Interleukin 21-Armed EGFR-VHH-CAR-T Cell Therapy for the Treatment of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Culture
2.2. Generation of EGFR-Deficient ESCC Cell Lines
2.3. Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR
2.4. Western Blot
2.5. Isolation and Expansion of T Cells
2.6. Lentivirus Production and T Cell Transduction
2.7. Flow Cytometry Assays
2.8. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Assay
2.9. Cytotoxicity Assays
2.10. ELISA Assay
2.11. Xenograft Tumor Models
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
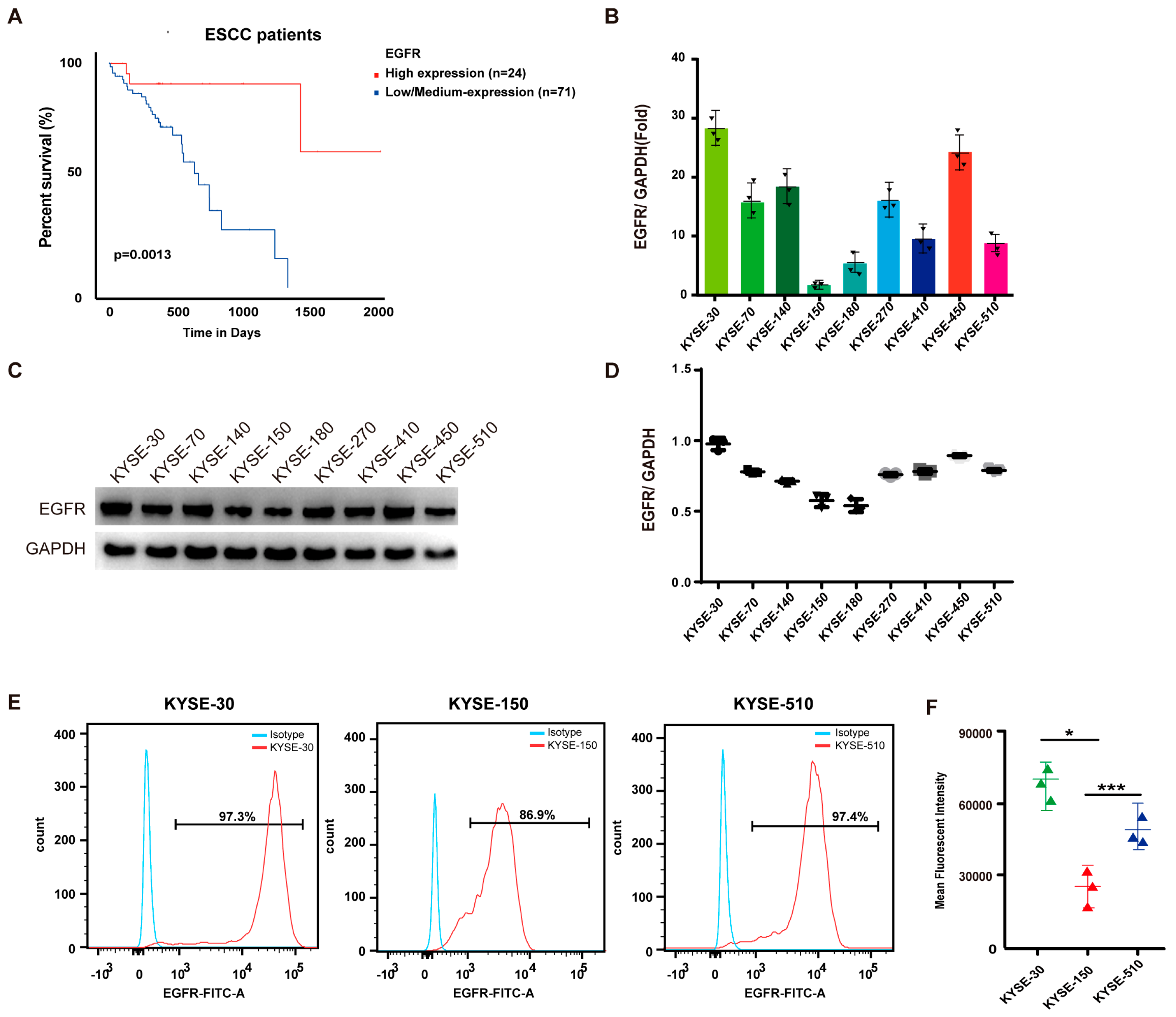
3.1. EGFR Is Upregulated in ESCC and Associated with Poor Prognosis
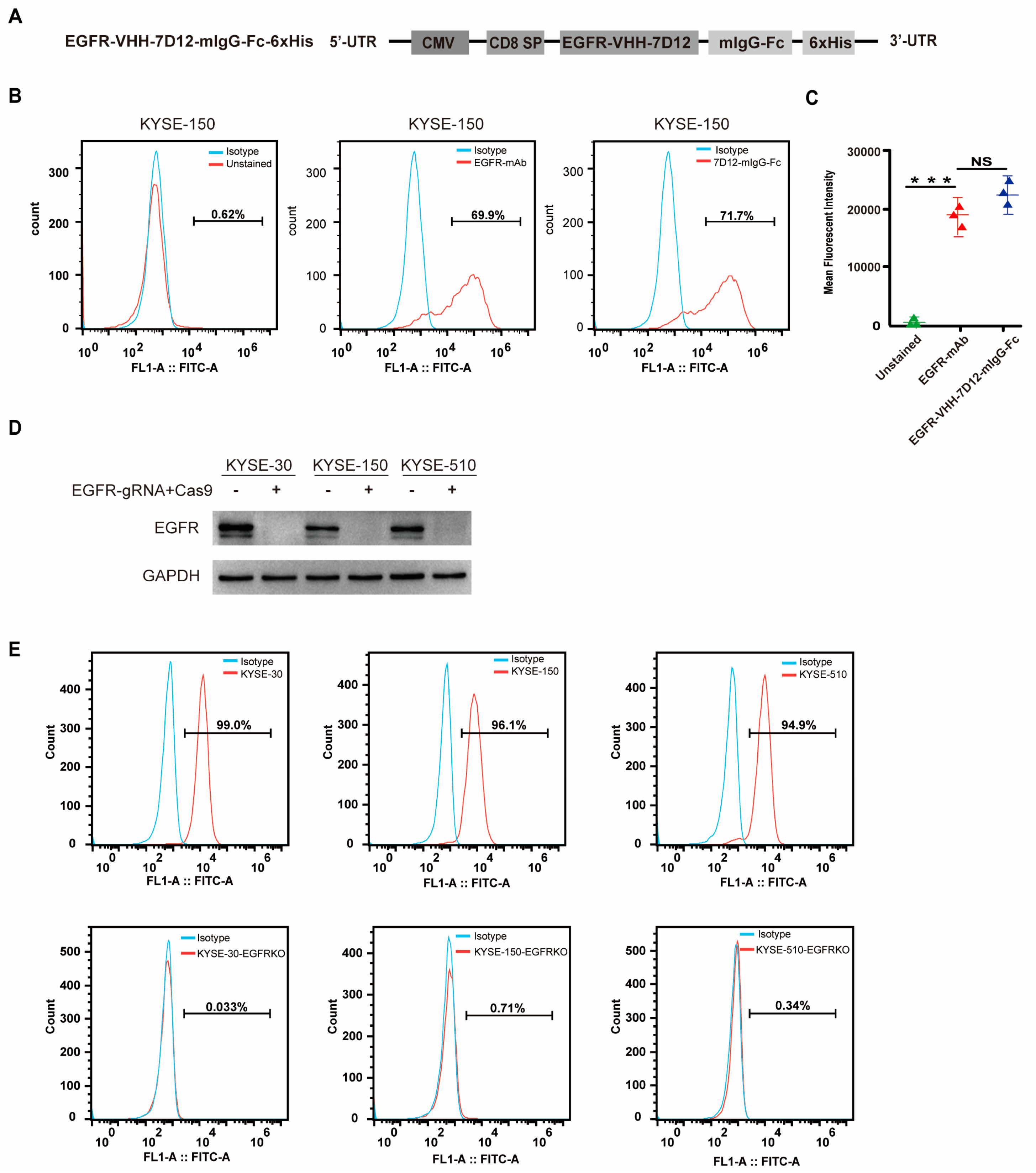
3.2. EGFR-VHH-7D12 Nanobody Effectively Identifies EGFR
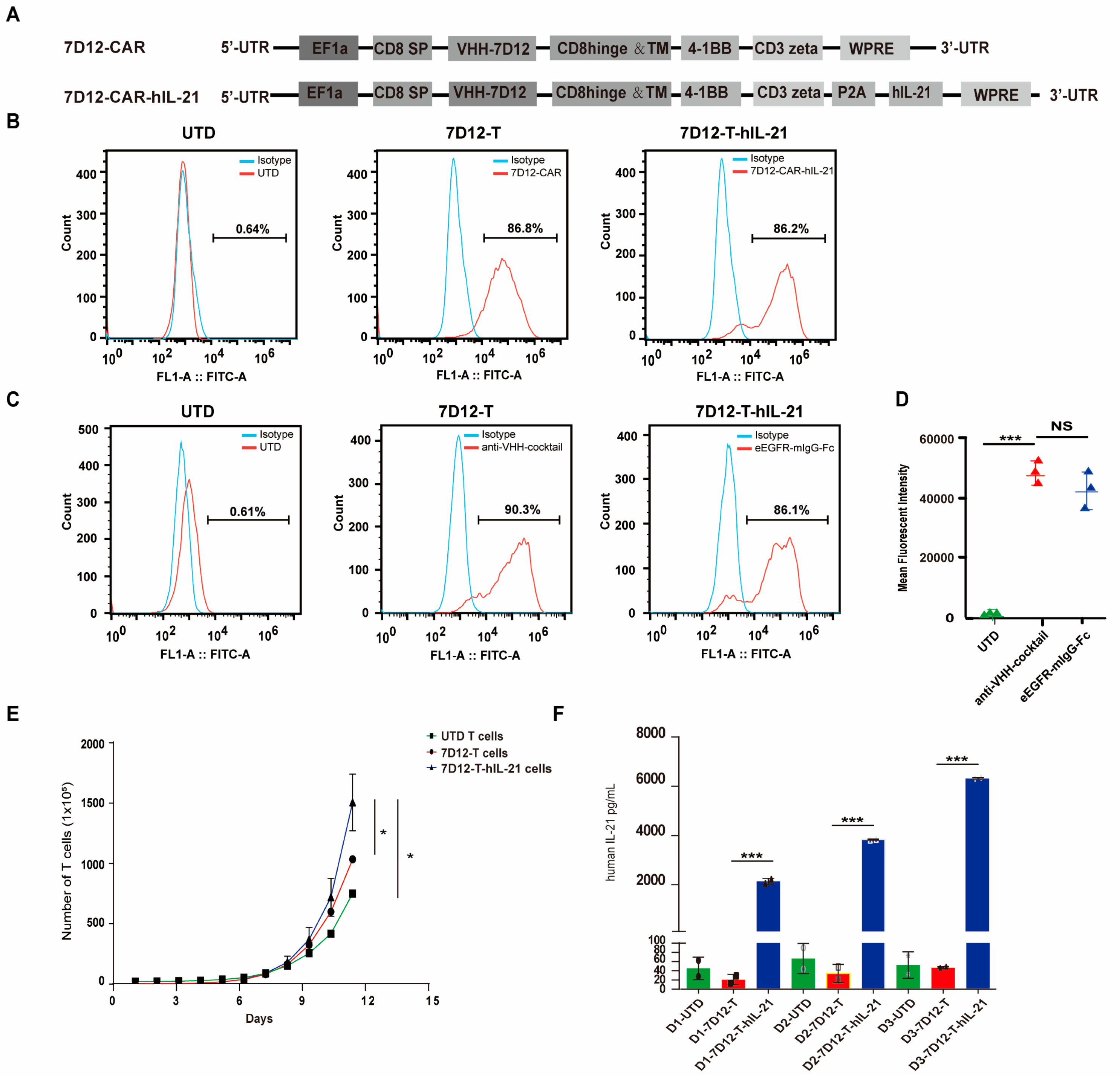
3.3. Generation of hIL-21-Armed VHH-7D12 Nanobody CAR-T Cells
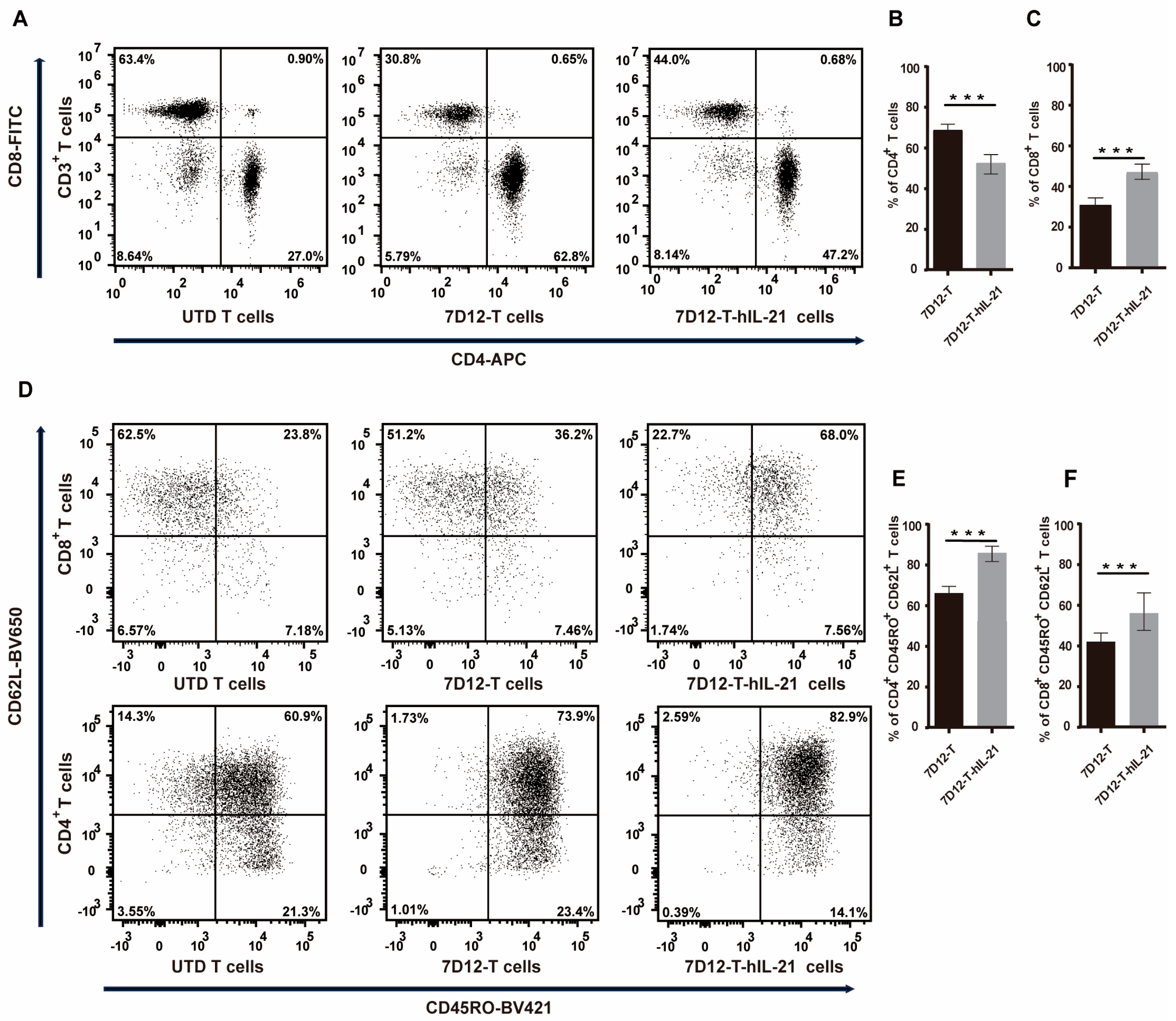
3.4. Influence of hIL-21 on the Phenotype of 7D12-T Cells
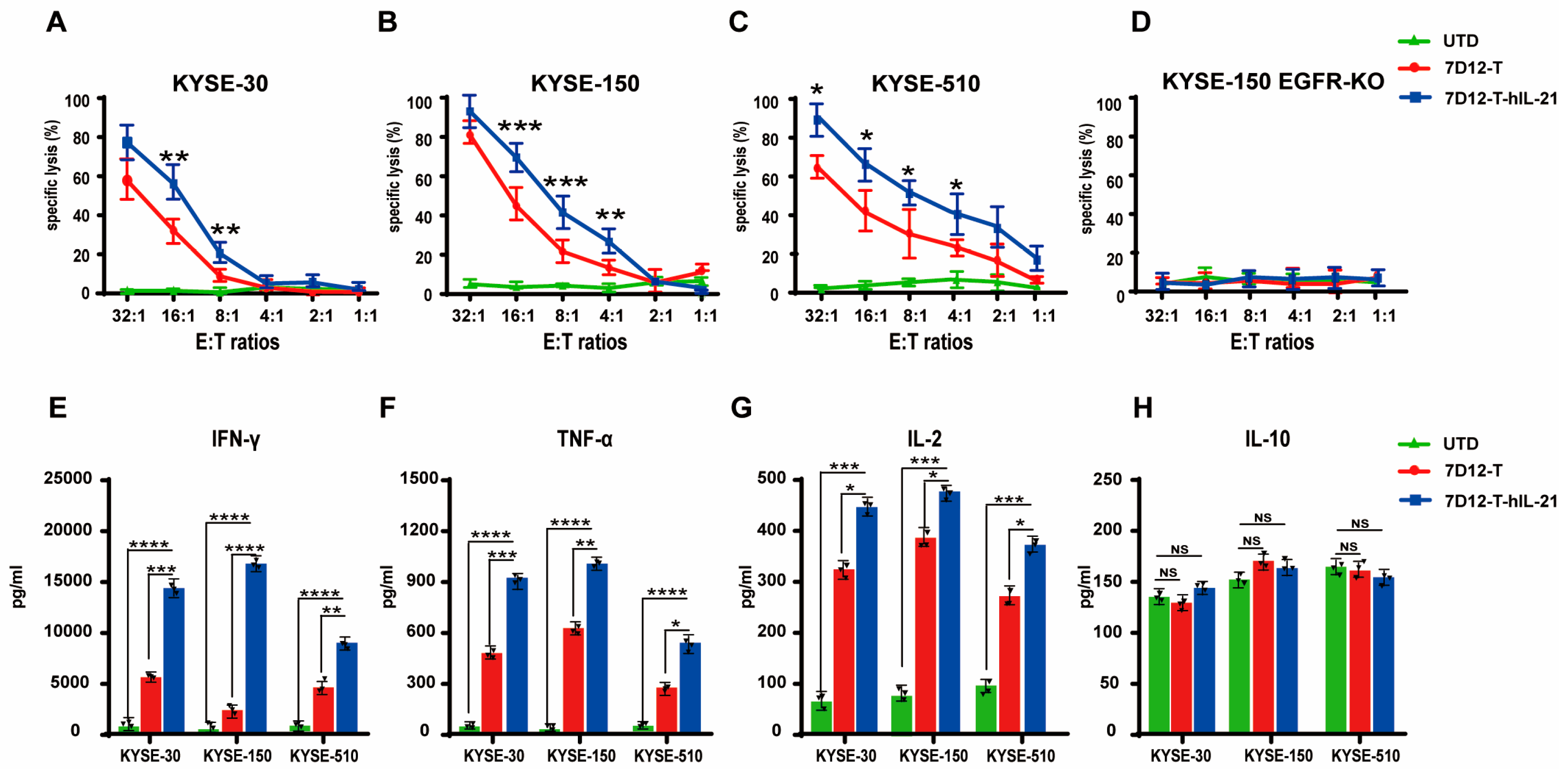
3.5. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of CAR-T Cells Against ESCC Cell Lines
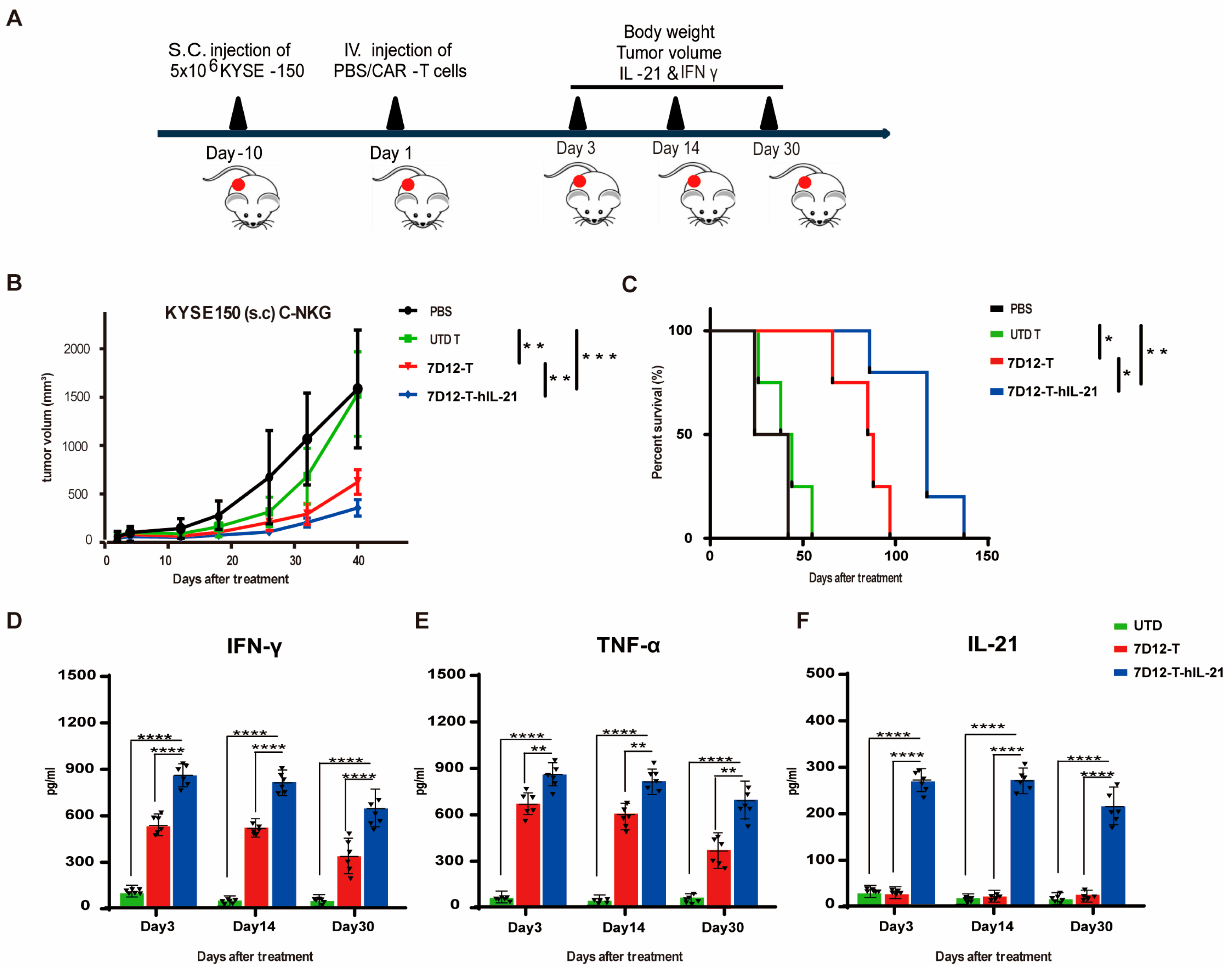
3.6. Efficacy of EGFR-CAR-T Cells in ESCC Cell Mouse Xenograft Models
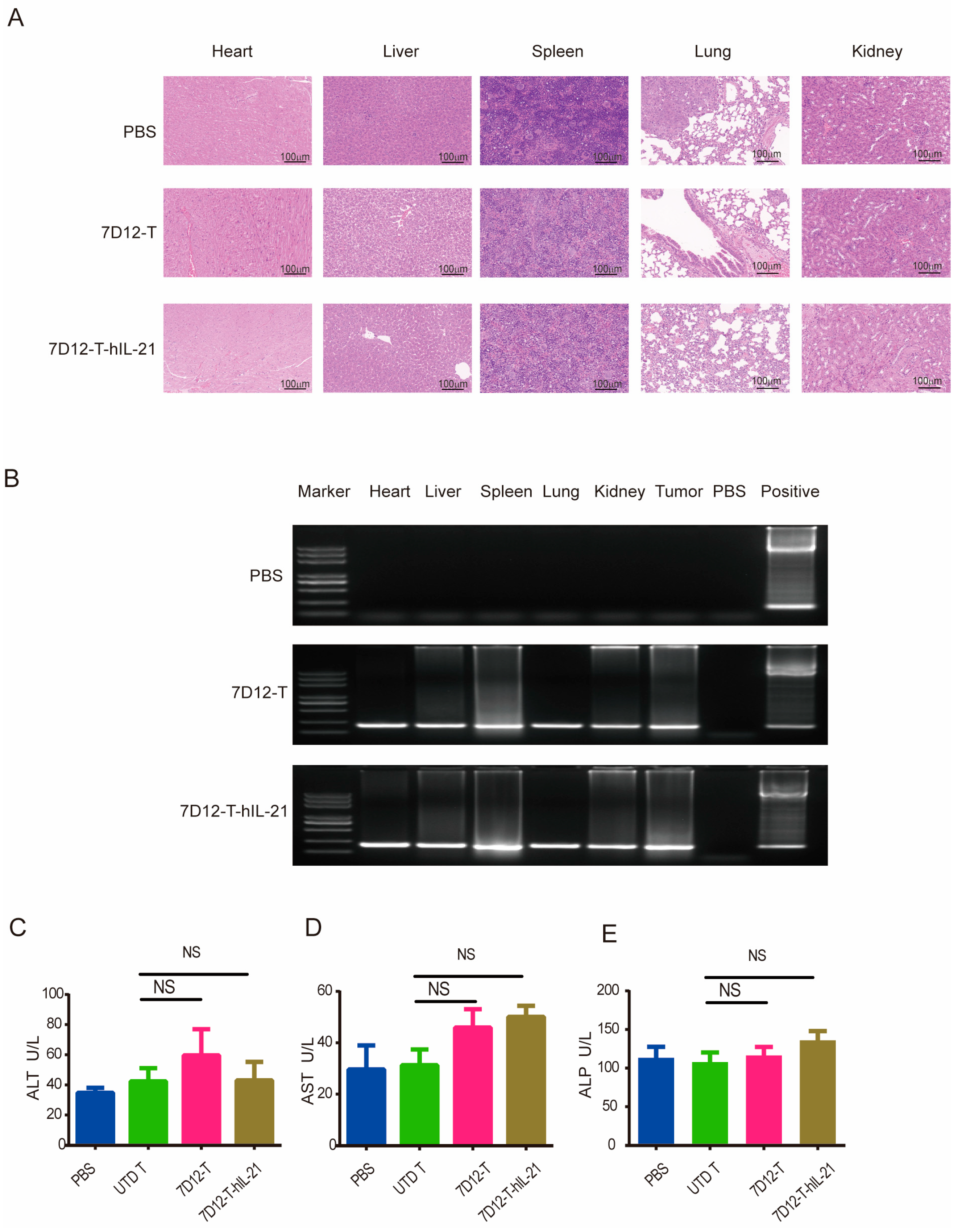
3.7. Safety Profile of EGFR-CAR-T Cells in ESCC Cell Mouse Xenograft Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ESCC | esophageal squamous cell carcinoma |
| EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor |
| VHHs | variable domain of llama heavy chain of heavy-chain antibodies |
| Nbs | nanobodies |
| ScFv | single-chain variable fragment |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| IL-2 | Interleukin-2 |
| IL-21 | Interleukin-21 |
| IFN-γ | interferon-gamma |
| VEGFR2 | vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 |
| BCMA | B cell maturation antigen |
| HER2 | human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| TAG-72 | tumor-associated glycoprotein 72 |
| PSMA | prostate-specific membrane antigen |
| MUC1 | mucin 1 |
| MM | multiple myeloma |
| CR | complete response |
| OR | overall response |
| UALCAN | University of Alabama at Birmingham Cancer Database |
References
- Abnet, C.C.; Arnold, M.; Wei, W.Q. Epidemiology of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Ma, X.; Ye, T.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, K. Esophageal cancer in China: Practice and research in the new era. Int. J. Cancer 2023, 152, 1741–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Chen, W.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, S.; Ji, J.S.; Zou, X.; Xia, C.; Sun, K.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; et al. Changing cancer survival in China during 2003-15: A pooled analysis of 17 population-based cancer registries. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e555–e567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, H.; Fujiwara, H.; Shiozaki, A.; Shoda, K.; Kosuga, T.; Kubota, T.; Okamoto, K.; Otsuji, E. Effects of Neoadjuvant 5-Fluorouracil and Cisplatin Therapy in Patients with Clinical Stage II/III Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Hagen, P.; Hulshof, M.C.; van Lanschot, J.J.; Steyerberg, E.W.; van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; Wijnhoven, B.P.; Richel, D.J.; Nieuwenhuijzen, G.A.; Hospers, G.A.; Bonenkamp, J.J.; et al. Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, K.H.; Li, Y.; Fang, X.; An, L.; Wang, F.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, A.; et al. EGFR-specific CAR-T cells trigger cell lysis in EGFR-positive TNBC. Aging 2019, 11, 11054–11072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P.T.; Vyse, S.; Huang, P.H. Rare epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 61, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Shi, Y.; Xu, C.; Lu, S.; Huang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, H.; Su, J.; et al. The prognostic value of EGFR overexpression and amplification in Esophageal squamous cell Carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.C.; Sterner, R.M. EGFRVIII and EGFR targeted chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy in glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1434495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haist, C.; Poschinski, Z.; Bister, A.; Hoffmann, M.J.; Grunewald, C.M.; Hamacher, A.; Kassack, M.; Wiek, C.; Scheckenbach, K.; Hanenberg, H. Engineering a single-chain variable fragment of cetuximab for CAR T-cell therapy against head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Oral Oncol. 2022, 129, 105867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, J.Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Ding, J.; Hu, G.S.; Hu, Y.H.; Liu, S.; Luo, W.X.; Xia, N.S.; et al. Targeting Triple-Negative Breast Cancer with Combination Therapy of EGFR CAR T Cells and CDK7 Inhibition. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2021, 9, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, D.Q.; Cui, L.Z.; He, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.W.; Zhu, H.L.; Ding, Y.M.; Li, L.F.; et al. Antitumor activity of EGFR-specific CAR T cells against non-small-cell lung cancer cells in vitro and in mice. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safarzadeh Kozani, P.; Naseri, A.; Mirarefin, S.M.J.; Salem, F.; Nikbakht, M.; Evazi Bakhshi, S.; Safarzadeh Kozani, P. Nanobody-based CAR-T cells for cancer immunotherapy. Biomark. Res. 2022, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, C.; Gao, Q.; Li, L.L.; Han, L.; Zhang, B.; Ding, Y.; Song, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.H. The Application of Nanobody in CAR-T Therapy. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhang, J.S.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, K.S.; Xu, B.L.; Li, L.L.; Fang, B.J.; Yin, Q.S.; Zhu, X.H.; Zhou, H.; et al. Single VHH-directed BCMA CAR-T cells cause remission of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2021, 35, 3002–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossotti, M.A.; Bélanger, K.; Henry, K.A.; Tanha, J. Immunogenicity and humanization of single-domain antibodies. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 4304–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.H.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.Y.; Chen, Y.X.; Cao, X.M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, F.X.; Zhang, P.Y.; Lei, B.; et al. A phase 1, open-label study of LCAR-B38M, a chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy directed against B cell maturation antigen, in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, Y.; Kanaya, N.; Moleirinho, S.; Du, W.; Reinshagen, C.; Attia, N.; Bronisz, A.; Revai Lechtich, E.; Sasaki, H.; Mora, J.L.; et al. Anti-EGFR VHH-armed death receptor ligand-engineered allogeneic stem cells have therapeutic efficacy in diverse brain metastatic breast cancers. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narbona, J.; Hernández-Baraza, L.; Gordo, R.G.; Sanz, L.; Lacadena, J. Nanobody-Based EGFR-Targeting Immunotoxins for Colorectal Cancer Treatment. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, K.R.; Bagchi, A.; Roovers, R.C.; van Bergen en Henegouwen, P.M.; Ferguson, K.M. Structural evaluation of EGFR inhibition mechanisms for nanobodies/VHH domains. Structure 2013, 21, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hasan, F.; Frey, A.C.; Li, H.S.; Park, J.; Pan, K.; Haymaker, C.; Bernatchez, C.; Lee, D.A.; Watowich, S.S.; et al. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors and IL21 Cooperate to Reprogram Human Effector CD8(+) T Cells to Memory T Cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 794–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Sun, Z.; Qiao, J.; Liang, Y.; Liu, L.; Dong, C.; Shen, A.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Fu, Y.X.; et al. Targeting tumors with IL-21 reshapes the tumor microenvironment by proliferating PD-1intTim-3-CD8+ T cells. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e132000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Kong, J.; Yin, F.; Shi, J.; Li, J.; Qiu, Z.; Yue, B.; Wang, S.; Sun, N.; Lin, Q.; et al. Optimizing CAR-T cell Culture: Differential effects of IL-2, IL-12, and IL-21 on CAR-T cells. Cytokine 2024, 184, 156758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, K.; Singh, P.B.; Bulfone-Paus, S.; Rückert, R. Interleukin-21: A new modulator of immunity, infection, and cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007, 18, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Gong, F.; Liu, S.; Xie, Y.; Ye, X.; Lin, X.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, Q.; Sun, Y. IL-21- and CXCL9-engineered GPC3-specific CAR-T cells combined with PD-1 blockade enhance cytotoxic activities against hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 24, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štach, M.; Ptáčková, P.; Mucha, M.; Musil, J.; Klener, P.; Otáhal, P. Inducible secretion of IL-21 augments anti-tumor activity of piggyBac-manufactured chimeric antigen receptor T cells. Cytotherapy 2020, 22, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, L.; Ran, F.A.; Cox, D.; Lin, S.; Barretto, R.; Habib, N.; Hsu, P.D.; Wu, X.; Jiang, W.; Marraffini, L.A.; et al. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science 2013, 339, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doench, J.G.; Fusi, N.; Sullender, M.; Hegde, M.; Vaimberg, E.W.; Donovan, K.F.; Smith, I.; Tothova, Z.; Wilen, C.; Orchard, R.; et al. Optimized sgRNA design to maximize activity and minimize off-target effects of CRISPR-Cas9. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Adsani, A.M.; Barhoush, S.A.; Bastaki, N.K.; Al-Bustan, S.A.; Al-Qattan, K.K. Comparing and Optimizing RNA Extraction from the Pancreas of Diabetic and Healthy Rats for Gene Expression Analyses. Genes 2022, 13, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yao, J.; Liu, L.; Chen, J.; Mei, L.; Huangfu, J.; Luo, D.; Wang, X.; Lin, C.; Chen, X.; et al. S-acylation of p62 promotes p62 droplet recruitment into autophagosomes in mammalian autophagy. Mol. Cell 2023, 83, 3485–3501.e3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, P.C.; Zhuo, L.; Lin, J.; Chang, C.; Goddard, A.; Yoon, O.K. Impact of delayed PBMC processing on functional and genomic assays. J. Immunol. Methods 2023, 519, 113514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spolski, R.; Leonard, W.J. Interleukin-21: A double-edged sword with therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Zajac, A.J. IL-21 and T Cell Differentiation: Consider the Context. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbah, D.A.; Hajjo, R.; Sweidan, K. Review on Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Structure, Signaling Pathways, Interactions, and Recent Updates of EGFR Inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 815–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normanno, N.; De Luca, A.; Bianco, C.; Strizzi, L.; Mancino, M.; Maiello, M.R.; Carotenuto, A.; De Feo, G.; Caponigro, F.; Salomon, D.S. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling in cancer. Gene 2006, 366, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribe, M.L.; Marrocco, I.; Yarden, Y. EGFR in Cancer: Signaling Mechanisms, Drugs, and Acquired Resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, E.D.S.; Nogueira, K.A.B.; Fernandes, L.C.C.; Martins, J.R.P.; Reis, A.V.F.; Neto, J.B.V.; Júnior, I.; Pessoa, C.; Petrilli, R.; Eloy, J.O. EGFR targeting for cancer therapy: Pharmacology and immunoconjugates with drugs and nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 592, 120082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Niu, H.; Fan, Q.; Lu, P.; Ma, C.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Hu, S.; Ling, Y.; et al. Predictive value of EGFR overexpression and gene amplification on icotinib efficacy in patients with advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 24744–24751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanawa, M.; Suzuki, S.; Dobashi, Y.; Yamane, T.; Kono, K.; Enomoto, N.; Ooi, A. EGFR protein overexpression and gene amplification in squamous cell carcinomas of the esophagus. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Q.; Pan, Y.; Jiang, D.; Lu, P.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, X.; Feng, J.; Yang, S.; et al. Paclitaxel and cisplatin with or without cetuximab in metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A randomized, multicenter phase II trial. Innovation 2022, 3, 100239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatino, M.; Hu, J.; Sommariva, M.; Gautam, S.; Fellowes, V.; Hocker, J.D.; Dougherty, S.; Qin, H.; Klebanoff, C.A.; Fry, T.J.; et al. Generation of clinical-grade CD19-specific CAR-modified CD8+ memory stem cells for the treatment of human B-cell malignancies. Blood 2016, 128, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, M.; Moon, E.K. CAR T Cells for Solid Tumors: New Strategies for Finding, Infiltrating, and Surviving in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condeminas, M.; Macias, M.J. Overcoming challenges in structural biology with integrative approaches and nanobody-derived technologies. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2024, 84, 102764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossotti, M.A.; Trempe, F.; van Faassen, H.; Hussack, G.; Arbabi-Ghahroudi, M. Isolation and Characterization of Single-Domain Antibodies from Immune Phage Display Libraries. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2702, 107–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruijn, H.S.; Mashayekhi, V.; Schreurs, T.J.L.; van Driel, P.; Strijkers, G.J.; van Diest, P.J.; Lowik, C.; Seynhaeve, A.L.B.; Hagen, T.; Prompers, J.J.; et al. Acute cellular and vascular responses to photodynamic therapy using EGFR-targeted nanobody-photosensitizer conjugates studied with intravital optical imaging and magnetic resonance imaging. Theranostics 2020, 10, 2436–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigismund, S.; Avanzato, D.; Lanzetti, L. Emerging functions of the EGFR in cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voldborg, B.R.; Damstrup, L.; Spang-Thomsen, M.; Poulsen, H.S. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and EGFR mutations, function and possible role in clinical trials. Ann. Oncol. 1997, 8, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lev, S. Targeted therapy and drug resistance in triple-negative breast cancer: The EGFR axis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonetti, A.; Sharma, S.; Minari, R.; Perego, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Tiseo, M. Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Aksoy, O.; Zheng, T.; Fan, Q.W.; Weiss, W.A. Epidermal growth factor receptor and EGFRvIII in glioblastoma: Signaling pathways and targeted therapies. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1561–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinke, H.; Shi, E.; Lin, Z.; Quadt, T.; Kranz, G.; Zhou, J.; Wang, H.; Hess, J.; Heuer, S.; Belka, C.; et al. A transcriptomic map of EGFR-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition identifies prognostic and therapeutic targets for head and neck cancer. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabab, G.; Bonnefoy, N.; Lafont, V. IL-21 Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1240, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batra, S.A.; Rathi, P.; Guo, L.; Courtney, A.N.; Fleurence, J.; Balzeau, J.; Shaik, R.S.; Nguyen, T.P.; Wu, M.F.; Bulsara, S.; et al. Glypican-3-Specific CAR T Cells Coexpressing IL15 and IL21 Have Superior Expansion and Antitumor Activity against Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Wu, H.; Huang, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, Z.; Chen, X.; Lai, X.; Zheng, R.; et al. IL-21 induces pyroptosis of Treg cells via Akt-mTOR-NLRP3-caspase 1 axis in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 152, 641–655.e614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Sakaguchi, S. Regulatory T cells in cancer immunotherapy. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Guo, H.; Peng, Y.; Huang, L.; Lu, S.; Wang, Z. Interleukin 21-Armed EGFR-VHH-CAR-T Cell Therapy for the Treatment of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071598
Zhang C, Liu Y, Guo H, Peng Y, Huang L, Lu S, Wang Z. Interleukin 21-Armed EGFR-VHH-CAR-T Cell Therapy for the Treatment of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(7):1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071598
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chenglin, Yanyan Liu, Haoran Guo, Ying Peng, Lei Huang, Shuangshuang Lu, and Zhimin Wang. 2025. "Interleukin 21-Armed EGFR-VHH-CAR-T Cell Therapy for the Treatment of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Biomedicines 13, no. 7: 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071598
APA StyleZhang, C., Liu, Y., Guo, H., Peng, Y., Huang, L., Lu, S., & Wang, Z. (2025). Interleukin 21-Armed EGFR-VHH-CAR-T Cell Therapy for the Treatment of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biomedicines, 13(7), 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071598






