Investigating the Genetic Links Between Immune Cell Profiles and Bladder Cancer: A Multidisciplinary Bioinformatics Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Batch Effect Removal
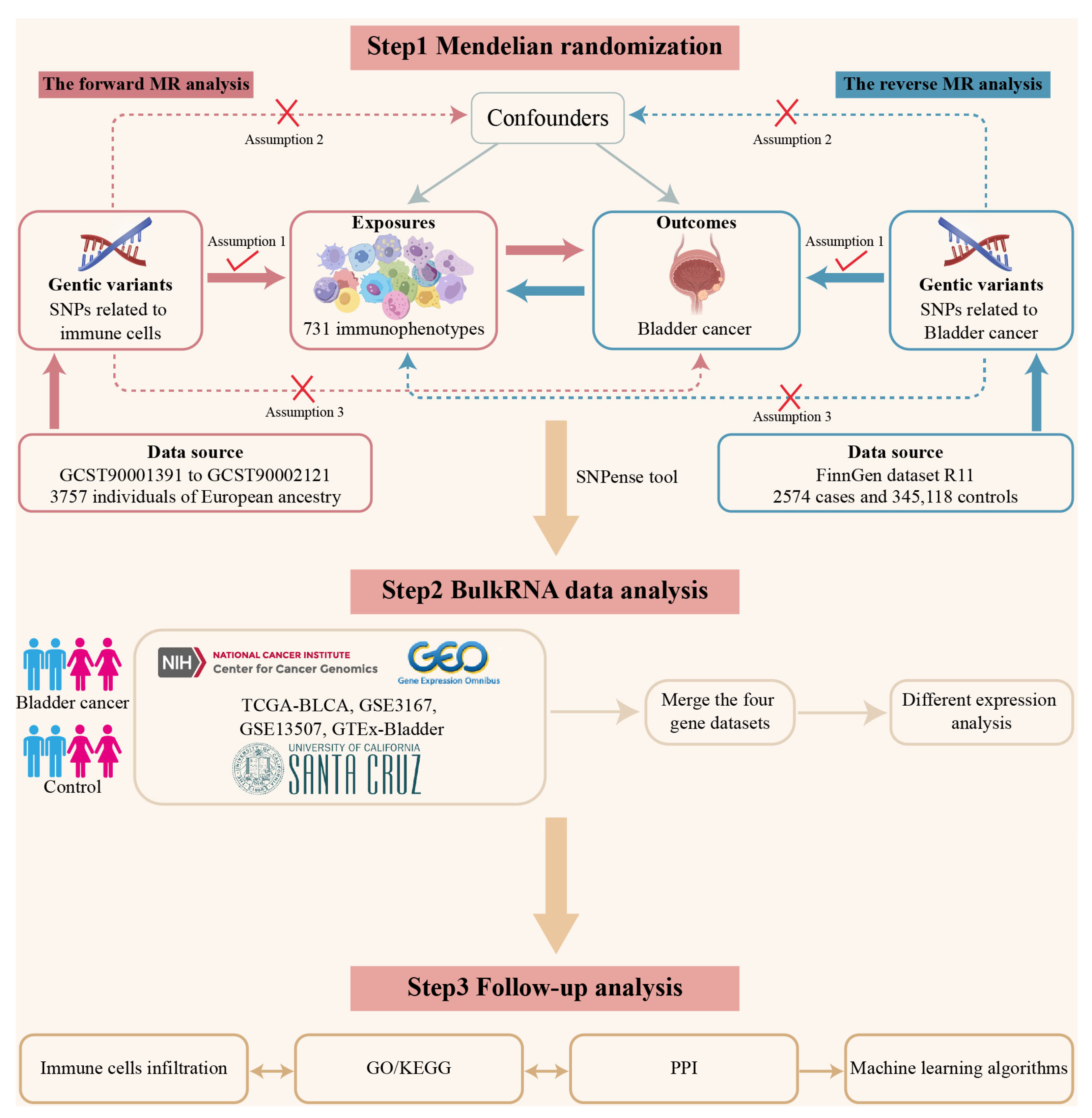
2.3. Mendelian Randomization Analysis
2.4. Reverse Mendelian Randomization Analysis
2.5. Profiling of Differentially Expressed Genes
2.6. Immune Cells Infiltration
2.7. GO/KEGG Enrichment Analysis
2.8. Construction of the Protein–Protein Interaction Network
2.9. Machine Learning Algorithms
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Design
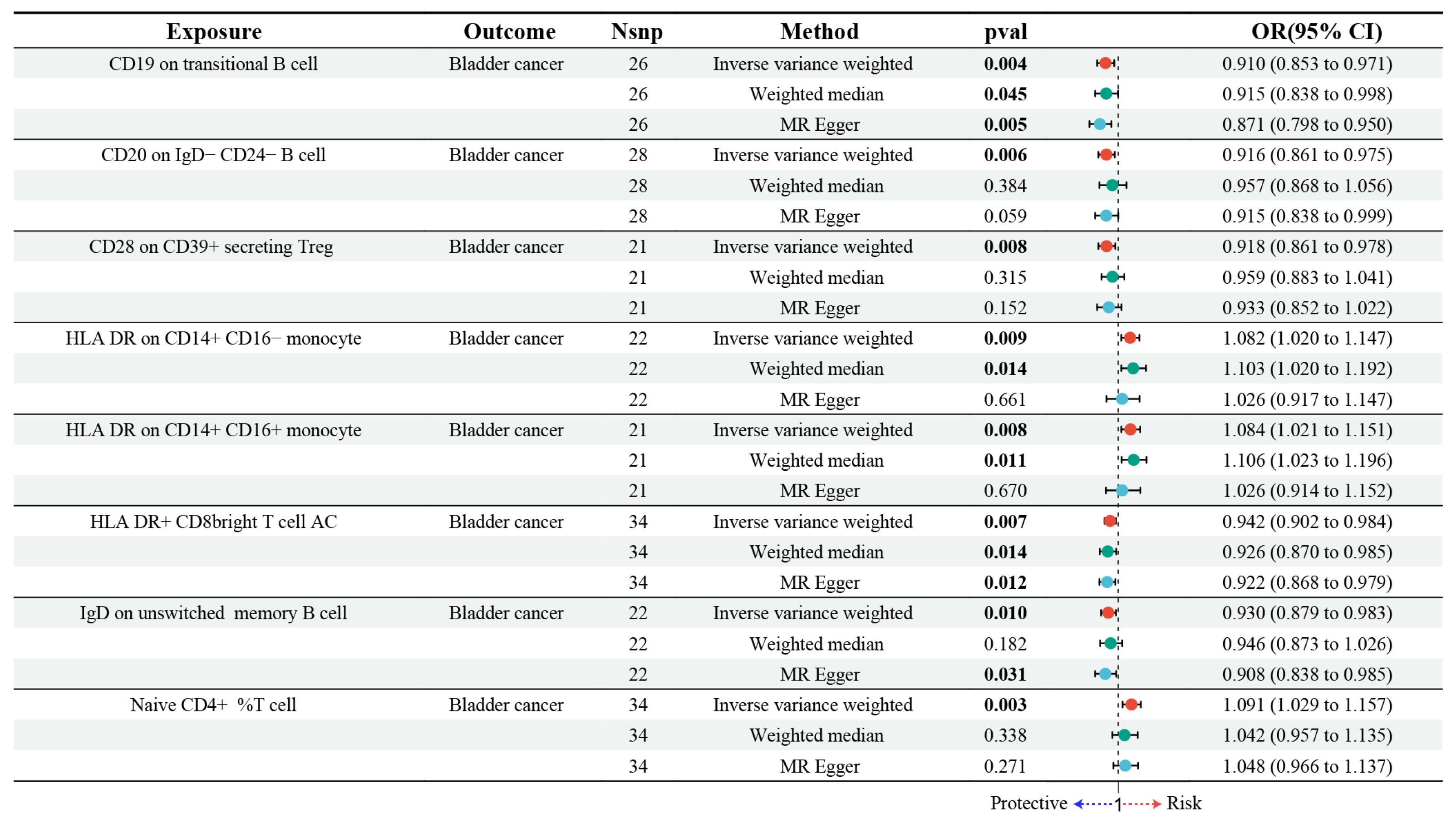
3.2. Estimating the Causal Impact of Immune Cells on Bladder Cancer
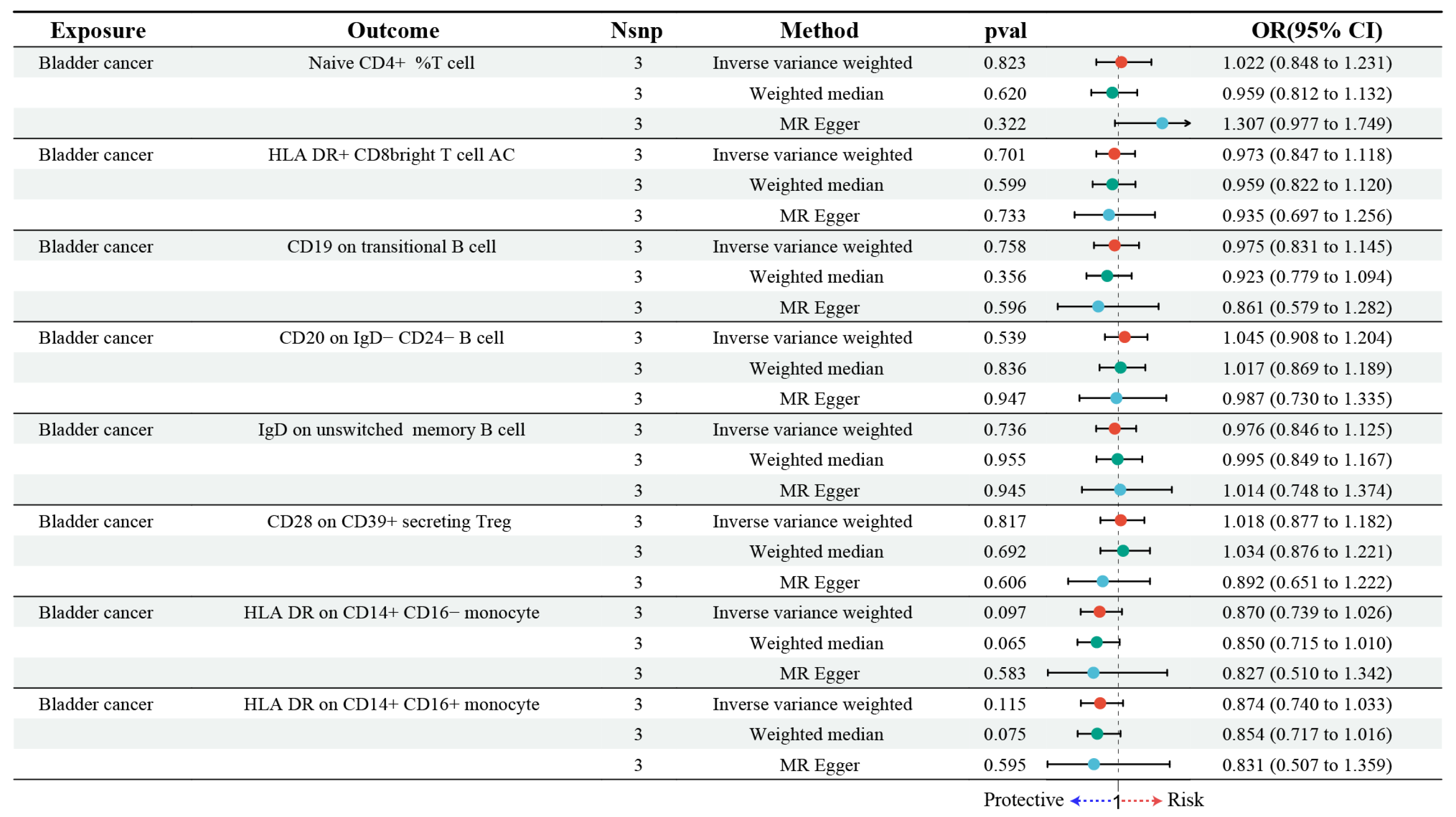
3.3. Estimating the Causal Impact of Bladder Cancer on Immune Cells
3.4. Identification of iDEGs in Bladder Cancer
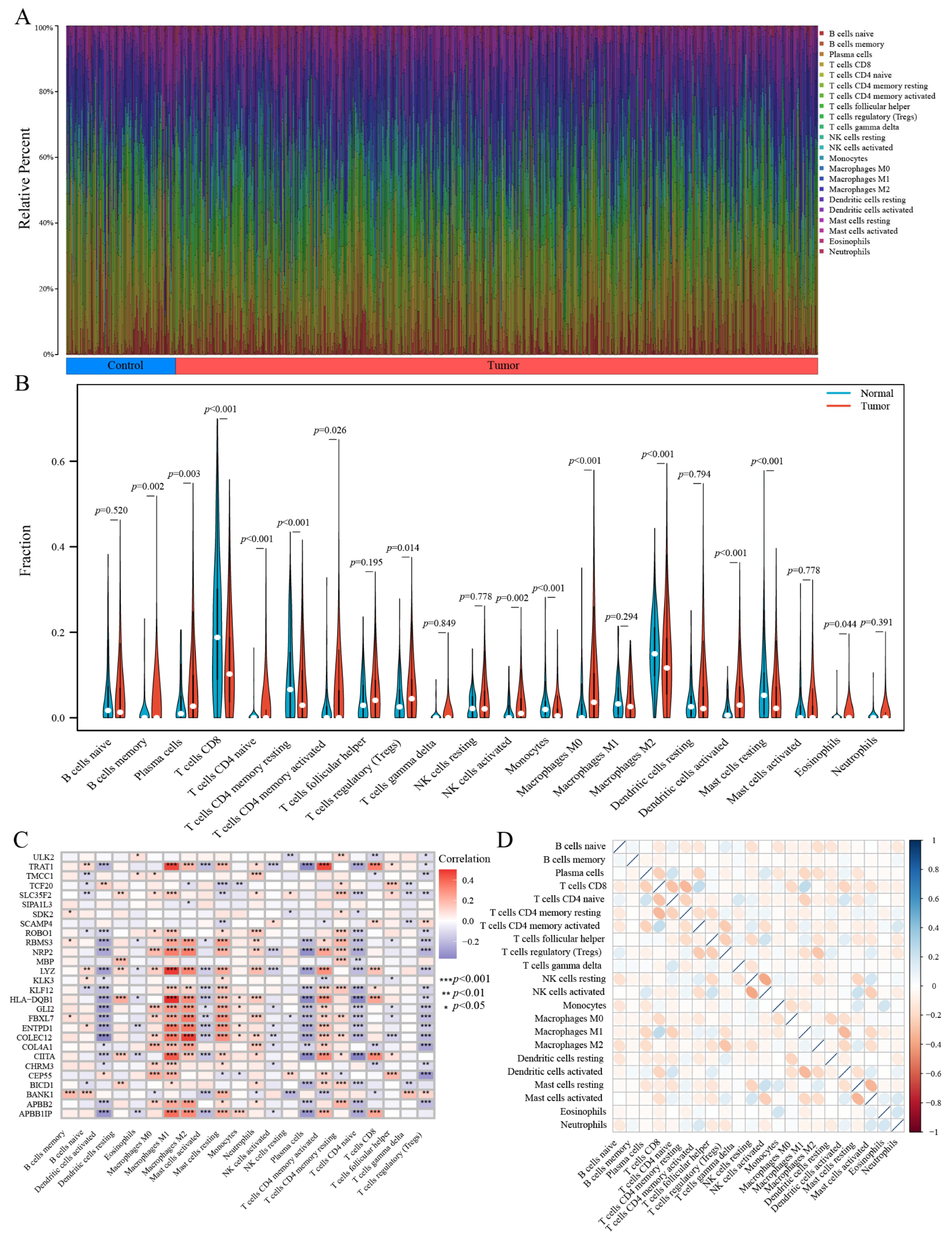
3.5. Evaluation of Immune Infiltration Patterns
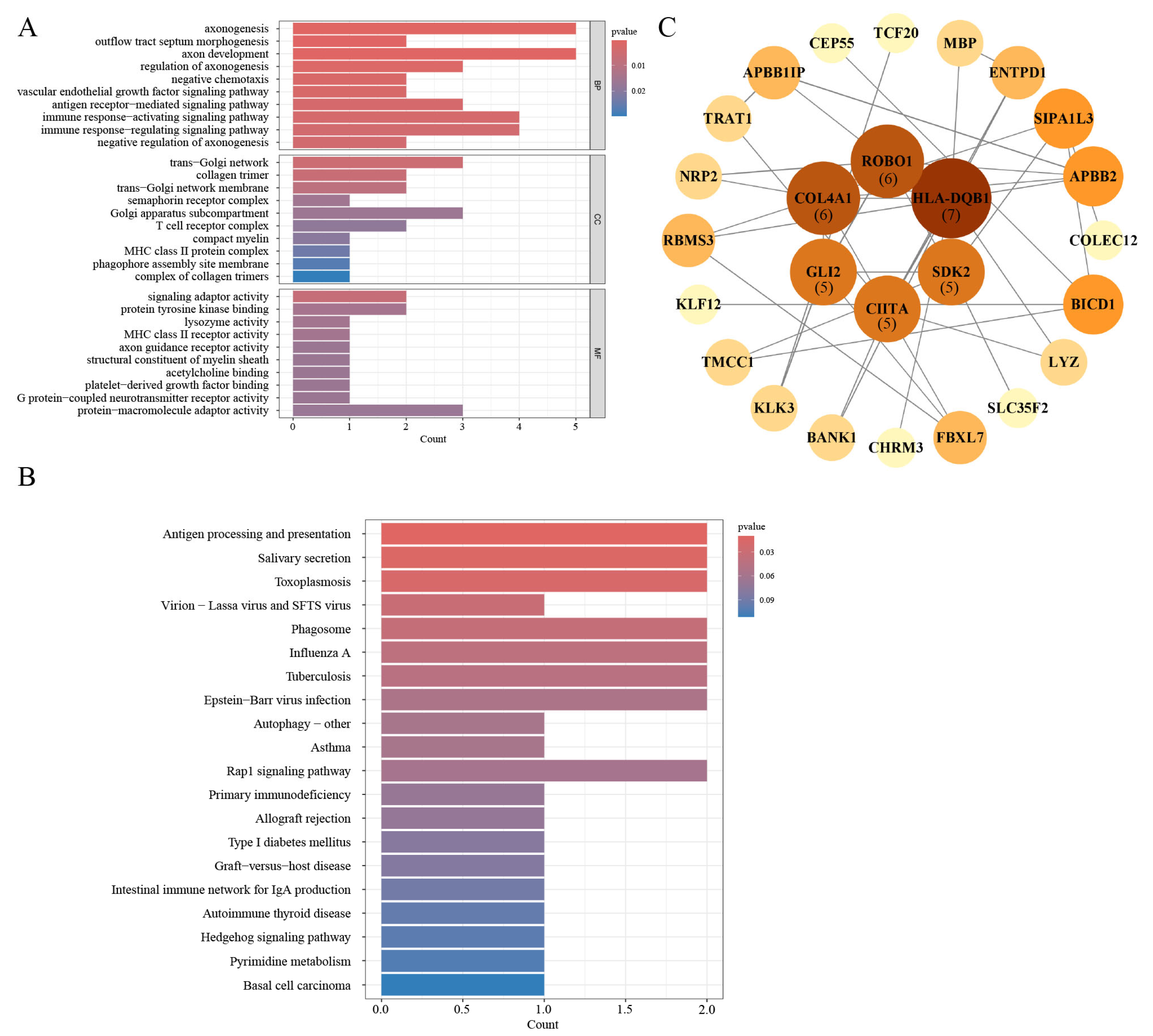
3.6. Gene Ontology and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
3.7. PPI Network Construction
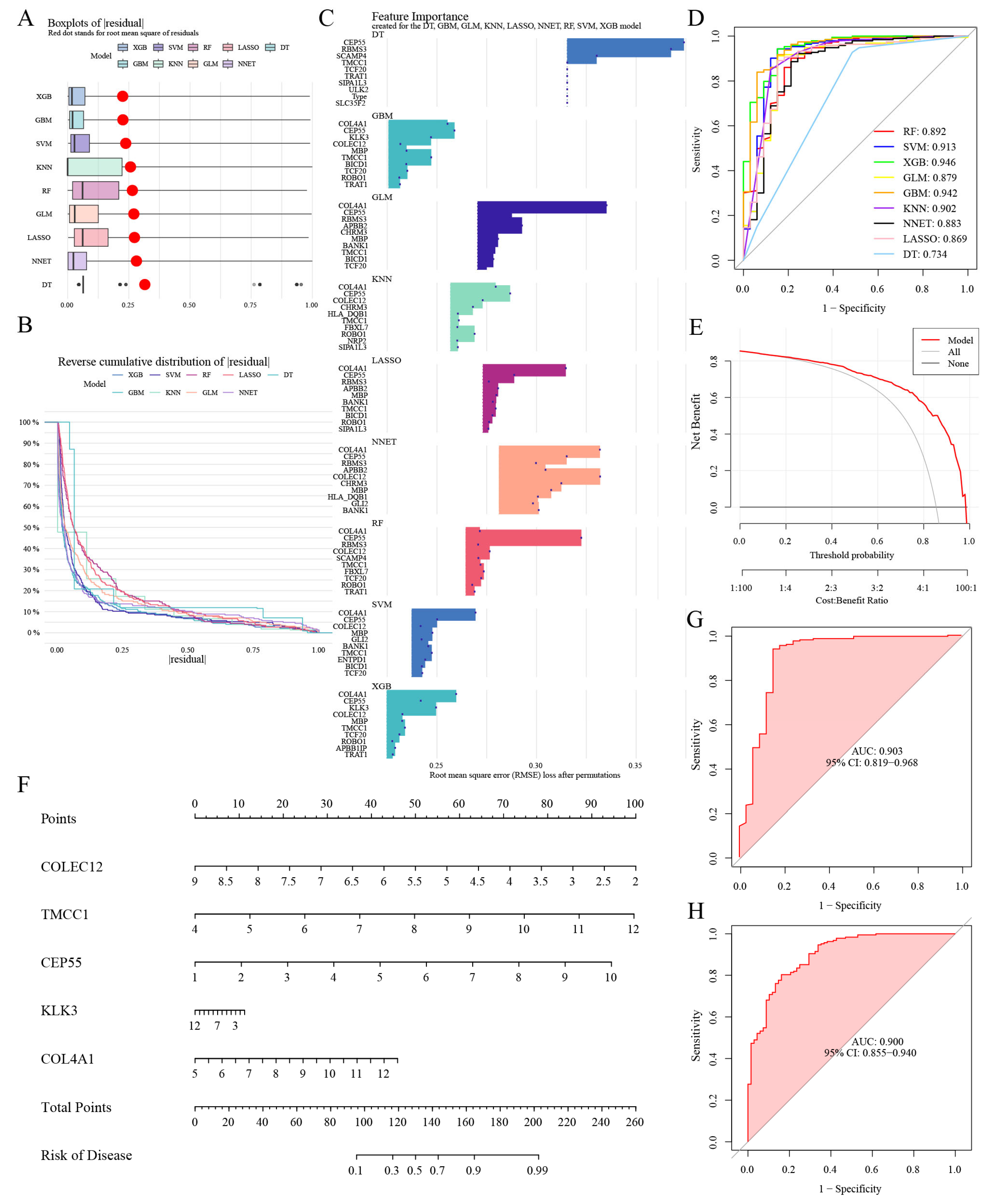
3.8. Selection of Machine Learning Models and Diagnosis Efficacy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BC | Bladder Cancer |
| NMIBC | Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer |
| MIBC | Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer |
| TME | Tumor Microenvironment |
| MR | Mendelian randomization |
| SNPs | Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms |
| rsIDs | Reference SNP IDs |
| IVs | Instrumental Variables |
| IVW | Inverse Variance-weighted |
| TPM | Transcripts Per Million |
| iDEGs | Immune-related Differentially Expressed Genes |
| PPI | Protein–protein Interaction |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| GBM | Gradient Boosting Machine |
| GLM | Generalized Linear Model |
| NNET | Neural Network |
| KNN | K-nearest Neighbors |
| DT | Decision Tree |
| LASSO | Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator |
| RF | Random Forest |
| SVM | Support Vector Machines |
| XGB | Extreme Gradient Boosting |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square of Residuals |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
References
- Zi, H.; He, S.-H.; Leng, X.-Y.; Xu, X.-F.; Huang, Q.; Weng, H.; Zhu, C.; Li, L.-Y.; Gu, J.-M.; Li, X.-H.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of kidney, bladder, and prostate cancers and their attributable risk factors, 1990–2019. Mil. Med. Res. 2021, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witjes, J.A.; Bruins, H.M.; Cathomas, R.; Compérat, E.M.; Cowan, N.C.; Gakis, G.; Hernández, V.; Espinós, E.L.; Lorch, A.; Neuzillet, Y.; et al. European Association of Urology guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: Summary of the 2020 guidelines. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 82–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claps, F.; Pavan, N.; Ongaro, L.; Tierno, D.; Grassi, G.; Trombetta, C.; Tulone, G.; Simonato, A.; Bartoletti, R.; Mertens, L.S.; et al. BCG-unresponsive non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Current treatment landscape and novel emerging molecular targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, F.; Milla, P.; Fiorito, C.; Pisano, F.; Sogni, F.; Di Marco, M.; Pagliarulo, V.; Dosio, F.; Gontero, P. Efficacy and safety of a new device for intravesical thermochemotherapy in non-grade 3 BCG recurrent NMIBC: A phase I–II study. World J. Urol. 2016, 34, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eturi, A.; Bhasin, A.; Zarrabi, K.K.; Tester, W.J. Predictive and prognostic biomarkers and tumor antigens for targeted therapy in urothelial carcinoma. Molecules 2024, 29, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojeij, R.; Domingos-Pereira, S.; Nkosi, M.; Gharbi, D.; Derré, L.; Schiller, J.T.; Jichlinski, P.; Nardelli-Haefliger, D. Immunogenic human papillomavirus pseudovirus-mediated suicide-gene therapy for bladder cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Kim, M.; Kang, S.J.; Choi, Y.W.; Maeng, S.; Kim, S.-H.; Chang, I.H. Enhanced antitumor effect of the combination of bacille calmette-guérin and an immune checkpoint inhibitor in bladder cancer-on-a-chip. BioChip J. 2023, 17, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powles, T.; Assaf, Z.J.; Davarpanah, N.; Banchereau, R.; Szabados, B.E.; Yuen, K.C.; Grivas, P.; Hussain, M.; Oudard, S.; Gschwend, J.E.; et al. ctDNA guiding adjuvant immunotherapy in urothelial carcinoma. Nature 2021, 595, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, M.; Strissel, P.; Strick, R.; Weyerer, V.; Wirtz, R.; Pfannstiel, C.; Wullweber, A.; Lange, F.; Erben, P.; Stoehr, R.; et al. Cytotoxic T-cell-related gene expression signature predicts improved survival in muscle-invasive urothelial bladder cancer patients after radical cystectomy and adjuvant chemotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfannstiel, C.; Strissel, P.L.; Chiappinelli, K.B.; Sikic, D.; Wach, S.; Wirtz, R.M.; Wullweber, A.; Taubert, H.; Breyer, J.; Otto, W.; et al. The tumor immune microenvironment drives a prognostic relevance that correlates with bladder cancer subtypes. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 923–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Kuang, X.; Xie, Z.; Liang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, F.; Gao, Q.; Chang, R.; Lee, H.-H.; et al. Small-molecule MMP2/MMP9 inhibitor SB-3CT modulates tumor immune surveillance by regulating PD-L1. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galsky, M.D.; Saci, A.; Szabo, P.M.; Han, G.C.; Grossfeld, G.; Collette, S.; Siefker-Radtke, A.; Necchi, A.; Sharma, P. Nivolumab in patients with advanced platinum-resistant urothelial carcinoma: Efficacy, safety, and biomarker analyses with extended follow-up from CheckMate 275. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2020, 26, 5120–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, L.; Xia, H.; Yan, Y.; Zhu, X.; Sun, F.; Sun, L.; Li, S.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; et al. Tumor microenvironment remodeling after neoadjuvant immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing. Genome Med. 2023, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.K.; Chevalier, M.F.; Derré, L. The multifaceted immune regulation of bladder cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2019, 16, 613–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.S.; Jeong, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.-D.; Kim, A.R.; Kwon, M.; Park, S.-H.; Woo, C.G.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, K.H.; et al. TOX-expressing terminally exhausted tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells are reinvigorated by co-blockade of PD-1 and TIGIT in bladder cancer. Cancer Lett. 2021, 499, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacher, A.G.; Paul, M.S.; Paige, C.J.; Ohashi, P.S. Cytotoxic CD4+ T cells in bladder cancer—A new license to kill. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Mao, X.; Yan, Y.; Huang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Bao, M.; Dai, Y.; Fang, B.; Mi, J.; et al. Single-cell sequencing reveals the heterogeneity of B cells and tertiary lymphoid structures in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, G.; Xu, T.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Tang, Y.; Jin, S.; Li, J.; Xing, N. High and selective cytotoxicity of ex vivo expanded allogeneic human natural killer cells from peripheral blood against bladder cancer: Implications for natural killer cell instillation after transurethral resection of bladder tumor. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koll, F.J.; Banek, S.; Kluth, L.; Köllermann, J.; Bankov, K.; Chun, F.K.-H.; Wild, P.J.; Weigert, A.; Reis, H. Tumor-associated macrophages and Tregs influence and represent immune cell infiltration of muscle-invasive bladder cancer and predict prognosis. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Huang, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, B.; Liang, J.; Zhang, B. B cells and tertiary lymphoid structures in tumors: Immunity cycle, clinical impact, and therapeutic applications. Theranostics 2025, 15, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanderson, E.; Glymour, M.M.; Holmes, M.V.; Kang, H.; Morrison, J.; Munafò, M.R.; Palmer, T.; Schooling, C.M.; Wallace, C.; Zhao, Q. Mendelian randomization. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2022, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.D.; Ebrahim, S. ‘Mendelian randomization’: Can genetic epidemiology contribute to understanding environmental determinants of disease? Int. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 32, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.C.; Butterworth, A.S.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization for cardiovascular diseases: Principles and applications. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 4913–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orrù, V.; Steri, M.; Sidore, C.; Marongiu, M.; Serra, V.; Olla, S.; Sole, G.; Lai, S.; Dei, M.; Mulas, A.; et al. Complex genetic signatures in immune cells underlie autoimmunity and inform therapy. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 1036–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurki, M.I.; Karjalainen, J.; Palta, P.; Sipilä, T.P.; Kristiansson, K.; Donner, K.M.; Reeve, M.P.; Laivuori, H.; Aavikko, M.; Kaunisto, M.A.; et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature 2023, 613, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, J.N.; Collisson, E.A.; Mills, G.B.; Shaw, K.R.; Ozenberger, B.A.; Ellrott, K.; Shmulevich, I.; Sander, C.; Stuart, J.M. The cancer genome atlas pan-cancer analysis project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyrskjøt, L.; Kruhøffer, M.; Thykjaer, T.; Marcussen, N.; Jensen, J.L.; Møller, K.; Ørntoft, T.F. Gene expression in the urinary bladder: A common carcinoma in situ gene expression signature exists disregarding histopathological classification. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 4040–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-J.; Kim, E.-J.; Kim, S.-K.; Kim, Y.-J.; Ha, Y.-S.; Jeong, P.; Kim, M.-J.; Yun, S.-J.; Lee, K.M.; Moon, S.-K.; et al. Predictive value of progression-related gene classifier in primary non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carithers, L.J.; Ardlie, K.; Barcus, M.; Branton, P.A.; Britton, A.; Buia, S.A.; Compton, C.C.; DeLuca, D.S.; Peter-Demchok, J.; Gelfand, E.T.; et al. A novel approach to high-quality postmortem tissue procurement: The GTEx project. Biopreserv. Biobank. 2015, 13, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leek, J.T.; Johnson, W.E.; Parker, H.S.; Jaffe, A.E.; Storey, J.D. The sva package for removing batch effects and other unwanted variation in high-throughput experiments. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 882–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemani, G.; Zheng, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. Elife 2018, 7, e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehm, F.J.; Zhou, X. Statistical methods for Mendelian randomization in genome-wide association studies: A review. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 2338–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, N.M.; Holmes, M.V.; Davey Smith, G. Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: A guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians. BMJ 2018, 362, k601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolberg, L.; Raudvere, U.; Kuzmin, I.; Adler, P.; Vilo, J.; Peterson, H. g:Profiler-interoperable web service for functional enrichment analysis and gene identifier mapping (2023 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W207–W212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otasek, D.; Morris, J.H.; Bouças, J.; Pico, A.R.; Demchak, B. Cytoscape Automation: Empowering workflow-based network analysis. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Deng, X.; Zhang, J.; Shao, R.; Song, C.; Zhao, J.; Tang, H. Causal relationship between immune cells and prostate cancer: A Mendelian randomization study. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1381920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvaria, A.; Madrigal, J.A.; Saudemont, A. B cell regulation in cancer and anti-tumor immunity. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horii, M.; Matsushita, T. Regulatory B cells and T cell Regulation in Cancer. J. Mol. Biol. 2021, 433, 166685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, R.; Naseem, M.; Lo, J.H.; Battaglin, F.; Soni, S.; Puccini, A.; Berger, M.D.; Zhang, W.; Baba, H.; Lenz, H.J. B cell and B cell-related pathways for novel cancer treatments. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2019, 73, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, R.H.; Barrington, R.A. Signaling by the CD19/CD21 complex on B cells. Curr. Dir. Autoimmun. 2004, 7, 4–32. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, R.H.; Wang, Y.; Brooks, S. Role of CD19 signal transduction in B cell biology. Immunol. Res. 2002, 26, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiura, N.; Nakashima, H.; Watanabe, R.; Kuwano, Y.; Adachi, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Tsubata, T.; Okochi, H.; Tamaki, K.; Tedder, T.F.; et al. Differential phosphorylation of functional tyrosines in CD19 modulates B-lymphocyte activation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Fu, Q.; Chang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J. CD19(+) tumor-infiltrating B-cells prime CD4(+) T-cell immunity and predict platinum-based chemotherapy efficacy in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsthuber, T.G.; Cimbora, D.M.; Ratchford, J.N.; Katz, E.; Stüve, O. B cell-based therapies in CNS autoimmunity: Differentiating CD19 and CD20 as therapeutic targets. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2018, 11, 1756286418761697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeniuk-Wojtaś, A.; Modzelewska, M.; Poddębniak-Strama, K.; Kołaczyńska, S.; Lubas, A.; Górnicka, B.; Jakieła, A.; Stec, R. CD4, CD20 and PD-L1 as Markers of Recurrence in Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Zappasodi, R. Modulating Treg stability to improve cancer immunotherapy. Trends Cancer 2023, 9, 911–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Villar, M.; Baecher-Allan, C.M.; Hafler, D.A. Identification of T helper type 1-like, Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in human autoimmune disease. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 673–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addey, C.; White, M.; Dou, L.; Coe, D.; Dyson, J.; Chai, J.G. Functional plasticity of antigen-specific regulatory T cells in context of tumor. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 4557–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blinova, V.G.; Zhdanov, D.D. Many Faces of Regulatory T Cells: Heterogeneity or Plasticity? Cells 2024, 13, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler-Heitbrock, L.; Ancuta, P.; Crowe, S.; Dalod, M.; Grau, V.; Hart, D.N.; Leenen, P.J.; Liu, Y.J.; MacPherson, G.; Randolph, G.J.; et al. Nomenclature of monocytes and dendritic cells in blood. Blood 2010, 116, e74–e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugel, S.; Canè, S.; De Sanctis, F.; Bronte, V. Monocytes in the Tumor Microenvironment. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2021, 16, 93–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twohig, J.P.; Cardus Figueras, A.; Andrews, R.; Wiede, F.; Cossins, B.C.; Derrac Soria, A.; Lewis, M.J.; Townsend, M.J.; Millrine, D.; Li, J.; et al. Activation of naïve CD4(+) T cells re-tunes STAT1 signaling to deliver unique cytokine responses in memory CD4(+) T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, K.; Hayashi, R.; Lafond-Walker, A.; Lowenstein, C.; Pardoll, D.; Levitsky, H. The central role of CD4(+) T cells in the antitumor immune response. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 2357–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, Q.; Shu, P.; Lin, X.; Gao, X.; Shen, K. COLEC12 Promotes Tumor Progression and Is Correlated With Poor Prognosis in Gastric Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 22, 15330338231218163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Z.; Deng, J.F.; Qi, Y.Z.; Liu, R.; Liu, Z.X. COLEC12 regulates apoptosis of osteosarcoma through Toll-like receptor 4-activated inflammation. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Kho, Y.S.; Wang, Z.; Chiang, Y.T.; Ng, G.K.; Shaw, P.C.; Wang, Y.; Qi, R.Z. Transmembrane and coiled-coil domain family 1 is a novel protein of the endoplasmic reticulum. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, M.J.; Chitwood, P.J.; Ebmeier, C.C.; Striepen, J.F.; Qi, R.Z.; Old, W.M.; Voeltz, G.K. A Novel Class of ER Membrane Proteins Regulates ER-Associated Endosome Fission. Cell 2018, 175, 254–265.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, H. CEP55 3′-UTR promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and enhances tumorigenicity of bladder cancer cells by acting as a ceRNA regulating miR-497-5p. Cell. Oncol. 2022, 45, 1217–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koistinen, H.; Kovanen, R.M.; Hollenberg, M.D.; Dufour, A.; Radisky, E.S.; Stenman, U.H.; Batra, J.; Clements, J.; Hooper, J.D.; Diamandis, E.; et al. The roles of proteases in prostate cancer. IUBMB Life 2023, 75, 493–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.G.; Lai, J.; Clements, J.A. Kallikreins on steroids: Structure, function, and hormonal regulation of prostate-specific antigen and the extended kallikrein locus. Endocr. Rev. 2010, 31, 407–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, J.; Miyamoto, H. Androgen Receptor Signaling in Bladder Cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Heemers, H.; Sharifi, N. Androgen Signaling in Prostate Cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7, a030452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, Y.; Kozaki, K.; Imoto, I.; Obara, W.; Tsuda, H.; Mizutani, Y.; Shuin, T.; Fujioka, T.; Miki, T.; Inazawa, J. Association of KLK5 overexpression with invasiveness of urinary bladder carcinoma cells. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokas, T.; Avgeris, M.; Alamanis, C.; Scorilas, A.; Stravodimos, K.G.; Constantinides, C.A. Downregulated KLK13 expression in bladder cancer highlights tumor aggressiveness and unfavorable patients’ prognosis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, M.; Hori, S.; Morizawa, Y.; Tatsumi, Y.; Toritsuka, M.; Ohnishi, S.; Shimada, K.; Furuya, H.; Khadka, V.S.; Deng, Y.; et al. Collagen type IV alpha 1 (COL4A1) and collagen type XIII alpha 1 (COL13A1) produced in cancer cells promote tumor budding at the invasion front in human urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 36099–36114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, M.; Morizawa, Y.; Hori, S.; Tatsumi, Y.; Onishi, S.; Owari, T.; Iida, K.; Onishi, K.; Gotoh, D.; Nakai, Y.; et al. Diagnostic and prognostic role of urinary collagens in primary human bladder cancer. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 2221–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Jin, J.; Kadeerhan, G.; Guo, H.; Wang, D. Investigating the Genetic Links Between Immune Cell Profiles and Bladder Cancer: A Multidisciplinary Bioinformatics Approach. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051203
Zhang J, Jiang Z, Jin J, Kadeerhan G, Guo H, Wang D. Investigating the Genetic Links Between Immune Cell Profiles and Bladder Cancer: A Multidisciplinary Bioinformatics Approach. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(5):1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051203
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jin, Zhongji Jiang, Jiali Jin, Gaohaer Kadeerhan, Hong Guo, and Dongwen Wang. 2025. "Investigating the Genetic Links Between Immune Cell Profiles and Bladder Cancer: A Multidisciplinary Bioinformatics Approach" Biomedicines 13, no. 5: 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051203
APA StyleZhang, J., Jiang, Z., Jin, J., Kadeerhan, G., Guo, H., & Wang, D. (2025). Investigating the Genetic Links Between Immune Cell Profiles and Bladder Cancer: A Multidisciplinary Bioinformatics Approach. Biomedicines, 13(5), 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051203





