Venetoclax-Based Regimens in CLL: Immunoglobulin G Levels, Absolute Neutrophil Counts, and Infectious Complications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. VenO Patients Group
2.3. VenR Patients Group
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
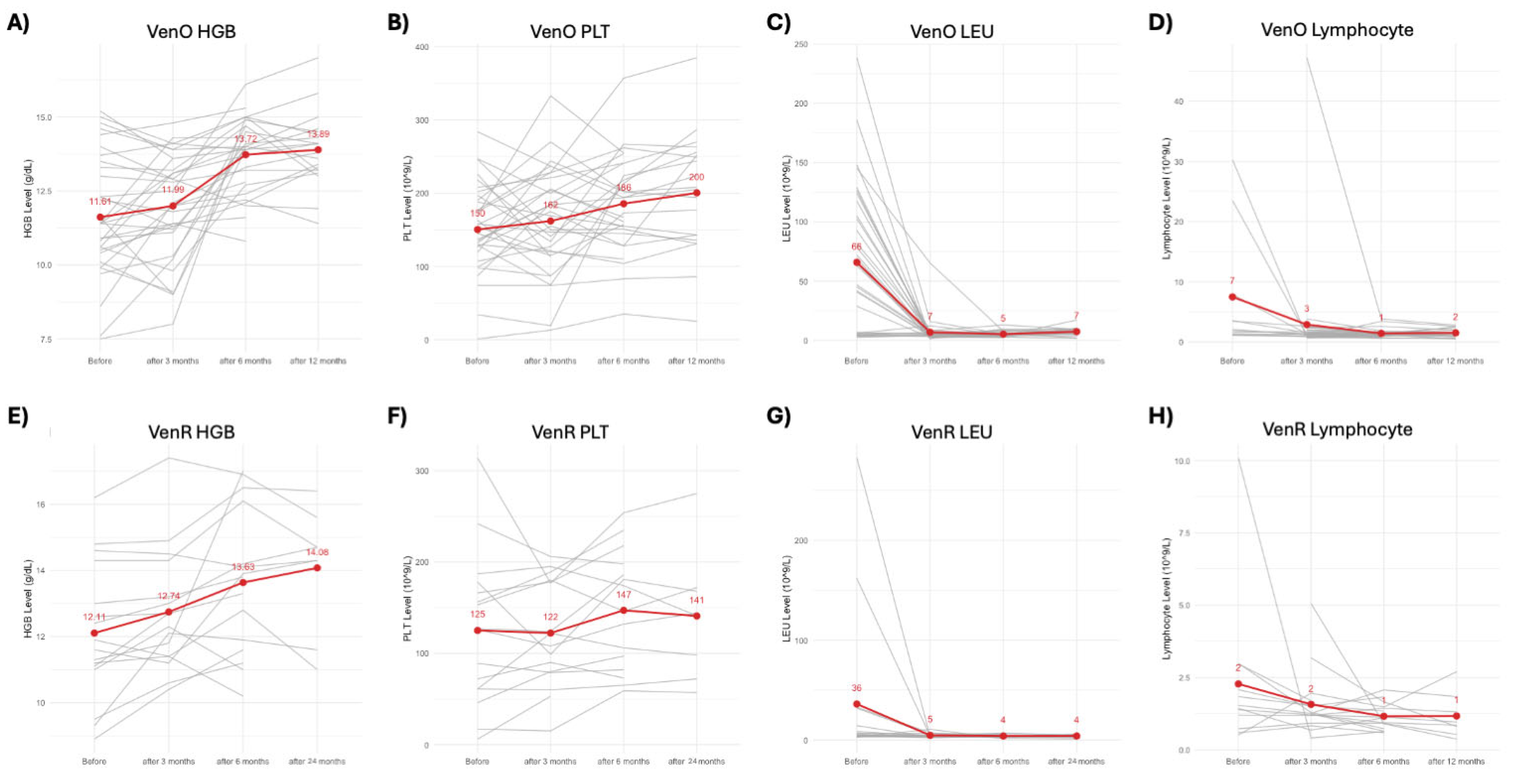
3.1. Complete Blood Count Monitoring During the Therapy
3.2. ANC and IgG Trends During the Therapy
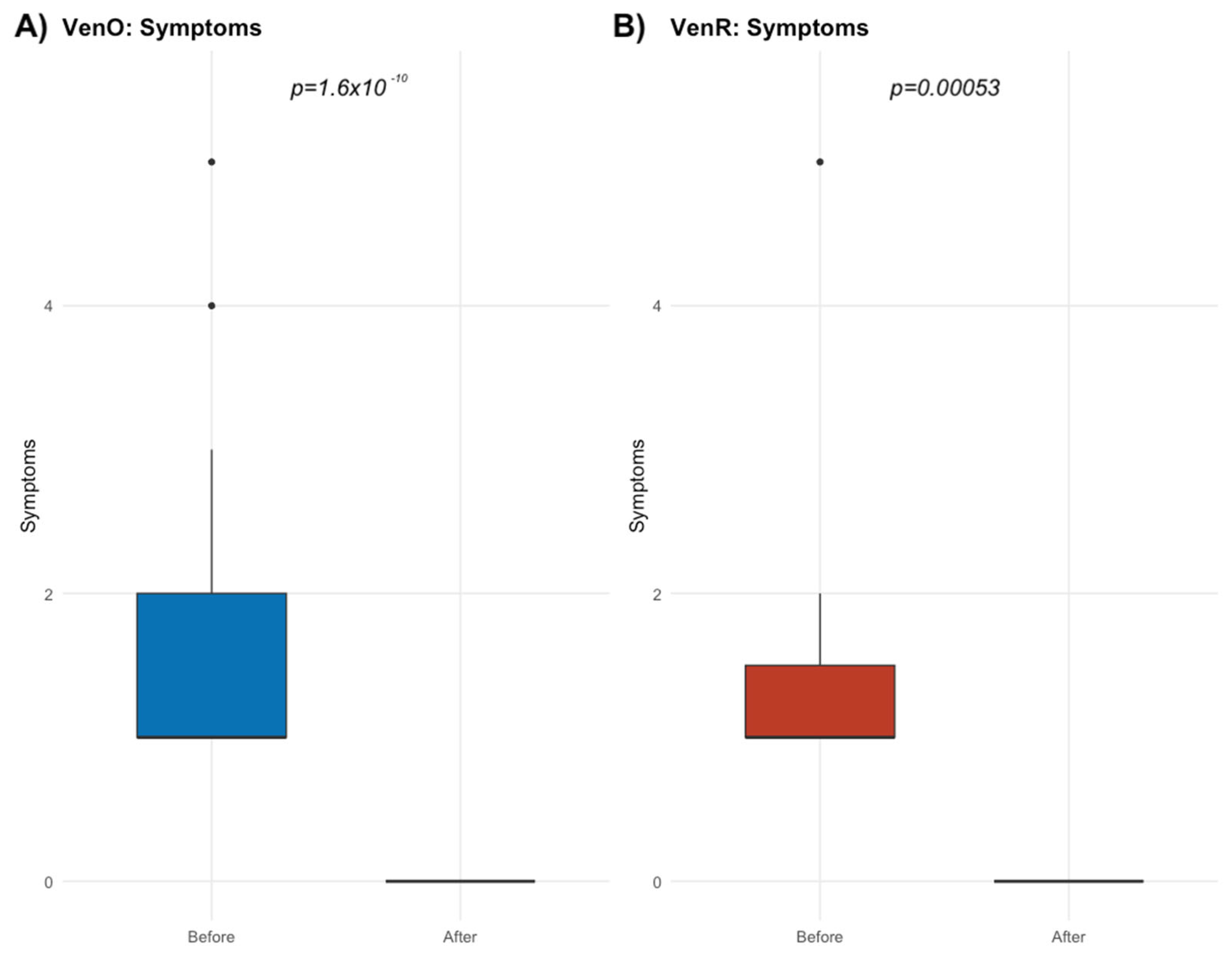
3.3. Impact of the Lowest IgG Level on the Occurrence of Infections During the Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hallek, M.; Al-Sawaf, O. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: 2022 Update on Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 1679–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, P.J.; Parikh, S.A. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Treatment Algorithm 2022. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhssine, S.; Maher, N.; Kogila, S.; Cerchione, C.; Martinelli, G.; Gaidano, G. Current Therapeutic Sequencing in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Hematol. Rep. 2024, 16, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliakas, P.; Hadzidimitriou, A.; Sutton, L.A.; Rossi, D.; Minga, E.; Villamor, N.; Larrayoz, M.; Kminkova, J.; Agathangelidis, A.; Davis, Z.; et al. Recurrent Mutations Refine Prognosis in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Leukemia 2015, 29, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, K.R.; Jain, P. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)-Then and Now. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidano, G.; Rossi, D. The Mutational Landscape of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Its Impact on Prognosis and Treatment. Hematology 2017, 2017, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catherwood, M.A.; Gonzalez, D.; Donaldson, D.; Clifford, R.; Mills, K.; Thornton, P. Relevance of TP53 for CLL Diagnostics. J. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 72, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knittel, G.; Liedgens, P.; Reinhardt, H.C. Targeting ATM-Deficient CLL through Interference with DNA Repair Pathways. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, D.; Smith, L.; Rogers-Broadway, K.R.; Karydis, L.; Woo, J.; Blunt, M.D.; Forconi, F.; Stevenson, F.K.; Goodnow, C.; Russell, A.; et al. Network Analysis Reveals a Major Role for 14q32 Cluster MiRNAs in Determining Transcriptional Differences between IGHV-Mutated and Unmutated CLL. Leukemia 2023, 37, 1454–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, S.A.; Strati, P.; Tsang, M.; West, C.P.; Shanafelt, T.D. Should IGHV Status and FISH Testing Be Performed in All CLL Patients at Diagnosis? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Blood 2016, 127, 1752–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dighiero, G.; Hallek, M.J.; Gribben, J.G. CLL Biology and Prognosis. Hematology 2005, 2005, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, K.; Al-Sawaf, O.; Bahlo, J.; Fink, A.-M.; Tandon, M.; Dixon, M.; Robrecht, S.; Warburton, S.; Humphrey, K.; Samoylova, O.; et al. Venetoclax and Obinutuzumab in Patients with CLL and Coexisting Conditions. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odetola, O.; Ma, S. Relapsed/Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL). Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2023, 18, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerquozzi, S.; Owen, C. Clinical Role of Obinutuzumab in the Treatment of Naive Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Biologics 2015, 9, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Elias, S.; Kahlon, S.; Kotzur, R.; Kaynan, N.; Mandelboim, O. Obinutuzumab Activates FcγRI More Potently than Other Anti-CD20 Antibodies in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL). Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1428158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelmann, J.; Dokal, A.D.; Vilventhraraja, E.; Holzmann, K.; Britton, D.; Klymenko, T.; Döhner, H.; Cragg, M.; Braun, A.; Cutillas, P.; et al. Rituximab and Obinutuzumab Differentially Hijack the B Cell Receptor and NOTCH1 Signaling Pathways. iScience 2021, 24, 102089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, W.; Hiddemann, W.; Buske, C.; Cartron, G.; Cunningham, D.; Dyer, M.J.S.; Gribben, J.G.; Phillips, E.H.; Dreyling, M.; Seymour, J.F.; et al. Obinutuzumab Versus Rituximab Immunochemotherapy in Previously Untreated INHL: Final Results from the GALLIUM Study. Hemasphere 2023, 7, E919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitai, I.; Gafter-Gvili, A.; Shargian-Alon, L.; Raanani, P.; Gurion, R. Obinutuzumab-Related Adverse Events: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, C.L.; Sehn, L.H. A Tale of Two Antibodies: Obinutuzumab versus Rituximab. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 182, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Pagel, J.M. Current and Future Treatment Strategies in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.; Thompson, P.A. BTK Inhibitors in CLL: Second-Generation Drugs and Beyond. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 2300–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sawaf, O.; Robrecht, S.; Zhang, C.; Olivieri, S.; Chang, Y.M.; Fink, A.M.; Tausch, E.; Schneider, C.; Ritgen, M.; Kreuzer, K.A.; et al. Venetoclax-Obinutuzumab for Previously Untreated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: 6-Year Results of the Randomized Phase 3 CLL14 Study. Blood 2024, 144, 1924–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flinn, I.W.; Gribben, J.G.; Dyer, M.J.S.; Wierda, W.; Maris, M.B.; Furman, R.R.; Hillmen, P.; Rogers, K.A.; Iyer, S.P.; Quillet-Mary, A.; et al. Phase 1b Study of Venetoclax-Obinutuzumab in Previously Untreated and Relapsed/Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Blood 2019, 133, 2765–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntington, S.F.; Manzoor, B.S.; Jawaid, D.; Puckett, J.T.; Emechebe, N.; Ravelo, A.; Kamal-Bahl, S.; Doshi, J.A. Real-World Comparison of Health Care Costs of Venetoclax-Obinutuzumab vs Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Use among US Medicare Beneficiaries with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia in the Frontline Setting. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2024, 30, 1106–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noto, A.; Cassin, R.; Mattiello, V.; Bortolotti, M.; Reda, G.; Barcellini, W. Should Treatment of Hypogammaglobulinemia with Immunoglobulin Replacement Therapy (IgRT) Become Standard of Care in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia? Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1062376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haage, T.R.; Zeremski, V.; Berisha, M.; Mougiakakos, D. Hypogammaglobulinemia and Anti-CD20 Therapy-Induced Acute Thrombocytopenia: Perhaps More than a Coincidence? Oncol. Res. Treat. 2024, 47, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNulty, C.M.; Isikwei, E.A.; Shrestha, P.; Snyder, M.R.; Kabat, B.F.; Rabe, K.G.; Slager, S.L.; Parikh, S.A.; Joshi, A.Y. Risk Factors for Hypogammaglobulinemia in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Patients Treated with Anti-CD20 Monoclonal Antibody-Based Therapies. J. Hematop. 2020, 13, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athni, T.S.; Barmettler, S. Hypogammaglobulinemia, Late-Onset Neutropenia, and Infections Following Rituximab. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023, 130, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimony, S.; Bar-Sever, E.; Berger, T.; Itchaki, G.; Gurion, R.; Yeshurun, M.; Lahav, M.; Raanani, P.; Wolach, O. Late Onset Neutropenia after Rituximab and Obinutuzumab Treatment—Characteristics of a Class-Effect Toxicity. Leuk. Lymphoma 2021, 62, 2921–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogiatzi, F.; Heymann, J.; Muller, K.; Winterberg, D.; Drakul, A.; Rosner, T.; Lenk, L.; Heib, M.; Gehlert, C.L.; Cario, G.; et al. Venetoclax Enhances the Efficacy of Therapeutic Antibodies in B-Cell Malignancies by Augmenting Tumor Cell Phagocytosis. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 4847–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchor, J.; Garcia-Lacarte, M.; Grijalba, S.C.; Arnaiz-Leché, A.; Pascual, M.; Panizo, C.; Blanco, O.; Segura, V.; Novo, F.J.; Valero, J.G.; et al. Original Research: Venetoclax Improves CD20 Immunotherapy in a Mouse Model of MYC/BCL2 Double-Expressor Diffuse Large β-Cell Lymphoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e006113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, J.F.; Kipps, T.J.; Eichhorst, B.F.; D’Rozario, J.; Owen, C.J.; Assouline, S.; Lamanna, N.; Robak, T.; de la Serna, J.; Jaeger, U.; et al. Enduring Undetectable MRD and Updated Outcomes in Relapsed/Refractory CLL after Fixed-Duration Venetoclax-Rituximab. Blood 2022, 140, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soboń, A.; Drozd-Sokołowska, J.; Paszkiewicz-Kozik, E.; Popławska, L.; Morawska, M.; Tryc-Szponder, J.; Bołkun, Ł.; Rybka, J.; Pruszczyk, K.; Juda, A.; et al. Clinical Efficacy and Tolerability of Venetoclax plus Rituximab in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia—A Real-World Analysis of the Polish Adult Leukemia Study Group. Ann. Hematol. 2023, 102, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Emond, B.; Qureshi, Z.P.; Wu, L.H.; Forbes, S.P.; Hilts, A.; Liu, S.; Lafeuille, M.H.; Lefebvre, P.; Huang, Q.; et al. Real-World Time to Discontinuation of First-Line Venetoclax + Obinutuzumab in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2023, 39, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorst, B.; Niemann, C.U.; Kater, A.P.; Fürstenau, M.; von Tresckow, J.; Zhang, C.; Robrecht, S.; Gregor, M.; Juliusson, G.; Thornton, P.; et al. First-Line Venetoclax Combinations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1739–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| VenO Group | VenR Group | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Patients | 35 | 16 |
| Gender (M/F) | 22/13 | 11/5 |
| Average Age (years) | 70.3 | 71.1 |
| Average Time to Treatment (days) | 158 | 144 |
| Time to Treatment Range (days) | 0–690 | 1–1099 |
| Median CLL-IPI Score (SD) | 4.39 (2.25) | 4.86 (2.41) |
| Deaths | 1 | 0 |
| Median Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 11.61 | 12.11 |
| Median Platelet Count (×109/L) | 150 | 125 |
| Median Leukocyte Count (×109/L) | 66 | 36 |
| Median Lymphocyte Count (×109/L) | 7 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szlasa, W.; Kisielewska, M.; Sobczyńska-Konefał, A.; Jaskuła, E.; Mordak-Domagała, M.; Kwiatkowski, J.; Tatara, K.; Kuś, A.; Sawicki, M.; Dereń-Wagemann, I.; et al. Venetoclax-Based Regimens in CLL: Immunoglobulin G Levels, Absolute Neutrophil Counts, and Infectious Complications. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071609
Szlasa W, Kisielewska M, Sobczyńska-Konefał A, Jaskuła E, Mordak-Domagała M, Kwiatkowski J, Tatara K, Kuś A, Sawicki M, Dereń-Wagemann I, et al. Venetoclax-Based Regimens in CLL: Immunoglobulin G Levels, Absolute Neutrophil Counts, and Infectious Complications. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(7):1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071609
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzlasa, Wojciech, Monika Kisielewska, Anna Sobczyńska-Konefał, Emilia Jaskuła, Monika Mordak-Domagała, Jacek Kwiatkowski, Katarzyna Tatara, Agnieszka Kuś, Mateusz Sawicki, Izabela Dereń-Wagemann, and et al. 2025. "Venetoclax-Based Regimens in CLL: Immunoglobulin G Levels, Absolute Neutrophil Counts, and Infectious Complications" Biomedicines 13, no. 7: 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071609
APA StyleSzlasa, W., Kisielewska, M., Sobczyńska-Konefał, A., Jaskuła, E., Mordak-Domagała, M., Kwiatkowski, J., Tatara, K., Kuś, A., Sawicki, M., Dereń-Wagemann, I., Sędzimirska, M., Giordano, U., & Dybko, J. (2025). Venetoclax-Based Regimens in CLL: Immunoglobulin G Levels, Absolute Neutrophil Counts, and Infectious Complications. Biomedicines, 13(7), 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071609





