Plasma Multiplatform Metabolomics Towards Evaluation of Gender Differences in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension—A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Study Groups
2.2. Untargeted Metabolomics with LC-Q-ToF/MS and GC-QqQ/MS
2.2.1. Plasma Sample Preparation, Analytical Measurements, and Raw Data Processing
2.2.2. Multivariate Statistics and Metabolite Identification
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| 13-HODE | 13-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid |
| 15-LOX | 15-lipoxygenase |
| 5-LOX | 5-lipoxygenase |
| 9-HODE | 9-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| BCAA | branched-chain amino acids |
| BMPR2 | bone morphogenetic protein receptor type 2 |
| BNP | brain natriuretic peptide |
| BSTFA | N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide |
| CDCA | chenodeoxycholic acid |
| CDP-DG | cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol |
| DG | diacylglycerol |
| E,E-13-HpODE | 13(S)-hydroperoxy-9Z,11E-octadecadienoic acid |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| ERα | estrogen receptor alpha |
| FAO | fatty acid oxidation |
| FDG | 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose |
| FFA | free fatty acids |
| FXR | farnesoid X receptor |
| G3P | glycerol-3-phosphate |
| G6PD | glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| GC-EI-QqQ/MS | gas chromatography electron ionization triple quadrupole mass spectrometry |
| HDL-C | high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol |
| HIF1α | hypoxia-inducible factor 1α |
| HO-1 | heme oxygenase-1 |
| hPASMCs | human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells |
| IDO | indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase |
| IP3 | inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate |
| IS | internal standard |
| LA | linoleic acid |
| LC-ESI-Q-ToF/MS | liquid chromatography electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry |
| LDHB | lactate dehydrogenase B |
| LDL-C | low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol |
| LPA | lysophosphatidic acids |
| LPE | lysophosphatidylethanolamine |
| MCT | monocrotaline |
| mPAP | mean pulmonary artery pressure |
| mRAP | mean pressure in right atrium of the heart |
| MVEC | microvascular endothelial cells |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| OPLS-DA | orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant analysis |
| PA | phosphatidic acid |
| PAECs | pulmonary artery endothelial cells |
| PAH | pulmonary arterial hypertension |
| PASMCs | pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells |
| PAWP | pulmonary artery wedge pressure |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
| PCWP | pulmonary capillary wedge pressure |
| PE | phosphatidylethanolamine |
| PH | pulmonary hypertension |
| PI | phosphatidylinositol |
| PI3Ks | phosphoinositide 3-kinases |
| PIP2 | phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate |
| PIS | phosphatidylinositol synthase |
| PS | phosphatidylserine |
| PVR | pulmonary vascular resistance |
| QA | quality assurance |
| QC | quality control |
| RI | retention index |
| RV | right ventricle |
| RV:LV | ratio of the basal diameter of the right ventricle to the left ventricle in apical 4-chamber view |
| RVSP | right ventricular systolic pressure |
| S1P | sphingosine-1-phosphate |
| SERT | serotonin transporter |
| SMC | smooth muscle cell |
| TCA | tricarboxylic acid |
| TG | triacylglycerol |
| TMCS | trimethylchlorosilane |
| TPH1 | tryptophan hydroxylase 1 |
| UV | unit variance |
| VIP | variable importance in projection |
| VSMCs | vascular smooth muscle cells |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| WU | Wood units |
References
- Simonneau, G.; Montani, D.; Celermajer, D.S.; Denton, C.P.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Krowka, M.; Williams, P.G.; Souza, R. Haemodynamic definitions and updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghi, S.; Novikov, A.; Trandafirescu, T. Clinical update on pulmonary hypertension. J. Investig. Med. 2020, 68, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Arias, J.J.; García-Álvarez, A. Sex Differences in Pulmonary Hypertension. Front. Aging 2021, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Johnson, M.K.; Kiely, D.G.; Condliffe, R.; Elliot, C.A.; Gibbs, J.S.R.; Howard, L.S.; Pepke-Zaba, J.; Sheares, K.K.K.; Corris, P.A.; et al. Changing demographics, epidemiology, and survival of incident pulmonary arterial hypertension: Results from the pulmonary hypertension registry of the United Kingdom and Ireland. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGoon, M.D.; Miller, D.P. REVEAL: A contemporary US pulmonary arterial hypertension registry. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2012, 21, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benza, R.L.; Miller, D.P.; Gomberg-Maitland, M.; Frantz, R.P.; Foreman, A.J.; Coffey, C.S.; Frost, A.; Barst, R.J.; Badesch, D.B.; Elliott, C.G.; et al. Predicting survival in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Insights from the registry to evaluate early and long-term pulmonary arterial hypertension disease management (REVEAL). Circulation 2010, 122, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, M.; Sitbon, O.; Chaouat, A.; Bertocchi, M.; Habib, G.; Gressin, V.; Yaïci, A.; Weitzenblum, E.; Cordier, J.F.; Chabot, F.; et al. Survival in patients with idiopathic, familial, and anorexigen-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension in the modern management era. Circulation 2010, 122, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, K.M.; Delcroix, M.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Tiede, H.; Huscher, D.; Speich, R.; Grünig, E.; Staehler, G.; Rosenkranz, S.; Halank, M.; et al. Anticoagulation and survival in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Results from the comparative, prospective registry of newly initiated therapies for pulmonary hypertension (COMPERA). Circulation 2014, 129, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahm, T.; Tuder, R.M.; Petrache, I. Progress in solving the sex hormone paradox in pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2014, 307, L7–L26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docherty, C.K.; Harvey, K.Y.; Mair, K.M.; Griffin, S.; Denver, N.; MacLean, M.R. The Role of Sex in the Pathophysiology of Pulmonary Hypertension. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1065, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofovic, S.P.; Jackson, E.K. Estradiol Metabolism: Crossroads in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wawrzyniak, R.; Grešner, P.; Lewicka, E.; Macioszek, S.; Furga, A.; Zieba, B.; Markuszewski, M.J.; Da̧browska-Kugacka, A. Metabolomics Meets Clinics: A Multivariate Analysis of Plasma and Urine Metabolic Signatures in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Proteome Res. 2024, 23, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzyniak, R.; Biesemans, M.; Kugacka-Dąbrowska, A.; Lewicka, E.; Bartoszewski, R.; Markuszewski, M.J. Plasma untargeted metabolomics with proteinase K discloses phospholipid signature associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Janocha, A.J.; Erzurum, S.C. Metabolism in Pulmonary Hypertension. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2021, 83, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.M.F.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A.J.S.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Zhou, G.; Sun, M.; Zhou, G. An AMPK paradox in pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2013, 6, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Nie, Y.; Wen, Y.; Hua, S.; Hou, Y.; He, H.; Sun, S. The role and mechanism of AMPK in pulmonary hypertension. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2024, 18, 17534666241271990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.M. Regulation and function of AMPK in physiology and diseases. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morecroft, I.; Dempsie, Y.; Bader, M.; Walther, D.J.; Kotnik, K.; Loughlin, L.; Nilsen, M.; MacLean, M.R. Effect of tryptophan hydroxylase 1 deficiency on the development of hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Hypertension 2007, 49, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, E.; García-Álvarez, A.; Vázquez, J. The Quest for Metabolic Biomarkers of Pulmonary Hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsie, Y.; MacLean, M.R. Pulmonary hypertension: Therapeutic targets within the serotonin system. Br. J. Pharmacol. John. 2008, 155, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talati, M.; Hemnes, A. Fatty acid metabolism in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Role in right ventricular dysfunction and hypertrophy. Pulm. Circ. 2015, 5, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brittain, E.L.; Talati, M.; Fessel, J.P.; Zhu, H.; Penner, N.; Calcutt, M.W.; West, J.D.; Funke, M.; Lewis, G.D.; Gerszten, R.E.; et al. Fatty Acid Metabolic Defects and Right Ventricular Lipotoxicity in Human Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Circulation 2016, 133, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Shu, S.; Wang, P.; Ding, S.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Y.; et al. Promising dawn in the management of pulmonary hypertension: The mystery veil of gut microbiota. iMeta 2024, 3, e159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Peng, J.; Lu, C.; Hsin, M.; Mura, M.; Wu, L.; Chu, L.; Zamel, R.; Machuca, T.; Waddell, T.; et al. Metabolomic Heterogeneity of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodzicz-Jażdżyk, S.; Jażdżyk, P.; Łysik, W.; Cudnoch-Jȩdrzejewska, A.; Czarzasta, K. Sphingolipid metabolism and signaling in cardiovascular diseases. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 915961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrache, I.; Berdyshev, E.V. Ceramide Signaling and Metabolism in Pathophysiological States of the Lung. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2016, 78, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignozzi, L.; Morelli, A.; Cellai, I.; Filippi, S.; Comeglio, P.; Sarchielli, E.; Maneschi, E.; Vannelli, G.B.; Adorini, L.; Maggi, M. Cardiopulmonary protective effects of the selective FXR agonist obeticholic acid in the rat model of monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 165, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, H.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Dai, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Unveiling the metabolic landscape of pulmonary hypertension: Insights from metabolomics. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, M.V.; James, J.; Rafikova, O.; Rafikov, R. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency contributes to metabolic abnormality and pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2021, 320, L508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Hong, J.; Umar, S. Comparative analysis of right ventricular metabolic reprogramming in pre-clinical rat models of severe pulmonary hypertension-induced right ventricular failure. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 935423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, N.; Pi, H.; Gadkari, M.; Yun, X.; Huetsch, J.; Zhang, C.; Harlan, R.; Roux, A.; Graham, D.; Shimoda, L.; et al. Transpulmonary amino acid metabolism in the sugen hypoxia model of pulmonary hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 2023, 13, e12205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wertheim, B.M.; Wang, R.S.; Guillermier, C.; Hütter, C.V.R.; Oldham, W.M.; Menche, J.; Steinhauser, M.L.; Maron, B.A. Proline and glucose metabolic reprogramming supports vascular endothelial and medial biomass in pulmonary arterial hypertension. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e163932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.D.; Chu, L.; Lin, K.; Granton, E.; Yin, L.; Peng, J.; Hsin, M.; Wu, L.; Yu, A.; Waddell, T.; et al. A Biochemical Approach to Understand the Pathogenesis of Advanced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Metabolomic Profiles of Arginine, Sphingosine-1-Phosphate, and Heme of Human Lung. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nuffel, S.; Quatredeniers, M.; Pirkl, A.; Zakel, J.; Le Caer, J.P.; Elie, N.; Vanbellingen, Q.P.; Dumas, S.J.; Nakhleh, M.K.; Ghigna, M.R.; et al. Multimodal Imaging Mass Spectrometry to Identify Markers of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Human Lung Tissue Using MALDI-ToF, ToF-SIMS, and Hybrid SIMS. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 12079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duflot, T.; Tu, L.; Leuillier, M.; Messaoudi, H.; Groussard, D.; Feugray, G.; Azhar, S.; Thuillet, R.; Bauer, F.; Humbert, M.; et al. Preventing the Increase in Lysophosphatidic Acids: A New Therapeutic Target in Pulmonary Hypertension? Metabolites 2021, 11, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Takeda, Y.; Tomimoto, S.; Tani, T.; Narita, H.; Kimura, G. Bilirubin as a prognostic marker in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. BMC Pulm. Med. 2010, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deidda, M.; Piras, C.; Cadeddu Dessalvi, C.; Locci, E.; Barberini, L.; Orofino, S.; Musu, M.; Mura, M.N.; Manconi, P.E.; Finco, G.; et al. Distinctive metabolomic fingerprint in scleroderma patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 241, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, S.H.; Mitsialis, A.S.; Liang, O.D.; Liu, X.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, A.; Christou, H.; Wu, X.; McGowan, F.X.; Kourembanas, S. Divergent cardiopulmonary actions of heme oxygenase enzymatic products in chronic hypoxia. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Ruffenach, G.; Umar, S.; Motayagheni, N.; Reddy, S.T.; Eghbali, M. Role of oxidized lipids in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 2016, 6, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopeć, G.; Waligóra, M.; Tyrka, A.; Jonas, K.; Pencina, M.J.; Zdrojewski, T.; Moertl, D.; Stokwiszewski, J.; Zagozdzon, P.; Podolec, P. Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and survival in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiè, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachiery, J.L.; Gibbs, S.; Lang, I.; Torbicki, A.; Simonneau, G.; Peacock, A.; Noordegraaf, A.V.; Beghetti, M.; et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 903–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
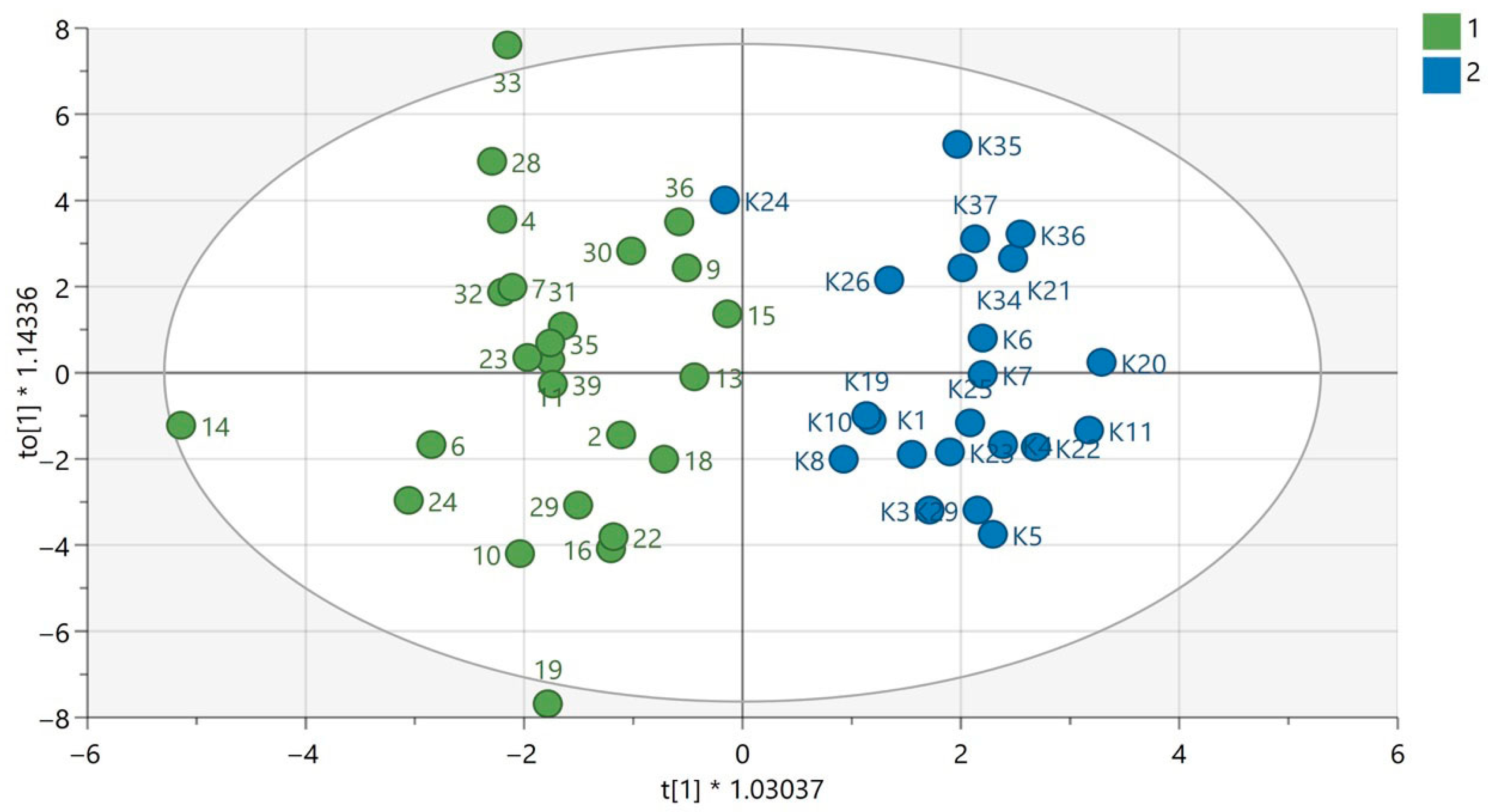

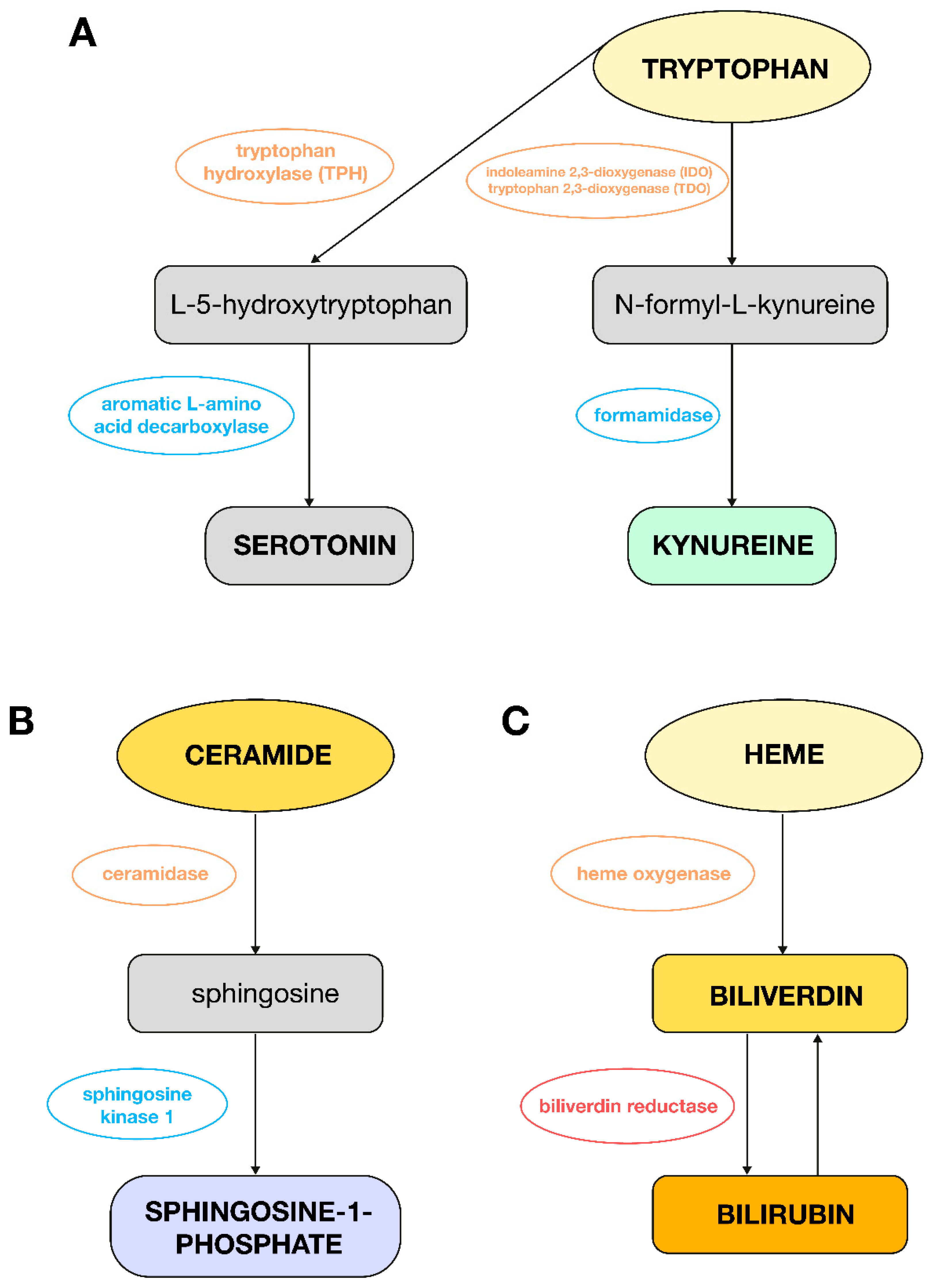
| Variables | Whole Study Population (n = 43) | Females (n = 27) | Males (n = 16) | p Value (Females vs. Males) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 46 ± 18 | 51 ± 19 | 39 ± 14 | <0.05 (0.039) |
| Height (cm) | 162 ± 10 | 160 ± 8 | 170 ± 10 | <0.001 (0.00012) |
| Weight (kg) | 67 ± 15 | 66 ± 15 | 69 ± 18 | 0.63 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26 ± 6 | 27 ± 6 | 24 ± 7 | 0.24 |
| Diagnosis (n): | ||||
| Idiopathic PAH | 22 | 15 | 7 | |
| Connective tissue disease | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0.19 |
| Congenital heart disease | 18 | 9 | 9 | |
| WHO functional class (n): | ||||
| I | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| II | 18 | 11 | 7 | |
| III | 16 | 10 | 6 | 0.903 # |
| IV | 8 | 5 | 3 | |
| Co-morbidities (n/%): | ||||
| Arterial hypertension | 11 | 9 | 2 | 0.33 |
| Hypothyreosis | 12 | 10 | 2 | 0.23 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1.0 |
| Renal failure | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0.32 |
| Coronary artery disease | 6 | 4 | 2 | 1.0 |
| Lung disease | 8 | 6 | 2 | 0.81 |
| Paroxysmal/persistent AF | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1.0 |
| Physiological measurements: | ||||
| HR (beats/min) | 77 ± 12 | 76 ± 12 | 80 ± 11 | 0.38 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 116 ± 17 | 118 ± 18 | 110 ± 13 | 0.15 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 72 ± 13 | 72 ± 10 | 72 ± 18 | 0.98 |
| Pulse pressure (mmHg) | 43 ± 18 | 46 ± 18 | 38 ± 17 | 0.20 |
| Laboratory measurements: | ||||
| BNP (pg/mL) | 103 ± 142 | 99 ± 139 | 108 ± 151 | 0.85 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 16.3 ± 3.4 | 15.3 ± 3.3 | 18.0 ± 3.0 | <0.05 (0.02) |
| PLT (tys./uL) | 187 ± 67 | 197 ± 70 | 168 ± 58 | 0.18 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 138 ± 3 | 139 ± 3 | 138 ± 2 | 0.58 |
| Iron (mg/dL) | 88 ± 58 | 79 ± 55 | 104 ± 62 | 0.20 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 6.8 ± 2.2 | 6.4 ± 2.2 | 7.6 ± 2,2 | 0.11 |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.09 ± 0.58 | 1.0 ± 0.58 | 1.2 ± 0.6 | 0.25 |
| GGT (U/l) | 47 ± 46 | 37 ± 43 | 61 ± 48 | 0.22 |
| ALP (U/l) | 82 ± 32 | 75 ± 26 | 90 ± 37 | 0.27 |
| AST (U/l) | 20 ± 7 | 21 ± 7 | 20 ± 7 | 0.58 |
| ALT (U/l) | 19 ± 9 | 20 ± 10 | 17 ± 7 | 0.31 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.92 ± 0.29 | 0.9 ± 0.3 | ±0.3 | 0.32 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 161 ± 46 | 169 ± 52 | 145 ± 27 | 0.16 |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 102 ± 34 | 103 ± 36 | 98 ± 28 | 0.69 |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 45 ± 10 | 47 ± 10 | 38 ± 9 | <0.05 (0.011) |
| Triglicerydes (mg/dL) | 119 ± 66 | 133 ± 74 | 87 ± 29 | 0.06 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 95.4 ± 24.9 | 91.2 ± 29.4 | 98.9± 15.7 | 0.39 |
| 6 MWT (m) | 404 ± 116 | 403 ± 112 | 407 ± 127 | 0.91 |
| PAH-specific treatment (n/%): | ||||
| Calcium blockers | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0.28 |
| Bosentan | 14 | 4 | 10 | <0.05 (0.002) |
| Macitentan | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0.28 |
| Sildenafil | 28 | 21 | 7 | <0.05 (0.045) |
| Inhaled Iloprost | 6 | 5 | 1 | 0.39 |
| Treprostinil s.c. | 11 | 7 | 4 | 1.0 |
| Combined therapy | 22 | 16 | 6 | 0.22 |
| Other medication (n: | ||||
| Beta blockers | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1.0 |
| Statins | 9 | 6 | 3 | 1.0 |
| ACEI/sartans | 6 | 3 | 3 | 0.65 |
| Diuretics | 17 | 12 | 5 | 0.52 |
| Anticoagulants | 8 | 6 | 2 | 0.69 |
| Euthyrox | 10 | 8 | 2 | 0.28 |
| other | 22 | 15 | 7 | 0.54 |
| Right heart catheterization parameters | ||||
| mPAP (mmHg) | 56 ± 18 | 53 ± 20 | 66 ± 14 | <0.05 (0.045) |
| PCWP (mmHg) | 8.8 ± 3.5 | 7.9 ± 2.6 | 10.4 ± 4.4 | <0.05 (0.046) |
| mRAP (mmHg) | 6.1 ± 3.6 | 5.5 ± 3.7 | 7.6 ± 2.7 | 0.08 |
| CI (ml/kg/min) | 2.6 ± 0.7 | 2.6 ± 0.7 | 2.5 ± 0.9 | 0.62 |
| PVR (Wood units) | 12.1 ± 7.1 | 12.0 ± 8.8 | 13.3 ± 5.7 | 0.62 |
| Echocardiographic variables | ||||
| RVEDD (mm) | 43 ± 7 | 41 ± 8 | 48 ± 17 | 0.06 |
| LVEDD (mm) | 37 ± 9 | 37 ± 7 | 37 ± 12 | 0.81 |
| RV:LV | 1.21 ± 0.35 | 1.16 ± 0.35 | 1.23 ± 0.36 | 0.27 |
| Right atrial area (cm2) | 19.9 ± 5.7 | 19.0 ± 5.4 | 21.7 ± 6.1 | 0.14 |
| Tricuspid regurgitant velocity (cm/s) | 4.1 ± 0.7 | 3.9 ± 0.8 | 4.4 ± 0,3 | <0.05 (0.029) |
| RVSP (mmHg) | 76 ± 23 | 69 ± 27 | 85 ± 11 | <0.05 (0.042) |
| TAPSE (mm) | 19 ± 5 | 20 ± 5 | 18 ± 5 | 0.18 |
| RV S’ (cm/s) | 12 ± 3 | 12 ± 3 | 12 ± 2 | 0.83 |
| RVFAC (%) | 36 ± 12 | 38 ± 12 | 33 ± 11 | 0.17 |
| RVstrain (%) | −18 ± 8 | −19 ± 9 | −16 ± 4 | 0.16 |
| LVEF (%) | 59 ± 7 | 60 ± 7 | 59 ± 7 | 0.64 |
| LVESV (ml) | 29 ± 12 | 27 ± 12 | 32 ± 12 | 0.22 |
| LVEDV (ml) | 70 ± 24 | 66 ± 24 | 78 ± 22 | 0.11 |
| LV GLS (%) | −19 ± 3 | −19 ± 4 | −18 ± 3 | 0.30 |
| Pericardial effusion (number of pts) | 6 (14) | 5 | 1 | |
| Biochemical Pathway | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein and amino acid metabolism | Fatty acid metabolism | Lipid metabolism | Bile acid metabolism |
|
|
|
|
| Carbohydrate metabolism | Nucleotide synthesis | ||
|
| ||
| Biochemical Pathway | ||
|---|---|---|
| Protein and amino acid metabolism | Fatty acid metabolism | Lipid metabolism |
|
|
|
| Heme catabolism | Lipoxygenase pathway (lox) | Steroid biosynthesis |
|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wawrzyniak, R.; Gaillard, T.; Biesemans, M.; Zięba, B.; Lewicka, E.; Markuszewski, M.; Dąbrowska-Kugacka, A. Plasma Multiplatform Metabolomics Towards Evaluation of Gender Differences in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension—A Pilot Study. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1637. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071637
Wawrzyniak R, Gaillard T, Biesemans M, Zięba B, Lewicka E, Markuszewski M, Dąbrowska-Kugacka A. Plasma Multiplatform Metabolomics Towards Evaluation of Gender Differences in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension—A Pilot Study. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(7):1637. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071637
Chicago/Turabian StyleWawrzyniak, Renata, Tamara Gaillard, Margot Biesemans, Bożena Zięba, Ewa Lewicka, Michał Markuszewski, and Alicja Dąbrowska-Kugacka. 2025. "Plasma Multiplatform Metabolomics Towards Evaluation of Gender Differences in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension—A Pilot Study" Biomedicines 13, no. 7: 1637. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071637
APA StyleWawrzyniak, R., Gaillard, T., Biesemans, M., Zięba, B., Lewicka, E., Markuszewski, M., & Dąbrowska-Kugacka, A. (2025). Plasma Multiplatform Metabolomics Towards Evaluation of Gender Differences in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension—A Pilot Study. Biomedicines, 13(7), 1637. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071637







