Growth Factors and the Choroid Plexus: Their Role in Posthemorrhagic Hydrocephalus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Isolated Rat Choroid Plexuses
2.3. Hemoglobin Treatment
2.4. MTT Assay
2.5. Scratch Wound Healing Assay
2.6. Cell Counting and Total Cell Protein Measurement
2.7. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
2.8. RT-qPCR
2.9. Statistical Analysis
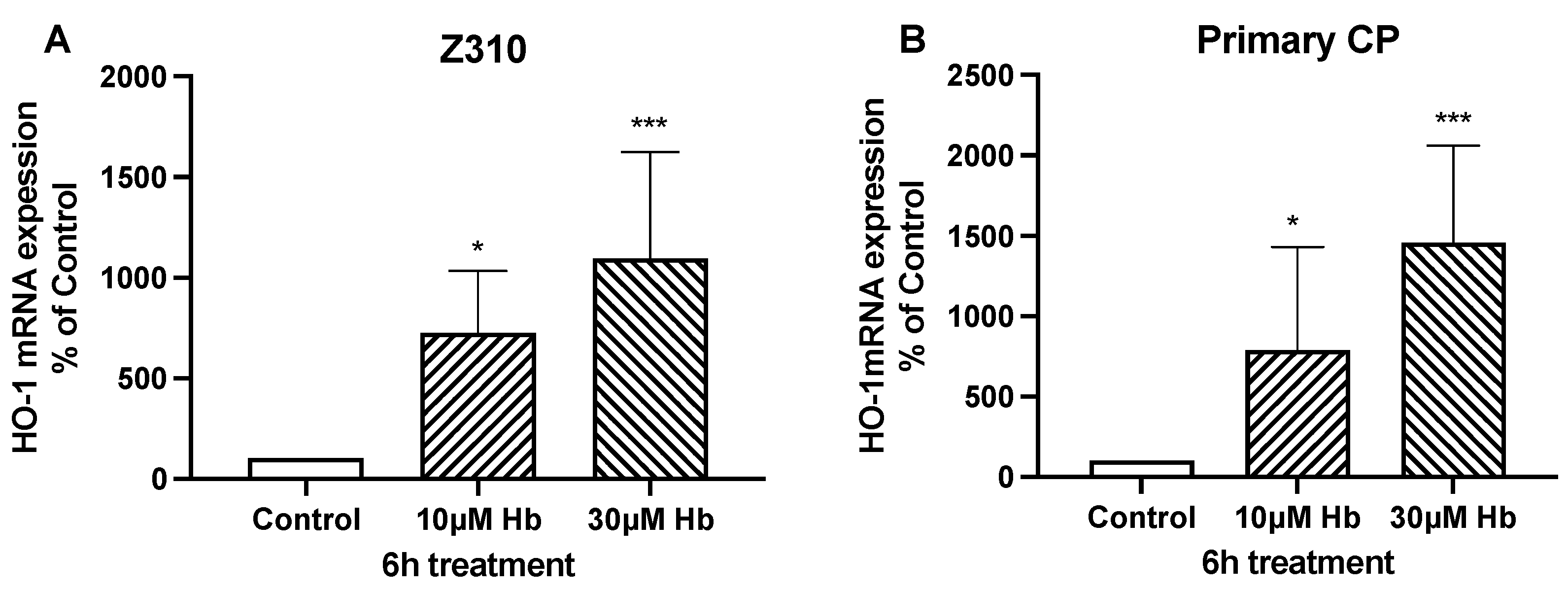
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhattathiri, P.S.; Gregson, B.; Prasad, K.S.; Mendelow, A.D.; Investigators, S. Intraventricular hemorrhage and hydrocephalus after spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: Results from the STICH trial. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2006, 96, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rosen, D.S.; Macdonald, R.L.; Huo, D.; Goldenberg, F.D.; Novakovic, R.L.; Frank, J.I.; Rosengart, A.J. Intraventricular hemorrhage from ruptured aneurysm: Clinical characteristics, complications, and outcomes in a large, prospective, multicenter study population. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 107, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.Y.; Shim, S.Y.; Sung, I.K. Intraventricular Hemorrhage and Post Hemorrhagic Hydrocephalus among Very-Low-Birth-Weight Infants in Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2015, 30 (Suppl. 1), S52–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballabh, P. Intraventricular hemorrhage in premature infants: Mechanism of disease. Pediatr. Res. 2010, 67, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Feng, Z.; Tan, Q.; Guo, J.; Tang, J.; Tan, L.; Feng, H.; Chen, Z. Post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus: Recent advances and new therapeutic insights. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 375, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherian, S.; Whitelaw, A.; Thoresen, M.; Love, S. The pathogenesis of neonatal post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Brain Pathol. 2004, 14, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, D.F. Intraventricular hemorrhage: Severity factor and treatment target in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2009, 40, 1533–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbarli, R.; Reinhard, M.; Roelz, R.; Shah, M.; Niesen, W.D.; Kaier, K.; Taschner, C.; Weyerbrock, A.; Velthoven, V.V. The predictors and clinical impact of intraventricular hemorrhage in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Int. J. Stroke 2016, 11, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahle, J.M.; Garton, T.; Bazzi, A.A.; Kilaru, H.; Garton, H.J.; Maher, C.O.; Muraszko, K.M.; Keep, R.F.; Xi, G. Role of hemoglobin and iron in hydrocephalus after neonatal intraventricular hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 2014, 75, 696–705, discussion 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaestner, S.; Dimitriou, I. TGF beta1 and TGF beta2 and their role in posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus following SAH and IVH. J. Neurol. Surg. Part A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2013, 74, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipina, R.; Reguli, S.; Novácková, L.; Podesvová, H.; Brichtová, E. Relation between TGF-beta 1 levels in cerebrospinal fluid and ETV outcome in premature newborns with posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2010, 26, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodbelt, A.; Stoodley, M. CSF pathways: A review. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 21, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulat, M.; Klarica, M. Recent insights into a new hydrodynamics of the cerebrospinal fluid. Brain Res. Rev. 2011, 65, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, D.; Fadelalla, M.G.; Kanodia, A.K.; Hossain-Ibrahim, K. Choroid plexus and CSF: An updated review. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 36, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, E.A.; Luros, J.T. Hydrocephalus from overproduction of cerebrospinal fluid, and experiences with other parillomas of the choroid plexus. J. Neurosurg. 1952, 9, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimy, J.K.; Zhang, J.; Kurland, D.B.; Theriault, B.C.; Duran, D.; Stokum, J.A.; Furey, C.G.; Zhou, X.; Mansuri, M.S.; Montejo, J.; et al. Inflammation-dependent cerebrospinal fluid hypersecretion by the choroid plexus epithelium in posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, R.W.; Page, L.; Galicich, J.; Watters, G.V. Formation and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid in man. Brain 1968, 91, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damkier, H.H.; Brown, P.D.; Praetorius, J. Cerebrospinal fluid secretion by the choroid plexus. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1847–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreskovic, D.; Rados, M.; Klarica, M. Role of choroid plexus in cerebrospinal fluid hydrodynamics. Neuroscience 2017, 354, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speake, T.; Whitwell, C.; Kajita, H.; Majid, A.; Brown, P.D. Mechanisms of CSF secretion by the choroid plexus. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2001, 52, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, D.B.; Toft-Bertelsen, T.L.; Barbuskaite, D.; Stubbe, J.; Nietzsche, S.; Capion, T.; Norager, N.H.; Olsen, M.H.; Sørensen, A.T.; Dimke, H.; et al. The Na+, K+, 2Cl− Cotransporter, Not Aquaporin 1, Sustains Cerebrospinal Fluid Secretion While Controlling Brain K+ Homeostasis. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2409120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praetorius, J.; Damkier, H.H. Transport across the choroid plexus epithelium. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2017, 312, C673–C686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadegh, C.; Xu, H.; Sutin, J.; Fatou, B.; Gupta, S.; Pragana, A.; Taylor, M.; Kalugin, P.N.; Zawadzki, M.E.; Alturkistani, O.; et al. Choroid plexus-targeted NKCC1 overexpression to treat post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Neuron 2023, 111, 1591–1608.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fèvre Montange, M.; Vasiljevic, A.; Bergemer Fouquet, A.M.; Bernier, M.; Champier, J.; Chrétien, F.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Kemeny, J.L.; Lechapt-Zalcman, E.; Michalak, S.; et al. Histopathologic and ultrastructural features and claudin expression in papillary tumors of the pineal region: A multicenter analysis. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 916–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolburg, H.; Wolburg-Buchholz, K.; Liebner, S.; Engelhardt, B. Claudin-1, claudin-2 and claudin-11 are present in tight junctions of choroid plexus epithelium of the mouse. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 307, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, M.; Onuma, T.; Kameyama, M.; Motohashi, O.; Kon, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Ishii, K.; Tominaga, T. Hydrocephalus due to cerebrospinal fluid overproduction by bilateral choroid plexus papillomas. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2004, 20, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gram, M.; Sveinsdottir, S.; Cinthio, M.; Sveinsdottir, K.; Hansson, S.R.; Morgelin, M.; Akerstrom, B.; Ley, D. Extracellular hemoglobin-mediator of inflammation and cell death in the choroid plexus following preterm intraventricular hemorrhage. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; He, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Tan, C.; Liao, J.; Tong, L.; Xiao, G. Targeting choroid plexus epithelium as a novel therapeutic strategy for hydrocephalus. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Alesi, G.N.; Zhou, N.; Keep, R.F. Protective effects of isothiocyanates on blood-CSF barrier disruption induced by oxidative stress. Am. J. Physiology. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2012, 303, R1–R7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakka, L.; Coll, G.; Chazal, J. Anatomy and physiology of cerebrospinal fluid. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2011, 128, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filis, A.K.; Aghayev, K.; Vrionis, F.D. Cerebrospinal Fluid and Hydrocephalus: Physiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Cancer Control 2017, 24, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orešković, D.; Radoš, M.; Klarica, M. New Concepts of Cerebrospinal Fluid Physiology and Development of Hydrocephalus. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2017, 52, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, C.; Rathnasamy, G.; Ling, E.A. The Choroid Plexus in Healthy and Diseased Brain. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 75, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow, S.A. Development of the choroid plexus and blood-CSF barrier. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, A.M. The role of the blood-CNS barrier in CNS disorders and their treatment. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumani, H.; Huss, A.; Bachhuber, F. The cerebrospinal fluid and barriers-anatomic and physiologic considerations. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 146, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keep, R.F.; Hua, Y.; Xi, G. Intracerebral haemorrhage: Mechanisms of injury and therapeutic targets. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 720–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieber, A.C.; Mocco, J. CD163, Hemoglobin, and Secondary Brain Injury After Intracerebral Hemorrhage. World Neurosurg. 2018, 117, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, G.; Keep, R.F.; Hoff, J.T. Mechanisms of brain injury after intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillardon, F.; Lenz, C.; Kuschinsky, W.; Zimmermann, M. Evidence for apoptotic cell death in the choroid plexus following focal cerebral ischemia. Neurosci. Lett. 1996, 207, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, C.; Hultberg, B.M.; Gammeltoft, S. Autocrine role of insulin-like growth factor II secretion by the rat choroid plexus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1996, 8, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johanson, C.E.; Stopa, E.G.; McMillan, P.N. The blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier: Structure and functional significance. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 686, 101–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, H.J.; Berry, M.; Hill, D.J.; Cwyfan-Hughes, S.; Holly, J.M.; Logan, A. Distinct sites of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-II expression and localization in lesioned rat brain: Possible roles of IGF binding proteins (IGFBPs) in the mediation of IGF-II activity. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fejes, Z.A.-O.; Pócsi, M.; Takai, J.; Erdei, J.A.-O.; Tóth, A.; Balogh, E.; Rusznyák, Á.A.-O.; Fenyvesi, F.A.-O.; Nagy, A.; Kappelmayer, J.; et al. Preterm Intraventricular Hemorrhage-Induced Inflammatory Response in Human Choroid Plexus Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, I.B.; Gyldenholm, T.; Damkier, H.H.; Praetorius, J. Polarization of membrane associated proteins in the choroid plexus epithelium from normal and slc4a10 knockout mice. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Gene | Accession No. | Forward (5′–3′) | Reverse (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BDNF | M61178.1 | ATAATGTCTGACCCCAGTGCC | CTGAGGGAACCCGGTCTCAT |
| IGF2 | NM_031511 | TGTCTACCTCTCAGGCCGTACTT | TCCAGGTGTCGAATTTGAAGAA |
| NGF | NM_001277055.1 | GAAACGGAGACTCCGTTCACC | GATTGTACCATGGGCCTGGA |
| TGF-β1 | NM_021578.2 | TGGCGTTACCTTGGTAACC | GGTGTTGAGCCCTTTCCAG |
| TGF-β2 | AF153012.2 | ATCGATGGCACCTCCACATATG | GCGAAGGCAGCAATTATGCTG |
| TGF-β3 | NM_013174.2 | AAGCGCACAGAGCAGAGAATC | AGTGTCAGTGACATCGAAG |
| BFGF-2 | EF030430.1 | AAGCGGCTCTACTGCAAG | CAGGCCCCGTTTTGGATCCG |
| NKCC1 | AF051561 | CCCGCGGCGCCCTCGTCT | GCACCGTGTCCCCGCCGTTCTG |
| Na/K ATPase ∂1 | NM_012504.1 | ATCTGCTCCGACAAGACTGGAACTCT | TTCTGGGGCGCCCTTCATCAC |
| Na/K ATPase β1 | NM_013113.2 | ACTGAAATTTCCTTCCGTCCTAAT | CGTCAGAGGGTAAGTCTCCAA |
| Na/K ATPase β2 | U45946.1 | TCCTGGGCGATATTATGAGCAACC | CCACGCGGGCAGCAAACTT |
| Claudin-2 | NM_001106846.2 | AGGGTTTCCGGGACAATAA | TAAAGTATCTGGTAGGGTTGCC |
| Claudin-11 | BC070927.1 | CGGGCTGGATCGGTGCTGTG | AATGGAACGCCCGAGGAAAGGAG |
| Occludin | AB016425.1 | GCGACCGCGGTGGAGTTG | AAGCCGCTGCCGTAAGGGTAGT |
| HO-1 | BC091164.1 | AGGTCAAGCACAGGGTGACAGA | CTAGCAGGCCTCTGGCGAAGA |
| GAPDH | AF106860.2 | AGACAGCCGCATCTTCTTGT | CTTGCCGTGGGTAGAGTCAT |
| (A) Growth Factors | ||
| mRNA | Control Expression (Ratio to GAPDH) | Hb-Induced Expression (% of Control) |
| BDNF | 0.00072 ± 0.00012 | 180 ± 6 ** |
| IGF-2 | 4.3 ± 0.21 | 139 ± 12 ** |
| TGF-β1 | 0.038 ± 0.0044 | 158 ± 25 * |
| NGF | 0.095 ± 0.016 | 179 ± 35 ** |
| BFGF-2 | 0.014 ± 0.003 | 153 ± 41 |
| TGF-β2 | 0.17 ± 0.05 | 99 ± 35 |
| TGF-β3 | 0.021 ± 0.003 | 90 ± 14 |
| (B) Ion Transporters and TJ Proteins | ||
| mRNA | Control Expression (Ratio to GAPDH) | Hb-Induced Expression (% of Control) |
| NKCC1 | 0.0008 ± 0.0001 | 150 ± 15 ** |
| Na/K ATPase ∂1 | 1.43 ± 0.12 | 90 ± 2.3 |
| Na/K ATPase β1 | 1.57 ± 0.16 | 97 ± 9.2 |
| Na/K ATPase β2 | 0.35 ± 0.07 | 117 ± 21 |
| Claudin-2 | 0.017 ± 0.008 | 254 ± 53 * |
| Claudin-11 | 0.0007 ± 0.0003 | 546 ± 268 |
| Occludin | 0.25 ± 0.0027 | 91 ± 18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, H.; Miao, W.; Keep, R.F.; Xiang, J. Growth Factors and the Choroid Plexus: Their Role in Posthemorrhagic Hydrocephalus. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061366
Ye H, Miao W, Keep RF, Xiang J. Growth Factors and the Choroid Plexus: Their Role in Posthemorrhagic Hydrocephalus. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(6):1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061366
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Hong, Wei Miao, Richard F. Keep, and Jianming Xiang. 2025. "Growth Factors and the Choroid Plexus: Their Role in Posthemorrhagic Hydrocephalus" Biomedicines 13, no. 6: 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061366
APA StyleYe, H., Miao, W., Keep, R. F., & Xiang, J. (2025). Growth Factors and the Choroid Plexus: Their Role in Posthemorrhagic Hydrocephalus. Biomedicines, 13(6), 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061366







