Exploratory Insights into Gastric Cancer Metabolism Through Amino Acid and Acylcarnitine Profiling in Plasma Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Characteristics and Sample Collection
2.2. Analysis of Amino Acids and Acylcarnitines
2.3. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
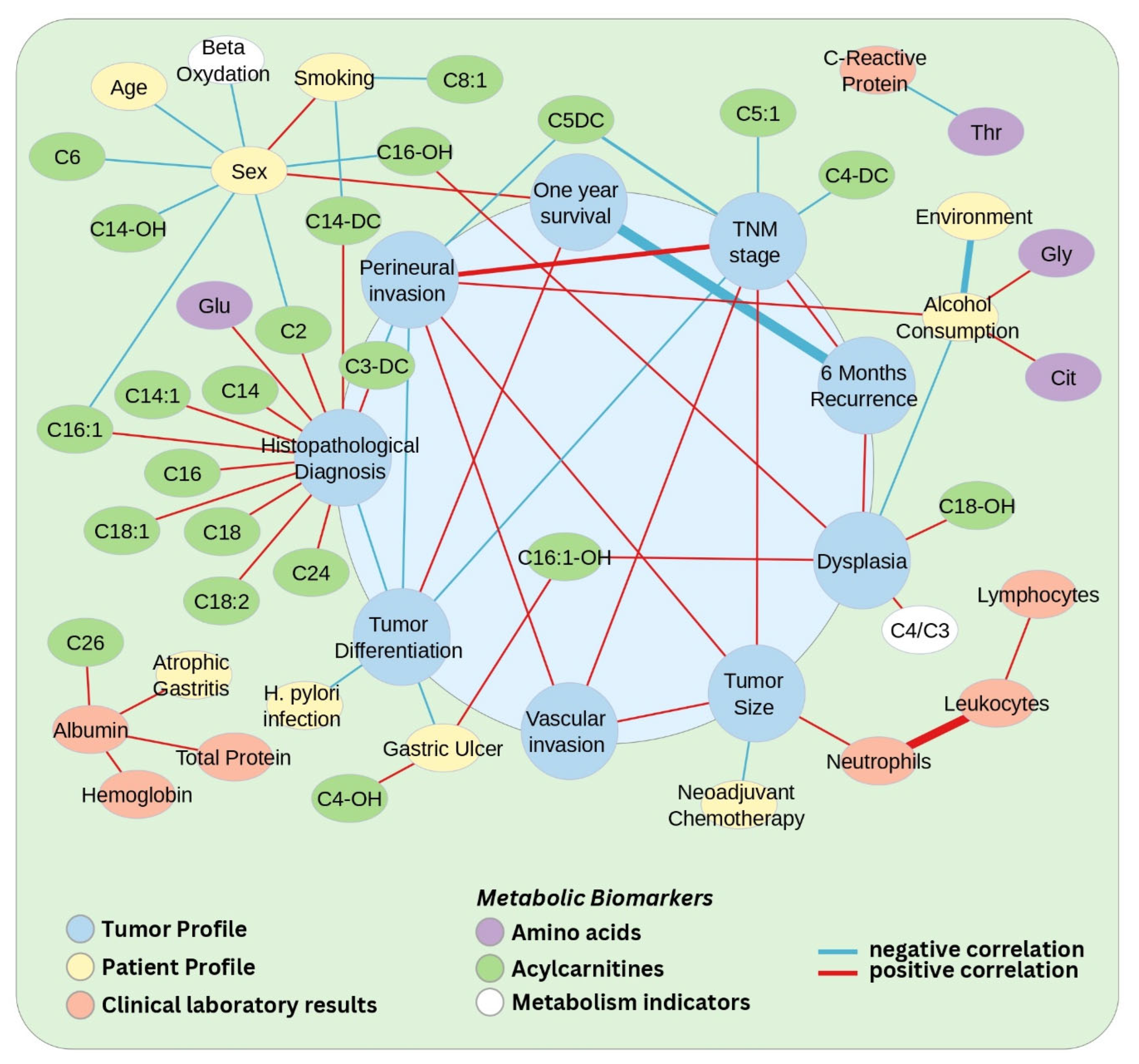
3.1. Correlations Between Clinicopathological Data and Metabolites
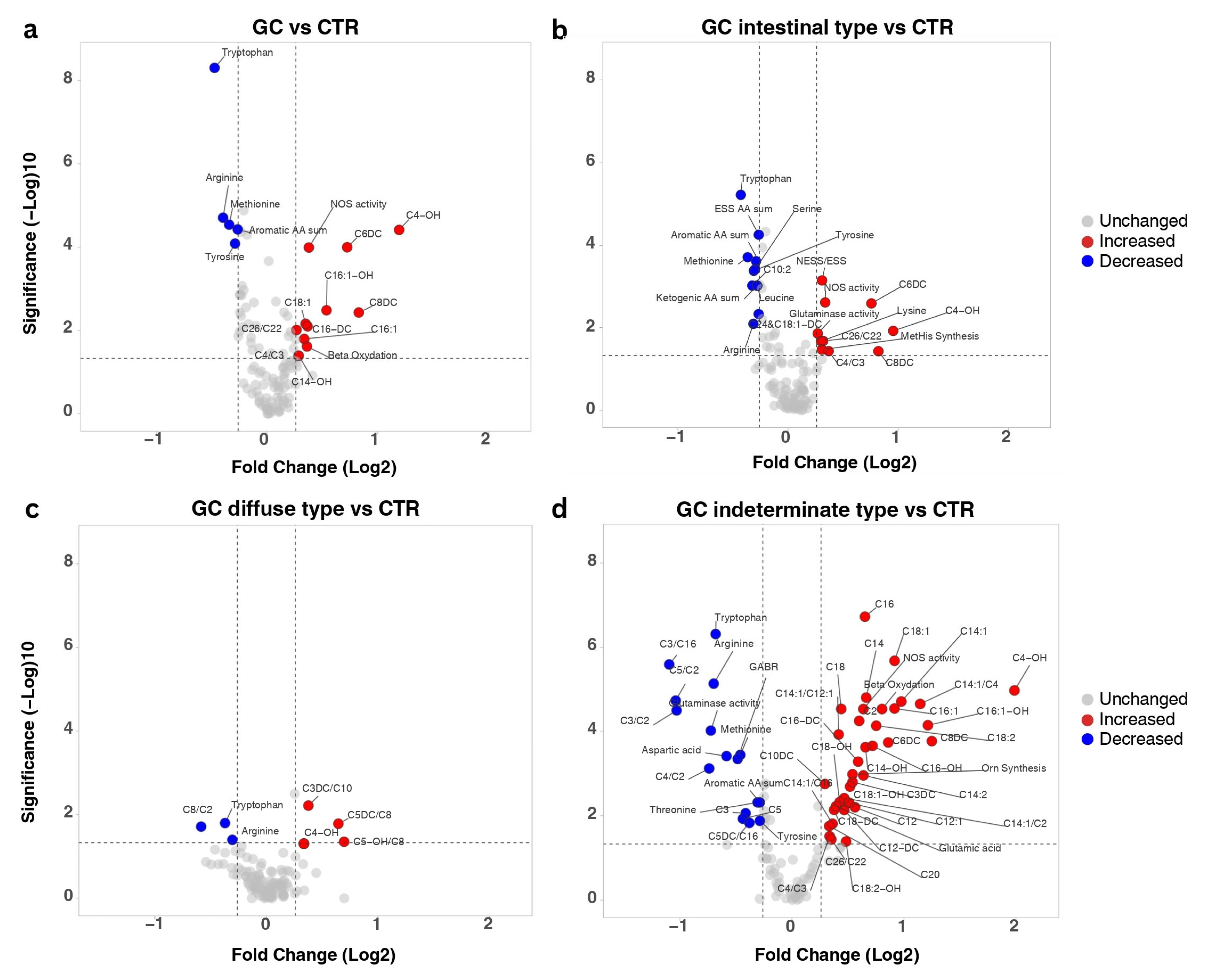
3.2. Metabolic Alterations Induced by Gastric Cancer
3.3. Metabolites Linked to GC Recurrence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurén, P. The Two Histological Main Types of Gastric Carcinoma: Diffuse and so-Called Intestinal-Type Carcinoma. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. 1965, 64, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Shen, H.; Kapesa, L.; Zeng, S. Lauren Classification and Individualized Chemotherapy in Gastric Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 2959–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; El Hajj, N.; Sittler, S.; Lammert, N.; Barnes, R.; Meloni-Ehrig, A. Gastric Cancer: Classification, Histology and Application of Molecular Pathology. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2012, 3, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.W.; Gill, R.S.; Schiller, D.; Sawyer, M.B. Potential Role of Metabolomics in Diagnosis and Surveillance of Gastric Cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 12874–12882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, P.; Ma, J.; Xu, J.; Yang, L.; Xu, W.; Que, H.; Chen, M.; Xu, H. Serum Biomarker Panels for the Diagnosis of Gastric Cancer. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 1576–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Guo, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, T.; You, W.; Pan, K.; Li, W. A Systematic Review of Metabolomic Profiling of Gastric Cancer and Esophageal Cancer. Cancer Biol. Med. 2020, 17, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.H.; Coloff, J.L. The Diverse Functions of Non-Essential Amino Acids in Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gao, D.; Jiang, Y. Function, Detection and Alteration of Acylcarnitine Metabolism in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Metabolites 2019, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lario, S.; Ramírez-Lázaro, M.J.; Sanjuan-Herráez, D.; Brunet-Vega, A.; Pericay, C.; Gombau, L.; Junquera, F.; Quintás, G.; Calvet, X. Plasma Sample Based Analysis of Gastric Cancer Progression Using Targeted Metabolomics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, F.; Yan, L.; Yang, X.; Wei, L.; Yang, X.; Yuan, X.; Yang, K. Targeted Metabolomic Profiles of Serum Amino Acids and Acylcarnitines Related to Gastric Cancer. PeerJ 2022, 10, e14115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, F.; Hu, X.; Cao, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, Y.; Jing, Y.; Hu, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, Z. Discriminating Gastric Cancer and Gastric Ulcer Using Human Plasma Amino Acid Metabolic Profile. IUBMB Life 2018, 70, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagi, Y.; Higashiyama, M.; Gochi, A.; Akaike, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Miura, T.; Saruki, N.; Bando, E.; Kimura, H.; Imamura, F.; et al. Plasma Free Amino Acid Profiling of Five Types of Cancer Patients and Its Application for Early Detection. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Tao, Q.; Qiao, X.; Yang, Y.; Peng, C.; Han, M.; Dong, K.; Zhang, W.; Xu, M.; Wang, D.; et al. Targeting Amino Acid Metabolism to Inhibit Gastric Cancer Progression and Promote Anti-Tumor Immunity: A Review. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1508730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.; Lee, Y. Genome-Scale Metabolic Model Analysis of Metabolic Differences between Lauren Diffuse and Intestinal Subtypes in Gastric Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avram, L.; Crișan, D.; Moldovan, R.-C.; Bogos, L.-G.; Iuga, C.-A.; Andraș, D.; Crișan, S.; Bodolea, C.; Nemeş, A.; Donca, V. Metabolomic Exploration of Colorectal Cancer Through Amino Acids and Acylcarnitines Profiling of Serum Samples. Cancers 2025, 17, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, M.; Labarthe, F.; Fortier, A.; Bouchard, B.; Legault, J.T.; Bolduc, V.; Rigal, O.; Chen, J.; Ducharme, A.; Crawford, P.A.; et al. Circulating Acylcarnitine Profile in Human Heart Failure: A Surrogate of Fatty Acid Metabolic Dysregulation in Mitochondria and Beyond. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2017, 313, 768–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Feng, X.F.; Huang, T.; Luo, H.H.; Chen, J.X.; Zeng, J.; Gu, M.; Li, J.; Sun, X.Y.; Sun, D.; et al. The Association Between Acylcarnitine Metabolites and Cardiovascular Disease in Chinese Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L.; Han, X.; Ji, L. Human Serum Acylcarnitine Profiles in Different Glucose Tolerance States. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 104, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ye, C.; Yao, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y. The Role of Serum Acylcarnitine Profiling for the Detection of Multiple Solid Tumors in Humans. Heliyon 2024, 10, e23867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhao, T.T.; Xu, H.M.; Wang, Z.N.; Xu, Y.Y.; Song, Y.X.; Ni, Z.R.; Xu, H.; Yin, S.C.; Liu, X.Y.; et al. Association between Alcohol Consumption and the Risk of Gastric Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 84459–84472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lin, J.; Chen, L.Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.J.; Guo, Z.Q.; Yu, J.M. Perineural Invasion and Postoperative Complications Are Independent Predictors of Early Recurrence and Survival Following Curative Resection of Gastric Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 7601–7610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhan, C.; Shi, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Metabolic Profiling Analysis upon Acylcarnitines in Tissues of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Revealed the Inhibited Carnitine Shuttle System Caused by the Downregulated Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase 2. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Martínez, R.; Cruz-Gil, S.; García-Álvarez, M.S.; Reglero, G.; De Molina, A.R. Complementary ACSL Isoforms Contribute to a Non-Warburg Advantageous Energetic Status Characterizing Invasive Colon Cancer Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambrova, M.; Makrecka-Kuka, M.; Kuka, J.; Vilskersts, R.; Nordberg, D.; Attwood, M.M.; Smesny, S.; Sen, Z.D.; Guo, A.C.; Oler, E.; et al. Acylcarnitines: Nomenclature, Biomarkers, Therapeutic Potential, Drug Targets, and Clinical Trials. Pharmacol. Rev. 2022, 74, 506–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klouwer, F.C.C.; Ferdinandusse, S.; van Lenthe, H.; Kulik, W.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Poll-The, B.T.; Waterham, H.R.; Vaz, F.M. Evaluation of C26:0-lysophosphatidylcholine and C26:0-carnitine as Diagnostic Markers for Zellweger Spectrum Disorders. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2017, 40, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, G.L.; Xu, F.; Jiang, K.; Wang, Y.M.; Ji, W.; Zhuang, Y.P. Evaluation of a Panel of Very Long-Chain Lysophosphatidylcholines and Acylcarnitines for Screening of X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy in China. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 503, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, K.; Ganesan, K. Occurrence of Differing Metabolic Dysregulations, a Glucose Driven and Another Fatty Acid Centric in Gastric Cancer Subtypes. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2020, 20, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierziak, J.; Burgberger, M.; Wojtasik, W. 3-Hydroxybutyrate As a Metabolite and a Signal Molecule Regulating Processes of Living Organisms. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Su, B.; Shan, Z.; Gao, Z.; Guo, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Sun, W.; Yuan, S.; Sun, S.; et al. Metabolic Reprogramming of Gastric Cancer Revealed by a Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Study. Metabolites 2025, 15, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimazu, T.; Hirschey, M.D.; Newman, J.; He, W.; Shirakawa, K.; Le Moan, N.; Grueter, C.A.; Lim, H.; Saunders, L.R.; Stevens, R.D.; et al. Suppression of Oxidative Stress by β-Hydroxybutyrate, an Endogenous Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor. Science 2013, 339, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youm, Y.H.; Nguyen, K.Y.; Grant, R.W.; Goldberg, E.L.; Bodogai, M.; Kim, D.; D’Agostino, D.; Planavsky, N.; Lupfer, C.; Kanneganti, T.D.; et al. The Ketone Metabolite β-Hydroxybutyrate Blocks NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Inflammatory Disease. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wangler, M.F.; Lesko, B.; Dahal, R.; Jangam, S.; Bhadane, P.; Wilson, T.E.; McPheron, M.; Miller, M.J. Dicarboxylic Acylcarnitine Biomarkers in Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2023, 140, 107680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Han, X.; Mancuso, D.J.; Abendschein, D.R.; Gross, R.W. Accumulation of Long-Chain Acylcarnitine and 3-Hydroxy Acylcarnitine Molecular Species in Diabetic Myocardium: Identification of Alterations in Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Processing in Diabetic Myocardium by Shotgun Lipidomics. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 5234–5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, D.A.; Han, X.; Horner, C.C.; Gross, R.W. Accumulation of Unsaturated Acylcarnitine Molecular Species during Acute Myocardial Ischemia: Metabolic Compartmentalization of Products of Fatty Acyl Chain Elongation in the Acylcarnitine Pool. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 7903–7909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, S.C.; St Louis, J.D.; Lowe, J.E.; Abdel-aleem, S. Free Fatty Acid Metabolism during Myocardial Ischemia and Reperfusion. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1997, 166, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.P.; Zhang, C.D.; Yusupu, M.; Zhang, C.; Dai, D.Q. Screening and Validation of the Hypoxia-Related Signature of Evaluating Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Predicting Prognosis in Gastric Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 705511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Lu, J.; Du, W. Tryptophan Metabolism in Digestive System Tumors: Unraveling the Pathways and Implications. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarz-Misa, I.; Fleszar, M.G.; Fortuna, P.; Lewandowski, Ł.; Mierzchała-Pasierb, M.; Diakowska, D.; Krzystek-Korpacka, M. Altered L-Arginine Metabolic Pathways in Gastric Cancer: Potential Therapeutic Targets and Biomarkers. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Han, J. Arginine Metabolism and Its Potential in Treatment of Colorectal Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 658861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanderson, S.M.; Gao, X.; Dai, Z.; Locasale, J.W. Methionine Metabolism in Health and Cancer: A Nexus of Diet and Precision Medicine. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livneh, I.; Cohen-Kaplan, V.; Fabre, B.; Abramovitch, I.; Lulu, C.; Nataraj, N.B.; Lazar, I.; Ziv, T.; Yarden, Y.; Zohar, Y.; et al. Regulation of Nucleo-Cytosolic 26S Proteasome Translocation by Aromatic Amino Acids via MTOR Is Essential for Cell Survival under Stress. Mol. Cell 2023, 83, 3333–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livneh, I.; Fabre, B.; Goldhirsh, G.; Lulu, C.; Zinger, A.; Shammai Vainer, Y.; Kaduri, M.; Dahan, A.; Ziv, T.; Schroeder, A.; et al. Inhibition of Nucleo-Cytoplasmic Proteasome Translocation by the Aromatic Amino Acids or Silencing Sestrin3—Their Sensing Mediator—Is Tumor Suppressive. Cell Death Differ. 2024, 31, 1242–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieu, E.L.; Nguyen, T.; Rhyne, S.; Kim, J. Amino Acids in Cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, D.; Yang, P.; Chen, S.; Zhao, C.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, C.; Zhong, S.; et al. Tryptophan Metabolites as Biomarkers for Esophageal Cancer Susceptibility, Metastasis, and Prognosis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 800291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotti, S.; D’Angelo, E.; Bedin, C.; Fassan, M.; Pucciarelli, S.; Nitti, D.; Bertazzo, A.; Agostini, M. Tryptophan Metabolism along the Kynurenine and Serotonin Pathways Reveals Substantial Differences in Colon and Rectal Cancer. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, N.; Gunter, M.J.; Murphy, N.; Gicquiau, A.; Achaintre, D.; Brezina, S.; Gumpenberger, T.; Baierl, A.; Ose, J.; Geijsen, A.J.M.R.; et al. Circulating Tryptophan Metabolites and Risk of Colon Cancer: Results from Case-control and Prospective Cohort Studies. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 1659–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munn, D.H.; Mellor, A.L. IDO in the Tumor Microenvironment: Inflammation, Counter-Regulation, and Tolerance. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Zhang, A.H.; Miao, J.H.; Sun, H.; Yan, G.L.; Wu, F.F.; Wang, X.J. Targeting Regulation of Tryptophan Metabolism for Colorectal Cancer Therapy: A Systematic Review. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 3072–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhanam, S.; Alvarado, D.M.; Ciorba, M.A. Therapeutic Targeting of Inflammation and Tryptophan Metabolism in Colon and Gastrointestinal Cancer. Transl. Res. 2016, 167, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larussa, T.; Leone, I.; Suraci, E.; Nazionale, I.; Procopio, T.; Conforti, F.; Abenavoli, L.; Hribal, M.L.; Imeneo, M.; Luzza, F. Enhanced Expression of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase in Helicobacter pylori-Infected Human Gastric Mucosa Modulates Th1/Th2 Pathway and Interleukin 17 Production. Helicobacter 2015, 20, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Jing, Y.; Xu, M.H.; Zhu, Z.T.; Wang, Q.J. Abnormal Arginine Metabolism Is Associated with Prognosis in Patients of Gastric Cancer. Transl. Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 2451–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Y.S.; Hsu, H.P.; Lai, M.D.; Yen, M.C.; Chen, W.C.; Fang, J.H.; Weng, T.Y.; Chen, Y.L. Argininosuccinate Synthetase 1 Suppression and Arginine Restriction Inhibit Cell Migration in Gastric Cancer Cell Lines. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanthakumaran, S.; Brown, I.; Heys, S.D.; Schofield, A.C. Inhibition of Gastric Cancer Cell Growth by Arginine: Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 28, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.X.; Cheng, Q.M.; Fei, X.F.; Li, S.F.; Yin, H.R.; Lin, Y.Z. A Study of Preoperative Methionine-Depleting Parenteral Nutrition plus Chemotherapy in Gastric Cancer Patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 6, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graziosi, L.; Mencarelli, A.; Renga, B.; D’Amore, C.; Bruno, A.; Santorelli, C.; Cavazzoni, E.; Cantarella, F.; Rosati, E.; Donini, A.; et al. Epigenetic Modulation by Methionine Deficiency Attenuates the Potential for Gastric Cancer Cell Dissemination. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2013, 17, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Yue, Z.; Liu, J.; Fan, L.; Xu, H.; Xin, L. The Role of Methionine Restriction in Gastric Cancer: A Summary of Mechanisms and a Discussion on Tumor Heterogeneity. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Zhou, L.Q.; Liu, L.; Yuan, Y.W.; Zhang, H.T.; Zeng, F. METase Promotes Cell Autophagy via Promoting SNHG5 and Suppressing MiR-20a in Gastric Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 1046–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soom, T.; El Bakkali, S.; Gebruers, N.; Verbelen, H.; Tjalma, W.; van Breda, E. The Effects of Chemotherapy on Energy Metabolic Aspects in Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 1863–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchi, A.; Dell’Anna, G.; Massimino, L.; Mandarino, F.V.; Vespa, E.; Viale, E.; Passaretti, S.; Annese, V.; Malesci, A.; Danese, S.; et al. Unraveling the Pathogenesis of Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: The “Omics” Era. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1458138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Anna, G.; Mandarino, F.; Centanni, L.; Lodola, I.; Fanizza, J.; Fasulo, E.; Bencardino, S.; Fuccio, L.; Facciorusso, A.; Donatelli, G.; et al. Transforming Gastrointestinal Diagnosis with Molecular Endoscopy: Challenges and Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| GC Patients | CTR | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 62 | 70 | |
| Sex (% males) | 67.7 | 68.6 | |
| Median age (years) | 70 | 70 | |
| Percentiles—25 | 57.8 | 57.0 | |
| Percentiles—75 | 74.0 | 74.0 | |
| Associated pathologies | |||
| Gastric ulcer | 30 (48.4%) | - | |
| Atrophic gastritis | 42 (67.7%) | - | |
| Helicobacter pylori infection | 32 (51.6%) | - | |
| Lifestyle habits | |||
| Smoking | 35 (51.6%) | - | |
| Alcohol consumption | 15 (24.2%) | - | |
| GC TNM stages | |||
| I | 13 (21.0%) | - | |
| II | 16 (25.8%) | - | |
| III | 33 (53.2%) | - | |
| Tumour histology | |||
| Laurén classification | WHO classification | ||
| Intestinal type | Tubular adenocarcinoma | 34 (54.8%) | - |
| Diffuse type | Signet ring cell carcinoma | 6 (9.7%) | - |
| Poorly cohesive carcinoma | 7 (11.3%) | - | |
| Indeterminate type | Adenocarcinoma with mixed subtypes | 15 (24.2%) | - |
| GC differentiation | |||
| Poorly differentiated | 27 (43.5%) | - | |
| Moderately differentiated | 21 (33.9%) | - | |
| Well differentiated | 14 (22.6%) | - | |
| Treatment | |||
| Neoadjuvant chemotherapy | 35 (56.5%) | - | |
| Surgery | 62 (100%) | - | |
| 6-month tumour recurrence | 21 (33.9%) | - | |
| One-year survival | 50 (80.6%) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ursu, Ș.; Ursu, C.-P.; Bogos, L.-G.; Pralea, I.-E.; Moldovan, R.-C.; Zaharie, F.; Spârchez, Z.; Ciocan, R.A.; Pop, R.S.; Bodea, C.I.; et al. Exploratory Insights into Gastric Cancer Metabolism Through Amino Acid and Acylcarnitine Profiling in Plasma Samples. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2220. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092220
Ursu Ș, Ursu C-P, Bogos L-G, Pralea I-E, Moldovan R-C, Zaharie F, Spârchez Z, Ciocan RA, Pop RS, Bodea CI, et al. Exploratory Insights into Gastric Cancer Metabolism Through Amino Acid and Acylcarnitine Profiling in Plasma Samples. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(9):2220. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092220
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrsu, Ștefan, Cristina-Paula Ursu, Luisa-Gabriela Bogos, Ioana-Ecaterina Pralea, Radu-Cristian Moldovan, Florin Zaharie, Zeno Spârchez, Răzvan Alexandru Ciocan, Rodica Sorina Pop, Cătălin Ioan Bodea, and et al. 2025. "Exploratory Insights into Gastric Cancer Metabolism Through Amino Acid and Acylcarnitine Profiling in Plasma Samples" Biomedicines 13, no. 9: 2220. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092220
APA StyleUrsu, Ș., Ursu, C.-P., Bogos, L.-G., Pralea, I.-E., Moldovan, R.-C., Zaharie, F., Spârchez, Z., Ciocan, R. A., Pop, R. S., Bodea, C. I., Gherman, C. D., Iuga, C.-A., & Al Hajjar, N. (2025). Exploratory Insights into Gastric Cancer Metabolism Through Amino Acid and Acylcarnitine Profiling in Plasma Samples. Biomedicines, 13(9), 2220. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092220










