Distinct Roles of apoE Receptor-2 Cytoplasmic Domain Splice Variants in Cardiometabolic Disease Modulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Models
2.2. Endothelial Denudation of the Carotid Arteries
2.3. Smooth Muscle Cell Isolation and Culture
2.4. Body Composition and Plasma Chemistry
2.5. Glucose Tolerance and Insulin Secretion Assays
2.6. Gene Expression Analysis
2.7. Atherosclerosis Characterization
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Impact of apoER2 Exon 19 in Terms of Modulating Sensitivity to Injury-Induced Neointima Formation
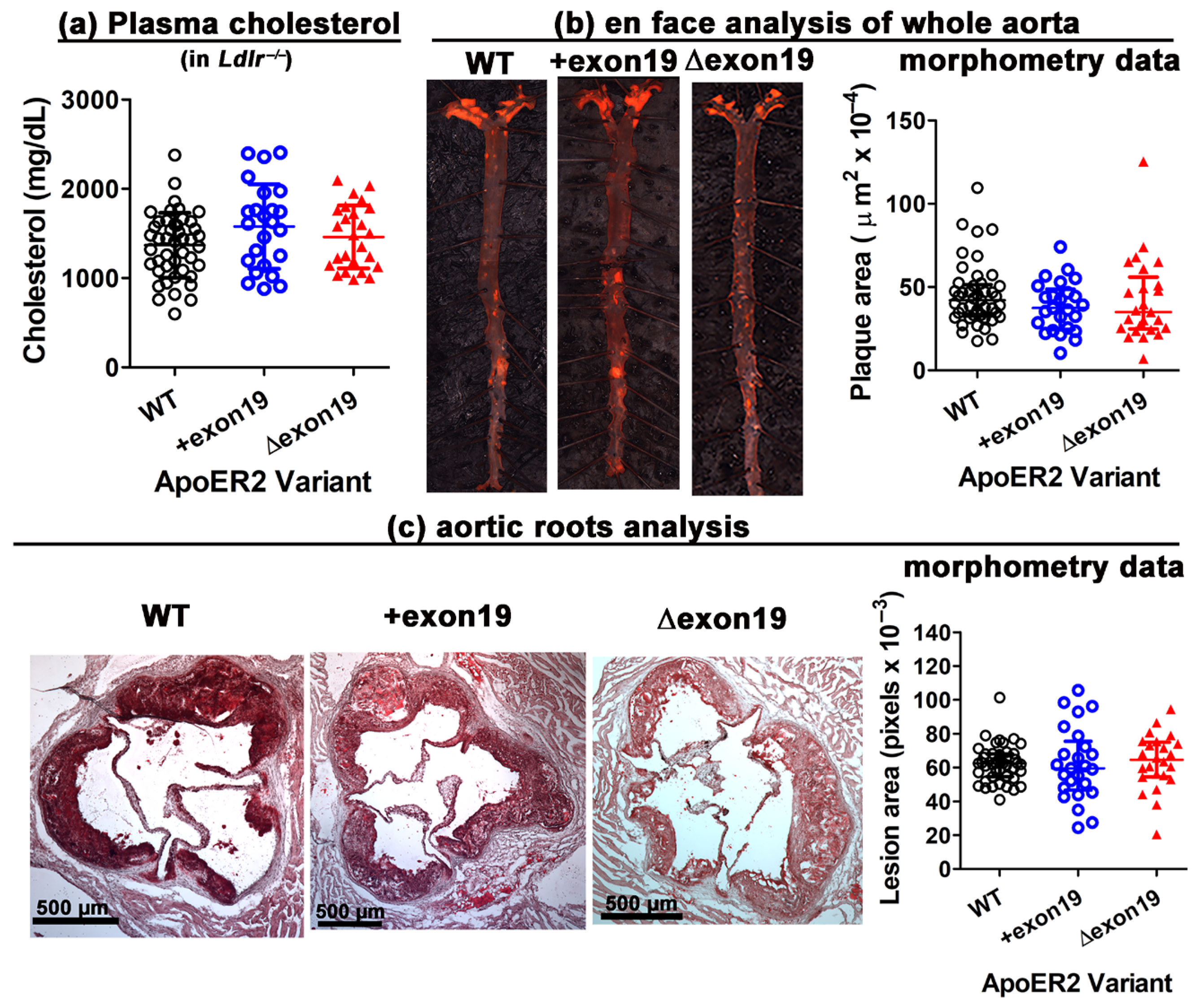
3.2. apoER2 Cytoplasmic Splice Variants Have Minimal Impact on Atherosclerosis in Ldlr−/− Mice
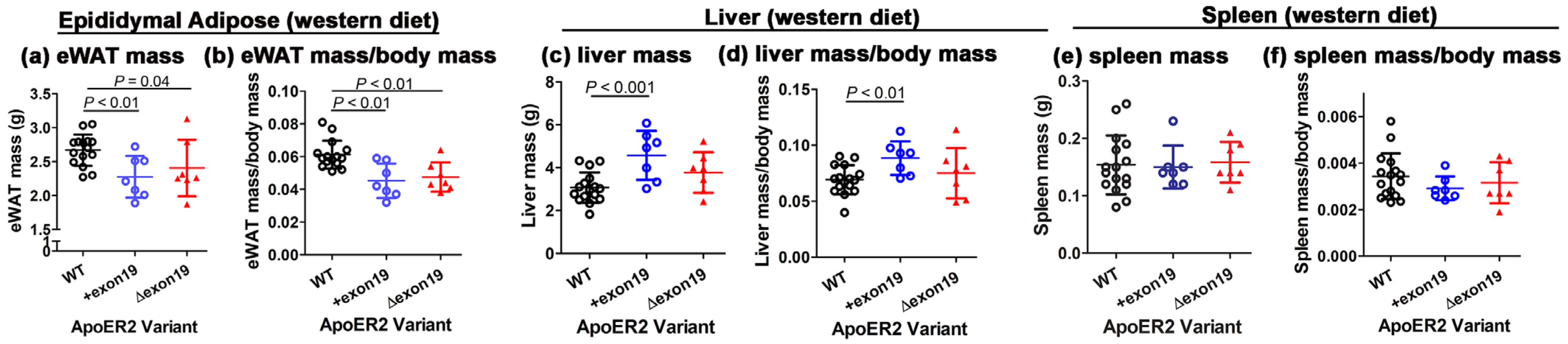
3.3. Influence of ApoER2 Exon 19 on Body Weight and Adiposity
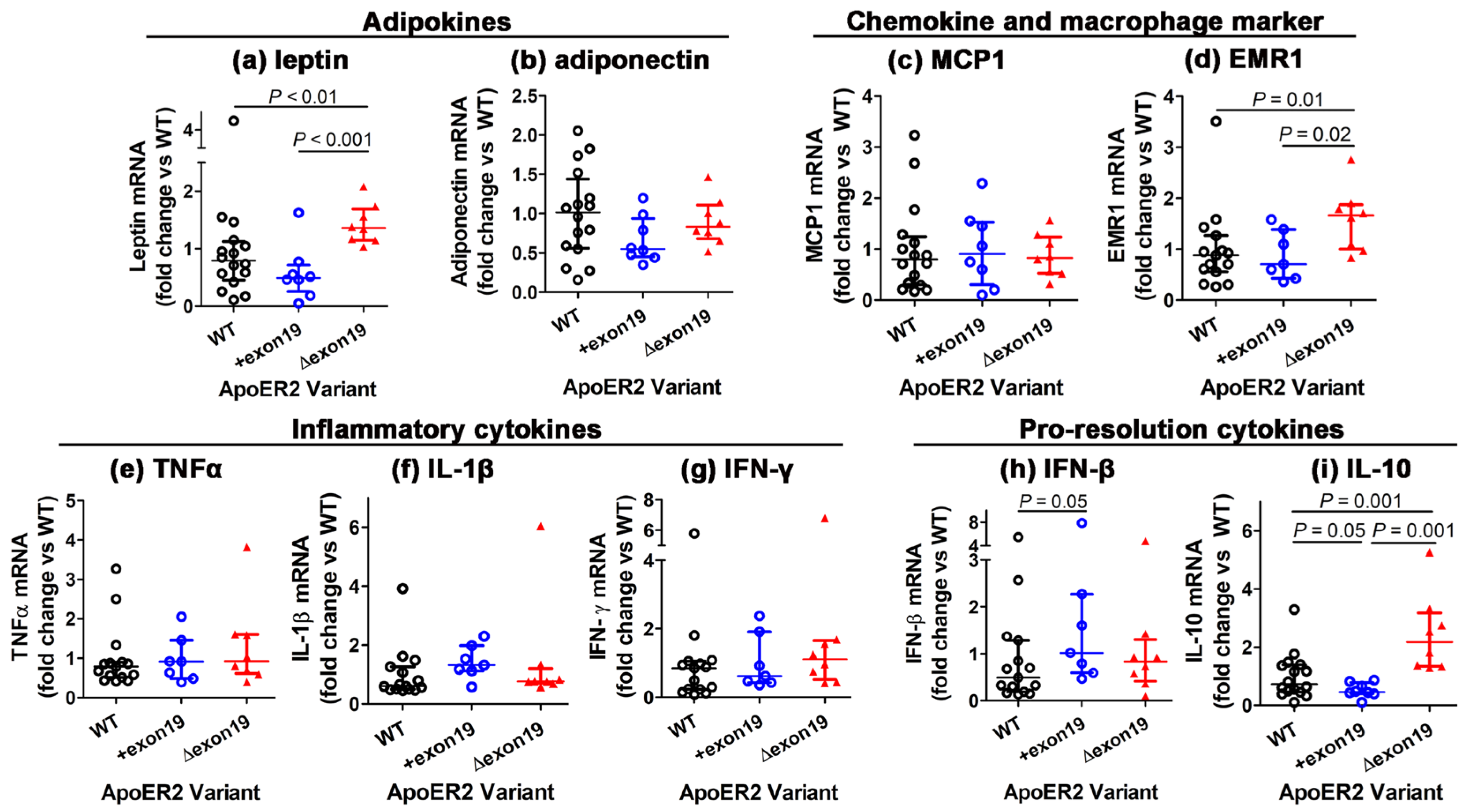
3.4. Influence of apoER2 Exon 19 on Adipose Tissue Inflammation
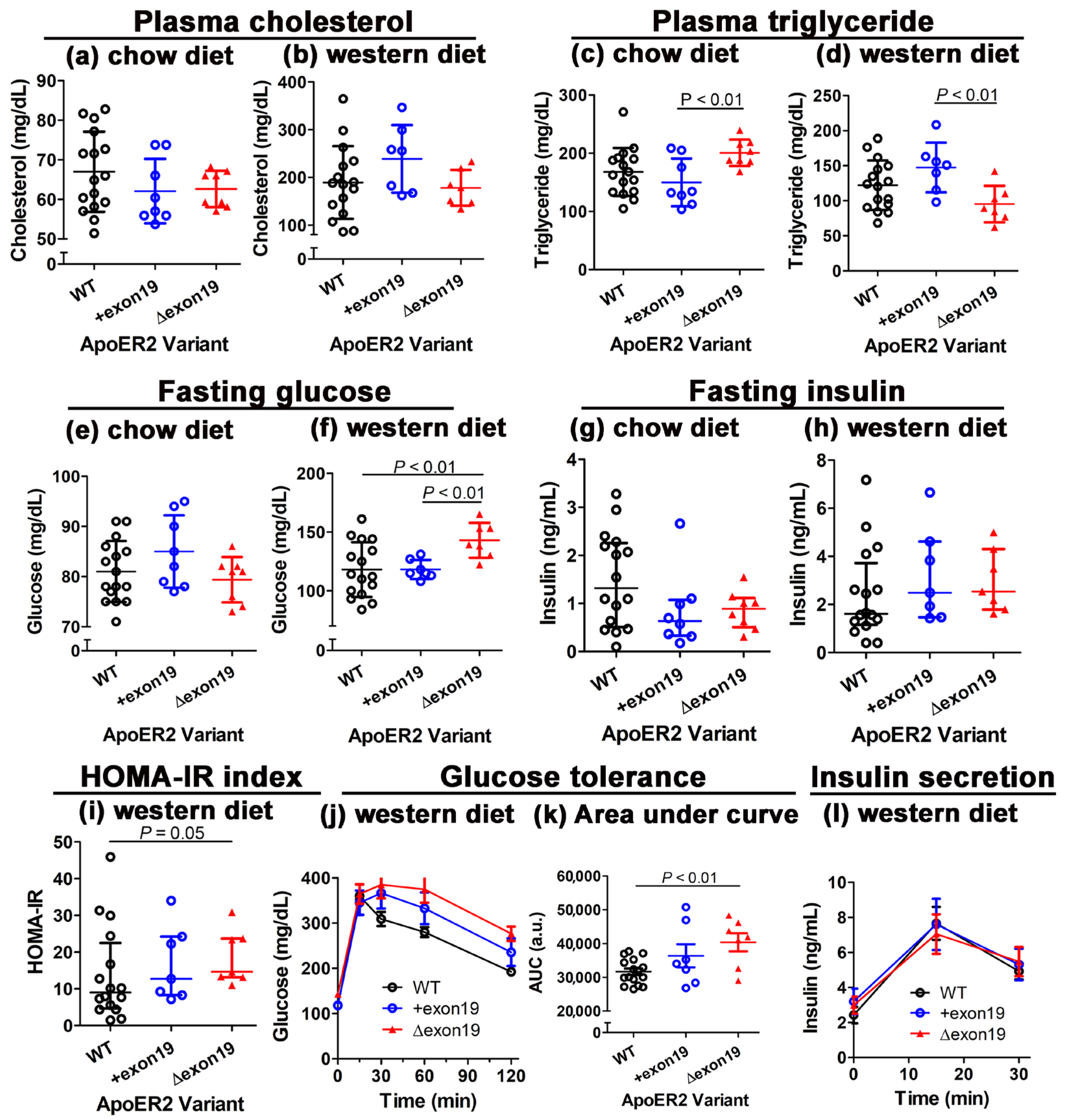
3.5. Distinct Effects of apoER2 Exon 19 Splice Variants on Diet-Induced Hyperglycemia and Glucose Intolerance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ApoER2 | Apolipoprotein E receptor-2 |
| LDL | Low-density lipoproteins |
| PP2A | Protein phosphatase-2A |
| JNK | cJun N-terminal kinase |
| JIP | JNK-interacting protein |
| LDLR | LDL receptor |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| WT | Wild type |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| MCP1 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| EMR1 | EGF-like module receptor 1 (also called F4/80) |
| TNFα | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IFN | Interferon |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance |
| Akt | Akt serine/threonine kinase (also called protein kinase B) |
References
- Cuitino, L.; Matute, R.; Ratamal, C.; Bu, G.; Inestrosa, N.C.; Marzolo, M.-P. ApoER2 is endocytosed by a clathrin-mediated process involving the adaptor protein Dab2 independent of its rafts’ association. Traffic 2005, 6, 820–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lu, W.; Paz Marzolo, M.; Bu, G. Differential functions of members of the low density lipoprotein receptor family suggested by their distinct endocytosis rates. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 18000–18006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.M.; Soutar, A.K. Expression in vitro of alternatively spliced variants of the messenger RNA for human apolipoprotein E receptor-2 identified in human tissues by ribonuclease protection assays. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 262, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacharidou, A.; Chambliss, K.L.; Ulrich, V.; Salmon, J.E.; Shen, Y.-M.; Herz, J.; Hui, D.Y.; Terada, L.S.; Shaul, P.W.; Mineo, C. Antiphospholipid antibodies induce thrombosis by PP2A activation via apoER2-Dab2-SHC1 complex formation in endothelium. Blood 2018, 131, 2097–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockinger, W.; Brandes, C.; Fasching, D.; Hermann, M.; Gotthardt, M.; Herz, J.; Schneider, W.J.; Nimpf, J. The reelin receptor apoER2 recruits JNK-interacting proteins -1 and -2. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 25625–25632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotthardt, M.; Trommsdorff, M.; Nevitt, M.F.; Shelton, J.; Richardson, J.A.; Stockinger, W.; Nimpf, J.; Herz, J. Interactions of the low density lipoprotein receptor gene family with cytosolic adaptor and scaffold proteins suggest diverse biological functions in cellular communication and signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 25616–25624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beffert, U.; Weeber, E.J.; Durudas, A.; Qiu, S.; Masiulis, I.; Sweatt, J.D.; Li, W.-P.; Adelmann, G.; Frotscher, M.; Hammer, R.E.; et al. Modulation of synaptic plasticity and memory by reelin involves differential splicing of the lipoprotein receptor ApoER2. Neuron 2005, 47, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masiulis, I.; Quill, T.A.; Burk, R.F.; Herz, J. Differential functions of the apoER2 intracellular domain in selenium uptake and cell signaling. Biol. Chem. 2009, 390, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komaravolu, R.K.; Waltmann, M.D.; Konaniah, E.S.; Jaeschke, A.; Hui, D.Y. ApoER2 (apolipoprotein E receptor-2) deficiency accelerates smooth muscle cell senescence via cytokinesis impairment and promotes fibrotic neointima after vascular injury. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 2132–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltmann, M.D.; Basford, J.E.; Konaniah, E.S.; Weintraub, N.L.; Hui, D.Y. Apolipoprotein E receptor-2 deficiency enhances macrophage susceptibility to lipid accumulation and cell death to augment atherosclerotic plaque progression and necrosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfkiel, P.R.; Haller, A.M.; Kirby, J.; Jaeschke, A.; Hui, D.Y. Different sensitivity to diet-induced hyperinsulinemia and hyperglycemia between mice with global or bone marrow-specific apoE receptor-2 deficiency. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2023, 325, R55–R68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, D.Y. Intimal hyperplasia in murine models. Curr. Drug Targets 2008, 9, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkson, V.; Haller, A.; Jaeschke, A.; Hui, D.Y. ApoE receptor-2 R952Q variant in macrophages elevates soluble LRP1 to potentiate hyperlipidemia and accelerate atherosclerosis in mice. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2025, 45, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhel, D.G.; Zhu, B.; Witte, D.P.; Hui, D.Y. Distinction in genetic determinants for injury-induced neointimal hyperplasia and diet-induced atherosclerosis in inbred mice. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, F.; van Dinther, M.; ten Dijke, P. LRP8 mediates Wnt/β-catenin signaling and controls osteoblast differentiation. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2012, 27, 2065–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchant, A.; Bruyns, C.; Vandenabeele, P.; Ducarme, M.; Gerard, C.; Delvaux, A.; De Groote, D.; Abramowicz, D.; Velu, T.; Goldman, M. Interleukin-10 controls interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor production during experimental endotoxemia. Eur. J. Immunol. 1994, 24, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauw, F.N.; Pajkrt, D.; Hack, C.E.; Kurimoto, M.; van Deventer, S.J.; van der Poll, T. Proinflammatory effects of IL-10 during human endotoxemia. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 2783–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chait, A.; den Hartigh, L.J. Adipose tissue distribution, inflammation and Its metabolic consequences, including diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzu, V.; Vacca, M.; Virtue, S.; Allison, M.; Vidal-Puig, A. Adipose tissue-liver cross talk in the control of whole-body metabolism: Implications in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1899–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, F.K.; Levi, J.; Denroche, H.C.; Gray, S.L.; Voshol, P.J.; Neumann, U.H.; Speck, M.; Chua, S.C.; Covey, S.D.; Kieffer, T.J. Disruption of hepatic leptin signaling protects mice from age- and diet-related glucose intolerance. Diabetes 2010, 59, 3032–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, J.J.; Pitman, W.; Wolfbauer, G.; Cheung, M.C.; Kennedy, H.; Tu, A.Y.; Marcovina, S.M.; Paigen, B. Relationship between phospholipid transfer protein activity and HDL level and size among inbred mosue strains. J. Lipid Res. 1999, 40, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, V.; Konaniah, E.S.; Herz, J.; Gerard, R.D.; Jung, E.; Yuhanna, I.S.; Ahmed, M.; Hui, D.Y.; Mineo, C.; Shaul, P.W. Genetic variants of apoE and apoER2 differentially modulate endothelial function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13493–13498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.S.; Connor, T.E.; Weeber, E.J.; Rebeck, W. Similarities and differences in structure, expression, and functions of VLDLR and apoER2. Mol. Neurodegener. 2011, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manceau, R.; Majeur, D.; Alquier, T. Neuronal control of peripheral nutrient partitioning. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yucel, N.; Arany, Z. Fat, obesity, and the endothelium. Curr. Opin. Physiol. 2019, 12, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, H.; Yoshida, K.; Morimoto, H.; Teramachi, J.; Ochiai, K.; Heneji, T.; Yamamoto, A. Role of protein phosphatase 2A in osteoblast differentiation and function. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaggar, M.; Mills, M.; Liu, D. Interferon beta overexpression attenuates adipose tissue inflammation and high-fat diet-induced obesity and maintains glucose homeostasis. Gene Ther. 2017, 24, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| Cyclophilin | TCATGTGCCAGGGTGGTGAC | CCATTCAGTCTTGGCAGTGC |
| Leptin | GCAGCACACGATGGAAGCACTTAT | TTGGGCAGACCCATCAATAGGATT |
| Adiponectin | AAAGATGTGAAGGTGAGCCTCTTC | CTGGTCCACATTCTTTTCCTGAT |
| MCP1 | CCTCCTCCACCACCATGCA | CCAGCCGGCAACTGTGA |
| EMR1 | TGTCTGACAATTGGGATCTGCCCT | ATACGTTCCGAGAGTGTTGTGGCA |
| TNFα | ATCCGCGACGTGGAACTG | ACCGCCTGGAGTTCTGGAA |
| IL-1β | CTACAGGCTCCGAGATGAACAAC | TCCATTGAGGTGGAGAGCTTTC |
| IFN-γ | CTACACACTGCATCTTGGCTTTG | TGACTGTGCCGTGGCAGTA |
| IFN-β | CCATCATGAACAACAGGTGGAT | GAGAGGGCTGTGGTGGAGAA |
| IL-10 | TGAATTCCCTGGGTGAGAAGCTGC | TGGCCTTGTAGACACCTTGGTCTT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaeschke, A.; Haller, A.; Hui, D.Y. Distinct Roles of apoE Receptor-2 Cytoplasmic Domain Splice Variants in Cardiometabolic Disease Modulation. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1692. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071692
Jaeschke A, Haller A, Hui DY. Distinct Roles of apoE Receptor-2 Cytoplasmic Domain Splice Variants in Cardiometabolic Disease Modulation. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(7):1692. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071692
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaeschke, Anja, April Haller, and David Y. Hui. 2025. "Distinct Roles of apoE Receptor-2 Cytoplasmic Domain Splice Variants in Cardiometabolic Disease Modulation" Biomedicines 13, no. 7: 1692. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071692
APA StyleJaeschke, A., Haller, A., & Hui, D. Y. (2025). Distinct Roles of apoE Receptor-2 Cytoplasmic Domain Splice Variants in Cardiometabolic Disease Modulation. Biomedicines, 13(7), 1692. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071692






