Retinoic Acid Profiles in Proliferative Verrucous Versus Homogeneous Leukoplakia: A Preliminary Nested Case–Control Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects of Study
2.2. Sample Size Calculation
2.3. Post-Hoc Power Analysis
2.4. Collection and Treatment of Blood Samples
2.5. atRA Extraction Process
2.6. atRA Quantification
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Follow-Up Findings
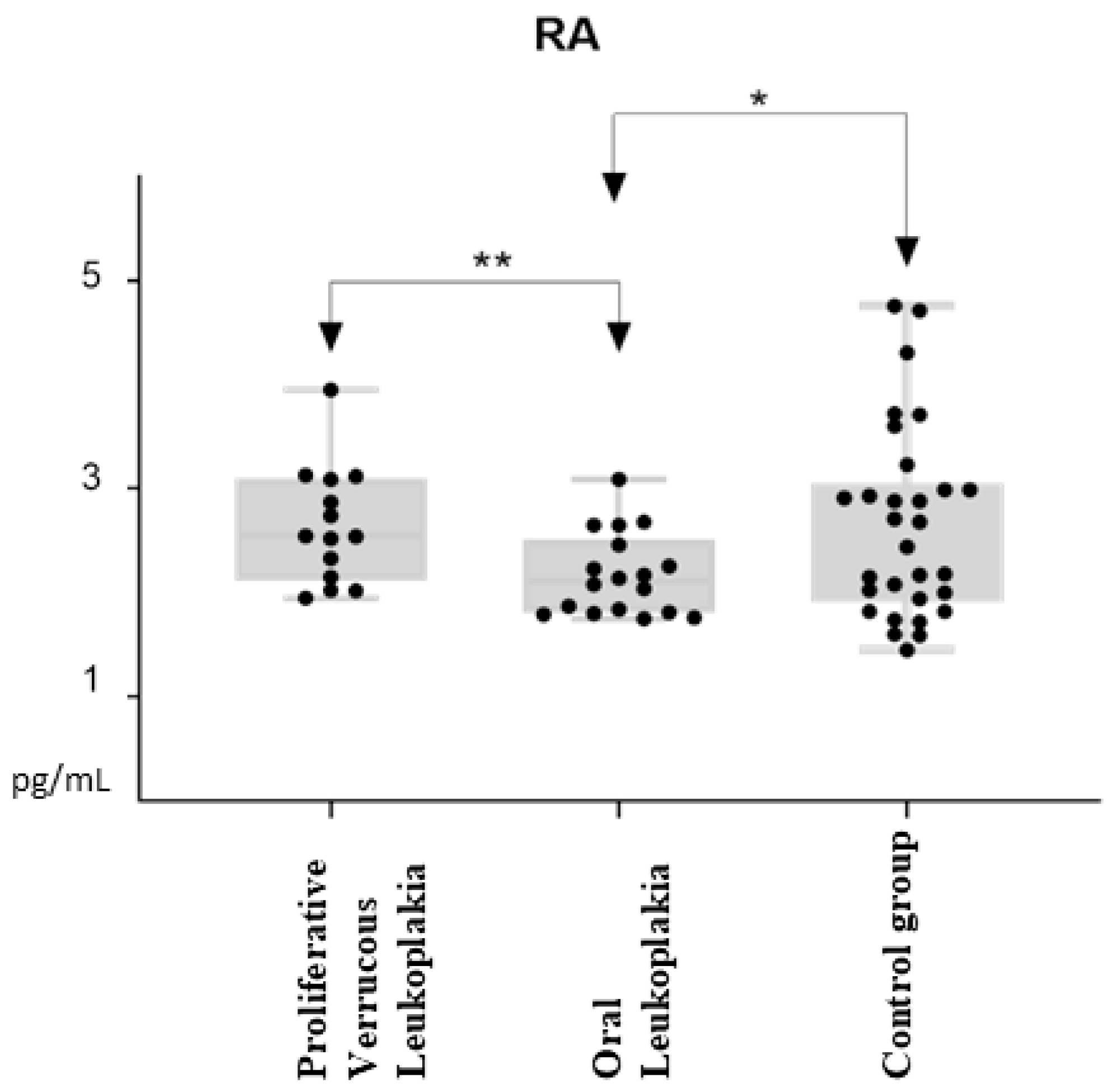
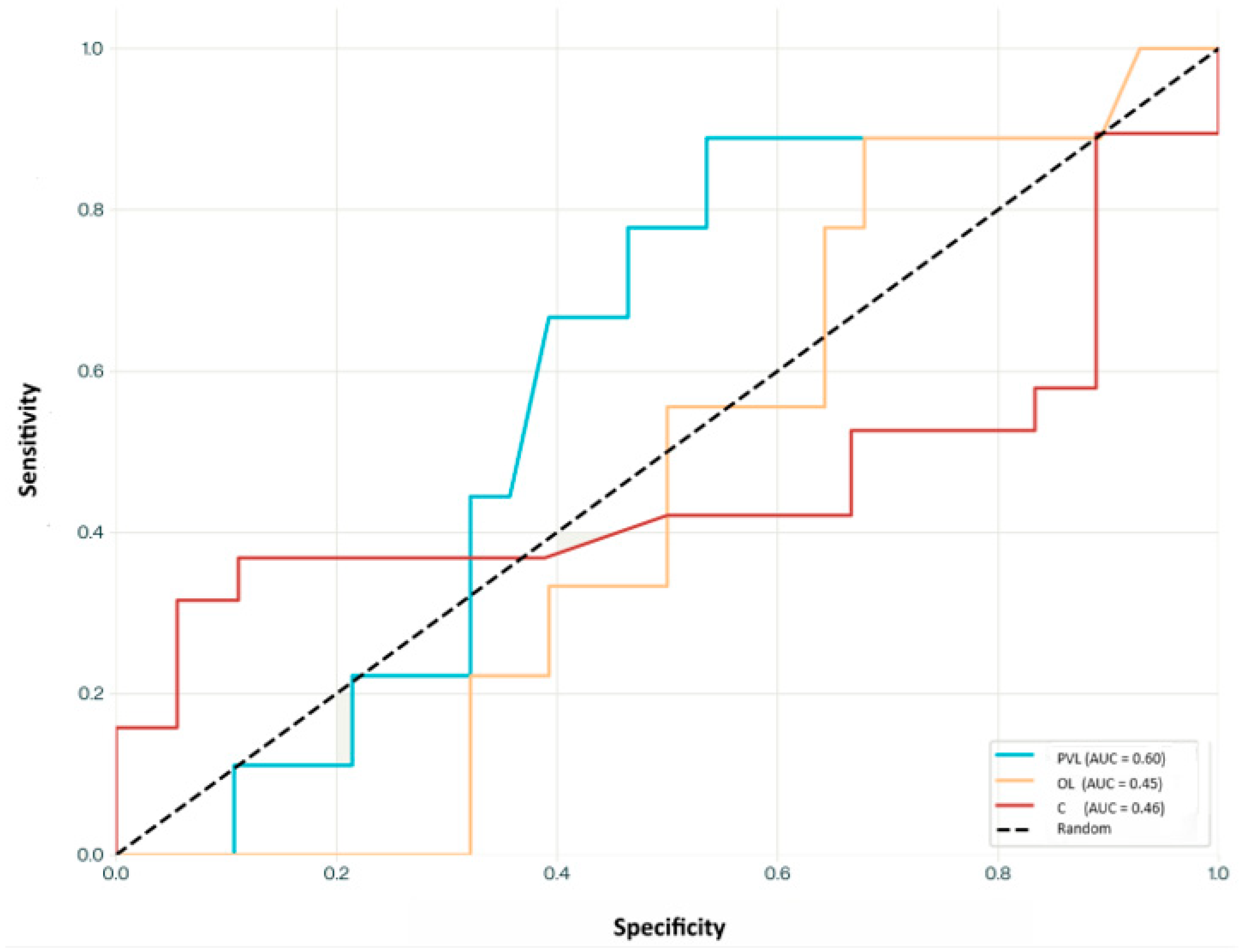
3.2. All-Trans Retinoic Acid Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.; Li, B.; Zeng, X.; Hu, X.; Hua, H. The global prevalence of oral leukoplakia: A systematic review and meta-analysis from 1996 to 2022. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnakulasuriya, S.; Kujan, O.; Aguirre-Urizar, J.M.; Bagan, J.V.; González-Moles, M.Á.; Kerr, A.R.; Lodi, G.; Mello, F.W.; Monteiro, L.; Ogden, G.R.; et al. Oral potentially malignant disorders: A consensus report from an international seminar on nomenclature and classification, convened by the WHO Collaborating Centre for Oral Cancer. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 1862–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaber, M.A.; Porter, S.R.; Speight, P.; Eveson, J.W.; Scully, C. Oral epithelial dysplasia: Clinical characteristics of western European residents. Oral Oncol. 2003, 39, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta-Barros, L.A.; Ramos-García, P.; González-Moles, M.Á.; Aguirre-Urizar, J.M.; Warnakulasuriya, S. Malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia: Systematic review and comprehensive meta-analysis. Oral Dis. 2024, 31, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, J.D.; Burtness, B.; Ferris, R.L. Immunotherapy for head and neck cancer: Recent advances and future directions. Oral Oncol. 2019, 99, 104460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Urizar, J.M.; Lafuente-Ibáñez de Mendoza, I.; Warnakulasuriya, S. Malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia: Systematic review and meta-analysis of the last 5 years. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 1881–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petti, S. Lifestyle risk factors for oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagan, J.; Martorell, M.; Cebrián, J.L.; Rubert, A.; Bagán, L.; Mezquida, C.; Hervás, D. Effect of clinical and histologic features on time to malignancy in 224 cases of oral leukoplakia treated by surgery. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 5181–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadakamadla, J.; Kumar, S.; Lalloo, R.; Johnson, N.W. Qualitative analysis of the impact of Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders on daily life activities. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagan, J.; Scully, C.; Jimenez, Y.; Martorell, M. Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia: A concise update. Oral Dis. 2010, 16, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, C.; Robinson, L.; Ker-Fox, J.; Fonseca, F.P.; van Heerden, W.F.P.; Uys, A. Clinicoradiologic features of ameloblastomas: A single-centre study of 155 cases. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2024, 53, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mendoza, I.L.I.; Pouso, A.I.L.; Urízar, J.M.A.; Montero, C.B.; Carrión, A.B.; Vila, P.G.; Sayáns, M.P. Malignant development of proliferative verrucous/multifocal leukoplakia: A critical systematic review, meta-analysis and proposal of diagnostic criteria. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2022, 51, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, A.; Menon, R.; Kerr, A.; Alves, F.D.A.; Guollo, A.; Ojeda, D.; Woo, S. Proliferative leukoplakia: Proposed new clinical diagnostic criteria. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba-Montero, C.; Lorenzo-Pouso, A.I.; Gándara-Vila, P.; Blanco-Carrión, A.; Marichalar-Mendía, X.; García-García, A.; Pérez-Sayáns, M. Lichenoid areas may arise in early stages of proliferative verrucous leukoplakia: A long-term study of 34 patients. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2022, 51, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabdulaaly, L.; Villa, A.; Chen, T.; Kerr, A.; Ross, N.; Alves, F.A.; Guollo, A.; Woo, S.-B. Characterization of initial/early histologic features of proliferative leukoplakia and correlation with malignant transformation: A multicenter study. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herreros-Pomares, A.; Hervás, D.; Bagan-Debon, L.; Proaño, A.; Garcia, D.; Sandoval, J.; Bagan, J. Oral cancers preceded by proliferative verrucous leukoplakia exhibit distinctive molecular features. Oral Dis. 2024, 30, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, C.S.; Shearston, K.; Turner, E.C.; Vacher, M.; Fox, S.A. Global gene expression profile of proliferative verrucous leukoplakia and its underlying biological disease mechanisms. Oral Oncol. 2024, 151, 106737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, S.R.; Ukwas, A. Cachexia and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A scoping review. Oral Dis. 2024, 30, 1746–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celentano, A.; Glurich, I.; Borgnakke, W.S.; Farah, C.S. World Workshop on Oral Medicine VII: Prognostic biomarkers in oral leukoplakia and proliferative verrucous leukoplakia-A systematic review of retrospective studies. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 848–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, W.K.; Endicott, J.; Itri, L.M.; Doos, W.; Batsakis, J.G.; Bell, R.; Fofonoff, S.; Byers, R.; Atkinson, E.N.; Vaughan, C.; et al. 13- cis -Retinoic Acid in the Treatment of Oral Leukoplakia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 315, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaassen, I.; Braakhuis, B.J.M. Anticancer activity and mechanism of action of retinoids in oral and pharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 2002, 38, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodi, G.; Franchini, R.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; Varoni, E.M.; Sardella, A.; Kerr, A.R.; Carrassi, A.; MacDonald, L.C.; Worthington, H.V. Interventions for treating oral leukoplakia to prevent oral cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 2016, CD001829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotan, R. Retinoids and chemoprevention of aerodigestive tract cancers. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1997, 16, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, J.A.; Partridge, M. Expression of retinoic acid receptors in normal, dysplastic and malignant oral epithelia. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1997, 35, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, E.M.; Lotan, D.; Issa, J.P.; Wakasa, K.; Fan, Y.H.; Mao, L.; Hassan, K.; Feng, L.; Lee, J.J.; Lippman, S.M.; et al. Hypermethylation of the Retinoic Acid Receptor-β2 Gene in Head and Neck Carcinogenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Guan, B.; Men, T.; Hoque, A.; Lotan, R.; Xu, X.C. Antitumor effect of retinoic acid receptor-β2 associated with suppression of cyclooxygenase-2. Cancer Prev. Res. 2009, 2, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stevison, F.; Jing, J.; Tripathy, S.; Isoherranen, N. Role of Retinoic Acid-Metabolizing Cytochrome P450s, CYP26, in Inflammation and Cancer. Adv. Pharmacol. 2015, 74, 373–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ye, D.; Wang, T.; Guo, W.; Song, H.; Liao, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, J. Repression of GPRC5A is associated with activated STAT3, which contributes to tumor progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2017, 17, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C. Regulating Retinoic Acid Availability during Development and Regeneration: The Role of the CYP26 Enzymes. J. Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osanai, M.; Takasawa, A.; Takasawa, K.; Kyuno, D.; Ono, Y.; Magara, K. Retinoic acid metabolism in cancer: Potential feasibility of retinoic acid metabolism blocking therapy. Med. Mol. Morphol. 2023, 56, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sayáns, M.; Chamorro-Petronacci, C.M.; Bravo, S.B.; Padín-Iruegas, M.E.; Guitián-Fernández, E.; Barros-Angueira, F.; Quintas-Rey, R.; García-García, A. Genetic linkage analysis of head and neck cancer in a Spanish family. Oral Dis. 2024, 30, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrivankova, V.W.; Richmond, R.C.; Woolf, B.A.R.; Yarmolinsky, J.; Davies, N.M.; Swanson, S.A.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Timpson, N.J.; Dimou, N.; et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA 2021, 326, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandara-Vila, P.; Perez-Sayans, M.; Suarez-Penaranda, J.; Gallas-Torreira, M.; Somoza-Martin, J.; Lopez, R.; Blanco-Carrion, A.; Garcia-Garcia, A. Survival study of leukoplakia malignant transformation in a region of northern Spain. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2018, 23, e413–e420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Zorrilla, S.; Lorenzo-Pouso, A.I.; Fais, S.; Logozzi, M.A.; Mizzoni, D.; Di Raimo, R.; Giuliani, A.; García-García, A.; Pérez-Jardón, A.; Ortega, K.L.; et al. Increased Plasmatic Levels of Exosomes Are Significantly Related to Relapse Rate in Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Cohort Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 5693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, M.A.; Chen, N.; Sparks, S.; Napoli, J.L. Quantification of endogenous retinoic acid in limited biological samples by LC/MS/MS. Biochem. J. 2005, 388, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayáns, M.P.; Petronacci, C.M.C.; Pouso, A.I.L.; Iruegas, E.P.; Carrión, A.B.; Peñaranda, J.M.S.; García, A.G. Comprehensive Genomic Review of TCGA Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas (HNSCC). J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro-Petronacci, C.M.; De Mendoza, I.M.L.-I.; Suarez-Peñaranda, J.M.; Padin-Iruegas, E.; Blanco-Carrion, A.; Lorenzo-Pouso, A.I.; Ortega, K.L.; Pérez-Sayáns, M. Immunohistochemical Characterization of Bcl-2 in Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders. AIMM Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2021, 29, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Zhong, R.; Tian, J.; Li, J.; Zhai, K.; Ke, J.; Lou, J.; Chen, W.; Zhu, B.; Shen, N.; et al. Exome-wide analyses identify low-frequency variant in CYP26B1 and additional coding variants associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechien, J.R.; Burns, J.A.; Akst, L.M. The Use of 532-Nanometer-Pulsed Potassium-Titanyl-Phosphate (KTP) Laser in Laryngology: A Systematic Review of Current Indications, Safety, and Voice Outcomes. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021, 100, 4S–13S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaia, G.; Bellisario, A.; Pampena, R.; Pippi, R.; Romeo, U. Oral Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia: Progression to Malignancy and Clinical Implications. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; Ray, A.; Singh, R.; Mondal, P.; Basu, A.; De Sarkar, N.; Majumder, M.; Maiti, G.; Baral, A.; Jha, G.N.; et al. Sequence and expression variations in 23 genes involved in mitochondrial and non-mitochondrial apoptotic pathways and risk of oral leukoplakia and cancer. Mitochondrion 2015, 25, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongan, N.P.; Gudas, L.J. Diverse actions of retinoid receptors in cancer prevention and treatment. Differentiation 2007, 75, 853–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poveda-Roda, R.; Bagan, J.V.; Jiménez-Soriano, Y.; Díaz-Fernández, J.-M.; Gavaldá-Esteve, C. Retinoids and proliferative verrucous leukoplakia (PVL). A preliminary study. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2010, 15, e3–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, V.d.M.; Laureano, N.K.; Frank, L.A.; Rados, P.V.; Visioli, F. Chemoprevention in oral leukoplakia: Challenges and current landscape. Front. Oral Health 2023, 4, 1191347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorsky, M.; Epstein, J.B. The effect of retinoids on premalignant oral lesions: Focus on topical therapy. Cancer 2002, 95, 1258–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, A.; Liu, J. Chemoprevention of oral cancer in leukoplakia patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2017, 67, 1415–1419. [Google Scholar]
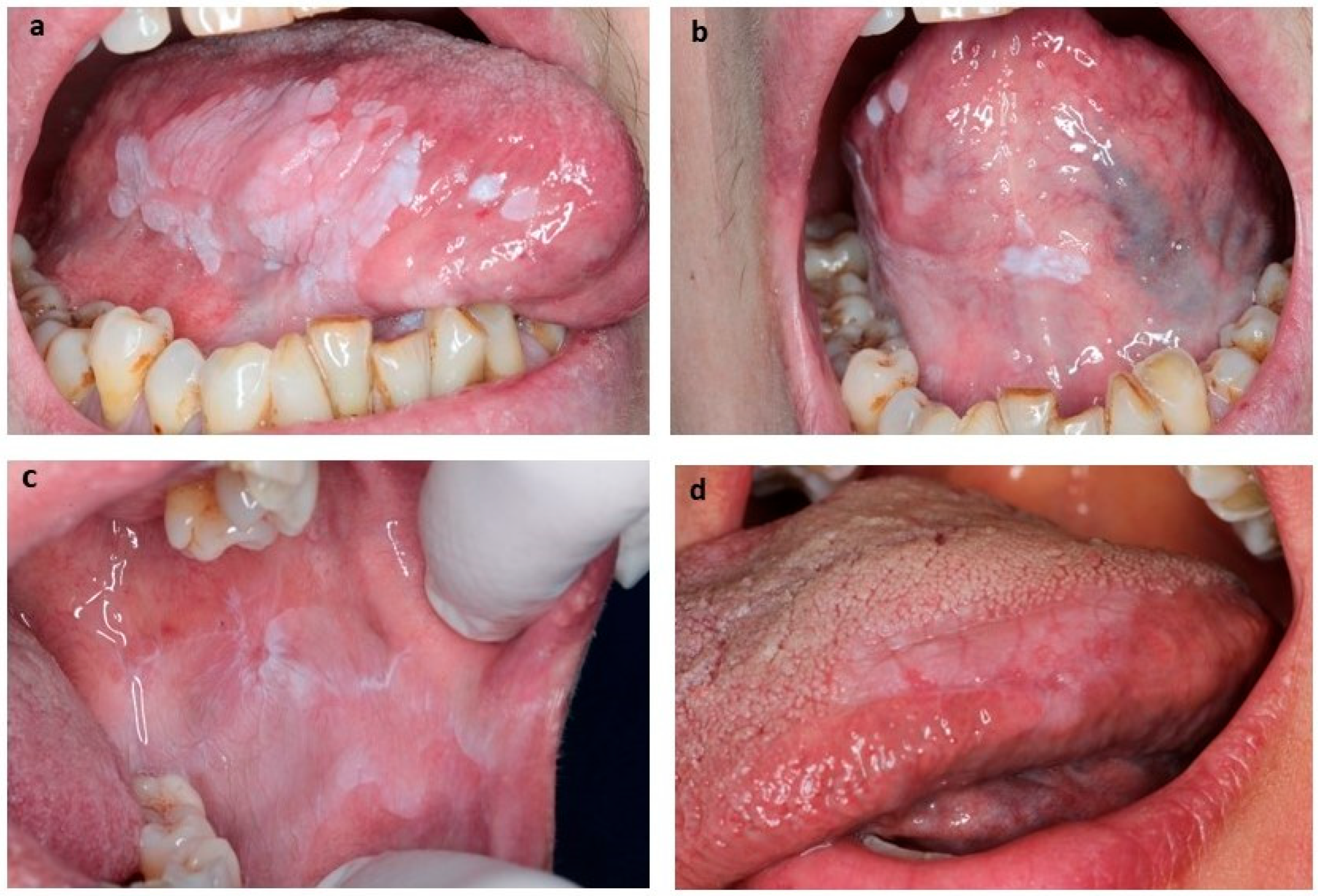
| Clinical Variable | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Group | |
| Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia (PVL) | 9 (25.0%) |
| Oral Leukoplakia (OL) | 10 (27.8%) |
| Control | 17 (47.2%) |
| Sex | |
| Male | 15 (41.7%) |
| Female | 21 (58.3%) |
| Tobacco Use | |
| Non-smoker | 21 (58.3%) |
| Smoker | 5 (13.9%) |
| Ex-smoker | 10 (27.8%) |
| Alcohol Consumption | |
| Non-drinkers | 18 (50.0%) |
| Moderate drinkers | 12 (33.3%) |
| Heavy drinkers | 6 (16.7%) |
| Malignant Transformation | |
| No | 17 (85.0%) |
| Yes | 3 (15.0%) |
| Patient ID | Gender | Smoking Status | Alcohol Use | Anatomical Site | Clinical Diagnosis | Histopathological Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVL Group (N = 9) | ||||||
| PVL001 | Female | Smoker | Drinker | Buccal Mucosa, Lateral tongue | PVL | EHK |
| PVL002 | Female | Smoker | Drinker | Buccal Mucosa, Lateral tongue | PVL | Moderate OED |
| PVL003 | Male | Non-smoker | Drinker | Alveolar ridge, Lateral tongue | PVL | Mild OED |
| PVL004 | Female | Non-smoker | Non-drinker | Lateral tongue, Gingiva | PVL | Mild OED |
| PVL005 * | Female | Non-smoker | Non-drinker | Gingiva, Soft palate | PVL | Severe OED |
| PVL006 | Female | Non-smoker | Non-drinker | Gingiva, Buccal mucosa | PVL | EHK |
| PVL007 * | Female | Smoker | Non-drinker | Alveolar ridge | PVL | Severe OED |
| PVL008 | Male | Smoker | Drinker | Gingiva, Soft palate | PVL | Mild OED |
| PVL009 * | Female | Smoker | Non-drinker | Buccal mucosa, Gingiva | PVL | Severe OED |
| OL Group (N = 10) | ||||||
| OL001 | Female | Non-smoker | Non-drinker | Lateral tongue | OL | Moderate OED |
| OL002 | Female | Smoker | Non-drinker | Lateral tongue | OL | Mild OED |
| OL003 | Female | Non-smoker | Non-drinker | Ventral tongue | OL | Moderate OED |
| OL004 | Male | Smoker | Non-drinker | Buccal mucosa | OL | Mild OED |
| OL005 | Female | Smoker | Non-drinker | Buccal mucosa | OL | Mild OED |
| OL006 | Female | Non-smoker | Non-drinker | Buccal mucosa | OL | Moderate OED |
| OL007 | Female | Smoker | Non-drinker | Lateral tongue | OL | Mild OED |
| OL008 | Male | Smoker | Non-drinker | Buccal mucosa | OL | Mild OED |
| OL009 | Male | Smoker | Drinker | Floor of mouth | OL | Mild OED |
| OL010 | Male | Smoker | Non-drinker | Lateral tongue | OL | Moderate OED |
| Control Group (N = 17) | ||||||
| CTRL001 | Female | Non-smoker | Non-drinker | – | Control | Normal |
| CTRL002 | Male | Ex-smoker | Moderate drinker | – | Control | Normal |
| CTRL003 | Female | Non-smoker | Non-drinker | – | Control | Normal |
| CTRL004 | Male | Ex-smoker | Non-drinker | – | Control | Normal |
| CTRL005 | Female | Non-smoker | Moderate drinker | – | Control | Normal |
| CTRL006 | Male | Smoker | Drinker | – | Control | Normal |
| CTRL007 | Female | Non-smoker | Non-drinker | – | Control | Normal |
| CTRL008 | Male | Ex-smoker | Moderate drinker | – | Control | Normal |
| CTRL009 | Female | Non-smoker | Non-drinker | – | Control | Normal |
| CTRL010 | Male | Ex-smoker | Non-drinker | – | Control | Normal |
| CTRL011 | Female | Smoker | Moderate drinker | – | Control | Normal |
| CTRL012 | Male | Ex-smoker | Drinker | – | Control | Normal |
| CTRL013 | Female | Non-smoker | Non-drinker | – | Control | Normal |
| CTRL014 | Male | Ex-smoker | Moderate drinker | – | Control | Normal |
| CTRL015 | Female | Non-smoker | Non-drinker | – | Control | Normal |
| CTRL016 | Male | Smoker | Drinker | – | Control | Normal |
| CTRL017 | Female | Smoker | Non-drinker | – | Control | Normal |
| Variable | OL | PVL | Control | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group comparison | ||||
| Overall (N) | 18 | 14 | 30 | |
| Mean (SD) | 2.17 (0.39) | 2.64 (0.55) | 2.65 (0.92) | 0.009 * |
| Range | 1.75–3.09 | 1.95–3.95 | 1.45–4.76 | 0.039 †, 0.953 ‡ |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 1.69 (0.67) [N = 5] | 2.23 (0.51) [N = 3] | 2.82 (0.88) [N = 7] | 0.105 |
| Female | 2.31 (0.32) [N = 5] | 2.41 (0.84) [N = 6] | 2.24 (0.98) [N = 10] | 0.743, 0.231 |
| Tobacco | ||||
| Non-smoker | 2.05 (0.21) [N = 5] | 2.29 (0.99) [N = 5] | 2.54 (1.14) [N = 11] | 0.329 |
| Smoker | 1.44 (1.34) [N = 2] | 2.33 (0.09) [N = 3] | - | 0.892 |
| Ex-smoker | 2.28 (0.41) [N = 3] | 2.72 [N = 1] | 2.38 (0.57) [N = 6] | 0.756 |
| Alcohol | ||||
| Non-drinker | 2.11 (0.39) [N = 6] | 2.52 (0.23) [N = 4] | 2.48 (1.10) [N = 9] | 0.478 |
| Moderate drinker | 1.95 (0.18) [N = 2] | 2.81 (0.41) [N = 3] | 2.77 (0.74) [N = 6] | 0.387 |
| Heavy drinker | 2.40 (0.97) [N = 2] | 2.71 (0.55) [N = 2] | 2.90 (0.56) [N = 2] | 0.421 |
| Treatment | ||||
| Follow-up | 2.03 (0.72) [N = 7] | 1.99 (0.42) [N = 2] | - | 0.813 |
| Laser | 1.92 (0.13) [N = 3] | 2.24 (1.05) [N = 3] | - | 0.629 |
| Exeresis | - | 2.62 (0.61) [N = 4] | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chamorro-Petronacci, C.M.; Pérez-Jardón, A.; Bravo, S.B.; Gándara-Vila, P.; Blanco-Carrión, A.; Avila-Granizo, Y.V.; Lorenzo-Pouso, A.I.; Prieto-Barros, S.A.; Pérez-Sayáns, M. Retinoic Acid Profiles in Proliferative Verrucous Versus Homogeneous Leukoplakia: A Preliminary Nested Case–Control Study. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081881
Chamorro-Petronacci CM, Pérez-Jardón A, Bravo SB, Gándara-Vila P, Blanco-Carrión A, Avila-Granizo YV, Lorenzo-Pouso AI, Prieto-Barros SA, Pérez-Sayáns M. Retinoic Acid Profiles in Proliferative Verrucous Versus Homogeneous Leukoplakia: A Preliminary Nested Case–Control Study. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(8):1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081881
Chicago/Turabian StyleChamorro-Petronacci, Cintia M., Alba Pérez-Jardón, Susana B. Bravo, Pilar Gándara-Vila, Andrés Blanco-Carrión, Yajaira Vanessa Avila-Granizo, Alejandro I. Lorenzo-Pouso, Sara A. Prieto-Barros, and Mario Pérez-Sayáns. 2025. "Retinoic Acid Profiles in Proliferative Verrucous Versus Homogeneous Leukoplakia: A Preliminary Nested Case–Control Study" Biomedicines 13, no. 8: 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081881
APA StyleChamorro-Petronacci, C. M., Pérez-Jardón, A., Bravo, S. B., Gándara-Vila, P., Blanco-Carrión, A., Avila-Granizo, Y. V., Lorenzo-Pouso, A. I., Prieto-Barros, S. A., & Pérez-Sayáns, M. (2025). Retinoic Acid Profiles in Proliferative Verrucous Versus Homogeneous Leukoplakia: A Preliminary Nested Case–Control Study. Biomedicines, 13(8), 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081881








