Efficacy of Combined Oral Isotretinoin and Desloratadine or Levocetirizine vs. Isotretinoin Monotherapy in Treating Acne Vulgaris: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Extracted Variables
2.4. Data Collection Process
2.5. Endpoints
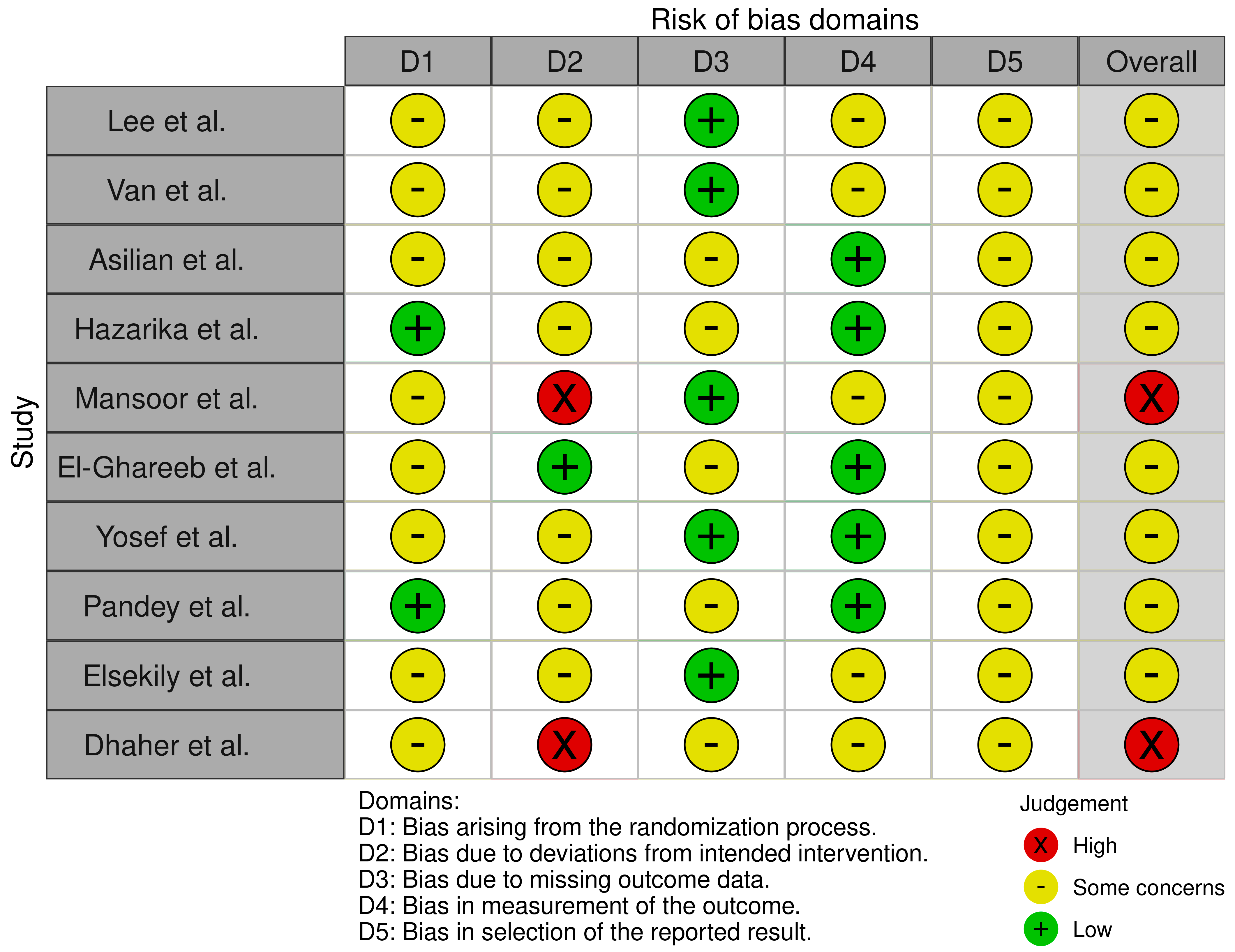
2.6. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Certainty of Evidence
3. Results
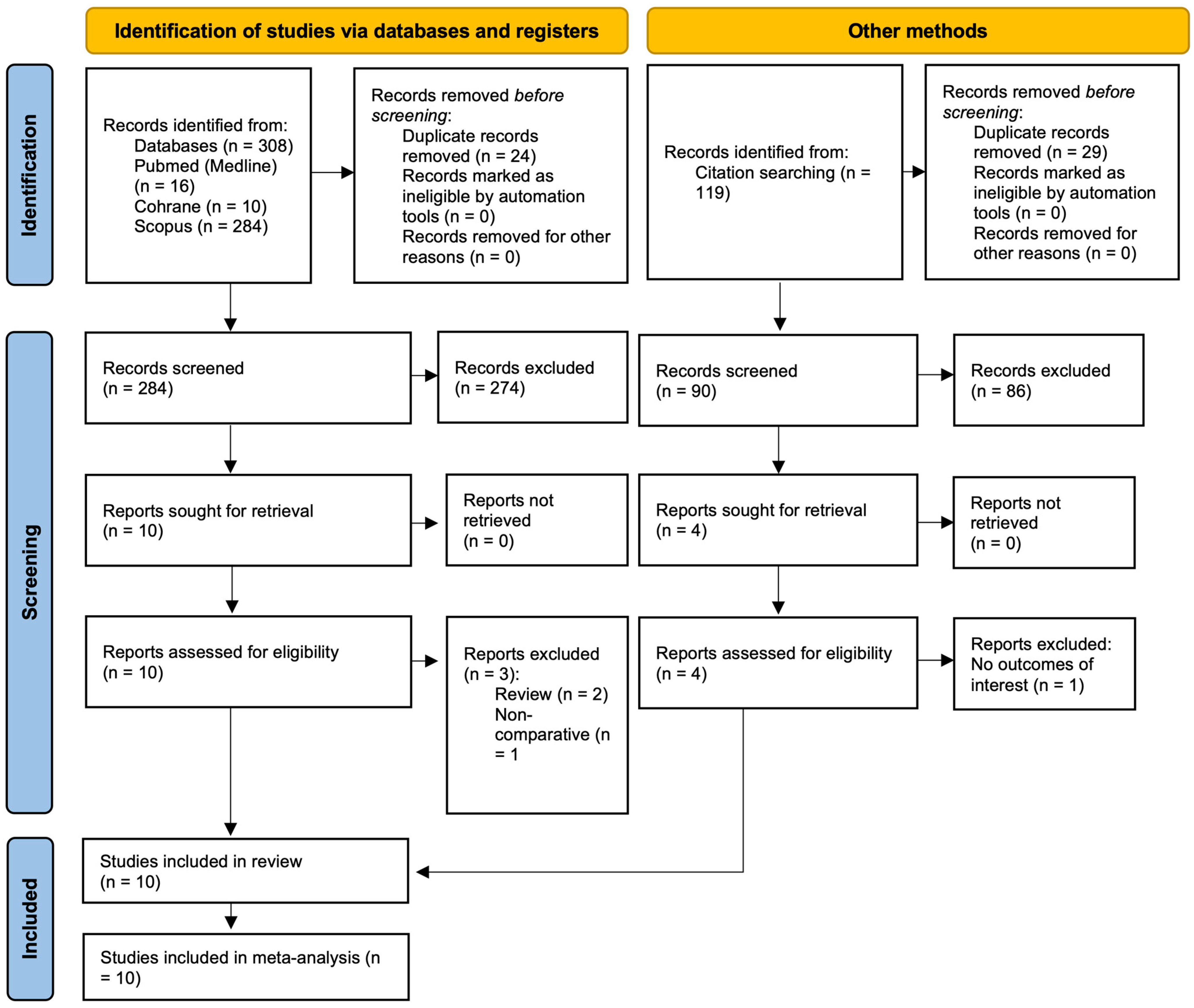
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Study Characteristics
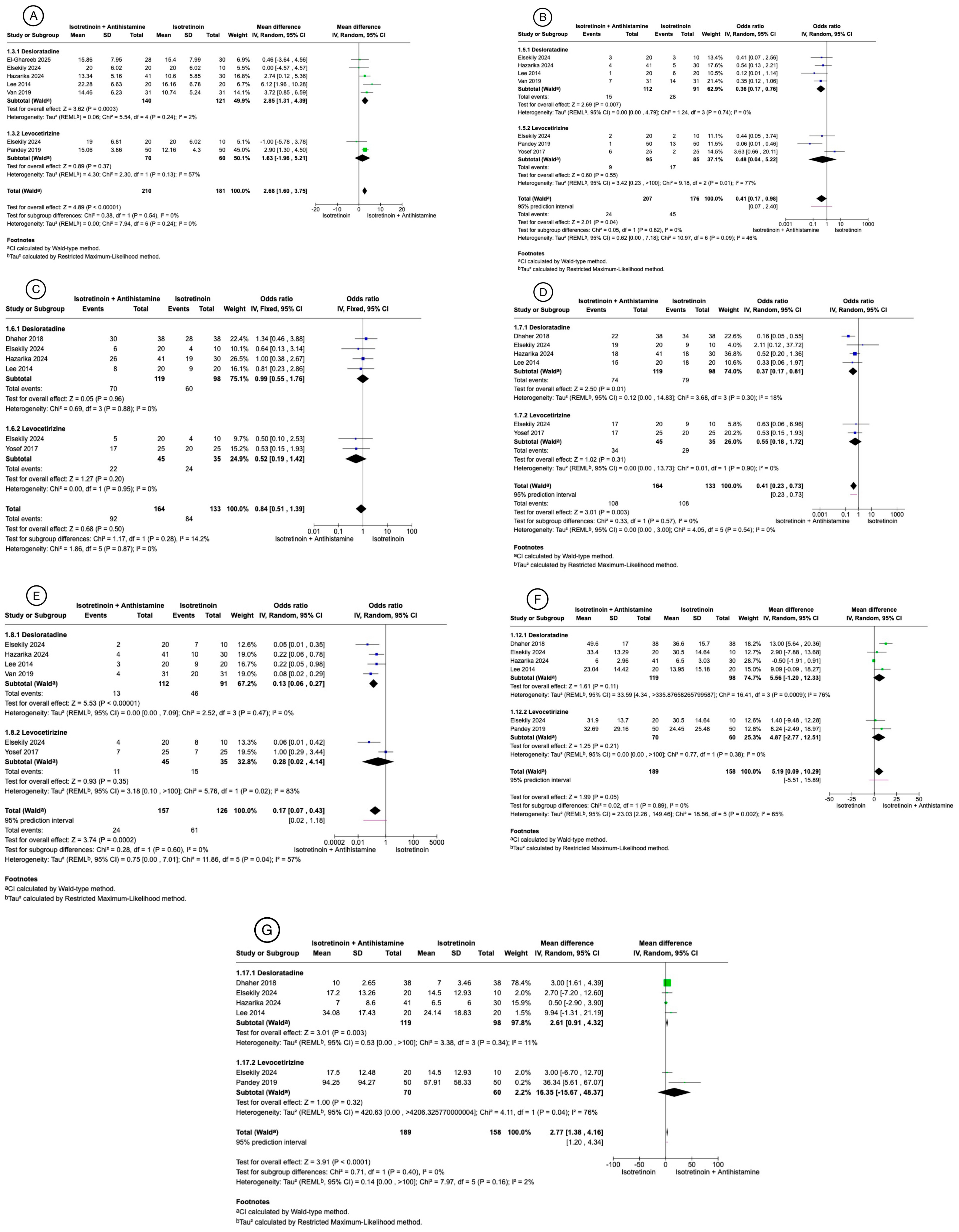
3.3. Meta-Analysis Results
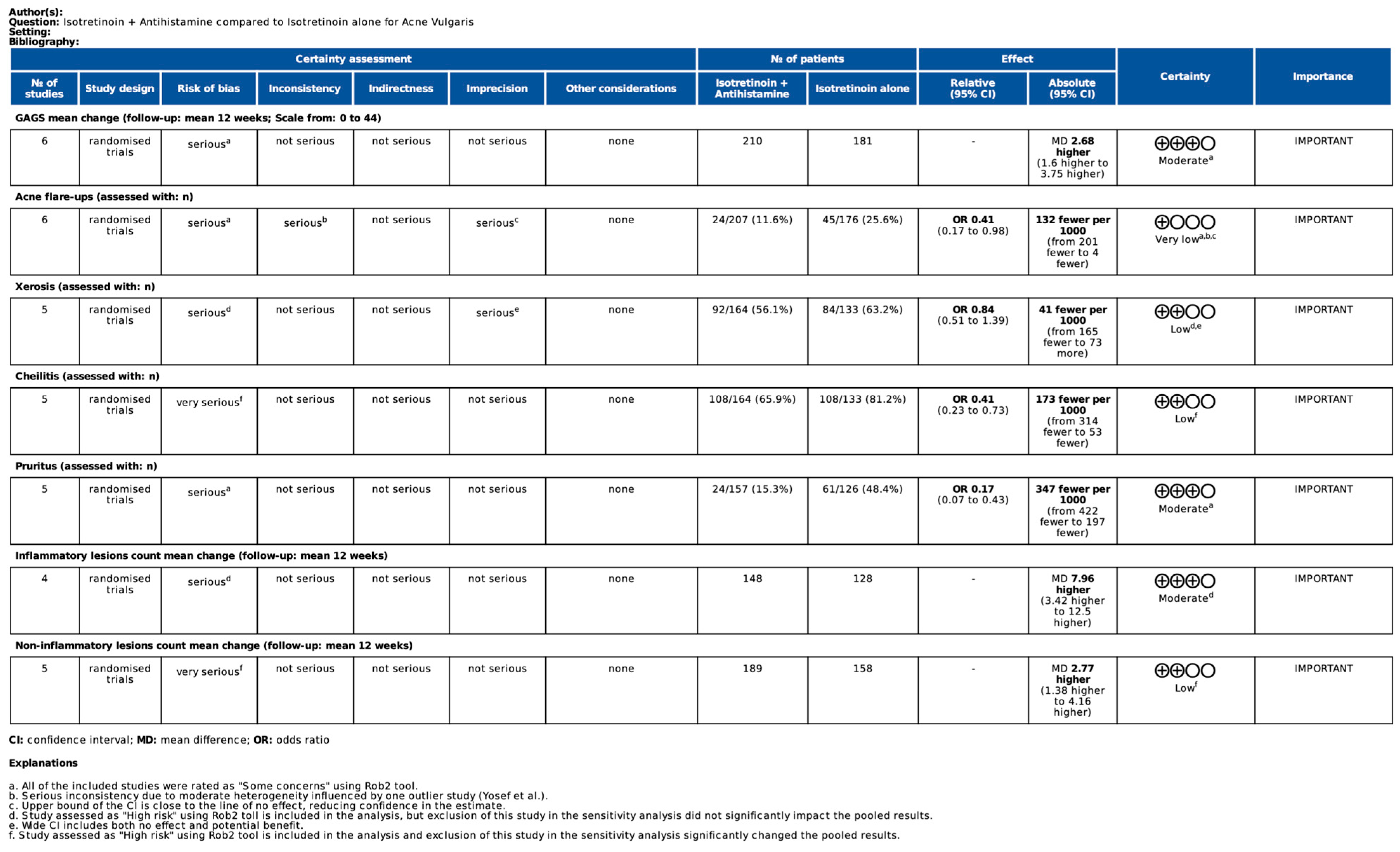
3.3.1. Global Acne Grading Scale Mean Change from Baseline
3.3.2. Side Effects
3.3.3. Inflammatory Lesions Count Mean Change from Baseline
3.3.4. Non-Inflammatory Lesion Count Mean Change from Baseline
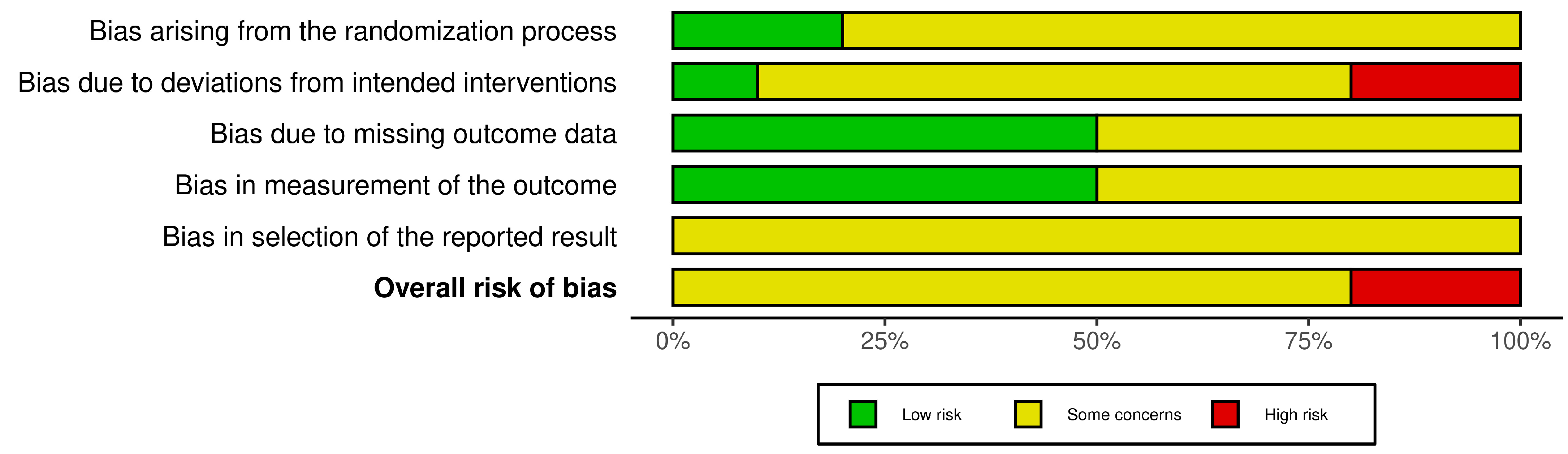
3.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
3.5. Publication Bias
3.6. Certainty of Evidence
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhate, K.; Williams, H. Epidemiology of acne vulgaris. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 168, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichenfield, D.Z.; Sprague, J.; Eichenfield, L.F. Management of Acne Vulgaris. JAMA 2021, 326, 2055–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, O.; Bewley, A. Is it really ever ‘just acne’? Considering the psychodermatology of acne. Br. J. Dermatol. 2023, 189, i11–i16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimkhani, C.; Dellavalle, R.P.; Coffeng, L.E.; Flohr, C.; Hay, R.J.; Langan, S.M.; Nsoesie, E.O.; Ferrari, A.J.; Erskine, H.E.; Silverberg, J.I.; et al. Global Skin Disease Morbidity and Mortality. JAMA Dermatol. 2017, 153, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, R.V.; Yeung, H.; Cheng, C.E.; Cook-Bolden, F.; Desai, S.R.; Druby, K.M.; Freeman, E.E.; Keri, J.E.; Gold, L.F.S.; Tan, J.K.; et al. Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2024, 90, 1006.e1–1006.e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biset, N.; Lelubre, M.; Senterre, C.; Amighi, K.; Bugnon, O.; Schneider, M.P.; De Vriese, C. Assessment of medication adherence and responsible use of isotretinoin and contraception through Belgian community pharmacies by using pharmacy refill data. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2018, 12, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelle, E.; McCarthy, J.; Seltmann, H.; Huang, X.; Mammone, T.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Maes, D. Identification of Histamine Receptors and Reduction of Squalene Levels by an Antihistamine in Sebocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.; Kornmehl, H.; Tan, X. Antihistamines reduce initial flaring and speed improvement during isotretinoin treatment for acne: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAAD Rev. 2025, 3, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrurodzi, D.S.; Thadanipon, K.; Rattanasiri, S.; Thakkinstian, A. Antihistamine as an adjunctive treatment in acne vulgaris: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian J. Soc. Humanit. 2023, 2, 1504–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, H.M.; Barbosa, L.M.; Silva, V.C.; Araujo, B.; Pinto, L.R.; de Oliveira, L.M.L. The role of antihistamines in acne treatment: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis of randomized controlled trials. JAAD Rev. 2024, 2, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Chang, I.; Lee, Y.; Kim, C.; Seo, Y.; Lee, J.; Im, M. Effect of antihistamine as an adjuvant treatment of isotretinoin in acne: A randomized, controlled comparative study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 28, 1654–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, T.N.; Thi, L.D.; Trong, H.N.; Van, T.C.; Minh, T.T.; Minh, P.P.T.; Huu, N.D.; Cam, V.T.; Le Huyen, M.; Hau, K.T.; et al. Efficacy of Oral Isotretinoin in Combination with Desloratadine in the Treatment of Common Vulgaris Acne in Vietnamese Patients. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asilian, A.; Abedini, M.; Iraji, F.; Jahanshahi, A. Comparing the Efficacy of Oral Isotretinoin Alone and in Combination with Desloratadine in Treating Moderate to Severe Acne Vulgaris: A Randomized Clinical Tri-al. Iran. J. Dermatol. 2024, 27, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazarika, N.; Yadav, P.; Bagri, M.; Chandrasekaran, D.; Bhatia, R. Oral isotretinoin with desloratadine compared with oral isotretinoin alone in the treatment of moderate to severe acne: A randomized, assessor-blinded study. Int. J. Dermatol. 2024, 63, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansoor, M. Efficacy of Oral Isotretinoin in Combination with Desloratadine versus Oral Isotretinoin Alone in the Treatment of Moderate Acne Vulgaris. J. Pak. Assoc. Dermatol. 2024, 34. Available online: https://www.jpad.com.pk/index.php/jpad/article/view/2628 (accessed on 24 July 2025).
- El-Ghareeb, M.I.; Kandeel, A.H.; Khayrullah, N.M. Efficacy and safety of combined oral isotretinoin and desloratadine vs. isotretinoin alone in acne vulgaris: A comparative study. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2025, 317, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosef, A.; Dawoud, N.M.; Gharib, K. Preliminary evaluation of the clinical efficacy of antihistamines as an adjuvant treatment to isotretinoin for acne vulgaris. J. Egypt. Women’s Dermatol. Soc. 2017, 14, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, D.; Agrawal, S. Efficacy of Isotretinoin and Antihistamine versus Isotretinoin Alone in the Treatment of Moderate to Severe Acne: A Randomised Control Trial. Kathmandu Univ. Med. J. 2019, 17, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Elsekily, E.M.; Elgmal, E.; Aboelwafa, H.O. Comparative study between Isotretinoin alone versus Isotretinoin combined with either Levocetirizine or Desloratadine in the treatment of acne Vulgaris. Int. J. Med. Arts 2024, 6, 5236–5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaher, S.; Jasim, Z.M. The adjunctive effect of desloratadine on the combined azithromycin and isotretinoin in the treatment of severe acne: Randomized clinical trial. J. Dermatol. Dermatol. Surg. 2018, 22, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohaninasab, M.; Rasi, A.; Behrangi, E.; Nahad, Z.M. Efficacy of fixed daily 20 mg of isotretinoin in moderate to severe scar prone acne. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2014, 3, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paichitrojjana, A. Oral Isotretinoin and Its Uses in Dermatology: A Review. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2023, 17, 2573–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnik, B.C. Acne Transcriptomics: Fundamentals of Acne Pathogenesis and Isotretinoin Treatment. Cells 2023, 12, 2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villani, A.; Nastro, F.; Di Vico, F.; Fabbrocini, G.; Annunziata, M.C.; Genco, L. Oral isotretinoin for acne: A complete overview. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2022, 21, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuchayi, S.M.; Alexander, T.M.; Nadkarni, A.; Feldman, S.R. Interventions to increase adherence to acne treatment. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2016, 10, 2091–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhaidat, J.; Alhuneafat, L.; Asfar, R.; Al-Qarqaz, F.; Alshiyab, D.; Alhuneafat, L. Exploring the Incidence and Risk Factors of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Severe Acne Vulgaris on Systemic Isotretinoin Therapy: Findings from a Prospective Study. Medicina 2025, 61, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pile, H.D.; Pile, P.P.; Mikkilineni, S.N. Isotretinoin. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525949/ (accessed on 24 July 2025).
- Demircay, Z.; Kus, S.; Sur, H. Predictive factors for acne flare during isotretinoin treatment. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2008, 18, 452–456. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18573721/ (accessed on 24 July 2025).
- Hsieh, C.-Y.; Tsai, T.-F. Use of H-1 Antihistamine in Dermatology: More than Itch and Urticaria Control: A Systematic Review. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 11, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnik, B.C. Isotretinoin and FoxO1: A scientific hypothesis. Dermato-Endocrinology 2011, 3, 141–165. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22110774/ (accessed on 24 July 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woźna, J.; Korecka, K.; Stępka, J.; Bałoniak, A.; Żaba, R.; Schwartz, R.A. Ryszard Acne fulminans treatment: Case report and literature review. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1450666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Cao, Z.; Wei, J.; Li, M.; Han, C.; Zhang, C. Fire needle pretreatment with 5-aminolevulinic acid photodynamic therapy combined with low-dose isotretinoin in the treatment of severe refractory nodulocystic acne. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2024, 47, 104215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, L.; Hamblin, M.R.; Wen, X. Combinations of Energy-based Devices plus isotretinoin for management of acne and acne scars: A systematic review. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2024, 23, 3090–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jongudomsombat, T.; Lee, Y.I.; Kim, J.; Oh, S.H.; Hong, J.W.; Lee, J.H. Combined use of energy-based interventions with low-dose isotretinoin for the treatment of inflammatory acne: An retrospective cohort analysis. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 4383–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Tang, L.; Yang, L.; Ye, F. Isotretinoin Combined Laser/Light-Based Treatments Versus Isotretinoin Alone for the Treatment of Acne Vulgaris: A Meta-Analysis. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2024, 24, e16639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Hadsall, S.; Ju, T.; Keri, J.E. Use of Oral Supplements and Topical Adjuvants for Isotretinoin-Associated Side Effects: A Narrative Review. Ski. Appendage Disord. 2023, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamu-O’BRien, C.; Jafferany, M.; Carniciu, S.; Abdelmaksoud, A. Psychodermatology of acne: Psychological aspects and effects of acne vulgaris. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 20, 1080–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernyshov, P.V.; Sampogna, F.; Raimondi, G.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Boffa, M.J.; Marron, S.E.; Manolache, L.; Pustišek, N.; Bettoli, V.; Koumaki, D.; et al. Development of the acne-specific quality of life questionnaire Quality of Life Relevance-Acne. JAAD Int. 2024, 16, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eicher, L.; Knop, M.; Aszodi, N.; Senner, S.; French, L.; Wollenberg, A. A systematic review of factors influencing treatment adherence in chronic inflammatory skin disease–strategies for optimizing treatment outcome. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 2253–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzi, C.; Picardi, A.; Abeni, D.; Agostini, E.; Baliva, G.; Pasquini, P.; Puddu, P.; Braga, M. Association of Dissatisfaction With Care and Psychiatric Morbidity With Poor Treatment Compliance. Arch. Dermatol. 2002, 138, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- See, J.; Goh, C.L.; Hayashi, N.; Suh, D.H.; Casintahan, F.A. Optimizing the use of topical retinoids in Asian acne patients. J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muizzuddin, N.; Hellemans, L.; Van Overloop, L.; Corstjens, H.; Declercq, L.; Maes, D. Structural and functional differences in barrier properties of African American, Caucasian and East Asian skin. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2010, 59, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathmarajah, P.; Peterknecht, E.; Cheung, K.; Elyoussfi, S.; Muralidharan, V.; Bewley, A. Acne Vulgaris in Skin of Color: A Systematic Review of the Effectiveness and Tolerability of Current Treatments. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2022, 15, 43–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Qarqaz, F.; Bodoor, K.; Baba, A.; Al-Yousef, A.; Muhaidat, J.; Alshiyab, D. Post-Acne Hyperpigmentation: Evaluation of risk factors and the use of Artificial Neural Network as a predictive classifier. Dermatol. Rep. 2021, 13, 8223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.K.; Alexis, A.F. Acne in skin of color: Practical approaches to treatment. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2010, 21, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.Y.; Hurley, K.; Moore, S.A. A Post Hoc Analysis of Efficacy Data on Sarecycline in Hispanics with Acne from Two Phase 3, Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | Country | No. of Patients | Females (%) | Mean Age (SD) | Isotretinoin Dose | Anthistamine Dose | Follow-Ups |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lee [11] 2014 | South Korea | 40 | 60% | 21.45 (2.22) | I–20 mg/day C–20 mg/day | Desloratadine 5 mg/day | Week 2, 4, 8, 12 |
| Van [12] 2019 | Vietnam | 62 | 63.9% | 21.98 (4.12) | I–20 mg/day C–20 mg/day | Desloratadine 5 mg/day | Week 2, 4, 8, 12, 16 |
| Asilian [13] 2024 | Iran | 56 | N/A | 22.29 (2.82) | I–20 mg every other day C–20 mg every other day | Desloratadine 5 mg/day | Week 8, 16, 24 |
| Hazarika [14] 2024 | India | 71 | 46.67% | 20.25 (3.72) | I–0.3 mg/kg/day C–0.3 mg/kg/day | Desloratadine 5 mg/day | Week 4, 8, 12 |
| Mansoor [15] 2024 | Pakistan | 108 | 73.1% | 22.1 (1.26) | I–20 mg/day C–20 mg/day | Desloratadine 5 mg/day | Week 4, 8, 12, 16 |
| El-Ghareeb [16] 2025 | Egypt | 58 | 52.5% | 18.59 (0.91) | I–0.5 mg/kg/day C–0.5 mg/kg/day I–0.25 mg/kg/day C–0.25 mg/kg/day | Desloratadine 5 mg/day | Week 4, 8, 12 |
| Yosef [17] 2017 | Egypt | 50 | 64% | 19.38 (1.93) | I–0.4–0.6 mg/kg/day C–0.4–0.6 mg/kg/day | Levocetirizine 5mg/day | Week 4, 8, 12, 16 |
| Pandey [18] 2019 | India | 100 | 66% | 21.67 (4.05) | I–0.5–0.6 mg/kg/day C | Levocetirizine 5 mg/day | Week 4, 8, 12 |
| Elsekily [19] 2024 | Egypt | 60 | 60% | 21.1 (1.8) | I–0.25–1 mg/kg/day C–0.25–1 mg/kg/day | Levocetirizine/Desloratadine 5 mg/day | Week 4, 12, 24 |
| Dhaher [20] 2018 | Iraq | 76 | 55% | 19.2 (NA) | I–20 mg 3x per week C–20 mg 3x per week | Desloratadine 5 mg/day | Week 4, 8, 12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Woźna, J.; Bałoniak, A.; Stępka, J.; Polańska, A.; Mojs, E.; Żaba, R. Efficacy of Combined Oral Isotretinoin and Desloratadine or Levocetirizine vs. Isotretinoin Monotherapy in Treating Acne Vulgaris: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081847
Woźna J, Bałoniak A, Stępka J, Polańska A, Mojs E, Żaba R. Efficacy of Combined Oral Isotretinoin and Desloratadine or Levocetirizine vs. Isotretinoin Monotherapy in Treating Acne Vulgaris: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(8):1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081847
Chicago/Turabian StyleWoźna, Julia, Andrzej Bałoniak, Jan Stępka, Adriana Polańska, Ewa Mojs, and Ryszard Żaba. 2025. "Efficacy of Combined Oral Isotretinoin and Desloratadine or Levocetirizine vs. Isotretinoin Monotherapy in Treating Acne Vulgaris: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" Biomedicines 13, no. 8: 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081847
APA StyleWoźna, J., Bałoniak, A., Stępka, J., Polańska, A., Mojs, E., & Żaba, R. (2025). Efficacy of Combined Oral Isotretinoin and Desloratadine or Levocetirizine vs. Isotretinoin Monotherapy in Treating Acne Vulgaris: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Biomedicines, 13(8), 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081847