Physics-Informed Neural Network for Modeling the Pulmonary Artery Blood Pressure from Magnetic Resonance Images: A Reduced-Order Navier–Stokes Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
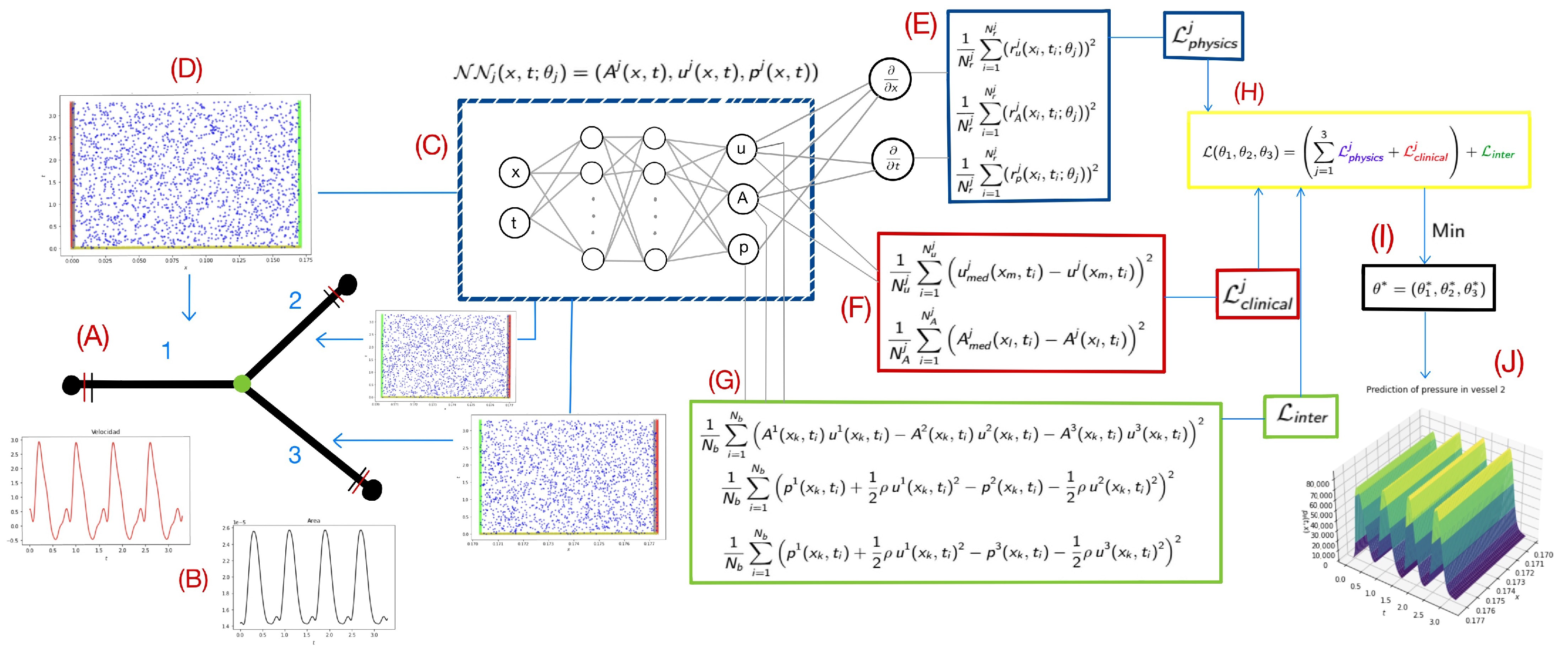
2.1. Reduced-Order Flow Model for the Pulmonary Artery
2.2. Physics-Informed Neural Networks
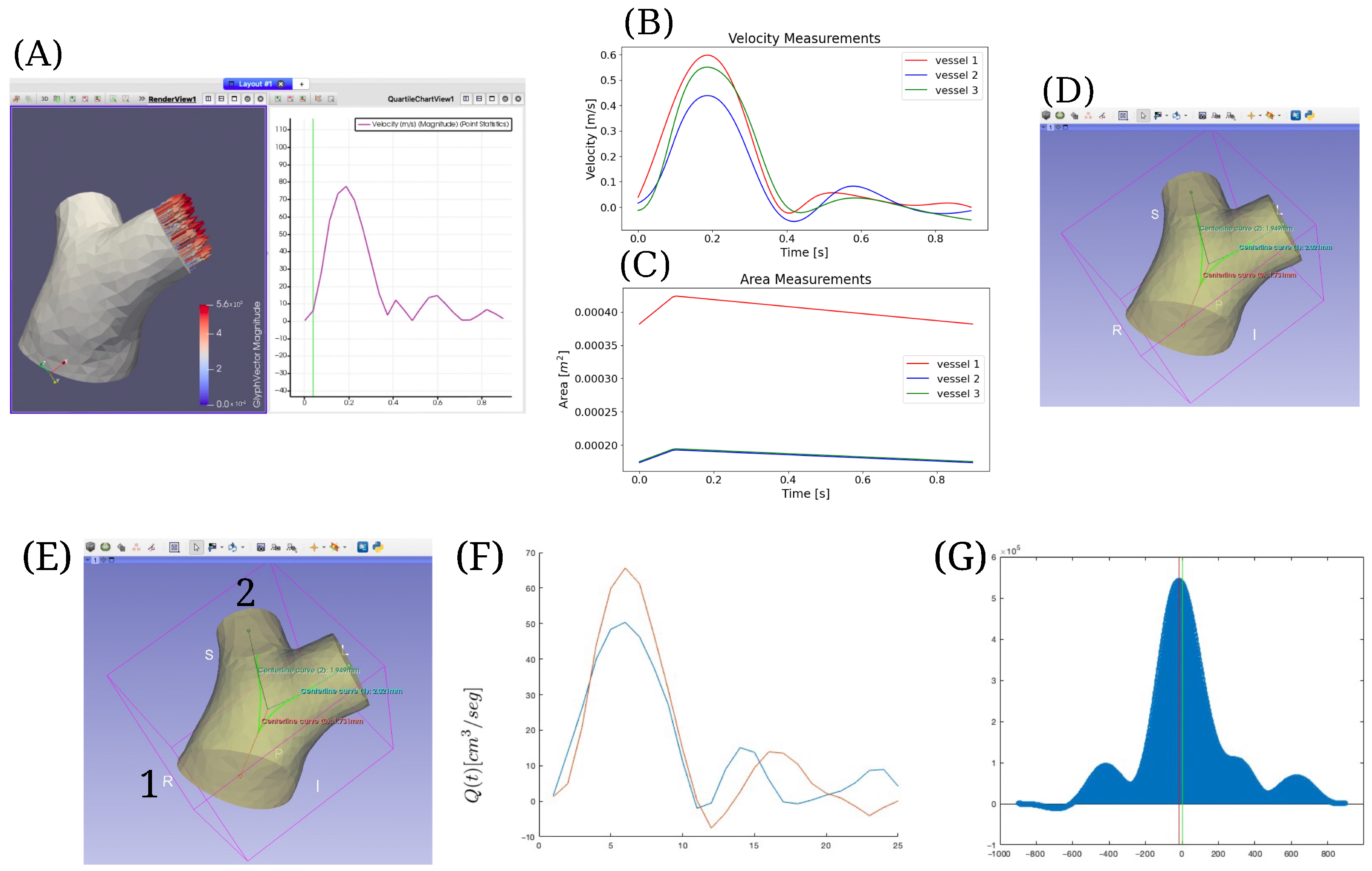
2.3. Implementation in a Clinical Case
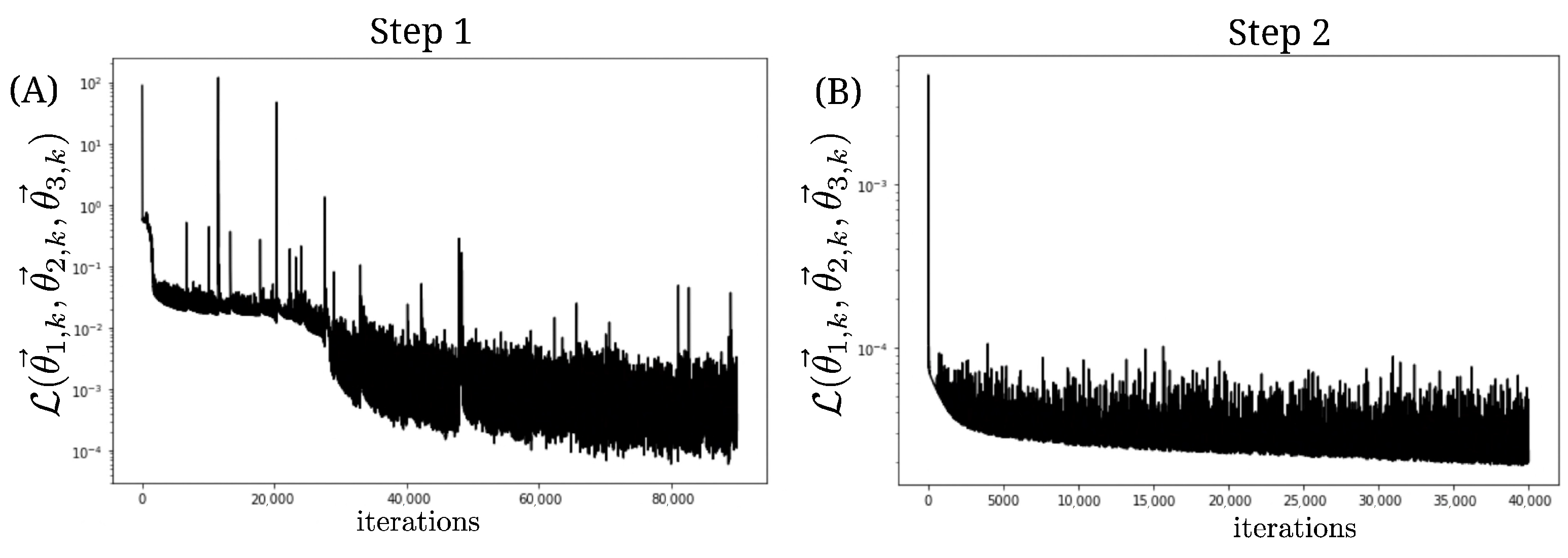
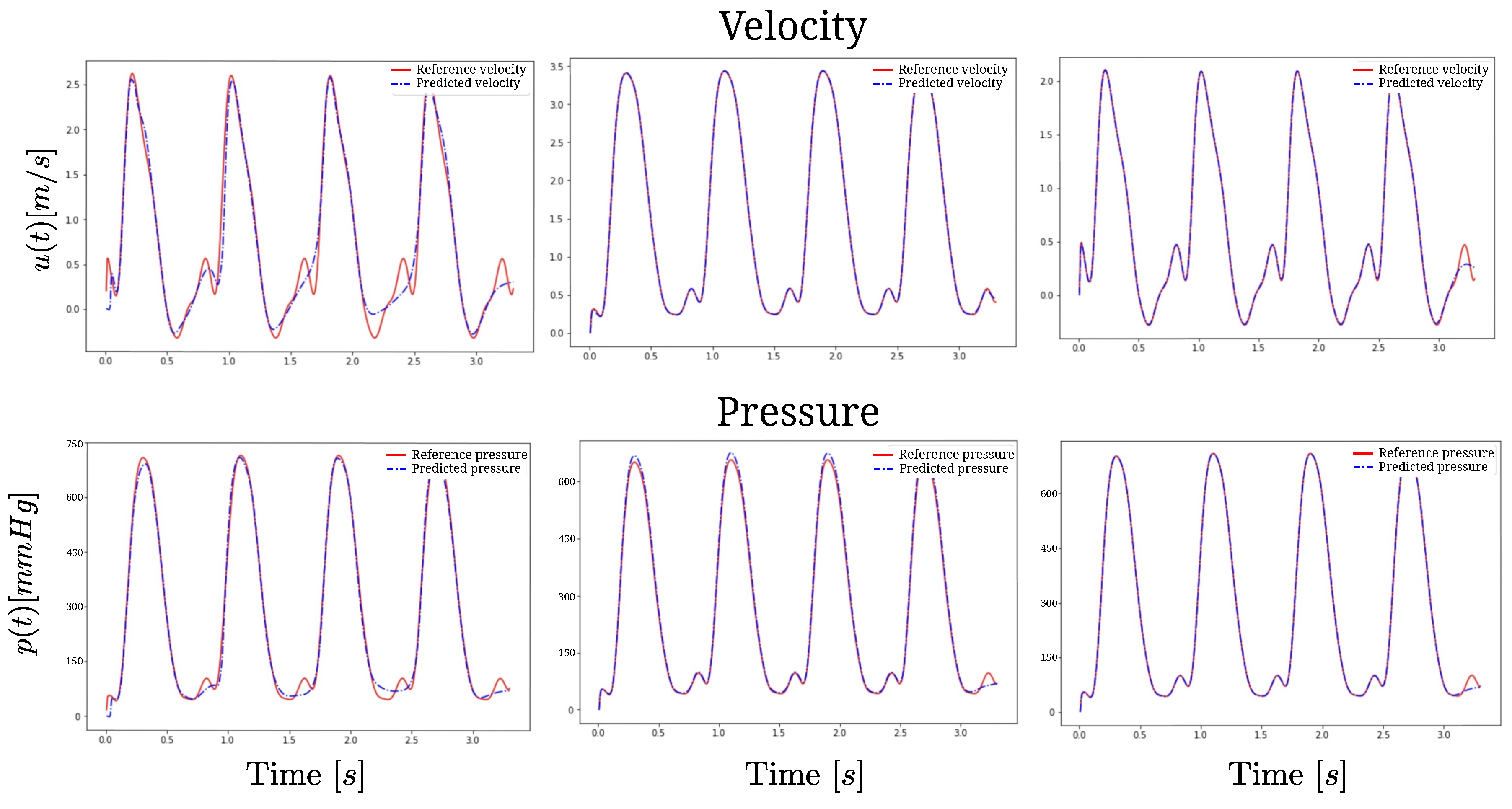
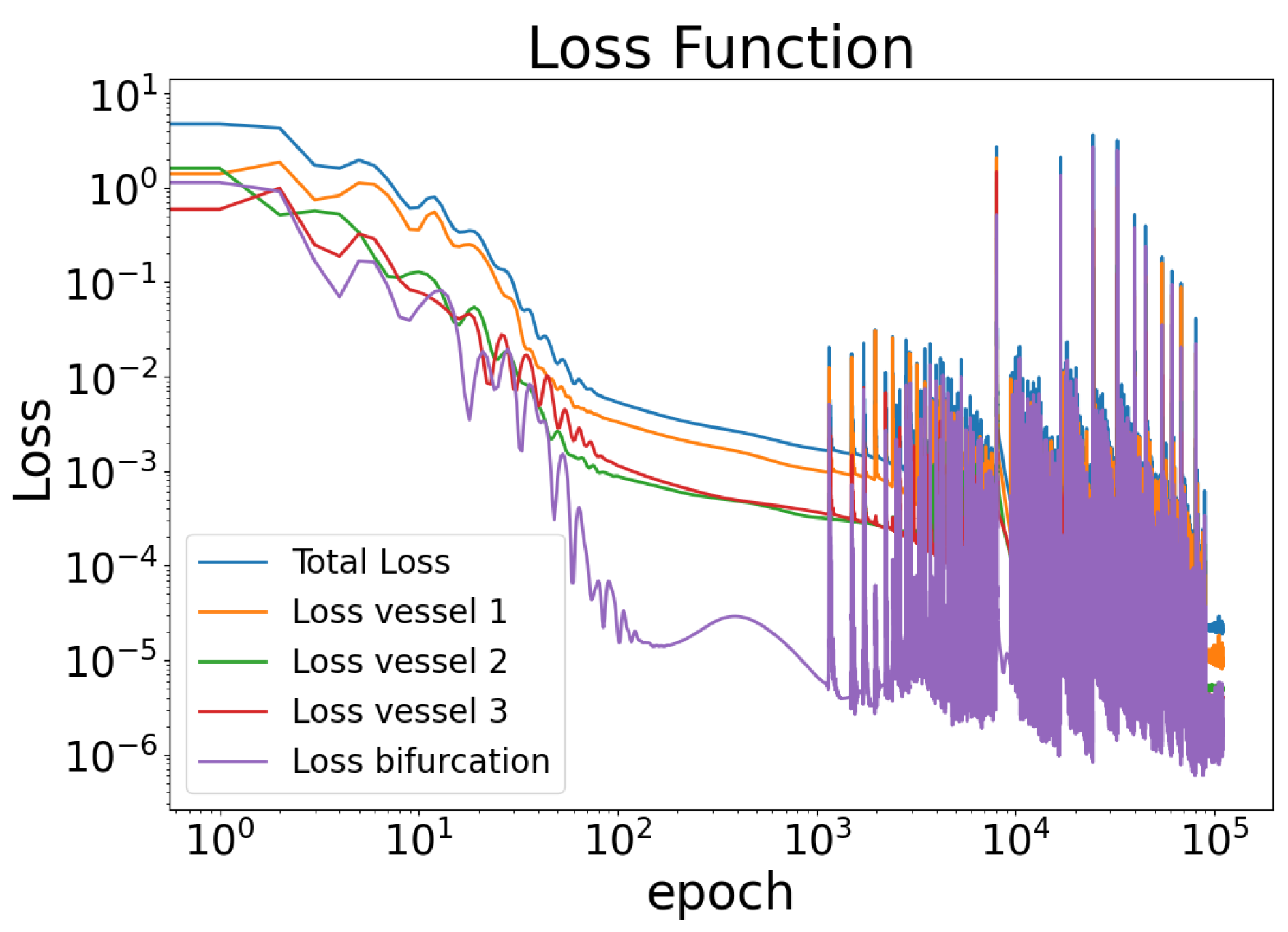
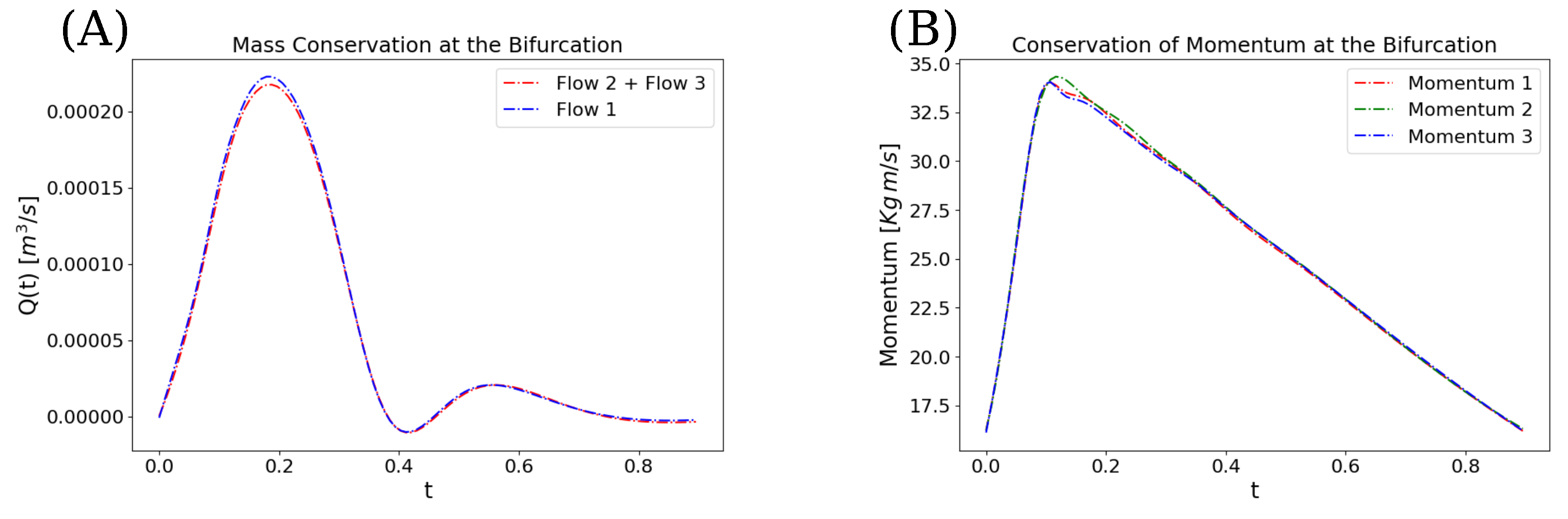
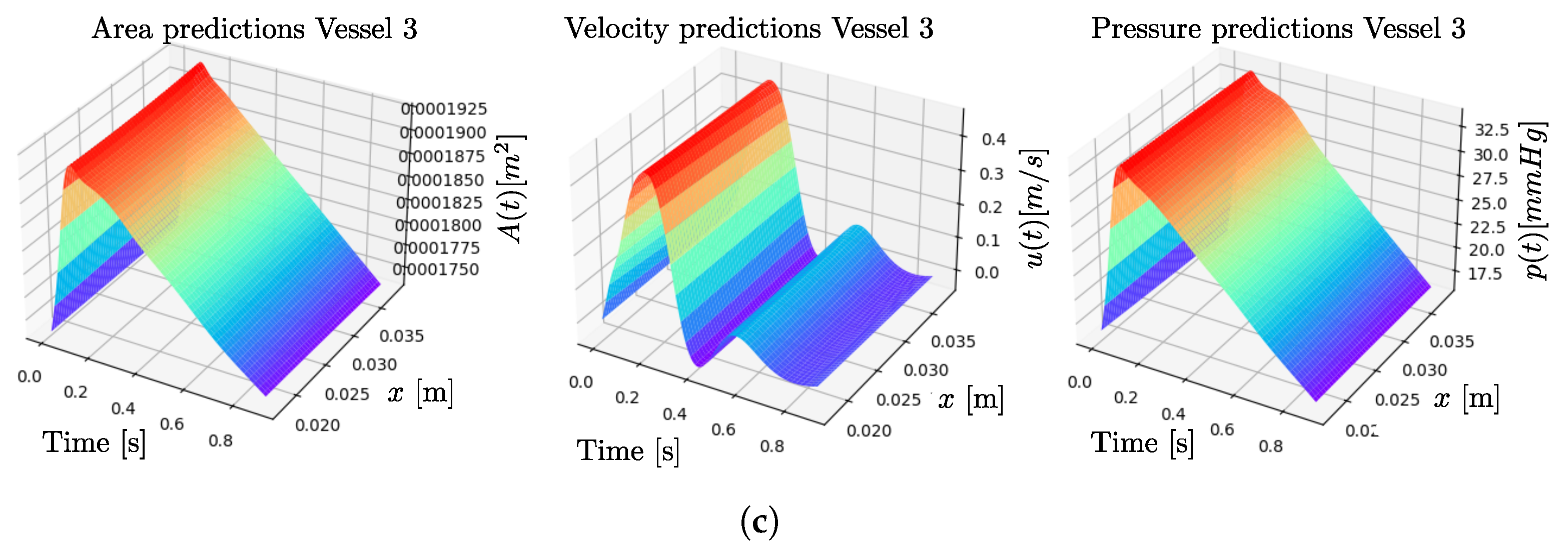
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PINNs | Physics-Informed Neural Networks |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Image |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| DG | Discontinuous Galerkin |
Appendix A. Variables Non-Dimensionalization and Normalization
Appendix B. Validation of the Model
| Artery Segment | Length (m) | (Pa/m) | Cross-Sectional Area at Equilibrium (m2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.1703 | ||
| 2 | 0.007 | ||
| 3 | 0.0067 |
| Artery 1 | Artery 2 | Artery 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
References
- Arthurs, C.J.; Xiao, N.; Moireau, P.; Schaeffter, T.; Figueroa, C.A. A flexible framework for sequential estimation of model parameters in computational hemodynamics. Adv. Model. Simul. Eng. Sci. 2020, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoglio, C.; Moireau, P.; Gerbeau, J.F. Sequential parameter estimation for fluid–structure problems: Application to hemodynamics. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2012, 28, 434–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagolín Blancaire, M. Sobrevida en hipertensión pulmonar. Rev. Méd. Chile 2016, 144, 827–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.M.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A.J.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: Developed by the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Endorsed by the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) and the European Reference Network on rare respiratory diseases (ERN-LUNG). Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3618–3731. [Google Scholar]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Grünig, E.; Klose, H.; Olschewski, H.; Rosenkranz, S. Pulmonary hypertension. Dtsch. Ärztebl. Int. 2017, 114, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.; Zurita, C.; Mellado, D.; Nicolis, O.; Saavedra, C.; Tuesta, M.; Salinas, M.; Bertini, A.; Pedemonte, O.; Querales, M.; et al. Predicting Cardiovascular Rehabilitation of Patients with Coronary Artery Disease Using Transfer Feature Learning. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, E.; Baptista, R.; Calisto, J.; Faria, H.; Monteiro, P.; Pan, M.; Pêgo, M. Optical coherence tomography of the pulmonary arteries: A systematic review. J. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raissi, M.; Perdikaris, P.; Karniadakis, G. Physics-informed neural networks: A deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 2019, 378, 686–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, S.; Salas, R.; Ñanculef, R.; Valverde, I.; Uribe, S.; Sotelo, J. Prediction of Peak-to-Peak Pressure Gradient in Patients with Aortic Coarctation Using Physics-Informed Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2024 L Latin American Computer Conference (CLEI), Buenos Aires, Argentina, 12–16 August 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Raissi, M.; Yazdani, A.; Karniadakis, G.E. Hidden fluid mechanics: Learning velocity and pressure fields from flow visualizations. Science 2020, 367, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karniadakis, G.; Kevrekidis, Y.; Lu, L.; Perdikaris, P.; Wang, S.; Yang, L. Physics-informed machine learning. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2021, 3, 422–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garay, J.; Dunstan, J.; Uribe, S.; Costabal, F.S. Physics-informed neural networks for parameter estimation in blood flow models. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 178, 108706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kissas, G.; Yang, Y.; Hwuang, E.; Witschey, W.R.; Detre, J.A.; Perdikaris, P. Machine learning in cardiovascular flows modeling: Predicting arterial blood pressure from non-invasive 4D flow MRI data using physics-informed neural networks. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2020, 358, 112623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabian, M.; Babaee, H.; Laksari, K. Physics-informed neural networks for improving cerebral hemodynamics predictions. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.11498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tai, X.C.; Chan, R.H.F. A new method to compute the blood flow equations using the physics-informed neural operator. J. Comput. Phys. 2024, 519, 113380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csala, H.; Mohan, A.; Livescu, D.; Arzani, A. Physics-constrained coupled neural differential equations for one dimensional blood flow modeling. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025, 186, 109644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Diao, X.; Huo, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Geng, J.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J.; Xi, Q.; Xia, Y.; Xu, O.; et al. Deep Learning-Enhanced Non-Invasive Detection of Pulmonary Hypertension and Subtypes via Chest Radiographs, Validated by Catheterization. Chest 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.Y.; Hsing, S.C.; Tsai, D.J.; Lin, C.; Lin, C.S.; Wang, C.H.; Fang, W.H. A deep-learning-enabled electrocardiogram and chest X-ray for detecting pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Imaging Inform. Med. 2024, 38, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.H.; Sun, X.; Elliot, C.; Condliffe, R.; Kiely, D.G.; Alabed, S.; Swift, A.J.; van der Geest, R.J.; Kiely, D.G.; Watson, L.; et al. Mean pulmonary artery pressure prediction with explainable multi-view cardiovascular magnetic resonance cine series deep learning model. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2025, 27, 101133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Huang, Z.; Diao, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Xia, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, Z.; Xi, Q.; Huo, Y.; et al. Development and validation of multimodal deep learning algorithms for detecting pulmonary hypertension. npj Digit. Med. 2025, 8, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, N.; Burton, T.; Fathieh, F.; Gillins, H.R.; Shadforth, I.; Ramchandani, S.; Bridges, C.R. Pulmonary Hypertension Detection Non-Invasively at Point-of-Care Using a Machine-Learned Algorithm. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olufsen, M.S.; Peskin, C.S.; Kim, W.Y.; Pedersen, E.M.; Nadim, A.; Larsen, J. Numerical simulation and experimental validation of blood flow in arteries with structured-tree outflow conditions. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 28, 1281–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Alastruey, J.; Alberto Figueroa, C. A systematic comparison between 1-D and 3-D hemodynamics in compliant arterial models. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2014, 30, 204–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Vosse, F.N.; Stergiopulos, N. Pulse wave propagation in the arterial tree. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2011, 43, 467–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinberg, L.; Cheever, E.; Anor, T.; Madsen, J.R.; Karniadakis, G. Modeling blood flow circulation in intracranial arterial networks: A comparative 3D/1D simulation study. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 39, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glorot, X.; Bengio, Y. Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Sardinia, Italy, 13–15 May 2010; JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings. pp. 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, M.; Barham, P.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; Ghemawat, S.; Irving, G.; Isard, M.; et al. TensorFlow: A system for Large-Scale machine learning. In Proceedings of the 12th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI 16), Savannah, GA, USA, 2–4 November 2016; pp. 265–283. [Google Scholar]
- Uribe, S.; Beerbaum, P.; Sørensen, T.S.; Rasmusson, A.; Razavi, R.; Schaeffter, T. Four-dimensional (4D) flow of the whole heart and great vessels using real-time respiratory self-gating. Magn. Reson. Med. 2009, 62, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotelo, J.; Mura, J.; Hurtado, D.; Uribe, S. A novel MATLAB toolbox for processing 4D Flow MRI data. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Meeting and Exhibition of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM), Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–16 May 2019; p. Abstract No. 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, W.W.; O’Rourke, M.; Edelman, E.R.; Vlachopoulos, C. McDonald’s Blood Flow in Arteries: Theoretical, Experimental and Clinical Principles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Antiga, L.; Piccinelli, M.; Botti, L.; Ene-Iordache, B.; Remuzzi, A.; Steinman, D.A. An image-based modeling framework for patient-specific computational hemodynamics. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2008, 46, 1097–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markl, M.; Wallis, W.; Brendecke, S.; Simon, J.; Frydrychowicz, A.; Harloff, A. Estimation of global aortic pulse wave velocity by flow-sensitive 4D MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 63, 1575–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olufsen, M.S.; Hill, N.; Vaughan, G.D.; Sainsbury, C.; Johnson, M. Rarefaction and blood pressure in systemic and pulmonary arteries. J. Fluid Mech. 2012, 705, 280–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. 1D Modeling of Blood Flow in Networks: Numerical Computing and Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris VI, Paris, France, 2014. English. NNT: 2014PA066626. Available online: https://theses.hal.science/tel-01149085v1/file/2014PA066626.pdf (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- Schäfer, M.; Barker, A.J.; Kheyfets, V.; Stenmark, K.R.; Crapo, J.; Yeager, M.E.; Truong, U.; Buckner, J.K.; Fenster, B.E.; Hunter, K.S. Helicity and vorticity of pulmonary arterial flow in patients with pulmonary hypertension: Quantitative analysis of flow formations. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e007010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, D.; Fredenburgh, L.E.; Tschumperlin, D.J. Measured pulmonary arterial tissue stiffness is highly sensitive to AFM indenter dimensions. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 74, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnapriyan, A.; Gholami, A.; Zhe, S.; Kirby, R.; Mahoney, M.W. Characterizing possible failure modes in physics-informed neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 26548–26560. [Google Scholar]

| Artery Segment | Length (m) | (Pa/m) | Cross-Sectional Area at Equil. (m2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.01763 | ||
| 2 | 0.01892 | ||
| 3 | 0.02024 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jara, S.; Sotelo, J.; Ortiz-Puerta, D.; Estévez, P.A.; Uribe, S.; Chabert, S.; Salas, R. Physics-Informed Neural Network for Modeling the Pulmonary Artery Blood Pressure from Magnetic Resonance Images: A Reduced-Order Navier–Stokes Model. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092058
Jara S, Sotelo J, Ortiz-Puerta D, Estévez PA, Uribe S, Chabert S, Salas R. Physics-Informed Neural Network for Modeling the Pulmonary Artery Blood Pressure from Magnetic Resonance Images: A Reduced-Order Navier–Stokes Model. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(9):2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092058
Chicago/Turabian StyleJara, Sebastián, Julio Sotelo, David Ortiz-Puerta, Pablo A. Estévez, Sergio Uribe, Steren Chabert, and Rodrigo Salas. 2025. "Physics-Informed Neural Network for Modeling the Pulmonary Artery Blood Pressure from Magnetic Resonance Images: A Reduced-Order Navier–Stokes Model" Biomedicines 13, no. 9: 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092058
APA StyleJara, S., Sotelo, J., Ortiz-Puerta, D., Estévez, P. A., Uribe, S., Chabert, S., & Salas, R. (2025). Physics-Informed Neural Network for Modeling the Pulmonary Artery Blood Pressure from Magnetic Resonance Images: A Reduced-Order Navier–Stokes Model. Biomedicines, 13(9), 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092058





