Cell-Free Fat Extract for the Treatment of Lumbar Disc Degeneration: A Novel Approach Using Adipose-Derived Biologic
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of CEFFE
2.2. Rat Primary Nucleus Pulposus Isolation
2.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.4. Liperfluo, FerroOrange and ROS Staining
2.5. High-Density Culture
2.6. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription, and RT-qPCR
2.7. Extraction of Total Cellular Protein and Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.9. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.10. Animals and Surgery Procedure
2.11. Histological and Immunohistochemistry
2.12. Data Statistical Analysis
3. Results
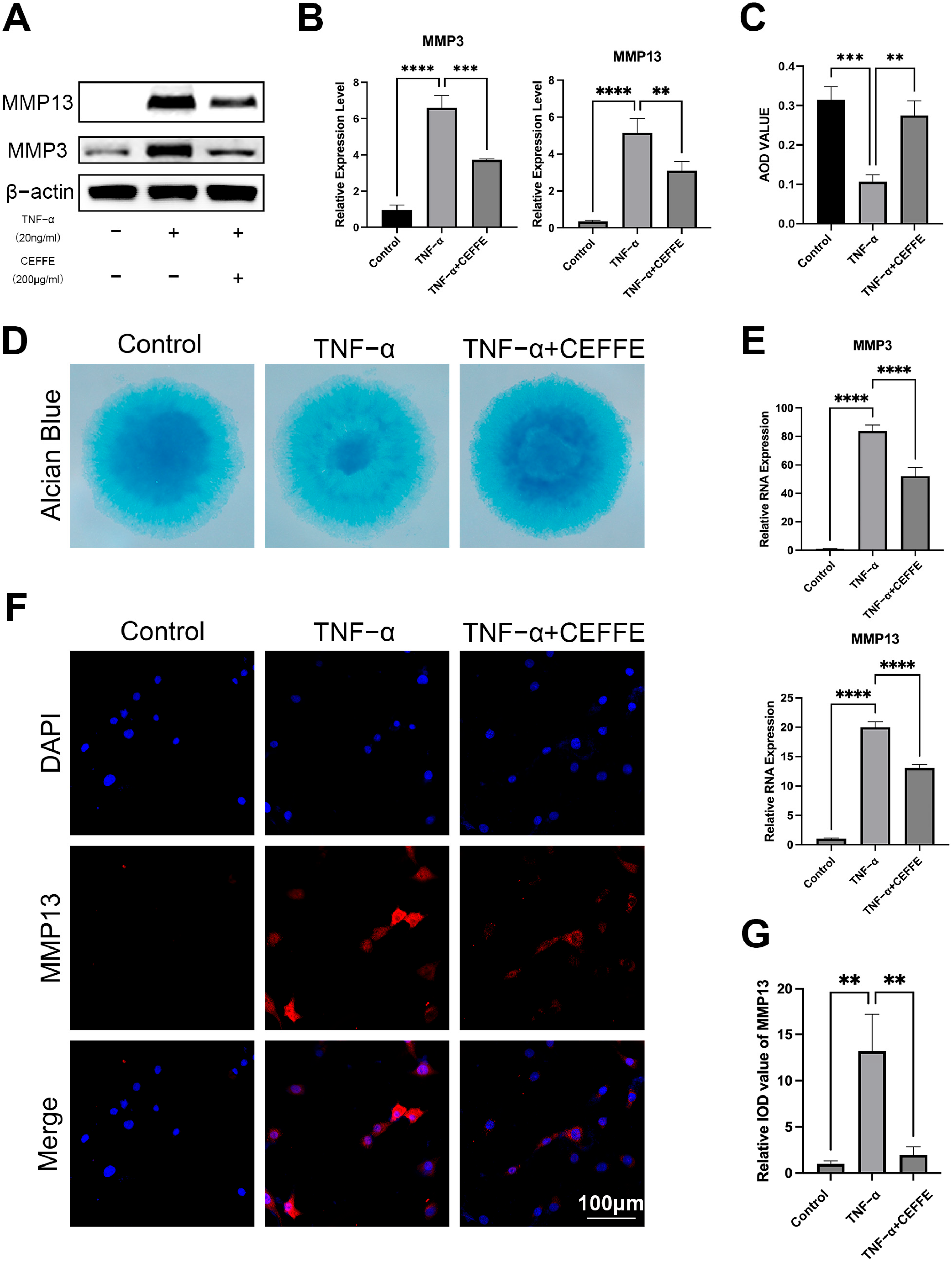
3.1. CEFFE Promotes Regeneration and Reduces Matrix Degradation of Rat Primary NPCs
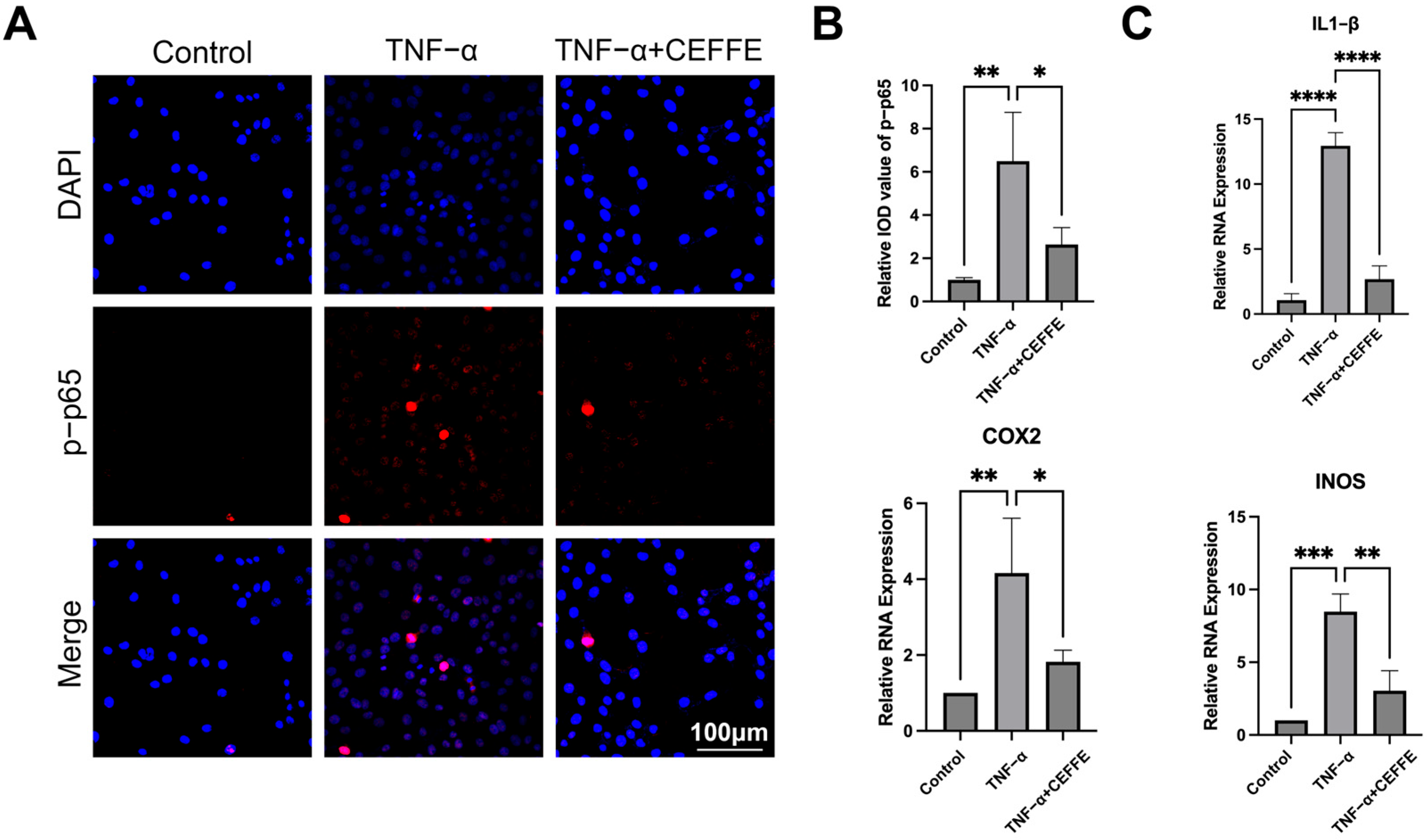
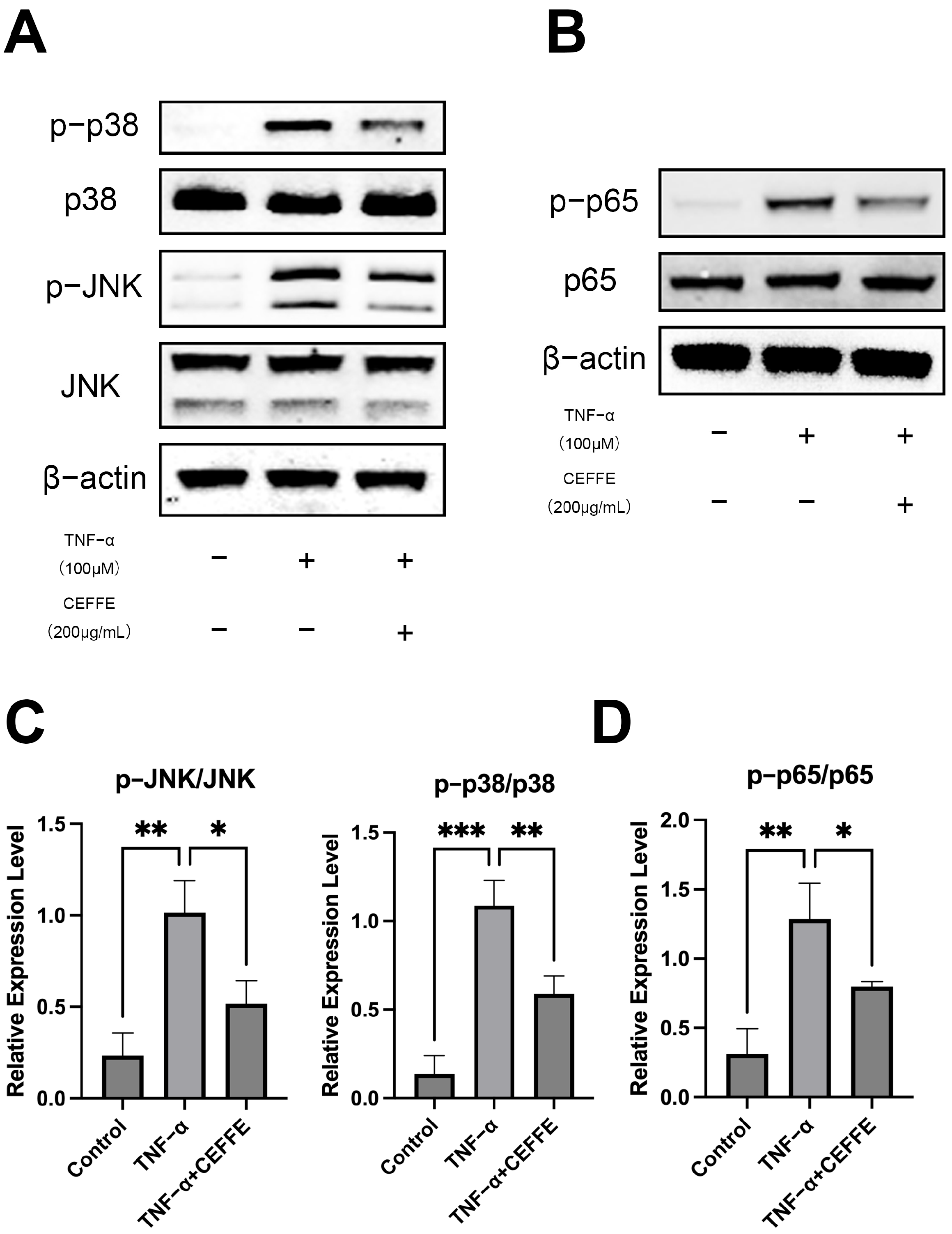
3.2. CEFFE Alleviates the Inflammatory Response in NPCs by Inhibiting the NF-κB and MAPK Pathways
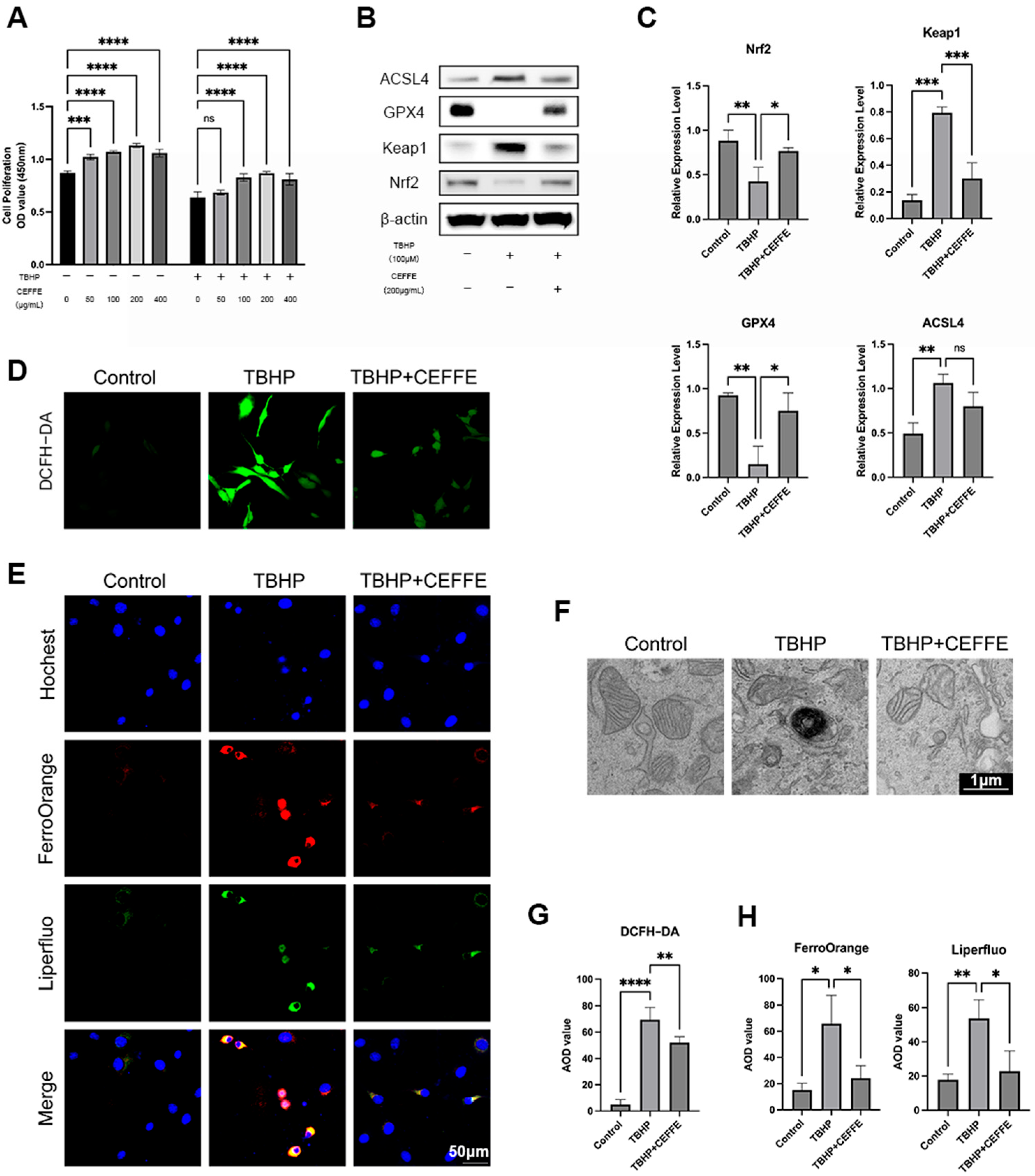
3.3. CEFFE Inhibits TBHP-Induced Ferroptosis in NPCs
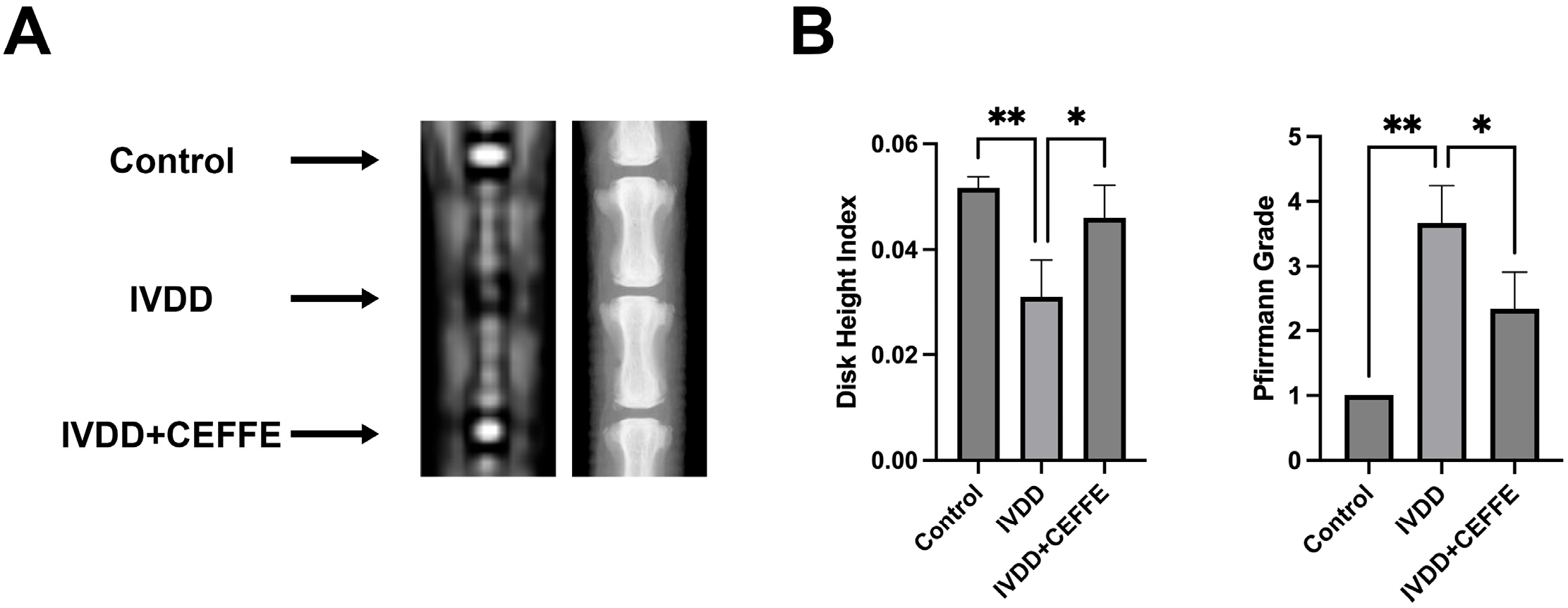
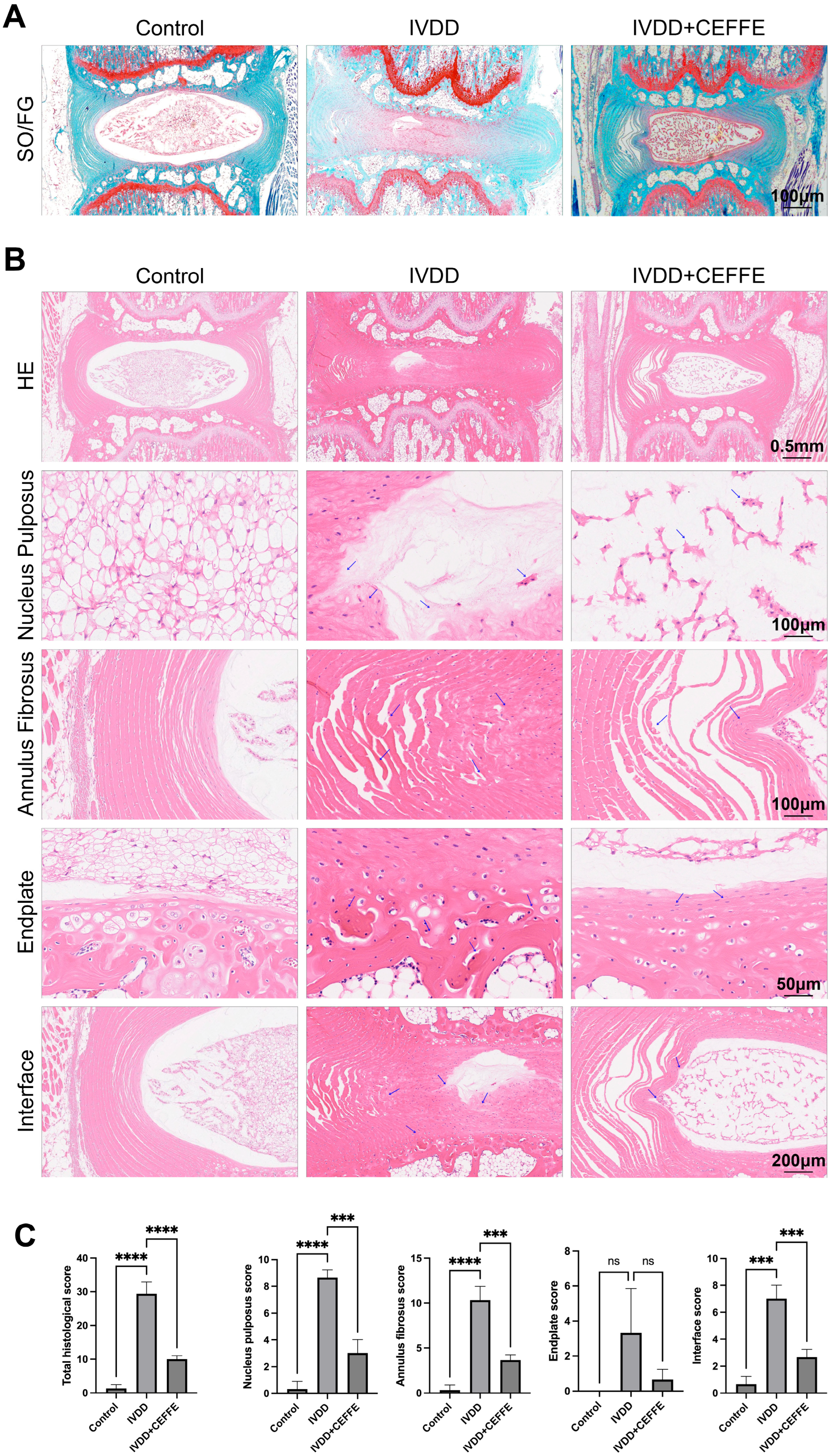
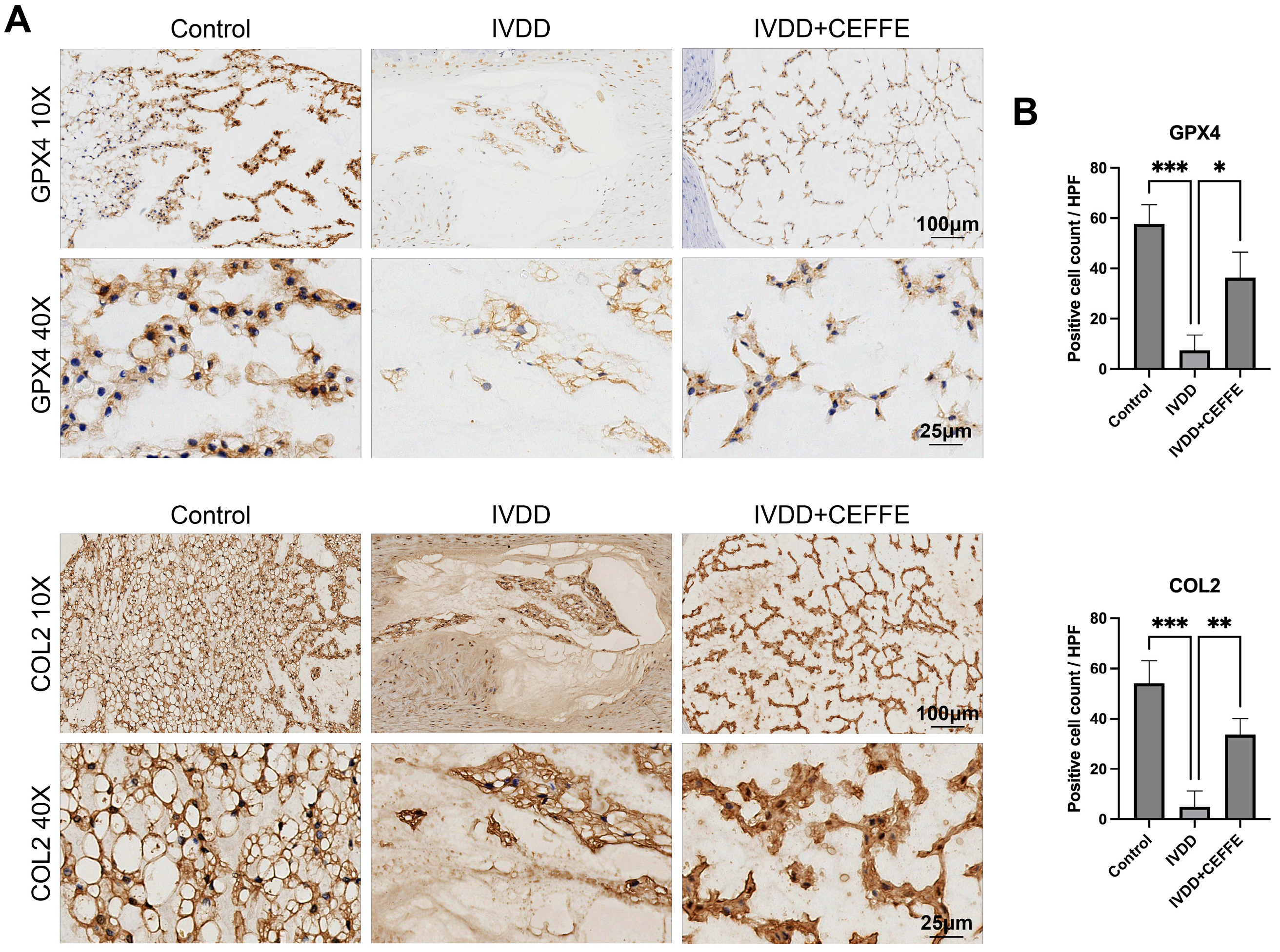
3.4. CEFFE Effectively Prevents IVDD in Rat Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADAMT | A disintegrin and metalloproteinases with thrombospondin motifs |
| ADSC | Adipose-derived stem cell |
| CCK-8 | Cell counting kit-8 |
| CEFFE | Cell-free fat extract |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| IGF1 | Insulin-like growth factor-1 |
| ITS | Insulin–transferrin–selenium |
| IVDD | Intervertebral disc degeneration |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinases |
| NIH | National Institutes of Health |
| NPC | Nucleus pulposus cell |
| rt-qPCR | Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| TBHP | Tert-butyl hydroperoxide |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-beta |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Chou, R. Low Back Pain. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, itc113–itc128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knezevic, N.N.; Candido, K.D.; Vlaeyen, J.W.S.; Van Zundert, J.; Cohen, S.P. Low back pain. Lancet 2021, 398, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koes, B.W.; van Tulder, M.W.; Thomas, S. Diagnosis and treatment of low back pain. BMJ 2006, 332, 1430–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, S.Z.; Fritz, J.M.; Silfies, S.P.; Schneider, M.J.; Beneciuk, J.M.; Lentz, T.A.; Gilliam, J.R.; Hendren, S.; Norman, K.S.; Beattie, P.F.; et al. Interventions for the Management of Acute and Chronic Low Back Pain: Revision 2021. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2021, 51, CPG1–CPG60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silwal, P.; Nguyen-Thai, A.M.; Mohammad, H.A.; Wang, Y.; Robbins, P.D.; Lee, J.Y.; Vo, N.V. Cellular Senescence in Intervertebral Disc Aging and Degeneration: Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Opportunities. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Yang, T.; Gao, S.; Bai, L.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Liang, X.; Li, Y.; Gao, L.; et al. Exosomes from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate intervertebral disc degeneration via repairing mitochondrial dysfunction. J. Orthop. Transl. 2024, 46, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, S.-D.; Huo, X.-W.; Yang, D.-L.; Ma, L.; Ding, W.-Y. 17β-Estradiol inhibits intervertebral disc degeneration by down-regulating MMP-3 and MMP-13 and up-regulating type II collagen in a rat model. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46 (Suppl. S2), 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Zhang, Z.; Mao, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ying, L.; Xu, H.; Hu, S. Injectable exosome-functionalized extracellular matrix hydrogel for metabolism balance and pyroptosis regulation in intervertebral disc degeneration. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Xiang, Q.; Zhan, S.; Song, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhao, K.; Li, S.; Shao, Z.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y. Restoration of Autophagic Flux Rescues Oxidative Damage and Mitochondrial Dysfunction to Protect against Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 7810320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risbud, M.V.; Shapiro, I.M. Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: Pain and disc content. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 10, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, F.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, J. TGF-β1 suppresses CCL3/4 expression through the ERK signaling pathway and inhibits intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation-related pain in a rat model. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.J.; Liao, H.Y.; Bai, D.Y.; Wang, Z.Q.; Xie, X.W. MAPK /ERK signaling pathway: A potential target for the treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Stockwell, B.R.; Conrad, M. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.; Minikes, A.M.; Jiang, X. Ferroptosis at the intersection of lipid metabolism and cellular signaling. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 2215–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Huang, Z.; Ying, X.; Liu, X.; Ruan, K.; Hua, S.; Zhang, X.; Jin, H.; Liu, Q.; Yang, J. Ferroptosis exacerbates hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis by enhancing lipid peroxidation and modulating the immune microenvironment. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Wei, X.; Hu, W.; Tang, S.; Ding, J.; Fu, W.; Zhang, H.; Chen, F.; et al. TRPM7 channel inhibition attenuates rheumatoid arthritis articular chondrocyte ferroptosis by suppression of the PKCα-NOX4 axis. Redox Biol. 2022, 55, 102411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Chen, M.; Liu, M.; Chen, X.; Zhu, L.; Xu, J.; Xue, J.; Wu, H.; Du, Y. Semaphorin 5A suppresses ferroptosis through activation of PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhan, L.-N.; Huang, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhou, X.; Kapilevich, L.; Wang, Z.; Ning, K.; Sun, M. Moderate mechanical stress suppresses chondrocyte ferroptosis in osteoarthritis by regulating NF-κB p65/GPX4 signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Rong, K.; Guo, J.; Cui, L.; Kong, K.; Zhao, C.; Yang, H.; Xu, H.; Qin, A.; Ma, P.; et al. Cynarin alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration via protecting nucleus pulposus cells from ferroptosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Yang, H.; Rong, K.; Zhou, T.; Fu, J.; Zhao, J. Polydopamine Nanoparticles Targeting Ferroptosis Mitigate Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Via Reactive Oxygen Species Depletion, Iron Ions Chelation, and GPX4 Ubiquitination Suppression. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2207216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.; Liao, Z.; Liang, H.; Tong, B.; Song, Y.; Li, G.; Ma, L.; Wang, K.; Feng, X.; Li, S.; et al. Stiff Substrate Induces Nucleus Pulposus Cell Ferroptosis via YAP and N-Cadherin Mediated Mechanotransduction. Adv. Health Mater. 2023, 12, e2300458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; Xiang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Liu, L.; Zhu, X.; Yu, R.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, K.; Wang, Z.; et al. Selenium-SelK-GPX4 axis protects nucleus pulposus cells against mechanical overloading-induced ferroptosis and attenuates senescence of intervertebral disc. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2024, 81, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Sun, R.; Sun, K.; Yan, C.; Jiang, J.; Kong, F.; Shi, J. The deubiquitinase USP11 ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration by regulating oxidative stress-induced ferroptosis via deubiquitinating and stabilizing Sirt3. Redox Biol. 2023, 62, 102707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.; Chu, G.; Yu, Z.; Ji, Z.; Kong, F.; Yao, L.; Wang, J.; Geng, D.; Wu, X.; Mao, H. The role of ferroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1219840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Niu, H.; Li, L.; Han, J.; Liu, Z.; Chu, M.; Sha, X.; Zhao, J. Anti-CHAC1 exosomes for nose-to-brain delivery of miR-760-3p in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury mice inhibiting neuron ferroptosis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Shi, Q.; Yang, E.; Zhang, B.; Qian, Y.; Lian, X.; Xu, J. ADSC-Exos enhance functional recovery after spinal cord injury by inhibiting ferroptosis and promoting the survival and function of endothelial cells through the NRF2/SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 172, 116225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Tong, H.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J.; Hu, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z. ADSC-Exosomes Alleviate MTX-induced Rat Neuronal Damage by Activating Nrf2-ARE Pathway. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 72, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ngo, H.T.; Hwang, E.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Yi, T.-H. Conditioned Medium from Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Culture Prevents UVB-Induced Skin Aging in Human Keratinocytes and Dermal Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, S. Pluripotent Stem Cell-Based Cell Therapy—Promise and Challenges. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zou, F.; Ma, X.; Xia, X.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, J.; Song, J. Cell-Free Extracts from Human Fat Tissue with a Hyaluronan-Based Hydrogel Attenuate Inflammation in a Spinal Cord Injury Model through M2 Microglia/Microphage Polarization. Small 2022, 18, e2107838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, T.; Ran, Z.; Sun, L.; Jiang, X.; Hou, L.; Yang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Yan, M.; et al. Cell-free fat extract-loaded microneedles attenuate inflammation-induced apoptosis and mitochondrial damage in tendinopathy. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 22, 100738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Kang, B.; Dong, Y.; Fan, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, W. Annexin A5 Derived from Cell-free Fat Extract Attenuates Osteoarthritis via Macrophage Regulation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 20, 2994–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Gu, Q.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Zhou, L.; Jin, Q.; Li, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, S.; Luo, X.; et al. Cell-free fat extract regulates oxidative stress and alleviates Th2-mediated inflammation in atopic dermatitis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1373419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Deng, M.; Yu, Z.; Cai, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhou, G.; Wang, X.; Cao, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, W. Cell-free fat extract accelerates diabetic wound healing in db/db mice. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 4216–4227. [Google Scholar]
- Melgoza, I.P.; Chenna, S.S.; Tessier, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, S.Y.; Ohnishi, T.; Novais, E.J.; Kerr, G.J.; Mohanty, S.; Tam, V.; et al. Development of a standardized histopathology scoring system using machine learning algorithms for intervertebral disc degeneration in the mouse model—An ORS spine section initiative. JOR Spine 2021, 4, e1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, E.J.; Darai, A.; Kyung, J.W.; Choi, H.; Kwon, S.Y.; Bhujel, B.; Kim, K.T.; Han, I. Genetic Therapy for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-Z.; Rui, Y.-F.; Tan, Q.; Wang, C. Enhancing intervertebral disc repair and regeneration through biology: Platelet-rich plasma as an alternative strategy. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Kang, B.; Cai, Y.; Chen, C.; Yu, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, W. Cell-free fat extract attenuates osteoarthritis via chondrocytes regeneration and macrophages immunomodulation. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Chen, B.; Zhang, W. Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Adipocytes Attenuate Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in Rats by Rejuvenating Senescent Nucleus Pulposus Cells and Endplate Cells by Delivering Exogenous NAMPT. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Zeng, Z.; Fang, B.; Tao, M.; Gu, C.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Fang, C.; Mei, S.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorate intervertebral disc degeneration via anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 143, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Xu, M.; Kong, F.; Zhu, P.; Mao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Dong, Z.; Yu, Z.; Du, T.; et al. CB2R Attenuates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Delaying Nucleus Pulposus Cell Senescence through AMPK/GSK3β Pathway. Aging Dis. 2022, 13, 552–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Zheng, H.; Meng, H.; Liu, C.; Duan, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, T. Mitochondrial DNA induces nucleus pulposus cell pyroptosis via the TLR9-NF-κB-NLRP3 axis. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shitany, N.A.; Eid, B.G. Icariin modulates carrageenan-induced acute inflammation through HO-1/Nrf2 and NF-kB signaling pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 120, 109567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weston, C.R.; Davis, R.J. The JNK signal transduction pathway. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2007, 19, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, H.-Y.; Koh, M.-S.; Moon, A. The p38 MAPK inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases and cancer. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 18, 1893–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Yu, Z.; Deng, M.; Cai, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, W. Fat extract improves fat graft survival via proangiogenic, anti-apoptotic and pro-proliferative activities. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Ru, X.; Wen, T. NRF2, a Transcription Factor for Stress Response and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, C.; Zhou, X.; Yang, C.; Zhou, F.; Xie, Y. Cell-Free Fat Extract for the Treatment of Lumbar Disc Degeneration: A Novel Approach Using Adipose-Derived Biologic. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061344
Xu C, Zhou X, Yang C, Zhou F, Xie Y. Cell-Free Fat Extract for the Treatment of Lumbar Disc Degeneration: A Novel Approach Using Adipose-Derived Biologic. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(6):1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061344
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Chenyang, Xianhao Zhou, Cheng Yang, Fanshangmin Zhou, and Youzhuan Xie. 2025. "Cell-Free Fat Extract for the Treatment of Lumbar Disc Degeneration: A Novel Approach Using Adipose-Derived Biologic" Biomedicines 13, no. 6: 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061344
APA StyleXu, C., Zhou, X., Yang, C., Zhou, F., & Xie, Y. (2025). Cell-Free Fat Extract for the Treatment of Lumbar Disc Degeneration: A Novel Approach Using Adipose-Derived Biologic. Biomedicines, 13(6), 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061344







