The Comprehensive Effect of Depression, Anxiety, and Headache on Pain Intensity and Painkiller Use in Patients with Headache Analyzed by Unsupervised Clustering Using Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
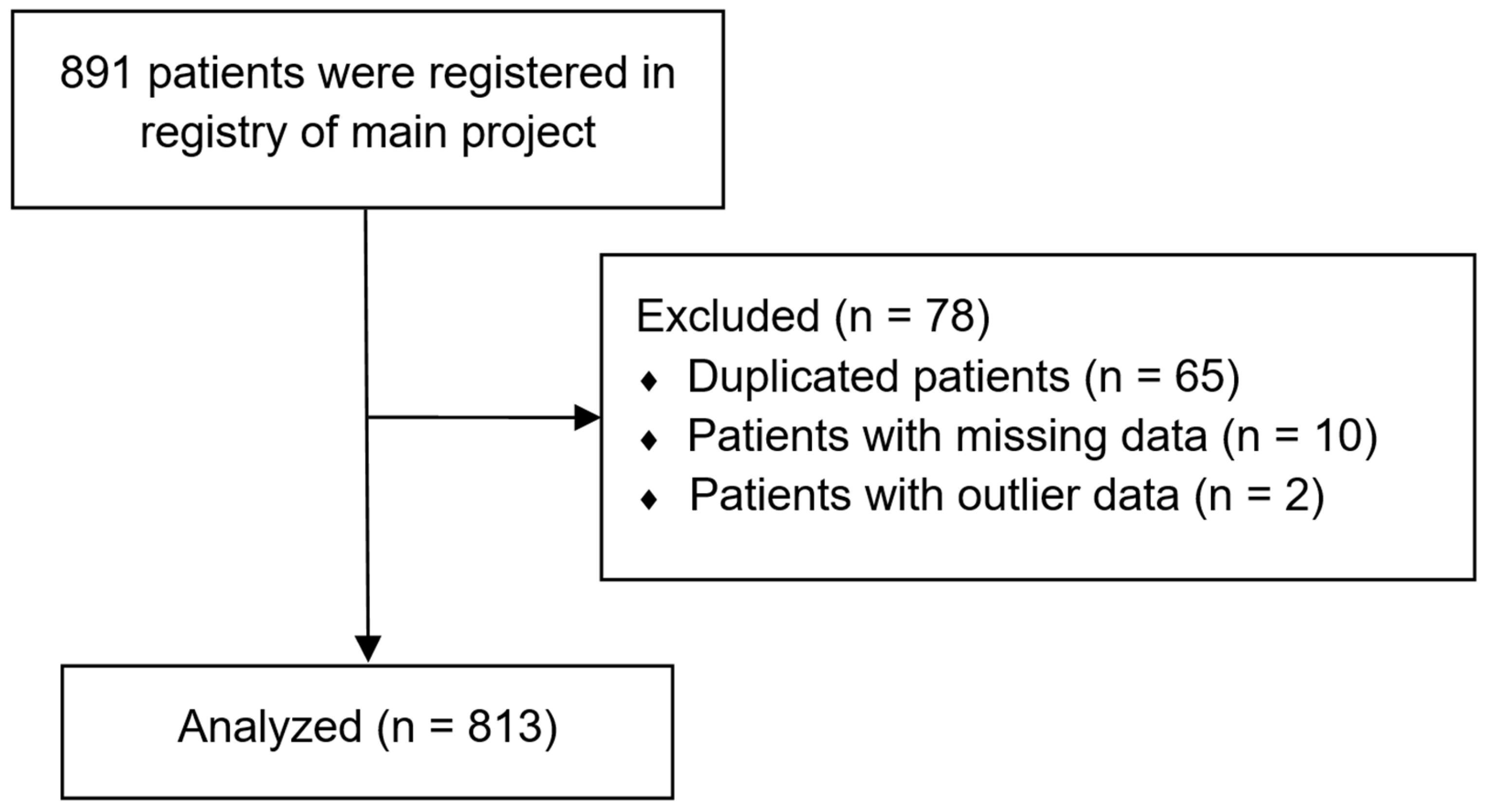
2.1. Study Design, Ethical Approval, and Informed Consent
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Primary Outcomes
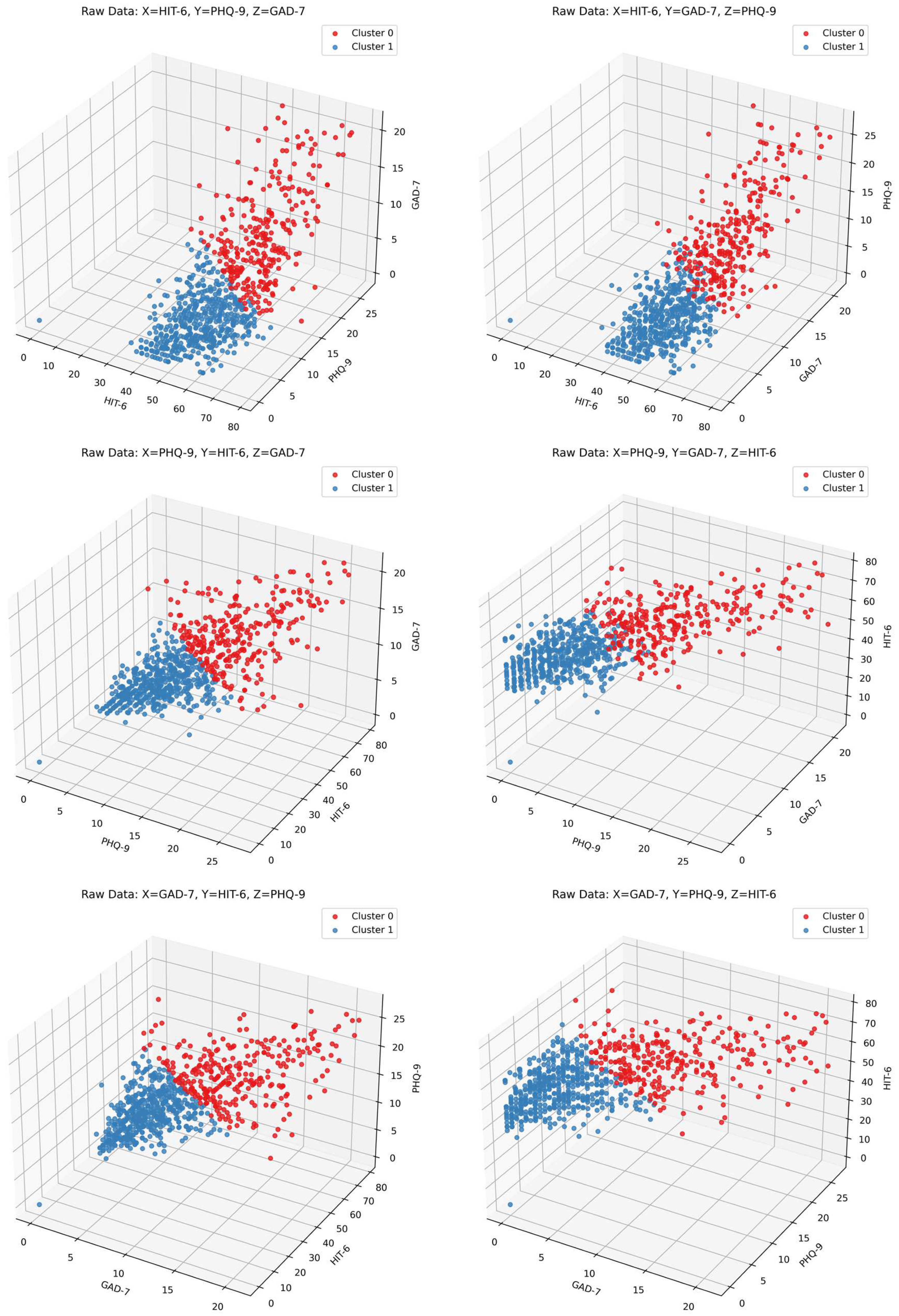
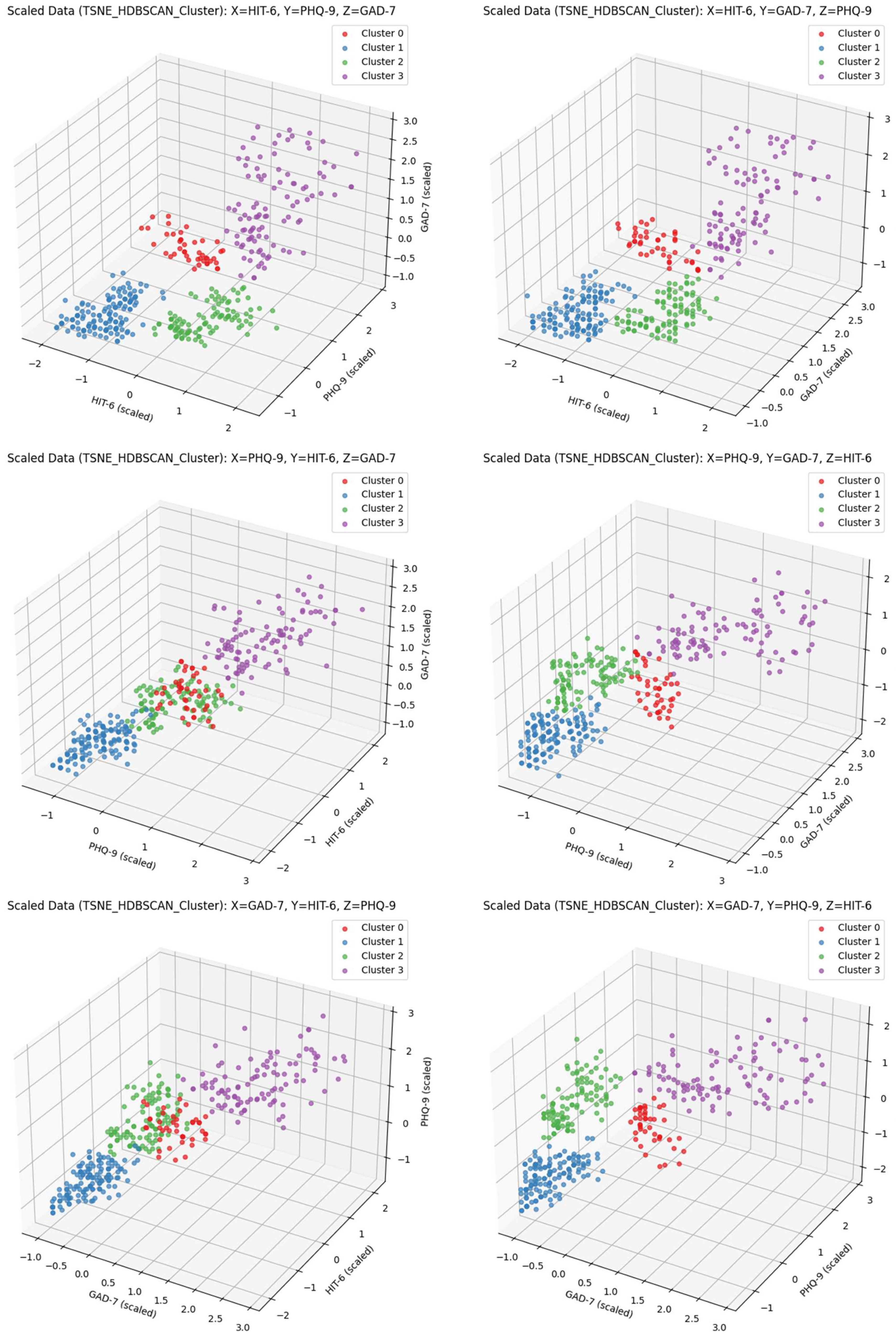
2.4. Clustering Factors and Other Headache-Associated Variables
- Severity of headache impact on quality of life, based on the Headache Impact Test-6 (HIT-6; range: 36–78)
- Depression, based on the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9; range: 0–27)
- Anxiety, based on the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-Item Scale (GAD-7; range: 0–21)
2.5. Data Preprocessing
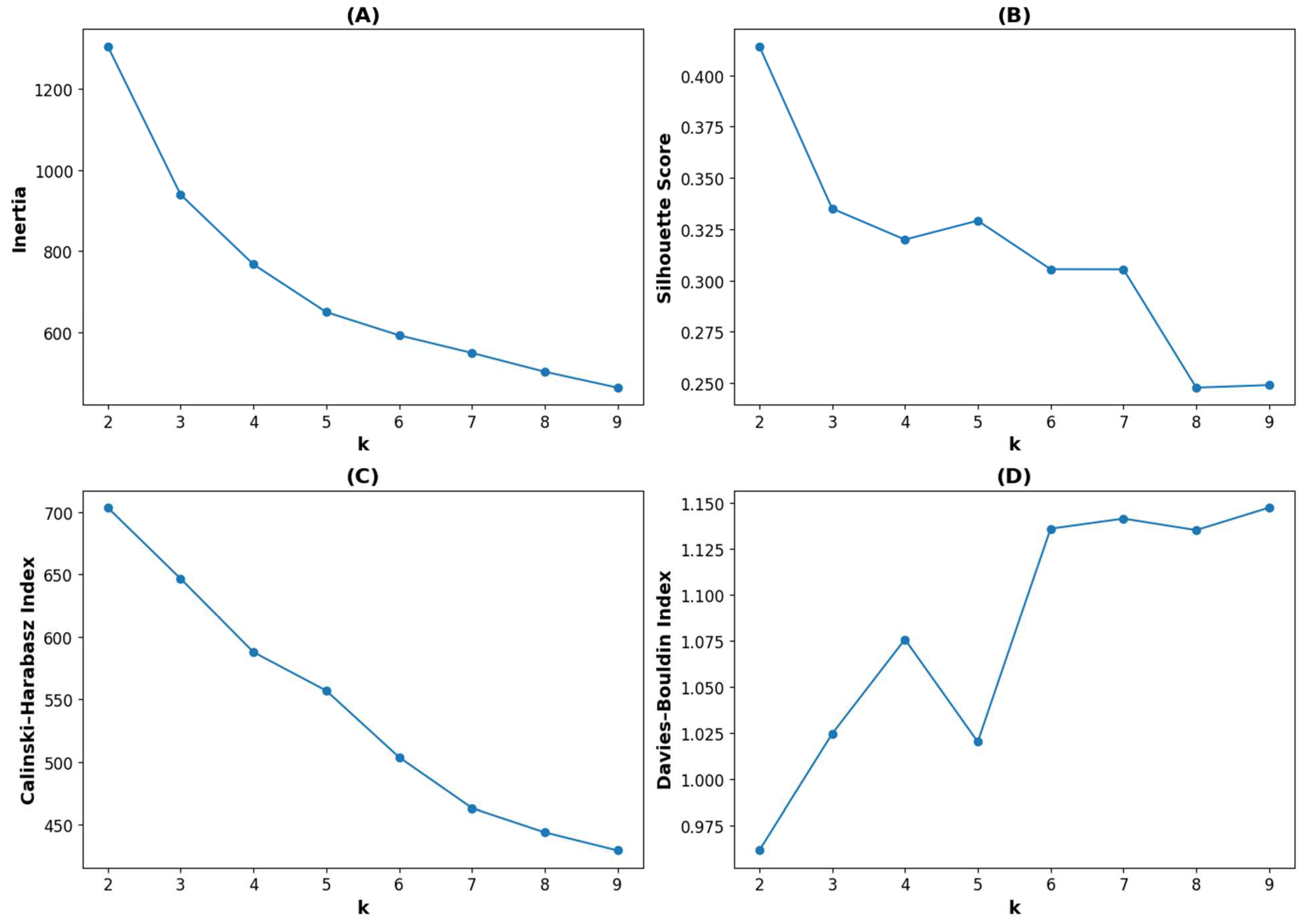
2.6. Clustering
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Use of Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI)
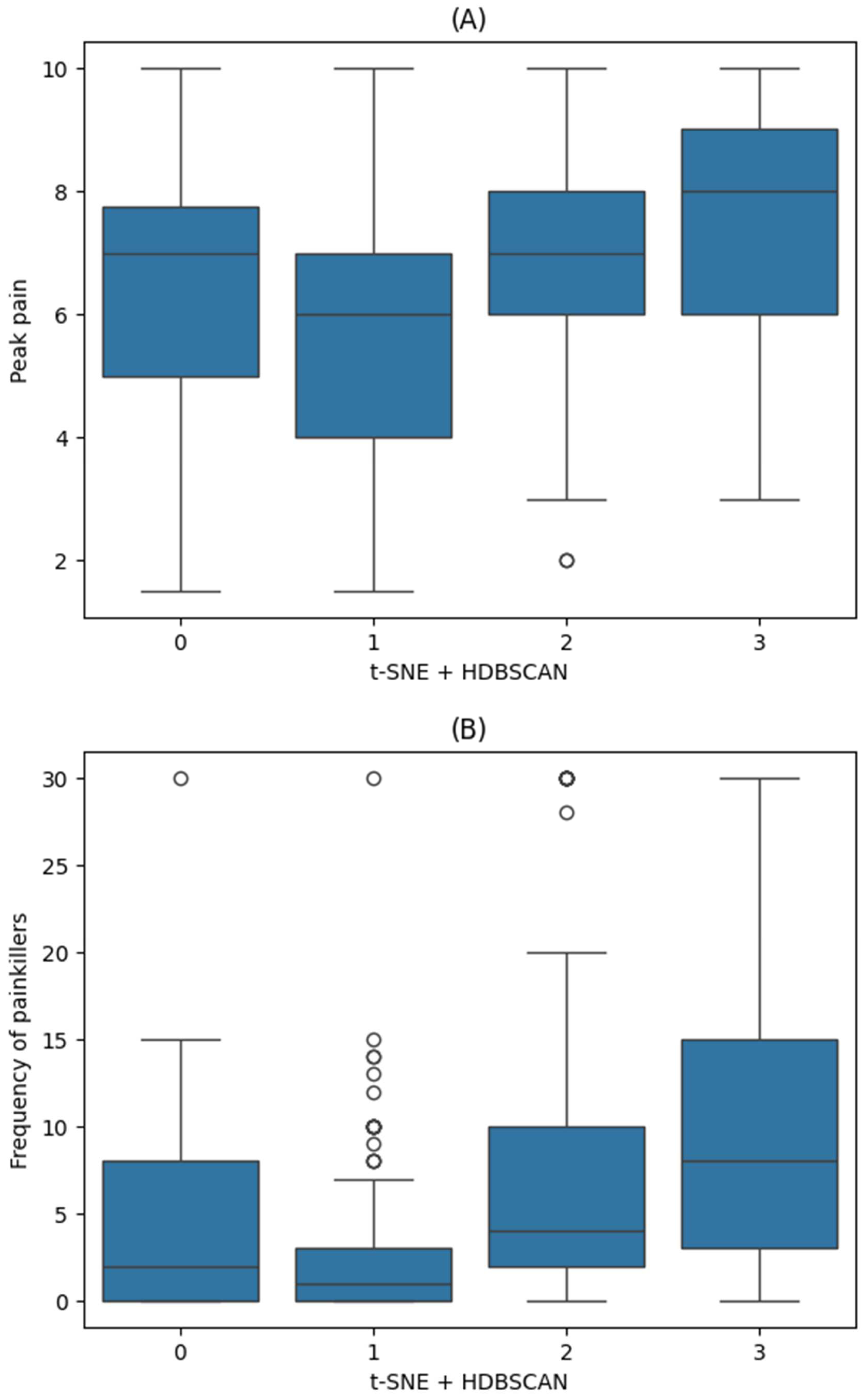
3. Results
| Cluster 0 (n = 43) | Cluster 1 (n = 136) | Cluster 2 (n = 101) | Cluster 3 (n = 98) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 51 (46, 61) | 53 (40, 62) | 43 (31, 58) | 44 (29, 57) | |
| Sex | Male | 14 (32.6) | 61 (44.9) | 39 (38.6) | 31 (31.6) |
| Female | 29 (67.4) | 75 (55.1) | 62 (61.4) | 67 (68.4) | |
| Diagnosis | Migraine | 5 (11.6) | 13 (9.6) | 28 (27.7) | 15 (15.3) |
| TTHA | 10 (23.3) | 26 (19.1) | 13 (12.9) | 24 (24.5) | |
| Other headache | 28 (65.1) | 97 (71.3) | 60 (59.4) | 59 (60.2) | |
| Duration of headache history (days) | 365 (26, 1460) | 60 (7, 1095) | 730 (30, 3650) | 730 (41, 3468) | |
| Average frequency of headache attacks (times per month) | <1 | 0 (0) | 9 (6.6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| 1–3 | 8 (18.6) | 32 (23.5) | 18 (17.8) | 6 (6.1) | |
| 4–11 | 23 (53.5) | 70 (51.5) | 35 (34.7) | 31 (31.6) | |
| ≥12 | 12 (27.9) | 25 (18.4) | 48 (47.5) | 61 (62.2) | |
| Average headache attack duration | <30 min | 5 (11.6) | 42 (30.9) | 3 (3) | 2 (2) |
| 30 min to 4 h | 10 (23.3) | 38 (27.9) | 15 (14.9) | 25 (25.5) | |
| 4–72 h | 16 (37.2) | 29 (21.3) | 44 (43.6) | 31 (31.6) | |
| ≥72 h | 12 (27.9) | 27 (19.9) | 39 (38.6) | 40 (40.8) |
| Peak Pain Intensity | Frequency of Painkiller Use | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coef (95% CI) | p | Coef (95% CI) | p | ||
| Clusters | Reference: Cluster 1 | ||||
| Cluster 0 | 0.6 (−0.1, 1.2) | 0.098 | 0.8 (−1.6, 3.2) | 0.52 | |
| Cluster 2 | 1.1 (0.5, 1.7) | <0.001 | 2.5 (0.4, 4.5) | 0.02 | |
| Cluster 3 | 1.6 (1, 2.2) | <0.001 | 4.4 (2.2, 6.7) | <0.001 | |
| Age (years) | 0 (0, 0) | 0.116 | 0 (−0.1, 0) | 0.317 | |
| Sex | Female | 0.6 (0.2, 1) | 0.007 | −0.7 (−2.2, 0.8) | 0.375 |
| Diagnosis | Reference: other headache | ||||
| Migraine | 0.3 (−0.3, 0.8) | 0.367 | 1.1 (−0.9, 3.2) | 0.281 | |
| TTHA | −0.2 (−0.7, 0.3) | 0.419 | 0.2 (−1.7, 2) | 0.844 | |
| Average frequency of headache attacks (times per month) | Reference: <1 | ||||
| 1–3 | −1.3 (−2.6, 0.1) | 0.066 | 1.2 (−3.6, 6.1) | 0.624 | |
| 4–11 | −1.8 (−3.1, −0.5) | 0.008 | 2.8 (−1.9, 7.5) | 0.243 | |
| ≥12 | −2 (−3.3, −0.6) | 0.004 | 6.5 (1.7, 11.3) | 0.008 | |
| Average headache attack duration | Reference: <30 min | ||||
| 30 min to 4 h | 0 (−0.7, 0.7) | 0.987 | 1.4 (−1, 3.9) | 0.245 | |
| 4–72 h | −0.2 (−0.9, 0.5) | 0.632 | 0.1 (−2.3, 2.6) | 0.916 | |
| ≥72 h | −0.1 (−0.8, 0.6) | 0.771 | 3.8 (1.4, 6.3) | 0.002 | |
| Duration of headache history (days) | 0 (0, 0) | 0.465 | 0 (0, 0) | 0.428 | |
| Frequency of painkillers/Peak pain intensity * | 0 (0, 0.1) | 0.017 | 0.4 (0.1, 0.8) | 0.017 | |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| HIT-6 | Headache Impact Test-6 |
| PHQ-9 | Patient Health Questionnaire-9 |
| GAD-7 | Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item scale |
| t-SNE | t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding |
| HDBSCAN | Hierarchical density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise |
| OLS | Ordinary least squares |
| TTHA | Tension-type headache |
Appendix A
| No | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIT-6 | 63 | 57 | 54 | 62 | 66 | 62 | 36 | 49 | 53 | 67 |
| PHQ-9 | 4 | 9 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 17 | 4 | 4 | 7 | 16 |
| GAD-7 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 8 |
References
- Steinmetz, J.D.; Seeher, K.M.; Schiess, N.; Nichols, E.; Cao, B.; Servili, C.; Cavallera, V.; Cousin, E.; Hagins, H.; Moberg, M.E. Global, regional, and national burden of disorders affecting the nervous system, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Neurol. 2024, 23, 344–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Migraine and Other Headache Disorders. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/headache-disorders (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Abu-Arafeh, I. Headache and psychological comorbidities: An appraisal of the evidence. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hommer, R.; Lateef, T.; He, J.-P.; Merikangas, K. Headache and mental disorders in a nationally representative sample of American youth. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2022, 31, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peres, M.F.P.; Mercante, J.P.; Tobo, P.R.; Kamei, H.; Bigal, M.E. Anxiety and depression symptoms and migraine: A symptom-based approach research. J. Headache Pain 2017, 18, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.-B.; Jia, J.-P.; Wang, F.; Zhou, A.-H.; Zuo, X.-M.; Chu, C.-B. Overlap between headache, depression, and anxiety in general neurological clinics: A cross-sectional study. Chin. Med. J. 2016, 129, 1394–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimia, P.; Garrido-Cumbrera, M.; Santos-Lasaosa, S.; Aguirre-Vazquez, M.; Correa-Fernández, J.; Colomina, I.; Pozo-Rosich, P. Impact of monthly headache days on anxiety, depression and disability in migraine patients: Results from the Spanish Atlas. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Asif, S.; Bali, A.; Dang, A.K.; Gonzalez, D.A. The development and impact of anxiety with migraines: A narrative review. Cureus 2022, 14, e26419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calixtre, L.B.; Oliveira, A.B.; Alburquerque-Sendin, F.; Armijo-Olivo, S. What is the minimal important difference of pain intensity, mandibular function, and headache impact in patients with temporomandibular disorders? Clinical significance analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2020, 46, 102108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Ferrus, M.; Gallardo, V.J.; Alpuente, A.; Pozo-Rosich, P. Influence of headache pain intensity and frequency on migraine-related disability in chronic migraine patients treated with OnabotulinumtoxinA. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelides, A.; Zis, P. Depression, anxiety and acute pain: Links and management challenges. Postgrad. Med. 2019, 131, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harte, N.; Aaron, R.V.; Bhattiprolu, K.; Bisby, M.A.; Gandy, M.; Hathway, T.; Dear, B.F.; Dudeney, J. The association between anxiety and depression symptoms and pain and function in adolescents and young adults with chronic pain: A meta-analysis. J. Psychosom. Res. 2024, 187, 111945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.A.; Jan, A. Medication-Overuse Headache. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538150/ (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Müller, B.; Dresler, T.; Gaul, C.; Glass, Ä.; Jürgens, T.P.; Kropp, P.; Ruscheweyh, R.; Straube, A.; Förderreuther, S. More attacks and analgesic use in old age: Self-reported headache across the lifespan in a German sample. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonassen, R.; Hilland, E.; Harmer, C.J.; Abebe, D.S.; Bergem, A.K.; Skarstein, S. Over-the-counter analgesics use is associated with pain and psychological distress among adolescents: A mixed effects approach in cross-sectional survey data from Norway. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, K.; Cho, S.-J.; Chung, Y.K.; Kim, J.-M.; Chu, M.K. Combination of anxiety and depression is associated with an increased headache frequency in migraineurs: A population-based study. BMC Neurol. 2014, 14, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roalsø, E.S.; Klonteig, S.; Kraft, B.; Skarstein, S.; Aalberg, M.; Jonassen, R. Associations between over-the-counter analgesics usage and symptoms of anxiety and depression in adolescents: A network analysis. BMC Psychiatry 2024, 24, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.-K.; Im, H.-J.; Ju, Y.-S.; YU, K.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, J.; Lee, B.-C. Validity and reliability assessment of Korean headache impact test-6 (HIT-6). J. Korean Neurol. Assoc. 2009, 27, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Imai, N.; Matsumori, Y. Different effects of migraine associated features on headache impact, pain intensity, and psychiatric conditions in patients with migraine. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauro, K.M.; Rose, M.S.; Becker, W.J.; Christie, S.N.; Giammarco, R.; Mackie, G.F.; Eloff, A.G.; Gawel, M.J. HIT-6 and MIDAS as measures of headache disability in a headache referral population. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2010, 50, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Antonio, S.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Ponzano, M.; Bovis, F.; Torelli, P.; Finocchi, C.; Castaldo, M. Profiling migraine patients according to clinical and psychophysical characteristics: A cluster analysis approach. Pain Med. 2023, 24, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalinay Dikmen, P.; Ari, C.; Sahin, E.; Ertas, M.; Mayda Domac, F.; Ilgaz Aydinlar, E.; Sahin, A.; Ozge, A.; Ozguner, H.; Karadas, O.; et al. Cluster Analysis Revealed Two Hidden Phenotypes of Cluster Headache. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 898022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Sohn, J.-H.; Hwang, S.-M.; Lee, J.-J.; Kwon, Y.-S. Functional Disability and Psychological Impact in Headache Patients: A Comparative Study Using Conventional Statistics and Machine Learning Analysis. Medicina 2025, 61, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-H.; Sohn, J.-H.; Hwang, S.-M.; Lee, J.-J.; Kwon, Y.-S. Relationship Between Frequency Domain Indicators of Heart Rate Variability and Both Age and Duration of Illness in Patients with Headache: A Cross-Sectional Study. Biomedicines 2024, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scikit-Learn_Developers. Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python. Available online: https://scikit-learn.org (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Campello, R.J.; Moulavi, D.; Zimek, A.; Sander, J. Hierarchical density estimates for data clustering, visualization, and outlier detection. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data (TKDD) 2015, 10, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Astels, S. The hdbscan Clustering Library. Available online: https://hdbscan.readthedocs.io (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Hermesdorf, M.; Berger, K.; Baune, B.T.; Wellmann, J.; Ruscheweyh, R.; Wersching, H. Pain sensitivity in patients with major depression: Differential effect of pain sensitivity measures, somatic cofactors, and disease characteristics. J. Pain 2016, 17, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, A.K. Depression and anxiety in pain. Rev. Pain 2010, 4, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.G.; Eriksson, M.Y.; Joyce, L.; Mikail, S.F.; Emery, P.C. Major depression and insomnia in chronic pain. Clin. J. Pain 2002, 18, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliams, L.A.; Cox, B.J.; Enns, M.W. Mood and anxiety disorders associated with chronic pain: An examination in a nationally representative sample. Pain 2003, 106, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, D.C.; Reed, M.L.; Fanning, K.M.; Bostic, R.; Dodick, D.W.; Schwedt, T.J.; Munjal, S.; Singh, P.; Lipton, R.B. Comorbid and co-occurring conditions in migraine and associated risk of increasing headache pain intensity and headache frequency: Results of the migraine in America symptoms and treatment (MAST) study. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Bae, D.-W.; Park, S.-G.; Park, J.-W. The impact of Pain-related emotions on migraine. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi Nasiri, F.S.; Pakdaman, S.; Dehghani, M.; Togha, M. The Relationship between Pain Catastrophizing and Headache-Related Disability: T he Mediating Role of Pain Intensity. Jpn. Psychol. Res. 2017, 59, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenkovich, K.; Chockalingam, R.; Scherrer, J.F.; Panagopoulos, V.N.; Lustman, P.J.; Ray, J.M.; Freedland, K.E.; Svrakic, D.M. Prescription opioid analgesics increase risk of major depression: New evidence, plausible neurobiological mechanisms and management to achieve depression prophylaxis. Mo. Med. 2014, 111, 148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scherrer, J.F.; Salas, J.; Miller-Matero, L.R.; Sullivan, M.D.; Ballantyne, J.C.; Debar, L.; Grucza, R.A.; Lustman, P.J.; Ahmedani, B. Long-term prescription opioid users’ risk for new-onset depression increases with frequency of use. Pain 2022, 163, 1581–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumenta, T.; Ugwendum, D.F.; Chobufo, M.D.; Mungu, E.B.; Kogan, I.; Olupona, T.; Olupona, T. Prevalence and trends of opioid use in patients with depression in the United States. Cureus 2021, 13, e15309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRowe, L.R.; Powers, J.M.; Garey, L.; Rogers, A.H.; Zvolensky, M.J.; Ditre, J.W. Pain-related anxiety, sex, and co-use of alcohol and prescription opioids among adults with chronic low back pain. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020, 214, 108171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, J.; Santo, T., Jr.; Colledge-Frisby, S.; Mekonen, T.; Thomson, K.; Degenhardt, L.; Connor, J.P.; Hall, W.; Stjepanović, D. Mood and anxiety symptoms in persons taking prescription opioids: A systematic review with meta-analyses of longitudinal studies. Pain Med. 2022, 23, 1442–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwowarczyk, P.; Kaczmarska, A.; Kutnik, P.; Hap, A.; Chajec, J.; Myśliwiec, U.; Czuczwar, M.; Borys, M. Association of gender, painkiller use, and experienced pain with pain-related fear and anxiety among university students according to the Fear of Pain Questionnaire-9. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, D.C.; Pozo-Rosich, P.; Dupont-Benjamin, L.; Balkaran, B.L.; Lee, L.; Jauregui, A.; Gandhi, P.; Parikh, M.; Reuter, U. Impact of headache frequency and preventive medication failure on quality of life, functioning, and costs among individuals with migraine across several European countries: Need for effective preventive treatment. J. Headache Pain 2023, 24, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, B.; Gaul, C.; Glass, Ä.; Reis, O.; Jürgens, T.P.; Kropp, P.; Ruscheweyh, R.; Straube, A.; Brähler, E.; Förderreuther, S. Physical activity is associated with less analgesic use in women reporting headache—A cross-sectional study of the German Migraine and Headache Society (DMKG). Pain Ther. 2022, 11, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, B.; Gaul, C.; Reis, O.; Jürgens, T.P.; Kropp, P.; Ruscheweyh, R.; Straube, A.; Brähler, E.; Förderreuther, S.; Schroth, J. Headache impact and socioeconomic status: Findings from a study of the German Migraine and Headache Society (DMKG). J. Headache Pain 2023, 24, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwedt, T.J.; Sahai-Srivastava, S.; Murinova, N.; Birlea, M.; Ahmed, Z.; Digre, K.; Lopez, K.; Mullally, W.; Blaya, M.T.; Pippitt, K. Determinants of pain interference and headache impact in patients who have chronic migraine with medication overuse: Results from the MOTS trial. Cephalalgia 2021, 41, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falke, C.; Karapinar, F.; Bouvy, M.; Emmelot, M.; Belitser, S.; Boland, B.; O’Mahony, D.; Murphy, K.D.; Haller, M.; Salari, P. The association between medication use and health-related quality of life in multimorbid older patients with polypharmacy. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2024, 15, 1713–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alwhaibi, M.; Balkhi, B.; AlRuthia, Y. Anxiety and depression and health-related quality of life among adults with migraine: A National Population-Based Study. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1241800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bair, M.J.; Robinson, R.L.; Katon, W.; Kroenke, K. Depression and pain comorbidity: A literature review. Arch. Intern. Med. 2003, 163, 2433–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenes, G.A. Anxiety, depression, and quality of life in primary care patients. Prim. Care Companion J. Clin. Psychiatry 2007, 9, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Ren, Z.; Xia, H.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, T.; Li, G.; Liu, L.; Liu, Z. Associations between anxiety, depression with migraine, and migraine-related burdens. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1090878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, R.B.; Seng, E.K.; Chu, M.K.; Reed, M.L.; Fanning, K.M.; Adams, A.M.; Buse, D.C. The effect of psychiatric comorbidities on headache-related disability in migraine: Results from the Chronic Migraine Epidemiology and Outcomes (CaMEO) study. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2020, 60, 1683–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Xu, X. Clustering-based method for large group decision making with hesitant fuzzy linguistic information: Integrating correlation and consensus. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 87, 105973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, M.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kwon, Y.S. Cluster analysis integrating age and body temperature for mortality in patients with sepsis: A multicenter retrospective study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.X.; Dwyer, D.; Zhu, Y.; Smith, C.L.; Du, L.; Filia, K.M.; Bayer, J.; Menssink, J.M.; Wang, T.; Bergmeir, C. An overview of clustering methods with guidelines for application in mental health research. Psychiatry Res. 2023, 327, 115265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Li, Y.; Kianifard, F.; Obi, E.; Arcona, S. Cluster analysis and its application to healthcare claims data: A study of end-stage renal disease patients who initiated hemodialysis. BMC Nephrol. 2016, 17, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nithya, N.; Duraiswamy, K.; Gomathy, P. A survey on clustering techniques in medical diagnosis. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Trends Technol. (IJCST) 2013, 1, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.-C.; Lai, J.-P.; Liu, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-L.; Hou, H.-P.; Pai, P.-F. Using medical data and clustering techniques for a smart healthcare system. Electronics 2023, 13, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismkhan, H. Ik-means−+: An iterative clustering algorithm based on an enhanced version of the k-means. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 79, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinaga, K.P.; Yang, M.S. Unsupervised K-Means Clustering Algorithm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 80716–80727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E.; Roweis, S. Stochastic neighbor embedding. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2002, 15, 857–864. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.; Dagobert, T.; Morel, J.-M.; Facciolo, G. A Review of t-SNE. Image Process. Line 2024, 14, 250–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malzer, C.; Baum, M. A hybrid approach to hierarchical density-based cluster selection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems (MFI), Virtual, 14–16 September 2020; pp. 223–228. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, G.; Al-Khassaweneh, M. An implementation of the HDBSCAN* clustering algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, K.; Naldi, M.C.; Sander, J.; Choo, E. Unsupervised Parameter-free Outlier Detection using HDBSCAN* Outlier Profiles. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (BigData), Washington, DC, USA, 18 December 2024; pp. 7021–7030. [Google Scholar]
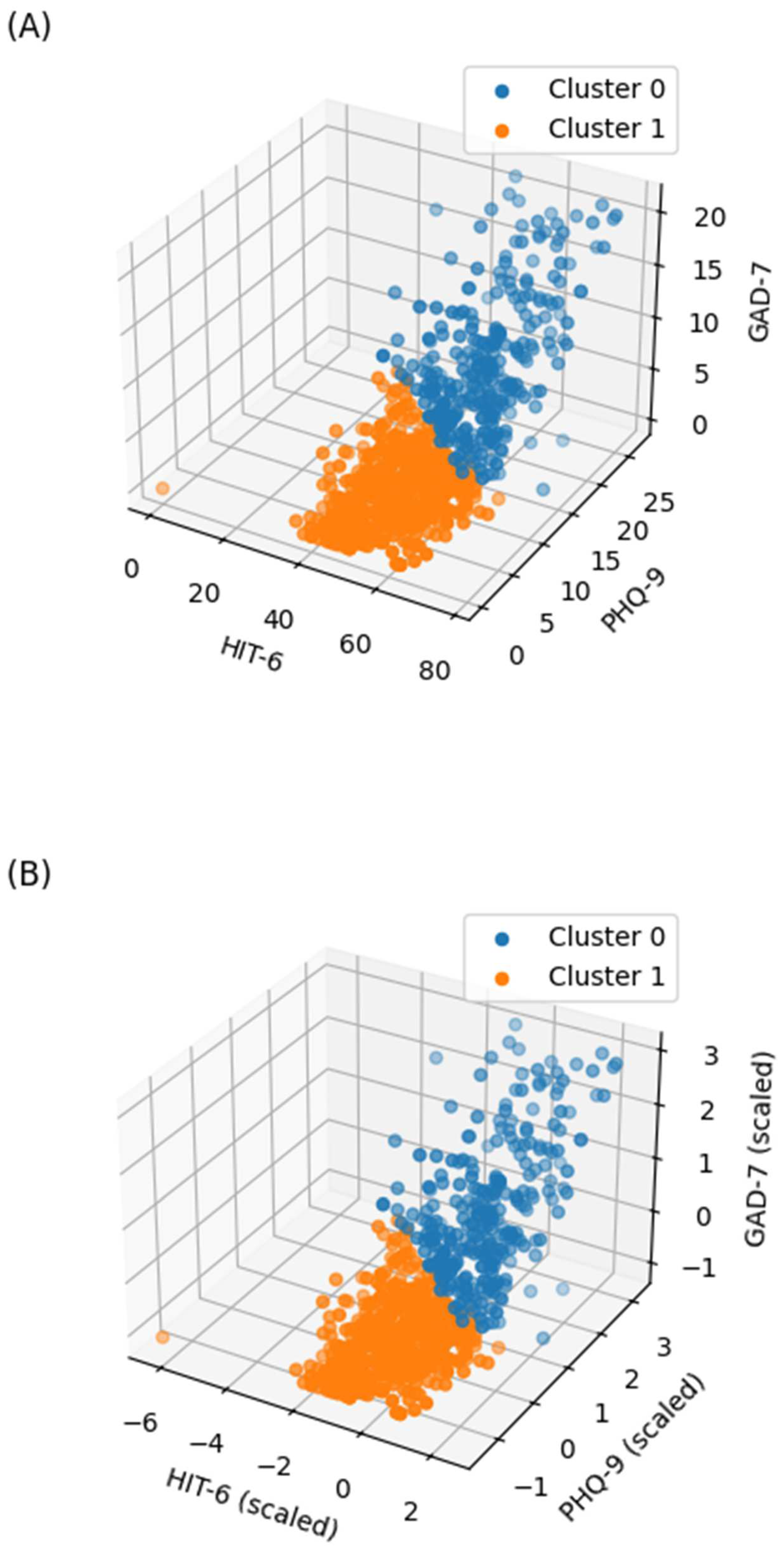
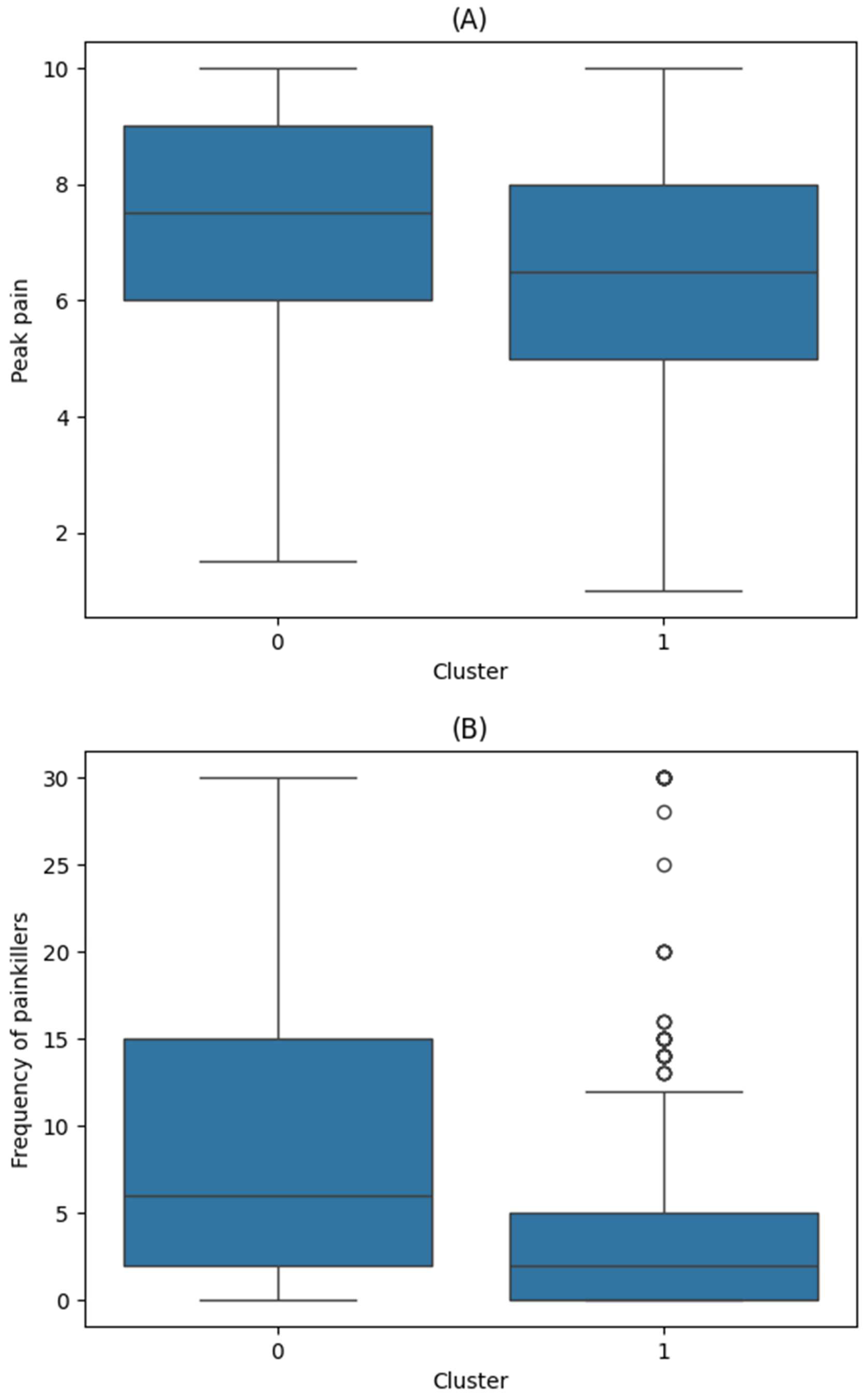
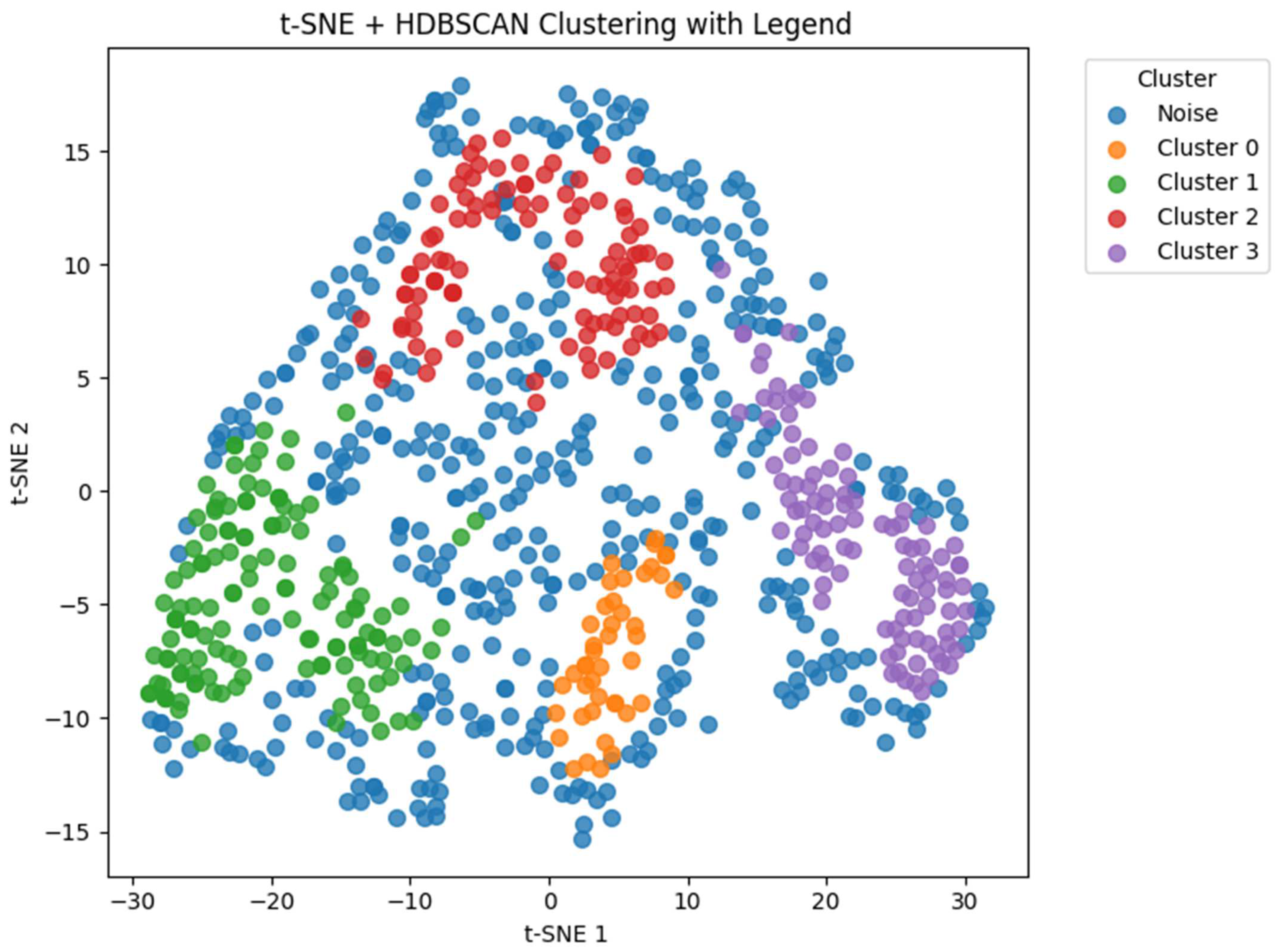
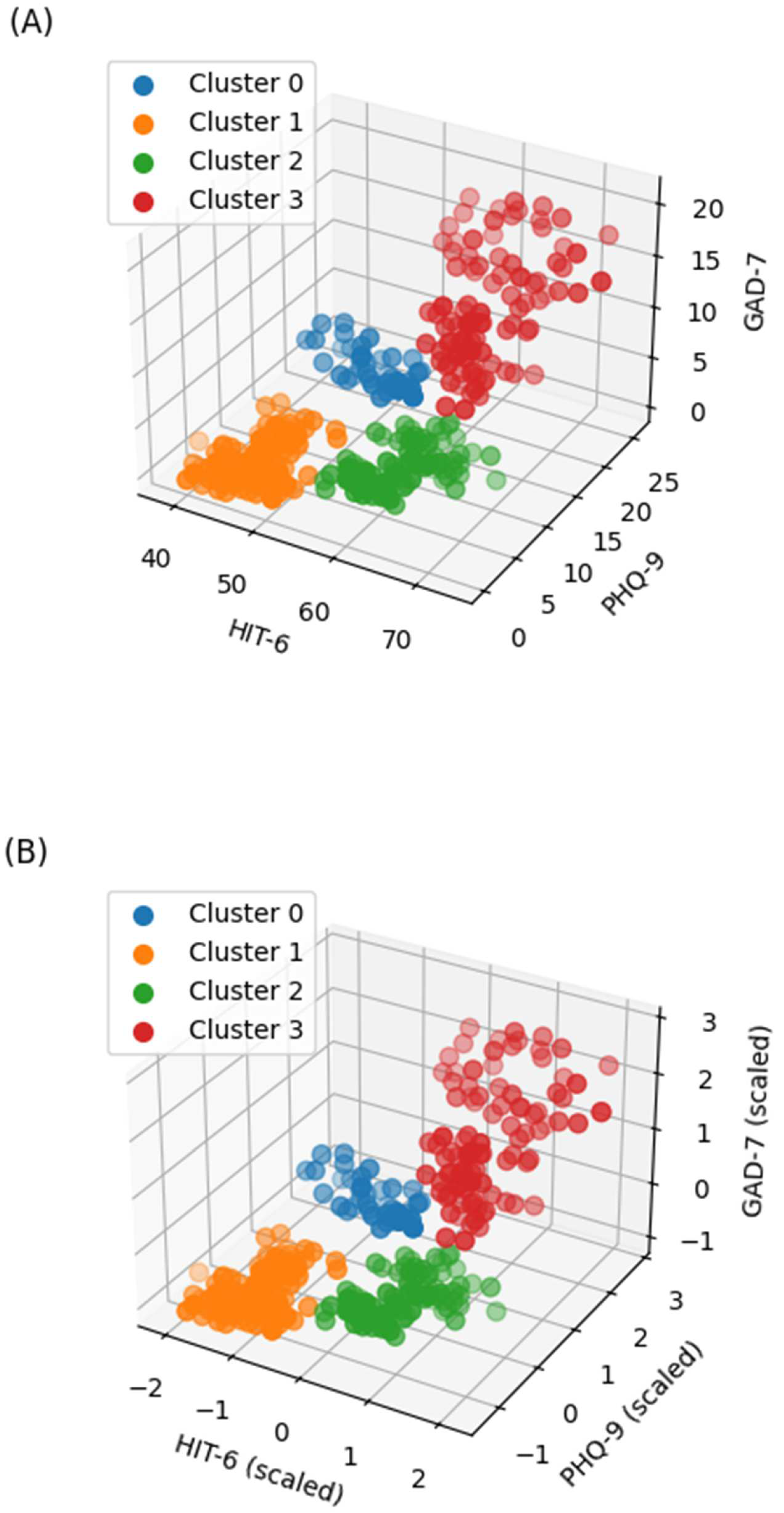
| Cluster 0 (n = 291) | Cluster 1 (n = 522) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 47 (33.5, 58) | 49 (36, 61) | |
| Sex | Male | 93 (32) | 190 (36.4) |
| Female | 198 (68) | 332 (63.6) | |
| Diagnosis | Migraine | 58 (19.9) | 90 (17.2) |
| TTHA | 61 (21) | 74 (14.2) | |
| Other headache | 172 (59.1) | 358 (68.6) | |
| Duration of headache history (days) | 1095 (60, 3650) | 97.5 (10, 1825) | |
| Average frequency of headache attacks (times per month) | <1 | 0 (0) | 11 (2.1) |
| 1–3 | 37 (12.7) | 137 (26.2) | |
| 4–11 | 93 (32) | 235 (45) | |
| ≥12 | 161 (55.3) | 139 (26.6) | |
| Average headache attack duration | ≤30 min | 21 (7.2) | 87 (16.7) |
| 30 min to 4 h | 53 (18.2) | 106 (20.3) | |
| 4–72 h | 100 (34.4) | 181 (34.7) | |
| ≥72 h | 117 (40.2) | 148 (28.4) |
| Peak Pain Intensity | Frequency of Painkiller Use | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coef (95% CI) | p | Coef (95% CI) | p | ||
| Cluster | Reference: Cluster 0 | ||||
| Cluster 1 | −0.7 (−1, −0.4) | <0.001 | −2.3 (−3.4, −1.3) | <0.001 | |
| Age (years) | 0 (0, 0) | 0.678 | 0 (−0.1, 0) | 0.317 | |
| Sex | Female | 0.7 (0.4, 1.0) | <0.001 | −0.7 (−1.7, 0.4) | 0.221 |
| Diagnosis | Reference: other headache | ||||
| Migraine | 0.5 (0.1, 0.9) | 0.008 | 1.5 (0.1, 2.9) | 0.035 | |
| TTHA | 0 (−0.4, 0.4) | 0.854 | 1 (−0.4, 2.3) | 0.153 | |
| Average frequency of headache attacks (times per month) | Reference: <1 | ||||
| 1–3 | −1.2 (−2.5, 0) | 0.045 | 1.7 (−2.6, 6) | 0.436 | |
| 4–11 | −1.4 (−2.6, −0.2) | 0.021 | 3.7 (−0.5, 7.9) | 0.086 | |
| ≥12 | −1.5 (−2.8, −0.3) | 0.014 | 8.4 (4.2, 12.7) | <0.001 | |
| Average headache attack duration | Reference: <30 min | ||||
| 30 min to 4 h | 0.2 (−0.3, 0.7) | 0.384 | 0.7 (−1, 2.5) | 0.393 | |
| 4–72 h | 0.6 (0.1, 1.1) | 0.011 | 1.2 (−0.4, 2.8) | 0.151 | |
| ≥72 h | 0.8 (0.3, 1.3) | 0.001 | 4.3 (2.6, 5.9) | <0.001 | |
| Duration of headache history (days) | 0 (0, 0) | 0.27 | 0 (0, 0) | 0.079 | |
| Frequency of painkillers /Peak pain intensity * | 0 (0, 0.1) | <0.001 | 0.5 (0.3, 0.8) | <0.001 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.-H.; Ahn, M.; Sohn, J.-H.; Hwang, S.-M.; Lee, J.-J.; Kwon, Y.-S. The Comprehensive Effect of Depression, Anxiety, and Headache on Pain Intensity and Painkiller Use in Patients with Headache Analyzed by Unsupervised Clustering Using Machine Learning. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061345
Kim J-H, Ahn M, Sohn J-H, Hwang S-M, Lee J-J, Kwon Y-S. The Comprehensive Effect of Depression, Anxiety, and Headache on Pain Intensity and Painkiller Use in Patients with Headache Analyzed by Unsupervised Clustering Using Machine Learning. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(6):1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061345
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jong-Ho, Minha Ahn, Jong-Hee Sohn, Sung-Mi Hwang, Jae-Jun Lee, and Young-Suk Kwon. 2025. "The Comprehensive Effect of Depression, Anxiety, and Headache on Pain Intensity and Painkiller Use in Patients with Headache Analyzed by Unsupervised Clustering Using Machine Learning" Biomedicines 13, no. 6: 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061345
APA StyleKim, J.-H., Ahn, M., Sohn, J.-H., Hwang, S.-M., Lee, J.-J., & Kwon, Y.-S. (2025). The Comprehensive Effect of Depression, Anxiety, and Headache on Pain Intensity and Painkiller Use in Patients with Headache Analyzed by Unsupervised Clustering Using Machine Learning. Biomedicines, 13(6), 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061345






