Raloxifene-Loaded Lipid Nanovesicles: A Journey to Select the Optimal Nanocarrier Formulation Through Characterization and Cytotoxic Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Media
2.2. Preparation of Raloxifene-Loaded Nanocarriers
2.2.1. Preparation of Self-Assembled Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles (LCNPs)
2.2.2. Preparation of Raloxifene-Loaded Nanoliposomes
2.2.3. Preparation of Raloxifene-Loaded Noisome
2.3. Particle Size and Polydispersity Index (Pdi) Determination
2.4. Zeta Potential Measurements for Various Nanocarriers
2.5. Morphological Evaluation of Raloxifene-Loaded Nanovesicles
2.6. Entrapment Efficiency of Raloxifene in the Vesicular System
2.7. In Vitro Anticancer Studies
2.7.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.7.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.8. In Vitro Drug Release Profile
2.9. Statistical Analysis
2.10. Storage Stability Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Raloxifene-Loaded Nanovesicles
3.1.1. Particle Size and Pdi Evaluation of the Different Nanovesicles
3.1.2. Zeta Potential of Different Nanocarriers
3.1.3. Morphological Study of Raloxifene-Loaded Nanocarriers
3.2. Encapsulation Efficiency of the Formulated Nanocarriers
3.2.1. Entrapment Efficiency Evaluation
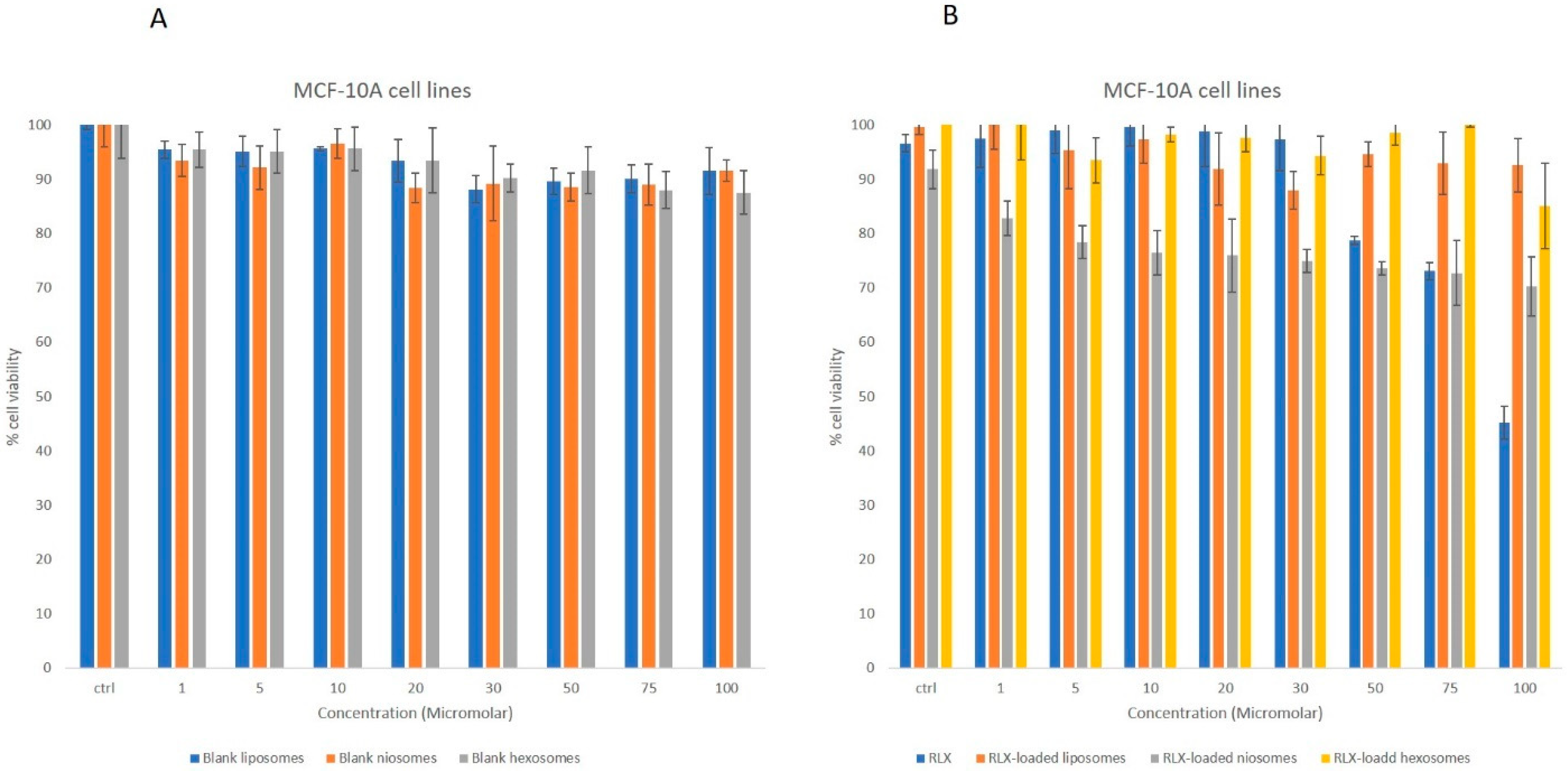
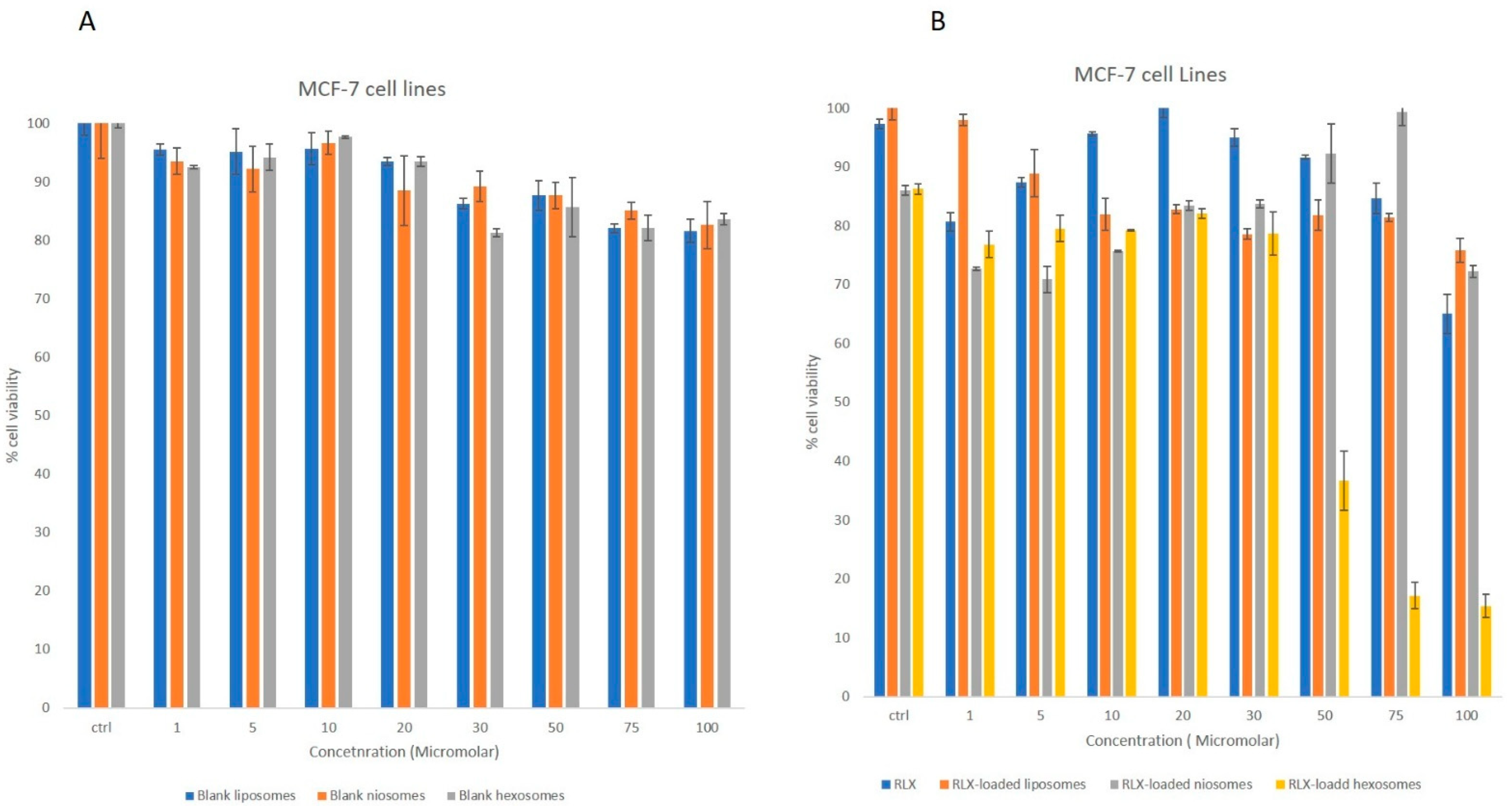
3.2.2. MTT Studies
3.2.3. In Vitro Release
3.2.4. Stability upon Storage
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, X.; Cheng, H.; Hou, J.; Jia, Z.; Wu, G.; Lü, X.; Li, H.; Zheng, X.; Chen, C. Detection of breast cancer based on novel porous silicon Bragg reflector surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy-active structure. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2020, 18, 051701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Ding, N.; Liu, X.; He, X.; Zhou, W.; Xie, H.; Feng, J.; Li, Y.; He, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. Prognostic Value of the Baseline Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index in HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer: Exploratory Analysis of Two Prospective Trials. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2025, 32, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; Chen, C.; Song, H.; Li, M.; Yan, J.; Lv, X. Serum Raman spectroscopy combined with convolutional neural network for rapid diagnosis of HER2-positive and triple-negative breast cancer. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 286, 122000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodai, I.B.; Tuso, P. Breast Cancer Survivorship: A Comprehensive Review of Long-Term Medical Issues and Lifestyle Recommendations. Perm. J. 2015, 19, 48–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.-B.; Yan, Y.; Sun, Y.-N.; Zhu, J.-R. Resveratrol induces apoptosis in human esophageal carcinoma cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 9, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boncel, S.; Herman, A.P.; Budniok, S.; Jędrysiak, R.G.; Jakóbik-Kolon, A.; Skepper, J.N.; Müller, K.H. In Vitro Targeting and Selective Killing of T47D Breast Cancer Cells by Purpurin and 5-Fluorouracil Anchored to Magnetic CNTs: Nitrene-Based Functionalization versus Uptake, Cytotoxicity, and Intracellular Fate. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, S.; Pastero, L.; Serpe, L.; Trotta, F.; Vavia, P.; Aquilano, D.; Trotta, M.; Zara, G.; Cavalli, R. Cyclodextrin-based nanosponges encapsulating camptothecin: Physicochemical characterization, stability and cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 74, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpalatha, R.; Selvamuthukumar, S.; Kilimozhi, D. Cross-linked, cyclodextrin-based nanosponges for curcumin delivery–Physicochemical characterization, drug release, stability and cytotoxicity. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 45, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebmann, J.; Cook, J.; Lipschultz, C.; Teague, D.; Fisher, J.; Mitchell, J. Cytotoxic studies of paclitaxel (Taxol®) in human tumour cell lines. Br. J. Cancer 1993, 68, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballout, F.; Habli, Z.; Rahal, O.N.; Fatfat, M.; Gali-Muhtasib, H. Thymoquinone-based nanotechnology for cancer therapy: Promises and challenges. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett-Connor, E. Raloxifene: Risks and Benefits. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2001, 949, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundararajan, V.; Rosengren, R.J.; Chen, S. Raloxifene: Promises and Challenges as a Drug Treatment for Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer. Enliven Toxicol. Allied Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 4, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, P.H.; Belgamwar, V.S.; Patil, P.R.; Surana, S.J. Solubility Enhancement of Raloxifene Using Inclusion Complexes and Cogrinding Method. J. Pharm. 2013, 2013, 527380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.; Seth, A.K.; Balaraman, R. Bioavailability Enhancement of Poorly Soluble Raloxifene by Designing Inclusion Complex with β–Cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 7, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Battani, S.; Pawar, H.; Suresh, S. Evaluation of Oral Bioavailability and Anticancer Potential of Raloxifene Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 5638–5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Lu, J. Lipid-Based Nanotechnology: Liposome. Pharmaceutics 2023, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Tiwari, H.; Lakkakula, J.; Roy, A.; Bin Emran, T.; Rashid, S.; Alghamdi, S.; Rajab, B.S.; Almehmadi, M.; Allahyani, M.; et al. A decade’s worth of impact: Dox loaded liposomes in anticancer activity. Mater. Today Adv. 2022, 16, 100313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadian, A.; Robattorki, F.F.; Dibah, H.; Soheili, A.; Ghanbarzadeh, E.; Sartipnia, N.; Hajrasouliha, S.; Pasban, K.; Andalibi, R.; Ch, M.H.; et al. Niosomes-loaded selenium nanoparticles as a new approach for enhanced antibacterial, anti-biofilm, and anticancer activities. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, M.K.; Riaz, M.A.; Zhang, X.; Lin, C.; Wong, K.H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, G.; Lu, A.; Yang, Z. Surface functionalization and targeting strategies of liposomes in solid tumor therapy: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W. Liposome-based drug delivery in breast cancer treatment. Breast Cancer Res. 2002, 4, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dora, C.P.; Trotta, F.; Kushwah, V.; Devasari, N.; Singh, C.; Suresh, S.; Jain, S. Potential of erlotinib cyclodextrin nanosponge complex to enhance solubility, dissolution rate, in vitro cytotoxicity and oral bioavailability. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Li, M.; Wu, X.; Li, M.; Wu, Y. Preparation of thermoresponsive and pH-sensitivity polymer magnetic hydrogel nanospheres as anticancer drug carriers. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 88, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oerlemans, C.; Bult, W.; Bos, M.; Storm, G.; Nijsen, J.F.W.; Hennink, W.E. Polymeric Micelles in Anticancer Therapy: Targeting, Imaging and Triggered Release. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 2569–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazaruk, E.; Majkowska-Pilip, A.; Bilewicz, R. Lipidic Cubic-Phase Nanoparticles—Cubosomes for Efficient Drug Delivery to Cancer Cells. Chempluschem 2017, 82, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Far, S.W.; El-Enin, H.A.A.; Abdou, E.M.; Nafea, O.E.; Abdelmonem, R. Targeting Colorectal Cancer Cells with Niosomes Systems Loaded with Two Anticancer Drugs Models; Comparative In Vitro and Anticancer Studies. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthu, M.S.; Feng, S.-S. Theranostic liposomes for cancer diagnosis and treatment: Current development and pre-clinical success. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2012, 10, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malam, Y.; Loizidou, M.; Seifalian, A.M. Liposomes and nanoparticles: Nanosized vehicles for drug delivery in cancer. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Jin, C.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; Di, Y.; Ni, Q.; Fu, D. Liposome based delivery systems in pancreatic cancer treatment: From bench to bedside. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2011, 37, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgia, S.; Bonacchi, S.; Falchi, A.M.; Lampis, S.; Lippolis, V.; Meli, V.; Monduzzi, M.; Prodi, L.; Schmidt, J.; Talmon, Y.; et al. Drug-Loaded Fluorescent Cubosomes: Versatile Nanoparticles for Potential Theranostic Applications. Langmuir 2013, 29, 6673–6679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohyeldin, S.M.; Mehanna, M.M.; Elgindy, N.A. Superiority of liquid crystalline cubic nanocarriers as hormonal transdermal vehicle: Comparative human skin permeation-supported evidence. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1049–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar-Yuli, I.; Wachtel, E.; Ben Shoshan, E.; Danino, D.; Aserin, A.; Garti, N. Hexosome and Hexagonal Phases Mediated by Hydration and Polymeric Stabilizer. Langmuir 2007, 23, 3637–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badie, H.; Abbas, H. Novel small self-assembled resveratrol-bearing cubosomes and hexosomes: Preparation, charachterization, andex vivopermeation. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 2013–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarei, M.; Yaraghtala, S. Preparation and Assessment of Gingerol-loaded Nanoliposomes and their Effect on Breast Cancer Cell Lines (MCF-7). In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Researches in Science & Engineering & International Congress on Civil, Architecture and Urbanism in Asia, Bangkok, Thailand, 18 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, S.A.; Abdelmalak, N.S.; Badawi, A.; Elbayoumy, T.; Sabry, N.; El Ramly, A. Tretinoin-loaded liposomal formulations: From lab to comparative clinical study in acne patients. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasin, M.N.; Hussain, S.; Malik, F.; Hameed, A.; Sultan, T.; Qureshi, F.; Riaz, H.; Perveen, G.; Wajid, A. Preparation and Characterization of Chloramphenicol Niosomes and Comparison with Chloramphnicol Eye Drops (0.5%w/v) in Experimental Conjunctivitis in Albino Rabbits. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 25, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Q.; Chen, W.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, L. Novel nanoliposomal delivery system for polydatin: Preparation, characterization, and in vivo evaluation. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelbary, G.A.; Tadros, M.I. Brain targeting of olanzapine via intranasal delivery of core–shell difunctional block copolymer mixed nanomicellar carriers: In vitro characterization, ex vivo estimation of nasal toxicity and in vivo biodistribution studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 452, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanna, M.M.; Sarieddine, R.; Alwattar, J.K.; Chouaib, R.; Gali-Muhtasib, H. Anticancer Activity of Thymoquinone Cubic Phase Nanoparticles Against Human Breast Cancer: Formulation, Cytotoxicity and Subcellular Localization. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 9557–9570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwattar, J.K.; Chouaib, R.; Khalil, A.; Mehanna, M.M. A novel multifaceted approach for wound healing: Optimization and in vivo evaluation of spray dried tadalafil loaded pro-nanoliposomal powder. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 587, 119647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, V.K.; Pathak, N.; Bhaskar, R.; Nandi, B.C.; Dey, S.; Tyagi, L.K. Optimization of immediate release tablet of raloxifene hydrochloride by wet granulation method. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Drug Res. 2009, 1, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Bar, H.M.; Khater, S.E.; Ghorab, D.M.; Al-Mahallawi, A.M. Hexosomes as Efficient Platforms for Possible Fluoxetine Hydrochloride Repurposing with Improved Cytotoxicity against HepG2 Cells. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 26697–26709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barauskas, J.; Cervin, C.; Jankunec, M.; Špandyreva, M.; Ribokaitė, K.; Tiberg, F.; Johnsson, M. Interactions of lipid-based liquid crystalline nanoparticles with model and cell membranes. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 391, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Liao, L. Applications of Nanoparticles for Anticancer Drug Delivery: A Review. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 4753–4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Huang, L.; Yang, X.-L.; Tang, J.; Feng, S.-S. Pharmaceutical nanotechnology for oral delivery of anticancer drugs. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 65, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Rezaei-Sadabady, R.; Davaran, S.; Joo, S.W.; Zarghami, N.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Samiei, M.; Kouhi, M.; Nejati-Koshki, K. Liposome: Classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarnakar, N.K.; Jain, V.; Dubey, V.; Mishra, D.; Jain, N. Enhanced Oromucosal Delivery of Progesterone Via Hexosomes. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 2223–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelova, A.; Angelov, B.; Mutafchieva, R.; Lesieur, S.; Couvreur, P. Self-Assembled Multicompartment Liquid Crystalline Lipid Carriers for Protein, Peptide, and Nucleic Acid Drug Delivery. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 44, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estanqueiro, M.; Amaral, M.H.; Conceição, J.; Lobo, J.M.S. Nanotechnological carriers for cancer chemotherapy: The state of the art. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces. 2015, 126, 631–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, J.L.; Clares, B.; Morales, M.E.; Gallardo, V.; Ruiz, M.A. Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Treatment. Curr. Drug Targets 2011, 12, 1151–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari-Vanani, R.; Karimian, K.; Azarpira, N.; Heli, H. Capecitabine-loaded nanoniosomes and evaluation of anticancer efficacy. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, Z.; Hamidi, M. Cubosomes: Remarkable drug delivery potential. Drug Discov. 2016, 21, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, J.-C.; Zhu, J.-X.; Zhu, N.; Zhang, H.-M.; Liang, L.; Sun, L. Folic Acid-Targeted Etoposide Cubosomes for Theranostic Application of Cancer Cell Imaging and Therapy. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 2426–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, S.; Gardouh, A.R.; Ghorab, M.M. Factors affecting liposomes particle size prepared by ethanol injection method. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 12, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowroozi, F.; Almasi, A.; Javidi, J.; Haeri, A.; Dadashzadeh, S. Effect of Surfactant Type, Cholesterol Content and Various Downsizing Methods on the Particle Size of Niosomes. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Mohamed, M.S.; Raveendran, S.; Rochani, A.K.; Maekawa, T.; Kumar, D.S. Formulation, characterization and evaluation of morusin loaded niosomes for potentiation of anticancer therapy. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 32621–32636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedeek, M.S.; Al-Mahallawi, A.M.; Hussien, R.A.A.; Ali, A.M.A.; Naguib, I.A.; Mansour, M.K. Hexosomal Dispersion: A Nano-Based Approach to Boost the Antifungal Potential of Citrus Essential Oils against Plant Fungal Pathogens. Molecules 2021, 26, 6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junyaprasert, V.B.; Teeranachaideekul, V.; Supaperm, T. Effect of Charged and Non-ionic Membrane Additives on Physicochemical Properties and Stability of Niosomes. Aaps Pharmscitech 2008, 9, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, A.M.; Gany, S.A.S.; Gray, I.A.; Young, L.; Igoli, O.J.; Ferro, A.V. Niosome-encapsulated balanocarpol: Compound isolation, characterisation, and cytotoxicity evaluation against human breast and ovarian cancer cell lines. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 195101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, I.A.; Madan, J.; Kaushik, D.; Sardana, S.; Pandey, R.S.; Ali, A. Comparative study of transfersomes, liposomes, and niosomes for topical delivery of 5-fluorouracil to skin cancer cells. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2011, 22, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshav, J. Niosomes as a Potential Carrier System: A Review. Int. J. Pharm. Chem. Biol. Sci. 2015, 5, 947–959. [Google Scholar]
- Lohumi, A. A Novel Drug Delivery System: Niosomes Review. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2012, 2, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirlekar, R.; Jain, S.; Patel, M.; Garse, H.; Kadam, V. Hexosomes: A Novel Drug Delivery System. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
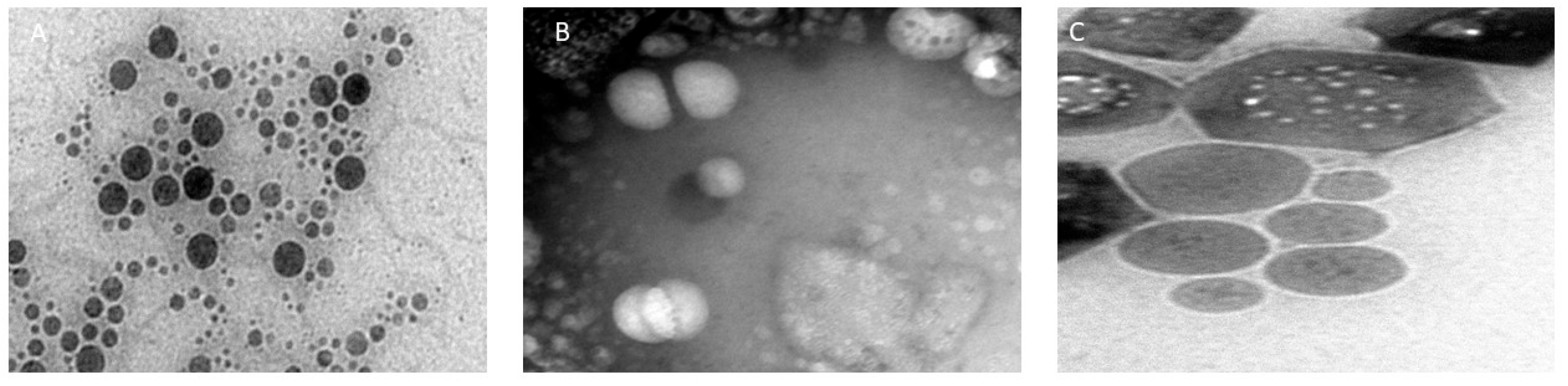

| Formulation | Particle Size (nm) | PDI |
|---|---|---|
| Raloxifene-loaded hexosomes | 125 ± 3.1 * | 0.126 |
| Raloxifene-loaded liposomes | 263 ± 4.4 * | 0.535 |
| Raloxifene-loaded niosomes | 627 ± 7.6 * | 0.245 |
| Blank hexosomes | 115.3 ± 6.51 * | 0.190 |
| Blank liposomes | 257.2 ± 12.3 * | 0.341 |
| Blank niosomes | 523.6 ± 13.5 * | 0.381 |
| Formulation | RLX-Loaded Hexosomes | RLX-Loaded Liposomes | RLX-Loaded Niosomes | Blank Hexosomes | Blank Liposomes | Blank Niosomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zeta potential (mV) | –36.5 ± 2.8 * | –27.19 ± 7.3 * | –18.21 ± 3.6 * | –32.5 ± 4.2 | –25.2 ± 2.5 | –20.2 ± 1.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
ALwattar, J.K.; Assi, M.A.; Nasser, S.; Rahal, M.; Mehanna, M.M. Raloxifene-Loaded Lipid Nanovesicles: A Journey to Select the Optimal Nanocarrier Formulation Through Characterization and Cytotoxic Analysis. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092056
ALwattar JK, Assi MA, Nasser S, Rahal M, Mehanna MM. Raloxifene-Loaded Lipid Nanovesicles: A Journey to Select the Optimal Nanocarrier Formulation Through Characterization and Cytotoxic Analysis. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(9):2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092056
Chicago/Turabian StyleALwattar, Jana K, Mohammad Ahmad Assi, Sahar Nasser, Mohamad Rahal, and Mohammed M. Mehanna. 2025. "Raloxifene-Loaded Lipid Nanovesicles: A Journey to Select the Optimal Nanocarrier Formulation Through Characterization and Cytotoxic Analysis" Biomedicines 13, no. 9: 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092056
APA StyleALwattar, J. K., Assi, M. A., Nasser, S., Rahal, M., & Mehanna, M. M. (2025). Raloxifene-Loaded Lipid Nanovesicles: A Journey to Select the Optimal Nanocarrier Formulation Through Characterization and Cytotoxic Analysis. Biomedicines, 13(9), 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092056






