Vagus Nerve Stimulation Regulates the Th17/Treg Balance and Alleviates Lung Injury in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Upregulating α7nAChR
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. ARDS Model
2.3. Electrical Stimulation of the Vagus Nerve
2.4. Splenectomy
2.5. Adrenalectomy
2.6. Administration of α7nAChR Agonist and Antagonist
2.7. H&E Staining
2.8. Lung Wet-to-Dry Ratio (W/D)
2.9. Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid (BALF)
2.10. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.11. Western Blotting (WB)
2.12. Flow Cytometry
2.13. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
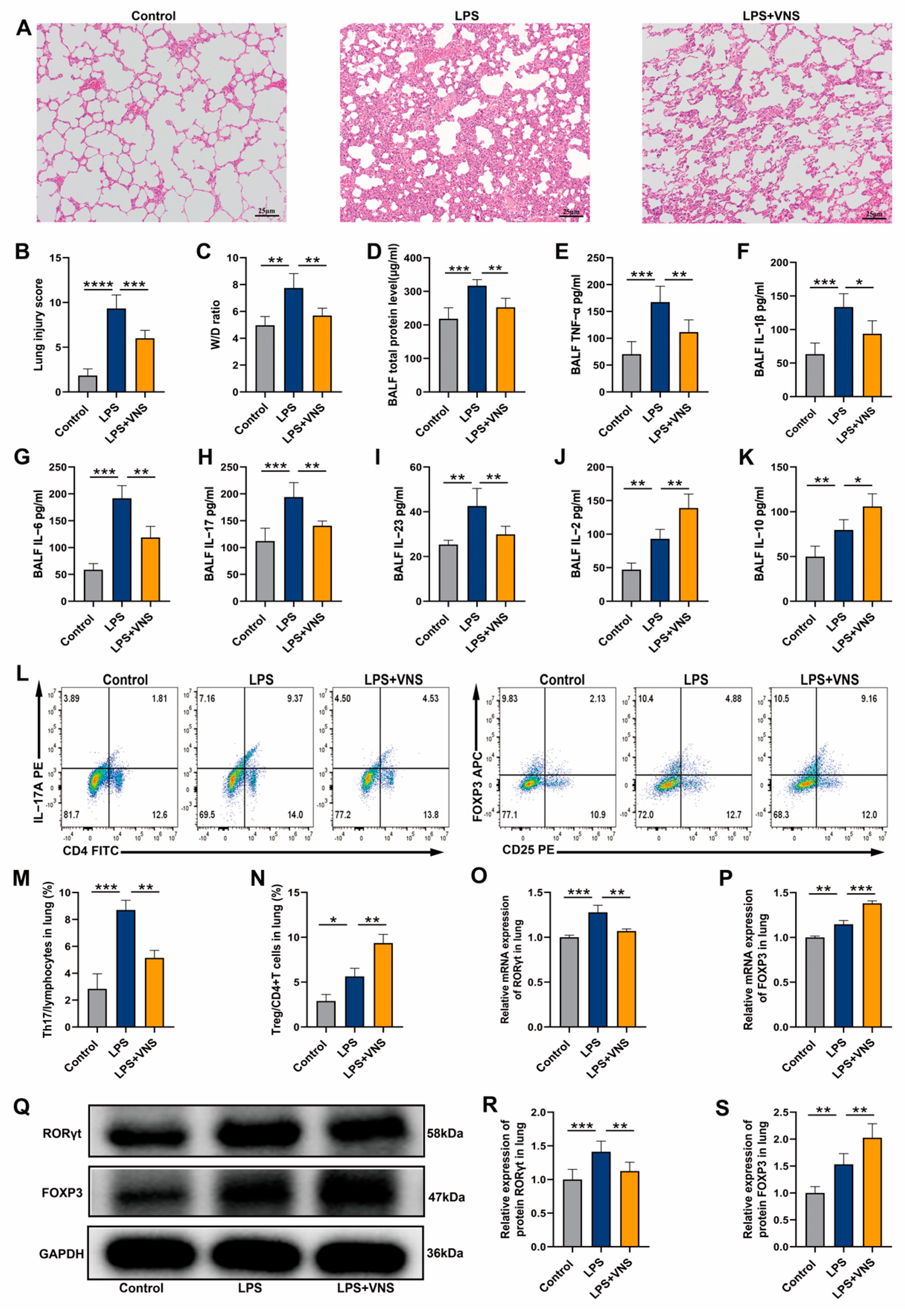
3.1. VNS Regulates Th17/Treg Homeostasis and Reduces Lung Inflammation in ARDS Model Rats
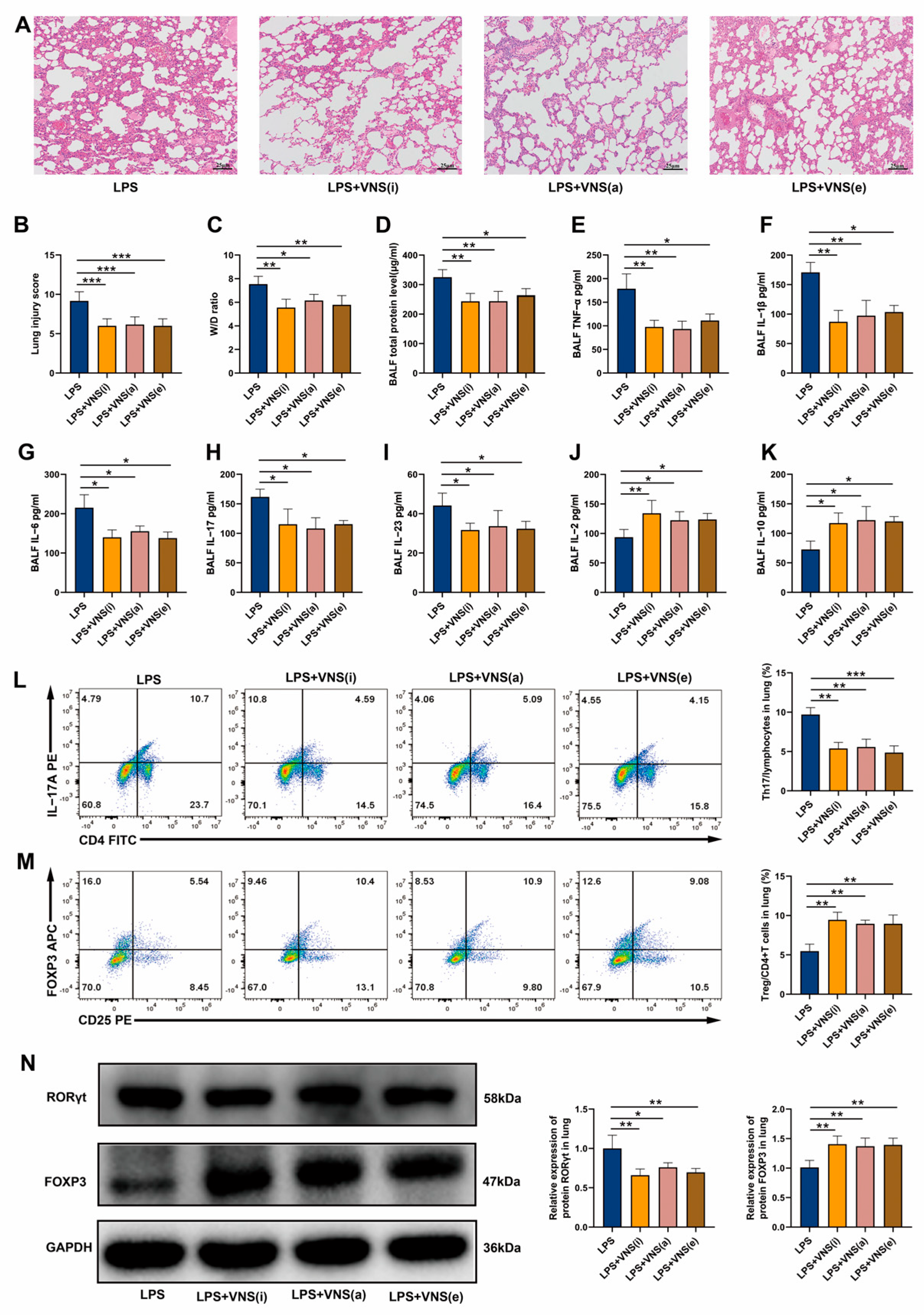
3.2. Afferent and Efferent VNS Regulates Th17/Treg Homeostasis and Reduces Lung Inflammation in ARDS Model Rats
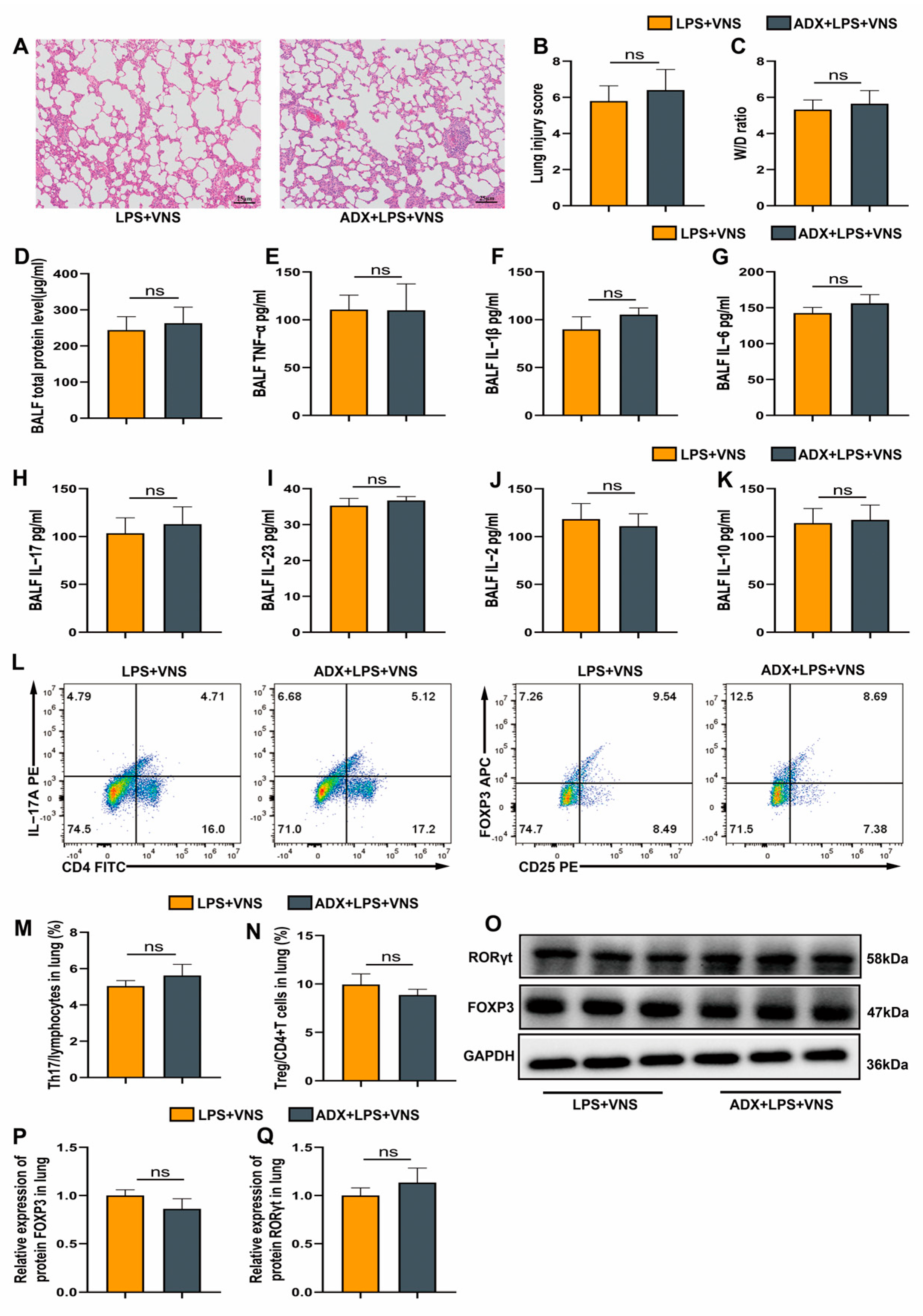
3.3. VNS Modulates Th17/Treg Homeostasis and Attenuates Pulmonary Inflammation Independently of the Adrenal Glands in a Rat Model of ARDS
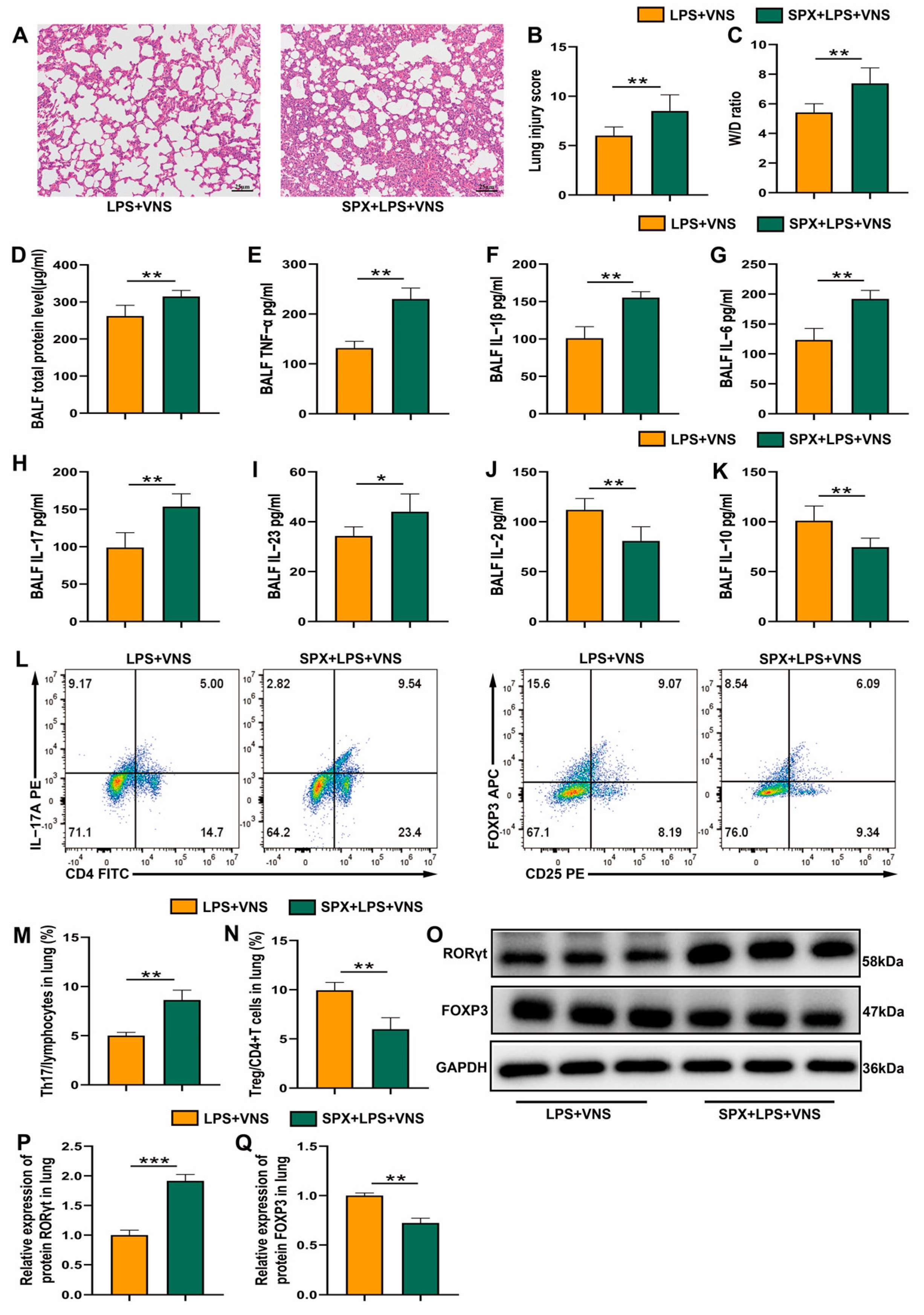
3.4. VNS Regulation of Th17/Treg Homeostasis and Attenuation of the Inflammatory Response in ARDS Model Rats Requires Spleen Involvement
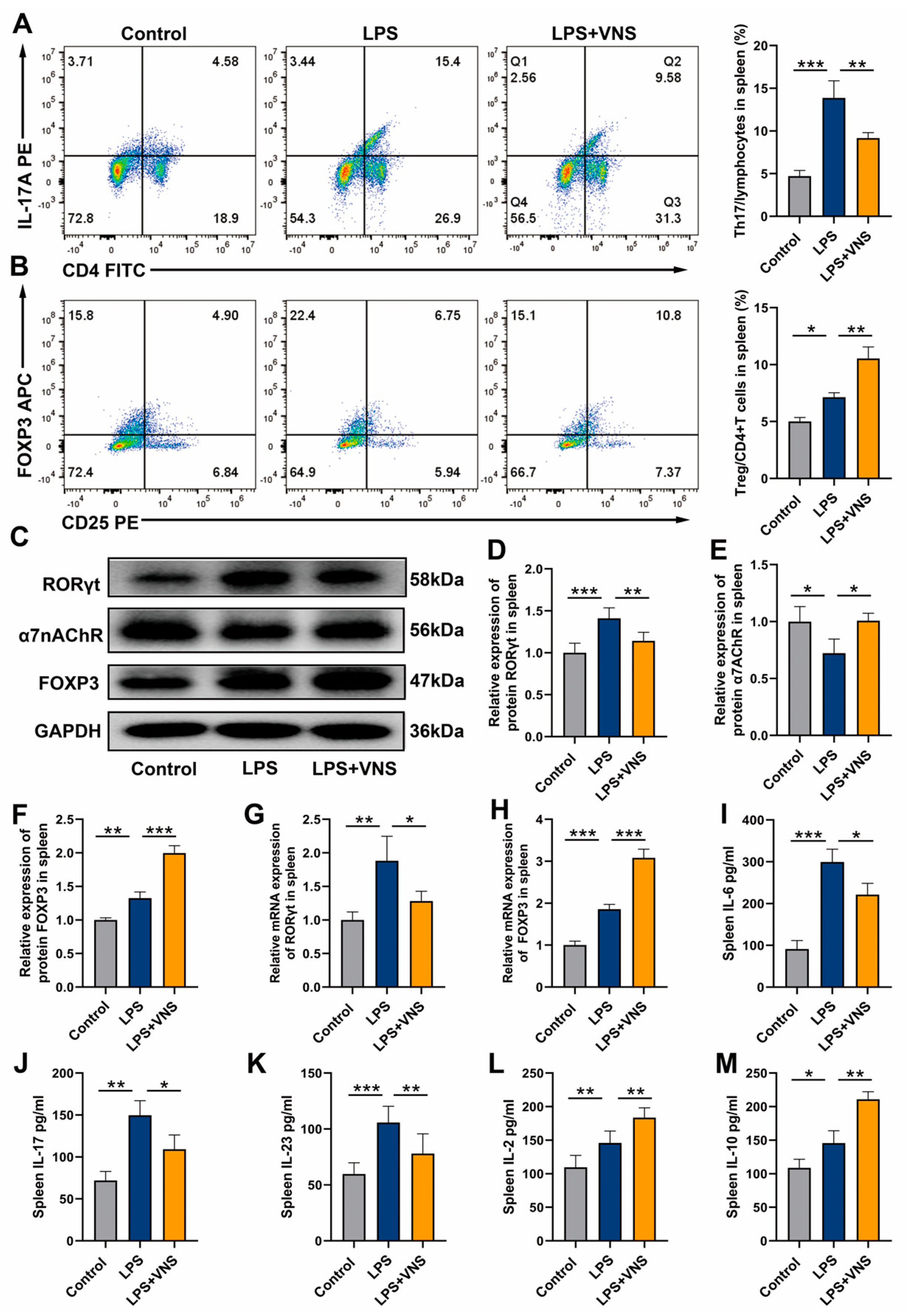
3.5. VNS Upregulates Splenic α7nAChR Expression and Modulates Splenic Th17/Treg Homeostasis in a Rat Model of ARDS
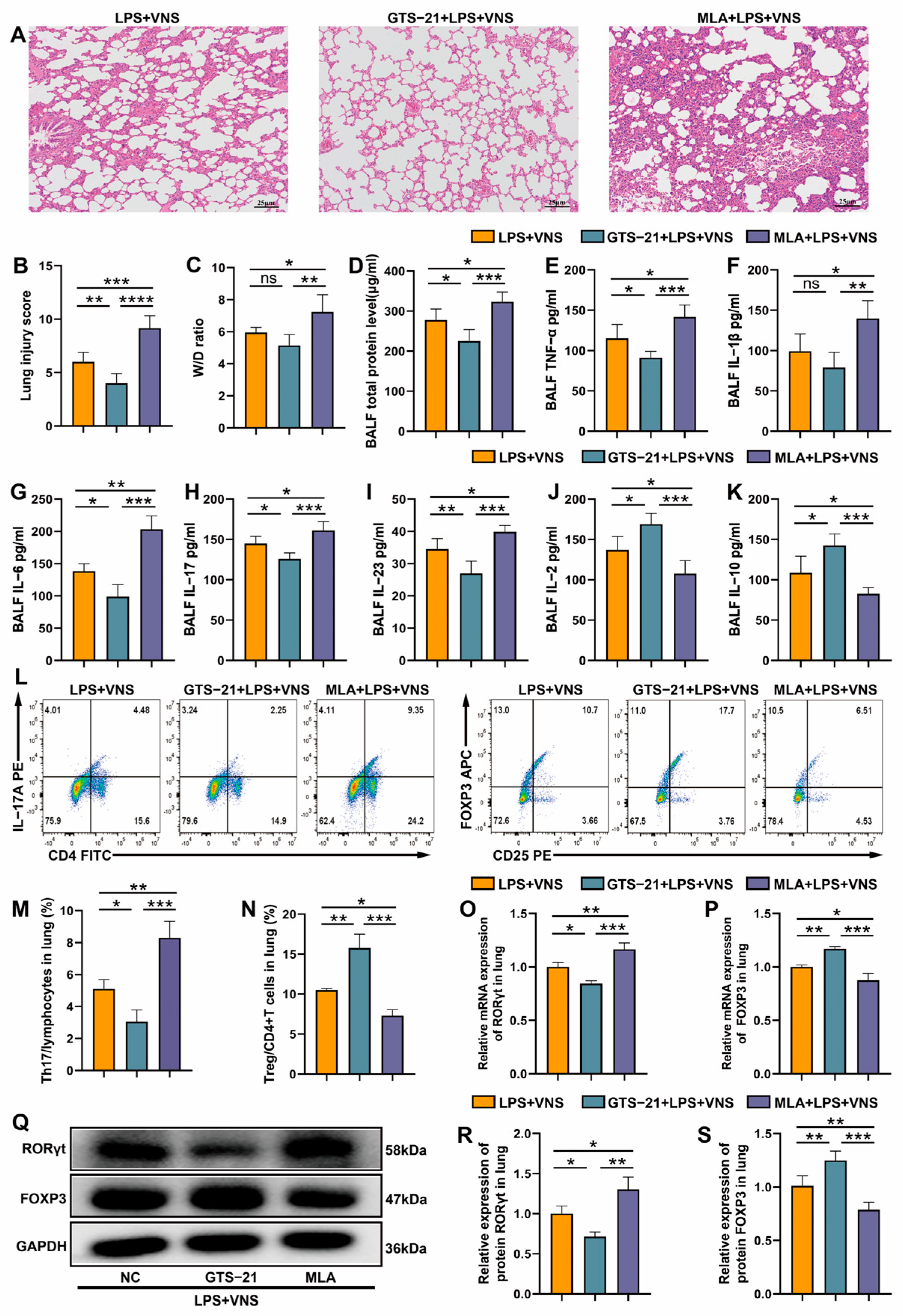
3.6. VNS Regulates Th17/Treg Homeostasis and Attenuates LPS-Induced ARDS Through α7nAChR Activation in the Spleen
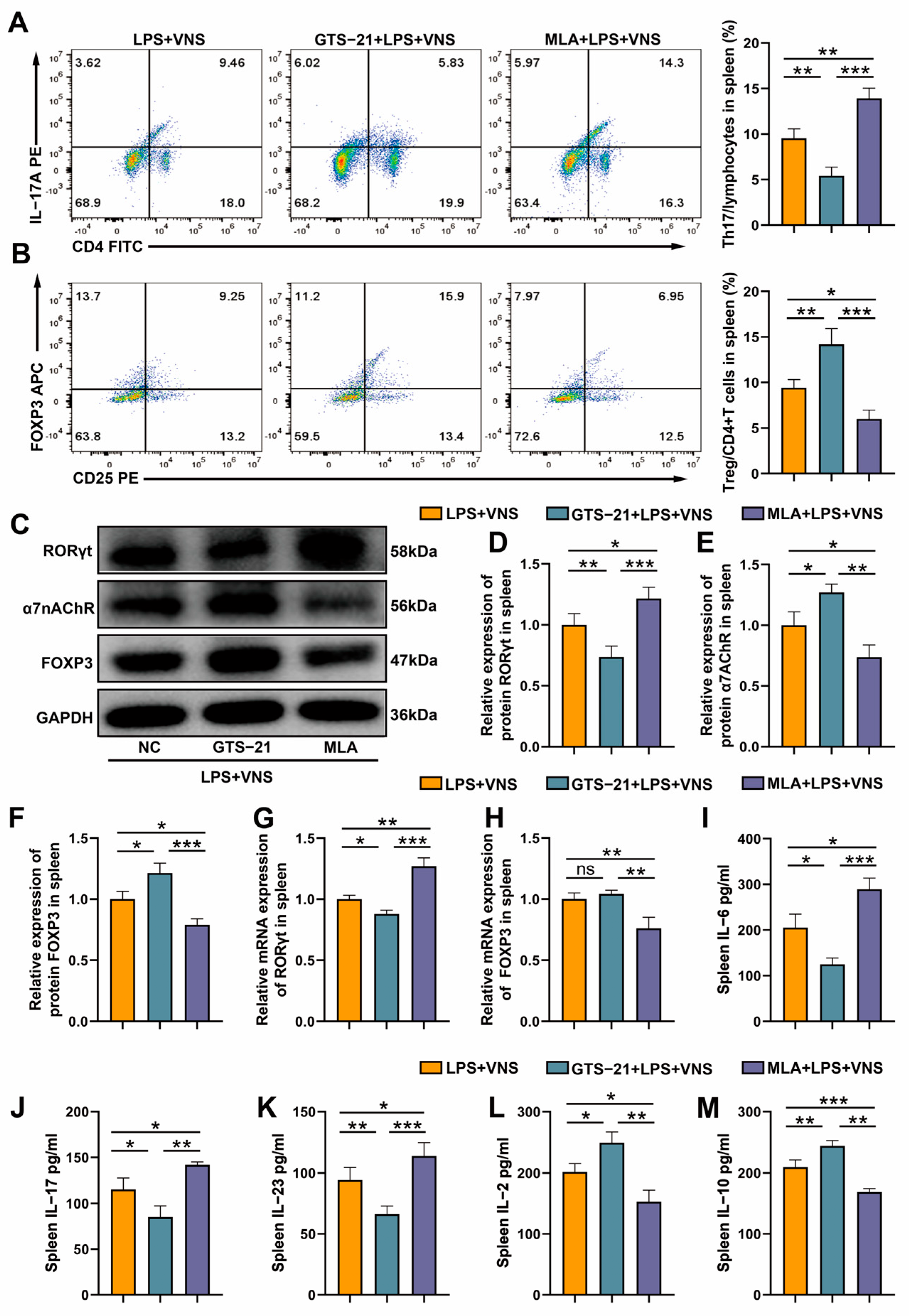
3.7. The Regulation of Splenic Th17/Treg Homeostasis by VNS Is α7nAChR Dependent
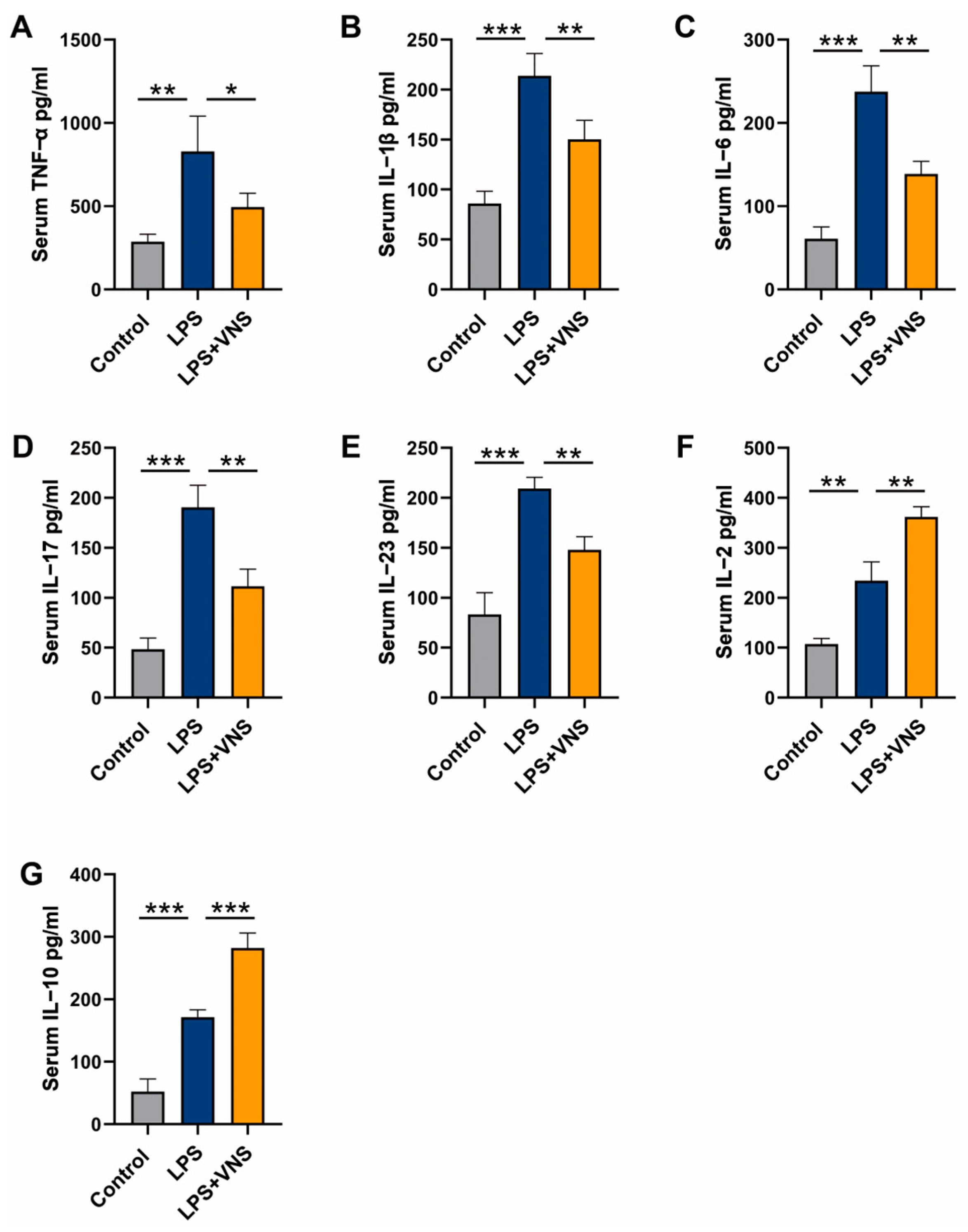
3.8. VNS Modulates Inflammatory Factors in the Serum of LPS-Induced ARDS Model Rats
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARDS | acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| VNS | vagus nerve stimulation |
| BALF | bronchoalveolar lavage fluid |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| HPA | hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis |
| α7nAChR | A7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor |
| Treg | regulatory T cell |
| Th17 | helper T 17 cell |
| IL-1β | interleukin-1β |
| IL-2 | interleukin-2 |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| IL-10 | interleukin-10 |
| IL-17 | interleukin-17 |
| IL-23 | interleukin-23 |
| TNF-α | transforming growth factor-α |
| RORγt | retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor gamma t |
| FOXP3 | forkhead box protein 3 |
| W/D | wet-to-dry ratio |
| SPX | splenectomy |
| ADX | adrenalectomy |
References
- Yildirim, F.; Karaman, I.; Kaya, A. Current situation in ARDS in the light of recent studies: Classification, epidemiology and pharmacotherapeutics. Tuberk. Toraks 2021, 69, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laffey, J.G.; Bellani, G.; Pham, T.; Fan, E.; Madotto, F.; Bajwa, E.K.; Brochard, L.; Clarkson, K.; Esteban, A.; Gattinoni, L.; et al. Potentially modifiable factors contributing to outcome from acute respiratory distress syndrome: The LUNG SAFE study. Intensive Care Med. 2016, 42, 1865–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthay, M.A.; Ware, L.B.; Zimmerman, G.A. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2731–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracey, K.J. The inflammatory reflex. Nature 2002, 420, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vida, G.; Pena, G.; Deitch, E.A.; Ulloa, L. alpha7-cholinergic receptor mediates vagal induction of splenic norepinephrine. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 4340–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Ballina, M.; Ochani, M.; Parrish, W.R.; Ochani, K.; Harris, Y.T.; Huston, J.M.; Chavan, S.; Tracey, K.J. Splenic nerve is required for cholinergic antiinflammatory pathway control of TNF in endotoxemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11008–11013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Qi, D.; Li, J.N.; Deng, X.Y.; Wang, D.X. Vagus nerve stimulation enhances the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway to reduce lung injury in acute respiratory distress syndrome via STAT3. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoi, T.; Okuma, Y.; Nomura, Y. Electrical stimulation of afferent vagus nerve induces IL-1beta expression in the brain and activates HPA axis. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2000, 279, R141–R147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, B.T. Glucocorticoids and acute lung injury. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31 (Suppl. S4), S253–S257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.C.; Pai, M.H.; Liu, J.J.; Yeh, S.L. Alanyl-glutamine resolves lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury in mice by modulating the polarization of regulatory T cells and T helper 17 cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; He, J.; Deng, W.; Cheng, L.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, D. Protein Kinase C Theta Inhibition Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury through Notch Signaling Pathway via Suppressing Th17 Cell Response in Mice. Inflammation 2019, 42, 1980–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Lv, J.; Yin, Q.; Liang, X.; Chu, Y.; He, R. BLT1-dependent alveolar recruitment of CD4+CD25+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells is important for resolution of acute lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, C.E.; Lalor, S.J.; Sweeney, C.M.; Brereton, C.F.; Lavelle, E.C.; Mills, K.H. Interleukin-1 and IL-23 induce innate IL-17 production from gammadelta T cells, amplifying Th17 responses and autoimmunity. Immunity 2009, 31, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, I.I.; McKenzie, B.S.; Zhou, L.; Tadokoro, C.E.; Lepelley, A.; Lafaille, J.J.; Cua, D.J.; Littman, D.R. The orphan nuclear receptor RORgammat directs the differentiation program of proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell 2006, 126, 1121–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettelli, E.; Carrier, Y.; Gao, W.; Korn, T.; Strom, T.B.; Oukka, M.; Weiner, H.L.; Kuchroo, V.K. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature 2006, 441, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Cao, X. Interleukin-17 and its expanding biological functions. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 7, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, S.; Nomura, T.; Sakaguchi, S. Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science 2003, 299, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurence, A.; Tato, C.M.; Davidson, T.S.; Kanno, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yao, Z.; Blank, R.B.; Meylan, F.; Siegel, R.; Hennighausen, L.; et al. Interleukin-2 signaling via STAT5 constrains T helper 17 cell generation. Immunity 2007, 26, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessio, F.R.; Tsushima, K.; Aggarwal, N.R.; West, E.E.; Willett, M.H.; Britos, M.F.; Pipeling, M.R.; Brower, R.G.; Tuder, R.M.; McDyer, J.F.; et al. CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs resolve experimental lung injury in mice and are present in humans with acute lung injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2898–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.X.; Ji, M.S.; Yan, J.; Cai, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, H.F.; Li, Y.; Jin, Z.C.; Zheng, J.X. The ratio of Th17/Treg cells as a risk indicator in early acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care. 2015, 19, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, K.; Coimbra, R.; Langness, S.; Eliceiri, B.P.; Costantini, T.W. Neuroenteric axis modulates the balance of regulatory T cells and T-helper 17 cells in the mesenteric lymph node following trauma/hemorrhagic shock. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 309, G202–G208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Chen, Q.; Wang, L.; Zheng, J.; Lin, Z.; Li, W. NF-kappaB-Induced MicroRNA-211 Inhibits Interleukin-10 in Macrophages of Rats with Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, N.M.; Santana, F.P.; Almeida, R.R.; Guerreiro, M.; Martins, M.A.; Caperuto, L.C.; Camara, N.O.; Wensing, L.A.; Prado, V.F.; Tiberio, I.F.; et al. Acute lung injury is reduced by the alpha7nAChR agonist PNU-282987 through changes in the macrophage profile. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S.; Niu, L.; Ma, J.; Wen, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, C. alpha7nAchR mediates transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation-induced neuroprotection in a rat model of ischemic stroke by enhancing axonal plasticity. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 730, 135031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, V.A.; Ochani, M.; Yang, L.H.; Gallowitsch-Puerta, M.; Ochani, K.; Lin, X.; Levi, J.; Parrish, W.R.; Rosas-Ballina, M.; Czura, C.J.; et al. Selective alpha7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist GTS-21 improves survival in murine endotoxemia and severe sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szapiel, S.V.; Elson, N.A.; Fulmer, J.D.; Hunninghake, G.W.; Crystal, R.G. Bleomycin-induced interstitial pulmonary disease in the nude, athymic mouse. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1979, 120, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prechtl, J.C.; Powley, T.L. The fiber composition of the abdominal vagus of the rat. Anat. Embryol. 1990, 181, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huston, J.M.; Ochani, M.; Rosas-Ballina, M.; Liao, H.; Ochani, K.; Pavlov, V.A.; Gallowitsch-Puerta, M.; Ashok, M.; Czura, C.J.; Foxwell, B.; et al. Splenectomy inactivates the cholinergic antiinflammatory pathway during lethal endotoxemia and polymicrobial sepsis. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 1623–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Lee, J.W.; Matthay, Z.A.; Mednick, G.; Uchida, T.; Fang, X.; Gupta, N.; Matthay, M.A. Activation of the alpha7 nAChR reduces acid-induced acute lung injury in mice and rats. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Jiao, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Jia, G. IL-33 Deficiency Attenuates Lung Inflammation by Inducing Th17 Response and Impacting the Th17/Treg Balance in LPS-Induced ARDS Mice via Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 9543083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Abe, C.; Sung, S.S.; Moscalu, S.; Jankowski, J.; Huang, L.; Ye, H.; Rosin, D.L.; Guyenet, P.G.; Okusa, M.D. Vagus nerve stimulation mediates protection from kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury through alpha7nAChR+ splenocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1939–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, K.; Rude, K.M.; Sladek, J.; Reardon, C. Divergence of neuroimmune circuits activated by afferent and efferent vagal nerve stimulation in the regulation of inflammation. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 2075–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.; Abe, C.; Abbott, S.; Zheng, S.; Yamaoka, Y.; Lipsey, J.E.; Skrypnyk, N.I.; Yao, J.; Inoue, T.; Nash, W.T.; et al. Vagus nerve stimulation activates two distinct neuroimmune circuits converging in the spleen to protect mice from kidney injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassi, G.S.; Dias, D.; Franchin, M.; Talbot, J.; Reis, D.G.; Menezes, G.B.; Castania, J.A.; Garcia-Cairasco, N.; Resstel, L.; Salgado, H.C.; et al. Modulation of experimental arthritis by vagal sensory and central brain stimulation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 64, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaz, B.; Sinniger, V.; Hoffmann, D.; Clarencon, D.; Mathieu, N.; Dantzer, C.; Vercueil, L.; Picq, C.; Trocme, C.; Faure, P.; et al. Chronic vagus nerve stimulation in Crohn’s disease: A 6-month follow-up pilot study. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 28, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Rabbi, M.F.; Labis, B.; Pavlov, V.A.; Tracey, K.J.; Ghia, J.E. Central cholinergic activation of a vagus nerve-to-spleen circuit alleviates experimental colitis. Mucosal Immunol. 2014, 7, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteoli, G.; Gomez-Pinilla, P.J.; Nemethova, A.; Di Giovangiulio, M.; Cailotto, C.; van Bree, S.H.; Michel, K.; Tracey, K.J.; Schemann, M.; Boesmans, W.; et al. A distinct vagal anti-inflammatory pathway modulates intestinal muscularis resident macrophages independent of the spleen. Gut 2014, 63, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, Z.; Tong, Z.; Yao, Q.; Wang, Z.; Li, W. Vagus Nerve Stimulation Decreases Pancreatitis Severity in Mice. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 595957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Kwan, K.; Levine, Y.A.; Olofsson, P.S.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Joshi, S.; Wang, H.; Andersson, U.; Chavan, S.S.; et al. alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor signaling inhibits inflammasome activation by preventing mitochondrial DNA release. Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yu, M.; Ochani, M.; Amella, C.A.; Tanovic, M.; Susarla, S.; Li, J.H.; Wang, H.; Yang, H.; Ulloa, L.; et al. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 subunit is an essential regulator of inflammation. Nature 2003, 421, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Chen, J.; Ren, X.; Song, Y.; Xu, J.; Xuan, S.; Jiang, X.; Kuang, Z.; Tang, Z. Vagus Nerve Stimulation Relives Irritable Bowel Syndrome and the Associated Depression via alpha7nAChR-mediated Anti-inflammatory Pathway. Neuroscience 2023, 530, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, X.; Su, E.M.; Huang, Y.; Li, L.; Matthay, M.A.; Su, X. Signals of vagal circuits engaging with AKT1 in alpha7 nAChR+CD11b+ cells lessen E. coli and LPS-induced acute inflammatory injury. Cell Discov. 2017, 3, 17009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huehn, J.; Hamann, A. Homing to suppress: Address codes for Treg migration. Trends Immunol. 2005, 26, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Kryczek, I.; Zou, W. Regulatory T-cell compartmentalization and trafficking. Blood. 2006, 108, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Barnett, B.; Safah, H.; Larussa, V.F.; Evdemon-Hogan, M.; Mottram, P.; Wei, S.; David, O.; Curiel, T.J.; Zou, W. Bone marrow is a reservoir for CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells that traffic through CXCL12/CXCR4 signals. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 8451–8455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, D.J. Control of Regulatory T Cell Migration, Function, and Homeostasis. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 2507–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Xu, J.; Bromberg, J.S. Regulatory T cell migration during an immune response. Trends Immunol. 2012, 33, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvis, G.; Lips, K.S.; Kummer, W. Expression of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on murine alveolar macrophages. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2006, 30, 107–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chikina, M.; Deshpande, R.; Menk, A.V.; Wang, T.; Tabib, T.; Brunazzi, E.A.; Vignali, K.M.; Sun, M.; Stolz, D.B.; et al. Treg Cells Promote the SREBP1-Dependent Metabolic Fitness of Tumor-Promoting Macrophages via Repression of CD8+ T Cell-Derived Interferon-gamma. Immunity 2019, 51, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proto, J.D.; Doran, A.C.; Gusarova, G.; Yurdagul, A.J.; Sozen, E.; Subramanian, M.; Islam, M.N.; Rymond, C.C.; Du, J.; Hook, J.; et al. Regulatory T Cells Promote Macrophage Efferocytosis during Inflammation Resolution. Immunity 2018, 49, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Fang, H.; Du, M.; Li, C.; Tang, R.; Liu, H.; Gao, Z.; Ji, Z.; Ke, B.; Chen, X.L. The Modulation of Regulatory T Cells via HMGB1/PTEN/beta-Catenin Axis in LPS Induced Acute Lung Injury. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soroosh, P.; Doherty, T.A.; Duan, W.; Mehta, A.K.; Choi, H.; Adams, Y.F.; Mikulski, Z.; Khorram, N.; Rosenthal, P.; Broide, D.H.; et al. Lung-resident tissue macrophages generate Foxp3+ regulatory T cells and promote airway tolerance. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zou, N.; Feng, B.; Claire, M.R.; Han, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Wei, W.; Rong, P. Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation improves gastric motility and visceral hypersensitivity in rodents of functional dyspepsia by balancing duodenal immune response: An experimental study. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 111, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Jia, G.; Cheng, L. Vagus Nerve Stimulation Regulates the Th17/Treg Balance and Alleviates Lung Injury in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Upregulating α7nAChR. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061294
Zheng F, Zhang X, Wang S, Jia G, Cheng L. Vagus Nerve Stimulation Regulates the Th17/Treg Balance and Alleviates Lung Injury in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Upregulating α7nAChR. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(6):1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061294
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Furong, Xin Zhang, Sisi Wang, Gongwei Jia, and Li Cheng. 2025. "Vagus Nerve Stimulation Regulates the Th17/Treg Balance and Alleviates Lung Injury in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Upregulating α7nAChR" Biomedicines 13, no. 6: 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061294
APA StyleZheng, F., Zhang, X., Wang, S., Jia, G., & Cheng, L. (2025). Vagus Nerve Stimulation Regulates the Th17/Treg Balance and Alleviates Lung Injury in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Upregulating α7nAChR. Biomedicines, 13(6), 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061294






