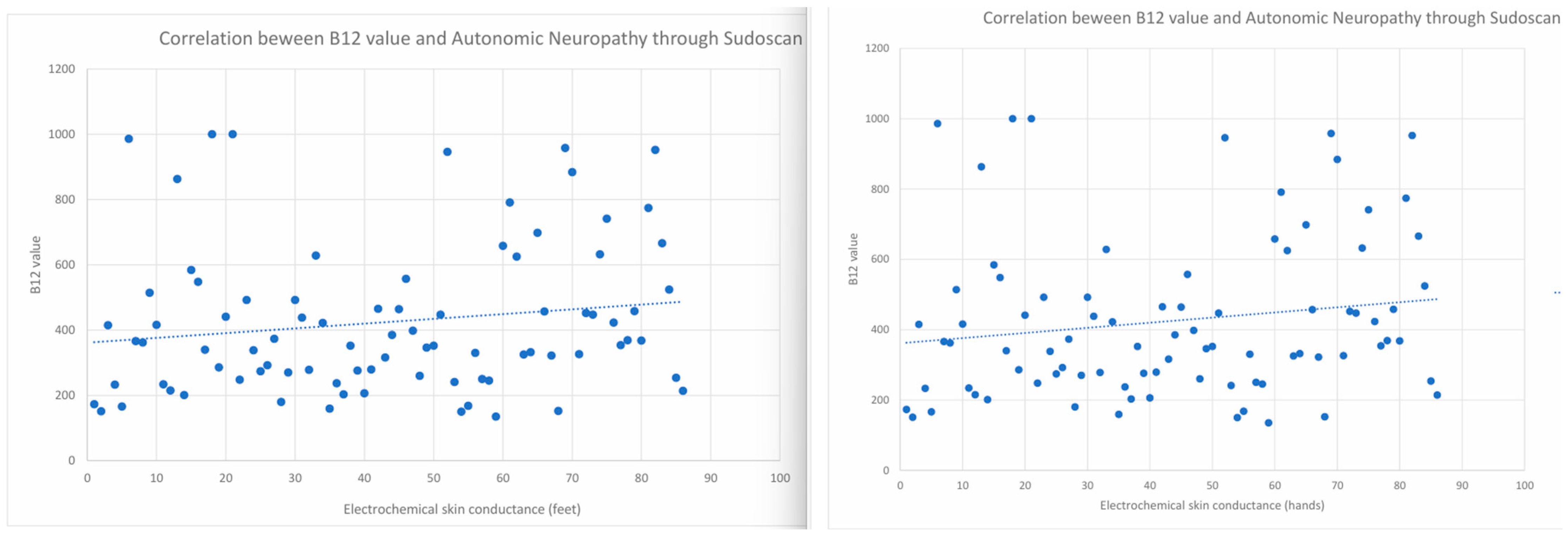
3.3. Correlations
4. Discussion
4.1. Further Directions
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| BP | Blood Pressure |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CV | Cardiovascular |
| CVD | Cardiovascular Disease |
| DM | Diabetes Mellitus |
| DPN | Diabetic Polyneuropathy |
| ESC | Electrochemical Skin Conductance |
| OH | Orthostatic Hypotension |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| TCNS | Toronto Clinical Neuropathy Score |
References
- Salmen, T.; Serbanoiu, L.-I.; Bica, I.-C.; Serafinceanu, C.; Muzurović, E.; Janez, A.; Busnatu, S.; Banach, M.; Rizvi, A.A.; Rizzo, M.; et al. A Critical View over the Newest Antidiabetic Molecules in Light of Efficacy—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, B.B.; Magliano, D.J.; Boyko, E.J. IDF diabetes atlas 11th edition 2025: Global prevalence and projections for 2050. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2025, gfaf177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrițculesei, R.-V.; Boldeanu, L.; Vladu, I.M.; Clenciu, D.; Mitrea, A.; Cîmpeanu, R.C.; Mustață, M.-L.; Siloși, I.; Boldeanu, M.V.; Vere, C.C. Correlation Between Prognostic Nutritional Index, Glasgow Prognostic Score, and Different Obesity-Related Indices in People with Diabetes or Prediabetes. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElSayed, N.A.; McCoy, R.G.; Aleppo, G.; Balapattabi, K.; Beverly, E.A.; Briggs Early, K.; Bruemmer, D.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; Ekhlaspour, L.; Garg, R.; et al. 11. Chronic Kidney Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48, S239–S251. [Google Scholar]
- ElSayed, N.A.; McCoy, R.G.; Aleppo, G.; Balapattabi, K.; Beverly, E.A.; Briggs Early, K.; Bruemmer, D.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; Ekhlaspour, L.; Garg, R.; et al. 12. Retinopathy, neuropathy, and foot care: Standards of care in diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48, S252–S265. [Google Scholar]
- Pop-Busui, R.; Boulton, A.J.; Feldman, E.L.; Bril, V.; Freeman, R.; Malik, R.A.; Sosenko, J.M.; Ziegler, D. Diabetic Neuropathy: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop-Busui, R.; Ang, L.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Feldman, E.L.; Marcus, R.L.; Mizokami-Stout, K.; Singleton, J.R.; Ziegler, D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Am. Diabetes Assoc. 2022, 2022, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trofin, D.; Salmen, B.-M.; Salmen, T.; Trofin, D.M.; Reurean-Pintilei, D. Advancing the Diagnosis of Diabetic Neuropathies: Electrodiagnostic and Skin Autofluorescence Methods. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, L.; Cowdin, N.; Mizokami-Stout, K.; Pop-Busui, R. Update on the Management of Diabetic Neuropathy. Diabetes Spectr. 2018, 31, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.; Cauquil, C.; Lozeron, P. Dysautonomies des neuropathies périphériques [Autonomic peripheral neuropathy]. Presse Med. 2012, 41, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajnik, C.S.; Kantikar, V.V.; Pande, A.J.; Deslypere, J.P. Quick and simple evaluation of sudomotor function for screening of diabetic neuropathy. ISRN Endocrinol. 2012, 2012, 103714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, S.; Boulton, A.J.; Dyck, P.J.; Freeman, R.; Horowitz, M.; Kempler, P.; Lauria, G.; Malik, R.A.; Spallone, V.; Vinik, A.; et al. Diabetic neuropathies: Update on definitions, diagnostic criteria, estimation of severity, and treatments. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2285–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roustit, M.; Loader, J.; Deusenbery, C.; Baltzis, D.; Veves, A. Endothelial Dysfunction as a Link Between Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Peripheral Neuropathy in Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 3401–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.O.; Cho, D.H.; Chung, D.J.; Chung, M.Y. Association between Diabetic Polyneuropathy and Cardiovascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Diabetes Metab. J. 2011, 35, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmen, T.; Pietrosel, V.-A.; Reurean-Pintilei, D.; Iancu, M.A.; Cimpeanu, R.C.; Bica, I.-C.; Dumitriu-Stan, R.-I.; Potcovaru, C.-G.; Salmen, B.-M.; Diaconu, C.-C.; et al. Assessing Cardiovascular Target Attainment in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in Tertiary Diabetes Center in Romania. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabrdalik, K.; Kwiendacz, H.; Moos, J.; Moos, Ł.; Kulpa, J.; Brzoza, Z.; Stompór, T.; Gumprecht, J.; Lip, G.Y. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy is associated with diabetic kidney disease and cardiovascular disease: The Silesia diabetes-heart project. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2023, 48, 101726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh Le, T.; Phi Thi Nguyen, N.; Thanh Thi Tran, H.; Luong Cong, T.; Ho Thi Nguyen, L.; Do Nhu, B.; Tien Nguyen, S.; Van Ngo, M.; Trung Dinh, H.; Thi Nguyen, H.; et al. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Associated with Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Concentrations Among Newly Diagnosed Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, N.A.; McCoy, R.G.; Aleppo, G.; Balapattabi, K.; Beverly, E.A.; Briggs Early, K.; Bruemmer, D.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; Ekhlaspour, L.; Garg, R.; et al. 10. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48, S207–S238. [Google Scholar]
- SCORE2 working group ESCCardiovascular risk collaboration SCORE2 risk prediction algorithms: New models to estimate 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease in Europe. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 2439–2454. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SCORE2-Diabetes Working Group the ESCCardiovascular Risk Collaboration SCORE2-Diabetes: 10-year cardiovascular risk estimation in type 2 diabetes in Europe. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 2544–2556. [CrossRef]
- Visseren, F.L.J.; Mach, F.; Smulders, Y.M.; Carballo, D.; Koskinas, K.C.; Bäck, M.; Benetos, A.; Biffi, A.; Boavida, J.M.; Capodanno, D.; et al. ESC Scientific Document Group. 2021 ESC Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3227–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.G.; Lessard, M.; Reyna, S.; Doudova, M.; Singleton, J.R. The diagnostic utility of Sudoscan for distal symmetric peripheral neuropathy. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2014, 28, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewandter, J.S.; Gibbons, C.H.; Campagnolo, M.; Lee, J.; Chaudari, J.; Ward, N.; Burke, L.; Cavaletti, G.; Herrmann, D.N.; McArthur, J.C.; et al. Clinician-rated measures for distal symmetrical axonal polyneuropathy: ACTTION systematic review. Neurology 2019, 93, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringer, M.; Hashmi, M.F.; Lappin, S.L. Orthostatic Hypotension. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- ElSayed, N.A.; McCoy, R.G.; Aleppo, G.; Balapattabi, K.; Beverly, E.A.; Briggs Early, K.; Bruemmer, D.; Ebekozien, O.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; Ekhlaspour, L.; et al. 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48, S27–S49. [Google Scholar]
- Sandu, C.; Bica, C.; Salmen, T.; Stoica, R.; Bohiltea, R.; Gherghiceanu, F.; Pacu, I.; Stefan, S.; Serafinceanu, C.; Stoian, A.P. Gestational diabetes—Modern management and therapeutic approach (Review). Exper Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.; Sierra, O.R.; Saavedra, G.; Moreno, S. Vitamin B12 deficiency and diabetic neuropathy in patients taking metformin: A cross-sectional study. Endocr. Connect. 2019, 8, 1324–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohiltea, R.E.; Zugravu, C.A.; Neacsu, A.; Navolan, D.; Berceanu, C.; Nemescu, D.; Bodean, O.; Turcan, N.; Baros, A.; Cirstoiu, M.M. The Prevalence of Vitamin D Defficiency and Its Obstetrical Effects. Children 2019, 5, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Wolffenbuttel, B.H.; McCaddon, A.; Ahmadi, K.R.; Green, R. A brief overview of the diagnosis and treatment of cobalamin (B12) deficiency. Food Nutr. Bull. 2024, 45, S40–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, T.J.; Song, Y.; Jang, H.C.; Choi, S.H. SUDOSCAN in Combination with the Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument Is an Effective Tool for Screening Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Diabetes Metab. J. 2022, 46, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, A.; Mediano, M.F.F.; De Lorenzo, A.; Rodrigues, L.F., Jr. Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in diabetes: Pathophysiology, clinical assessment and implications. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhiyenko, V.A.; Serhiyenko, A.A. Cardiac autonomic neuropathy: Risk factors, diagnosis and treatment. World J. Diabetes 2018, 9, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogan, A.; Potre, O.; Avram, V.-F.; Andor, M.; Caruntu, F.; Timar, B. Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy in Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenesis, Epidemiology, Diagnosis and Clinical Implications: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, A.; Wanono, R.; Flamant, M.; Vidal-Petiot, E. Orthostatic hypotension: A review. Nephrol. Ther. 2017, 13, S55–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop-Busui, R. What do we know and we do not know about cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in diabetes. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2012, 5, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Moscoso, P.A.; Esparza, A.S.; Botero, S.M.; Forero-Gómez, J.E. Fourth in a series on diabetes and heart: Diabetic cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy-an underestimated enemy. Escardio J. 2016, 14, 22–35. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, S.; Raheim, S.A.; Khan, M.I.; Rubab, U.; Kanagala, P.; Zhao, S.S.; Marshall, A.; Brown, E.; Alam, U. Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy in Type 1 and 2 Diabetes: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Management. Clin. Ther. 2022, 44, 1394–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, R.A. Pathology of human diabetic neuropathy. Handb. Clin. Neurol 2014, 126, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, C.A.; Navolan, D.; Calin, A.; Matei, A.; Bohiltea, R.; Dimitriu, M.; Ilinca, C.; Ples, L. Hormonal contraception in postpartum patients with gestational diabetes mellitus. Rev. Chim. 2018, 69, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayabalan, B.; Low, L.L. Vitamin B supplementation for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Singapore Med. J. 2016, 57, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Waqar, R.; Farsi, S.; Ali, S.; Asim, M.; Farooq, U. Vitamin B12 Deficiency in Patients with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Hospital-Based Cross-Sectional Study. Cureus 2025, 17, e87490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Geng, T.; Wan, Z.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, Z.; Li, L.; Zhu, K.; Liu, L.; Pan, A.; et al. Associations of Serum Folate and Vitamin B12 Levels with Cardiovascular Disease Mortality Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2146124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustață, M.-L.; Neagoe, C.-D.; Rădulescu, V.-M.; Dragne, I.-G.; Cîmpeanu, R.-C.; Radu, L.; Ahrițculesei, R.-V.; Forțofoiu, D.; Predoi, M.-C.; Ianoși, S.-L. Association Between Systemic Inflammation, Metabolic Syndrome and Quality of Life in Psoriasis Patients. Life 2025, 15, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karedath, J.; Batool, S.; Arshad, A.; Khalique, S.; Raja, S.; Lal, B.; Anirudh Chunchu, V.; Hirani, S. The Impact of Vitamin B12 Supplementation on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Diabetic Neuropathy: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Cureus 2022, 14, e31783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshyah, S.A. Clinical Use, Interpretation, and Limitations of Sudoscan in Diabetes Care. J. Diabetes Endocr. Pract. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lin, Y.; Liao, X.; Chen, J.; Wu, H. TRI-based heart rate variability parameterisation: Advancing autonomic dysfunction assessment in diabetes and aging—A cross-sectional observational study. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2025, 45, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Adults over 18 years old | Adults over 80 years old |
| Diagnosis of DM for at least 1 year | Diagnosis of DM for more than 10 years |
| High and very high cardiovascular risk or established cardiovascular disease | Moderate, low, or absent cardiovascular risk |
| Complete biologic profile | History of chronic diseases such as amyloidosis, Parkinson’s disease with or without treatment, hemiparesis/hemiplegia after stroke diseases, lower limb amputation, or presence of plantar lesions/ulcerations |
| Informed consent signed |
| Characteristic | n = 164 | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|
| Demographic characteristics | ||
| Male gender, n, (%) | 79, (48.17%) | |
| Age (years), mean ± SD | 63 ± 12.29 | 61.1, 64.9 |
| Urban settlement, n, (%) | 103, (62.81%) | |
| Clinical characteristics | ||
| BMI (kg/m2), mean ± SD | 31.37 ± 5.97 | 30.45, 32.29 |
| Clinostatic BP (mmHg), mean ± SD | Systolic BP 143 ± 17.3 | 140.33, 145.67 |
| Diastolic BP 76.40 ± 11.39 | 74.64, 78.16 | |
| Orthostatic BP (mmHg), mean ± SD | Systolic BP 138 ± 17.8 | 135.26, 170.74 |
| Diastolic BP 72.780 ± 12.27 | 70.89, 74.67 | |
| DM characteristics | ||
| DM type 2, n, (%) | 156, (95.12%) | |
| DM duration, mean ± SD | 7.22 ± 3.25 | 6.72, 7.72 |
| Insulin-therapy, n, (%) | 39, (23.78%) | |
| HbA1c (%), mean ± SD | 8.22 ± 1.74 | 7.95, 8.49 |
| DM complications | ||
| High and Very High Cardiovascular Risk, n, (%) | 66, (40.24%) | |
| Cardiovascular Disease, n, (%) | 98, (59.75%) | |
| Diabetic Polyneuropathy, n, (%) | 108, (65.85%) | |
| Neuropathic deformities/amputation of the limbs, n, (%) | 37, (22.56%) | |
| Comorbidities | ||
| Toxic/Viral hepatic ailments, n, (%) | 11, (6.70%) | |
| Neoplastic ailments with chemotherapy, n, (%) | 21, (12.80%) | |
| Neoplastic ailments with chemotherapy/radiotherapy, n, (%) | 9, (5.48%) | |
| Thyroiditis (hypo/hyperthyroidism), n, (%) | 19, (11.58%) | |
| Discopathy or other chronic rheumatological diseases, n, (%) | 46, (28.04%) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Mocanu, C.; Salmen, T.; Pantea Stoian, A.; Serafinceanu, C. The Assessment of the Autonomic Polyneuropathy Through Sudoscan and Vitamin B12 in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and High Cardiovascular Risk or Established Cardiovascular Disease. Biomedicines 2026, 14, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines14010018
Mocanu C, Salmen T, Pantea Stoian A, Serafinceanu C. The Assessment of the Autonomic Polyneuropathy Through Sudoscan and Vitamin B12 in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and High Cardiovascular Risk or Established Cardiovascular Disease. Biomedicines. 2026; 14(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines14010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleMocanu (Chitan), Cristina, Teodor Salmen, Anca Pantea Stoian, and Cristian Serafinceanu. 2026. "The Assessment of the Autonomic Polyneuropathy Through Sudoscan and Vitamin B12 in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and High Cardiovascular Risk or Established Cardiovascular Disease" Biomedicines 14, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines14010018
APA StyleMocanu, C., Salmen, T., Pantea Stoian, A., & Serafinceanu, C. (2026). The Assessment of the Autonomic Polyneuropathy Through Sudoscan and Vitamin B12 in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and High Cardiovascular Risk or Established Cardiovascular Disease. Biomedicines, 14(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines14010018






