Small Interfering RNAs Targeting VP4, VP3, 2B, or 3A Coding Regions of Enterovirus A71 Inhibit Viral Replication In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Cultures and Viruses
2.2. RT–PCR and Viral Genome Sequencing
2.3. siRNA Design
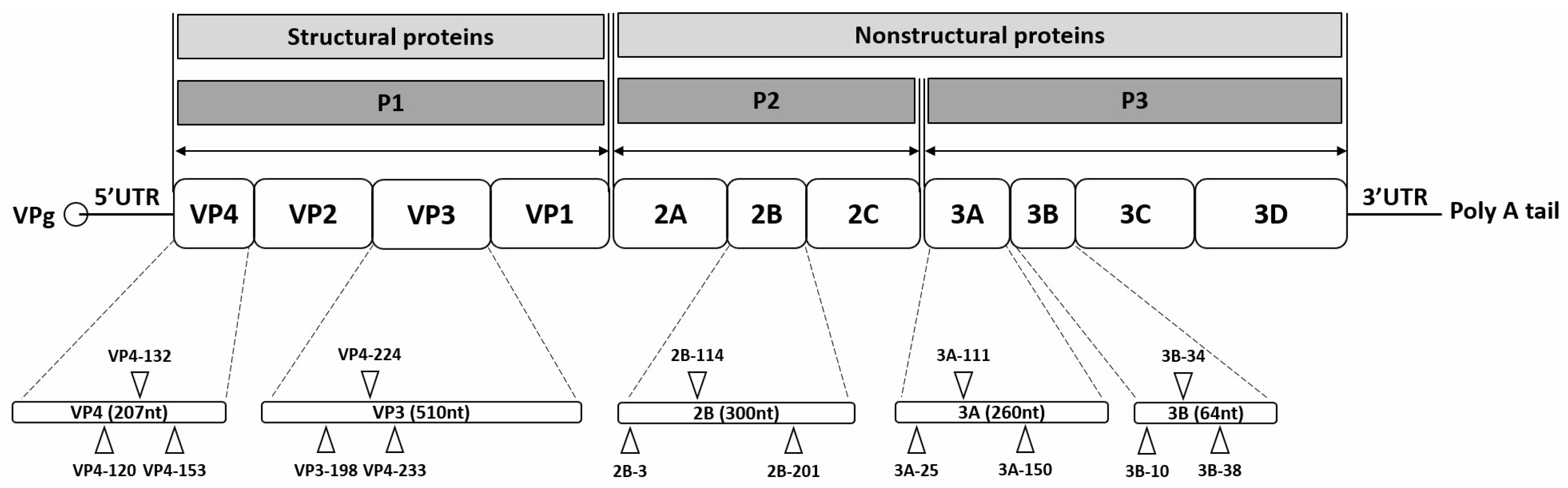
| siRNA Name | Target Nucleotide Sequence (5′-3′) | GC Ratio (%) | Target Gene | Genomic Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| scrambled control | AUUCUAUCACUAGCGUGAC | 38.1 | None | None |
| VP4-120 | CUGGAAAGCAAAGUCUCA | 40 | VP4 | 865–882 |
| VP4-132 | GUCUCAAACAAGAUCCUGA | 38.1 | VP4 | 877–895 |
| VP4-153 | AGUUUGCGAACCCUGUGAA | 42.86 | VP4 | 898–916 |
| VP3-224 | CAGUUGUGUGGAUAUUACA | 33.33 | VP3 | 2019–2037 |
| VP3-198 | GUCCUUGGCAAUCCACCAU | 47.62 | VP3 | 1993–2011 |
| VP3-233 | GGAUAUUACACCCAAUGGU | 38.1 | VP3 | 2028–2046 |
| 2B-201 | CAGCCACACUAGCUCUGAU | 47.62 | 2B | 3979–3997 |
| 2B-114 | CUGUUGAGAAGAUCUUGAA | 33.33 | 2B | 3892–3910 |
| 2B-3 | GGGUAUCUGAUUACAUCAA | 33.34 | 2B | 3781–3799 |
| 3A-150 | CACCAACUAAUGUGGAACG | 42.86 | 3A | 5203–5221 |
| 3A-111 | GACAGUACUGCAGGGAACA | 47.62 | 3A | 5164–5182 |
| 3A-25 | CAGGCCUAUAAGAAUUAGU | 33.34 | 3A | 5078–5096 |
| 3B-34 | GAAGCCCGUGUUAAGAACA | 42.86 | 3B | 5357–5375 |
| 3B-10 | UGGAGCGCCCAAGCAAAUU | 47.62 | 3B | 5333–5351 |
| 3B-38 | CCCGUGUUAAGAACAGCCA | 47.62 | 3B | 5361–5379 |
2.4. Transfection of siRNA
2.5. Flow Cytometry
2.6. Plaque Assay
2.7. Immunofluorescence
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.9. Evaluation of Cytopathic Effects and Cell Viability
2.10. Evaluation of Off-Target Effect (Activation of the Interferon Pathway)
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Design of siRNAs Against EV-A71
3.2. Optimization of siRNA Concentration to Minimize Cytotoxicity and Off-Target Effects
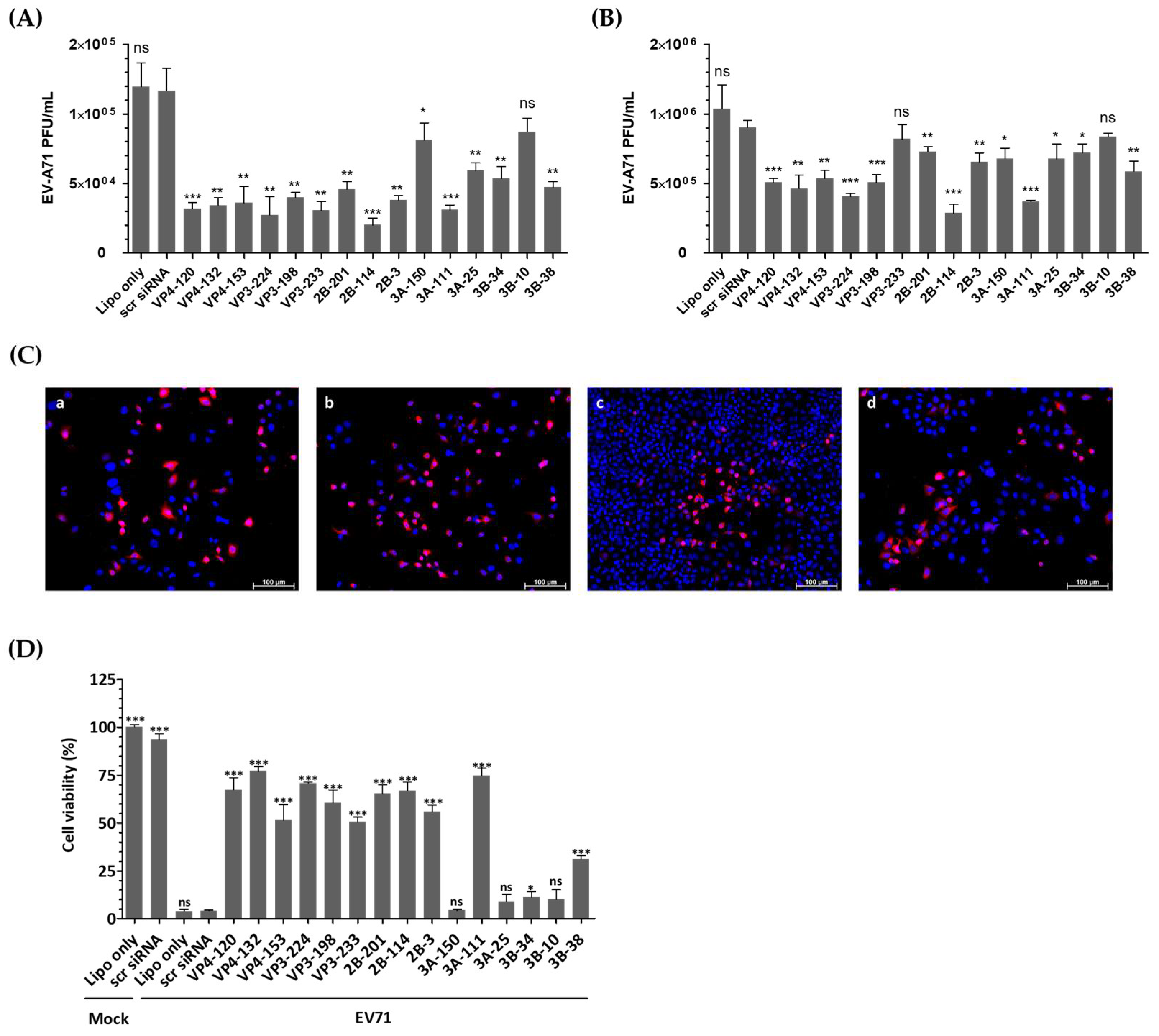
3.3. siRNA Treatments Inhibit EV-A71 Replication and Decrease Viral Protein Expression
3.4. siRNAs Delayed Cytopathic Effects and Increased the Viability of EV-A71-Infected HeLa Cells
3.5. No Activation of the Interferon Pathway When HeLa Cells Were Treated with siRNA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- McMinn, P.C. An overview of the evolution of enterovirus 71 and its clinical and public health significance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 26, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, T.; Lewthwaite, P.; Perera, D.; Cardosa, M.J.; McMinn, P.; Ooi, M.H. Virology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and control of enterovirus 71. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.M.; Ho, T.S.; Lin, H.C.; Lei, H.Y.; Wang, J.R.; Liu, C.C. Reemerging of enterovirus 71 in Taiwan: The age impact on disease severity. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 31, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, M.L.; Luo, S.T.; Chen, Y.Y.; Chung, W.Y.; Duong, V.; Dussart, P.; Chan, Y.F.; Perera, D.; Ooi, M.H.; Thao, N.T.T.; et al. Establishment of Asia-Pacific Network for Enterovirus Surveillance. Vaccine 2020, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puenpa, J.; Wanlapakorn, N.; Vongpunsawad, S.; Poovorawan, Y. The History of Enterovirus A71 Outbreaks and Molecular Epidemiology in the Asia-Pacific Region. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisbert, T.W.; Lee, A.C.; Robbins, M.; Geisbert, J.B.; Honko, A.N.; Sood, V.; Johnson, J.C.; de Jong, S.; Tavakoli, I.; Judge, A.; et al. Postexposure protection of non-human primates against a lethal Ebola virus challenge with RNA interference: A proof-of-concept study. Lancet 2010, 375, 1896–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Croyle, M.A. Emerging targets and novel approaches to Ebola virus prophylaxis and treatment. BioDrugs 2013, 27, 565–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, C.C.; Choy, K.W.; Du, Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Chung, T.K.; Tang, T. Therapeutic potentials of gene silencing by RNA interference: Principles, challenges, and new strategies. Gene 2014, 538, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gish, R.G.; Satishchandran, C.; Young, M.; Pachuk, C. RNA interference and its potential applications to chronic HBV treatment: Results of a Phase I safety and tolerability study. Antivir. Ther. 2011, 16, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebert, L.F.; Rebhan, M.A.; Crivelli, S.E.; Denzler, R.; Stoffel, M.; Hall, J. Miravirsen (SPC3649) can inhibit the biogenesis of miR-122. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, J.; Zamora, M.R.; Hodges, T.; Musk, A.W.; Sommerwerk, U.; Dilling, D.; Arcasoy, S.; DeVincenzo, J.; Karsten, V.; Shah, S.; et al. ALN-RSV01 for prevention of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after respiratory syncytial virus infection in lung transplant recipients. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2016, 35, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVincenzo, J.; Lambkin-Williams, R.; Wilkinson, T.; Cehelsky, J.; Nochur, S.; Walsh, E.; Meyers, R.; Gollob, J.; Vaishnaw, A. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of an RNAi-based therapy directed against respiratory syncytial virus. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8800–8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.W.; Hsu, Y.Y.; Yang, J.Y.; Kung, S.H. Selective inhibition of enterovirus 71 replication by short hairpin RNAs. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 325, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, A.C.; Luhur, A.; Tan, T.M.; Chow, V.T.; Poh, C.L. RNA interference against enterovirus 71 infection. Virology 2005, 341, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, E.L.; Tan, T.M.; Chow, V.T.; Poh, C.L. Enhanced potency and efficacy of 29-mer shRNAs in inhibition of Enterovirus 71. Antivir. Res. 2007, 74, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, F.; Zhao, R.; Zhao, L.; Guo, D.; Jin, Q. Identification of small interfering RNAs which inhibit the replication of several Enterovirus 71 strains in China. J. Virol. Methods 2009, 159, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.X.; Nie, X.J.; Lei, Y.F.; Ma, C.F.; Xu, D.L.; Li, B.; Xu, Z.K.; Zhang, G.C. The highly conserved 5’ untranslated region as an effective target towards the inhibition of Enterovirus 71 replication by unmodified and appropriate 2’-modified siRNAs. J. Biomed. Sci. 2012, 19, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Qin, Y.; Kong, Z.; Shao, Q.; Su, Z.; Wang, S.; Chen, J. siRNA Targeting the 2Apro Genomic Region Prevents Enterovirus 71 Replication In Vitro. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, E.L.; Tan, T.M.; Tak Kwong Chow, V.; Poh, C.L. Inhibition of enterovirus 71 in virus-infected mice by RNA interference. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 1931–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoll, G.J.; Melchers, W.J.; Kopecka, H.; Jambroes, G.; van der Poel, H.J.; Galama, J.M. General primer-mediated polymerase chain reaction for detection of enteroviruses: Application for diagnostic routine and persistent infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbashir, S.M.; Harborth, J.; Lendeckel, W.; Yalcin, A.; Weber, K.; Tuschl, T. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature 2001, 411, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbashir, S.M.; Lendeckel, W.; Tuschl, T. RNA interference is mediated by 21- and 22-nucleotide RNAs. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurreck, J. siRNA efficiency: Structure or sequence-that is the question. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2006, 2006, 83757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Varma, R.K.; Beauchamp, L.; Magdaleno, S.; Sendera, T.J. Selection of hyperfunctional siRNAs with improved potency and specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarzguioui, M.; Prydz, H. An algorithm for selection of functional siRNA sequences. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 316, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, A.; Leake, D.; Boese, Q.; Scaringe, S.; Marshall, W.S.; Khvorova, A. Rational siRNA design for RNA interference. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.Y.; Carmack, C.S.; Long, D.D.; Maliyekkel, A.; Shao, Y.; Roninson, I.B.; Ding, Y. A structural interpretation of the effect of GC-content on efficiency of RNA interference. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10 (Suppl. 1), S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, D.D.; Senzer, N.; Cleary, M.A.; Nemunaitis, J. Comparative assessment of siRNA and shRNA off target effects: What is slowing clinical development. Cancer Gene Ther. 2009, 16, 807–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, A.; Anderson, E.M.; Vermeulen, A.; Fedorov, Y.; Robinson, K.; Leake, D.; Karpilow, J.; Marshall, W.S.; Khvorova, A. Induction of the interferon response by siRNA is cell type- and duplex length-dependent. RNA 2006, 12, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parashar, D.; Paingankar, M.S.; Kumar, S.; Gokhale, M.D.; Sudeep, A.B.; Shinde, S.B.; Arankalle, V.A. Administration of E2 and NS1 siRNAs inhibit chikungunya virus replication in vitro and protects mice infected with the virus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Ga, Y.J.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, Y.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, C.; Yeh, J.Y. Small interfering RNA (siRNA)-based therapeutic applications against viruses: Principles, potential, and challenges. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 30, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, K.; Lakdawala, S.; Quadir, S.S.; Puri, D.; Mishra, D.K.; Joshi, G.; Sharma, S.; Choudhary, D. siRNA-Based Novel Therapeutic Strategies to Improve Effectiveness of Antivirals: An Insight. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023, 24, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, J.N.; Schaffer, D.V. Antiviral RNAi therapy: Emerging approaches for hitting a moving target. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.; Tantray, V.G.; Kirmani, A.R.; Ahangar, A.G. A review on current status of antiviral siRNA. A review on current status of antiviral siRNA. Rev. Med. Virol. 2018, 28, e1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, F.; Raghava, G.P. Designing of highly effective complementary and mismatch siRNAs for silencing a gene. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Ahn, J.; Jee, Y.; Seo, I.S.; Jeon, E.J.; Jeon, E.S.; Joo, C.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, H. Universal and mutation-resistant anti-enteroviral activity: Potency of small interfering RNA complementary to the conserved cis-acting replication element within the enterovirus coding region. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88 Pt 7, 2003–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothe, D.; Wade, E.J.; Kurreck, J. Design of small interfering RNAs for antiviral applications. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 721, 267–292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Shan, C.; Sun, Y.; Xu, P.; Zhou, H.; Yang, C.; Shi, P.Y.; Rao, Z.; Zhang, B.; et al. Crystal structure of enterovirus 71 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase complexed with its protein primer VPg: Implication for a trans mechanism of VPg uridylylation. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 5755–5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shan, C.; Chen, C.; Xu, P.; Song, M.; Zhou, H.; Yang, C.; Xu, W.; Shi, P.Y.; et al. Enterovirus 71 VPg uridylation uses a two-molecular mechanism of 3D polymerase. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 13662–13671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.V.; Peters, J.; Mugavero, J.; Yin, J.; van Boom, J.H.; Wimmer, E. Biochemical and genetic studies of the VPg uridylylation reaction catalyzed by the RNA polymerase of poliovirus. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 891–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Franco, D.; Paul, A.V.; Wimmer, E. Tyrosine 3 of poliovirus terminal peptide VPg(3B) has an essential function in RNA replication in the context of its precursor protein, 3AB. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5669–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, D.W.; Davis, M.E. Insights into the kinetics of siRNA-mediated gene silencing from live-cell and live-animal bioluminescent imaging. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoszewski, R.; Sikorski, A.F. Editorial focus: Understanding off-target effects as the key to successful RNAi therapy. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett 2019, 24, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sledz, C.A.; Holko, M.; de Veer, M.J.; Silverman, R.H.; Williams, B.R. Activation of the interferon system by short-interfering RNAs. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.; Li, M.M.H. All About the RNA: Interferon-Stimulated Genes That Interfere with Viral RNA Processes. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 605024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.H.; Lau, K.S.; Kuo, R.L.; Horng, J.T. dsRNA Binding Domain of PKR Is Proteolytically Released by Enterovirus A71 to Facilitate Viral Replication. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, X.; Chen, H.; Xing, Y. Role of protein Post-translational modifications in enterovirus infection. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1341599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ga, Y.J.; Go, Y.Y.; Yeh, J.-Y. Small Interfering RNAs Targeting VP4, VP3, 2B, or 3A Coding Regions of Enterovirus A71 Inhibit Viral Replication In Vitro. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071760
Ga YJ, Go YY, Yeh J-Y. Small Interfering RNAs Targeting VP4, VP3, 2B, or 3A Coding Regions of Enterovirus A71 Inhibit Viral Replication In Vitro. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(7):1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071760
Chicago/Turabian StyleGa, Yun Ji, Yun Young Go, and Jung-Yong Yeh. 2025. "Small Interfering RNAs Targeting VP4, VP3, 2B, or 3A Coding Regions of Enterovirus A71 Inhibit Viral Replication In Vitro" Biomedicines 13, no. 7: 1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071760
APA StyleGa, Y. J., Go, Y. Y., & Yeh, J.-Y. (2025). Small Interfering RNAs Targeting VP4, VP3, 2B, or 3A Coding Regions of Enterovirus A71 Inhibit Viral Replication In Vitro. Biomedicines, 13(7), 1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071760







