Impact of Acute and Chronic Stressors on the Morphofunctional Characteristics of Long Bones in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats: A Pilot Study Using Histological and Microtomographic Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
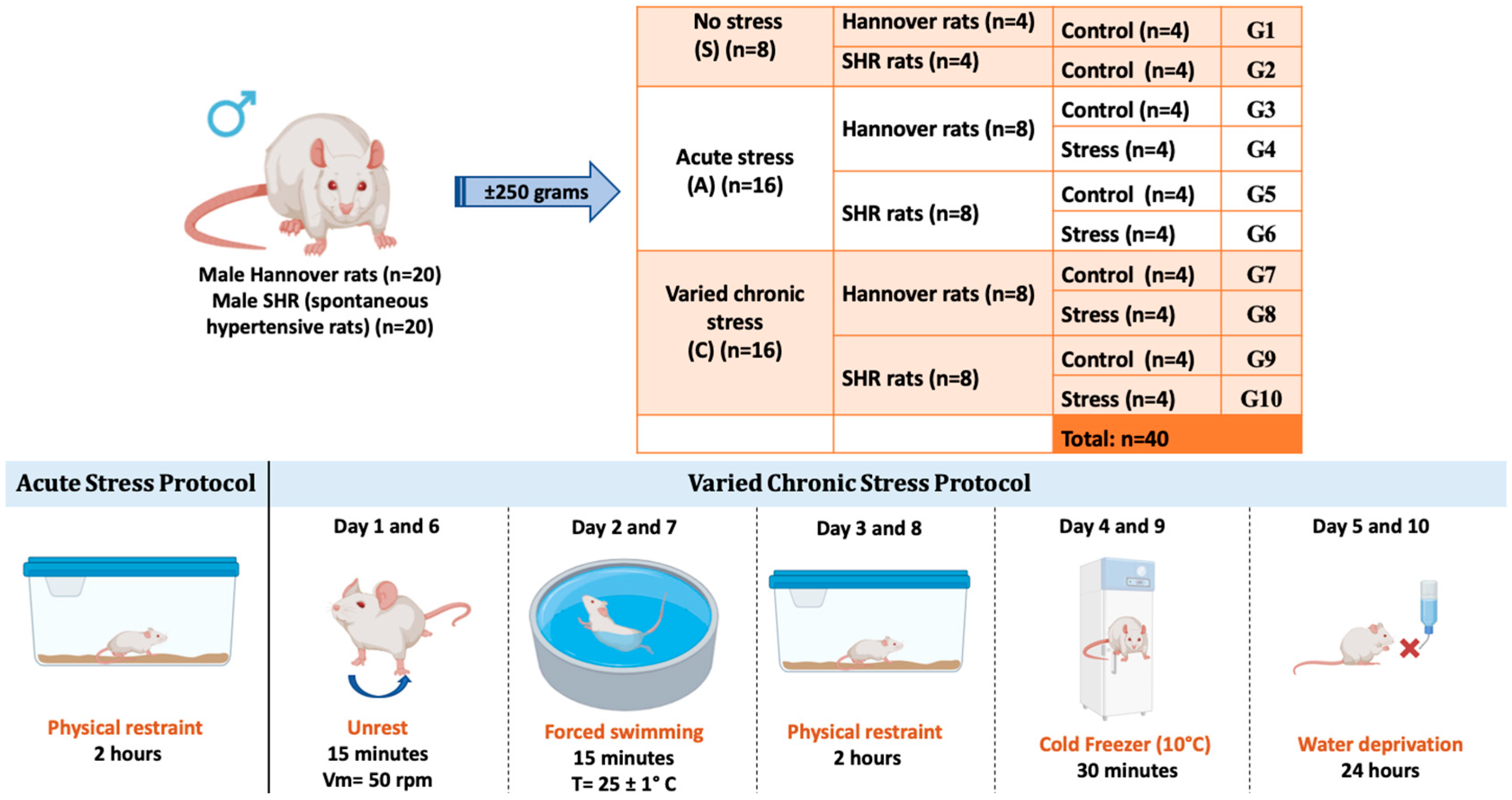
2.1. Ethical Aspects and Experimental Design
2.2. Acute Stress Protocol
2.3. Chronic Varied Stress Protocol
2.4. Tibia Collection and Microtomographic Evaluation
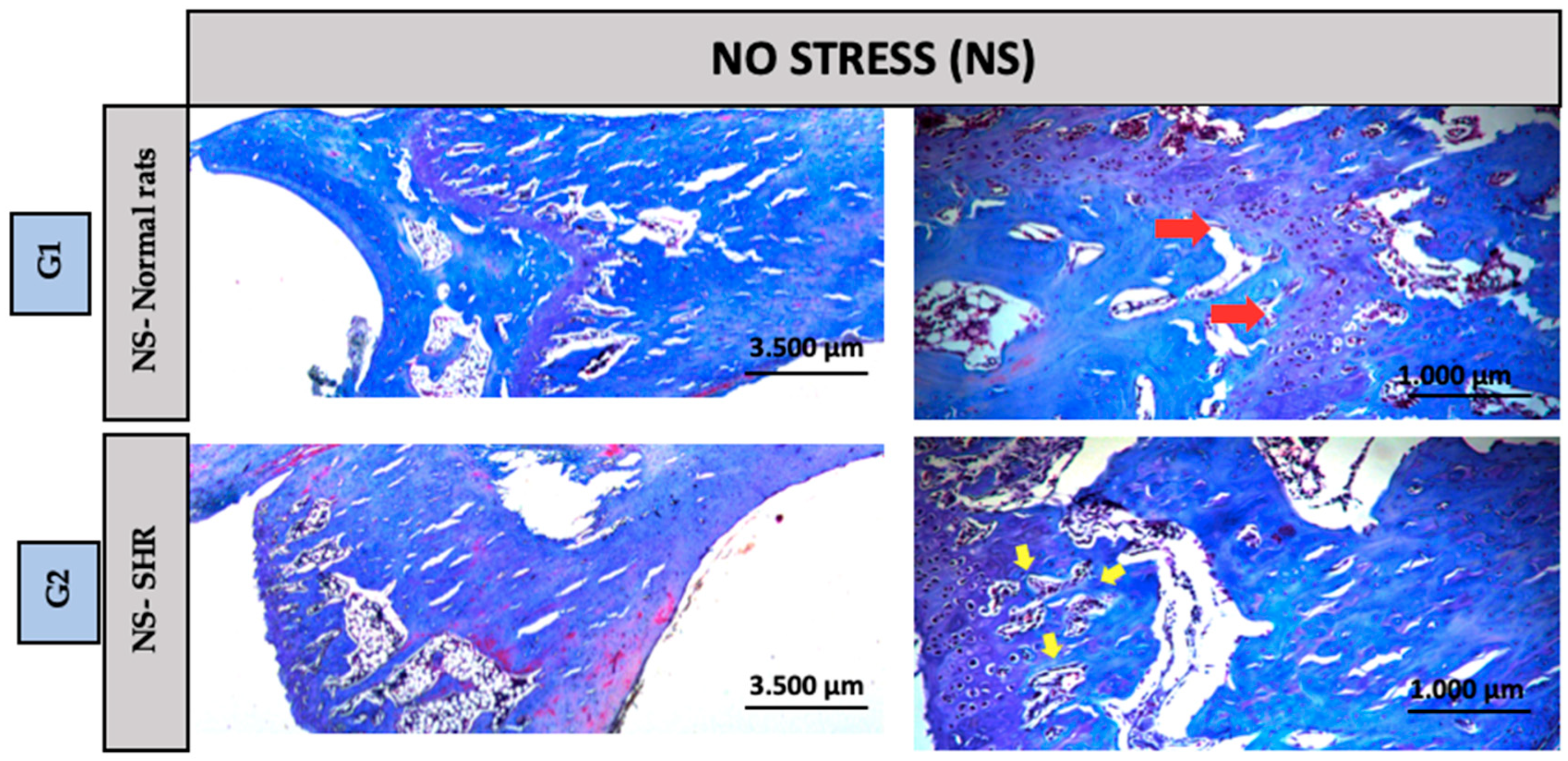
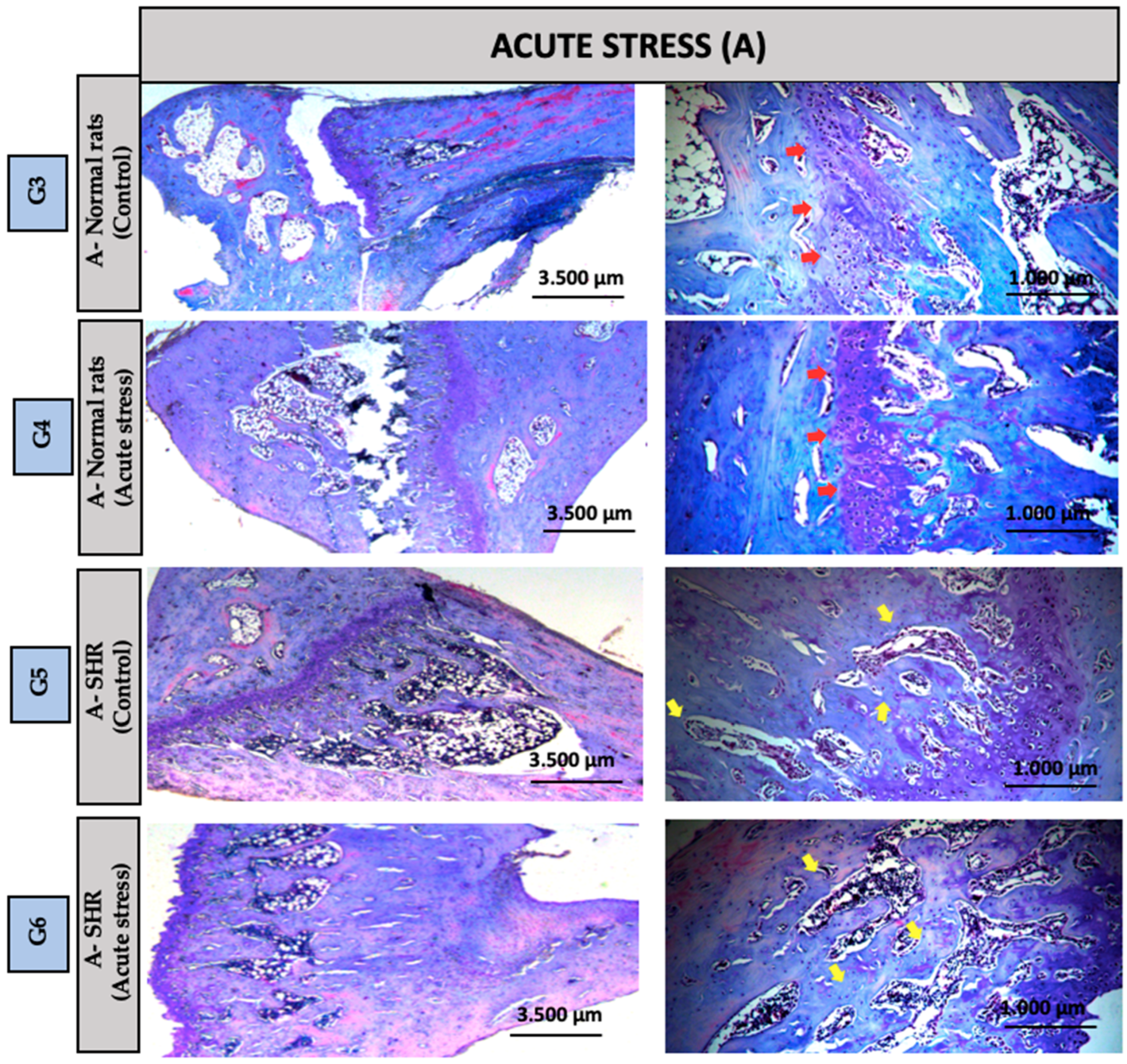
2.5. Histological Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Linear Measurements of the Tibia in Micro-CT Imagens
3.2. Descriptive Histology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dzau, V.J.; Hodgkinson, C.P. Precision Hypertension. Hypertension 2024, 81, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ondimu, D.O.; Kikuvi, G.M.; Otieno, W.N. Risk Factors for Hypertension Among Young Adults (18–35) Years Attending in Tenwek Mission Hospital, Bomet County, Kenya in 2018. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2019, 33, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwoke, O.C.; Nubila, N.I.; Ekowo, O.E.; Nwoke, N.C.; Okafor, E.N.; Anakwue, R.C. Prevalence of Prehypertension, Hypertension, and Its Determinants Among Young Adults in Enugu State, Nigeria. Niger. Med. J. 2024, 65, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wyszyńska, J.; Łuszczki, E.; Sobek, G.; Mazur, A.; Dereń, K. Association and Risk Factors for Hypertension and Dyslipidemia in Young Adults from Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, H.K.; Nguyen, D.V.; Vu, T.T.; Tran, H.B.; Nguyen, H.T.T. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Prehypertension/Hypertension Among Freshman Students from the Vietnam National University: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Y.; Li, N.; Li, W.A.; Khan, H. Association Between Psychosocial Stress and Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurol. Res. 2017, 39, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluknavsky, M.; Balis, P.; Liskova, S.; Micurova, A.; Skratek, M.; Manka, J.; Bernatova, I. Dimethyl Fumarate Prevents the Development of Chronic Social Stress-Induced Hypertension in Borderline Hypertensive Rats. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, C.; Kong, L.; Zheng, J.; Xu, M.; Xu, Y.; Li, M.; Zhao, Z.; Lu, J.; Chen, Y.; et al. Independent Associations of Education, Intelligence, and Cognition with Hypertension and the Mediating Effects of Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Hypertension 2023, 80, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, C.; Sciatti, E.; Favero, G.; Bonomini, F.; Vizzardi, E.; Rezzani, R. Essential Hypertension and Oxidative Stress: Novel Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojangba, T.; Boamah, S.; Miao, Y.; Guo, X.; Fen, Y.; Agboyibor, C.; Yuan, J.; Dong, W. Comprehensive Effects of Lifestyle Reform, Adherence, and Related Factors on Hypertension Control: A Review. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2023, 25, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildenauer, A.; Maurer, L.F.; Rötzer, L.; Eggert, T.; Schöbel, C. The Effects of a Digital Lifestyle Intervention in Patients with Hypertension: Results of a Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2024, 26, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muddle, S.; Jones, B.; Taylor, G.; Jacobsen, P. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Association Between Emotional Stress Reactivity and Psychosis. Early Interv. Psychiatry 2022, 16, 958–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Ortiz, J.L.; Islas-Valle, R.M.; Jiménez-Ortiz, J.D.; Pérez-Lizárraga, E.; Hernández-García, M.E.; González-Salazar, F. Emotional Exhaustion, Burnout, and Perceived Stress in Dental Students. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 4251–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaña, L.A.C.; Campos Lascano, L.; Jaramillo Castellon, L.; Cevallos, C.C.; Cevallos-Pozo, G.; Ron, B.V.; e Silva, F.F.V.; Perez-Sayans, M.; Fiorillo, L. The Prevalence of the Burnout Syndrome and Factors Associated in the Students of Dentistry in Integral Clinic: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Dent. 2023, 2023, 5576835. [Google Scholar]
- Minshew, L.M.; Bensky, H.P.; Zeeman, J.M. There’s No Time for No Stress! Exploring the Relationship Between Pharmacy Student Stress and Time Use. BMC Med. Educ. 2023, 23, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Choi, Y.; Kim, H. Positive Effects on Emotional Stress and Sleep Quality of Forest Healing Program for Exhausted Medical Workers During the COVID-19 Outbreak. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, J.; Kim, Y.; Choi, H.; Im, W.; Kim, H. Enhancing Sleep and Reducing Occupational Stress Through Forest Therapy: A Comparative Study Across Job Groups. Psychiatry Investig. 2024, 21, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, H.S.; Wiley, J.F.; Dunkel Schetter, C.; Robles, T.F. The Effects of Interpersonal Emotional Expression, Partner Responsiveness, and Emotional Approach Coping on Stress Responses. Emotion 2019, 19, 1315–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, N.H.; Newton, R.U.; Tan, J.; Rantalainen, T.; Chivers, P.; Siafarikas, A.; Nimphius, S. Biological Basis of Bone Strength: Anatomy, Physiology and Measurement. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2020, 20, 347–371. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N.; Liu, Y. The Role of the Immune Microenvironment in Bone Regeneration. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 3697–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.L.; Tan, M.Y.; Wang, G.P.; Zhu, S.X.; Shu, Q.C. The Association Between Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension Diet and Bone Mineral Density in US Adults: Evidence from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2011–2018). Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 23043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Li, Q.; Yang, C.; Zhi, L.; Zhuang, W.; Xu, X.S.; Tao, F. Waist-to-Height Ratio Is a Stronger Mediator in the Association Between DASH Diet and Hypertension: Potential Micro/Macro Nutrients Intake Pathways. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.Y.; Zhu, S.X.; Wang, G.P.; Liu, Z.X. Impact of Metabolic Syndrome on Bone Mineral Density in Men Over 50 and Postmenopausal Women According to U.S. Survey Results. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, V.; Haffner-Luntzer, M. Interaction Between Bone and Immune Cells: Implications for Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 123, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Lu, K.; Li, C.; Xu, M.-Z.; Ye, Y.-W.; Shan, H.-Q.; Yin, Y. Association Between Systemic Inflammatory Response Index and Bone Turnover Markers in Chinese Patients with Osteoporotic Fractures: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1404152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Cline-Smith, A.; Shashkova, E.; Perla, A.; Katyal, A.; Aurora, R. T-Cell Mediated Inflammation in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 687551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagami, H.; Morishita, R. Hypertension and osteoporosis. Clin. Calcium 2013, 23, 497–503. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Ye, J. Association Between Hypertension and Osteoporosis: A Population-Based Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2024, 25, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulini, M.R.; Aimone, M.; Feldman, S.; Buchaim, D.V.; Buchaim, R.L.; Issa, J.P.M. Relationship of Chronic Stress and Hypertension with Bone Resorption. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2025, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schemenz, V.; Scoppola, E.; Zaslansky, P.; Fratzl, P. Bone Strength and Residual Compressive Stress in Apatite Crystals. J. Struct. Biol. 2024, 216, 108141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyola, B.M.; Nascimento, G.C.; Fernández, R.A.; Iyomasa, D.M.; Pereira, Y.C.L.; Leite-Panissi, C.R.A.; Issa, J.P.M.; Iyomasa, M.M. Chronic Stress Effects in Contralateral Medial Pterygoid Muscle of Rats with Occlusion Alteration. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 164, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, R.A.R.; Pereira, Y.C.L.; Iyomasa, D.M.; Calzzani, R.A.; Leite-Panissi, C.R.A.; Iyomasa, M.M.; Nascimento, G.C. Metabolic and Vascular Pattern in Medial Pterygoid Muscle is Altered by Chronic Stress in an Animal Model of Hypodontia. Physiol. Behav. 2018, 185, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, Y.C.L.; Nascimento, G.C.; Iyomasa, D.M.; Fernández, R.A.R.; Calzzani, R.A.; Leite-Panissi, C.R.A.; Novaes, P.D.; Iyomasa, M.M. Exodontia-Induced Muscular Hypofunction by Itself or Associated to Chronic Stress Impairs Masseter Muscle Morphology and Its Mitochondrial Function. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2019, 82, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foertsch, S.; Haffner-Luntzer, M.; Kroner, J.; Gross, F.; Kaiser, K.; Erber, M.; Reber, S.O.; Ignatius, A. Chronic psychosocial stress disturbs long-bone growth in adolescent mice. Dis. Model. Mech. 2017, 10, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffner-Luntzer, M.; Foertsch, S.; Fischer, V.; Prystaz, K.; Tschaffon, M.; Mödinger, Y.; Bahney, C.S.; Marcucio, R.S.; Miclau, T.; Ignatius, A.; et al. Chronic psychosocial stress compromises the immune response and endochondral ossification during bone fracture healing via β-AR signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8615–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapolsky, R.M. Why stress is bad for your brain. Science 1996, 273, 749–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolagas, S.C. Birth and death of bone cells: Basic regulatory mechanisms and implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of osteoporosis. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 115–137. [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein, R.S. Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 39, 409–423. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, R.S.; Zhou, H.; Seibel, M.; Cooper, M.S. Glucocorticoids and Bone: Consequences of Endogenous and Exogenous Excess and Replacement Therapy. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 519–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosla, S. Pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013, 88, 1055–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein, R.S. Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis and osteonecrosis. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 41, 595–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheller, E.L.; Song, J.; Dishowitz, M.I.; Soki, F.N.; Hankenson, K.D.; Krebsbach, P.H. Prolonged treatment with dexamethasone causes bone fragility by impacting osteoblast function and apoptosis. Bone 2013, 54, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, N.E.; Yao, W. Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: New insights into the pathophysiology and treatments. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2008, 6, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, C.A.; Jia, D.; Plotkin, L.I.; Bellido, T.; Powers, C.C.; Stewart, S.A.; Manolagas, S.C.; Weinstein, R.S. Glucocorticoids act directly on osteoblasts and osteocytes to induce their apoptosis and reduce bone formation and strength. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 1835–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan-Speranza, T.C.; Henneicke, H.; Gasparini, S.J.; Blankenstein, K.I.; Heinevetter, U.; Cogger, V.C.; Svistounov, D.; Zhang, Y.; Cooney, G.J.; Buttgereit, F.; et al. Osteoblasts mediate the adverse effects of glucocorticoids on fuel metabolism. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 4172–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Okada, H.; Morikawa, K.; Ogata, E.; Yamamoto, M. Glucocorticoid enhances receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand expression and suppresses osteoprotegerin in human osteoblastic Saos-2 cells. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 2208–2213. [Google Scholar]
- Plotkin, L.I.; Bellido, T. Osteocytic signalling pathways as therapeutic targets for bone fragility. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.M.; Singh, P.; Khrimian, L.; Morgan, D.A.; Chowdhury, S.; Arteaga-Solis, E.; Horvath, T.L.; Domingos, A.I.; Marsland, A.L.; Yadav, V.K.; et al. Mediation of the Acute Stress Response by the Skeleton. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 890–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.K.; Liu, J.X.; Zhou, Z.K.; Zheng, C.X.; Sui, B.D.; Yuan, Y.; Kong, L.; Jin, Y.; Chen, J. Osteoporosis under psychological stress: Mechanisms and therapeutics. Life Med. 2024, 3, lnae009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, K.; Adachi, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Kubo, K.Y. Chronic Psychological Stress as a Risk Factor of Osteoporosis. J. UOEH 2015, 37, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henneicke, H.; Li, J.; Kim, S.; Gasparini, S.J.; Seibel, M.J.; Zhou, H. Chronic Mild Stress Causes Bone Loss via an Osteoblast-Specific Glucocorticoid-Dependent Mechanism. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 1939–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wippert, P.M.; Rector, M.; Kuhn, G.; Wuertz-Kozak, K. Stress and Alterations in Bones: An Interdisciplinary Perspective. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiyasatkulkovit, W.; Promruk, W.; Rojviriya, C.; Pakawanit, P.; Chaimongkolnukul, K.; Kengkoom, K.; Teerapornpuntakit, J.; Panupinthu, N.; Charoenphandhu, N. Impairment of Bone Microstructure and Upregulation of Osteoclastogenic Markers in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, R.M.; Silva, A.B.; Lima, R.M. Relationship of Chronic Stress and Hypertension with Bone Resorption. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2024, 10, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Z.; Lu, H.; Liu, P. Association Between Essential Hypertension and Bone Mineral Density: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 68916–68927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Richardson, D.; Cregor, M.; Davis, H.M.; Au, E.D.; McAndrews, K.; Zimmers, T.A.; Organ, J.M.; Peacock, M.; Plotkin, L.I.; et al. Glucocorticoids Induce Bone and Muscle Atrophy by Tissue-Specific Mechanisms Upstream of E3 Ubiquitin Ligases. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 3045–3055. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, R.M.; Souza, P.L.; Marques, F.A.; Fernandes, D.B.; Ribeiro, T.C.; Cardoso, M.F.; Nascimento, W.R.; Castro, L.F.; Barros, G.M.; Silva, H.L.; et al. Combined Effects of Hypertension and Chronic Stress on Bone Microarchitecture in Rats. Bone Rep. 2021, 14, 100752. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet, N.; Ferrari, S.L. Chronic psychosocial stress disturbs long-bone growth in adolescent mice. Dis. Model. Mech. 2010, 3, 681–690. [Google Scholar]
- Singewald, G.M.; Nguyen, N.K.; Neumann, I.D.; Singewald, N.; Reber, S.O. Effect of Chronic Psychosocial Stress-Induced by Subordinate Colony (CSC) Housing on Brain Neuronal Activity Patterns in Mice. Stress 2009, 12, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, B.; Londono, I.; Laporte, C.; Villemure, I. Validation of an in vivo micro-CT-based method to quantify longitudinal bone growth of pubertal rats. Bone 2022, 154, 116207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafy, T.; Benoit, A.; Londono, I.; Moldovan, F.; Villemure, I. Can repeated in vivo micro-CT irradiation during adolescence alter bone microstructure, histomorphometry and longitudinal growth in a rodent model? PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, R.M.; Phillips, J.E.; Lin, A.; Schwartz, Z.; Boyan, B.D.; Guldberg, R.E. Characterization of a small animal growth plate injury model using microcomputed tomography. Bone 2010, 46, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.C.; Fernandes, R.G.; Carvalho, Y.R.; Balducci, I.; Faig-Leite, H. Bone healing in drill hole defects in spontaneously hypertensive male and female rats’ femurs. A histological and histometric study. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2007, 88, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bastos, M.F.; Brilhante, F.V.; Bezerra, J.P.; Silva, C.A.; Duarte, P.M. Trabecular bone area and bone healing in spontaneously hypertensive rats: A histometric study. Braz. Oral Res. 2010, 24, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiyasatkulkovit, W.; Aksornthong, S.; Adulyaritthikul, P.; Upanan, P.; Wongdee, K.; Aeimlapa, R.; Teerapornpuntakit, J.; Rojviriya, C.; Panupinthu, N.; Charoenphandhu, N. Excessive salt consumption causes systemic calcium mishandling and worsens microarchitecture and strength of long bones in rats. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, T.K.; Simic, P.; Sendak, R.; Draca, N.; E Bowe, A.; O’Brien, S.; Schiavi, S.C.; McPherson, J.M.; Vukicevic, S. Thyroid-stimulating hormone restores bone volume, microarchitecture, and strength in aged ovariectomized rats. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2007, 22, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
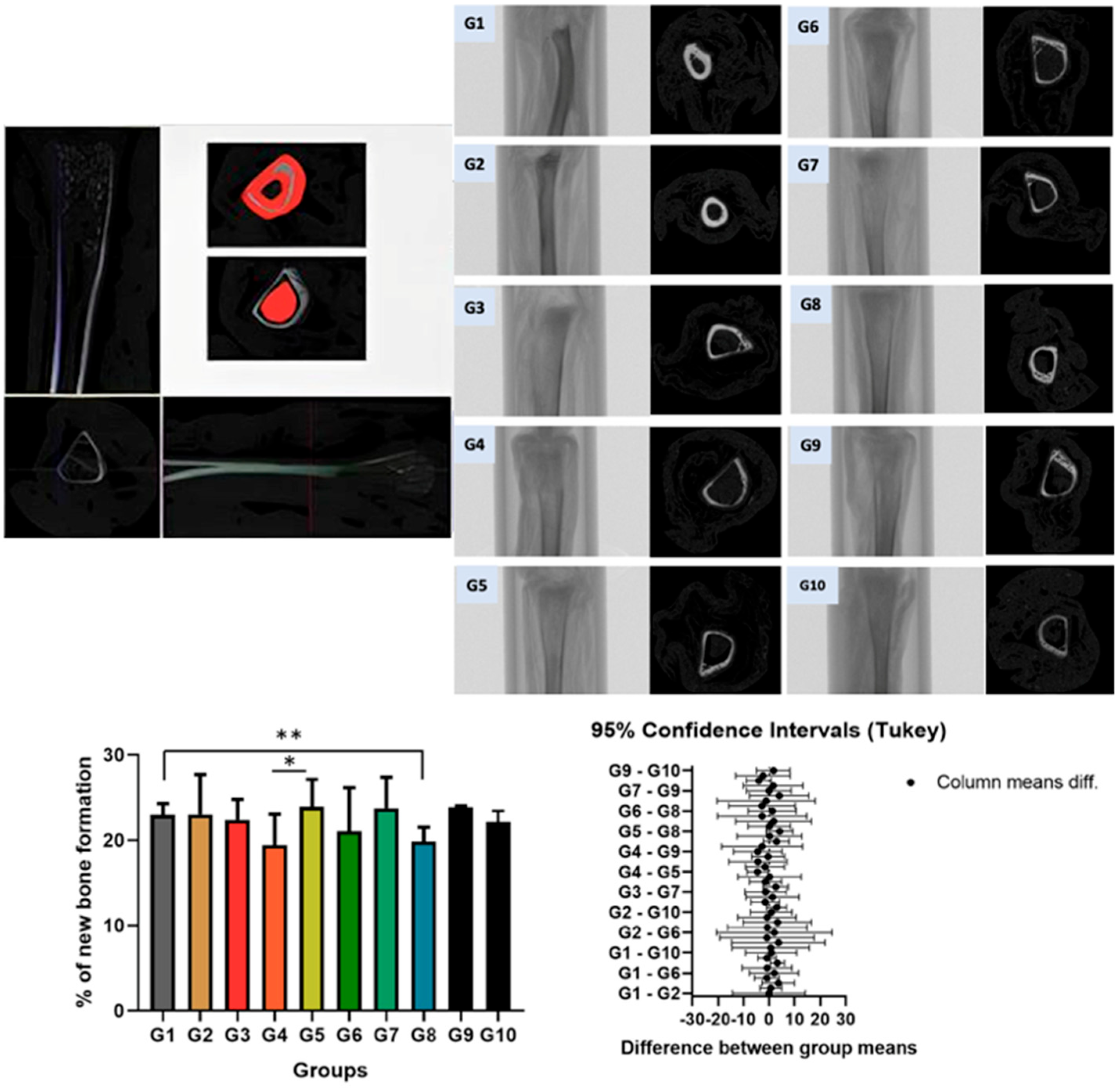
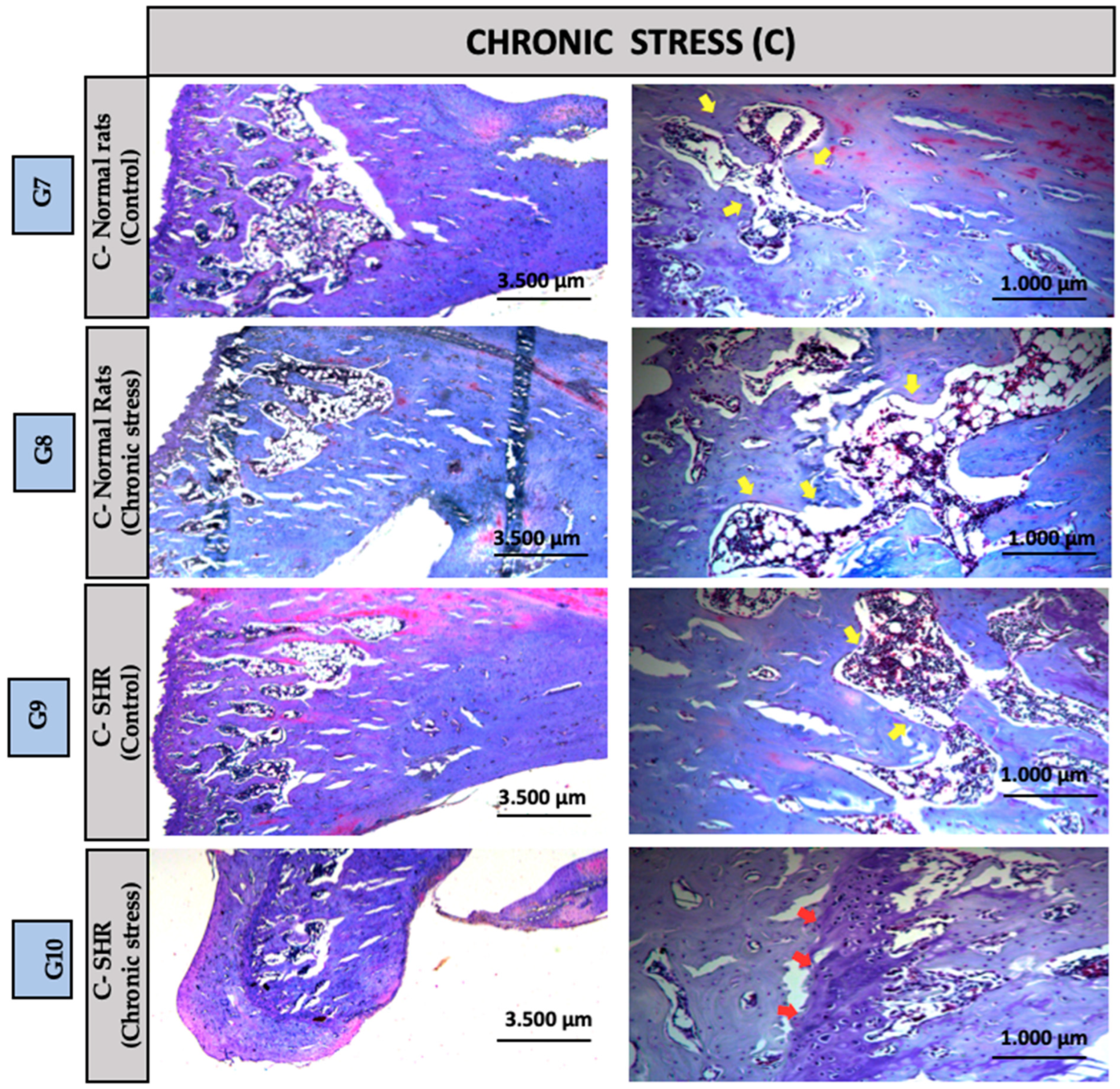
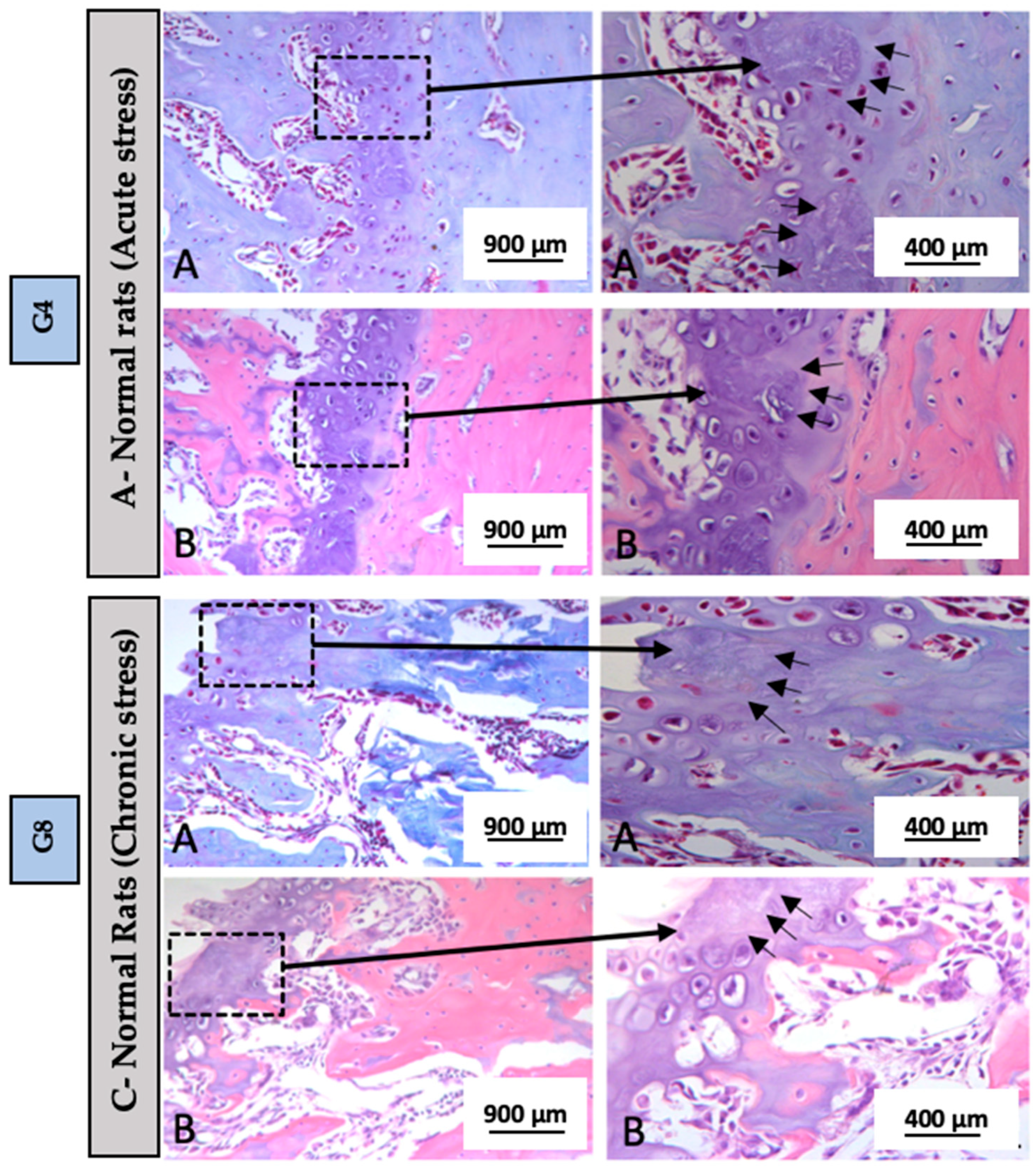
| G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | G5 | G6 | G7 | G8 | G9 | G10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | 23.02 ± 1.26 ** | 23.06 ± 4.66 | 22.41 ± 2.39 | 19.42 ± 3.65 * | 23.93 ± 3.21 * | 21.06 ± 5.01 | 23.78 ± 3.63 | 19.83 ± 1.73 ** | 23.85 ± 0.19 | 22.19 ± 2.81 |
| SS | DF | MS | F (DFn, DFd) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment (between columns) | 121.2 | 9 | 13.47 | F (1.745, 6.978) = 1.329 F (4, 36) = 1.124 |
| Individual (between rows) | 45.57 | 4 | 11.39 | |
| Residual (random) | 364.8 | 36 | 10.13 | |
| Total | 531.6 | 49 |
| G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | G5 | G6 | G7 | G8 | G9 | G10 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NS | NS | AS | AS | AS | AS | CS | CS | CS | CS | |||
| Normal rats | SHRs | Normal rats | Normal rats | SHRs | SHRs | Normal rats | Normal rats | SHRs | SHRs | |||
| Description | Abbreviation | Unit | Control | Control | Control | Acute Stress | Control | Acute Stress | Control | Chronic Stress | Control | Chronic Stress |
| Tissue volume | TV | mm3 | 12.733.594 | 12.789.941 | 131.448.460 | 15.228.645 | 124.989.966 | 13.912.630 | 1.245.267 | 1.482.602 | 1.241.090 | 13.474.538 |
| Bone volume | BV | mm3 | 293.806 | 295.706 | 294.576 | 295.588 | 298.976 | 293.189 | 296.706 | 294.312 | 296.888 | 299.654 |
| Percent bone volume | BV/TV | % | 23.0175 | 23.065 | 22.41 | 19.4175 | 23.925 | 21.0625 | 23.775 | 19.835 | 23.85 | 22.19 |
| Tissue surface | TS | mm2 | 4.993.918 | 3.831.324 | 4.778.871 | 4.593.316 | 3.279.641 | 4.546.161 | 2.957.578 | 4.232.392 | 4.501.669 | 3.974.099 |
| Bone surface | BS | mm2 | 4.451.017 | 2.971.198 | 3.846.521 | 3.455.365 | 2.914.445 | 3.792.720 | 2.434.846 | 3.828.748 | 4.733.449 | 3.709.413 |
| Intersection surface | i.S | mm2 | 255.385 | 718.400 | 188.105 | 203.964 | 235.366 | 229.826 | 198.548 | 222.050 | 210.603 | 194.604 |
| Bone surface/volume ratio | BS/BV | 1/mm | 1.521.402 | 1.495.429 | 1.716.925 | 1.588.229 | 1.480.302 | 1.597.593 | 1.597.775 | 1.367.958 | 1.711.046 | 1.543.679 |
| Bone surface density | BS/TV | 1/mm | 338.386 | 348.372 | 381.087 | 345.576 | 409.473 | 364.583 | 454.487 | 354.622 | 357.023 | 337.703 |
| Trabecular pattern factor | Tb.Pf | 1/mm | 239.666 | 534.249 | 379.008 | 364.828 | 275.185 | 296.569 | 307.904 | 219.751 | 182.072 | 209.109 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paulini, M.R.; Pitol, D.L.; Feldman, S.; Ribeiro, C.A.; Buchaim, D.V.; Buchaim, R.L.; Issa, J.P.M. Impact of Acute and Chronic Stressors on the Morphofunctional Characteristics of Long Bones in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats: A Pilot Study Using Histological and Microtomographic Analysis. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071689
Paulini MR, Pitol DL, Feldman S, Ribeiro CA, Buchaim DV, Buchaim RL, Issa JPM. Impact of Acute and Chronic Stressors on the Morphofunctional Characteristics of Long Bones in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats: A Pilot Study Using Histological and Microtomographic Analysis. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(7):1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071689
Chicago/Turabian StylePaulini, Marina Ribeiro, Dimitrius Leonardo Pitol, Sara Feldman, Camila Aparecida Ribeiro, Daniela Vieira Buchaim, Rogerio Leone Buchaim, and João Paulo Mardegan Issa. 2025. "Impact of Acute and Chronic Stressors on the Morphofunctional Characteristics of Long Bones in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats: A Pilot Study Using Histological and Microtomographic Analysis" Biomedicines 13, no. 7: 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071689
APA StylePaulini, M. R., Pitol, D. L., Feldman, S., Ribeiro, C. A., Buchaim, D. V., Buchaim, R. L., & Issa, J. P. M. (2025). Impact of Acute and Chronic Stressors on the Morphofunctional Characteristics of Long Bones in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats: A Pilot Study Using Histological and Microtomographic Analysis. Biomedicines, 13(7), 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071689








