Investigating the Role of GDF-15 in Diabetes and Obesity: A Comprehensive Analysis of a Cohort from the KDEP Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Study Design
2.2. Anthropometry and Vital Signs Measurements
2.3. Laboratory Measurements
2.4. Definition of Prediabetes and Diabetes
2.5. GDF15 Plasma Levels and R&D Custom Multiplexing Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Sample
3.2. Correlation Between GDF-15 and the Clinical Markers
3.3. Correlation Between GDF-15 and the Glycemic Indices
3.4. Correlation Between GDF-15 and the Biochemical Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GDF-15 | Growth differentiation factor 15 |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor-β |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| GLP-1 | glucagon-like peptide 1 |
| NAFLD | non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
References
- WHO. Obesity and Overweight; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Grundy, S.M. Multifactorial causation of obesity: Implications for prevention. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 67 (Suppl. 3), 563S–572S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, R.J.F.; Yeo, G.S.H. The genetics of obesity: From discovery to biology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, L.; Frias-Toral, E.; Cardenas, D. Editorial: Environmental factors implicated in obesity. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1171507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockhart, S.M.; Saudek, V.; O’Rahilly, S. GDF15: A Hormone Conveying Somatic Distress to the Brain. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, bnaa007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, E.C.; Koniaris, L.G.; Zimmers-Koniaris, T.; Sebald, S.M.; Huynh, T.V.; Lee, S.J. Characterization of growth-differentiation factor 15, a transforming growth factor beta superfamily member induced following liver injury. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 3742–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, A.P.; Chen, M.; Taskar, P.; Rimmington, D.; Patel, S.; Tadross, J.A.; Cimino, I.; Yang, M.; Welsh, P.; Virtue, S.; et al. GDF15 mediates the effects of metformin on body weight and energy balance. Nature 2020, 578, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Townsend, L.K.; DesOrmeaux, G.J.; Frangos, S.M.; Batchuluun, B.; Dumont, L.; Kuhre, R.E.; Ahmadi, E.; Hu, S.; Rebalka, I.A.; et al. GDF15 promotes weight loss by enhancing energy expenditure in muscle. Nature 2023, 619, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Day, E.A.; Townsend, L.K.; Djordjevic, D.; Jørgensen, S.B.; Steinberg, G.R. GDF15: Emerging biology and therapeutic applications for obesity and cardiometabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 592–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.-A.; He, Q.; Zeng, J.; Xia, X. GDF-15, a future therapeutic target of glucolipid metabolic disorders and cardiovascular disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 146, 112582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govaere, O.; Cockell, S.; Tiniakos, D.; Queen, R.; Younes, R.; Vacca, M.; Alexander, L.; Ravaioli, F.; Palmer, J.; Petta, S.; et al. Transcriptomic profiling across the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease spectrum reveals gene signatures for steatohepatitis and fibrosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaba4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, X.; Xie, Z.; Li, J.; Huang, C.; Huang, Y. Overview of growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF15) in metabolic diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 176, 116809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Recarte, D.; Barroso, E.; Guma, A.; Pizarro-Delgado, J.; Peña, L.; Ruart, M.; Palomer, X.; Wahli, W.; Vázquez-Carrera, M. GDF15 mediates the metabolic effects of PPARβ/δ by activating AMPK. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Luo, X.; Fu, N.; Chen, L. Mitochondrial unfolded protein response: A novel pathway in metabolism and immunity. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 168, 105603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochette, L.; Zeller, M.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C. Insights Into Mechanisms of GDF15 and Receptor GFRAL: Therapeutic Targets. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullican, S.E.; Lin-Schmidt, X.; Chin, C.-N.; Chavez, J.A.; Furman, J.L.; Armstrong, A.A.; Beck, S.C.; South, V.J.; Dinh, T.Q.; Cash-Mason, T.D.; et al. GFRAL is the receptor for GDF15 and the ligand promotes weight loss in mice and nonhuman primates. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnen, H.; Lin, S.; Kuffner, T.; Brown, D.A.; Tsai, V.W.-W.; Bauskin, A.R.; Wu, L.; Pankhurst, G.; Jiang, L.; Junankar, S.; et al. Tumor-induced anorexia and weight loss are mediated by the TGF-beta superfamily cytokine MIC-1. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayasu, E.S.; Syed, F.; Tersey, S.A.; Gritsenko, M.A.; Mitchell, H.D.; Chan, C.Y.; Dirice, E.; Turatsinze, J.-V.; Cui, Y.; Kulkarni, R.N.; et al. Comprehensive Proteomics Analysis of Stressed Human Islets Identifies GDF15 as a Target for Type 1 Diabetes Intervention. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 363–374.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pence, B.D. Growth Differentiation Factor-15 in Immunity and Aging. Front. Aging 2022, 3, 837575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, E.A.; Ford, R.J.; Smith, B.K.; Mohammadi-Shemirani, P.; Morrow, M.R.; Gutgesell, R.M.; Lu, R.; Raphenya, A.R.; Kabiri, M.; McArthur, A.G.; et al. Metformin-induced increases in GDF15 are important for suppressing appetite and promoting weight loss. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 1202–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchou, I.; Margeli, A.; Tsironi, M.; Skenderi, K.; Barnet, M.; Kanaka-Gantenbein, C.; Papassotiriou, I.; Beris, P. Growth-differentiation factor-15, endoglin and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide induction in athletes participating in an ultramarathon foot race. Biomarkers 2009, 14, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurens, C.; Parmar, A.; Murphy, E.; Carper, D.; Lair, B.; Maes, P.; Vion, J.; Boulet, N.; Fontaine, C.; Marquès, M.; et al. Growth and differentiation factor 15 is secreted by skeletal muscle during exercise and promotes lipolysis in humans. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e131870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, B.K.; Um, S.H.; Seo, D.S.; Joo, S.K.; Bae, J.M.; Park, J.H.; Chang, M.S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.; Jeong, W.; et al. Growth differentiation factor 15 predicts advanced fibrosis in biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkandari, A.; Alarouj, M.; Elkum, N.; Sharma, P.; Devarajan, S.; Abu-Farha, M.; Al-Mulla, F.; Tuomilehto, J.; Bennakhi, A. Adult Diabetes and Prediabetes Prevalence in Kuwait: Data from the Cross-Sectional Kuwait Diabetes Epidemiology Program. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genuth, S.M.; Palmer, J.P.; Nathan, D.M. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes. In Diabetes in America; Cowie, C.C., Casagrande, S.S., Menke, A., Cissell, M.A., Eberhardt, M.S., Meigs, J.B., Gregg, E.W., Knowler, W.C., Barrett-Connor, E., Becker, D.J., et al., Eds.; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kempf, T.; Horn-Wichmann, R.; Brabant, G.; Peter, T.; Allhoff, T.; Klein, G.; Drexler, H.; Johnston, N.; Wallentin, L.; Wollert, K.C. Circulating concentrations of growth-differentiation factor 15 in apparently healthy elderly individuals and patients with chronic heart failure as assessed by a new immunoradiometric sandwich assay. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajer, M.; Jorsal, A.; Tarnow, L.; Parving, H.-H.; Rossing, P. Plasma growth differentiation factor-15 independently predicts all-cause and cardiovascular mortality as well as deterioration of kidney function in type 1 diabetic patients with nephropathy. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breit, S.N.; Carrero, J.J.; Tsai, V.W.-W.; Yagoutifam, N.; Luo, W.; Kuffner, T.; Bauskin, A.R.; Wu, L.; Jiang, L.; Bárány, P.; et al. Macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 (MIC-1/GDF15) and mortality in end-stage renal disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.; Robinson-Cohen, C.; Smith, M.R.; Bellovich, K.A.; Bhat, Z.Y.; Bobadilla, M.; Brosius, F.; de Boer, I.H.; Essioux, L.; Formentini, I.; et al. Growth Differentiation Factor-15 and Risk of CKD Progression. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 2233–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempf, T.; Björklund, E.; Olofsson, S.; Lindahl, B.; Allhoff, T.; Peter, T.; Tongers, J.; Wollert, K.C.; Wallentin, L. Growth-differentiation factor-15 improves risk stratification in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart J. 2007, 28, 2858–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollert, K.C.; Kempf, T.; Peter, T.; Olofsson, S.; James, S.; Johnston, N.; Lindahl, B.; Horn-Wichmann, R.; Brabant, G.; Simoons, M.L.; et al. Prognostic value of growth-differentiation factor-15 in patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome. Circulation 2007, 115, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzikas, S.; Vassilikos, V.; Keller, T. GDF-15 as a risk stratification biomarker for cardiovascular disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 292, 246–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Candia, A.M.; de Avila, D.X.; Moreira, G.R.; Villacorta, H.; Maisel, A.S. Growth differentiation factor-15, a novel systemic biomarker of oxidative stress, inflammation, and cellular aging: Potential role in cardiovascular diseases. Am. Heart J. Plus: Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2021, 9, 100046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila, G.; Riedl, M.; Anderwald, C.; Resl, M.; Handisurya, A.; Clodi, M.; Prager, G.; Ludvik, B.; Krebs, M.; Luger, A. The relationship between insulin resistance and the cardiovascular biomarker growth differentiation factor-15 in obese patients. Clin. Chem. 2011, 57, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, B.S.; Ku, B.J. Growth Differentiation Factor 15 Predicts Chronic Liver Disease Severity. Gut Liver 2017, 11, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Number (%) |
|---|---|
| Age | |
| <40 | 750 (36.0) |
| 40–50 | 680 (32.7) |
| >50 | 653 (31.3) |
| Ethnicity | |
| Arab | 899 (46.6) |
| South Asian | 666 (34.5) |
| Southeast Asian | 364 (18.9) |
| Diabetic Status | |
| Non-Diabetic | 1425 (69.2) |
| Diabetic | 633 (30.8) |
| BMI | |
| Normal | 441 (21.2) |
| Overweight | 837 (40.2) |
| Obese | 805 (38.6) |
| HOMA-IR | |
| HOMA-IR ≤ 2 | 969 (50.3) |
| HOMA-IR > 2 | 958 (49.7) |
| Hip Circumference (HC), median (IQR) | 102.3 (13) |
| Waist Circumference (WC), median (IQR) | 95 (15) |
| SBP, median (IQR) | 131 (26) |
| DBP, median (IQR) | 80 (16) |
| HbA1c, median (IQR) | 5.8 (1.2) |
| TC, median (IQR) | 5.1 (1.33) |
| AST, median (IQR) | 21 (8) |
| CRP, median (IQR) | 3 (2) |
| Creatinine, median (IQR) | 76 (24) |
| Vitamin D, median (IQR) | 12.01 (10.8) |
| FBG, median (IQR) | 5.3 (1.7) |
| Insulin, median (IQR) | 7.9 (6.7) |
| TSH, median (IQR) | 1.53 (1.14) |
| FT4, median (IQR) | 11.78 (3.43) |
| FT3, median (IQR) | 4.76 (0.78) |
| ALT, median (IQR) | 37 (19) |
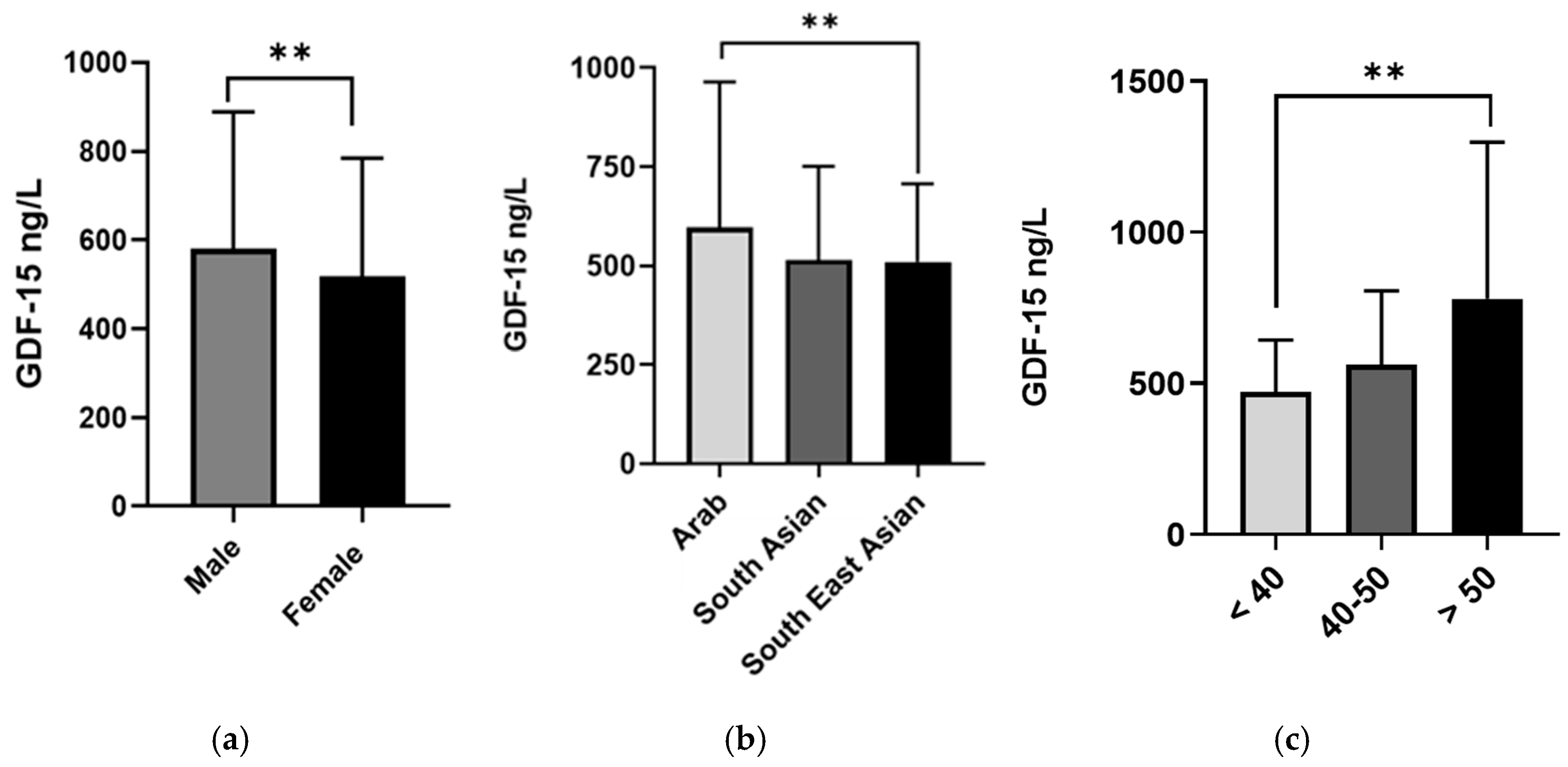
| Characteristics | Number of Patients | GDF-15 Levels (ng/L) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | <0.001 a | ||
| Male | 923 | 580.6 (308.3) | |
| Female | 762 | 519.3 (265.0) | |
| Age | <0.001 b | ||
| <40 | 691 | 471.5 (171.8) | |
| 40–50 | 565 | 563.4 (243.1) | |
| >50 | 429 | 781.4 (516.6) | |
| Ethnicity | <0.001 b | ||
| Arab | 714 | 597.0 (367.5) | |
| South Asian | 511 | 514.9 (236.5) | |
| Southeast Asian | 311 | 509.9 (198.0) | |
| Diabetes Status | <0.001 a | ||
| Non-Diabetic | 1405 | 528.2 (244.4) | |
| Diabetic | 259 | 839.9 (625.8) | |
| BMI | <0.001 b | ||
| Normal | 389 | 502.9 (218.5) | |
| Overweight | 690 | 549.9 (261.9) | |
| Obese | 606 | 598.1 (346.2) | |
| HOMA-IR | <0.001 a | ||
| HOMA-IR ≤ 2 | 892 | 520.6 (231.3) | |
| HOMA-IR > 2 | 642 | 597.4 (351.4) |
| Marker | GDF-15(r) | p-Value | Marker | GDF-15(r) | p-Value | Marker | GDF-15(r) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender a | 0.027 | 0.260 | HbA1c b | 0.297 | <0.001 | ALT b | 0.113 | <0.001 |
| Nationality a | 0.108 | <0.001 | Insulin b | 0.127 | <0.001 | AST b | 0.094 | 0.002 |
| Age b | 0.528 | <0.001 | TC b | −0.032 | <0.192 | CRP b | 0.106 | <0.001 |
| BMI b | 0.181 | <0.001 | TG b | 0.161 | <0.001 | Creatinine b | 0.209 | <0.001 |
| Hip b Circumference | 0.159 | <0.001 | HDL b | −0.118 | <0.001 | Vitamin D b | 0.063 | 0.014 |
| Waist b Circumference | 0.276 | <0.001 | LDL b | −0.063 | 0.011 | TSH b | 0.007 | <0.001 |
| SBP b | 0.230 | <0.001 | TNFAα b | −0.0172 | 0.480 | FT4 b | 0.008 | 0.444 |
| DBP b | 0.105 | <0.001 | FGF1 b | 0.0363 | 0.136 | FT3 b | 0.001 | 0.318 |
| FBG b | 0.269 | <0.001 | HOMA-IR b | 0.198 | <0.001 | RAGE/AGER b | 0.107 | <0.001 |
| CXCL10/IP10 b | 0.110 | <0.001 | FGF-23 b | 0.162 | <0.001 | RANTES b | −0.0218 | 0.903 |
| Variable | Unadjusted Median Regression β (95%CI) | p-Value | Adjusted Median Regression β (95%CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male gender | 61.1 (37.3, 84.8) | <0.001 | 30.1 (11.7, 48.5) | <0.001 |
| Age | 11.2 (10.1, 12.3) | <0.001 | 9.4 (8.0, 10.7) | <0.001 |
| South Asian | −82.8 (−108.1, −57.6) | <0.001 | −41.7 (−67.2, −16.2) | <0.001 |
| Southeast Asian | −87.8 (−114.5, −61.1) | <0.001 | −23.3 (−49.2, 2.56) | 0.077 |
| Diabetic | 311.6 (209.7, 413.6) | <0.001 | 59.6 (−42.8, 161.9) | 0.254 |
| BMI | 7.5 (5.1, 9.9) | <0.001 | −0.49 (−2.56, 1.57) | 0.641 |
| HbA1c | 70.6 (53.0, 88.1) | <0.001 | 14.8 (−16.1, 45.7) | 0.348 |
| HOMA-IR | 26.8 (14.35, 39.2) | <0.001 | 7.73 (1.47, 14.0) | 0.015 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abubaker, J.; Abu-Farha, M.; Albatineh, A.N.; Al-Khairi, I.; Cherian, P.; Ali, H.; Taher, I.; Alajmi, F.; Qaddoumi, M.; Abdul-Ghani, M.; et al. Investigating the Role of GDF-15 in Diabetes and Obesity: A Comprehensive Analysis of a Cohort from the KDEP Study. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071589
Abubaker J, Abu-Farha M, Albatineh AN, Al-Khairi I, Cherian P, Ali H, Taher I, Alajmi F, Qaddoumi M, Abdul-Ghani M, et al. Investigating the Role of GDF-15 in Diabetes and Obesity: A Comprehensive Analysis of a Cohort from the KDEP Study. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(7):1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071589
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbubaker, Jehad, Mohamed Abu-Farha, Ahmed N. Albatineh, Irina Al-Khairi, Preethi Cherian, Hamad Ali, Ibrahim Taher, Fahad Alajmi, Mohammed Qaddoumi, Muhammad Abdul-Ghani, and et al. 2025. "Investigating the Role of GDF-15 in Diabetes and Obesity: A Comprehensive Analysis of a Cohort from the KDEP Study" Biomedicines 13, no. 7: 1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071589
APA StyleAbubaker, J., Abu-Farha, M., Albatineh, A. N., Al-Khairi, I., Cherian, P., Ali, H., Taher, I., Alajmi, F., Qaddoumi, M., Abdul-Ghani, M., & Al-Mulla, F. (2025). Investigating the Role of GDF-15 in Diabetes and Obesity: A Comprehensive Analysis of a Cohort from the KDEP Study. Biomedicines, 13(7), 1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071589








