IgG4-Related Orbital Disease vs. Idiopathic Orbital Inflammation: Clinical Features, Therapy and Outcomes in a Central-European Retrospective Single-Center Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics
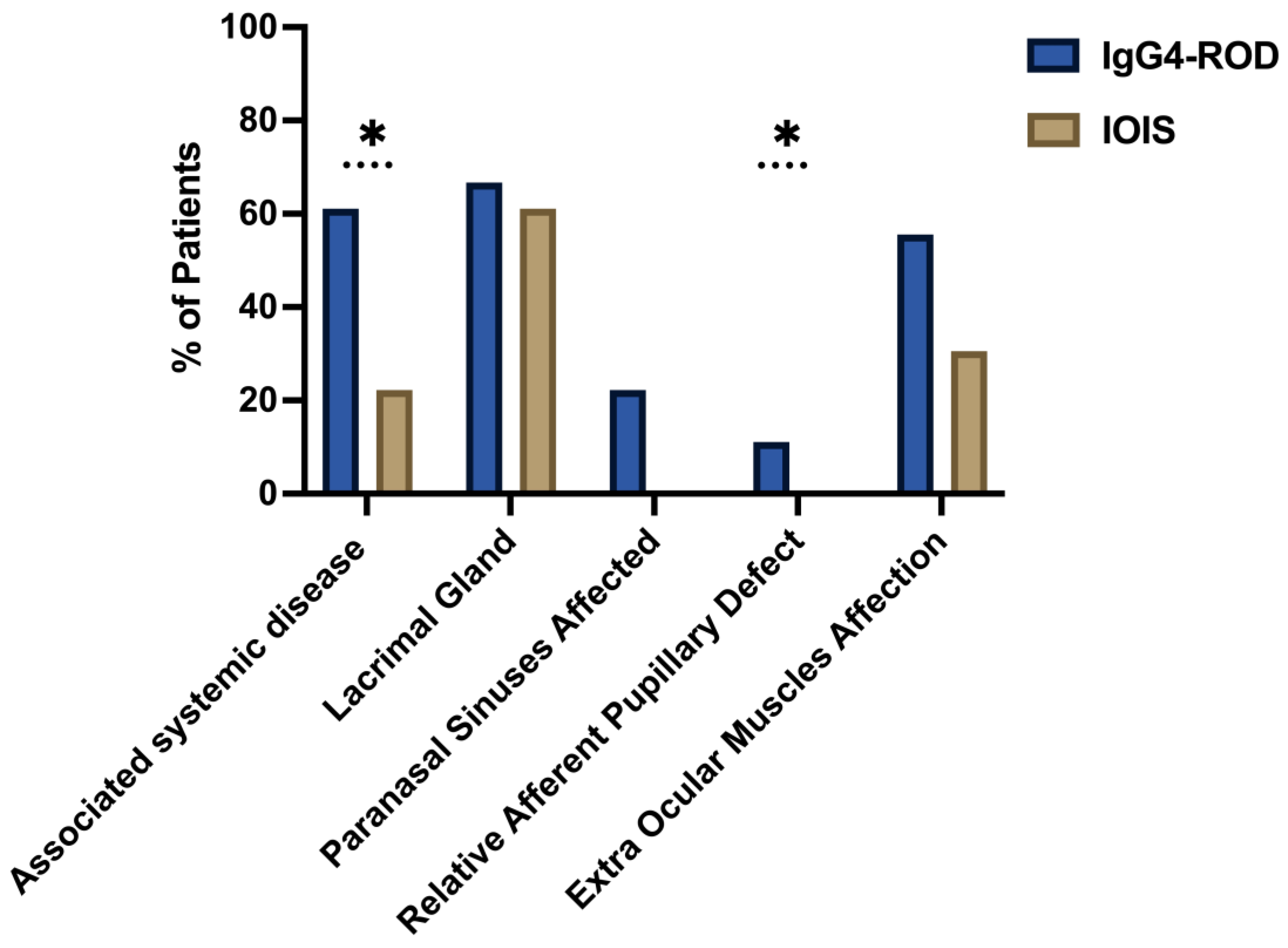
3.2. Systemic and Orbital Involvement
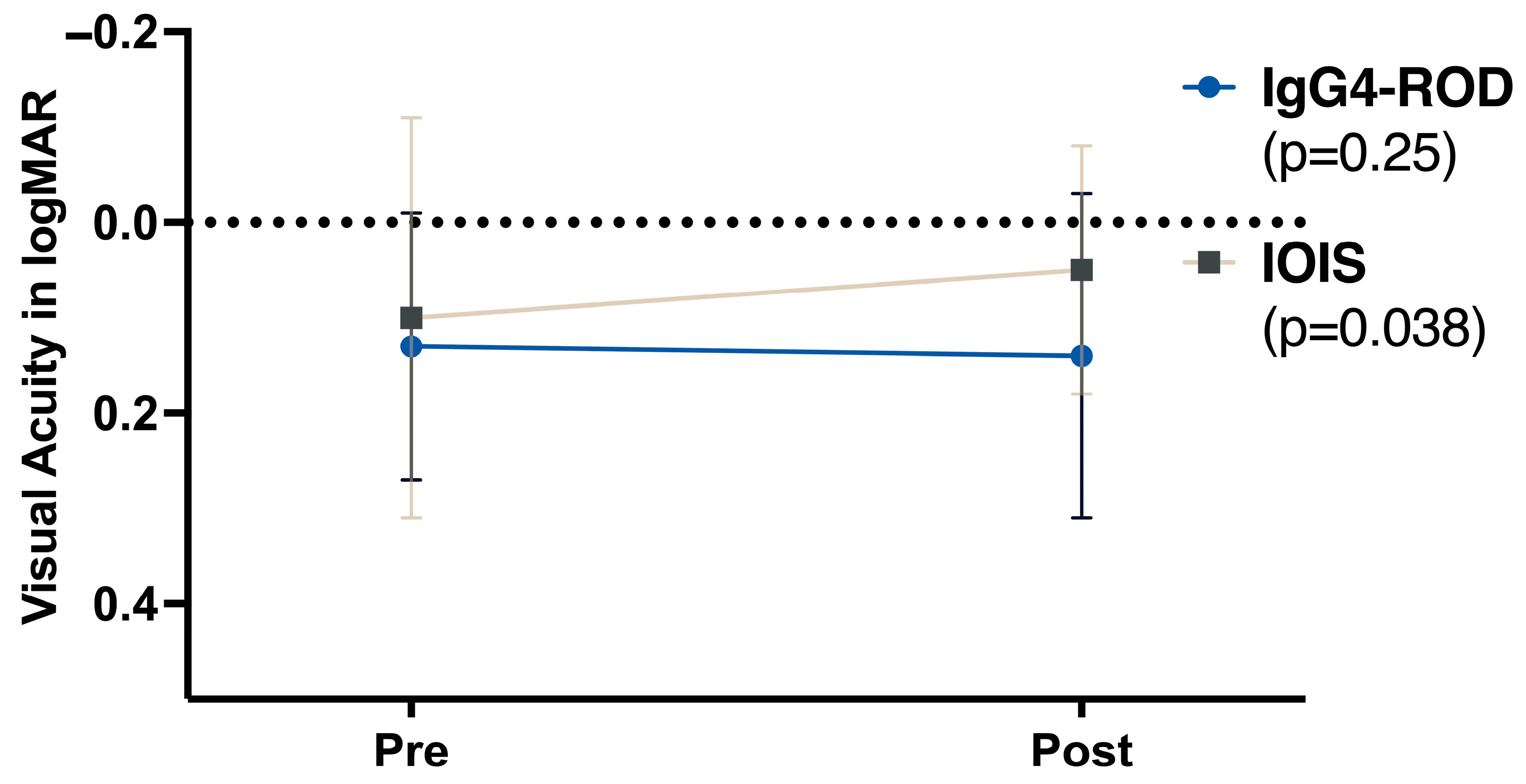
3.3. Visual Acuity
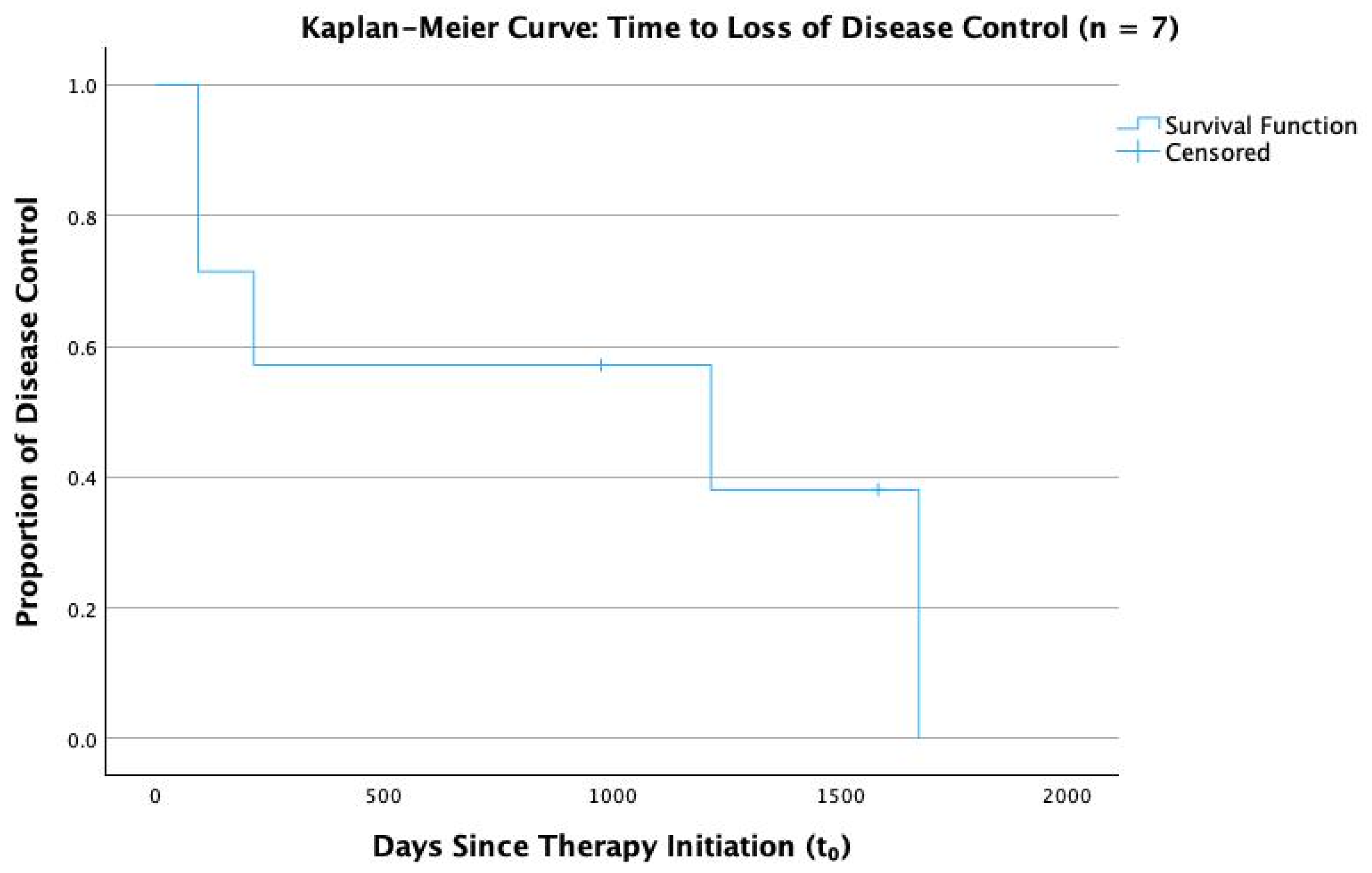
3.4. Therapy and Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCVA | Best-corrected visual acuity |
| DLBCL | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma |
| HPF | High-power field |
| IgG4-ROD | IgG4-related orbital disease |
| IgG4-RD | IgG4-related disease |
| IOD | Inflammatory orbital disease |
| IOIS | Idiopathic orbital inflammatory syndrome |
| logMAR | Logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| MALT | Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue |
| RAPD | Relative afferent pupillary defect |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| TED | Thyroid eye disease |
References
- Birch-Hirschfeld, A.; Sattler, C.H. Die Krankheiten der Orbita. Pulsierender Exophthalmus; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeşiltaş, Y.S.; Gündüz, A.K. Idiopathic Orbital Inflammation: Review of Literature and New Advances. Middle East Afr. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 25, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, B.N.; McCluskey, P.; Nemet, A.; Crouch, R.; Martin, P.; Benger, R.; Ghabriel, R.; Wakefield, D. Idiopathic orbital inflammatory syndrome: Clinical features and treatment outcomes. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 91, 1667–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombaerts, I.; Goldschmeding, R.; Schlingemann, R.O.; Koornneef, L. What is orbital pseudotumor? Surv. Ophthalmol. 1996, 41, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Shen, B.; Dai, Q.; Xie, Q.; Wu, W.; Wang, M. Orbital inflammatory pseudotumor: New advances in diagnosis, pathogenesis, and treatment. Eur. J. Med Res. 2023, 28, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, S.J.A. Idiopathic Orbital Inflammation: Distribution, Clinical Features, and Treatment Outcome. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2003, 121, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, I.; Shamsi, F.; Arat, Y.; Riley, F. Orbital pseudotumor: Distinct diagnostic features and management. Middle East Afr. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 15, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.L.; Romo, L.V.; Sabates, N.R. Pseudotumor of the orbit. Clinical, pathologic, and radiologic evaluation. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 1999, 37, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombaerts, I.; Saeed, P.; Kalmann, R. Idiopathic Orbital Inflammation. In Oculoplastic, Lacrimal and Orbital Surgery; Leoni, F.M.Q., Verity, D.H., Paridaens, D., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamano, H.; Kawa, S.; Horiuchi, A.; Unno, H.; Furuya, N.; Akamatsu, T.; Fukushima, M.; Nikaido, T.; Nakayama, K.; Usuda, N.; et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.C.; Mattman, A.; Seidman, M.A.; Carruthers, M.N. IgG4-related disease: What a hematologist needs to know. Haematologica 2019, 104, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNab, A.A.; McKelvie, P. IgG4-Related Ophthalmic Disease. Part II: Clinical Aspects. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 31, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umehara, H.; Okazaki, K.; Kawa, S.; Takahashi, H.; Goto, H.; Matsui, S.; Ishizaka, N.; Akamizu, T.; Sato, Y.; Kawano, M.; et al. The 2020 revised comprehensive diagnostic (RCD) criteria for IgG4-RD. Mod. Rheumatol. 2021, 31, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, H.; Takahira, M.; Azumi, A.; Japanese Study Group for IgG4-Related Ophthalmic Disease. Diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related ophthalmic disease. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 59, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahira, M.; Goto, H.; Azumi, A. The 2023 revised diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related ophthalmic disease. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 68, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledsoe, J.R.; Wallace, Z.S.; Stone, J.H.; Deshpande, V.; Ferry, J.A. Lymphomas in IgG4-related disease: Clinicopathologic features in a Western population. Virchows Arch. 2017, 472, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrew, N.H.; Sladden, N.; Kearney, D.J.; Selva, D. An analysis of IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) among idiopathic orbital inflammations and benign lymphoid hyperplasias using two consensus-based diagnostic criteria for IgG4-RD. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 99, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igawa, T.; Hayashi, T.; Ishiguro, K.; Maruyama, Y.; Takeuchi, M.; Takata, K.; Yoshino, T.; Sato, Y. IgG4-producing lymphoma arising in a patient with IgG4-related disease. Med Mol. Morphol. 2016, 49, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheuk, W.M.; Yuen, H.K.L.M.; Chan, A.C.L.M.; Shih, L.-Y.; Kuo, T.-T.; Ma, M.-W.M.; Lo, Y.-F.M.; Chan, W.-K.M.; Chan, J.K.C.M. Ocular Adnexal Lymphoma Associated With IgG4+ Chronic Sclerosing Dacryoadenitis: A Previously Undescribed Complication of IgG4-related Sclerosing Disease. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2008, 32, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, V.; Zen, Y.; Chan, J.K.; E Yi, E.; Sato, Y.; Yoshino, T.; Klöppel, G.; Heathcote, J.G.; Khosroshahi, A.; A Ferry, J.; et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Ohshima, K.; Ichimura, K.; Sato, M.; Yamadori, I.; Tanaka, T.; Takata, K.; Morito, T.; Kondo, E.; Yoshino, T. Ocular adnexal IgG4-related disease has uniform clinicopathology. Pathol. Int. 2008, 58, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, S.; Martin, A.; Héran, F.; Cucherousset, N.; Mouriaux, F.; Héron, E.; Sédira, N.; Zmuda, M.; Groh, M.; Abbas, A.; et al. IgG4-related disease in patients with idiopathic orbital inflammation syndrome: Data from the French SIOI prospective cohort. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018, 97, E648–E656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, P.; Ye, H.; Xiao, W.; Chen, R.; Mao, Y.; Ai, S.; Liu, Z.; Tang, L.; Yang, H. Clinical features and outcomes of IgG4-related idiopathic orbital inflammatory disease: From a large southern China-based cohort. Eye 2020, 35, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deschamps, R.; Deschamps, L.; Depaz, R.; Coffin-Pichonnet, S.; Belange, G.; Jacomet, P.V.; Vignal, C.; Benillouche, P.; Herdan, M.L.; Putterman, M.; et al. High prevalence of IgG4-related lymphoplasmacytic infiltrative disorder in 25 patients with orbital inflammation: A retrospective case series. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 97, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sa, H.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Woo, K.I.; Kim, Y.-D. IgG4-related disease in idiopathic sclerosing orbital inflammation. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 99, 1493–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Shi, L.; Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, C. Clinical Characteristics and CD4+ T Cell Subsets in IgG4-Related Disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 825386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-Y.; Kuo, K.-T.; Cheng, A.M.; Wei, Y.-H.; Chang, H.-C.; Chang, K.; Liao, S.-L. IgG4-related Ophthalmic Disease in Idiopathic Sclerosing and Non-Sclerosing Orbital Inflammation: A 25-Year Experience. Curr. Eye Res. 2019, 44, 1220–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, H.; Ueda, S.-I.; Nemoto, R.; Ohshima, K.-I.; Sogabe, Y.; Kitagawa, K.; Ogawa, Y.; Oyama, T.; Furuta, M.; Azumi, A.; et al. Clinical features and symptoms of IgG4-related ophthalmic disease: A multicenter study. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 65, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Andrew, N.H.; Tsirbas, A.; Tan, P.; Gajdatsy, A.; Selva, D. Rituximab for the treatment of IgG4-related orbital disease: Experience from five cases. Eye 2014, 29, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulholland, G.B.; Jeffery, C.C.; Satija, P.; Côté, D.W.J. Immunoglobulin G4-related diseases in the head and neck: A systematic review. J. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2015, 44, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, N.; Kearney, D.; Selva, D. IgG4-related orbital disease: A meta-analysis and review. Acta Ophthalmol. 2012, 91, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosroshahi, A.; Stone, J.H. A clinical overview of IgG4-related systemic disease. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2011, 23, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, S.; Kamisawa, T.; Kuruma, S.; Tabata, T.; Iwasaki, S.; Chiba, K.; Setoguchi, K.; Horiguchi, S.; Ozaki, N. Clinical features of IgG4-related dacryoadenitis. Graefe's Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2013, 252, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, T.G.; McNab, A.A.; Rose, G.E. Enlargement of the Infraorbital Nerve. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryasit, O.; Tiraset, N.; Preechawai, P.; Kayasut, K.; Sanghan, N.; Sittivarakul, W. IgG4-related disease in patients with idiopathic orbital inflammation. BMC Ophthalmol. 2021, 21, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Andrew, N.H.; A McNab, A.; Selva, D. Bilateral IgG4-related ophthalmic disease: A strong indication for systemic imaging. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 100, 1409–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiegs-Heiden, C.; Eckel, L.; Hunt, C.; Diehn, F.; Schwartz, K.; Kallmes, D.; Salomão, D.; Witzig, T.; Garrity, J. Immunoglobulin G4-related disease of the orbit: Imaging features in 27 patients. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1393–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carruthers, M.N.; Khosroshahi, A.; Augustin, T.; Deshpande, V.; Stone, J.H. The diagnostic utility of serum IgG4 concentrations in IgG4-related disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.H.; Brito-Zerón, P.; Bosch, X.; Ramos-Casals, M. Diagnostic Approach to the Complexity of IgG4-Related Disease. . Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, J.A.; Garrity, J.A.; Dogan, A.; Ananthamurthy, A.; Witzig, T.E.; Salomão, D.R. Orbital inflammation with IgG4-positive plasma cells: Manifestation of IgG4 systemic disease. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2011, 129, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaki, Y.; Dong, L.; Kurose, N.; Kitagawa, K.; Morikawa, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Takahashi, H.; Shinomura, Y.; Imai, K.; Saeki, T.; et al. Proposal for a new clinical entity, IgG4-positive multiorgan lymphoproliferative syndrome: Analysis of 64 cases of IgG4-related disorders. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, A.K.; Hudes, G.; Fizitskaya, A.; Ramesh, M.; Rosenstreich, D.; Ferastraoaru, D.; Gendalina, I.; Beronilla, M.; Jakubowicz, H. Increased IgG4 Levels Are Associated with Severe Asthma and Chronic Sinusitis in an Inner City Population with Persistent Eosinophilia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 153, AB369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divatia, M.; A Kim, S.; Ro, J.Y. IgG4-related sclerosing disease, an emerging entity: A review of a multi-system disease. Yonsei Med J. 2012, 53, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Soussan, J.; Deschamps, R.; Sadik, J.C.; Savatovsky, J.; Deschamps, L.; Puttermann, M.; Zmuda, M.; Heran, F.; Galatoire, O.; Picard, H.; et al. Infraorbital nerve involvement on magnetic resonance imaging in European patients with IgG4-related ophthalmic disease: A specific sign. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Coding Rule (Applied to Every Follow-Up Note) |
|---|---|
| Index date T0 | Start of systemic steroids (or biopsy date if untreated) |
| Initial response (IR) | First visit ≤ 6 months with no symptoms and no active exam signs |
| Remission | Any visit ≥ 6 months with (a) no symptoms and (b) no active signs |
| Loss of disease control | Recurrence of symptoms/signs requiring treatment escalation after an IR |
| Parameter | IgG4-ROD | IOIS | p-Value | Significant Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Demographics | ||||
| Average Age (years) | 61.78 ± 15.85 | 49.94 ± 15.04 | 0.02 | * |
| Female/Male Patients (%) | 44.44%/55.56% | 52.78%/47.22% | 0.564 | |
| Mean follow-up duration (months) | 21.72 ± 26.16 | 7.5 ± 10.33 | 0.02 | * |
| Associated systemic disease (%) | 61.11% | 22.22% | 0.005 | * |
| Lacrimal Gland Involvement (%) | 66.67% | 61.11% | 0.690 | |
| Extraocular Muscle Involvement (%) | 55.56% | 30.56% | 0.076 | |
| Paranasal Sinus Involvement (%) | 22.22% | 0% | 0.003 | * |
| Clinical Symptoms | ||||
| Eyelid Swelling (%) | 83.33% | 86.11% | 0.786 | |
| Exophthalmos (%) | 50.00% | 36.11% | 0.327 | |
| RAPD (%) | 11.11% | 0.00% | 0.042 | * |
| Chemosis (%) | 22.2% | 2.8% | 0.02 | * |
| Systemic Therapy Line | IgG4-ROD (n = 18) | IOIS (n = 36) |
|---|---|---|
| No systemic therapy (incl. radiotherapy-only) | 3 (16.7%) | 11 (30.6%) |
| First-line only: steroids (±local therapy) | 5 (27.8%) | 24 (66.7%) |
| Escalated: ≥ 1 steroid-sparing systemic agent | 7 (38.9%) | 1 (2.8%) |
| Multi-agent escalation: ≥ 2 steroid-sparing agents | 3 (16.7%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| Modality | IgG4-ROD (n = 18) | IOIS (n = 36) |
|---|---|---|
| Cytotoxic immunosuppressants (any) | 9 (50.0%) | 1 (2.8%) |
| Azathioprine | 7 (38.9%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| Cyclophosphamide | 3 (16.7%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| Methotrexate | 1 (5.6%) | 1 (2.8%) |
| Rituximab † | 4 (22.2%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| Radiotherapy | 2 (11.1%) | 6 (16.7%) |
| Exenteration | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (2.8%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rattunde, A.L.; Knecht, V.A.; Bertelmann, E. IgG4-Related Orbital Disease vs. Idiopathic Orbital Inflammation: Clinical Features, Therapy and Outcomes in a Central-European Retrospective Single-Center Cohort. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2311. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092311
Rattunde AL, Knecht VA, Bertelmann E. IgG4-Related Orbital Disease vs. Idiopathic Orbital Inflammation: Clinical Features, Therapy and Outcomes in a Central-European Retrospective Single-Center Cohort. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(9):2311. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092311
Chicago/Turabian StyleRattunde, Alexander Lukas, Vitus André Knecht, and Eckart Bertelmann. 2025. "IgG4-Related Orbital Disease vs. Idiopathic Orbital Inflammation: Clinical Features, Therapy and Outcomes in a Central-European Retrospective Single-Center Cohort" Biomedicines 13, no. 9: 2311. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092311
APA StyleRattunde, A. L., Knecht, V. A., & Bertelmann, E. (2025). IgG4-Related Orbital Disease vs. Idiopathic Orbital Inflammation: Clinical Features, Therapy and Outcomes in a Central-European Retrospective Single-Center Cohort. Biomedicines, 13(9), 2311. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092311






