Abstract
Background/Objectives: Neutropenia is a common adverse effect of oral valganciclovir (VGCV) treatment in infants with congenital cytomegalovirus infection (CCMVI), with an estimated prevalence of 20%. However, its clinical course and associated factors, including the influence of VGCV dosage, remain inadequately characterized. Methods: We conducted a single-center retrospective cohort study of infants treated with VGCV for symptomatic congenital CMV infection (CCMVI) at the Kobe University Hospital between 1 April 2009 and 31 March 2017. Detailed descriptive analyses of neutropenia were performed, and factors associated with its onset were explored using univariable logistic regression analyses. Results: A total of 31 patients were included, and neutropenia occurred in 35% of them during the 6-week treatment period. Its occurrence was observed throughout the treatment course, with no substantial difference in incidence between the 16 mg/kg/day and 32 mg/kg/day dosing groups. Neutropenia was more likely to occur in infants with shorter gestational age. Conclusions: Neutropenia occurred in 35% of patients during 6 weeks of VGCV treatment, irrespective of dosage, and was more common in those with shorter gestational age.
1. Introduction
Congenital cytomegalovirus infection (CCMVI) is the most common congenital infection caused by transplacental transmission, with a reported incidence of 0.3–0.7% [1,2,3]. Approximately 40–60% of symptomatic cases of CCMVI develop neurodevelopmental sequelae, with sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) being the most common, followed by cognitive impairment and cerebral palsy [4]. In recent years, valganciclovir (VGCV) treatment for CCMVI in the early postnatal period has been shown to improve neurodevelopmental outcomes [5,6,7,8,9,10]. Previously, our group revealed that VGCV treatment for either 6 weeks or 6 months could improve mild-to-moderate SNHL but was ineffective for severe cases [11]. More recently, we showed that initiation of VGCV treatment within 2 months of age was as effective as initiation of treatment within 1 month, which is the classical treatment time limit [12].
The known side effects of oral VGCV treatment include neutropenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia due to myelosuppression, as well as liver dysfunction, pancreatitis, and renal dysfunction [5,13,14]. Neutropenia has been reported to occur in approximately 20% of treated cases [5,14], and a substantial amount of these cases require drug cessation owing to the high risk of serious infection. Based on the results of recent analyses from our multi-center prospective studies using a 6-month regimen of VGCV dosed at 32 mg/kg, 62.5% of infants experienced their lowest neutrophil count within the first 6 weeks of treatment [15]. Meanwhile, reducing the VGCV dosage has been suggested as a treatment approach for neutropenia; however, its effectiveness in alleviating neutropenia has yet to be clarified [16].
In contrast, a case report indicated VGCV treatment was successfully completed by administering granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) to account for neutropenia [17], implying that neutropenia can be controlled by G-CSF. Nevertheless, there is no clear correlation between the degree of neutropenia and blood concentration of VGCV [12], and the changes in neutrophil count during VGCV treatment remain to be elucidated.
This study aims to provide a detailed descriptive analysis of neutropenia and to explore factors related to its onset, including the potential association between valganciclovir (VGCV) dosage and neutropenia.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients
This single-center retrospective cohort study included infants who were treated with VGCV for symptomatic CCMVI at the Kobe University Hospital from 1 April 2009 to 31 March 2017. Infants aged > 60 days at the start of VGCV treatment, those with other congenital anomalies, and those who deviated from the treatment protocol described below were excluded from the study. For each case, patient background, changes in neutrophil count up to 6 weeks consecutively after the start of VGCV therapy, history of suspension/reduction/discontinuation of VGCV treatment, G-CSF use, and CMV DNA titers in the plasma and urine before treatment were collected from medical records. As part of a prospective cohort study for universal congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) screening at the Kobe University Hospital [18], we examined CMV DNA from urine samples collected on filter paper within the first week of life from all newborns born at our hospital and measured urine viral loads using quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) in neonates suspected of having CCMVI [19]. To clarify the characteristics of the study population, background information on asymptomatic CCMVI infants will also be presented as external control data. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine (approval numbers: 923, 1214), and written informed consent was obtained from the guardians of all participants.
2.2. Diagnostic Criteria
CCMVI was diagnosed based on a positive CMV-DNA qRT-PCR result from a liquid urine sample within 21 days of birth. According to our previous reports [19,20,21], symptomatic CCMV was defined as having at least one of the following symptoms: small for gestational age (SGA) (birthweight < 10th percentile for gestational age based on sex-specific Japanese standards [22]); microcephaly (head circumference < −1.5 the standard deviation of the mean value for Japanese newborns of the same gestational age [22]); thrombocytopenia (platelet count < 1 × 105/µL); liver dysfunction (serum aspartate aminotransferase level > 100 U/L); eye complications (CMV-associated retinopathy, such as chorioretinitis, diagnosed by a pediatric ophthalmologist); brain computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities (such as intracranial calcifications, ventricular dilation, white matter abnormalities, and cortical dysplasia) as diagnosed by a radiologist; or unilateral or bilateral hearing dysfunction, diagnosed based on auditory brain stem response abnormalities using a Neuropack S1 (Nihon Kohden Co., Tokyo, Japan) (including absent wave V to 40 dB or 50 dB at a postconceptional age of 37 weeks or 34–36 weeks, respectively) [11,23].
2.3. Treatment Protocol
Between April 2009 and December 2015, oral VGCV doses of 32 mg/kg/day for 6 weeks were adopted, and from January 2016, oral VGCV of 32 mg/kg/day for 6 months were adopted as an oral treatment for symptomatic CCMVI in our institute [5]. Among CCMVI types, central nervous system-localized types in which complications were limited to brain imaging abnormalities, hearing dysfunction, and eye complications were treated with a reduced dosage regimen (VGCV 16 mg/kg/day) [24,25]. Complete blood counts and biochemistry were evaluated before treatment and weekly for 6 weeks after treatment. If neutrophil count became <500/mm3 during VGCV treatment, treatment was interrupted. Neutropenia onset was defined as a decrease in the neutrophil count falling to <500/mm3. Administration was resumed when neutrophil counts recovered to ≥750/mm3. Thereafter, if the neutrophil count decreased to <750/mm3 again, the dosage was reduced to 50%. If neutrophil count became <500/mm3 again, treatment was discontinued. In cases of neutropenia, G-CSF was administered at the discretion of the attending physician.
2.4. Statistical Consideration
Given the retrospective study design and the rarity of the target disease, all patients that met the eligibility criteria were included as study participants. Based on a rough prior estimate of the number of neutropenia events, we assumed that it would be feasible to explore factors associated with neutropenia using at least univariable analysis.
Descriptive data were presented as median (range, i.e., minimum to maximum) for continuous variables, and as number (percentage) for binary variables. Time to neutropenia onset, defined from the initiation of treatment, was described using the Kaplan–Meier method. To explore patient factors associated with the onset of neutropenia within 6 weeks after the initiation of treatment, univariable logistic regression analysis was performed using the presence or absence of neutropenia as the outcome. A two-sided p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using R software, version 4.4.2 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
During the study period, 31 infants were enrolled in this study (Table 1). Among these infants, 20 started VGCV treatment before December 2015, and 11 were administered VGCV 16 mg/kg/day because of central nervous system-localized types, as detected on brain imaging abnormalities, ophthalmological complications, or auditory brain stem response (ABR) abnormalities alone. Eleven infants received VGCV treatment after January 2016. Accordingly, 11 patients received VGCV 16 mg/kg/day for 6 weeks, while 20 received VGCV 32 mg/kg/day for 6 weeks as initial treatment. The mean gestational age was 36 (range, 30–40) weeks and mean birthweight was 2210 (940–3312) g. In addition, we included asymptomatic CCMVI infants who did not require VGCV treatment but were managed during the same period as an untreated control group.

Table 1.
Patient characteristics.
Before treatment, the median plasma CMV DNA level was 5.6 × 102 (2.1 × 100–9.3 × 104) copies/106 white blood cells, and the median urinary CMV DNA level was 5.6 × 107 (1.0 × 103–1.7 × 109) copies/mL. Various clinical symptoms, including microcephaly (n = 9, 29%), SGA (n = 11, 35%), thrombocytopenia (n = 15, 48%), liver dysfunction (n = 9, 29%), brain imaging abnormalities (n = 28, 90%), CMV-related eye complications (n = 7, 23%), and ABR abnormalities (n = 22, 71%), were noted. In the untreated control group, fewer complications were observed compared to the treatment group, and there was a tendency toward lower neutrophil counts and viral loads. However, because the timing of sample collection differed between the two groups, a direct comparison could not be made.
3.2. Description of Neutropenia Onset During 6 Weeks of VGCV Treatment
During 6 weeks of VGCV treatment, neutropenia onset (neutrophil count fell to <500/mm3) was observed in 11 patients (35%) (Figure 1, Table 2). Seven patients (23%) required drug interruption due to neutropenia after starting VGCV treatment. Additionally, nine patients (29%) received G-CSF treatment for neutropenia. Regarding the time to first onset of neutropenia, occurrences were most frequent on the first day of VGCV treatment, but incidences were observed throughout the 6-week period (Figure 1). Even when focusing on the neutrophil nadir in individual patients, the timing of the nadir was distributed across the entire 6-week period (Table 2). The detailed neutrophil count trajectories in individual patients are shown in Figure 2.
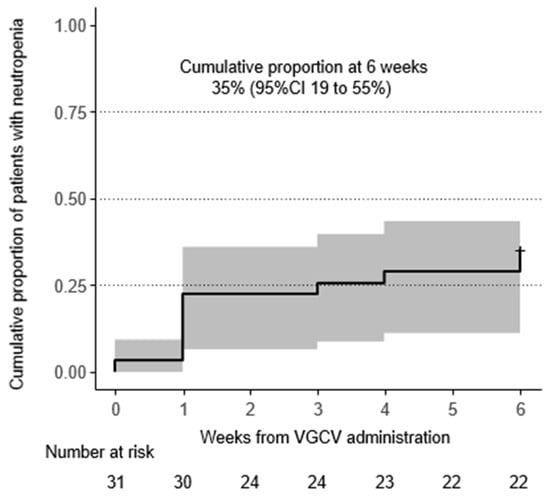
Figure 1.
Incidence of neutropenia (neutrophil count < 500/μL): Incidence of neutropenia (neutrophil count < 500/μL) was described using Kaplan–Meier method. The cumulative proportion of patients with neutropenia reached 35% at 6 weeks. Abbreviation: VGCV, valganciclovir; CI, confidence interval.

Table 2.
Summary of events during follow-up.
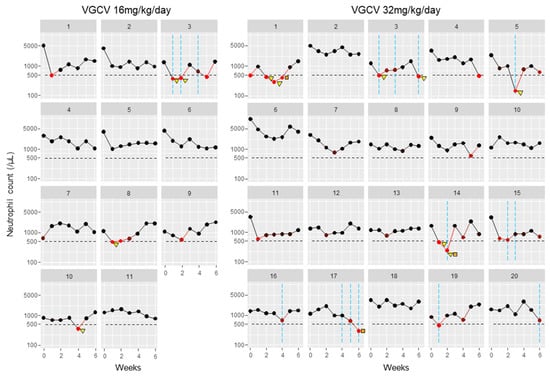
Figure 2.
Neutrophil count trajectories in individual patients: Neutrophil counts in individual cases were plotted as circle plots against weeks after treatment initiation, stratified by VGCV dose. Black circles indicate the number of neutrophil counts. Red circles indicate neutrophil counts < 500/mm3, with darker red representing counts closer to this threshold. Orange squares indicate VGCV dose reductions, and yellow triangles indicate VGCV discontinuations. Blue vertical lines show the timing of G-CSF treatments. Abbreviation: VGCV, valganciclovir; G-CSF, granulocyte-colony stimulating factor.
3.3. Factors Associated with the Onset of Neutropenia Within 6 Weeks After the Initiation of Treatment
The results of the series of univariable logistic regression analyses to explore patient factors associated with the onset of neutropenia are presented in Table 3. A longer gestational age was negatively associated with neutropenia onset (odds ratio per 1-week-increase in gestational age: 0.72, 95% confidence interval: 0.54–0.97, p = 0.031). We performed a similar logistic regression analysis with the occurrence of neutropenia after two weeks of VGCV treatment as the outcome, which yielded generally consistent results (Supplementary Table S1). As a post hoc analysis, the distribution of gestational age was plotted for patients with and without neutropenia at 6 weeks, as shown in Figure 3. The median gestational ages for patients with and without neutropenia were 35 and 38 weeks, respectively. The p-value from the Wilcoxon rank-sum test comparing the two groups was 0.019.

Table 3.
Exploration of patient factors associated with neutropenia using univariable logistic regression analyses.
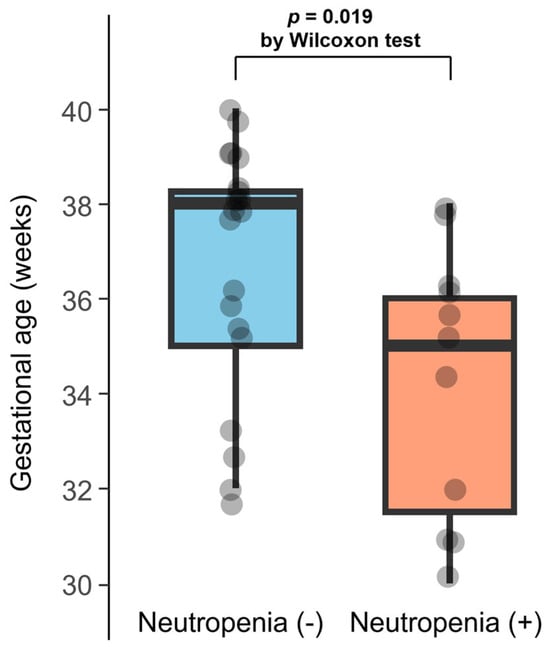
Figure 3.
Distribution of gestational age in patients with and without neutropenia at 6 weeks: Gestational age is plotted according to the presence or absence of neutropenia at 6 weeks. The horizontal line within each box indicates the median; the top and bottom edges represent the interquartile range (IQR). Whiskers extend to the most extreme values within 1.5 × IQR from the hinges.
4. Discussion
To our knowledge, this study is one of the few reports that have investigated factors associated with neutropenia in children with CCMVI treated with valganciclovir (VGCV). Neutropenia occurred in 35% of patients during the 6-week period of VGCV treatment. Its occurrence was observed throughout the treatment period, and there was no substantial difference in incidence between the 16 mg/kg/day and 32 mg/kg/day dosing groups. In addition, neutropenia was more likely to occur in patients with shorter gestational age.
Neutropenia is the most frequent complication of oral VGCV treatment for CCMVI [5,26]. Previous reports have investigated the frequency of neutropenia in children with CCMVI who received 6 weeks of ganciclovir treatment [27], children with CCMVI who received 6 weeks of VGCV treatment [13], and children with CCMVI who received 6 months of VGCV treatment [5]; however, to date, no study has revealed the changes in neutrophil counts throughout the 6 weeks period after VGCV treatment. Based on the results of recent randomized controlled trials, oral VGCV was administered for 6 months as an antiviral treatment in children with symptomatic CCMVI [26]. According to Kimberlin et al., neutropenia occurred in 19% of infants with CCMVI within the first 6 weeks during their 6 months of VGCV treatment, and 2.8% required treatment discontinuation; however, significant neutropenia did not occur after 6 weeks of treatment [5]. Ziv et al. reported that 28.8% of children with CCMVI treated with VGCV experienced at least one episode of neutropenia, the majority (84.8%) of which experienced it within the first 3 months of treatment [28]. Moreover, Rawlinson et al. recommended a close neutrophil count follow-up within 6 weeks of treatment initiation in their consensus recommendation [26]. The results of this study are consistent with the abovementioned reports, which have shown that neutropenia is common up to 6 weeks after starting treatment.
As discussed above, neutropenia occurs after VGCV administration, but the reason for individual differences in the timing and degree of neutropenia is unclear. In addition to cytomegalovirus itself [29,30], viral infections such as herpes simplex virus [31], rotavirus [32], enterovirus [33], and measles [34] have previously been reported to cause neutropenia in neonates. However, in our current study, no co-infections with viruses other than CMV were observed. Other agents known to cause neutropenia as an adverse effect include antiepileptic drugs such as phenobarbital, phenytoin, carbamazepine, and valproic acid [35,36,37,38,39]. However, in the NICU setting, the use of these drugs—except for phenobarbital—is limited. Although we investigated the use of phenobarbital in our study population, its overall use was minimal, and in most cases, it was administered only temporarily as a sedative during mechanical ventilation. Moreover, the previous literature suggests that the incidence of phenobarbital-induced neutropenia in neonates is extremely low [40]. Therefore, phenobarbital is unlikely to have contributed significantly to the neutropenia observed in this study. In addition, rare causes of neonatal neutropenia include severe congenital neutropenia due to gene mutations, such as ELANE, HAX1, and G6PC3 [41,42,43,44], as well as neonatal alloimmune neutropenia caused primarily by maternally derived anti-neutrophil antibodies [45,46,47,48]. However, in our cohort, neutropenia was transient and resolved after the completion of valganciclovir therapy. Therefore, although no further investigations were performed, we considered the presence of these disorders to be unlikely.
Although few studies on the timing of chemotherapy-induced neutropenia have been conducted, Furuya et al. tested for neutropenia early after treatment initiation (day 8) in different chemotherapy regimens for patients with early-stage breast cancer and reported that neutropenia occurred earlier with docetaxel-based chemotherapy than with other regimens [49], suggesting that the timing of the neutropenic nadir may vary depending on patient characteristics and the drug mechanism of action. Intriguingly, regarding the mechanism by which VGCV causes neutropenia, Billat et al. [50] investigated the association of a selected panel of membrane transporter polymorphisms and the evolution of neutrophil counts in 174 renal transplant recipients and found that a variant of ABCC4 (rs11568658) was associated with decreased neutrophil count following valganciclovir administration. Moreover, HEK293 cells transfected with this ABCC4 variant showed significantly increased intracellular ganciclovir accumulation in in vitro assays, and it was concluded that multidrug resistance-associated protein 4 (MRP4 = ABCC4) controls the intracellular accumulation of ganciclovir and contributes to ganciclovir-induced neutropenia in patients undergoing renal transplant. Therefore, future research that considers the influence of the patient’s genetic background is necessary.
The study findings should be interpreted in light of several limitations. First, although we collected as many cases as possible given the rarity of the disease, the sample size remained small. Therefore, the results should be considered exploratory. Nevertheless, this study specifically targeted severe symptomatic congenital CMV infection and rigorously monitored neutrophil count changes during six months of VGCV treatment, ensuring high data reliability. Second, as a retrospective single-center study, treatment management was not as tightly standardized as in an interventional trial. Consequently, the analysis of factors associated with neutropenia may have been subject to confounding bias. At the same time, the study setting closely reflects real-world clinical practice and should be interpreted as such. In our cohort, different VGCV dosing regimens (16 mg/kg/day vs. 32 mg/kg/day) were used according to the extent of clinical manifestations. Specifically, infants with localized CNS involvement or isolated sensory symptoms (such as ABR or ophthalmologic abnormalities) without systemic signs (e.g., hepatosplenomegaly or petechiae) were treated with 16 mg/kg/day, based on an institutional safety-oriented protocol designed to minimize hematological toxicity. This approach was originally informed by our prior prospective experience [20], which demonstrated acceptable outcomes with this lower dose in a similar patient population. While this dosing strategy may raise concerns about confounding by phenotype, our analysis revealed no significant difference in neutropenia incidence or treatment discontinuation rates between the dosing groups. Furthermore, logistic regression analysis did not identify VGCV dosage as a significant predictor of neutropenia risk. It should also be noted that since the regulatory approval in Japan of oral VGCV at 32 mg/kg/day for 6 months is the standard treatment for symptomatic congenital CMV infection [12], our institution has adopted this dosage universally, regardless of the specific phenotype of disease. Finally, we did not measure drug concentrations over time during VGCV treatment. However, previous reports have shown that there is no correlation between blood drug concentrations and therapeutic outcomes and side effects [14], and that blood concentrations remained stable without major fluctuations owing to the stable pharmacokinetics of oral VGCV [13,51]. In the future, we plan to conduct a prospective study on symptomatic CMV infections treated with VGCV, reporting blood VGCV concentrations and genetic polymorphisms related to drug metabolism as well as neutrophil counts.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, neutropenia occurred in 35% of patients during the 6-week VGCV treatment period, with no marked difference between the 16 mg/kg/day and 32 mg/kg/day dosing groups. Its occurrence was distributed throughout the treatment period and was more frequent in patients with shorter gestational age.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biomedicines13071739/s1, Table S1: Exploration of patient factors associated with neutropenia occurring after two weeks of VGCV treatment (N of events: 8) using univariable logistic regression analyses.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.K., S.A. and K.F.; methodology, H.M., Y.K. and T.I.; formal analysis, A.K., S.A. and Y.K.; investigation, Y.K. and K.F.; data curation, S.A., K.S., Y.M., Y.I., Y.N., T.K., M.A. and K.F.; writing—original draft preparation, A.K. and K.F.; writing—review and editing, K.T., Y.K. and K.F.; supervision, K.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was partially supported by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, AMED (grant numbers: JP15gk0110003, JP16gk0110021, JP18gk0110021, JP19gk0110037, JP20gk0110037, JP21gk0110037, JP22gk0110037, JP23gn0110037, JP24gn0110061, JP24lk0221195, and JP25gn0110094).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine (Approval No.: 923, Approval Date: 15 January 2024; 1214, 13 February 2017), and written informed consent was obtained from the guardians of all participants.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all patients involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank Kosuke Nishida, Shohei Ohyama (Department of Pediatrics, Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine), and Ichiro Morioka (Department of Pediatrics and Child Health, Nihon University School of Medicine) for their support in treating infants with CCMVI.
Conflicts of Interest
Outside the submitted work, K.F. received clinical trial expenses from the Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| VGCV | valganciclovir |
| CCMVI | congenital cytomegalovirus infection |
| SNHL | sensorineural hearing loss |
| G-CSF | granulocyte-colony stimulating factor |
| CMV | cytomegalovirus |
| qRT-PCR | quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| SGA | small for gestational age |
References
- Koyano, S.; Inoue, N.; Oka, A.; Moriuchi, H.; Asano, K.; Ito, Y.; Yamada, H.; Yoshikawa, T.; Suzutani, T.; Japanese Congenital Cytomegalovirus Study Group. Screening for congenital cytomegalovirus infection using newborn urine samples collected on filter paper: Feasibility and outcomes from a multicentre study. BMJ Open 2011, 1, e000118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenneson, A.; Cannon, M.J. Review and meta-analysis of the epidemiology of congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection. Rev. Med. Virol. 2007, 17, 253–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, K.B.; Boppana, S.B. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Semin. Perinatol. 2018, 42, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollard, S.C.; Grosse, S.D.; Ross, D.S. New estimates of the prevalence of neurological and sensory sequelae and mortality associated with congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Rev. Med. Virol. 2007, 17, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimberlin, D.W.; Jester, P.M.; Sanchez, P.J.; Ahmed, A.; Arav-Boger, R.; Michaels, M.G.; Ashouri, N.; Englund, J.A.; Estrada, B.; Jacobs, R.F.; et al. Valganciclovir for symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilavsky, E.; Shahar-Nissan, K.; Pardo, J.; Attias, J.; Amir, J. Hearing outcome of infants with congenital cytomegalovirus and hearing impairment. Arch. Dis. Child. 2016, 101, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, S.A.; Kimberlin, D. Clinical outcome and the role of antivirals in congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Antivir. Res. 2021, 191, 105083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boscarino, G.; Romano, R.; Tegoni, F.; Iotti, C.; Perrone, S.; Esposito, S.; Buonsenso, D. Congenital Cytomegalovirus Severity Definitions and Treatment Decisions around the World: A Systematic Scoping Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulc, W.; Szydlowska, N.; Smyk, J.M.; Majewska, A. Progress and Challenges in the Management of Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. Clin. Pract. 2024, 14, 2445–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.; Heath, P.T.; Jones, C.E.; Soe, A.; Ville, Y.G.; The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection: Update on Screening, Diagnosis and Treatment: Scientific Impact Paper No. 56. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2025, 132, e42–e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyama, S.; Morioka, I.; Fukushima, S.; Yamana, K.; Nishida, K.; Iwatani, S.; Fujioka, K.; Matsumoto, H.; Imanishi, T.; Nakamachi, Y.; et al. Efficacy of Valganciclovir Treatment Depends on the Severity of Hearing Dysfunction in Symptomatic Infants with Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morioka, I.; Kakei, Y.; Omori, T.; Nozu, K.; Fujioka, K.; Takahashi, N.; Yoshikawa, T.; Moriuchi, H.; Ito, Y.; Oka, A.; et al. Oral Valganciclovir Therapy in Infants Aged ≤2 Months with Congenital Cytomegalovirus Disease: A Multicenter, Single-Arm, Open-Label Clinical Trial in Japan. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimberlin, D.W.; Acosta, E.P.; Sanchez, P.J.; Sood, S.; Agrawal, V.; Homans, J.; Jacobs, R.F.; Lang, D.; Romero, J.R.; Griffin, J.; et al. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic assessment of oral valganciclovir in the treatment of symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganuma, E.; Sakata, H.; Adachi, N.; Asanuma, S.; Furuichi, M.; Uejima, Y.; Sato, S.; Abe, T.; Matsumoto, D.; Takahashi, R.; et al. Efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of oral valganciclovir in patients with congenital cytomegalovirus infection. J. Infect. Chemother. 2021, 27, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakei, Y.; Morioka, I.; Imai, T.; Itohara, K.; Yano, I.; Takahashi, N.; Yoshikawa, T.; Moriuchi, H.; Ito, Y.; Fujioka, K.; et al. Assessment of patients’ characteristics associated with the efficacy and safety of oral valganciclovir treatment for infants with symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus disease. J. Infect. Chemother. 2024, 30, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, S.E.; Wieringa, J.W.; Blazquez-Gamero, D.; Henneke, P.; Schuster, K.; Butler, K.; Capretti, M.G.; Cilleruelo, M.J.; Curtis, N.; Garofoli, F.; et al. Congenital Cytomegalovirus: A European Expert Consensus Statement on Diagnosis and Management. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mace, A.O.; Carter, T.; Rueter, K.; Bowen, A.C. Congenital cytomegalovirus and infantile neutropaenia: A causal relationship? J. Paediatr. Child. Health 2018, 54, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimura, K.; Tairaku, S.; Morioka, I.; Ozaki, K.; Nagamata, S.; Morizane, M.; Deguchi, M.; Ebina, Y.; Minematsu, T.; Yamada, H. Universal Screening With Use of Immunoglobulin G Avidity for Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 1652–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyama, S.; Fujioka, K.; Fukushima, S.; Abe, S.; Ashina, M.; Ikuta, T.; Nishida, K.; Matsumoto, H.; Nakamachi, Y.; Tanimura, K.; et al. Diagnostic Value of Cytomegalovirus IgM Antibodies at Birth in PCR-Confirmed Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, K.; Morioka, I.; Nakamachi, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Imanishi, T.; Kawano, S.; Iwatani, S.; Koda, T.; Deguchi, M.; Tanimura, K.; et al. Neurological outcomes in symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus-infected infants after introduction of newborn urine screening and antiviral treatment. Brain Dev. 2016, 38, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, K.; Fujioka, K.; Sugioka, Y.; Abe, S.; Ashina, M.; Fukushima, S.; Ohyama, S.; Ikuta, T.; Tanimura, K.; Yamada, H.; et al. Prediction of Neurodevelopmental Impairment in Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection by Early Postnatal Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Neonatology 2020, 117, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itabashi, K.; Miura, F.; Uehara, R.; Nakamura, Y. New Japanese neonatal anthropometric charts for gestational age at birth. Pediatr. Int. 2014, 56, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kido, T.; Kyono, Y.; Suga, S.; Nakasone, R.; Abe, S.; Ashina, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Tanimura, K.; Nozu, K.; Fujioka, K. Change in Viral Load during Antiviral Therapy Is Not Useful for the Prediction of Hearing Dysfunction in Symptomatic Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, J.; Wolf, D.G.; Levy, I. Treatment of symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection with intravenous ganciclovir followed by long-term oral valganciclovir. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2010, 169, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, G.; Garofoli, F.; Villani, P.; Tizzoni, M.; Angelini, M.; Cusato, M.; Bollani, L.; De Silvestri, A.; Regazzi, M.; Stronati, M. Oral valganciclovir treatment in newborns with symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 28, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawlinson, W.D.; Boppana, S.B.; Fowler, K.B.; Kimberlin, D.W.; Lazzarotto, T.; Alain, S.; Daly, K.; Doutre, S.; Gibson, L.; Giles, M.L.; et al. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection in pregnancy and the neonate: Consensus recommendations for prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, e177–e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimberlin, D.W.; Lin, C.Y.; Sanchez, P.J.; Demmler, G.J.; Dankner, W.; Shelton, M.; Jacobs, R.F.; Vaudry, W.; Pass, R.F.; Kiell, J.M.; et al. Effect of ganciclovir therapy on hearing in symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus disease involving the central nervous system: A randomized, controlled trial. J. Pediatr. 2003, 143, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziv, L.; Yacobovich, J.; Pardo, J.; Yarden-Bilavsky, H.; Amir, J.; Osovsky, M.; Bilavsky, E. Hematologic Adverse Events Associated With Prolonged Valganciclovir Treatment in Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2019, 38, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.L.; Le, M.G.; Phung, T.B.T.; Le, T.H.; Nguyen, T.Q.N. Postnatal cytomegalovirus infection in preterm infants at a tertiary hospital in Vietnam: Incidence, characteristics, and short-term outcomes. Early Hum. Dev. 2025, 207, 106306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Han, Y.S.; Sung, T.J.; Kim, D.H.; Kwak, B.O. Clinical presentation and transmission of postnatal cytomegalovirus infection in preterm infants. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 1022869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, N.; Sthapit, B.; Mhanna, M.; Abughali, N. Evaluation of suspected neonatal herpes simplex virus infection in preterm versus term newborns in the neonatal intensive care unit. J. Neonatal Perinat. Med. 2020, 13, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, J.O.; Son, D.W.; Shim, S.Y.; Ryoo, E.; Kim, W.; Jung, Y.C. Clinical characteristics and genotypes of rotaviruses in a neonatal intensive care unit. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2012, 53, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penner, J.; Burns, J.E.; Breuer, J.; Gilmour, K.C.; Bamford, A.; Rao, A. Case series: Congenital enterovirus infection-associated haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and subsequent neutropaenia. EJHaem 2024, 5, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Vecchio, A.; Krzysztofiak, A.; Montagnani, C.; Valentini, P.; Rossi, N.; Garazzino, S.; Raffaldi, I.; Di Gangi, M.; Esposito, S.; Vecchi, B.; et al. Complications and risk factors for severe outcome in children with measles. Arch. Dis. Child. 2020, 105, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurenson, I.F.; Buckoke, C.; Davidson, C.; Gutteridge, C. Delayed fatal agranulocytosis in an epileptic taking primidone and phenytoin. Lancet 1994, 344, 332–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, C.R.; Schraeder, P.L.; Kurland, A.H.; O’Connor, W.H. Evaluation of the mechanisms of antiepileptic drug-related chronic leukopenia. Epilepsia 1994, 35, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, P. Granulocytopenia after treatment with phenytoin sodium. Br. Med. J. 1960, 1, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keranen, T.; Sivenius, J. Side effects of carbamazepine, valproate and clonazepam during long-term treatment of epilepsy. Acta Neurol. Scand. Suppl. 1983, 97, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, R.D.; Copeland, S.A.; Stockwell, M.L.; Morris, N.; Kelton, J.C. Valproic acid and immune thrombocytopenia. Arch. Dis. Child. 1982, 57, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherpelli, J.L.; Cruz, A.M.; Tsanaclis, L.M.; Costa, H.P.; Garcia, T.G.; Segre, C.A.; Spina-Franca, A. Phenobarbital in newborns with neonatal seizures. A study of plasma levels after intravenous administration. Brain Dev. 1993, 15, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzareschi, I.; Rossi, E.; Curatola, A.; Capozio, G.; Benacquista, L.; Iezzi, L.; Rigante, D. Assessment of Congenital Neutropenia in Children: Common Clinical Sceneries and Clues for Management. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 14, e2022008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, B.; Lyu, W.; Zhang, X. Kostmann Syndrome With Neurological Abnormalities: A Case Report and Literature Review. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 586859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadieu, J.; Fenneteau, O.; Beaupain, B.; Mahlaoui, N.; Chantelot, C.B. Congenital neutropenia: Diagnosis, molecular bases and patient management. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2011, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skokowa, J.; Dale, D.C.; Touw, I.P.; Zeidler, C.; Welte, K. Severe congenital neutropenias. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinkel, G.K.; Schneider, I.; Gebhardt, B.; Leverenz, S. Alloimmune neonatal neutropenia: Clinical observations and therapeutic consequences. Acta Paediatr. Hung. 1986, 27, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lalezari, P. Alloimmune neonatal neutropenia and neutrophil-specific antigens. Vox Sang. 1984, 46, 415–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agueda, S.; Rocha, G.; Ferreira, F.; Vitor, B.; Lima, M.; Guimaraes, H. Neonatal alloimmune neutropenia: Still a diagnostic and therapeutical challenge. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2012, 34, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasath, A.; Grafius, A.; Bonanno, M.; Ambrusko, S.; Nair, J. Alloimmune Neutropenia in a Neonate: Case Report and Review of Literature. Antibodies 2022, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, Y. Early neutropenia on day 8 treated with adjuvant Docetaxel-based chemotherapy in early breast cancer patients: Putative mechanisms within the neutrophil pool system. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billat, P.A.; Ossman, T.; Saint-Marcoux, F.; Essig, M.; Rerolle, J.P.; Kamar, N.; Rostaing, L.; Kaminski, H.; Fabre, G.; Otyepka, M.; et al. Multidrug resistance-associated protein 4 (MRP4) controls ganciclovir intracellular accumulation and contributes to ganciclovir-induced neutropenia in renal transplant patients. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, B.C.; Koch, W.C. Antivirals for cytomegalovirus infection in neonates and infants: Focus on pharmacokinetics, formulations, dosing, and adverse events. Paediatr. Drugs 2009, 11, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).