Is Cerebrolysin Useful in Psychiatry Disorders?
Abstract
1. Introduction
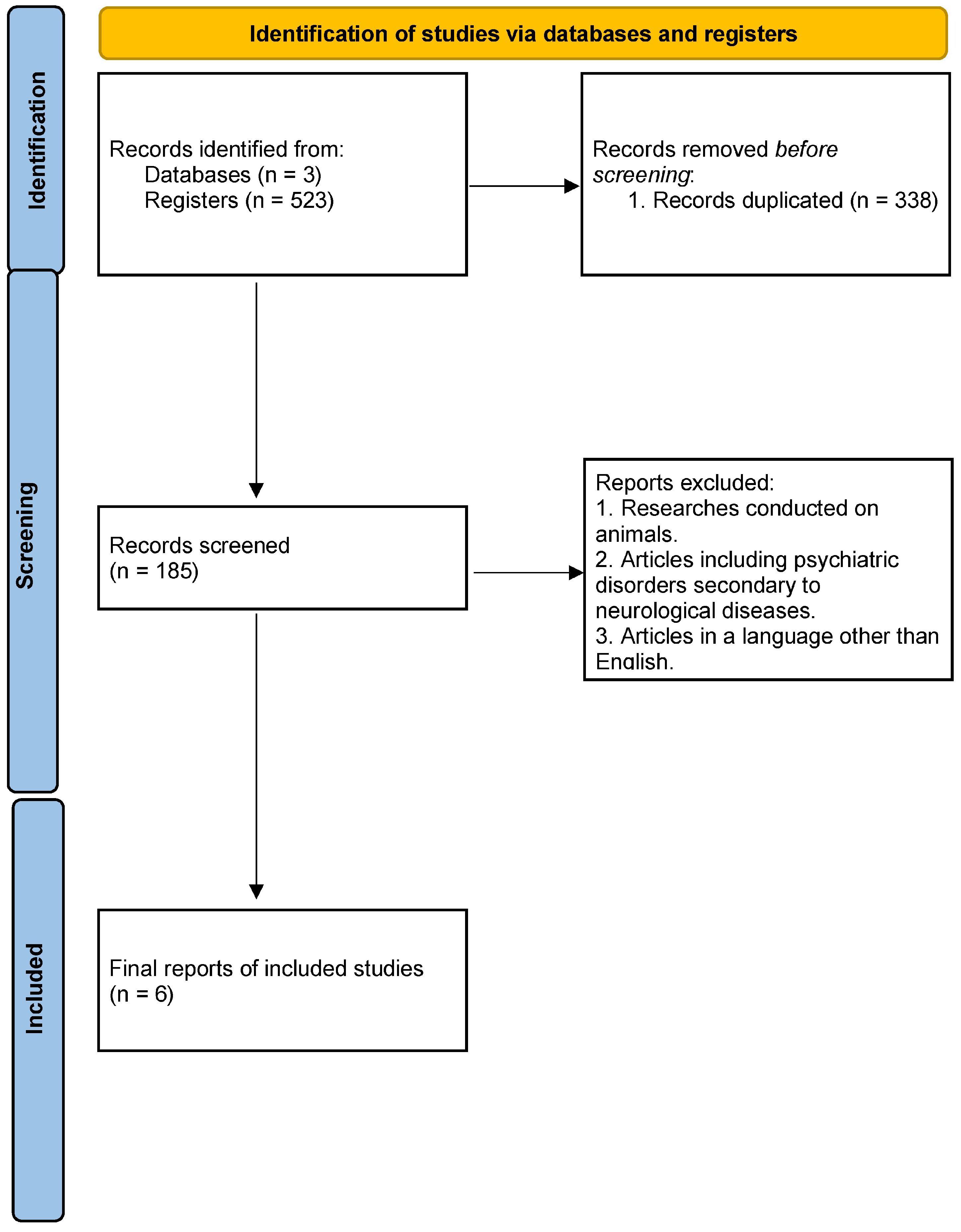
2. Materials and Methods
Bibliometric Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The small number of studies available on the use of cerebrolysin indicates that it may have some significance in alleviating adverse effects and improving cognitive functions during treatment with neuroleptics.
- There are isolated reports concerning the potential efficacy of cerebrolysin in augmenting the treatment of depression, anorexia, autism spectrum disorder, and pervasive developmental disorders.
- In the future, it would be beneficial to design and conduct studies with a particular emphasis on the use of cerebrolysin in supporting the treatment of mental disorders.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hartbauer, M.; Hutter-Paier, B.; Skofitsch, G.; Windisch, M. Antiapoptotic effects of the peptidergic drug cerebrolysin on primary cultures of embryonic chick cortical neurons. J. Neural Transm. 2001, 108, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gromova, O.A.; Avdeenko, T.V.; Burtsev, E.M.; Skal’nyĭ, A.V.; Solov’ev, O.I. Effects of cerebrolysin on the oxidant homeostasis, the content of microelements and electrolytes in children with minimal brain dysfunction. Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr. Im. S. S. Korsakova 1998, 98, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- EVER Neuro Pharma GmbH. Cerebrolysin—Product Monograph; EVER Neuro Pharma GmbH: Oberburgau, Austria, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Al Mosawi, A. Clinical uses of Cerebrolysin in Pediatric Neuropsychiatry. Sci. World J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziganshina, L.E.; Abakumova, T.; Nurkhametova, D.; Ivanchenko, K. Cerebrolysin for acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 10, CD007026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, C.; Sabbagh, M.N. Successes and Failures for Drugs in Late-Stage Development for Alzheimer’s Disease. Drugs Aging 2013, 30, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ever Neuro Pharma GmbH. Cerebrolysin REGistry Study in Stroke—A High-Quality Observational Study of Comparative Effectiveness (ISRCTN98553245); ISRCTN Registry; Ever Neuro Pharma GmbH: Oberburgau, Austria, 2024; Available online: https://www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN98553245 (accessed on 8 June 2025).
- Zhang, L.; Chopp, M.; Meier, D.H.; Winter, S.; Wang, L.; Szalad, A.; Lu, M.; Wei, M.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Z.G. Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway mediates cerebrolysin-improved neurological function after stroke. Stroke 2013, 44, 1965–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Tung, Y.-C.; Li, B.; Iqbal, K.; Grundke-Iqbal, I. Trophic factors counteract elevated FGF-2-induced inhibition of adult neurogenesis. Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 1148–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chopp, M.; Cui, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Lu, M.; Szalad, A.; Doppler, E.; Hitzl, M.; et al. Cerebrolysin enhances neurogenesis in the ischemic brain and improves functional outcome after stroke. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 88, 3275–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, C.; Salinas, P.; Muñoz, D.; Olivares, S.; González, J.; Sáez, V.; Romero, V. A retrospective study of Cerebrolysin in patients with moderate to severe traumatic brain injury: Cognitive and functional outcomes. J. Med. Life 2023, 16, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.H.; Lee, J.; Shin, Y.-I.; Ko, M.-H.; Kim, D.Y.; Sohn, M.K.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.-H. Cerebrolysin Combined with Rehabilitation Enhances Motor Recovery and Prevents Neural Network Degeneration in Ischemic Stroke Patients with Severe Motor Deficits. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Zekry, S.H.; Alruwaili, M.; Alexiou, A.; Papadakis, M.; Batiha, G.E. The possible role of cerebrolysin in the management of vascular dementia: Leveraging concepts. Neuroscience 2025, 568, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, X.A.; Winston, C.N.; Barlow, J.W.; Sarsoza, F.M.; Alvarez, I.; Aleixandre, M.; Linares, C.; García-Fantini, M.; Kastberger, B.; Winter, S.; et al. Modulation of Amyloid-β and Tau in Alzheimer’s Disease Plasma Neuronal-Derived Extracellular Vesicles by Cerebrolysin® and Donepezil. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2022, 90, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homberg, V.; Jianu, D.C.; Stan, A.; Strilciuc, Ș.; Chelaru, V.F.; Karliński, M.; Brainin, M.; Heiss, W.D.; Muresanu, D.F.; Enderby, P.M. Speech Therapy Combined with Cerebrolysin in Enhancing Nonfluent Aphasia Recovery after Acute Ischemic Stroke: ESCAS Randomized Pilot Study. Stroke 2025, 56, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drożdżal, S.; Rosik, J.; Lechowicz, K.; Machaj, F.; Szostak, B.; Przybyciński, J.; Lorzadeh, S.; Kotfis, K.; Ghavami, S.; Łos, M.J. An update on drugs with therapeutic potential for SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) treatment. Drug Resist. Updat. 2021, 59, 100794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strilciuc, S.; Vécsei, L.; Boering, D.; Pražnikar, A.; Kaut, O.; Riederer, P.; Battistin, L. Safety of Cerebrolysin for Neurorecovery after Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojder, K.; Jarosz, K.; Bosiacki, M.; Andrzejewska, A.; Zacha, S.; Solek-Pastuszka, J.; Jurczak, A. Cerebrolysin in Patients with Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th Revision (ICD-10); WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Diseases for Mortality and Morbidity Statistics, 11th Revision; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; Available online: https://icd.who.int (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Chen, N.; Yang, M.; Guo, J.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, C.; He, L. Cerebrolysin for vascular dementia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 1, CD008900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, G.S.; Mann, J.J. Depression. Lancet 2018, 392, 2299–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, R.A.; Reis Marques, T.; Howes, O.D. Schizophrenia—An Overview. JAMA Psychiatry 2020, 77, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boksha, I.; Savushkina, O.; Sheshenin, V.; Tereshkina, E.; Prokhorova, T.; Pochueva, V.; Burbaeva, G. Late onset psychosis treatment with adjunctive medicines. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1319891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Xue, H.; Li, G.; Yuan, C.; Li, X.; Chen, C.; Wu, H.Z.; Mitchell, P.; Zhang, M. Therapeutic effects of cerebrolysin added to risperidone in patients with schizophrenia dominated by negative symptoms. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2012, 46, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, S. Cerebrolysin and its emerging clinical applications in psychiatry. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2013, 47, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pochueva, V.; Safarova, T.; Yakovleva, O. Complex antidepressant therapy with the inclusion of various neuroprotectors in inpatient gerontopsychiatric practice. Eur. Psychiatry 2024, 67, S233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykhailova, I.; Mitelov, D.; Matkovska, T.; Mayorov, O. Model of therapeutic intervention in anorexia nervosa of adolescents with depressive behavioral disorders. Eur. Psychiatry 2021, 64, S225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosawi, A.A.P. The use of cerebrolysin in pervasive developmental disorders. Arch. Dis. Child. 2019, 104, A321. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.S.; Kavalali, E.T.; Monteggia, L.M. BDNF signaling in context: From synaptic regulation to psychiatric disorders. Cell 2022, 185, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zutphen, E.M.; Rhebergen, D.; van Exel, E.; Sienaert, P.; Vandenbulcke, M.; Stek, M.; Dols, A. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor as a possible predictor of electroconvulsive therapy outcome. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, L.F. Neurotrophin-regulated signalling pathways. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 1545–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akarachkova, E.S. Chronic Fatigue and Approaches to Its Treatment. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2011, 41, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, L.; Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Farajdokht, F.; Salehi-Pourmehr, H.; Pasokh, A.; Ziaee, M.; Sandoghchian Shotorbani, S.; Hosseini, M.J.; Mahmoudi, J. Synergistic effects of combined therapy with cerebrolysin and enriched environment on anxiety-like behavior and spatial cognitive deficits in posttraumatic stress disorder-like mouse model. Behav. Pharmacol. 2023, 34, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudieu, L.; Mennetrier, M.; Llorca, P.-M.; Samalin, L. The Efficacy and Safety of Intranasal Formulations of Ketamine and Esketamine for the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peitl, V.; Puljić, A.; Škrobo, M.; Nadalin, S.; Fumić Dunkić, L.; Karlović, D. Clozapine in Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia and Its Augmentation with Electroconvulsive Therapy in Ultra-Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Extrapharma. Cerebrolysin® Instructions—Dosage and Administration; NeuroPharma GmbH: Unterach, Austria, 2007. [Google Scholar]

| Author | Country, Year of Publication | Study Design | Simple Description | Intervention | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boksha et al. [15] | Russia, 2023 | Original article, experimental, clinical trial | Late-onset psychosis, 59 patients (56 females, 3 males), 5 people with cerebrolysin | 2152 mg per day for 10 days | Cerebrolysin reduces the side effects of neuroleptics. |
| Kapoor [16] | USA, 2012 | Letter to the editor, opinion | Autism spectrum disorder | - | Cerebrolysin, when administered in combination with neuroleptics, may alleviate cognitive impairment in patients with mild to moderate autism. It may also alleviate side effects. |
| Xiao et al. [17] | China, 2012 | Original article, experimental, placebo-controlled | Schizophrenia, 52 people with cerebrolysin (41 male, 11 female), 49 with placebo (34 male, 15 female) | 30 mL of cerebrolysin in 250 mL physiological saline intravenous infusion; the placebo group: 30 mL of placebo in 250 mL physiological saline intravenous infusion daily from Monday to Friday over 4 weeks. | Cerebrolysin did not increase the efficacy of risperidone in treating positive and negative symptoms, but improved cognitive function. |
| Pochueva et al. [18] | Russia, 2024 | Conference, experimental, clinical trial | Depression, 21 people (7 men, 14 women) with actovegin; 20 patients (5 men, 15 women) with cerebrolysin | No data available | Cerebrolysin is effective in treating depression in a geriatric population. |
| Mykhailova et al. [19] | Ukraine, 2021 | Conference, experimental, clinical trial | Anorexia nervosa, 54 adolescent girls with cerebrolysin | Cerebrolysin 10.0 with 0.9 % sodium chloride 200.0, no more data available | Depression in anorexia requires a special approach. |
| Mosawi et al. [20] | Iraq, 2019 | Conference, experimental, clinical trial | Pervasive developmental disorders, 6 patients with cerebrolysin | Courses of cerebrolysin were given in individualized | Significant reduction in autistic features, with some patients showing complete disappearance of core autistic features. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Florek, S.; Główczyński, P.; Badura-Brzoza, K.; Pudlo, R. Is Cerebrolysin Useful in Psychiatry Disorders? Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071661
Florek S, Główczyński P, Badura-Brzoza K, Pudlo R. Is Cerebrolysin Useful in Psychiatry Disorders? Biomedicines. 2025; 13(7):1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071661
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlorek, Szymon, Patryk Główczyński, Karina Badura-Brzoza, and Robert Pudlo. 2025. "Is Cerebrolysin Useful in Psychiatry Disorders?" Biomedicines 13, no. 7: 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071661
APA StyleFlorek, S., Główczyński, P., Badura-Brzoza, K., & Pudlo, R. (2025). Is Cerebrolysin Useful in Psychiatry Disorders? Biomedicines, 13(7), 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071661







