Dual Inhibition of the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System and Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter-2: Mechanistic and Clinical Evidence for Cardiorenal Protection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Trials
2.1. T2D and CV Risk Factors
2.2. Heart Failure
| Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study No. | Drugs | Study Name, Reference | Patient No. | Patient Population | Study Design | Clinical Outcomes | Adverse Effects |
| 1 | Dapagliflozin vs. Placebo (in addition to GDMT) | Weber et al., 2016 [4] | 449 | T2D and hypertension | Multicentre, prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial |
|
|
| 2 | Empagliflozin vs. Placebo (in addition to ARB) | SACRA, Kario et al., 2019 [5] | 132 | T2D and nocturnal hypertension | Multicentre, prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial |
|
|
| 3 | Canagliflozin vs. Placebo (in addition to GDMT) | CANVAS programme, Rådholm et al., 2018 [6] | 10,142 | T2D and symptomatic ASCVD or increased CV risk | Multicentre, prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial, with pre-specified sub-group analysis |
|
|
| 4 | Empagliflozin vs. Placebo, analyzed by baseline attainment of CV risk factor goals (one goal was ACEI/ARB therapy) | EMPAREG OUTCOME risk-factor-control analysis, Inzucchi et al., 2020 [7] | 7020 | T2D and established ASCVD | Post hoc sub-group analysis of a multicentre, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial |
| Safety not reported beyond the parent study |
| 5 | Dapagliflozin vs. Placebo (in addition to GDMT), analyzed by baseline use of ACEIs/ARBs, beta-blockers, diuretics, MRAs | DECLARE-TIMI 58, Oyama et al., 2022 [8] | 17,160 | T2D and established ASCVD or multiple CV risk factors | Multicentre, prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial, with pre-specified sub-group analysis |
|
|
| 6 | Dapagliflozin + ACEIs or ARBs vs. Placebo + ACEIs or ARBs | Heerspink et al., 2016 [9] | 356 | T2D, hypertension and albuminuria | Post hoc analysis of a subset of patients from two randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trials |
|
|
| 7 | Empagliflozin vs. Placebo (in addition to GDMT), analyzed by baseline use of antihypertensives and diuretic or ACEI/ARB | EMPAREG BP TRIAL, Mancia et al., 2016 [10] | 824 | T2D and hypertension | Post hoc sub-group analysis from a multicentre, prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial |
|
|
| 8 | Empagliflozin vs. Placebo (in addition to GDMT), analyzed by baseline drugs, including ACEI/ARB | EMPAREG OUTCOME TRIAL, Mayer et al., 2019 [11] | 7020 | T2D with established CV disease | Post hoc sub-group analysis from a multicentre, prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial |
|
|
| 9 | Group 1: ARNI + SGLT2i; Group 2: ARNI only; Group 3: SGLT2i only; Group 4: neither | Kim et al., 2021 [12] | 206 | T2D and HFrEF | Multicentre, retrospective, observational cohort study |
| Not reported |
| 10 | Group 1: No RAASi or SGLT2i Group 2: SGLT2i only Group 3: RAASi only 4: SGLT2i + RAASi | Korean National Health Database Cohort, Hong et al., 2025 [13] | 261,783 | T2D and hypertension | Retrospective observational cohort study |
| Safety outcomes not reported |
| 11 | Ramipril vs. Ramipril + Dapagliflozin | Karalliedde et al., Front 2022 [14] | 33 | T2D with persistent microalbuminuria | Single-centre, prospective, parallel randomized clinical trial |
| Overall adverse effect profile was similar between the groups |
| 12 | Empagliflozin + Ramipril vs. Placebo + Ramipril | Lytvyn et al., 2022 [15] | 30 | T1D and renal hyperfiltration | Single-centre, prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind crossover |
|
|
| Heart Failure | |||||||
| 13 | Dapagliflozin vs. Placebo (in addition to GDMT) | DAPA-HF, McMurray et al., 2019 [16] | 4744 | HFrEF | Multicentre, prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial, with pre-specified sub-group analysis |
|
|
| 14 | Empagliflozin vs. Placebo (in addition to GDMT) | EMPEROR-Reduced, Packer et al., 2021 [17] | 3730 | HFrEF | Multicentre, prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial, with pre-specified sub-group analysis |
|
|
| 15 | Empagliflozin vs. Placebo (in addition to GDMT) | EMPEROR-Preserved, Anker et al., 2021 [18] | 5988 | HFpEF | Multicentre, prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial, with pre-specified sub-group analysis |
|
|
| 16 | Empagliflozin vs. Placebo (in addition to GDMT) | EMPACT-MI, Hernandez et al., 2024 [19] | 6522 | Acute MI at risk of HF (new LVEF <45%) or congestion | Multicentre, prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial, with pre-specified sub-group analysis |
| AEs not reported systematically |
| 17 | Ertugliflozin vs. Placebo (in addition to GDMT) | EFFORT, Kang et al., 2024 [20] | 128 | HF with mildly or moderately reduced EF and chronic functional MR | Multicentre, prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial, with pre-specified sub-group analysis |
|
|
| 18 | Dapagliflozin vs. Placebo (In addition to GDMT), analyzed by baseline HF treatments, including MRA, sacubitril/valsartan, and by ≥50% vs. <50% guideline dose of RAASi, MRA; and by triple/quadruple-therapy combinations | DAPA-HF- therapy-sub-group interaction analysis, Docherty et al., 2020 [21] | 4744 | HFrEF | Post hoc sub-group analysis of a multicentre, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial |
|
|
| 19 | Dapagliflozin vs. Placebo (in addition to GDMT), analyzed by baseline sacubitril/valsartan use (ARNI) | DAPA-HF, sacubitril/valsartan (ARNI) sub-analysis, Solomon et al., 2020 [22] | 4744 | HFrEF | Post hoc sub-group analysis of a multicentre, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial |
|
|
| 20 | Dapagliflozin vs. Placebo (in addition to GDMT), analyzed by baseline MRA use | DAPA-HF MRA sub-analysis, Shen et al., 2021 [23] | 4744 | HFrEF | Post hoc sub-group analysis of a multicentre, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial |
|
|
| 21 | Dapagliflozin vs. placebo (in addition to GDMT), sub-grouped by baseline background; HF therapies counted as 0–1, 2, or 3 classes (ACEI or ARB or ARNI, beta blocker, MRA). | DELIVER, Pabon et al., 2023 [24] | 1151 | HF with improved EF (HFimpEF) | Post hoc sub-group analysis from a multicentre, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial |
| Adding dapagliflozin did not significantly increase AEs across strata |
| 22 | Finerenone vs. Placebo (in addition to GDMT), pre-specified sub-group by baseline SGLT2i use | FINEARTS-HF, Vaduganathan et al., 2025 [25] | 6001 | Symptomatic HFmrEF or HFpEF | Multicentre, prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial, with pre-specified sub-group analysis |
|
|
| 23 | Comprehensive quadruple therapy (ARNI + βblocker + MRA + SGLT2i) vs. Conventional therapy (ACEI/ARB + βblocker) | Combined modelling of EMPHASIS-HF PARADIGM-HF DAPA-HF Vaduganathan et al., 2020 [26] | EMPHASIS-HF: 2, 737 PARADIGM-HF: 8, 399 DAPA-HF: 4744 | HFrEF | Cross-trial and actuarial lifetable modelling |
| Not reported |
| 24 | Baseline ARNI vs. ARNI + SGLT2i (dapagliflozin or empagliflozin) | Fumarulo et al., 2025 [27] | 136 | HFrEF | Single-centre observational cohort study |
| Not reported |
| 25 | Rapid sequencing of β-blocker + SGLT2i, ARNI, MRA within 4 weeks vs. Conventional sequencing: same four drugs introduced stepwise over ≈ 6 months | NovCon Sequencing Study (protocol), Karamchand et al., 2025 [28] | Anticipated: 584 | HFrEF | Single-centre, prospective, randomized, double-blind randomized clinical trial | Results pending on primary: composite of all-cause death + HF hospitalization. Secondary: CV death, 6 min walk, NYHA class, Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) score, echo parameters, NT-proBNP | No reference to systematic evaluation of adverse effects |
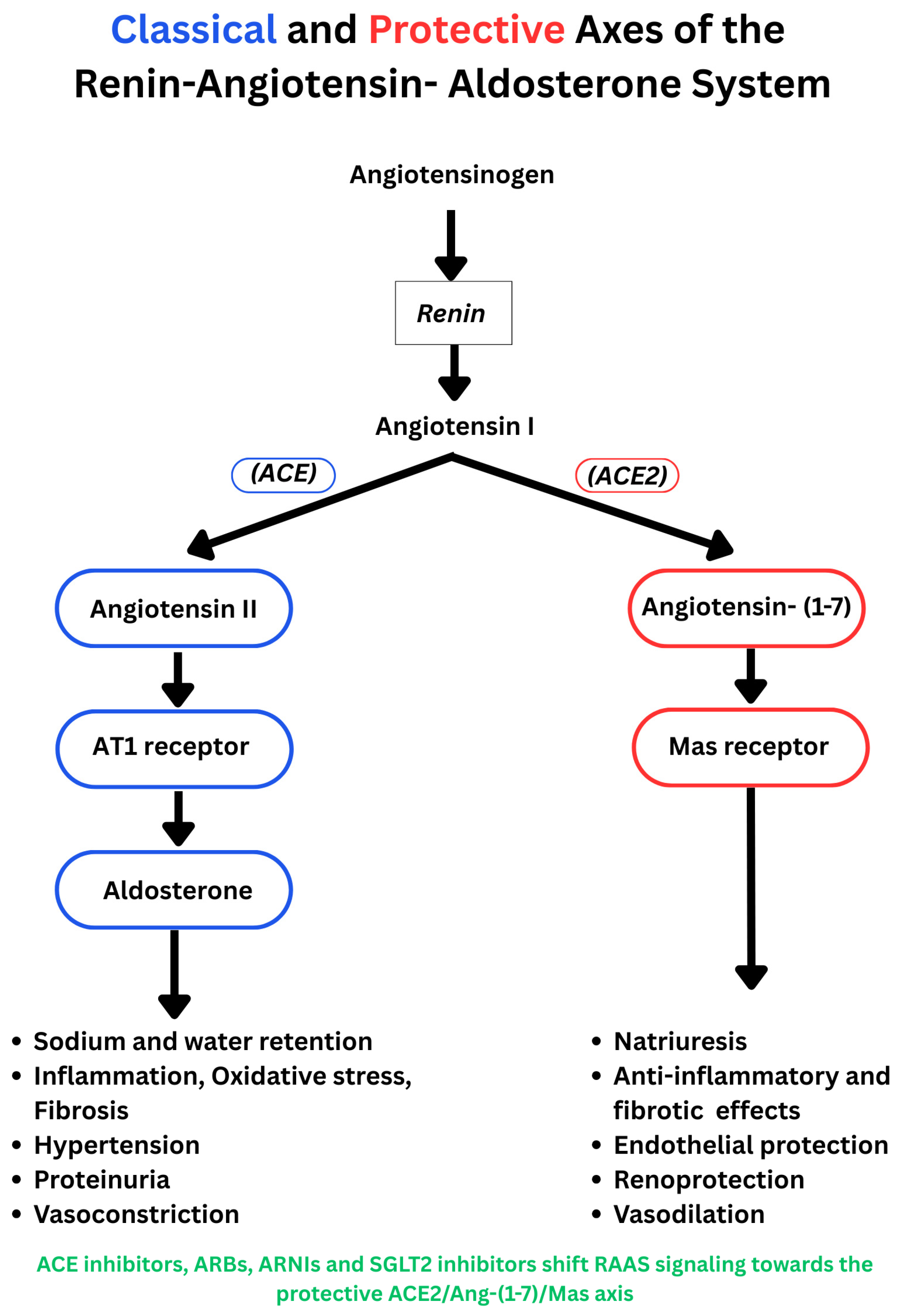
3. Mechanistic Insight
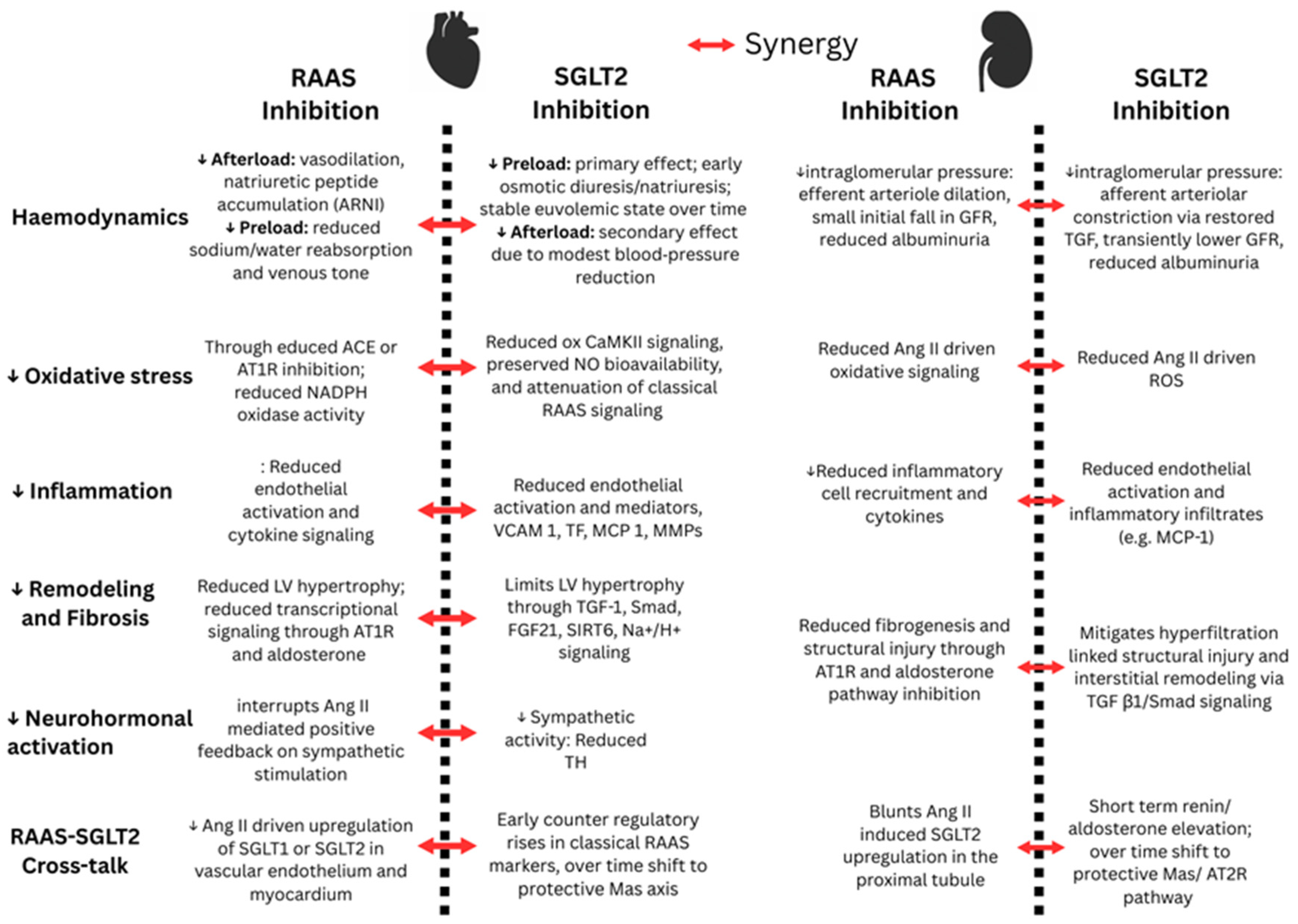
3.1. Effects of SGLT Inhibition on RAAS-Induced Cardiorenal Pathologies
3.2. Effects of SGLT and RAAS Inhibition on Renal Haemodynamics, Fluid, and Electrolyte Balance
3.3. Effects of SGLT2 Inhibition on Activation of the RAAS Pathway
4. Discussion and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RAAS | Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system |
| RAASi | Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system inhibitor |
| ACEI | Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor |
| ARB | Angiotensin receptor blocker |
| ARNI | Angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitor |
| MRA | Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist |
| SGLT2i | Sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor |
| CV | Cardiovascular |
| HF | Heart failure |
| HFrEF | Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction |
| HFmrEF | Heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction |
| HFpEF | Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction |
| HFimpEF | Heart failure with improved ejection fraction |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| T2D | Type 2 diabetes |
| T1D | Type 1 diabetes |
| GDMT | Guideline-directed medical therapy |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| UACR | Urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio |
| MR | Mitral regurgitation |
| BNP | B-type natriuretic peptide |
| NT-proBNP | N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide |
| ANP | Atrial natriuretic peptide |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| VCAM-1 | Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| MMPs | Matrix metalloproteinases |
| TGF-β1 | Transforming growth factor-beta 1 |
| Smad | SMAD family signalling proteins |
| ACE2 | Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 |
| Ang I | Angiotensin I |
| Ang II | Angiotensin II |
| Ang-(1–7) | Angiotensin-(1–7) |
| AT1R | Angiotensin II type 1 receptor |
| AT2R | Angiotensin II type 2 receptor |
| NHE | Sodium–hydrogen exchanger |
| SOCCs | Store-operated calcium channels |
| ox-CaMKII | Oxidized Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II |
| FGF21 | Fibroblast growth factor-21 |
| UNx | Unilateral nephrectomy |
| DOCA | Deoxycorticosterone acetate |
| LC-MS | Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| SIRT | Sirtuin family |
References
- Fountain, J.H.; Kaur, J.; Lappin, S.L. Physiology, Renin Angiotensin System. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470410/ (accessed on 23 November 2025).
- Ksiazek, S.H.; Hu, L.; Andò, S.; Pirklbauer, M.; Säemann, M.D.; Ruotolo, C.; Zaza, G.; La Manna, G.; De Nicola, L.; Mayer, G.; et al. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System: From History to Practice of a Secular Topic. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E.M. SGLT2 Inhibitors: Physiology and Pharmacology. Kidney360 2021, 2, 2027–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, M.A.; Mansfield, T.A.; Cain, V.A.; Iqbal, N.; Parikh, S.; Ptaszynska, A. Blood Pressure and Glycaemic Effects of Dapagliflozin versus Placebo in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes on Combination Antihypertensive Therapy. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 211–220, Erratum in Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kario, K.; Okada, K.; Kato, M.; Nishizawa, M.; Yoshida, T.; Asano, T.; Uchiyama, K.; Niijima, Y.; Katsuya, T.; Urata, H.; et al. Twenty Four Hour Blood Pressure–Lowering Effect of a Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor in Patients with Diabetes and Uncontrolled Nocturnal Hypertension, SACRA Study. Circulation 2019, 139, 2089–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rådholm, K.; Figtree, G.; Perkovic, V.; Solomon, S.D.; Mahaffey, K.W.; de Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Barrett, T.D.; Shaw, W.; Desai, M.; et al. Canagliflozin and Heart Failure in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Results from the CANVAS Program. Circulation 2018, 138, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inzucchi, S.E.; Khunti, K.; Fitchett, D.H.; Wanner, C.; Mattheus, M.; George, J.T.; Ofstad, A.P.; Zinman, B. Cardiovascular Benefit of Empagliflozin across the Spectrum of Cardiovascular Risk Factor Control in the EMPA REG OUTCOME Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, dgaa321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyama, K.; Raz, I.; Cahn, A.; Goodrich, E.L.; Bhatt, D.L.; Leiter, L.A.; McGuire, D.K.; Wilding, J.P.H.; Gause-Nilsson, I.A.M.; Mosenzon, O.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Dapagliflozin According to Background Use of Cardiovascular Medications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Prespecified Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2022, 7, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Johnsson, E.; Gause Nilsson, I.; Cain, V.A.; Sjöström, C.D. Dapagliflozin Reduces Albuminuria in Patients with Diabetes and Hypertension Receiving Renin Angiotensin Blockers. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancia, G.; Cannon, C.P.; Tikkanen, I.; Zeller, C.; Ley, L.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C.; Johansen, O.E. Impact of Empagliflozin on Blood Pressure in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Hypertension by Background Antihypertensive Medication. Hypertension 2016, 68, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, G.J.; Wanner, C.; Weir, M.R.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Koitka Weber, A.; Hantel, S.; von Eynatten, M.; Zinman, B.; Cherney, D.Z.I. Analysis from the EMPA REG OUTCOME Trial Indicates Empagliflozin May Assist in Preventing the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Irrespective of Medications that Alter Intrarenal Hemodynamics. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.M.; Hwang, I.C.; Choi, W.; Yoon, Y.E.; Cho, G.Y. Combined Effects of ARNI and SGLT2 Inhibitors in Diabetic Patients with HFrEF. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Han, K.; Kim, K.S.; Park, C.Y. Effects of RAS and SGLT2 Inhibitors Alone or in Combination on ESKD and/or All Cause Death in Diabetes and Hypertension. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2025, 24, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karalliedde, J.; Fountoulakis, N.; Stathi, D.; Corcillo, A.; Flaquer, M.; Panagiotou, A.; Maltese, G.; Mangelis, A.; Ayis, S.; Gnudi, L. Does Dapagliflozin Influence Arterial Stiffness and Levels of Circulating Anti Aging Hormone Soluble Klotho in People with Type 2 Diabetes and Kidney Disease? Results of a Randomized Parallel Group Clinical Trial. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 992327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytvyn, Y.; Kimura, K.; Peter, N.; Lai, V.; Tse, J.; Cham, L.; Perkins, B.A.; Soleymanlou, N.; Cherney, D.Z.I. Renal and Vascular Effects of Combined SGLT2 and Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibition. Circulation 2022, 146, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; Solomon, S.D.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Martinez, F.A.; Ponikowski, P.; Sabatine, M.S.; Anand, I.S.; Bělohlávek, J.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M.; Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Ferreira, J.P.; Pocock, S.J.; Rocca, H.P.B.L.; Janssens, S.; Tsutsui, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. Influence of Neprilysin Inhibition on the Efficacy and Safety of Empagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure and a Reduced Ejection Fraction: The EMPEROR Reduced Trial. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Ferreira, J.P.; Bocchi, E.; Böhm, M.; Brunner La Rocca, H.P.; Choi, D.J.; Chopra, V.; Chuquiure Valenzuela, E.; et al. Empagliflozin in Heart Failure with a Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, A.F.; Udell, J.A.; Jones, W.S.; Anker, S.D.; Petrie, M.C.; Harrington, J.; Mattheus, M.; Seide, S.; Zwiener, I.; Amir, O.; et al. Effect of Empagliflozin on Heart Failure Outcomes After Acute Myocardial Infarction: Insights from the EMPACT MI Trial. Circulation 2024, 149, 1627–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.H.; Park, S.J.; Shin, S.H.; Hwang, I.C.; Yoon, Y.E.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, M.; Kim, M.S.; Yun, S.C.; Song, J.M.; et al. Ertugliflozin for Functional Mitral Regurgitation Associated with Heart Failure: EFFORT Trial. Circulation 2024, 149, 1865–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docherty, K.F.; Jhund, P.S.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Martinez, F.A.; Ponikowski, P.; DeMets, D.L.; Sabatine, M.S.; Bengtsson, O.; et al. Effects of Dapagliflozin in DAPA HF According to Background Heart Failure Therapy. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2379–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, S.D.; Jhund, P.S.; Claggett, B.L.; Dewan, P.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Martinez, F.A.; Ponikowski, P.; Sabatine, M.S.; Inzucchi, S.E.; et al. Effect of Dapagliflozin in Patients with HFrEF Treated with Sacubitril/Valsartan. JACC Heart Fail. 2020, 8, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Kristensen, S.L.; Bengtsson, O.; Böhm, M.; de Boer, R.A.; Docherty, K.F.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Katova, T.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; et al. Dapagliflozin in HFrEF Patients Treated with Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists. JACC Heart Fail. 2021, 9, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabon, M.; Claggett, B.L.; Wang, X.; Miao, Z.M.; Chatur, S.; Bhatt, A.S.; Vaduganathan, M.; Fang, J.C.; Desai, A.S.; Jhund, P.; et al. Influence of Background Medical Therapy on Efficacy and Safety of Dapagliflozin in Patients with Heart Failure with Improved Ejection Fraction in the DELIVER Trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2023, 25, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaduganathan, M.; Claggett, B.L.; Kulac, I.J.; Miao, Z.M.; Desai, A.S.; Jhund, P.S.; Henderson, A.D.; Brinker, M.; Lay Flurrie, J.; Viswanathan, P.; et al. Effects of the Non Steroidal MRA Finerenone with and without Concomitant SGLT2 Inhibitor Use in Heart Failure. Circulation 2025, 151, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaduganathan, M.; Claggett, B.L.; Jhund, P.S.; Cunningham, J.W.; Ferreira, J.P.; Zannad, F.; Packer, M.; Fonarow, G.C.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Solomon, S.D. Estimating Lifetime Benefits of Comprehensive Disease Modifying Pharmacological Therapies in Patients with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Comparative Analysis of Three Randomised Controlled Trials. Lancet 2020, 396, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumarulo, I.; Pasquini, A.; La Vecchia, G.; Pellizzeri, B.; Sten, A.; Garramone, B.; Vaccarella, M.; Ravenna, S.E.; Lombardo, A.; Burzotta, F.; et al. Evaluation of the Effects of the Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors and Sacubitril/Valsartan Combined Therapy in Patients with HFrEF: An Echocardiographic Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamchand, S.; Chipamaunga, T.; Naidoo, P.; Naidoo, K.; Rambiritch, V.; Ho, K.; Chilton, R.; McMahon, K.; Leisegang, R.; Weich, H.; et al. Novel Versus Conventional Sequencing of β Blockers, Sodium/Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitors, and Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists in Stable Patients with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction (NovCon Sequencing Study): Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2025, 14, e44027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteucci, A.; Pandozi, C.; Bonanni, M.; Mariani, M.V.; Sgarra, L.; Nesti, L.; Pierucci, N.; La Fazia, V.M.; Lavalle, C.; Nardi, F.; et al. Impact of Empagliflozin and Dapagliflozin on Sudden Cardiac Death: A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis of Adjudicated Randomized Evidence. Heart Rhythm 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes Pardo, H.; Bautista, R.; Vargas Robles, H.; Rios, A.; Sánchez, D.; Escalante, B. Role of Sodium/Glucose Cotransporter Inhibition on a Rat Model of Angiotensin II–Dependent Kidney Damage. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khemais Benkhiat, S.; Belcastro, E.; Idris Khodja, N.; Park, S.; Amoura, L.; Abbas, M.; Auger, C.; Kessler, L.; Mayoux, E.; Toti, F.; et al. Angiotensin II Induced Redox Sensitive SGLT1 and 2 Expression Promotes High Glucose Induced Endothelial Cell Senescence. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 2109–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castoldi, G.; Carletti, R.; Ippolito, S.; Colzani, M.; Barzaghi, F.; Stella, A.; Zerbini, G.; Perseghin, G.; di Gioia, C.R.T. Renal Anti Fibrotic Effect of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition in Angiotensin II Dependent Hypertension. Am. J. Nephrol. 2020, 51, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castoldi, G.; Carletti, R.; Ippolito, S.; Colzani, M.; Pelucchi, S.; Zerbini, G.; Perseghin, G.; Zatti, G.; di Gioia, C.R.T. Cardioprotective Effects of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition in Angiotensin II Dependent Hypertension Are Mediated by the Local Reduction of Sympathetic Activity and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Chu, Y.; Chen, X.; Du, H.; Zhang, H.; Xu, C.; Xie, H.; Ruan, Q.; Lin, J.; et al. Dapagliflozin: A Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor, Attenuates Angiotensin II Induced Cardiac Fibrotic Remodeling by Regulating TGFβ1/Smad Signaling. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckert, C.; Matsushita, K.; Mroueh, A.; Amissi, S.; Auger, C.; Houngue, U.; Remila, L.; Chaker, A.B.; Park, S.H.; Algara Suarez, P.; et al. Empagliflozin Prevents Angiotensin II Induced Hypertension Related Micro and Macrovascular Endothelial Cell Activation and Diastolic Dysfunction in Rats Despite Persistent Hypertension: Role of Endothelial SGLT1 and 2. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2022, 146, 107095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Tang, Y.; Bi, H.; Yang, X.; Xia, Y. Dapagliflozin: A Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor, Attenuates Angiotensin II Induced Atrial Fibrillation by Regulating Atrial Electrical and Structural Remodeling. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 978, 176712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.; Jia, Z.; Wang, H.; Zheng, P.; Xue, Y.; Gong, K.; Zhao, R. Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor Ameliorate Angiotensin II Induced Hypertension and Vascular Injury by Upregulating FGF21. Inflammation 2025, 48, 4031–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wu, K.; Dong, F.; Cai, B.; Wu, D.; Lu, H. Effects of Empagliflozin and Dapagliflozin in Alleviating Cardiac Fibrosis through SIRT6 Mediated Oxidative Stress Reduction. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jia, Z.; Wu, X.; Xue, Y.; Zheng, P.; Wang, H.; Zhao, R. Early Cardioprotective Effects of SGLT2i on Hypertensive Cardiac Remodeling via STIM1/Orai1 Dependent Calcium Signaling: Beyond Blood Pressure Control. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2025, 57, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.A.; Riella, L.V. Narrative Review of Immunomodulatory and Anti-inflammatory Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Unveiling Novel Therapeutic Frontiers. Kidney Int. Rep. 2024, 9, 1601–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Mauvecin, J.; Villar-Gómez, N.; Miño-Izquierdo, L.; Povo-Retana, A.; Ramos, A.M.; Ruiz-Hurtado, G.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Ortiz, A.; Sanz, A.B. Antioxidant Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Cardiovascular–Kidney–Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, D.Z.I.; Perkins, B.A.; Soleymanlou, N.; Maione, M.; Lai, V.; Lee, A.; Fagan, N.M.; Woerle, H.J.; Johansen, O.E.; Broedl, U.C.; et al. Renal Hemodynamic Effect of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Circulation 2014, 129, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauber, P.; Sinha, F.; Berger, R.S.; Gronwald, W.; Dettmer, K.; Kuhn, M.; Trum, M.; Maier, L.S.; Wagner, S.; Schweda, F. Empagliflozin Reduces Renal Hyperfiltration in Response to Uninephrectomy, but Is Not Nephroprotective in UNx/DOCA/Salt Mouse Models. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 761855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytvyn, Y.; Scholtes, R.A.; Boorsma, E.M.; Sridhar, V.S.; Kugathasan, L.; Liu, H.; Lovblom, L.E.; Handoko, L.; Mosterd, C.M.; Floras, J.S.; et al. Mechanistic Evaluation of Ertugliflozin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Heart Failure. Physiol. Rep. 2025, 13, e70275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, S.; Polidori, D.; Heise, T.; Natarajan, J.; Farrell, K.; Wang, S.S.; Sica, D.; Rothenberg, P.; Plum Mörschel, L. Effect of the Sodium Glucose Co Transporter 2 Inhibitor Canagliflozin on Plasma Volume in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eickhoff, M.K.; Dekkers, C.C.J.; Kramers, B.J.; Laverman, G.D.; Frimodt Møller, M.; Jørgensen, N.R.; Faber, J.; Danser, A.H.J.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Rossing, P.; et al. Effects of Dapagliflozin on Volume Status When Added to Renin–Angiotensin System Inhibitors. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagaito, M.; Imamura, T.; Joho, S.; Ushijima, R.; Nakamura, M.; Kinugawa, K. Renoprotective Effects of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with Decompensated Heart Failure. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2021, 21, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugathasan, L.; Sridhar, V.S.; Lytvyn, Y.; Lovblom, L.E.; Perkins, B.A.; Advani, A.; Cherney, D.Z.I. Effect of Hyperglycemia and Empagliflozin on Markers of Cardiorenal Injury and Inflammation in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 213, 111764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, Y.; Kidokoro, K.; Kondo, M.; Tokuyama, A.; Kadoya, H.; Nagasu, H.; Kanda, E.; Sasaki, T.; Cherney, D.Z.I.; Kashihara, N. Evaluation of Glomerular Hemodynamic Changes by Sodium–Glucose Transporter 2 Inhibition in Type 2 Diabetic Rats Using In Vivo Imaging. Kidney Int. 2024, 106, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, N.; Williams, J.M.; Slaughter, T.N.; Kato, S.; Takahashi, T.; Miyata, N.; Roman, R.J. Renoprotective Effects of Combined SGLT2 and ACE Inhibitor Therapy in Diabetic Dahl S Rats. Physiol. Rep. 2015, 3, e12436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilancio, G.; Hamzeh, S.; Vecchione, N.; Russo, D.; Iacuzzo, C.; Apicella, L.; Di Pietro, R.A.; Vitale, P.; Amicone, M.; Pisani, A.; et al. Dapagliflozin’s Effects on Urinary Albumin and Non-Albumin Proteins in Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Kidney Transplant Recipients. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotrin, J.C.; Santos, G.; Petito da Silva, T.I.; Macedo, E.; Souza Mello, V.; Barbosa da Silva, S. Empagliflozin Alleviates Left Ventricle Hypertrophy in High Fat Fed Mice by Modulating Renin Angiotensin Pathway. J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2022, 2022, 8861911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, H.; Batra, M.; Green, K.; Hejna, J.; Abuaysheh, S.; Makdissi, A.; Chaudhuri, A.; Dandona, P. Dapagliflozin Reduces Systolic Blood Pressure and Modulates Vasoactive Factors. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 1614–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.J.; Chung, S.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, E.M.; Yoo, Y.H.; Kim, J.W.; Ahn, Y.B.; Kim, E.S.; Moon, S.D.; Kim, M.J.; et al. Effect of Sodium Glucose Co Transporter 2 Inhibitor, Dapagliflozin, on Renal Renin–Angiotensin System in an Animal Model of Type 2 Diabetes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, T.C.; Satou, R.; Miyata, K.; Katsurada, A.; Dugas, C.M.; Klingenberg, N.C.; Fonseca, V.A.; Navar, L.G. Canagliflozin Prevents Intrarenal Angiotensinogen Augmentation and Mitigates Kidney Injury and Hypertension in Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Am. J. Nephrol. 2019, 49, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, T.; Scholtes, R.A.; Greasley, P.J.; Cherney, D.Z.I.; Dekkers, C.C.J.; Vervloet, M.G.; Danser, A.H.J.; Barbour, S.J.; Karlsson, C.; Laverman, G.D.; et al. Effects of Dapagliflozin on Volume Status and Systemic Haemodynamics in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease without Diabetes: Results from DAPASALT and DIAMOND. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 1578–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchi, A.; Pruijm, M.; Muller, M.E.; Ghajarzadeh Wurzner, A.; Maillard, M.; Dufour, N.; Bonny, O.; Wuerzner, G.; Burnier, M. Twenty Four Hour Blood Pressure Response to Empagliflozin and Its Determinants in Normotensive Non Diabetic Subjects. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 854230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Takano, K.; Iijima, H.; Kubo, H.; Maruyama, N.; Hashimoto, T.; Arakawa, K.; Togo, M.; Inagaki, N.; Kaku, K. Factors Affecting Canagliflozin Induced Transient Urine Volume Increase in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Adv. Ther. 2017, 34, 436–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solini, A.; Seghieri, M.; Giannini, L.; Biancalana, E.; Parolini, F.; Rossi, C.; Dardano, A.; Taddei, S.; Ghiadoni, L.; Bruno, R.M. The Effects of Dapagliflozin on Systemic and Renal Vascular Function Display an Epigenetic Signature. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 4253–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isshiki, M.; Sakuma, I.; Hayashino, Y.; Sumita, T.; Hara, K.; Takahashi, K.; Shiojima, I.; Satoh Asahara, N.; Kitazato, H.; Ito, D.; et al. Effects of Dapagliflozin on Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System under Renin–Angiotensin System Inhibitor Administration. Endocr. J. 2020, 67, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, A.; Poglitsch, M.; Kannenkeril, D.; Kolwelter, J.; Striepe, K.; Ott, C.; Rauh, M.; Schiffer, M.; Achenbach, S.; Schmieder, R.E. Angiotensin Pathways under Therapy with Empagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2023, 10, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawamura, T.; Karashima, S.; Nagase, S.; Nambo, H.; Shimizu, E.; Higashitani, T.; Aono, D.; Ohbatake, A.; Kometani, M.; Demura, M.; et al. Effect of Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors on Aldosterone to Renin Ratio in Diabetic Patients with Hypertension: A Retrospective Observational Study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2020, 20, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, M.; Rao, V.S.; Ivey Miranda, J.; Fleming, J.; Mahoney, D.; Maulion, C.; Suda, N.; Siwakoti, K.; Ahmad, T.; Jacoby, D.; et al. Empagliflozin in Heart Failure: Diuretic and Cardiorenal Effects. Circulation 2020, 142, 1028–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, B.F.; Clegg, D.J. SGLT2 Inhibition and Kidney Potassium Homeostasis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2024, 19, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Aazar, R.F.M.; Arzouni, R.; Nicolaou, P.A. Dual Inhibition of the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System and Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter-2: Mechanistic and Clinical Evidence for Cardiorenal Protection. Biomedicines 2026, 14, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines14010101
Aazar RFM, Arzouni R, Nicolaou PA. Dual Inhibition of the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System and Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter-2: Mechanistic and Clinical Evidence for Cardiorenal Protection. Biomedicines. 2026; 14(1):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines14010101
Chicago/Turabian StyleAazar, Reem F. M., Rayan Arzouni, and Persoulla A. Nicolaou. 2026. "Dual Inhibition of the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System and Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter-2: Mechanistic and Clinical Evidence for Cardiorenal Protection" Biomedicines 14, no. 1: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines14010101
APA StyleAazar, R. F. M., Arzouni, R., & Nicolaou, P. A. (2026). Dual Inhibition of the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System and Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter-2: Mechanistic and Clinical Evidence for Cardiorenal Protection. Biomedicines, 14(1), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines14010101






