Association Between COVID-19 Infection and Thyroid Cancer Development: A Retrospective Cohort Study Using the TriNetX Database
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setting
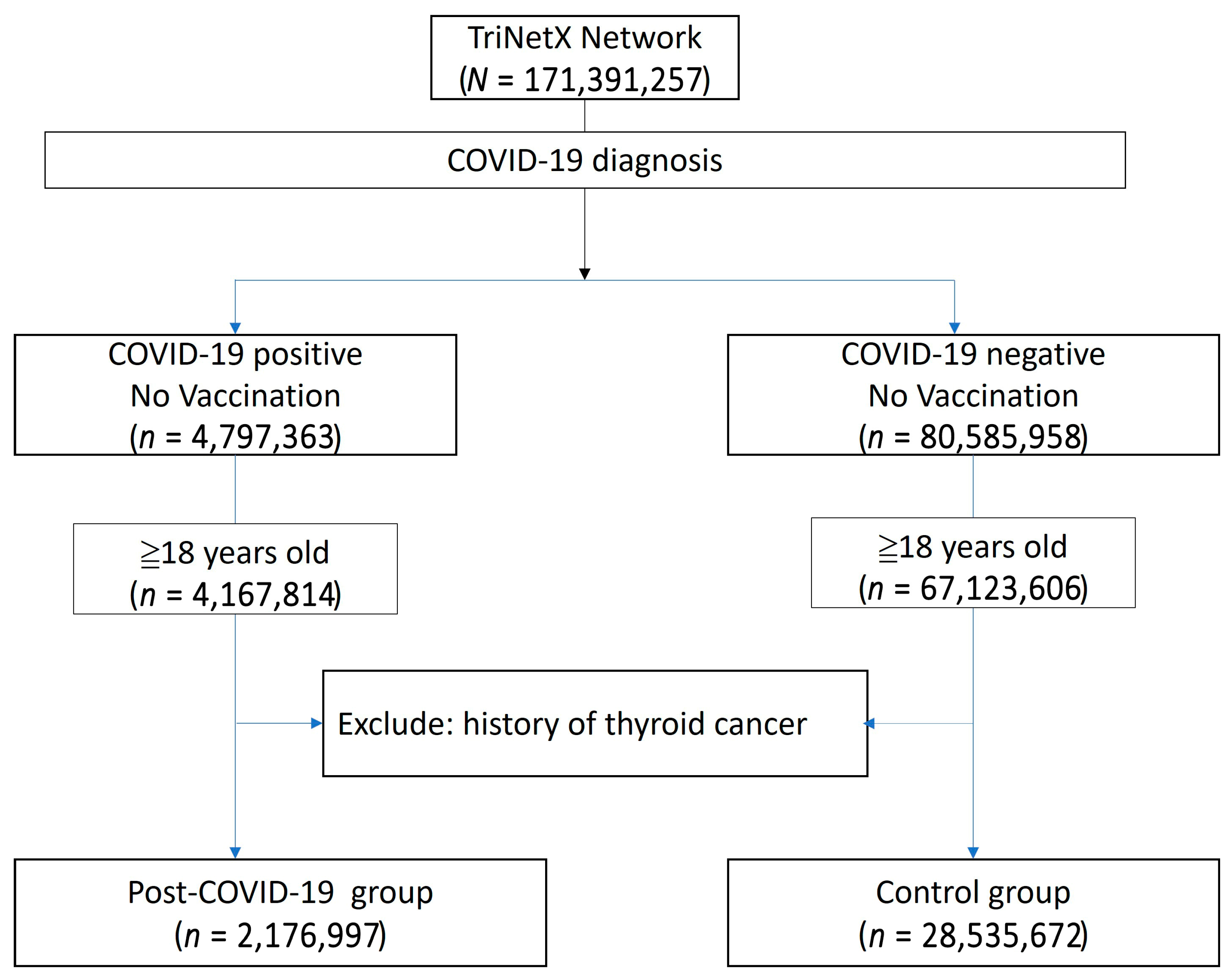
2.2. Cohort
2.3. Statistical Analysis
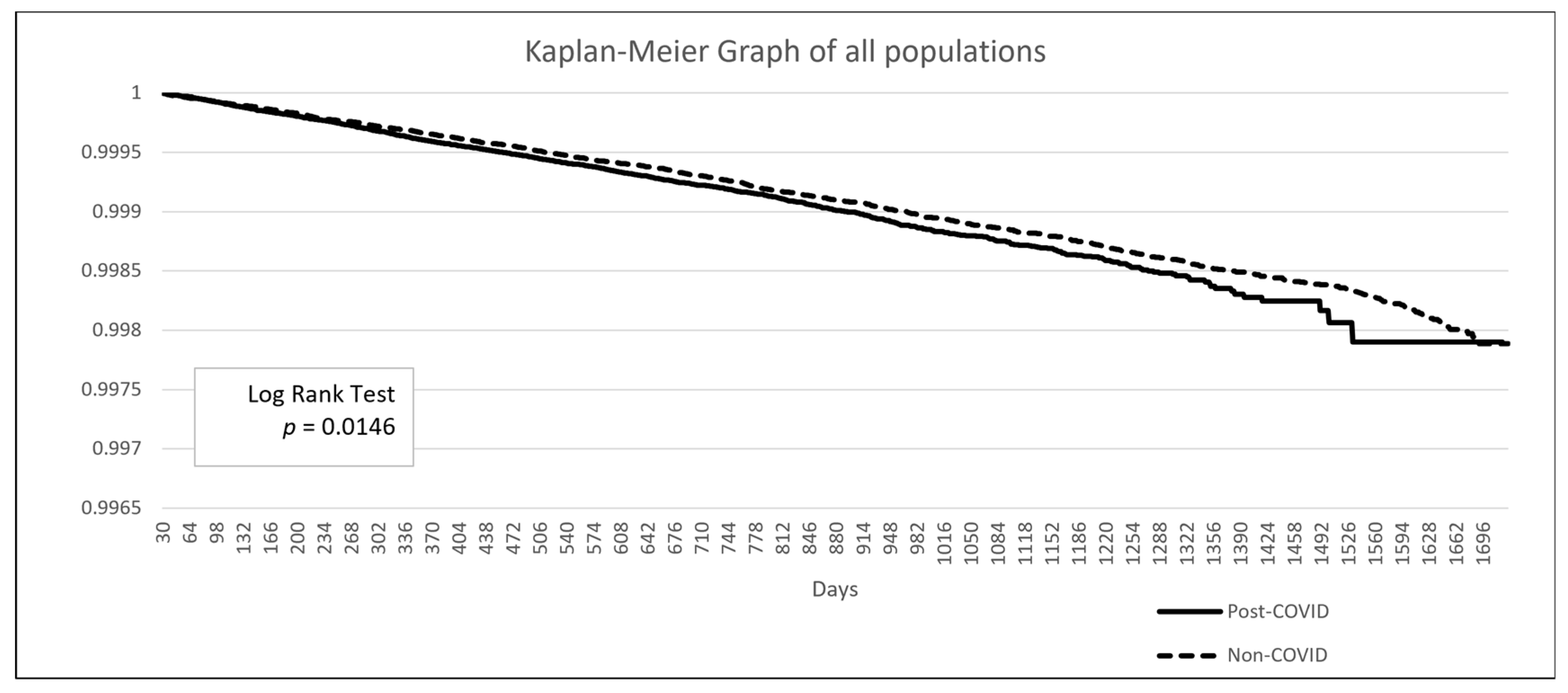
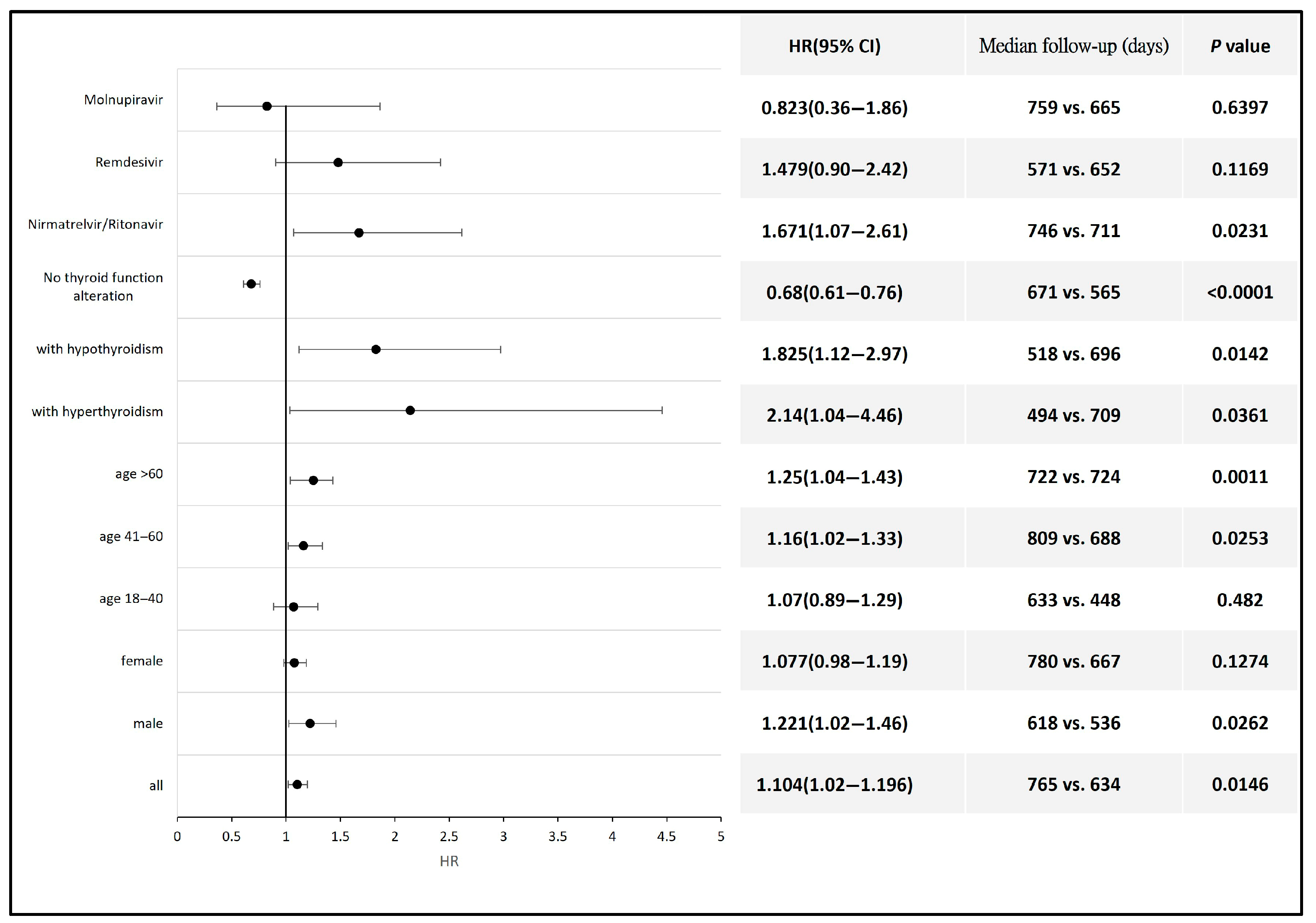
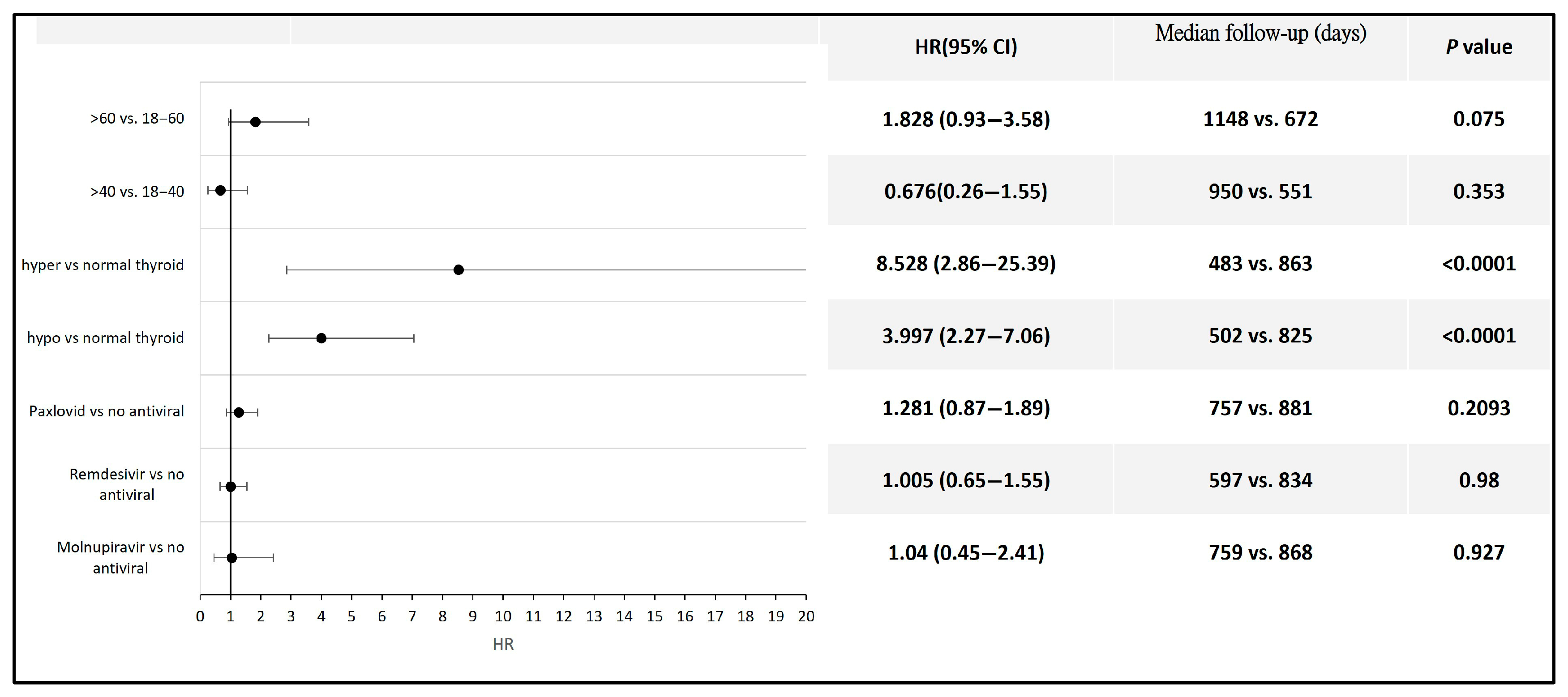
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE2 | angiotensin-converting enzyme II |
| CI | confidence interval |
| HCOs | healthcare organizations |
| HR | hazard ratio |
| MR | Mendelian randomization |
| nsp | nonstructural protein |
References
- Lai, C.C.; Shih, T.P.; Ko, W.C.; Tang, H.J.; Hsueh, P.R. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): The epidemic and the challenges. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 5 July 2023).
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marazuela, M.; Giustina, A.; Puig-Domingo, M. Endocrine and metabolic aspects of the COVID-19 pandemic. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2020, 21, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitahara, C.M.; Schneider, A.B. Epidemiology of Thyroid Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2022, 31, 1284–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, S.A., Jr. Progress in Endocrine Neoplasia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4981–4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almansoori, A.; Busch, H.; Bendardaf, R.; Hamoudi, R. Thyroid cancer incidence in the United Arab Emirates: A retrospective study on association with age and gender. F1000Research 2022, 11, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlader, N.; Noone, A.M.; Krapcho, M.; Miller, D.; Brest, A.; Yu, M.; Ruhl, J.; Tatalovich, Z.; Mariotto, A.; Lewis, D.R.; et al. (Eds.) SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2018; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, C.L.; Cazarin, J.; Hecht, F.; Beltrao, F.E.L.; Ferreira, A.C.F.; Fortunato, R.S.; Ramos, H.E.; de Carvalho, D.P. COVID-19 and thyroid function: What do we know so far? Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1041676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scappaticcio, L.; Pitoia, F.; Esposito, K.; Piccardo, A.; Trimboli, P. Impact of COVID-19 on the thyroid gland: An update. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2021, 22, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.S. Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide variety of human tissues. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Kruger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280 e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.; Kang, J.; Li, G.; Ge, J.; Gu, J. Analysis of 2019-nCoV receptor ACE2 expression in different tissues and its significance study. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gressens, S.B.; Leftheriotis, G.; Dussaule, J.C.; Flamant, M.; Levy, B.I.; Vidal-Petiot, E. Controversial Roles of the Renin Angiotensin System and Its Modulators During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 624052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues-Ferreira, S.; Nahmias, C. G-protein coupled receptors of the renin-angiotensin system: New targets against breast cancer? Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipoor, S.D.; Mortaz, E.; Jamaati, H.; Tabarsi, P.; Bayram, H.; Varahram, M.; Adcock, I.M. COVID-19: Molecular and Cellular Response. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 563085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortaz, E.; Tabarsi, P.; Varahram, M.; Folkerts, G.; Adcock, I.M. The Immune Response and Immunopathology of COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merad, M.; Martin, J.C. Pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19: A key role for monocytes and macrophages. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.J.X.; Purshouse, K. COVID-19 and cancer registries: Learning from the first peak of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 1777–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coperchini, F.; Chiovato, L.; Croce, L.; Magri, F.; Rotondi, M. The cytokine storm in COVID-19: An overview of the involvement of the chemokine/chemokine-receptor system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 53, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguib, R. Potential relationships between COVID-19 and the thyroid gland: An update. J. Int. Med. Res. 2022, 50, 3000605221082898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, K.; Liu, P.; Leibowitz, J.L.; Kao, C.C. The coronavirus endoribonuclease Nsp15 interacts with retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 4294–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stingi, A.; Cirillo, L. SARS-CoV-2 infection and cancer: Evidence for and against a role of SARS-CoV-2 in cancer onset. Bioessays 2021, 43, e2000289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma-Lauer, Y.; Carbajo-Lozoya, J.; Hein, M.Y.; Muller, M.A.; Deng, W.; Lei, J.; Meyer, B.; Kusov, Y.; von Brunn, B.; Bairad, D.R.; et al. p53 down-regulates SARS coronavirus replication and is targeted by the SARS-unique domain and PLpro via E3 ubiquitin ligase RCHY1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E5192–E5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, R.P.; Lin, Y.; Ma, W.; Wu, H.; Lemmers, B.; Chung, S.; Parant, J.M.; Lozano, G.; Hakem, R.; Benchimol, S. Pirh2, a p53-induced ubiquitin-protein ligase, promotes p53 degradation. Cell 2003, 112, 779–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesri, E.A.; Feitelson, M.A.; Munger, K. Human viral oncogenesis: A cancer hallmarks analysis. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duntas, L.H.; Jonklaas, J. COVID-19 and Thyroid Diseases: A Bidirectional Impact. J. Endocr. Soc. 2021, 5, bvab076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Wang, X.; Zhou, D. Exploring the Potential Association between COVID-19 and Thyroid Cancer: A Mendelian Randomization Study. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 49158–49164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, I.; Hassan, L.; Bacha, F.; Al Salameh, M.; Gatee, O.; Hassan, W. Papillary Thyroid Cancer Trends in the Wake of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Is There a Shift toward a More Aggressive Entity? Diseases 2024, 12, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, N.; Hui, Z.; Shen, Z.; Kan, C.; Hou, N.; Sun, X.; Han, F. Thyroid Cancer and COVID-19: Prospects for Therapeutic Approaches and Drug Development. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 873027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spartalis, E.; Plakopitis, N.; Theodori, M.A.; Karagiannis, S.P.; Athanasiadis, D.I.; Spartalis, M.; Boutzios, G.; Paschou, S.A.; Nikiteas, N.; Troupis, T. Thyroid cancer surgery during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic: Perioperative management and oncological and anatomical considerations. Future Oncol. 2021, 17, 4389–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.; Weinberger, D.M.; Venkatesh, M.; Fernandes-Taylor, S.; Francis, D.O.; Davies, L. Thyroid Cancer Incidence During 2020 to 2021 COVID-19 Variant Waves. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2024, 150, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrinceanu, D.; Dumitru, M.; Marinescu, A.; Serboiu, C.; Musat, G.; Radulescu, M.; Popa-Cherecheanu, M.; Ciornei, C.; Manole, F. Management of Giant Thyroid Tumors in Patients with Multiple Comorbidities in a Tertiary Head and Neck Surgery Center. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prete, A.; Falcone, M.; Bottici, V.; Giani, C.; Tiseo, G.; Agate, L.; Matrone, A.; Cappagli, V.; Valerio, L.; Lorusso, L.; et al. Thyroid cancer and COVID-19: Experience at one single thyroid disease referral center. Endocrine 2021, 72, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Means, J.H. The Thyroid and Its Diseases; Lippincott: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1937. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, T.V.; Kitahara, C.M.; de Vathaire, F.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; Journy, N. Thyroid dysfunction and cancer incidence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2020, 27, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.H.; Young, B.E.; Fong, S.W.; Ding, Y.; Goh, Y.S.; Chee, R.S.; Tan, S.Y.; Kalimuddin, S.; Tambyah, P.A.; Leo, Y.S.; et al. Differential Cytokine Responses in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients Limit Efficacy of Remdesivir. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 680188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Pang, Z.; Li, M.; Lou, F.; An, X.; Zhu, S.; Song, L.; Tong, Y.; Fan, H.; Fan, J. Molnupiravir and Its Antiviral Activity Against COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 855496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panza, F.; Fiorino, F.; Pastore, G.; Fiaschi, L.; Tumbarello, M.; Medaglini, D.; Ciabattini, A.; Montagnani, F.; Fabbiani, M. Does Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir Influence the Immune Response against SARS-CoV-2, Independently from Rebound? Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Hunt, B.J.; Stegemann, M.; Rochwerg, B.; Lamontagne, F.; Siemieniuk, R.A.; Agoritsas, T.; Askie, L.; Lytvyn, L.; Leo, Y.-S.; et al. A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19. BMJ 2020, 370, m3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinosoglou, K.; Schinas, G.; Gogos, C. Oral Antiviral Treatment for COVID-19: A Comprehensive Review on Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir. Viruses 2022, 14, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, C.J.; Tchesnokov, E.P.; Schinazi, R.F.; Gotte, M. Molnupiravir promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis via the RNA template. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 100770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfiky, A.A. Ribavirin, Remdesivir, Sofosbuvir, Galidesivir, and Tenofovir against SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp): A molecular docking study. Life Sci. 2020, 253, 117592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazavi, A.; Ganji, A.; Keshavarzian, N.; Rabiemajd, S.; Mosayebi, G. Cytokine profile and disease severity in patients with COVID-19. Cytokine 2021, 137, 155323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sendur, S.N.; Oguz, S.H.; Unluturk, U. COVID-19 vaccination and thyroiditis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 37, 101759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, R.J.; Anson, M.; Zirpel, H.; Thaci, D.; Olbrich, H.; Bieber, K.; Kridin, K.; Dempfle, A.; Curman, P.; Zhao, S.S.; et al. A comprehensive review of methodologies and application to use the real-world data and analytics platform TriNetX. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1516126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Code | Name |
|---|---|
| UMLS:LNC:94500-6 | SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) RNA [Presence] in respiratory specimen by NAA with probe detection (labResult: Positive) |
| UMLS:LNC:94309-2 | SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) RNA [Presence] in specimen by NAA with probe detection (labResult: Positive) |
| UMLS:LNC:94565-9 | SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) RNA [Presence] in nasopharynx by NAA with non-probe detection (labResult: Positive) |
| UMLS:LNC:94759-8 | SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) RNA [Presence] in nasopharynx by NAA with probe detection (labResult: Positive) |
| UMLS:LNC:95608-6 | SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) RNA [Presence] in respiratory specimen by NAA with non-probe detection (labResult: Positive) |
| UMLS:LNC:94845-5 | SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) RNA [Presence] in saliva (oral fluid) by NAA with probe detection (labResult: Positive) |
| UMLS:LNC:95406-5 | SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) RNA [Presence] in nose by NAA with probe detection (labResult: Positive) |
| Code | Name |
|---|---|
| NLM:CVX:208 | COVID-19, mRNA, LNP-S, PF, 30 mcg/0.3 mL dose |
| NLM:CVX:207 | COVID-19, mRNA, LNP-S, PF, 100 mcg/0.5 mL dose or 50 mcg/0.25 mL dose |
| NLM:CVX:212 | COVID-19 vaccine, vector-nr, rS-Ad26, PF, 0.5 mL |
| NLM:RXNORM:OMOP5042939 | COVID-19 vaccine |
| NLM:CVX:300 | COVID-19, mRNA, LNP-S, bivalent, PF, 30 mcg/0.3 mL dose |
| NLM:CVX:217 | COVID-19, mRNA, LNP-S, PF, 30 mcg/0.3 mL dose, tris-sucrose |
| NLM:CVX:229 | COVID-19, mRNA, LNP-S, bivalent, PF, 50 mcg/0.5 mL or 25 mcg/0.25 mL dose |
| NLM:CVX:218 | COVID-19, mRNA, LNP-S, PF, 10 mcg/0.2 mL dose, tris-sucrose |
| NLM:CVX:520 | COVID-19 mRNA, bivalent, original/Omicron BA.1, non-US vaccine product, Pfizer-BioNTech |
| NLM:CVX:519 | COVID-19 mRNA, bivalent, original/Omicron BA.1, non-US vaccine (Spikevax Bivalent), Moderna |
| NLM:CVX:301 | COVID-19, mRNA, LNP-S, bivalent, PF, 10 mcg/0.2 mL dose |
| NLM:CVX:219 | COVID-19, mRNA, LNP-S, PF, 3 mcg/0.2 mL dose, tris-sucrose |
| NLM:CVX:228 | COVID-19, mRNA, LNP-S, PF, pediatric 25 mcg/0.25 mL dose |
| NLM:CVX:230 | COVID-19, mRNA, LNP-S, bivalent booster, PF, 10 mcg/0.2 mL |
| NLM:CVX:221 | COVID-19, mRNA, LNP-S, PF, 50 mcg/0.5 mL dose |
| NLM:CVX:210 | COVID-19 vaccine, vector-nr, rS-ChAdOx1, PF, 0.5 mL |
| NLM:CVX:302 | COVID-19, mRNA, LNP-S, bivalent, PF, 3 mcg/0.2 mL dose |
| NLM:CVX:511 | COVID-19 IV non-US vaccine (CoronaVac, Sinovac) |
| NLM:RXNORM:2468231 | SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) vaccine, mRNA spike protein |
| UMLS:CPT:91300 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative-free, 30 mcg/0.3 mL dosage, diluent reconstituted, for intramuscular use |
| UMLS:CPT:0001A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative-free, 30 mcg/0.3 mL dosage, diluent-reconstituted; first dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0002A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative-free, 30 mcg/0.3 mL dosage, diluent-reconstituted; second dose |
| UMLS:CPT:91301 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative free, 100 mcg/0.5 mL dosage, for intramuscular use |
| UMLS:CPT:0011A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative-free, 100 mcg/0.5 mL dosage; first dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0012A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative-free, 100 mcg/0.5 mL dosage; second dose |
| UMLS:SNOMED:840534001 | Administration of SARS-CoV-2 antigen vaccine |
| NLM:CVX:213 | SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) vaccine |
| UMLS:CPT:1036660 | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative-free, 30 mcg/0.3 mL dosage, diluent reconstituted |
| UMLS:CPT:1036663 | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative-free, 100 mcg/0.5 mL dosage |
| UMLS:CPT:0124A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, bivalent spike protein, preservative free, 30 mcg/0.3 mL dosage, tris-sucrose formulation; booster dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0004A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative-free, 30 mcg/0.3 mL dosage, diluent-reconstituted; booster dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0003A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative-free, 30 mcg/0.3 mL dosage, diluent-reconstituted; third dose |
| UMLS:CPT:1037166 | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative-free, 30 mcg/0.3 mL dosage, tris-sucrose formulation |
| UMLS:CPT:0054A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative-free, 30 mcg/0.3 mL dosage, tris-sucrose formulation; booster dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0064A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative free, 50 mcg/0.25 mL dosage; booster dose |
| UMLS:CPT:90480 | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine; single dose |
| UMLS:CPT:1037171 | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative-free, 10 mcg/0.2 mL dosage, diluent reconstituted, tris-sucrose formulation |
| UMLS:CPT:0071A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative-free, 10 mcg/0.2 mL dosage, diluent reconstituted, tris-sucrose formulation; first dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0072A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative-free, 10 mcg/0.2 mL dosage, diluent reconstituted, tris-sucrose formulation; second dose |
| NLM:RXNORM:2610319 | SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) vaccine, mRNA-BNT162b2 0.05 MG/ML/SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) vaccine, mRNA-BNT162b2 OMICRON (BA.4/BA.5) 0.05 MG/ML injectable suspension |
| UMLS:CPT:91313 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, bivalent, preservative-free, 50 mcg/0.5 mL dosage, for intramuscular use |
| UMLS:CPT:0134A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, bivalent, preservative-free, 50 mcg/0.5 mL dosage; booster dose |
| UMLS:CPT:1037175 | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, DNA, spike protein, adenovirus type 26 (Ad26) vector, preservative-free, 5 × 1010 viral particles/0.5 mL dosage |
| NLM:RXNORM:2610347 | 0.3 ML SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) vaccine, mRNA-BNT162b2 0.05 MG/ML/SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) vaccine, mRNA-BNT162b2 OMICRON (BA.4/BA.5) 1 MG/ML injection |
| UMLS:CPT:1037228 | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative-free, 3 mcg/0.2 mL dosage, diluent-reconstituted, tris-sucrose formulation |
| UMLS:CPT:0013A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative-free, 100 mcg/0.5 mL dosage; third dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0081A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative-free, 3 mcg/0.2 mL dosage, diluent-reconstituted, tris-sucrose formulation; first dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0082A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative-free, 3 mcg/0.2 mL dosage, diluent-reconstituted, tris-sucrose formulation; second dose |
| NLM:RXNORM:2610328 | SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) vaccine, mRNA-1273 0.05 MG/ML/SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) vaccine, mRNA-1273 OMICRON (BA.4/BA.5) 0.05 MG/ML injectable suspension |
| UMLS:CPT:0154A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, bivalent spike protein, preservative free, 10 mcg/0.2 mL dosage, diluent reconstituted, tris-sucrose formulation; booster dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0053A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative free, 30 mcg/0.3 mL dosage, tris-sucrose formulation; third dose |
| UMLS:CPT:1037332 | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative free, 25 mcg/0.25 mL dosage |
| UMLS:CPT:0052A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative free, 30 mcg/0.3 mL dosage, tris-sucrose formulation; second dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0111A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative free, 25 mcg/0.25 mL dosage; first dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0051A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative free, 30 mcg/0.3 mL dosage, tris-sucrose formulation; first dose |
| UMLS:CPT:91311 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative free, 25 mcg/0.25 mL dosage, for intramuscular use |
| UMLS:CPT:0074A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative free, 10 mcg/0.2 mL dosage, diluent reconstituted, tris-sucrose formulation; booster dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0112A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative free, 25 mcg/0.25 mL dosage; second dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0083A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative free, 3 mcg/0.2 mL dosage, diluent reconstituted, tris-sucrose formulation; third dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0073A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative free, 10 mcg/0.2 mL dosage, diluent reconstituted, tris-sucrose formulation; third dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0173A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, bivalent spike protein, preservative free, 3 mcg/0.2 mL dosage, diluent reconstituted, tris-sucrose formulation; third dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0164A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, bivalent, preservative free, 10 mcg/0.2 mL dosage; booster dose |
| UMLS:CPT:1037838 | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative free, 50 mcg/0.5 mL dosage |
| UMLS:CPT:0094A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative free, 50 mcg/0.5 mL dosage; booster dose, when administered to individuals aged 18 years and over |
| UMLS:CPT:0034A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, DNA, spike protein, adenovirus type 26 (Ad26) vector, preservative free, 5 × 1010 viral particles/0.5 mL dosage; booster dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0144A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, bivalent, preservative free, 25 mcg/0.25 mL dosage; booster dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0091A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative free, 50 mcg/0.5 mL dosage; first dose, when administered to individuals aged 6 through 11 years |
| UMLS:CPT:0174A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, bivalent spike protein, preservative free, 3 mcg/0.2 mL dosage, diluent reconstituted, tris-sucrose formulation; booster |
| UMLS:CPT:0092A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative free, 50 mcg/0.5 mL dosage; second dose, when administered to individuals aged 6 through 11 years |
| UMLS:CPT:1036682 | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, recombinant spike protein nanoparticle, saponin-based adjuvant, preservative free, 5 mcg/0.5 mL dosage |
| UMLS:CPT:0041A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, recombinant spike protein nanoparticle, saponin-based adjuvant, preservative free, 5 mcg/0.5 mL dosage; first dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0113A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative free, 25 mcg/0.25 mL dosage; third dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0042A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, recombinant spike protein nanoparticle, saponin-based adjuvant, preservative free, 5 mcg/0.5 mL dosage; second dose |
| UMLS:CPT:0093A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, mRNA-LNP, spike protein, preservative free, 50 mcg/0.5 mL dosage; third dose, when administered to individuals aged 6 through 11 years |
| UMLS:CPT:1036666 | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, DNA, spike protein, chimpanzee adenovirus Oxford 1 (ChAdOx1) vector, preservative free, 5 × 1010 viral particles/0.5 mL dosage |
| UMLS:CPT:0044A | Immunization administration by intramuscular injection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (coronavirus disease [COVID-19]) vaccine, recombinant spike protein nanoparticle, saponin-based adjuvant, preservative free, 5 mcg/0.5 mL dosage; booster |
| Before Propensity Score Matching | After Propensity Score Matching | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort | Patients | Mean ± SD | p-Value | Std Diff. | Patients | Mean ± SD | p-Value | Std Diff. | |
| 1 2 | Age at Index | 2,176,997 28,535,672 | 48.8 +/− 20.1 48.5 +/− 20.4 | <0.001 | 0.014 | 2,176,997 2,176,997 | 48.8 +/− 20.1 48.8 +/− 20.1 | 1 | <0.001 |
| Cohort | Patients | % of Cohort | p-Value | Std diff. | Patients | % of Cohort | p-Value | Std diff. | |
| 1 2 | Male | 916,516 12,413,017 | 42.1% 43.5% | <0.001 | 0.028 | 916,516 916,516 | 42.1% 42.1% | 1 | <0.001 |
| 1 2 | Female | 1,260,481 16,221,655 | 57.9% 56.5% | <0.001 | 0.028 | 1,260,481 1,260,481 | 57.9% 57.9% | 1 | <0.001 |
| 1 2 | White | 1,254,735 13,920,716 | 54.5% 49.4% | <0.001 | 0.102 | 1,254,735 1,174,062 | 54.5% 51.0% | <0.001 | 0.070 |
| 1 2 | Asian | 54,299 972,965 | 2.4% 3.5% | <0.001 | 0.065 | 54,299 74,568 | 2.4% 3.2% | <0.001 | 0.053 |
| 1 2 | Black or African American | 345,156 3,320,705 | 15.0% 11.8% | <0.001 | 0.094 | 345,156 295,739 | 15.0% 12.8% | <0.001 | 0.062 |
| 1 2 | Other Race | 66,799 1,072,646 | 2.9% 3.8% | <0.001 | 0.050 | 66,799 82,598 | 2.9% 3.6% | <0.001 | 0.039 |
| 1 2 | Unknown Race | 564,364 8,707,668 | 24.5% 30.9% | <0.001 | 0.143 | 564,364 659,678 | 24.5% 28.7% | <0.001 | 0.094 |
| 1 2 | Personal history of nicotine dependence | 197,813 790,130 | 8.6% 2.8% | <0.001 | 0.252 | 197,813 96,657 | 8.6% 4.2% | <0.001 | 0.180 |
| 1 2 | Personal history of irradiation | 19,856 101,810 | 0.9% 0.4% | <0.001 | 0.064 | 19,856 11,444 | 0.9% 0.5% | <0.001 | 0.044 |
| 1 2 | Overweight and obesity | 391,198 1,656,174 | 17.0% 5.9% | <0.001 | 0.355 | 391,198 391,198 | 17.0% 17.0% | 1 | <0.001 |
| 1 2 | Diabetes mellitus | 293,835 1,534,074 | 12.8% 5.4% | <0.001 | 0.257 | 293,835 189,472 | 12.8% 8.2% | <0.001 | 0.148 |
| 1 2 | Hypertensive diseases | 635,880 3,663,669 | 27.6% 13.0% | <0.001 | 0.370 | 635,880 413,136 | 27.6% 17.9% | <0.001 | 0.232 |
| 1 2 | Ischemic heart diseases | 213,759 1,160,544 | 9.3% 4.1% | <0.001 | 0.208 | 213,759 127,732 | 9.3% 5.5% | <0.001 | 0.143 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.-Y.; Lin, Y.-C.; Hou, J.-U.; Chao, C.-H.; Tsai, S.-C. Association Between COVID-19 Infection and Thyroid Cancer Development: A Retrospective Cohort Study Using the TriNetX Database. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081933
Wang H-Y, Lin Y-C, Hou J-U, Chao C-H, Tsai S-C. Association Between COVID-19 Infection and Thyroid Cancer Development: A Retrospective Cohort Study Using the TriNetX Database. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(8):1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081933
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hsin-Yi, Yi-Ching Lin, Jing-Uei Hou, Chih-Hao Chao, and Shih-Chuan Tsai. 2025. "Association Between COVID-19 Infection and Thyroid Cancer Development: A Retrospective Cohort Study Using the TriNetX Database" Biomedicines 13, no. 8: 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081933
APA StyleWang, H.-Y., Lin, Y.-C., Hou, J.-U., Chao, C.-H., & Tsai, S.-C. (2025). Association Between COVID-19 Infection and Thyroid Cancer Development: A Retrospective Cohort Study Using the TriNetX Database. Biomedicines, 13(8), 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081933






