Iron Homeostasis as a Mediator Linking Central Obesity with MASLD and Primary Liver Cancer: A Two-Step Mendelian Randomization Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
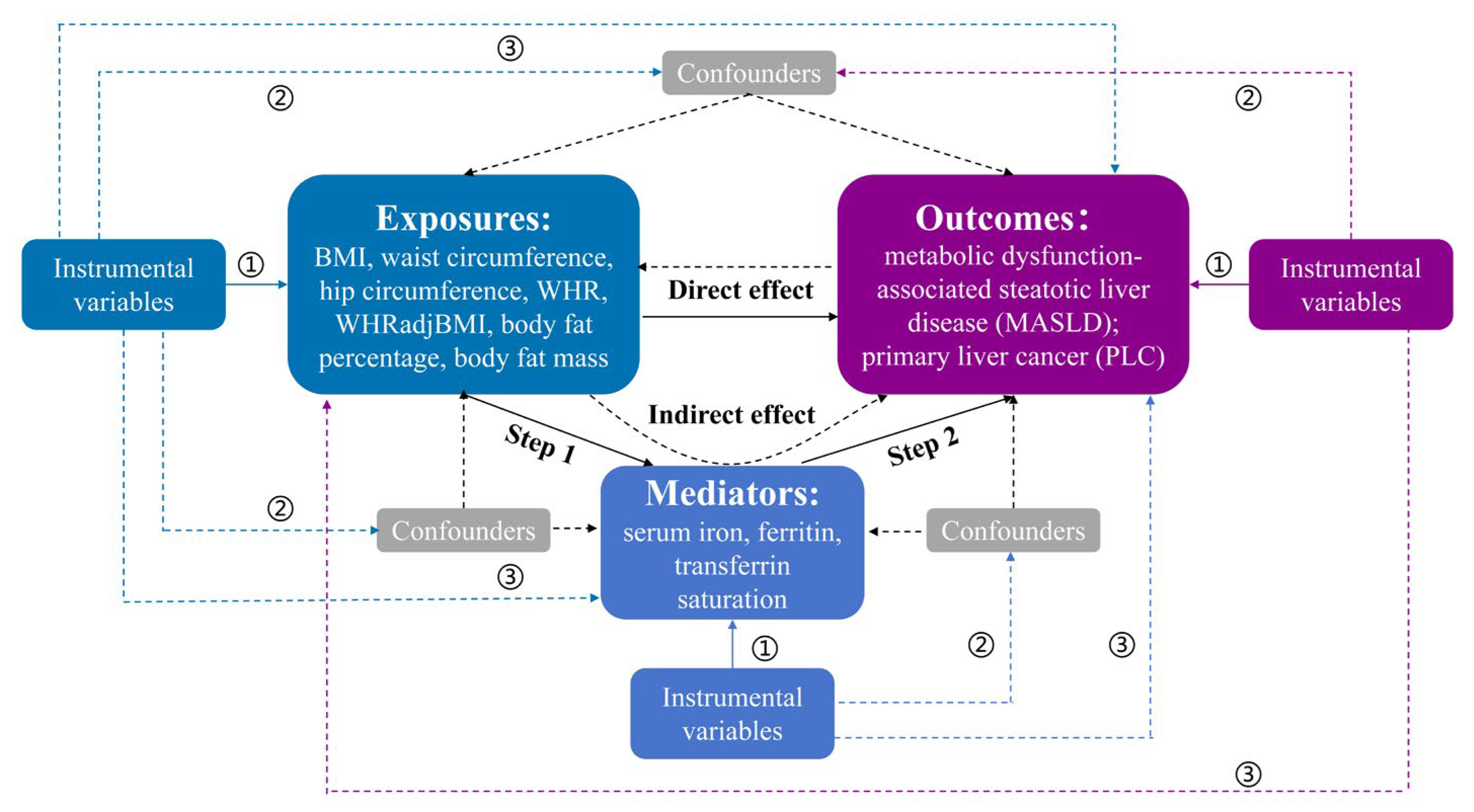
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Genetic Instrument Selection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. MR Analysis
2.4.2. Mediation Analysis
3. Results
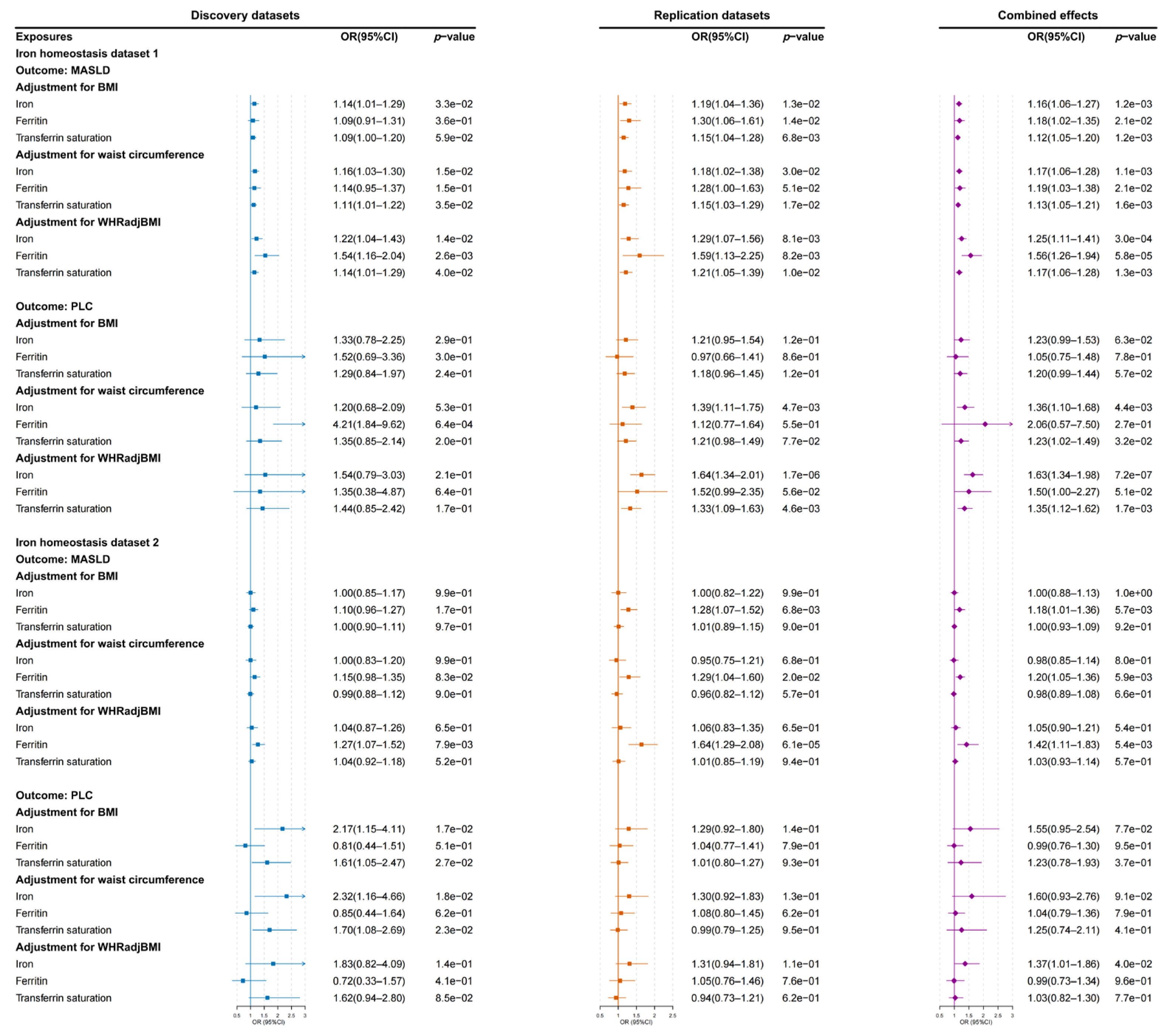
3.1. Causal Estimation from Obesity-Related Traits to MASLD and PLC Risks
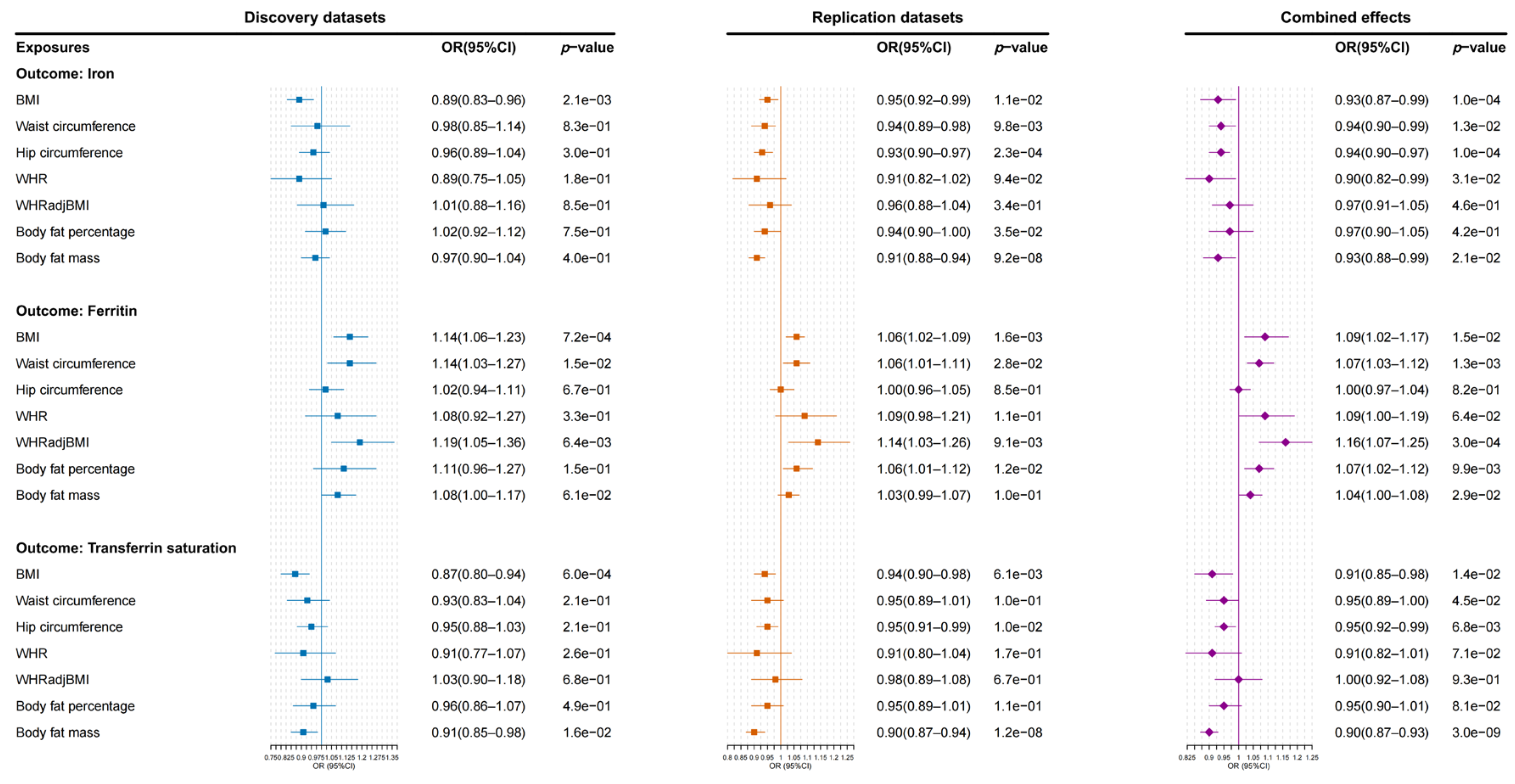
3.2. Causal Estimation from Obesity-Related Traits to Iron Homeostasis Biomarkers
3.3. Causal Estimation from Iron Homeostasis Biomarkers to MASLD and PLC Risks
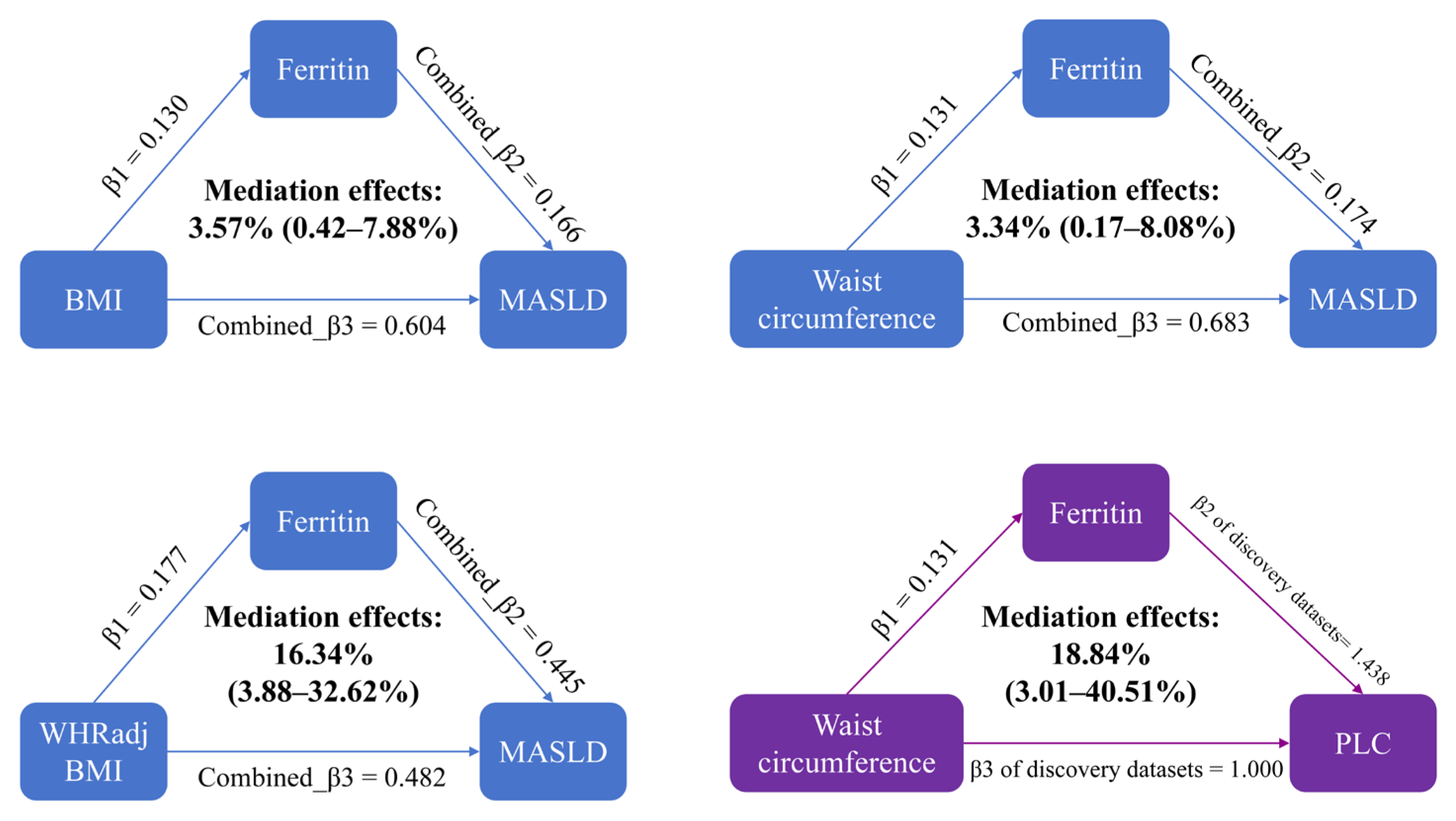
3.4. Mediation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.-S.; Xia, P.-F.; Ma, M.-N.; Li, Y.; Geng, T.-T.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Tu, Z.-Z.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, L.-R.; Zhang, B.-F.; et al. Trends in the Prevalence of Metabolically Healthy Obesity Among US Adults, 1999–2018. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e232145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohm, T.V.; Meier, D.T.; Olefsky, J.M.; Donath, M.Y. Inflammation in obesity, diabetes, and related disorders. Immunity 2022, 55, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quek, J.; Chan, K.E.; Wong, Z.Y.; Tan, C.; Tan, B.; Lim, W.H.; Tan, D.J.H.; Tang, A.S.P.; Tay, P.; Xiao, J.; et al. Global prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in the overweight and obese population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüher, M. An overview of obesity-related complications: The epidemiological evidence linking body weight and other markers of obesity to adverse health outcomes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2025, 27 (Suppl. 2), 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1542–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 492–542. [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.; Tacke, F.; Arrese, M.; Sharma, B.C.; Mostafa, I.; Bugianesi, E.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Yilmaz, Y.; George, J.; Fan, J.; et al. Global Perspectives on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2672–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrastro, O.; Panunzi, S.; Castagneto-Gissey, L.; De Gaetano, A.; Lembo, E.; Capristo, E.; Guidone, C.; Angelini, G.; Pennestrì, F.; Sessa, L.; et al. Bariatric-metabolic surgery versus lifestyle intervention plus best medical care in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (BRAVES): A multicentre, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet 2023, 401, 1786–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argenziano, M.E.; Kim, M.N.; Montori, M.; Di Bucchianico, A.; Balducci, D.; Ahn, S.H.; Baroni, G.S. Epidemiology, pathophysiology and clinical aspects of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in MAFLD patients. Hepatol. Int. 2024, 18, 922–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Ge, C.; Min, J.; Wang, F. The multifaceted role of ferroptosis in liver disease. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonorov, A.A.; Skalnaya, M.G.; Tinkov, A.A.; Skalny, A.V. Mutual interaction between iron homeostasis and obesity pathogenesis. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. Organ Soc. Miner. Trace Elem. (GMS) 2015, 30, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, L.; Corradini, E.; Adams, L.A.; Aigner, E.; Alqahtani, S.; Arrese, M.; Bardou-Jacquet, E.; Bugianesi, E.; Fernandez-Real, J.-M.; Girelli, D.; et al. Consensus Statement on the definition and classification of metabolic hyperferritinaemia. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Geng, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Meng, Z. Targeting the regulation of iron homeostasis as a potential therapeutic strategy for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2024, 157, 155953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zuo, R.; Xiao, S.; Wang, L. Association between iron metabolism and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES 2017–2018) and a controlled animal study. Nutr. Metab. 2022, 19, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, W.; Chen, P.; Liao, M.; Qin, W.; Liao, W.; Huang, Z. Correlation Analysis Between Preoperative Serum Iron Level and Prognosis as Well as Recurrence of HCC After Radical Resection. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Domínguez, Á.; Visiedo-García, F.M.; Domínguez-Riscart, J.; González-Domínguez, R.; Mateos, R.M.; Lechuga-Sancho, A.M. Iron Metabolism in Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Holmes, M.V. Meta-analysis and Mendelian randomization: A review. Res. Synth. Methods 2019, 10, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emdin, C.A.; Khera, A.V.; Kathiresan, S. Mendelian Randomization. JAMA 2017, 318, 1925–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Y.; Trzaskowski, M.; Maier, R.; Robinson, M.R.; McGrath, J.J.; Visscher, P.M.; Wray, N.R.; et al. Causal associations between risk factors and common diseases inferred from GWAS summary data. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Liao, S.; Zeng, Y.; Liang, L.; Chen, J.; Tao, C. Causal relationships between metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and iron status: Two-sample Mendelian randomization. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2022, 42, 2759–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Luo, S.; Bell, S.; Mo, J.M.Y.; He, B.; Zhou, Y.; Bai, X.; Yeung, S.L.A. Do iron homeostasis biomarkers mediate the associations of liability to type 2 diabetes and glycemic traits in liver steatosis and cirrhosis: A two-step Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yang, F.; Zhang, P.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, L. Genetic effects of iron levels on liver injury and risk of liver diseases: A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 964163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allara, E.; Bell, S.; Smith, R.; Keene, S.J.; Gill, D.; Gaziano, L.; Gysi, D.M.; Wang, F.; Tragante, V.; Mason, A.; et al. Novel loci and biomedical consequences of iron homoeostasis variation. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Ding, E.; Lu, D.; Rui, Z.; Shen, J.; Fan, G. Assessing the effect of modifiable risk factors on hepatocellular carcinoma: Evidence from a bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrivankova, V.W.; Richmond, R.C.; Woolf, B.A.R.; Yarmolinsky, J.; Davies, N.M.; Swanson, S.A.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Timpson, N.J.; Dimou, N.; et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA 2021, 326, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shungin, D.; Winkler, T.W.; Croteau-Chonka, D.C.; Ferreira, T.; Locke, A.E.; Mägi, R.; Strawbridge, R.J.; Pers, T.H.; Fischer, K.; Justice, A.E.; et al. New genetic loci link adipose and insulin biology to body fat distribution. Nature 2015, 518, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyamin, B.; Esko, T.; Ried, J.S.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Vermeulen, S.H.; Traglia, M.; Gögele, M.; Anderson, D.; Broer, L.; Podmore, C.; et al. Novel loci affecting iron homeostasis and their effects in individuals at risk for hemochromatosis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.; Rigas, A.S.; Ferkingstad, E.; Allara, E.; Bjornsdottir, G.; Ramond, A.; Sørensen, E.; Halldorsson, G.H.; Paul, D.S.; Burgdorf, K.S.; et al. A genome-wide meta-analysis yields 46 new loci associating with biomarkers of iron homeostasis. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodsian, N.; Abner, E.; Emdin, C.A.; Gobeil, É.; Taba, N.; Haas, M.E.; Perrot, N.; Manikpurage, H.D.; Gagnon, É.; Bourgault, J.; et al. Electronic health record-based genome-wide meta-analysis provides insights on the genetic architecture of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairfield, C.J.; Drake, T.M.; Pius, R.; Bretherick, A.D.; Campbell, A.; Clark, D.W.; Fallowfield, J.A.; Hayward, C.; Henderson, N.C.; Joshi, P.K.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of NAFLD Using Electronic Health Records. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaue, S.; Kanai, M.; Tanigawa, Y.; Karjalainen, J.; Kurki, M.; Koshiba, S.; Narita, A.; Konuma, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Akiyama, M.; et al. A cross-population atlas of genetic associations for 220 human phenotypes. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, A.K.; Hivert, M.-F.; A Scott, R.; Grimsby, J.L.; Bouatia-Naji, N.; Chen, H.; Rybin, D.; Liu, C.-T.; Bielak, L.F.; Prokopenko, I.; et al. A genome-wide approach accounting for body mass index identifies genetic variants influencing fasting glycemic traits and insulin resistance. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemani, G.; Zheng, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. eLife 2018, 7, e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.Y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofighi, D.; MacKinnon, D.P. RMediation: An R package for mediation analysis confidence interv9888als. Behav. Res. Methods 2011, 43, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavorska, O.O.; Burgess, S. MendelianRandomization: An R package, for performing Mendelian randomization analyses using summarized data. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1734–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parente, E.B.; Dahlström, E.H.; Harjutsalo, V.; Inkeri, J.; Mutter, S.; Forsblom, C.; Sandholm, N.; Gordin, D.; Groop, P.-H. The Relationship Between Body Fat Distribution and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1706–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.V.; Policarpo, S.; Coutinho, J.; Carvalhana, S.; Leitão, J.; Carvalho, A.; Silva, A.P.; Velasco, F.; Medeiros, I.; Alves, A.C.; et al. What Is the Role of the New Index Relative Fat Mass (RFM) in the Assessment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)? Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, S.; Tewara, M.A.; Ji, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dai, X.; Wang, Z.; Xue, F. Body surface area, height, and body fat percentage as more sensitive risk factors of cancer and cardiovascular disease. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 4433–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.-J.; Yang, L.-S.; Yan, Y.-C.; Tan, S.-Y.; Ding, Z.-N.; Liu, H.; Wang, D.-X.; Dong, Z.-R.; Li, T. Anthropometric indicators of adiposity and risk of primary liver cancer: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 185, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Jin, L.; Ye, T.; Du, C.; Gao, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, L.; et al. Visceral and ectopic fat are more predictively associated with primary liver cancer than overall obesity from genetic sights: A Mendelian randomization study. Int. J. Cancer 2024, 154, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, K.; Liu, C. Iron status and obesity-related traits: A two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 985338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguree, S.; Reddy, M.B. Inflammatory Markers and Hepcidin are Elevated but Serum Iron is Lower in Obese Women of Reproductive Age. Nutrients 2021, 13, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, P.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Wang, L. Mitochondrial GCN5L1 acts as a novel regulator for iron homeostasis to promote sorafenib sensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciardullo, S.; Oltolini, A.; Cannistraci, R.; Muraca, E.; Perseghin, G. Sex-related association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and liver fibrosis with body fat distribution in the general US population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 115, 1528–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, Y.; Wang, X.; Liao, S.; Li, C.; Chen, J.; He, H. Iron Homeostasis as a Mediator Linking Central Obesity with MASLD and Primary Liver Cancer: A Two-Step Mendelian Randomization Study. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071641
Zeng Y, Wang X, Liao S, Li C, Chen J, He H. Iron Homeostasis as a Mediator Linking Central Obesity with MASLD and Primary Liver Cancer: A Two-Step Mendelian Randomization Study. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(7):1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071641
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Yuping, Xia Wang, Shenlin Liao, Chuan Li, Jie Chen, and He He. 2025. "Iron Homeostasis as a Mediator Linking Central Obesity with MASLD and Primary Liver Cancer: A Two-Step Mendelian Randomization Study" Biomedicines 13, no. 7: 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071641
APA StyleZeng, Y., Wang, X., Liao, S., Li, C., Chen, J., & He, H. (2025). Iron Homeostasis as a Mediator Linking Central Obesity with MASLD and Primary Liver Cancer: A Two-Step Mendelian Randomization Study. Biomedicines, 13(7), 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071641





