Chronic Inflammation and Immune Dysregulation in Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Progression: From Steatosis to Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Immune Landscape in MASLD
2.1. Innate Immunity in MASLD
2.2. Adaptive Immunity and Chronic Inflammation
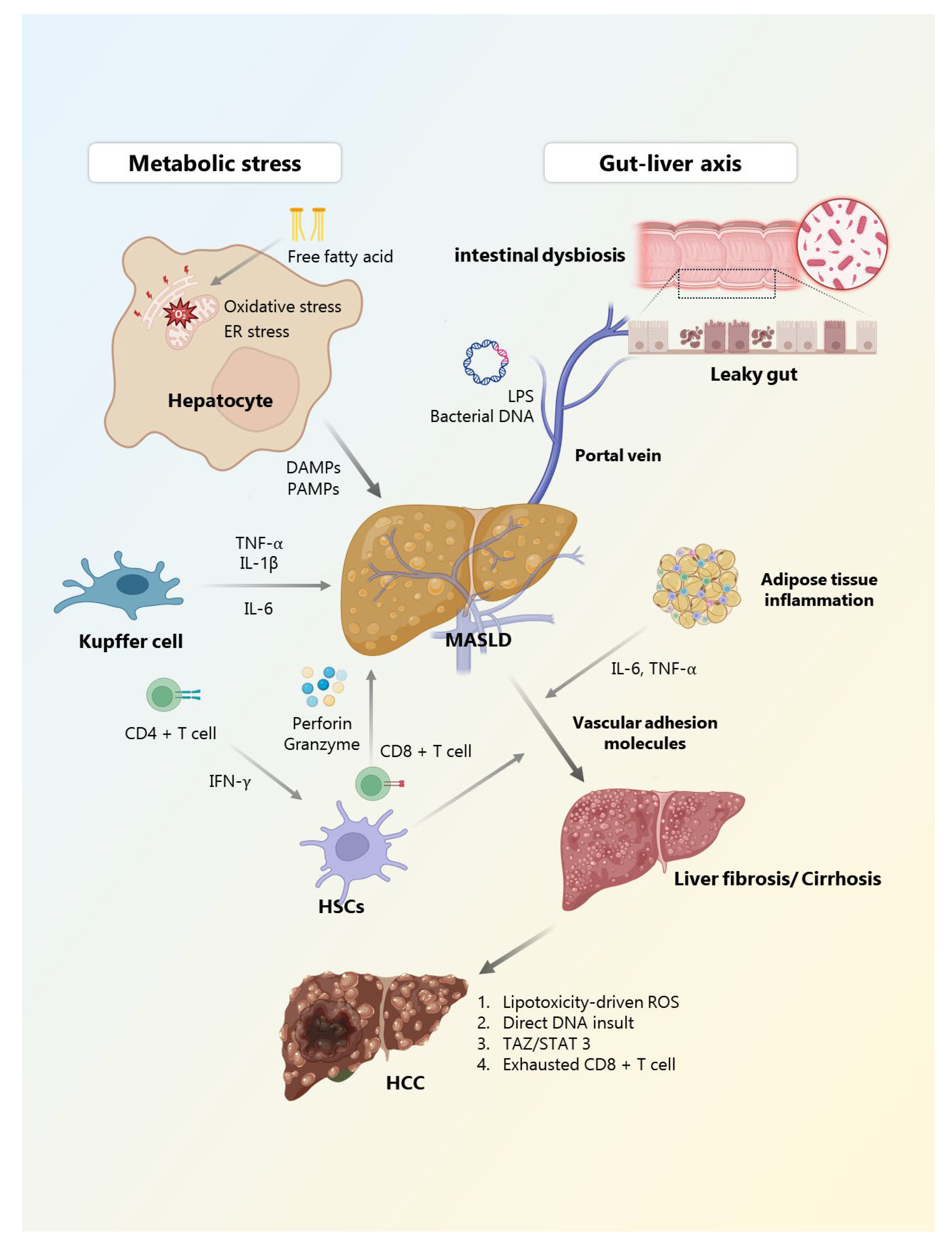
3. Chronic Inflammation in MASLD Progression
3.1. Metabolic Stress and Lipotoxicity as Initiating Triggers
3.2. Gut–Liver Axis: Microbial Signs and Barrier Dysfunction
3.3. Immune Activation and Cytokine Networks
3.4. Adaptive Immune Contribution and Imbalance
3.5. Fibrogenesis and Systemic Inflammatory Crosstalk
3.6. Dysregulated Innate Immune Pathways in MASLD
4. From Steatosis to HCC: Immune-Modulated Progression
4.1. Chronic Inflammation and Fibrosis as Pro-Carcinogenic Drivers
4.2. Immune Imbalance and Loss of Tumor Surveillance
4.3. Oxidative Stress, ER Dysfunction, and DNA Damage
4.4. Oncogenic Signaling Pathways
4.5. Tumor Evolution and Therapeutic Implications
5. Therapeutic Targets and Immune Modulation
5.1. Targeting Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and Immune Pathways
5.2. Anti-Fibrotic Therapies with Immunomodulatory Effects
5.3. Metabolic Reprogramming and Oxidative Stress Modulation
5.4. Gut–Liver Axis: Microbiota and Immune Crosstalk
5.5. Nutraceuticals and Adjunctive Immune Modulators
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACC | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase |
| ACMSD | Aminocarboxymuconate semialdehyde decarboxylase |
| CCL | C-C chemokine ligand |
| CCR | C-C chemokine receptor |
| DAMPs | Damage-associated molecular patterns |
| DC | Dendritic cell |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| FXR | Farnesoid X receptor |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HSC | Hepatic stellate cell |
| ICAM-1 | Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| LSEC | Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell |
| MASLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| MASH | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis |
| MyD88 | Myeloid differentiation primary response 88 |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NET | Neutrophil extracellular trap |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NLR | Nucleotide-binding and oligomerization domain-like receptor |
| NLRP3 | Nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich–containing family, pyrin domain–containing-3 |
| OCA | Obeticholic acid |
| PAMPs | Pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| PD-1 | Programmed death-1 |
| PPAR | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor |
| PRR | Pattern recognition receptor |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| TAZ | Transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif; |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-beta; |
| Th | T helper |
| TIM-3 | T cell immunoglobulin mucin domain-3 |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| Treg | Regulatory T cell |
| VCAM-1 | Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
References
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1966–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.K.; Baik, S.K.; Kim, M.Y. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Definition and subtypes. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, S5–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.A.; Moon, J.H.; Kim, W. Critical appraisal of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Implication of Janus-faced modernity. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoolchund, A.G.S.; Khakoo, S.I. MASLD and the Development of HCC: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Challenges. Cancers 2024, 16, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parola, M.; Pinzani, M. Liver fibrosis in NAFLD/NASH: From pathophysiology towards diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Mol. Aspects Med. 2024, 95, 101231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, I.; Codini, M.; Guarisco, G.; Chinucci, M.; Gaita, C.; Leonetti, F.; Capoccia, D. Hepatokines and MASLD: The GLP1-Ras-FGF21-Fetuin-A Crosstalk as a Therapeutic Target. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, G.; Petrasek, J. Inflammasome activation and function in liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Kalligeros, M.; Henry, L. Epidemiology of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2025, 31, S32–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, P.; Tatar, M.; Dasarathy, S.; Alkhouri, N.; Herman, W.H.; Taksler, G.B.; Deshpande, A.; Ye, W.; Adekunle, O.A.; McCullough, A.; et al. Estimated Burden of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in US Adults, 2020 to 2050. JAMA Netw. Open 2025, 8, e2454707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Cao, Y.Y.; Zheng, M.H. Current status and future trends of the global burden of MASLD. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 35, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.F.; Zhao, Z.B.; Yan, E.P.; Lian, Z.X.; Zhang, W. Complex interplay between the immune system, metabolism, and epigenetic factors in autoimmune liver diseases. Med. Adv. 2023, 1, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Gao, F.; Li, Y.; Su, D.; Han, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Feng, Z. Role of pattern recognition receptors in the development of MASLD and potential therapeutic applications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 175, 116724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coste, S.C.; Orasan, O.H.; Cozma, A.; Negrean, V.; Sitar-Taut, A.V.; Filip, G.A.; Hangan, A.C.; Lucaciu, R.L.; Iancu, M.; Procopciuc, L.M. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: The Associations between Inflammatory Markers, TLR4, and Cytokines IL-17A/F, and Their Connections to the Degree of Steatosis and the Risk of Fibrosis. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Tilg, H. MASLD: A systemic metabolic disorder with cardiovascular and malignant complications. Gut 2024, 73, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Garcia Diaz, J.; Um, E.; Hahn, Y.S. Major roles of kupffer cells and macrophages in NAFLD development. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1150118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.; Schwarzler, J.; Jukic, A.; Tilg, H. Innate Immunity and MASLD. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fa, P.; Ke, B.G.; Dupre, A.; Tsung, A.; Zhang, H. The implication of neutrophil extracellular traps in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1292679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuta, M.; Morel, C.; de Carvalho Ribeiro, M.; Calenda, C.; Ortega-Ribera, M.; Thevkar Nagesh, P.; Copeland, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cho, Y.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps activate hepatic stellate cells and monocytes via NLRP3 sensing in alcohol-induced acceleration of MASH fibrosis. Gut 2024, 73, 1854–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukacs-Kornek, V.; Hendrikx, T.; Sutti, S. Editorial: Inflammatory responses on the road from NASH to HCC: Pathogenic mechanisms and possible therapeutic strategies. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1512363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, F.; Eppler, N.; Jones, E.; Zhang, Y. Understanding Macrophage Complexity in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: Transitioning from the M1/M2 Paradigm to Spatial Dynamics. Livers 2024, 4, 455–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, X. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell: An important yet often overlooked player in the liver fibrosis. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2024, 30, 303–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Q.; Ain, Q.; Seth, N.; Rooney, M.; Zipprich, A. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells: Friend or foe in metabolic dysfunction- associated steatotic liver disease/metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2025, 57, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krenkel, O.; Hundertmark, J.; Abdallah, A.T.; Kohlhepp, M.; Puengel, T.; Roth, T.; Branco, D.P.P.; Mossanen, J.C.; Luedde, T.; Trautwein, C.; et al. Myeloid cells in liver and bone marrow acquire a functionally distinct inflammatory phenotype during obesity-related steatohepatitis. Gut 2020, 69, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nati, M.; Chung, K.J.; Chavakis, T. The Role of Innate Immune Cells in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Innate Immun. 2022, 14, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Xu, Q.; Su, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. The double roles of T cell-mediated immune response in the progression of MASLD. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 173, 116333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xia, N. The multifaceted roles of B lymphocytes in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1447391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, K.; Chung, H.; Softic, S.; Moreno-Fernandez, M.E.; Divanovic, S. The bidirectional immune crosstalk in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 1852–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Man, S.; Ma, L.; Guo, L.; Huang, L.; Gao, W. Immunological mechanisms in steatotic liver diseases: An overview and clinical perspectives. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2024, 30, 620–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelnabi, M.N.; Hassan, G.S.; Shoukry, N.H. Role of the type 3 cytokines IL-17 and IL-22 in modulating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1437046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.L.; Teijeiro, A.; Buren, S.; Tummala, K.S.; Yilmaz, M.; Waisman, A.; Theurillat, J.P.; Perna, C.; Djouder, N. Metabolic Inflammation-Associated IL-17A Causes Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tsung, A.; Mishra, L.; Huang, H. Regulatory T cell: A double-edged sword from metabolic-dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis to hepatocellular carcinoma. EBioMedicine 2024, 101, 105031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsomidis, I.; Voumvouraki, A.; Kouroumalis, E. Immune Checkpoints and the Immunology of Liver Fibrosis. Livers 2025, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenic, K.; Lenartic, M.; Marinovic, S.; Polic, B.; Wensveen, F.M. The “Domino effect” in MASLD: The inflammatory cascade of steatohepatitis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2024, 54, e2149641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed-Abdul, M.M. Lipid Metabolism in Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Metabolites 2023, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.S.; Kaufman, R.J. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress in cell fate decision and human disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2014, 21, 396–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Tan, J.; Yin, H.; Wang, Y.; Dai, Z.; Ding, D.; Yang, F. Mechanisms and therapeutic targets of mitochondria in the progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Ann. Hepatol. 2024, 30, 101774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, N.T.; McGrane, A.; Roberts, L.D. Linking the unfolded protein response to bioactive lipid metabolism and signalling in the cell non-autonomous extracellular communication of ER stress. Bioessays 2023, 45, e2300029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, N.; Doskey, L.C.; Malhi, H. The Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum in Lipotoxicity during Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) Pathogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2023, 193, 1887–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.J.; Liu, A.B.; Yu, Y.Y.; Ma, J.H. The role and mechanism of pyroptosis and potential therapeutic targets in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1407738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.W.; Ha, J.; Yoon, K.S.; Kang, I.; Choi, T.G.; Kim, S.S. Innate Immune System in the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wree, A.; Eguchi, A.; McGeough, M.D.; Pena, C.A.; Johnson, C.D.; Canbay, A.; Hoffman, H.M.; Feldstein, A.E. NLRP3 inflammasome activation results in hepatocyte pyroptosis, liver inflammation, and fibrosis in mice. Hepatology 2014, 59, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpellini, E.; Scarcella, M.; Tack, J.F.; Scarlata, G.G.M.; Zanetti, M.; Abenavoli, L. Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Codina, B.; Cacho-Pujol, J.; Moles, A.; Melgar-Lesmes, P. Reprogramming macrophages to treat liver diseases. Hepatology 2024. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Mu, T.; Tong, N.; Cheng, P. Hepatic stellate cells specific liposomes with the Toll-like receptor 4 shRNA attenuates liver fibrosis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 1299–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portincasa, P.; Khalil, M.; Graziani, A.; Fruhbeck, G.; Baffy, G.; Garruti, G.; Di Ciaula, A.; Bonfrate, L. Gut microbes in metabolic disturbances. Promising role for therapeutic manipulations? Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 119, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yan, Z.; Zhong, H.; Luo, R.; Liu, W.; Xiong, S.; Liu, Q.; Liu, M. Gut microbial metabolites in MASLD: Implications of mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathogenesis and treatment. Hepatol. Commun. 2024, 8, e0484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Sun, J.G.; Chen, S.C.; Sun, Y.L.; Zheng, Y.; Feng, J.C. The role of intestinal flora in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and treatment strategies. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1490929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, K.-Y.; Qi, N.-X.; Zhang, J.; Tie, S.-S.; Li, X.; Tian, P.-P.; Gu, S.-B. Cornus officinalis vinegar alters the gut microbiota, regulating lipid droplet changes in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease model mice. Food Med. Homol. 2024, 1, 9420002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhameed, F.; Mustafa, A.; Kite, C.; Lagojda, L.; Dallaway, A.; Than, N.N.; Kassi, E.; Kyrou, I.; Randeva, H.S. Gut microbiota and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD): Emerging pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Livers 2025, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, S.; Ye, W.; Chen, W.D. Kupffer cells, the limelight in the liver regeneration. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 146, 113808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Yin, X.; Zhang, P.; Mao, T.; Tian, Z.; Li, X. The role and therapeutic targeting of the CCL2/CCR2 signaling axis in inflammatory and fibrotic diseases. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1497026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Sterling, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Song, W. The role of inflammasomes in human diseases and their potential as therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehlen, N.; Crouchet, E.; Baumert, T.F. Liver Fibrosis: Mechanistic Concepts and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cells 2020, 9, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, L.; Gao, W.; Tang, T.L.; Yan, M. Interaction between macrophages and ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, T.; Kared, H.; Friedman, S.L.; Shoukry, N.H. IL-17A enhances the expression of profibrotic genes through upregulation of the TGF-beta receptor on hepatic stellate cells in a JNK-dependent manner. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 3925–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipitone, R.M.; Lupo, G.; Zito, R.; Javed, A.; Petta, S.; Pennisi, G.; Grimaudo, S. The PD-1/PD-L1 Axis in the Biology of MASLD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okwor, C.I.A.; Oh, J.S.; Crawley, A.M.; Cooper, C.L.; Lee, S.H. Expression of Inhibitory Receptors on T and NK Cells Defines Immunological Phenotypes of HCV Patients with Advanced Liver Fibrosis. iScience 2020, 23, 101513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudi, I.; Kawashima, K.; Isogawa, M. HBV-Specific CD8+ T-Cell Tolerance in the Liver. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 721975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Lv, M.; Ma, M.; Huang, Q.; Hu, R.; Li, J.; Yi, J.; Sun, J.; Zhou, X. State of CD8(+) T cells in progression from nonalcoholic steatohepatitis to hepatocellular carcinoma: From pathogenesis to immunotherapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, T.M.; Fortson, K.T.; de Los Santos-Alexis, K.; Oliveras-Alsina, A.; Rouanne, M.; Rae, S.S.; Gamarra, J.R.; Shayya, H.; Kornberg, A.; Cavero, R.; et al. Amphiregulin from regulatory T cells promotes liver fibrosis and insulin resistance in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Immunity 2024, 57, 303–318.e306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, M.; Schilling, A.K.; Meertens, J.; Hering, I.; Weiss, J.; Jurowich, C.; Kudlich, T.; Hermanns, H.M.; Bantel, H.; Beyersdorf, N.; et al. Progression from Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver to Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Is Marked by a Higher Frequency of Th17 Cells in the Liver and an Increased Th17/Resting Regulatory T Cell Ratio in Peripheral Blood and in the Liver. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Q.; Yi, Q.; Tang, L. Liver Fibrosis Resolution: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.Y.; Sakane, S.; Eguileor, A.; Carvalho Gontijo Weber, R.; Lee, W.; Liu, X.; Lam, K.; Ishizuka, K.; Rosenthal, S.B.; Diggle, K.; et al. The Origin and Fate of Liver Myofibroblasts. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 17, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Sechi, L.A.; Navarese, E.P.; Casu, G.; Vidili, G. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and cardiovascular risk: A comprehensive review. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilson, J.; Mantovani, A.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. Steatotic liver disease, MASLD and risk of chronic kidney disease. Diabetes Metab. 2024, 50, 101506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandireddy, R.; Sakthivel, S.; Gupta, P.; Behari, J.; Tripathi, M.; Singh, B.K. Systemic impacts of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) on heart, muscle, and kidney related diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1433857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frak, W.; Kucmierz, J.; Szlagor, M.; Mlynarska, E.; Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B. New Insights into Molecular Mechanisms of Chronic Kidney Disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, P.R.; Krishnan, P.; Prabu, S.; Srinivasan, V.; Niranjan, V. Diagnosis and management of metabolic dysfunction- associated steatotic liver disease in South Asians- A clinical review. Obes. Pillars 2024, 12, 100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, D.F.; Xu, W.Q.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, C.L.; Wang, S.Y.; Han, Y.L.; Li, H.G.; Liu, M.H.; Zhao, W.X. Molecular mechanisms of pyroptosis in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and feasible diagnosis and treatment strategies. Pharmacol. Res. 2025, 216, 107754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhou, R. NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell death. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 2114–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Ma, Y.; Song, Y.; Cen, Y.; You, M.; Yang, G. The Notch signaling pathway regulates macrophage polarization in liver diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 99, 107938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Masuda, A.; Nakano, D.; Amano, K.; Sano, T.; Nakano, M.; Kawaguchi, T. Pathogenic Mechanisms of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells 2025, 14, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Dong, B. Molecular mechanisms in MASLD/MASH-related HCC. Hepatology 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provera, A.; Vecchio, C.; Sheferaw, A.N.; Stoppa, I.; Pantham, D.; Dianzani, U.; Sutti, S. From MASLD to HCC: What’s in the middle? Heliyon 2024, 10, e35338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, M.; Seki, E. Hepatic Stellate Cell-Macrophage Crosstalk in Liver Fibrosis and Carcinogenesis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2020, 40, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.X.; Wei, S.; Yu, C.; Zhao, S.Q.; Yang, W.J.; Feng, Y.H.; Pan, C.; Yang, K.X.; Ma, Y. Activation of Kupffer cells in NAFLD and NASH: Mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1199519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Reeves, H.L.; Kotsiliti, E.; Govaere, O.; Heikenwalder, M. From NASH to HCC: Current concepts and future challenges. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ye, X.; Yang, L.; Zhao, J.; You, J.; Feng, Y. Linking fatty liver diseases to hepatocellular carcinoma by hepatic stellate cells. J. Natl. Cancer Cent. 2024, 4, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheu, J.W.; Wong, C.C. The immune microenvironment of steatotic hepatocellular carcinoma: Current findings and future prospects. Hepatol. Commun. 2024, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zheng, B.; Goswami, S.; Meng, L.; Zhang, D.; Cao, C.; Li, T.; Zhu, F.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Z.; et al. PD1(Hi) CD8(+) T cells correlate with exhausted signature and poor clinical outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Hyun, J. Altered lipid metabolism as a predisposing factor for liver metastasis in MASLD. Mol. Cells 2024, 47, 100010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Nie, C.; Lv, H.; Chen, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; He, Y.; Chen, X. Molecular subtypes based on Wnt-signaling gene expression predict prognosis and tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1010554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allameh, A.; Niayesh-Mehr, R.; Aliarab, A.; Sebastiani, G.; Pantopoulos, K. Oxidative Stress in Liver Pathophysiology and Disease. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakehashi, A.; Suzuki, S.; Ishii, N.; Okuno, T.; Kuwae, Y.; Fujioka, M.; Gi, M.; Stefanov, V.; Wanibuchi, H. Accumulation of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine, L-arginine and Glucose Metabolites by Liver Tumor Cells Are the Important Characteristic Features of Metabolic Syndrome and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis-Associated Hepatocarcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gungor, M.Z.; Uysal, M.; Senturk, S. The Bright and the Dark Side of TGF-beta Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Mechanisms, Dysregulation, and Therapeutic Implications. Cancers 2022, 14, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, S.G. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy dysregulation in alcoholic and non-alcoholic liver diseases. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakehashi, A.; Suzuki, S.; Wanibuchi, H. Recent Insights into the Biomarkers, Molecular Targets and Mechanisms of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis-Driven Hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancers 2023, 15, 4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rives, C.; Fougerat, A.; Ellero-Simatos, S.; Loiseau, N.; Guillou, H.; Gamet-Payrastre, L.; Wahli, W. Oxidative Stress in NAFLD: Role of Nutrients and Food Contaminants. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Caviglia, J.M.; Corey, K.E.; Herfel, T.M.; Cai, B.; Masia, R.; Chung, R.T.; Lefkowitch, J.H.; Schwabe, R.F.; et al. Hepatocyte TAZ/WWTR1 Promotes Inflammation and Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hwang, S.; Cai, Y.; Kim, S.J.; Xu, M.; Yang, D.; Guillot, A.; Feng, D.; Seo, W.; Hou, X.; et al. MicroRNA-223 Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Cancer by Targeting Multiple Inflammatory and Oncogenic Genes in Hepatocytes. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1150–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajos-Michniewicz, A.; Czyz, M. WNT/beta-catenin signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma: The aberrant activation, pathogenic roles, and therapeutic opportunities. Genes. Dis. 2024, 11, 727–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, W.; Kuzminskaya, M.; Lurje, I.; Tacke, F.; Hammerich, L. Overcoming Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Liver Cancer with Combination Therapy: Stronger Together? Semin. Liver Dis. 2024, 44, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malakmahmoudi, N.; Pisu, R.; Laconi, E.; Marongiu, F. Dietary Rhythms and MASLD-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2024, 16, 3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.K.; Choi, W.I.; Choi, W.; Moon, J.; Lee, W.H.; Choi, C.; Choi, I.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.K.; Ju, Y.S.; et al. A male mouse model for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Ho, Y.J.; Salomao, M.A.; Dapito, D.H.; Bartolome, A.; Schwabe, R.F.; Lee, J.S.; Lowe, S.W.; Pajvani, U.B. Notch activity characterizes a common hepatocellular carcinoma subtype with unique molecular and clinicopathologic features. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, F.; Strazzabosco, M. Emerging roles of Notch signaling in liver disease. Hepatology 2015, 61, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Friedman, S.L. Found in translation-Fibrosis in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH). Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eadi0759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.R.; Sui, G.; Lee, J.W.; Wang, F.; Park, J.S.; Ma, Y.; Ma, H.; Jeong, J.W.; Shin, D.S.; Wu, X.; et al. Jolkinolide B Ameliorates Liver Inflammation and Lipogenesis by Regulating JAK/STAT3 Pathway. Biomol. Ther. 2024, 32, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouchet, E.; Dachraoui, M.; Juhling, F.; Roehlen, N.; Oudot, M.A.; Durand, S.C.; Ponsolles, C.; Gadenne, C.; Meiss-Heydmann, L.; Moehlin, J.; et al. Targeting the liver clock improves fibrosis by restoring TGF-beta signaling. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo-Marin, M.A.; Alves-Bezerra, M. Targeting acetyl-CoA carboxylases for the treatment of MASLD. J. Lipid Res. 2024, 65, 100676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.; Li, J.; Li, M.Y.; Liu, Y. Patient-derived xenograft model in cancer: Establishment and applications. MedComm 2020 2025, 6, e70059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadizar, F.; Younossi, Z.M. Exploring Biomarkers in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Among Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2025, 59, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Wei, X.; Hua, H.; Tang, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; et al. Roles of immune dysregulation in MASLD. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 170, 116069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, A.; Tam, F.; Gursche, C.; Cheneval, C.; Besler, K.; Enns, W.; Manku, S.; Rey, K.; Hanson, P.J.; Rose-John, S.; et al. Overlapping and distinct biological effects of IL-6 classic and trans-signaling in vascular endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C554–C565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yin, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, Y. The Role of IL-6 in Fibrotic Diseases: Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 5405–5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; Vining, D.J.; Arora, S.P.; de Achaval, S.; Larson, J.; Kauh, J.; Cartwright, C.; Avritscher, R.; Alibhai, I.; Tweardy, D.J.; et al. Phase I Trial of TTI-101, a First-in-Class Oral Inhibitor of STAT3, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2025, 31, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Cheung, S.T. STAT3: An Emerging Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidt, M.M.; Hornung, V. Alternative inflammasome activation enables IL-1beta release from living cells. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2017, 44, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Cai, Q.; Tang, C.; Gao, J. Inflammasomes and Pyroptosis of Liver Cells in Liver Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 896473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Li, W.; Ding, D.; Tan, K.; Ding, W.; Wang, Z.; Fu, S.; Hou, G.; Zhou, W.P.; Gu, F. IL-17a promotes hepatocellular carcinoma by increasing FAP expression in hepatic stellate cells via activation of the STAT3 signaling pathway. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, S.; Ying, S.; Tang, S.; Ding, Y.; Li, Y.; Qiao, J.; Fang, H. The IL-23/IL-17 Pathway in Inflammatory Skin Diseases: From Bench to Bedside. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 594735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noviello, D.; Mager, R.; Roda, G.; Borroni, R.G.; Fiorino, G.; Vetrano, S. The IL23-IL17 Immune Axis in the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis: Successes, Defeats, and Ongoing Challenges. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 611256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabeti Touchaei, A.; Vahidi, S. MicroRNAs as regulators of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy: Targeting PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 pathways. Cancer Cell Int. 2024, 24, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Jeong, S.W.; Jang, J.Y. Recent updates on pharmacologic therapy in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2024, 30, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Fan, T.; Xiao, C.; Tian, H.; Zheng, Y.; Li, C.; He, J. TGF-beta signaling in health, disease, and therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahk, K.; Lee, S.G.; Joung, C.; Kim, E.O.; Kwon, H.W.; Kim, D.H.; Hwang, J.I.; Kim, S.; Kim, W.K. SP-1154, a novel synthetic TGF-beta inhibitor, alleviates obesity and hepatic steatosis in high-fat diet-induced mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, W.L.; Mills, K.H.; Lederer, J.A.; O’Sullivan, G.C. Targeting regulatory T cells in cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6915–6920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuyama, H.; Ueha, S.; Kurachi, M.; Matsushima, K.; Moriyasu, F.; Blumberg, R.S.; Kakimi, K. The simultaneous blockade of chemokine receptors CCR2, CCR5 and CXCR3 by a non-peptide chemokine receptor antagonist protects mice from dextran sodium sulfate-mediated colitis. Int. Immunol. 2005, 17, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, E.; Moyle, G.; Reshef, R.; Richman, L.P.; Thompson, M.; Hong, F.; Chou, H.L.; Hashiguchi, T.; Plato, C.; Poulin, D.; et al. Antifibrotic Effects of the Dual CCR2/CCR5 Antagonist Cenicriviroc in Animal Models of Liver and Kidney Fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Rodriguez-Araujo, G.; Landgren, H.; Park, G.S.; Bedossa, P.; Alkhouri, N.; Tacke, F.; et al. Cenicriviroc Lacked Efficacy to Treat Liver Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: AURORA Phase III Randomized Study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 22, 124–134.e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeqdadi, M.; Gordon, F.D. Farnesoid X Receptor Agonists: A Promising Therapeutic Strategy for Gastrointestinal Diseases. Gastro Hep Adv. 2024, 3, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Lopez, P.; Lawitz, E.J.; Lucas, K.J.; Loeffler, J.; Kim, W.; Goh, G.B.B.; Huang, J.F.; Serra, C.; Andreone, P.; et al. Tropifexor for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: An adaptive, randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2a/b trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Harrison, S.A.; Elkhashab, M.; Trotter, J.F.; Herring, R.; Rojter, S.E.; Kayali, Z.; Wong, V.W.; Greenbloom, S.; Jayakumar, S.; et al. Cilofexor, a Nonsteroidal FXR Agonist, in Patients With Noncirrhotic NASH: A Phase 2 Randomized Controlled Trial. Hepatology 2020, 72, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksson, E.; Andersen, B. FGF19 and FGF21 for the Treatment of NASH-Two Sides of the Same Coin? Differential and Overlapping Effects of FGF19 and FGF21 From Mice to Human. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 601349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barb, D.; Kalavalapalli, S.; Leiva, E.G.; Bril, F.; Huot-Marchand, P.; Dzen, L.; Rosenberg, J.T.; Junien, J.L.; Broqua, P.; Rocha, A.O.; et al. Pan-PPAR agonist lanifibranor improves insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in patients with T2D and MASLD. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bedossa, P.; Guy, C.D.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Loomba, R.; Taub, R.; Labriola, D.; Moussa, S.E.; Neff, G.W.; Rinella, M.E.; et al. A Phase 3, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Resmetirom in NASH with Liver Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares De Oliveira, L.; Kaserman, J.E.; Van Der Spek, A.H.; Lee, N.J.; Undeutsch, H.J.; Werder, R.B.; Wilson, A.A.; Hollenberg, A.N. Thyroid hormone receptor beta (THRbeta1) is the major regulator of T3 action in human iPSC-derived hepatocytes. Mol. Metab. 2024, 90, 102057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, R.; Patwa, S.A.; Ali, A.H.; Ibdah, J.A. Thyroid Hormone and Mitochondrial Dysfunction: Therapeutic Implications for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Cells 2023, 12, 2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, G.; Bansal, M.B. Resmetirom: An Orally Administered, Smallmolecule, Liver-directed, beta-selective THR Agonist for the Treatment of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis. touchREV Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratziu, V.; Scanlan, T.S.; Bruinstroop, E. Thyroid hormone receptor-beta analogues for the treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH). J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, P.; Tacke, F. Metabolic reprogramming in liver fibrosis. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 1439–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhouri, N.; Herring, R.; Kabler, H.; Kayali, Z.; Hassanein, T.; Kohli, A.; Huss, R.S.; Zhu, Y.; Billin, A.N.; Damgaard, L.H.; et al. Safety and efficacy of combination therapy with semaglutide, cilofexor and firsocostat in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomised, open-label phase II trial. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R.; Mohseni, R.; Lucas, K.J.; Gutierrez, J.A.; Perry, R.G.; Trotter, J.F.; Rahimi, R.S.; Harrison, S.A.; Ajmera, V.; Wayne, J.D.; et al. TVB-2640 (FASN Inhibitor) for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: FASCINATE-1, a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2a Trial. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1475–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Portuguez, R.; Sutphin, G.L. Kynurenine pathway, NAD(+) synthesis, and mitochondrial function: Targeting tryptophan metabolism to promote longevity and healthspan. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 132, 110841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Kimura, M.; Li, X.; Sulc, J.; Wang, Q.; Rodriguez-Lopez, S.; Scantlebery, A.M.L.; Strotjohann, K.; Gallart-Ayala, H.; Vijayakumar, A.; et al. ACMSD inhibition corrects fibrosis, inflammation, and DNA damage in MASLD/MASH. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Chalasani, N.; Kowdley, K.V.; McCullough, A.; Diehl, A.M.; Bass, N.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Lavine, J.E.; Tonascia, J.; Unalp, A.; et al. Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1675–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, R.; Lee, E.; Choi, T.G.; Lee, A.S.; Yoon, Y.I.; Park, G.C.; Namgoong, J.M.; Lee, S.G.; et al. Therapeutic strategies for liver diseases based on redox control systems. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 156, 113764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, A.D.; Thomassen, A.S.; Mashaw, S.A.; MacDonald, E.M.; Waguespack, A.; Hickey, L.; Singh, A.; Gungor, D.; Kallurkar, A.; Kaye, A.M.; et al. Vitamin E (alpha-Tocopherol): Emerging Clinical Role and Adverse Risks of Supplementation in Adults. Cureus 2025, 17, e78679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fock, E.M.; Parnova, R.G. Protective Effect of Mitochondria-Targeted Antioxidants against Inflammatory Response to Lipopolysaccharide Challenge: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, M.A.D.; Bilodeau, S.; Greten, T.F.; Wang, X.W.; Trinchieri, G. The gut-liver axis: Host microbiota interactions shape hepatocarcinogenesis. Trends Cancer 2022, 8, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Fang, T.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Deng, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y. The synbiotic combination of probiotics and inulin improves NAFLD though modulating gut microbiota. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2024, 125, 109546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Shi, J.; Peng, H.; Tong, R.; Hu, Y.; Yu, D. Probiotics and liver fibrosis: An evidence-based review of the latest research. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 109, 105773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Liao, J.; Ye, Z.; Mao, L. Efficacy of probiotics on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2023, 102, e32734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustijn, Q.J.J.; Grefhorst, A.; de Groen, P.; Wortelboer, K.; Seegers, J.F.M.; Gul, I.S.; Suenaert, P.; Verheij, J.; de Vos, W.M.; Herrema, H.; et al. Randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial protocol to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of lyophilised faecal microbiota capsules amended with next-generation beneficial bacteria in individuals with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis. BMJ Open 2025, 15, e088290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, P.F.; Yao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yu, H.T.; Qin, Y.; Yi, L.; Mi, M.T. Fecal microbiota transplantation improves hepatic steatosis induced by HFD in a mouse model associated with liver ILC1 regulation and indole-3-carbinol level. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1500293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Shirsalimi, N.; Hashempour, Z.; Salehi Omran, H.; Sedighi, E.; Beigi, F.; Mortezazadeh, M. Safety and efficacy of fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) as a modern adjuvant therapy in various diseases and disorders: A comprehensive literature review. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1439176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazziotta, C.; Tognon, M.; Martini, F.; Torreggiani, E.; Rotondo, J.C. Probiotics Mechanism of Action on Immune Cells and Beneficial Effects on Human Health. Cells 2023, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, T.; Chae, S.Y.; Lee, J.; Han, J.W.; Yang, H.; Chung, B.S.; Yang, K. Multivitamin supplementation and its impact in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggeletopoulou, I.; Tsounis, E.P.; Triantos, C. Vitamin D and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): Novel Mechanistic Insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzopalic, T.; Bozic-Nedeljkovic, B.; Jurisic, V. The role of vitamin A and vitamin D in modulation of the immune response with a focus on innate lymphoid cells. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 46, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Fu, N.; Wu, H. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on various parameters in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An updated meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2023, 9, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano, R.; Bermudez, V.; Galban, N.; Garrido, B.; Santeliz, R.; Gotera, M.P.; Duran, P.; Boscan, A.; Carbonell-Zabaleta, A.K.; Duran-Aguero, S.; et al. Dietary Polyphenols and Gut Microbiota Cross-Talk: Molecular and Therapeutic Perspectives for Cardiometabolic Disease: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, T.; Chang, Y.; Yoo, J.J.; Lee, S.H.; Jeong, S.W.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, H.S.; Yang, K.; Jang, J.Y. Glucosamine supplementation attenuates progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and related comorbidities. Clin. Nutr. 2025, 47, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veskovic, M.; Sutulovic, N.; Hrncic, D.; Stanojlovic, O.; Macut, D.; Mladenovic, D. The Interconnection between Hepatic Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease-The Transition from an Adipocentric to Liver-Centric Approach. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 9084–9102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lu, W.; Jiao, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, H.; Wan, C. Identifying disease progression biomarkers in metabolic associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) through weighted gene co-expression network analysis and machine learning. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Stage/Trigger | Immune Cells | Key Mediators/Pathways | Hepatic Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lipotoxicity | Kupffer cells [15] DCs [19] | NF-κB [12] ROS [17] DAMPs [15] | Inflammation [20] Immune cell recruitment [22] |
| Gut-derived signals | Kupffer cells [12] LSECs [21] HSCs [44] | LPS [42] TLR4/TLR9 [43] NLRP3 [14] | Inflammation [47] Fibrosis [44] |
| Chronic inflammation | Neutrophils [18] Macrophages [51] CD4+/CD8+ T cells [27,32] | IL-6 [66] IL-1β [76] TNF-α [66] NETs [18] | Hepatocyte injury [18] Fibrosis [33] |
| Adaptive response | Th17 [61] Tregs [60] CD8+ T cells [58] | IL-17A/F [61] IFN-γ [26] PD-1 [58] | Immune imbalance Sustained inflammation [60] |
| Fibrogenesis, Carcinogenesis | HSCs [77] TAMs [81] exhausted T cells [57] | TGF-β [63] STAT3 [93] Wnt/β-catenin [91] | Fibrosis Immune escape HCC development [79,97] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jee, Y.-M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Ryu, T. Chronic Inflammation and Immune Dysregulation in Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Progression: From Steatosis to Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051260
Jee Y-M, Lee J-Y, Ryu T. Chronic Inflammation and Immune Dysregulation in Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Progression: From Steatosis to Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(5):1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051260
Chicago/Turabian StyleJee, Young-Min, Jeong-Yoon Lee, and Tom Ryu. 2025. "Chronic Inflammation and Immune Dysregulation in Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Progression: From Steatosis to Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Biomedicines 13, no. 5: 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051260
APA StyleJee, Y.-M., Lee, J.-Y., & Ryu, T. (2025). Chronic Inflammation and Immune Dysregulation in Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Progression: From Steatosis to Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomedicines, 13(5), 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051260






