Key Common Genes with LTF and MMP9 Between Sepsis and Relapsed B-Cell Lineage Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Extraction
2.2. Screening for the Differentially Expressed Common Genes in Pediatric Sepsis and Relapsed B-ALL
2.3. Functional Enrichment Analysis of Common Genes
2.4. Screening for the Diagnostic Genes of Pediatric Sepsis and Relapsed B-ALL
2.5. Expression and FUNCTION Analysis of the Key Common Genes of Pediatric Sepsis and Relapsed B-ALL
2.6. Molecular Mechanism Analyses
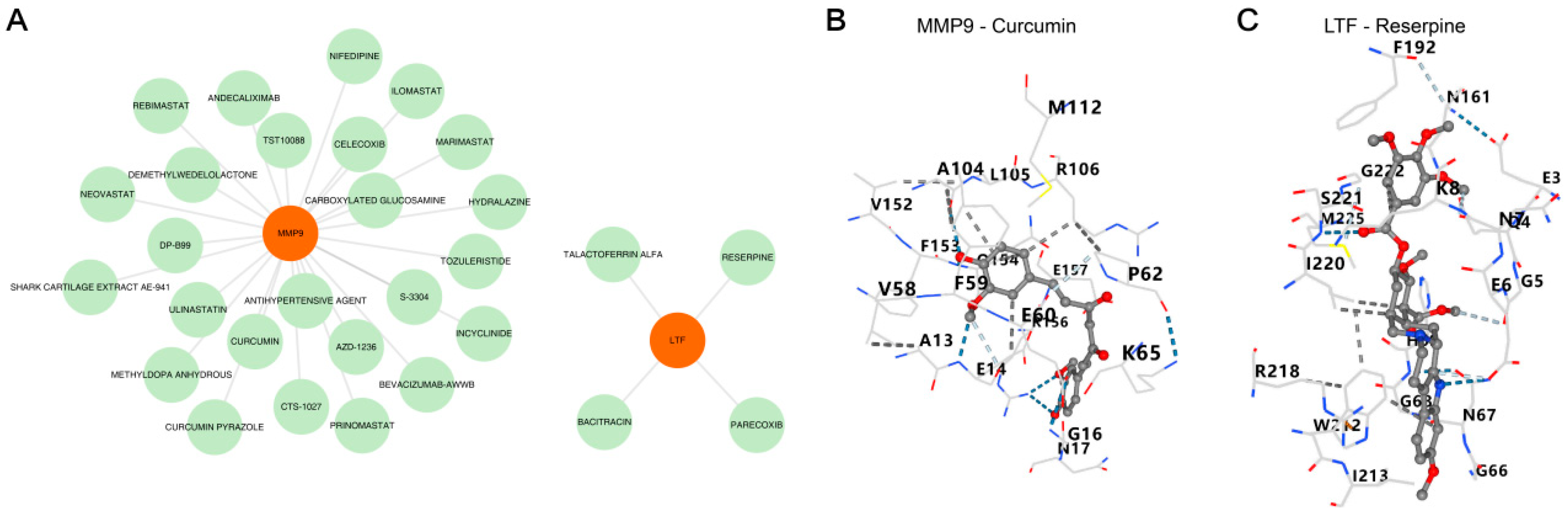
2.7. Drug Prediction and Molecular Docking
2.8. Real Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
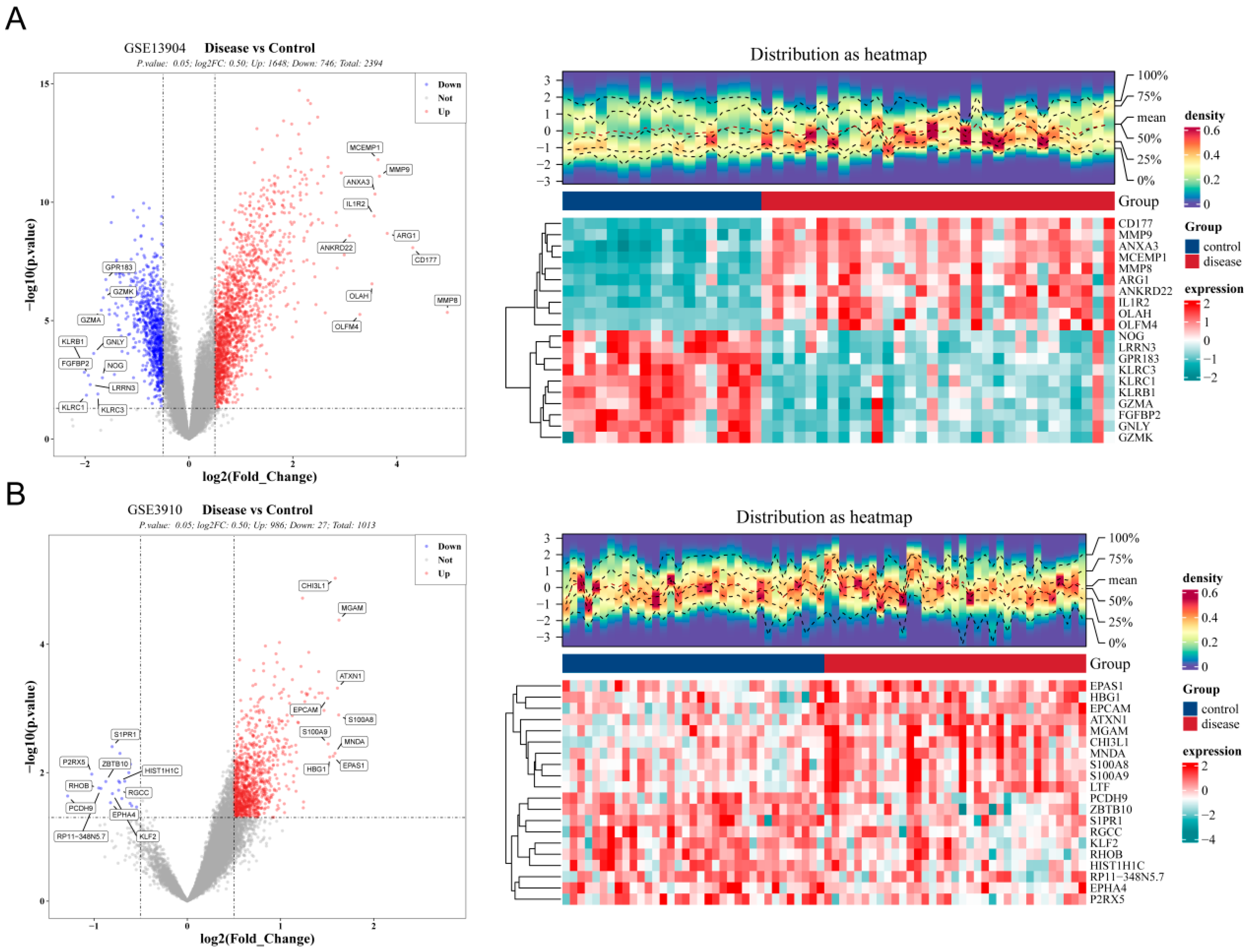
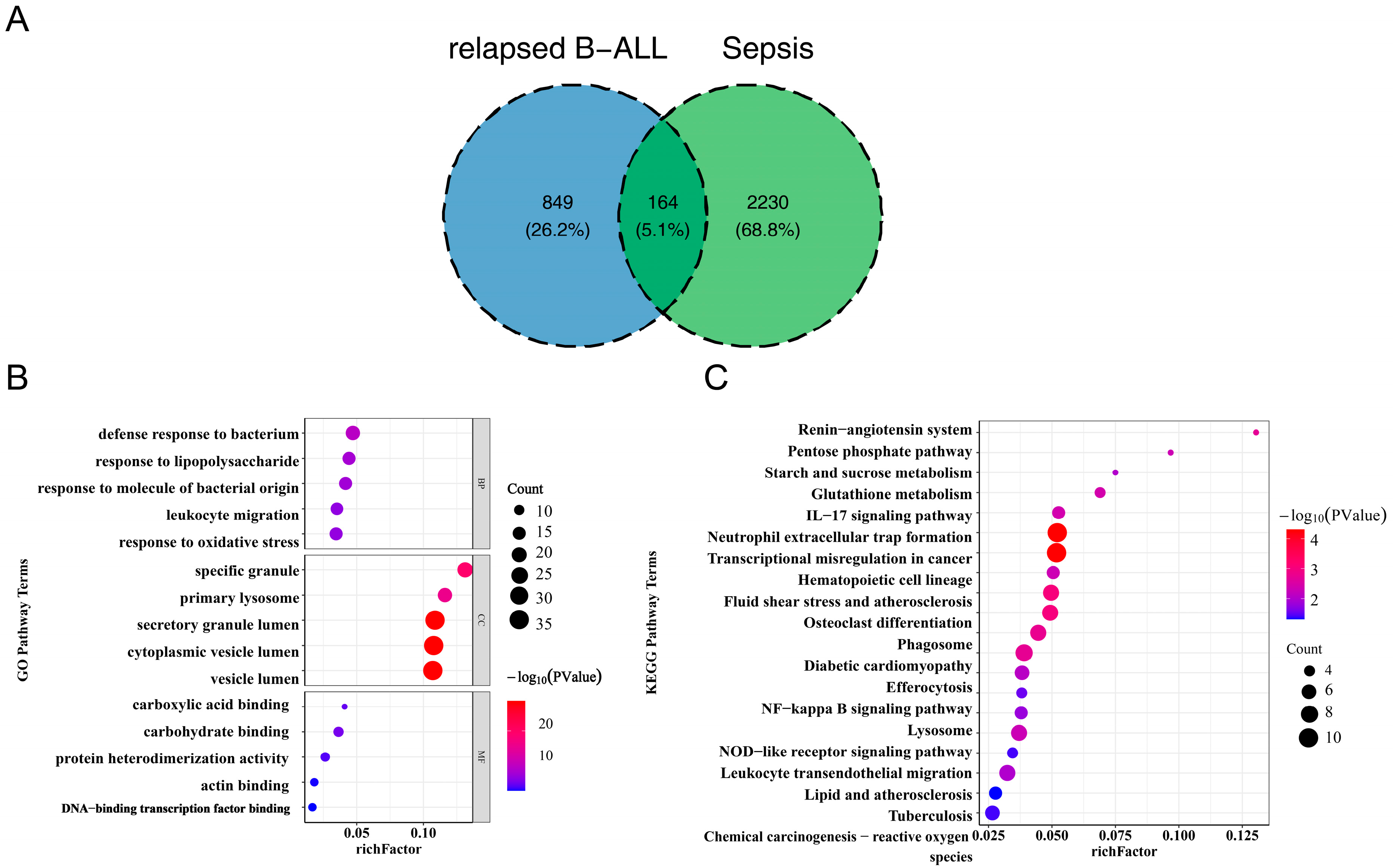
3.1. The 164 Common Genes in Pediatric Sepsis and Relapsed B-ALL Were Related to Inflammation and Immune Response
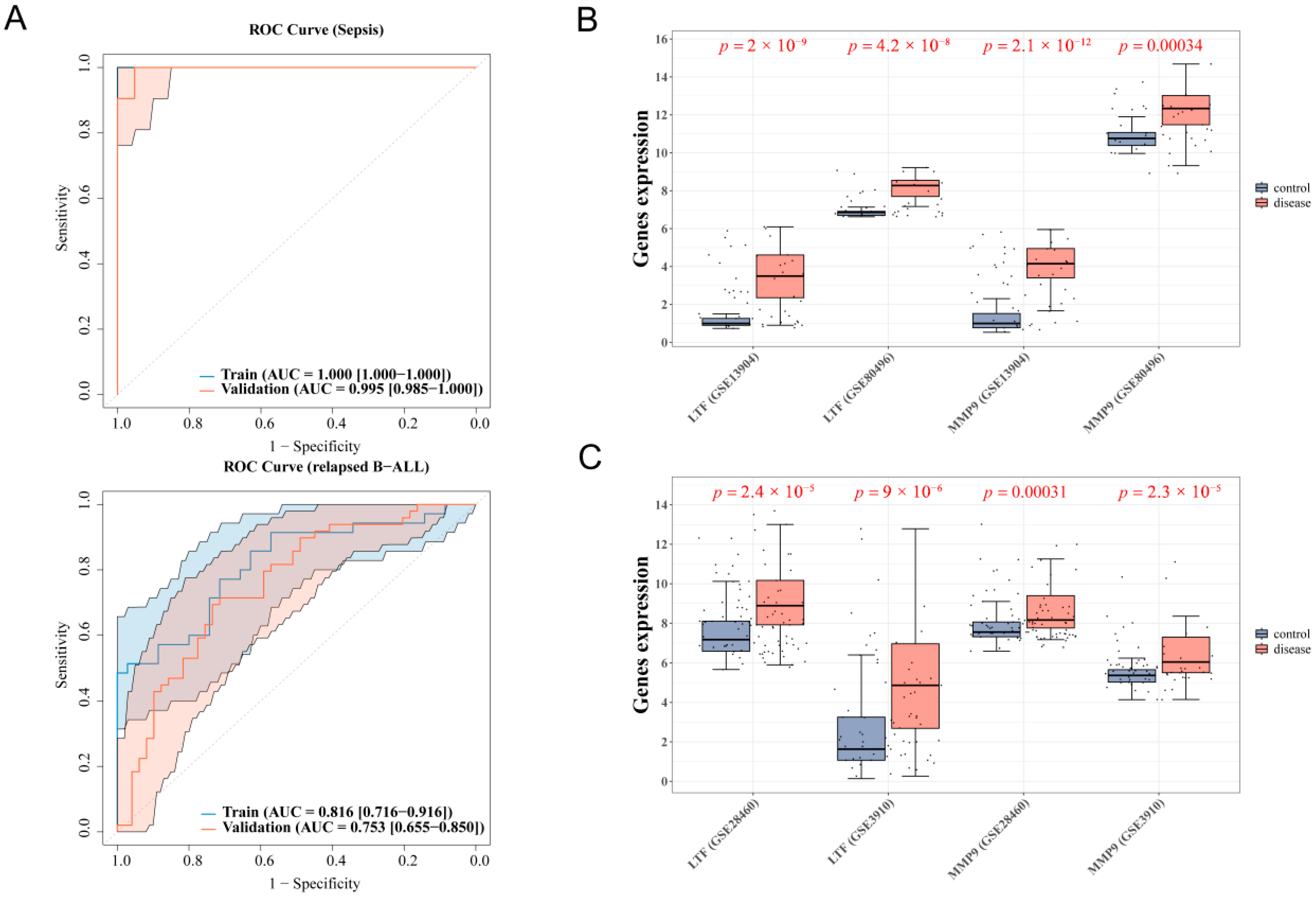
3.2. 4 Diagnostic Genes of Sepsis and 2 Diagnostic Genes of Relapsed B-ALL Were Screened
3.3. LTF and MMP9 Were the Key Common Genes of Pediatric Sepsis and Relapsed B-ALL
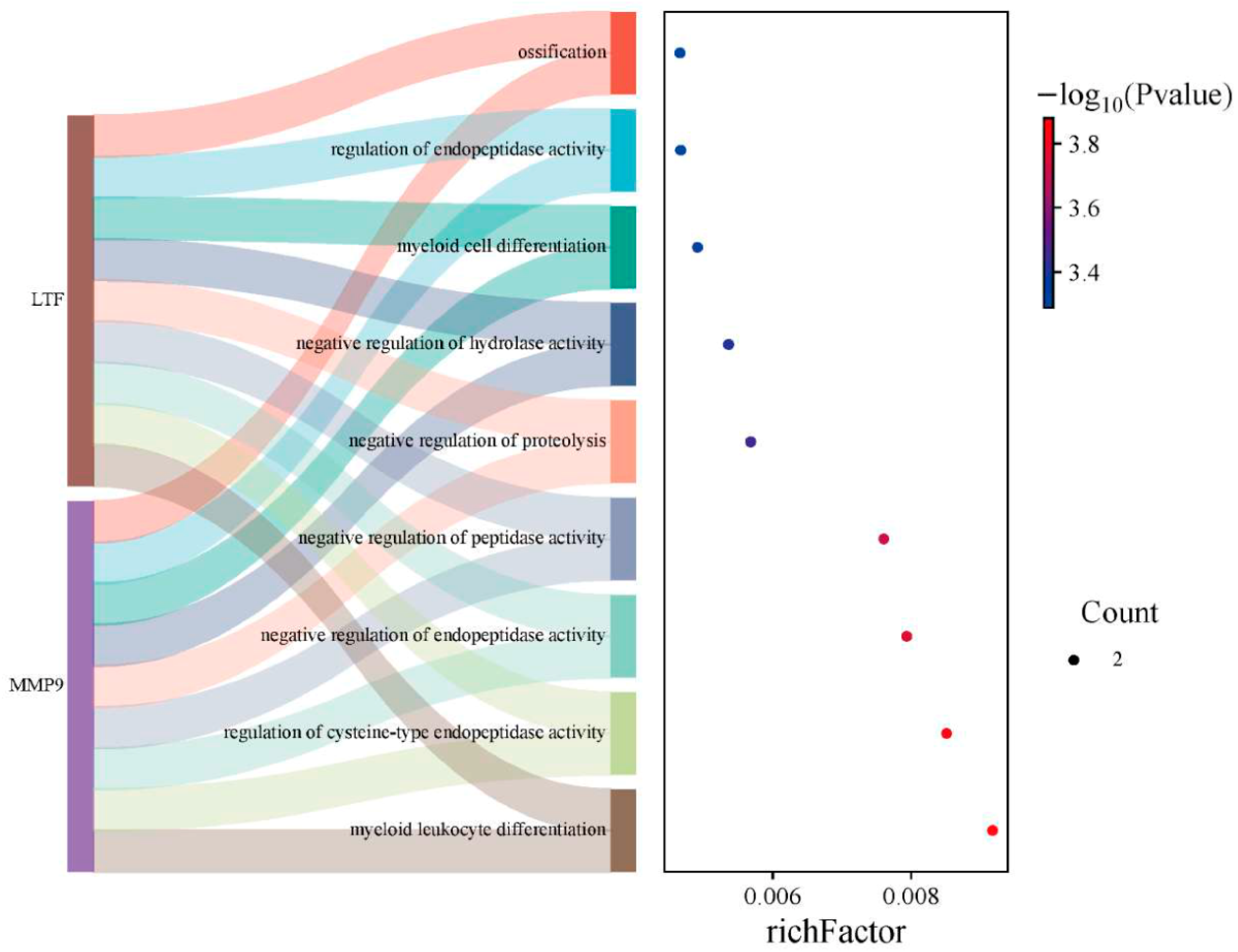
3.4. The Key Common Genes Were Associated with the Pathogenesis of Sepsis and Relapsed B-ALL
3.5. Molecular Mechanism Analyses of Key Common Genes
3.6. Prediction of MMP9/LTF-Targeted Drugs and Molecular Docking Validation
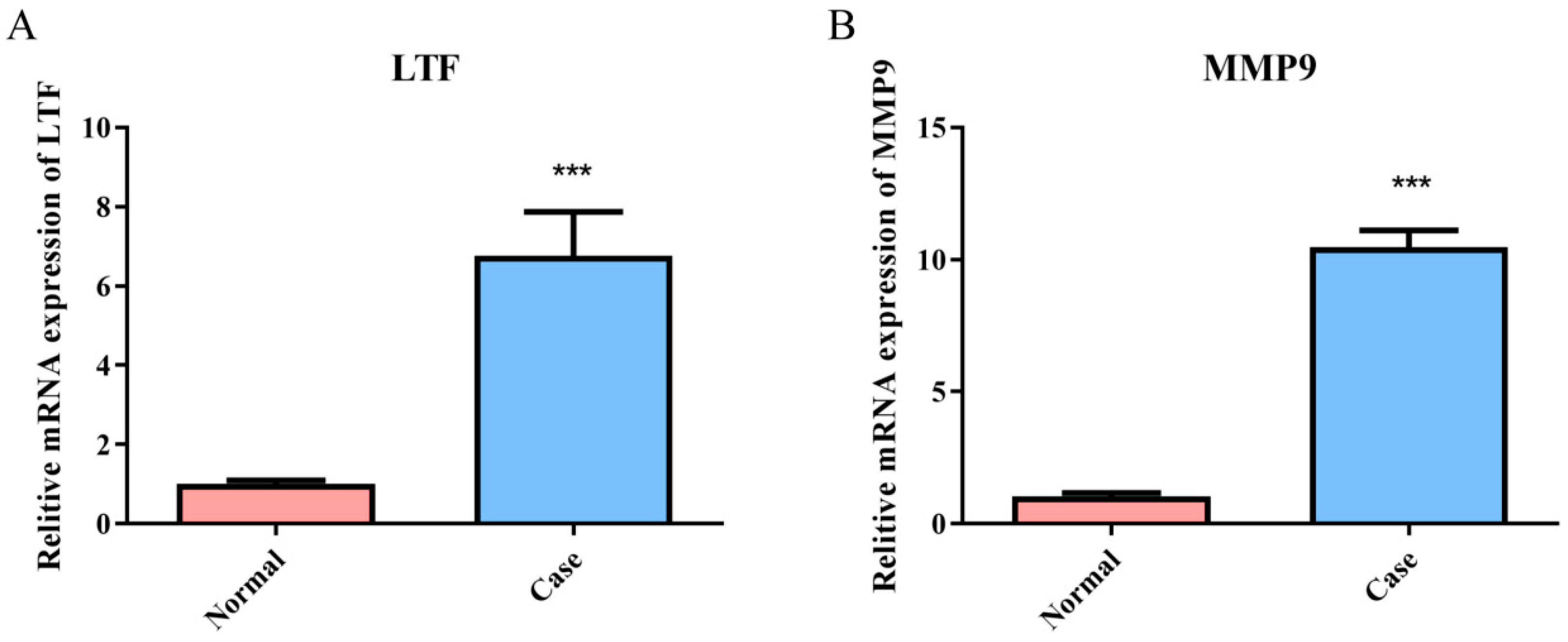
3.7. Validation of the Expression of Common Genes in the Relapsed B-ALL and Sepsis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Bhojwani, D.; Yang, J.J.; Pui, C.H. Biology of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 62, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmiegelow, K.; Forestier, E.; Hellebostad, M.; Heyman, M.; Kristinsson, J.; Söderhäll, S.; Taskinen, M. Long-term results of NOPHO ALL-92 and ALL-2000 studies of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2010, 24, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhojwani, D.; Kang, H.; Moskowitz, N.P.; Min, D.J.; Lee, H.; Potter, J.W.; Davidson, G.; Willman, C.L.; Borowitz, M.J.; Belitskaya-Levy, I.; et al. Biologic pathways associated with relapse in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A Children’s Oncology Group study. Blood 2006, 108, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; Machado, F.R.; McIntyre, L.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock 2021. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, e1063–e1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann-Struzek, C.; Goldfarb, D.M.; Schlattmann, P.; Schlapbach, L.J.; Reinhart, K.; Kissoon, N. The global burden of paediatric and neonatal sepsis: A systematic review. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.L.; Peters, M.J.; Alhazzani, W.; Agus, M.S.D.; Flori, H.R.; Inwald, D.P.; Nadel, S.; Schlapbach, L.J.; Tasker, R.C.; Argent, A.C.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign International Guidelines for the Management of Septic Shock and Sepsis-Associated Organ Dysfunction in Children. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 21, e52–e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diorio, C.; Shaw, P.A.; Pequignot, E.; Orlenko, A.; Chen, F.; Aplenc, R.; Barrett, D.M.; Bassiri, H.; Behrens, E.; DiNofia, A.M.; et al. Diagnostic biomarkers to differentiate sepsis from cytokine release syndrome in critically ill children. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5174–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goggin, K.P.; Lu, L.; Lee, D.E.; Howell, C.R.; Srivastava, D.; Brinkman, T.M.; Armstrong, G.T.; Bhakta, N.; Robison, L.L.; Ehrhardt, M.J.; et al. Severe Sepsis During Treatment for Childhood Leukemia and Sequelae Among Adult Survivors. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e242727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inaba, H.; Pei, D.; Wolf, J.; Howard, S.C.; Hayden, R.T.; Go, M.; Varechtchouk, O.; Hahn, T.; Buaboonnam, J.; Metzger, M.L.; et al. Infection-related complications during treatment for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.P.; Bate, J.; Brooks, R.; Chisholm, J.; Clarke, S.C.; Dixon, E.; Faust, S.N.; Galanopoulou, A.; Heath, P.T.; Maishman, T.; et al. Immune reconstitution in children following chemotherapy for acute leukemia. EJHaem 2020, 1, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weischendorff, S.; Rathe, M.; Petersen, M.J.; Weimann, A.; Enevold, C.; Nielsen, C.H.; Als-Nielsen, B.; Nygaard, U.; Moser, C.; Müller, K. Markers of intestinal mucositis to predict blood stream infections at the onset of fever during treatment for childhood acute leukemia. Leukemia 2024, 38, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.L.; Guan, X.M.; Wen, X.H.; Shen, Y.L.; Xiao, J.W.; Guo, Y.X.; Deng, M.Y.; Yu, J. Serious adverse events associated with chemotherapy in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 2020, 22, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, G.; Jiang, L.; Fang-fang, L.; Ming-li, X. Etiologic characteristics and risk factors of sepsis in children with acute leukemia during chemotherapy. Chin. J. Infect. Control. 2023, 22, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.P.; Cheng, Y.C.; Chen, C.; Xue, H.M.; Yang, M.; Lin, C. Identification of the Shared Gene Signatures of HCK, NOG, RNF125 and Biological Mechanism in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia and Pediatric Sepsis. Mol. Biotechnol. 2025, 67, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.R.; Cvijanovich, N.; Allen, G.L.; Lin, R.; Anas, N.; Meyer, K.; Freishtat, R.J.; Monaco, M.; Odoms, K.; Sakthivel, B.; et al. Genomic expression profiling across the pediatric systemic inflammatory response syndrome, sepsis, and septic shock spectrum. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, 1558–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herberg, J.A.; Kaforou, M.; Wright, V.J.; Shailes, H.; Eleftherohorinou, H.; Hoggart, C.J.; Cebey-López, M.; Carter, M.J.; Janes, V.A.; Gormley, S.; et al. Diagnostic Test Accuracy of a 2-Transcript Host RNA Signature for Discriminating Bacterial vs Viral Infection in Febrile Children. JAMA 2016, 316, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, L.E.; Meyer, J.A.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Wong, N.; Yang, W.; Condos, G.; Hunger, S.P.; Raetz, E.; Saffery, R.; et al. Integrated genomic analysis of relapsed childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia reveals therapeutic strategies. Blood 2011, 118, 5218–5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, P.M.; Reitsma, J.B.; Bruns, D.E.; Gatsonis, C.A.; Glasziou, P.P.; Irwig, L.; Lijmer, J.G.; Moher, D.; Rennie, D.; de Vet, H.C.; et al. STARD 2015: An updated list of essential items for reporting diagnostic accuracy studies. BMJ 2015, 351, h5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, P. FOXF1 Was Identified as a Novel Biomarker of Infantile Hemangioma by Weighted Coexpression Network Analysis and Differential Gene Expression Analysis. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2022, 2022, 8981078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Ebert, T.; Kreher, D.; Ernst, B.L.V.; de Fallois, J.; Schmalz, G. The Genetic Cross-Talk between Periodontitis and Chronic Kidney Failure Revealed by Transcriptomic Analysis. Genes 2023, 14, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Qiu, X.; Huang, J.; Zhuo, Z.; Chen, H.; Zeng, R.; Wu, H.; Guo, K.; Yang, Q.; Ye, H.; et al. Development and validation of a novel mitophagy-related gene prognostic signature for glioblastoma multiforme. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigden, D.J.; Fernández, X.M. The 2021 Nucleic Acids Research database issue and the online molecular biology database collection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1–D9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhu, H. Identification of molecular signatures in epicardial adipose tissue in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. ESC Heart Fail. 2024, 11, 2510–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatya, N.; Garg, A.V.; Gaffen, S.L. IL-17 Signaling: The Yin and the Yang. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yuan, S.; Zheng, K.; Liu, G.; Li, J.; Ye, B.; Yin, L.; Li, Y. IL-17 signaling pathway: A potential therapeutic target for reducing skeletal muscle inflammation. Cytokine 2024, 181, 156691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, G.; Cheng, M.; Ding, X.; Wang, K. Single-cell transcriptional gene signature analysis identifies IL-17 signaling pathway as the key pathway in sepsis. Immunobiology 2023, 228, 152763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, L.; Wu, J.; Ye, A.; Wu, J.; Yu, K.; Zhang, S.; Han, Y. Increased Th17 cells and IL-17A exist in patients with B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and promote proliferation and resistance to daunorubicin through activation of Akt signaling. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, K.P.; Marwaha, R.K. Mortality pattern in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia with sepsis as a major barrier. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2012, 34, 264–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Flores, J.; Espinoza-Zamora, R.; Garcia-Mendez, J.; Cervera-Ceballos, E.; Sosa-Espinoza, A.; Zapata-Canto, N. Treatment-Related Mortality From Infectious Complications in an Acute Leukemia Clinic. J. Hematol. 2020, 9, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mar, B.G.; Bullinger, L.B.; McLean, K.M.; Grauman, P.V.; Harris, M.H.; Stevenson, K.; Neuberg, D.S.; Sinha, A.U.; Sallan, S.E.; Silverman, L.B.; et al. Mutations in epigenetic regulators including SETD2 are gained during relapse in paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perner, A.; Gordon, A.C.; De Backer, D.; Dimopoulos, G.; Russell, J.A.; Lipman, J.; Jensen, J.U.; Myburgh, J.; Singer, M.; Bellomo, R.; et al. Sepsis: Frontiers in diagnosis, resuscitation and antibiotic therapy. Intensive Care Med. 2016, 42, 1958–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGeachy, M.J.; Cua, D.J.; Gaffen, S.L. The IL-17 Family of Cytokines in Health and Disease. Immunity 2019, 50, 892–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Y.; Long, J.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, Y. lncRNA IL-17RA-1 Attenuates LPS-Induced Sepsis via miR-7847-3p/PRKCG-Mediated MAPK Signaling Pathway. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 9923204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.R.; Smagul, A.; Simpson, D.; Clegg, P.D.; Rubio-Martinez, L.M.; Peffers, M.J. The synovial fluid proteome differentiates between septic and nonseptic articular pathologies. J. Proteom. 2019, 202, 103370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Hu, X.; Long, K.; Gao, C.; Dong, H.L.; Zhong, Q.; Gao, X.M.; Gong, F.Y. Extraordinarily potent proinflammatory properties of lactoferrin-containing immunocomplexes against human monocytes and macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, E.M.; Tang, Y.; Liao, C.; Lin, S.; Shen, H.; Wang, D.; Xu, L.; Zhang, P.; Song, H.; Xu, X.; et al. Multi-courses of blinatumomab combined with reduced dose chemotherapy has been successfully used in chemo-intolerant middle to high-risk pediatric B-ALL patients with invasive fungal disease. Ann. Hematol. 2025, 104, 3495–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruzel, M.L.; Zimecki, M.; Actor, J.K. Lactoferrin in a Context of Inflammation-Induced Pathology. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, T.; Crawford, J.C.; Hahn, G.; Hall, M.W.; Thair, S.A.; Newhams, M.M.; Chou, J.; Mourani, P.M.; Tarquinio, K.M.; Markovitz, B.; et al. Transcriptomic profiles of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome phenotypes in pediatric critical influenza. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1220028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Kim, W.J. The Role of Matrix Metalloproteinase in Inflammation with a Focus on Infectious Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.C.; Lin, C.C.; Jou, M.J.; Hsiao, L.D.; Yang, C.M. RTA 408 Inhibits Interleukin-1β-Induced MMP-9 Expression via Suppressing Protein Kinase-Dependent NF-κB and AP-1 Activation in Rat Brain Astrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, K.; Du, G.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Li, L.; Liu, W.; Wu, R. MMP-9 secreted by M2-type macrophages promotes Wilms’ tumour metastasis through the PI3K/AKT pathway. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 3469–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.; Chen, M.; Chen, X.; Li, D.; Zhang, P.; Yu, D. Screening and identification of the core immune-related genes and immune cell infiltration in severe burns and sepsis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2023, 27, 1493–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandooren, J.; Swinnen, W.; Ugarte-Berzal, E.; Boon, L.; Dorst, D.; Martens, E.; Opdenakker, G. Endotoxemia shifts neutrophils with TIMP-free gelatinase B/MMP-9 from bone marrow to the periphery and induces systematic upregulation of TIMP-1. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1671–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ung, T.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Sah, D.K.; Park, S.Y.; Jung, Y.D. Cholic Acid Stimulates MMP-9 in Human Colon Cancer Cells via Activation of MAPK, AP-1, and NF-κB Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sadi, R.; Engers, J.; Haque, M.; King, S.; Al-Omari, D.; Ma, T.Y. Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) induced disruption of intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier is mediated by NF-κB activation. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, D.; Zanetti, C.; Godavarthy, P.S.; Kumar, R.; Minciacchi, V.R.; Pfeiffer, J.; Metzler, M.; Lefort, S.; Maguer-Satta, V.; Nicolini, F.E.; et al. Bone marrow niche-derived extracellular matrix-degrading enzymes influence the progression of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1540–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; Costa, O.; Legrand, E.; Bigot, D.; Lecleire, S.; Grassi, V.; Vannier, J.P.; Vasse, M. In vitro secretion of matrix metalloprotease 9 is a prognostic marker in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2010, 34, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.D.; Wang, H.W.; Cai, X.J. Transcription factor Sp1 ameliorates sepsis-induced myocardial injury via ZFAS1/Notch signaling in H9C2 cells. Cytokine 2021, 140, 155426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safe, S.; Kasiappan, R. Natural Products as Mechanism-based Anticancer Agents: Sp Transcription Factors as Targets. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Cai, Y.H.; Liu, Q.; Pan, L.L.; Shi, S.L.; Liu, X.L.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.G.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; et al. ETS1 and SP1 drive DHX15 expression in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 2612–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Wang, Q.; Sun, D.; Suo, J. Curcumin suppresses colon cancer cell invasion via AMPK-induced inhibition of NF-κB, uPA activator and MMP9. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 4139–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Entezari, M.; Tayari, A.; Paskeh, M.D.A.; Kheirabad, S.K.; Naeemi, S.; Taheriazam, A.; Dehghani, H.; Salimimoghadam, S.; Hashemi, M.; Mirzaei, S.; et al. Curcumin in treatment of hematological cancers: Promises and challenges. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2024, 14, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.H.; Chiou, S.S.; Weng, J.P.; Lin, P.C. Curcumin and tetrahydrocurcumin induce cell death in Ara-C-resistant acute myeloid leukemia. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.Y.; Zhang, J.H.; Xie, Z.L.; Deng, H.; Huang, Y.F.; Huang, X.H. Apoptosis of mouse myeloma cells induced by curcumin via the Notch3-p53 signaling axis. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiang, J.; Zhu, N.; Ge, H.; Sheng, X.; Deng, S.; Chen, J.; Yu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, J. Curcumin in Combination With Omacetaxine Suppress Lymphoma Cell Growth, Migration, Invasion, and Angiogenesis via Inhibition of VEGF/Akt Signaling Pathway. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 656045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, K.; Paliwal, S.; Sharma, S. Therapeutic potential of reserpine in metabolic syndrome: An evidence based study. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 186, 106531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlings, S.J.; Kalman, D.S. Curcumin: A Review of Its Effects on Human Health. Foods 2017, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Anker, J.; Reed, M.D.; Allegaert, K.; Kearns, G.L. Developmental Changes in Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 58 (Suppl. S10), S10–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, H.K.; Marriott, J.F. Paediatric pharmacokinetics: Key considerations. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 79, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, K.; Li, Z. Identification and analysis of type 2 diabetes-mellitus-associated autophagy-related genes. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1164112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; He, K.; Du, H.; Wei, G.; Wen, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J. Bioinformatics prediction and experimental verification of key biomarkers for diabetic kidney disease based on transcriptome sequencing in mice. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|
| LTF-F | 5′-ATGGTGGTTTCATATACGAGGCA-3′ |
| LTF-R | 5′-CTTTCGGTCCCGTAGACTTCC-3′ |
| MMP9-F | 5′-TGTACCGCTATGGTTACACTCG-3′ |
| MMP9-R | 5′-GGCAGGGACAGTTGCTTCT-3 |
| GAPDH-F | 5′-GGAGTCCACTGGCGTCTTCA-3′ |
| GAPDH-R | 5′-GTCATGAGTCCTTCCACGATACC-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Y.-P.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Chen, C.; Xue, H.-M.; Yang, M.; Lin, C. Key Common Genes with LTF and MMP9 Between Sepsis and Relapsed B-Cell Lineage Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092307
Xiao Y-P, Cheng Y-C, Chen C, Xue H-M, Yang M, Lin C. Key Common Genes with LTF and MMP9 Between Sepsis and Relapsed B-Cell Lineage Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(9):2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092307
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Ying-Ping, Yu-Cai Cheng, Chun Chen, Hong-Man Xue, Mo Yang, and Chao Lin. 2025. "Key Common Genes with LTF and MMP9 Between Sepsis and Relapsed B-Cell Lineage Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children" Biomedicines 13, no. 9: 2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092307
APA StyleXiao, Y.-P., Cheng, Y.-C., Chen, C., Xue, H.-M., Yang, M., & Lin, C. (2025). Key Common Genes with LTF and MMP9 Between Sepsis and Relapsed B-Cell Lineage Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children. Biomedicines, 13(9), 2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092307







