Abstract
Background/Objectives: Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) is a multifaceted and diverse disorder with an ambiguous etiology. Recent evidence indicates that immune system impairment and inflammatory mechanisms are pivotal to the initiation and advancement of ME/CFS. Nonetheless, the causal relationships among these factors remain inadequately comprehended. Methods: This study investigated the causative contributions of immunological dysfunction and inflammatory variables in ME/CFS utilizing genome-wide association study (GWAS) data. We employed Mendelian randomization (MR) to investigate associations between 91 inflammatory cytokines, 731 immune cell characteristics, and the risk of ME/CFS. Summary statistics for immune cell traits and inflammatory cytokines were sourced from European GWAS cohorts (n = 3757 and n = 14,824, respectively), while ME/CFS data were obtained from the UK Biobank (n = 462,933, including 2076 cases). We predominantly employed the inverse variance weighted (IVW) approach, complemented by MR-Egger, weighted median, BWMR, and MR-RAPS tests to guarantee robust and precise outcomes. Results: The study revealed significant causal links between various inflammatory factors, immune cell characteristics, and the risk of ME/CFS. Increased CXCL5 and CCL20 levels were significantly linked to a higher risk of ME/CFS, while elevated TNF levels were inversely related to ME/CFS risk. Furthermore, 13 immune cell characteristics were identified as having substantial causal associations with the likelihood of ME/CFS. These data are supportive of the causality that immune system dysfunction and inflammatory variables play a pivotal role in the development of ME/CFS. Conclusions: This study provides new insights into the causal role of immune system dysfunction in the development of ME/CFS, contributing to a deeper understanding of its underlying mechanisms. These results offer a foundation for identifying diagnostic biomarkers and developing targeted therapeutic strategies. Future research should validate these findings using multi-center cohort studies and further investigate the mechanisms behind key factors to enable the development of personalized treatment approaches.
1. Introduction
The complex, long-term illness known as myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) is typified by post-exertional malaise (PEM), myalgia (muscle pain), cognitive impairments, and a variety of other symptoms like fever, pain, irritable bowel syndrome, and immune system abnormalities [1]. All of these symptoms adversely affect patients’ quality of life [2]. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, ME/CFS impacted around 1 to 2.5 million individuals in the US, with patients indicating a diminished quality of life relative to those suffering from conditions like multiple sclerosis or chronic kidney disease [3,4]. Following the pandemic, ME/CFS incidence has risen, and its clinical presentation has been noted to closely resemble that of post-COVID syndrome [5,6]. Despite the substantial impact of ME/CFS on patients’ lives, its underlying etiology and pathological mechanisms remain poorly understood.
Emerging evidence increasingly highlights a strong association between ME/CFS and immune system dysfunction. For instance, single-cell RNA sequencing studies of PEM in ME/CFS patients have identified significant dysregulation of monocyte function, with the number of dysregulated monocytes positively correlated with disease severity [7]. Immunological exhaustion, senescence, and hypersensitivity in ME/CFS patients have been linked to impaired functionality of immune cells, particularly T cells [8]. Other findings include increased T cell apoptosis, elevated levels of necrotic cell death, and structural and functional abnormalities in organelles [9]. While these studies emphasize the role of immune cells in ME/CFS pathophysiology, their findings often lack consistency, potentially due to differences in study design, individual patient heterogeneity, or methodological variations. This inconsistency underscores a predominant focus on correlational rather than causal relationships in current research. Additionally, the absence of reliable diagnostic biomarkers and effective therapeutic strategies for ME/CFS contributes to misdiagnosis and underrecognition of the disease [10]. Establishing a clear causal link between immune cell dysfunction and ME/CFS is critical for advancing our understanding of the disease’s underlying causes, identifying potential biomarkers, and discovering novel treatment targets.
This study applied Mendelian randomization (MR) to investigate the causal relationships involving immune cell function, inflammatory factors, and ME/CFS, aiming to bridge current gaps in scientific understanding. MR is an analytical method grounded in Mendel’s principles of heredity, employing genetic variants as instrumental variables (IVs) to ascertain if the observed correlations between exposures and outcomes are causative [11]. This approach minimizes confounding factors and reverse causation bias, as genetic variants are not influenced by environmental, social, or behavioral factors [12,13]. Based on the fact that studies have shown abnormalities in the immune system of patients with ME/CFS, including changes in TNF levels and B-cell dysfunction, we hypothesized that dysregulation of the TNF pathway and B-cell-associated immune pathway would be causally related to the development of ME/CFS. This analysis seeks to evaluate whether immune cell dysfunction and inflammatory factors are key contributors to the development of ME/CFS, examine the potential mediating role of inflammatory markers in these processes, and offer meaningful insights for the discovery of diagnostic biomarkers and the advancement of targeted treatment approaches.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
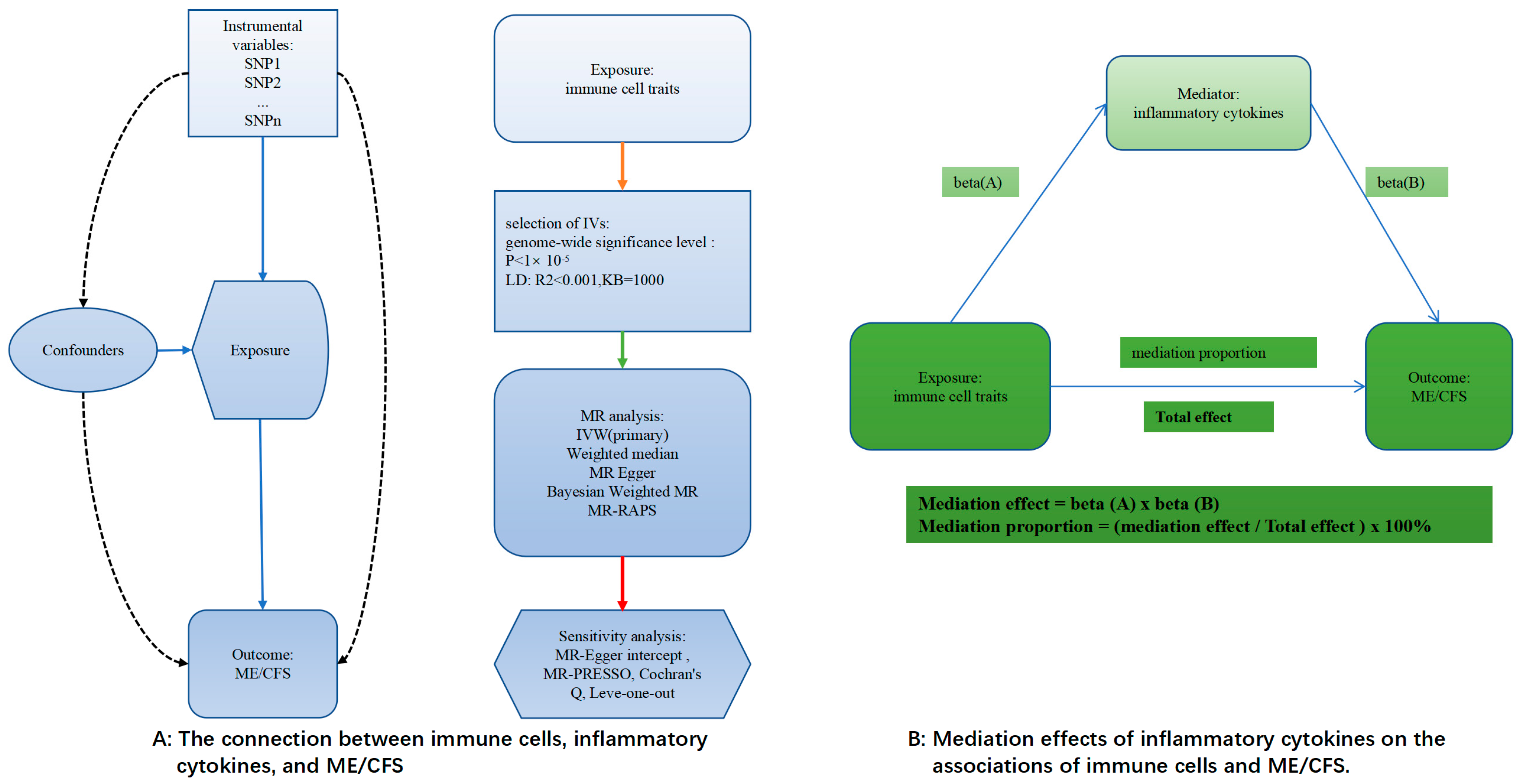
The two-sample MR method was used in this study to look into the links between ME/CFS, 91 circulating inflammatory cytokines, and 731 immune cell characteristics (Figure 1A). A two-step MR study was conducted to investigate if circulating inflammatory cytokines act as mediators in the relationship between immune cell characteristics and ME/CFS (Figure 1B).
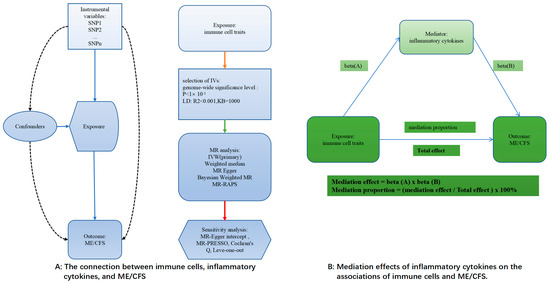
Figure 1.
An illustration of the principles and procedure of the analysis. The solid line indicates a clear effect downstream through this line, the dashed line indicates no effect, the color of the line has no special meaning, and β(A/B) indicates the effect value.
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. Datasets for Circulating Inflammatory Cytokines and Immune Cell
Summary statistics for immune cell traits were sourced from Orrù V et al. [14]. Data from 3757 European people served as the basis for the first GWAS on immunological characteristics, derived from flow cytometry and transcriptomic profiling of 731 immune phenotypes in European individuals. Information on 91 circulating inflammatory cytokines was obtained through a meta-analysis measured via multiplex immunoassays conducted on 14,824 individuals of European descent [15].
2.2.2. Datasets for ME/CFS
Additionally, we incorporated data from the UK Biobank, specifically from a study on non-cancer diseases (self-reported: chronic fatigue syndrome), selecting data related to ME/CFS, which included 462,933 individuals (case = 2076, control = 460,857). ME/CFS was a self-reported diagnosis from the UK Biobank, with cases confirmed using CDC criteria. Further details are provided in Table 1. Although the diagnosis of ME/CFS in this study was based on patient self-report, previous studies have validated the validity of self-reported data in studies of similar diseases [16,17].

Table 1.
Datasets employed for MR analyses.
2.3. IV Selection
To identify appropriate instrumental variables (IVs) for MR analysis, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were selected based on their meeting the genome-wide significance threshold (p < 1 × 10−5) [18,19]. SNPs located within a 10,000 kb genomic region and exhibiting an r2 value greater than 0.001 were excluded to minimize the effects of linkage disequilibrium. The association strength between IVs and exposure factors was evaluated using the F-statistic. SNPs with F-values below 10 were classified as weak instruments and excluded from the analysis. F-statistics were calculated following established formulas in previous studies [20].
2.4. MR Analysis
The inverse variance weighted (IVW) method served as the primary analytical approach in this study to explore the causal associations between immune cells, inflammatory factors, and ME/CFS [21]. The IVW method is widely used in MR analysis and provides an overall estimate by combining data from multiple genetic variants through a weighted approach. To strengthen the robustness and reliability of the findings, additional analytical techniques were employed. The weighted median (WM) method was utilized to generate reliable causal effect estimates, assuming that at least 50% of the total weight was derived from valid instrumental variables [22]. Additionally, MR-Egger regression was applied to assess the presence of directional pleiotropy and to produce causal estimates adjusted for potential bias [23]. The relevance of pleiotropy was assessed using the p-value of the intercept term in MR-Egger regression; p > 0.05 denoted negligible pleiotropic effects. Cochran’s Q test was conducted to evaluate heterogeneity among IVs, which helped evaluate potential variability in SNP distributions. The reliability of the causal estimations was increased by using the MR-PRESSO approach to further detect horizontal pleiotropy and eliminate possible outliers [24].
To address potential biases from weak instruments and pleiotropy, the study utilized MR-RAPS [25] and Bayesian weighted MR (BWMR) [26] methods. MR-RAPS offers reliable causal effect estimates despite weak instruments and horizontal pleiotropy, whereas BWMR enhances causal inference by addressing pleiotropy-induced violations of instrumental variable assumptions, particularly in weak-effect contexts. The leave-one-out (LOO) method was utilized for sensitivity analyses to evaluate the impact of individual SNPs on the overall causal estimates. The Steiger directionality test was also conducted to evaluate the potential impact of reverse causation [27]. Any SNPs identified as having reverse causal effects were manually excluded from the analysis to ensure the validity of the findings.
2.5. Mediation Analysis
Immune cells and inflammatory cytokines identified as having significant causal effects on ME/CFS in the two-sample MR analysis were further examined for causal relationships between them. If a significant causal relationship was detected, mediation analysis was conducted to evaluate whether inflammatory cytokines mediated the pathway from immune cells to ME/CFS.
3. Results
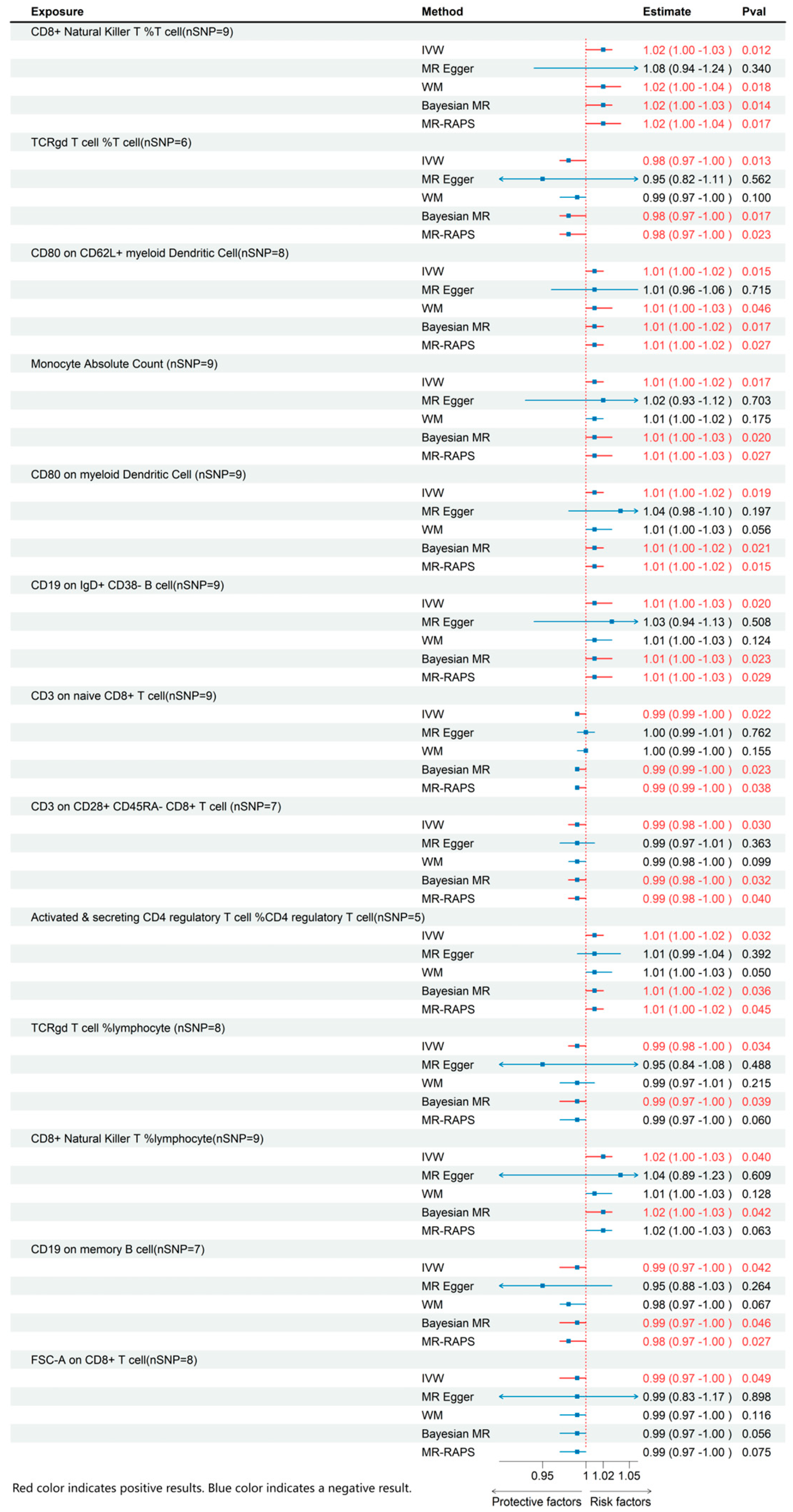
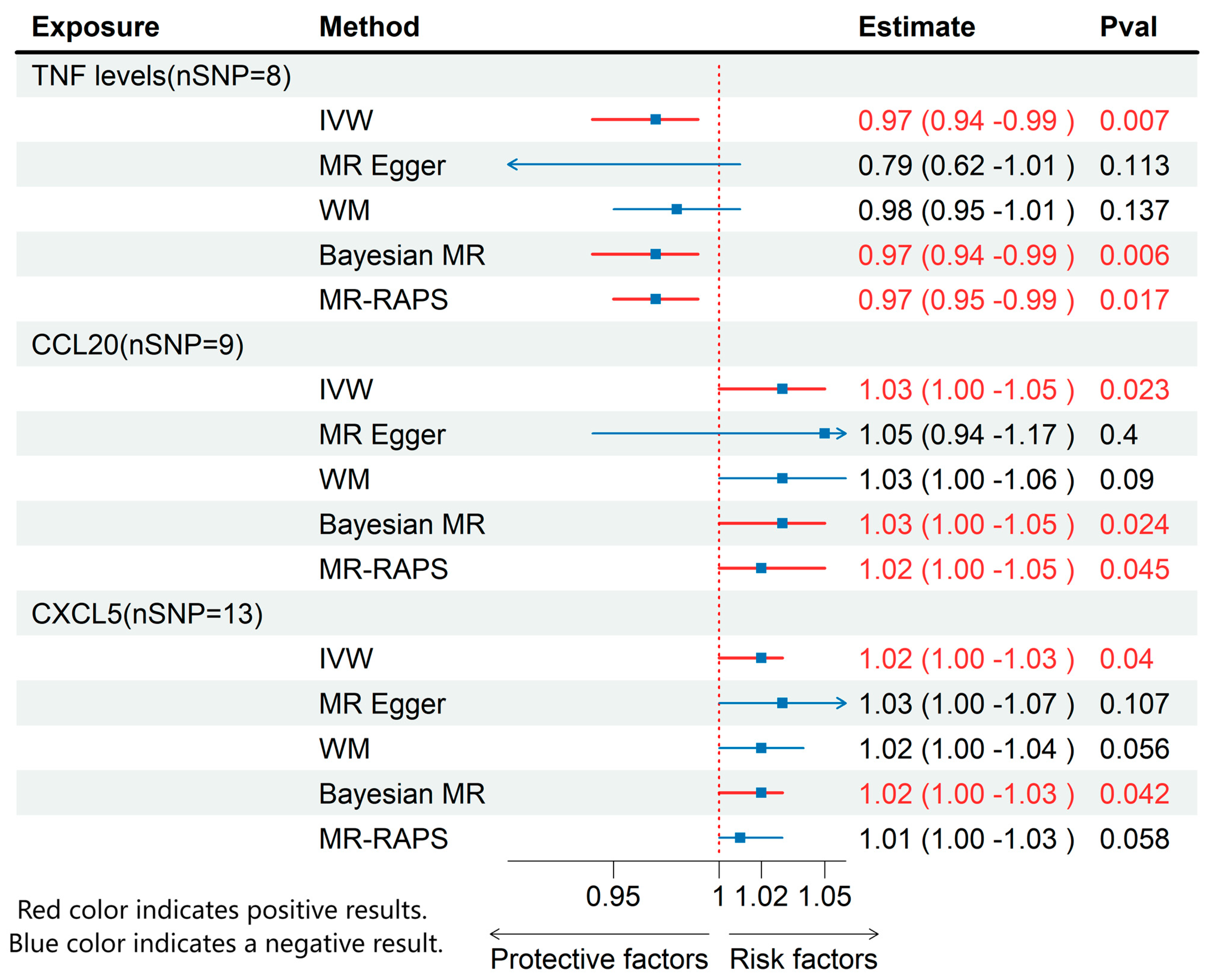
Through MR analysis of circulating inflammatory cytokines and immune cell phenotypes, we identified 3 inflammatory cytokines and 13 immune cells that were causally associated with ME/CFS. Details of all the IVs used are given in Supplementary Tables S1–S3. Detailed results are presented in Figure 2 and Figure 3, with sensitivity analysis findings provided in Supplementary Table S4.
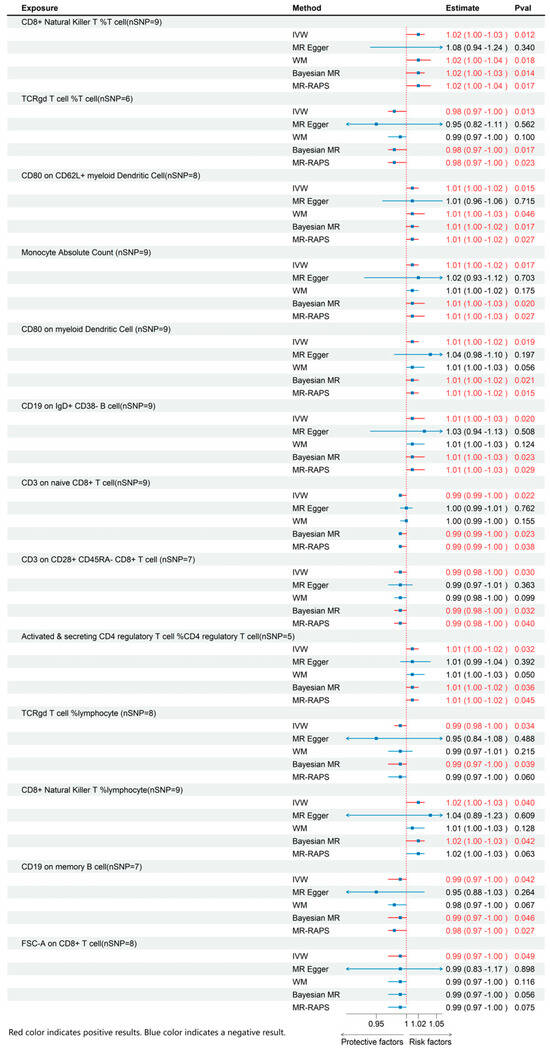
Figure 2.
MR effects of immune cell on ME/CFS. The red color of the numbers and the red dotted line indicate a positive result.
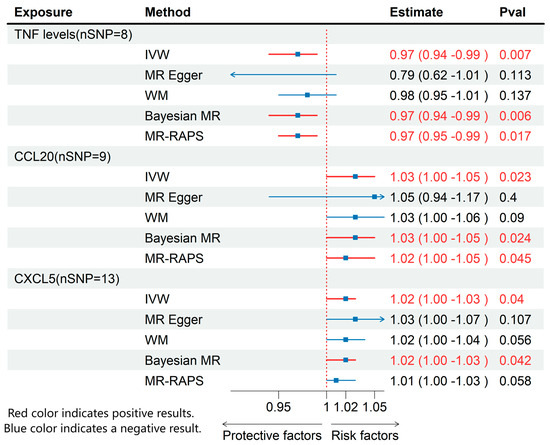
Figure 3.
MR effects of circulating inflammatory cytokines on ME/CFS. The red color of the numbers and the red dotted line indicate a positive result.
3.1. Effects of Immune Cell on ME/CFS
Regarding immune cell phenotypes (Figure 2), elevated levels of CD8+ natural killer T cells as a percentage of T cells and lymphocytes, CD19 on IgD+ CD38- B cells, absolute monocyte count, CD80 on CD62L+ myeloid dendritic cells, activated and secreting CD4 regulatory T cells as a percentage of CD4 regulatory T cells, and CD80 on myeloid dendritic cells were significantly linked to an increased risk of ME/CFS. Conversely, higher levels of CD3 on naive CD8+ T cell, CD3 on CD28+ CD45RA- CD8+ T cell, FSC-A on CD8+ T cell, TCRγδ T cell %lymphocyte, CD19 on memory B cell, and TCRγδ T cell %T cell were significantly linked to a decreased risk of ME/CFS.
3.2. Effects of Inflammatory Cytokines on ME/CFS
Using IVW method, we found that higher levels of TNF were associated with a decreased risk of ME/CFS (OR: 0.97; 95% CI: 0.94–0.99; p = 0.007), while increased levels of CXCL5 (OR: 1.02; 95% CI: 1.00–1.03; p = 0.04) and CCL20 (OR: 1.03; 95% CI: 1.00–1.05; p = 0.02) were associated with an elevated risk of ME/CFS (Figure 3). None of these cytokines exhibited pleiotropy or heterogeneity.
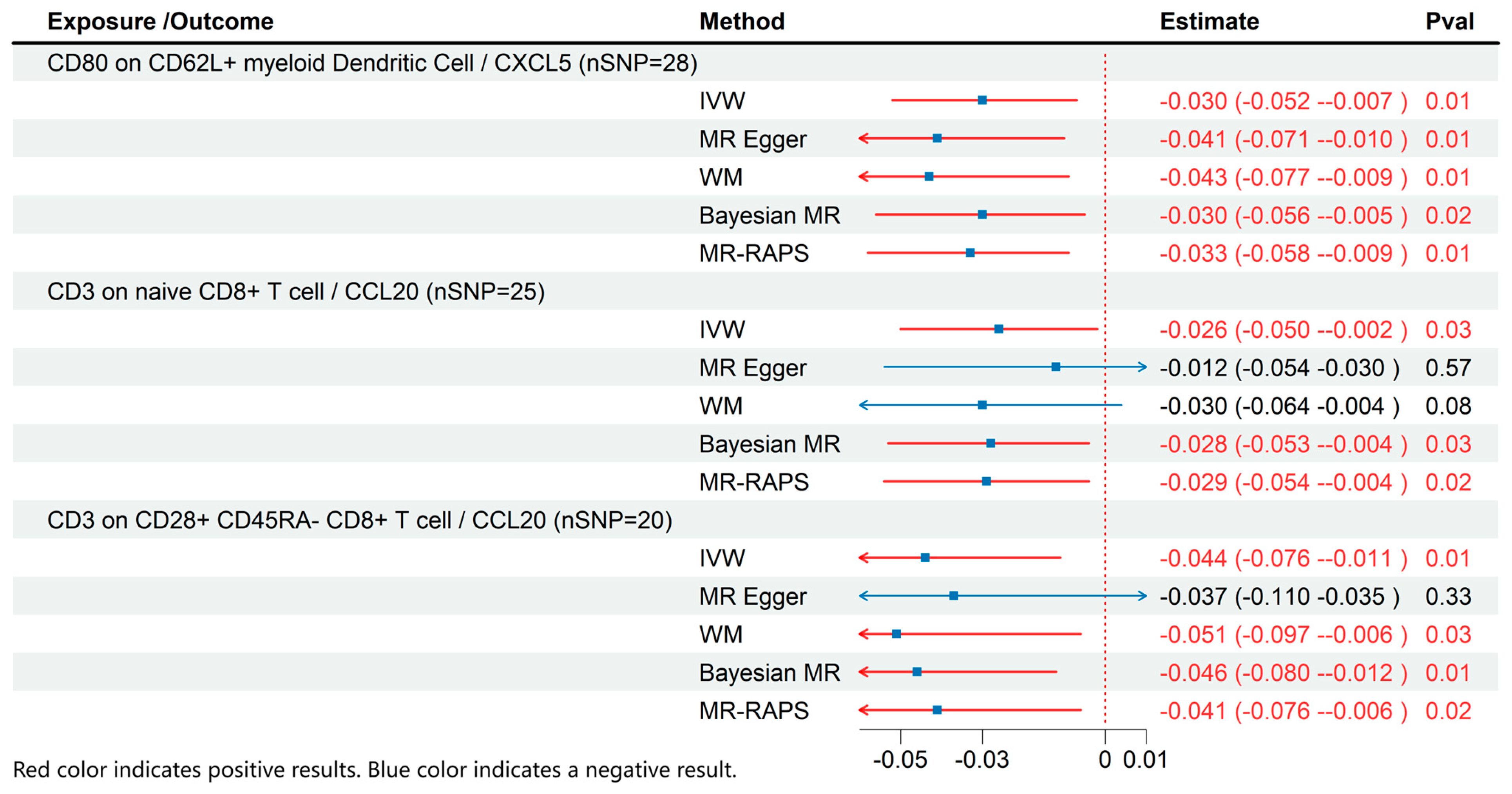
3.3. MR Results of Effects of Immune Cell on Inflammatory Cytokines
Based on the results of the previous analyses, we conducted additional MR analyses to evaluate immune cells and inflammatory cytokines with significant causal relationships to ME/CFS (Figure 4). The results demonstrated that CD80 on CD62L+ myeloid dendritic cells (β: −0.03; 95% CI: −0.052–−0.007; p = 0.01) was associated with reduced CXCL5 levels. Similarly, CD3 on naive CD8+ T cells (β: −0.026; 95% CI: −0.05–−0.002; p = 0.03) and CD3 on CD28+ CD45RA- CD8+ T cells (β: −0.044; 95% CI: −0.076–−0.011; p = 0.01) were associated with lower CCL20 levels.
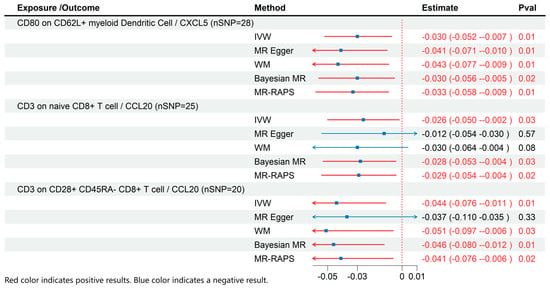
Figure 4.
MR effects of immune cells on Inflammatory Cytokines. The red color of the numbers and the red dotted line indicate a positive result.
3.4. Mediating Role of Circulating Inflammatory Cytokines
Expanding on the conclusions drawn from earlier analyses, we performed mediation analyses to explore possible intermediate effects, as shown in Table 2. Nevertheless, none of these mediation effects reached statistical significance, with all p-values exceeding 0.05. These findings imply that inflammatory cytokines are unlikely to play a significant role in mediating the connection between immune cells and ME/CFS. Although no significant mediating effects were found, it is possible that there are more complex indirect pathways that we have not yet detected, or that the mediating effects are only apparent at specific stages of disease progression, or that there may be some dose dependency, etc., which need to be elucidated by more in-depth studies.

Table 2.
MR results of mediation analysis.
4. Discussion
This is the inaugural MR examination, establishing a causal link among immune cells, inflammatory cytokines, and ME/CFS. Our study highlights CD8+ natural killer T cells as a percentage of T cells and lymphocytes, CD19 on IgD+ CD38- B cells, absolute monocyte count, CD80 on CD62L+ myeloid dendritic cells, activated and secreting CD4 regulatory T cells as a percentage of CD4 regulatory T cells, CD80 on myeloid dendritic cells, CXCL5, and CCL20 as key contributors to ME/CFS risk. Conversely, higher levels of CD3 on naive CD8+ T cell, CD3 on CD28+ CD45RA- CD8+ T cell, FSC-A on CD8+ T cell, TCRγδ T cell %lymphocyte, CD19 on memory B cell, TCRγδ T cell %T cell, and the inflammatory cytokine TNF were significantly linked to a decreased risk of ME/CFS. These results underscore the critical role of immune dysfunction in ME/CFS pathogenesis and provide essential insights into potential diagnostic biomarkers. This study uses MR analysis to offer strong evidence of the immune system’s role in ME/CFS, facilitating future research on targeted therapies.
The complicated pathophysiology of ME/CFS, a chronic, diverse illness, is still not fully understood. According to recent studies, ME/CFS is frequently associated with immune system abnormalities. Patients often exhibit significant T cell regulatory impairments, B cell proliferation, an abnormal increase in regulatory T (Treg) cell proportions, and markedly reduced cytotoxic activity of NK cells [28,29,30]. Additionally, it is believed that infections brought on by pathogens like Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) are a major factor in the development of ME/CFS [31]. γδ T cells (TCRγδ) represent a specialized subset of T cells that detect antigens through unique receptors and function by activating B cells or targeting EBV-infected cells for destruction [32,33,34]. Studies have found that defects in EBV-specific B memory cells and T memory cells in patients with ME/CFS may contribute to diminished viral clearance, suggesting that the activation of immune cells could be a critical aspect of ME/CFS treatment [35]. Recently, viral infection and ME/CFS studies have garnered attention. A systematic review and meta-analysis examined 64 trials with 18 viruses, including 4971 ME/CFS patients and 9221 controls. Two DNA viruses (human herpesvirus-7 and parvovirus B19) and three RNA viruses (Borna disease virus, enterovirus, and Coxsackievirus B) were substantially more prevalent in ME/CFS patients than in healthy and diseased controls [36]. The Ross River virus (RRV), an Australian zoonotic arbovirus, may also cause ME/CFS. RRV affects the host immune response through immune escape strategies, which may account for chronic idiopathic fatigue. These findings illuminate immune pathology and exhaustion after viral infections, particularly in cases of long COVID following SARS-CoV-2 infection [37].
Functional abnormalities in monocytes, T cells, NK cells, and myeloid dendritic cells are particularly pronounced in patients with ME/CFS. Single-cell RNA sequencing has revealed that monocyte dysregulation within patients correlates positively with disease severity [7]. The proportions and activities of T cell subsets, such as CD3+ and CD8+ T cells, are significantly reduced, while the proportion of Treg cells is abnormally elevated [38,39]. These changes may exacerbate the inflammatory state of ME/CFS by suppressing NK cell function and impairing antigen-presenting cell activity [30,39]. Treg cells notably suppress antigen-presenting cell function by interacting with CD80, CD86, and MHCII molecules on dendritic cells (DCs), which may lead to DC maturation defects and impact their antigen presentation and cytokine secretion by helper T (Th) cells [40,41]. The expression levels of genes linked to inflammation are closely linked to abnormal B cell proliferation, indicating that B cells may contribute to the pathogenic processes of ME/CFS by producing primary antigens [42]. Increased differentiation or defective activation of NK cells in response to external stimuli may affect NK cytotoxic activity through different mechanisms [43,44].
The presence of an inflammatory state in patients with ME/CFS is also noteworthy. ME/CFS is associated with increased pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β, contributing to the chronic inflammatory state and disease pathogenesis [45,46]. While TNF-α levels are elevated in ME/CFS [47,48], our MR analysis suggests a protective genetic predisposition, potentially due to reverse causality or confounding factors in observational studies. MR isolates lifelong genetic effects, which may reflect distinct etiological pathways. TNF-α has been linked to cognitive dysfunction and musculoskeletal pain in ME/CFS patients [49,50]. Elevated NF-κB levels contribute to oxidative stress and chronic inflammation [51,52], with TNF-α playing a central role in these processes. Studies show a correlation between TNF-α and fatigue, particularly in leukemia and depression patients [53,54].
CXCL5, a chemokine involved in neutrophil recruitment, shows altered levels in systemic lupus erythematosus [55], but its role in ME/CFS requires further study. Similarly, CCL20, a significant chemotactic factor, is elevated in rheumatoid arthritis [56,57] and may have a similar role in ME/CFS. Elevated chemokines like CXCL5 and CCL20 are also observed in fibromyalgia, suggesting common immune activation mechanisms with ME/CFS [58]. Understanding the inflammatory mechanisms in ME/CFS may provide insights into its etiology and therapeutic targets [48,59].
In this study, a two-sample MR method with IVW was used for the analysis, and various methods such as the MR-Egger regression, WM, Bayesian weighted MR method, and MR-RAPS were also combined to ensure the robustness of the results. This approach of using multiple methods together allows for a better understanding of cause-and-effect relationships and helps address issues like pleiotropy and weak instrumental variables, making the results more trustworthy than in earlier studies. Also, while looking at how circulating inflammatory cytokines affect the link between immune cell profiles and ME/CFS, this study used mediation analysis to dig deeper into the biological processes involved, unlike many earlier studies that only focused on basic correlation or single-factor causal links without thoroughly investigating mediating effects.
This study, while robust, has certain limitations. MR analysis depends on genetic variants as instrumental variables, which may not be available for all immune cell phenotypes, potentially diminishing statistical power. Secondly, while efforts were made to adhere to MR assumptions, the possibility of genetic variants directly influencing ME/CFS or related diseases cannot be completely excluded, which may introduce bias. Addressing these limitations will require future studies to incorporate diverse analytical methods and expand population diversity to validate and generalize the findings. While MR minimizes confounding, modest effect sizes (e.g., CXCL5 OR = 1.02) may reflect polygenic contributions or residual pleiotropy. Replication in larger cohorts is critical. Finally, the ME/CFS data are derived from self-reports and are subject to potential classification errors, but the dataset is the current ME/CFS dataset with a large sample size.
5. Conclusions
To sum up, this study offers the first proof of a link between ME/CFS, inflammatory cytokines, and immune cells. Immune cell function dysregulation has been found to be a substantial risk factor for ME/CFS, highlighting its potential utility as a biomarker for the condition. Moreover, these findings nominate CXCL5/CCL20 as potential diagnostic biomarkers and TNF modulation as a therapeutic strategy. Clinical trials targeting B-cell activity (e.g., rituximab) or myeloid dendritic cell CD80 pathways warrant exploration. Future studies should aim to uncover the precise mechanisms underlying immune cell dysfunction and inflammatory processes, thereby facilitating the creation of personalized therapeutic approaches.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biomedicines13051200/s1: Table S1: Detailed information of instrumental variables used for immune cells on ME/CFS; Table S2: Detailed information of instrumental variables used for inflammatory cytokines on ME/CFS; Table S3: Detailed information of instrumental variables used for immune cells on inflammatory cytokines in mediation analysis; Table S4: Sensitivity analysis in the MR analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.D. and J.Y.; Data curation, L.D., J.Y., J.Z., Z.C. and H.Y.; Funding acquisition, D.C.; Investigation, L.D., J.Z. and Z.C.; Methodology, L.D., J.Y. and H.Y.; Project administration, D.C.; Supervision, Z.C.; Visualization, J.Z.; Writing—original draft, L.D.; Writing—review and editing, D.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82274659), Sichuan Qihuang Scholars Capacity Enhancement Program (600008241001), and a project grant from Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Apricot Grove Scholars Program (330024651).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article or Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to the referenced studies and consortiums for providing open-access datasets that were instrumental in facilitating the analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| MR | Mendelian randomization |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association study |
| IV | Instrumental variable |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphisms |
| IVW | Inverse variance weighted |
| WM | Weighted median |
| BWMR | Bayesian weighted MR |
| (ME/CFS) | Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome |
| OR | Odds ratios |
| CI | Confidence interval |
References
- Grach, S.L.; Seltzer, J.; Chon, T.Y.; Ganesh, R. Diagnosis and Management of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2023, 98, 1544–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogl, T.; Kalka, I.N.; Klompus, S.; Leviatan, S.; Weinberger, A.; Segal, E. Systemic Antibody Responses against Human Microbiota Flagellins Are Overrepresented in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Patients. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabq2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, E.W. Beyond Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: An IOM Report on Redefining an Illness. JAMA 2015, 313, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingdon, C.C.; Bowman, E.W.; Curran, H.; Nacul, L.; Lacerda, E.M. Functional Status and Well-Being in People with Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Compared with People with Multiple Sclerosis and Healthy Controls. PharmacoEcon. Open 2018, 2, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, H.E.; McCorkell, L.; Vogel, J.M.; Topol, E.J. Long COVID: Major Findings, Mechanisms and Recommendations. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, L.; Bested, A.C.; Bonilla, H.F.; Chheda, B.V.; Chu, L.; Curtin, J.M.; Dempsey, T.T.; Dimmock, M.E.; Dowell, T.G.; Felsenstein, D.; et al. Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: Essentials of Diagnosis and Management. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2021, 96, 2861–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, L.T.; Ahmed, F.; Zhu, H.; Iu, D.S.H.; Fogarty, E.A.; Kwak, Y.; Chen, W.; Franconi, C.J.; Munn, P.R.; Tate, A.E.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomics of the Immune System in ME/CFS at Baseline and Following Symptom Provocation. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya, J. Surveying the Metabolic and Dysfunctional Profiles of T Cells and NK Cells in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanbani, F.; Maynard, R.D.; Sing, J.C.; Jahanbani, S.; Perrino, J.J.; Spacek, D.V.; Davis, R.W.; Snyder, M.P. Phenotypic Characteristics of Peripheral Immune Cells of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome via Transmission Electron Microscopy: A Pilot Study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bested, A.C.; Marshall, L.M. Review of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: An Evidence-Based Approach to Diagnosis and Management by Clinicians. Rev. Environ. Health 2015, 30, 223–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey Smith, G.; Hemani, G. Mendelian Randomization: Genetic Anchors for Causal Inference in Epidemiological Studies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, R89–R98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emdin, C.A.; Khera, A.V.; Kathiresan, S. Mendelian Randomization. JAMA 2017, 318, 1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahim, S.; Davey Smith, G. Mendelian Randomization: Can Genetic Epidemiology Help Redress the Failures of Observational Epidemiology? Hum. Genet. 2007, 123, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orrù, V.; Steri, M.; Sidore, C.; Marongiu, M.; Serra, V.; Olla, S.; Sole, G.; Lai, S.; Dei, M.; Mulas, A.; et al. Complex Genetic Signatures in Immune Cells Underlie Autoimmunity and Inform Therapy. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 1036–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.H.; Stacey, D.; Eriksson, N.; Macdonald-Dunlop, E.; Hedman, Å.K.; Kalnapenkis, A.; Enroth, S.; Cozzetto, D.; Digby-Bell, J.; Marten, J.; et al. Genetics of Circulating Inflammatory Proteins Identifies Drivers of Immune-Mediated Disease Risk and Therapeutic Targets. Nat. Immunol. 2023, 24, 1540–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Cao, Y.; Ma, H.; Guo, S.; Xu, W.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H. Causal Effects between Gut Microbiome and Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1190894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Hou, X.; Wu, M.; Zhu, L. Relationship between Major Depressive Disorder and Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Un, H.; Wusimanjiang, W.; Zhan, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Lei, J.; Lin, R.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z. Understanding Bladder Cancer Risk: Mendelian Randomization Analysis of Immune Cell and Inflammatory Factor Influence. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1460275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, B.; Feng, C.; Chen, W.; Wu, D. Exploring the Mediating Role of Immune Cells in the Pathogenesis of IgA Nephropathy through the Inflammatory Axis of Gut Microbiota from a Genomic Perspective. Mamm. Genome 2024, 36, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, T.M.; Lawlor, D.A.; Harbord, R.M.; Sheehan, N.A.; Tobias, J.H.; Timpson, N.J.; Davey Smith, G.; Sterne, J.A.C. Using Multiple Genetic Variants as Instrumental Variables for Modifiable Risk Factors. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2012, 21, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Scott, R.A.; Timpson, N.J.; Davey Smith, G.; Thompson, S.G.; EPIC-InterAct Consortium. Using Published Data in Mendelian Randomization: A Blueprint for Efficient Identification of Causal Risk Factors. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 30, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian Randomization with Invalid Instruments: Effect Estimation and Bias Detection through Egger Regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.-Y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Detection of Widespread Horizontal Pleiotropy in Causal Relationships Inferred from Mendelian Randomization between Complex Traits and Diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, J.; Hemani, G.; Bowden, J.; Small, D.S. Statistical Inference in Two-Sample Summary-Data Mendelian Randomization Using Robust Adjusted Profile Score. Ann. Stat. 2020, 48, 1742–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ming, J.; Hu, X.; Chen, G.; Liu, J.; Yang, C. Bayesian Weighted Mendelian Randomization for Causal Inference Based on Summary Statistics. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 1501–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemani, G.; Tilling, K.; Davey Smith, G. Orienting the Causal Relationship between Imprecisely Measured Traits Using GWAS Summary Data. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1007081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.; Berk, M.; Galecki, P.; Maes, M. The Emerging Role of Autoimmunity in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/Cfs). Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 49, 741–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenu, E.W.; Huth, T.K.; Hardcastle, S.L.; Fuller, K.; Kaur, M.; Johnston, S.; Ramos, S.B.; Staines, D.R.; Marshall-Gradisnik, S.M. Role of Adaptive and Innate Immune Cells in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis. Int. Immunol. 2013, 26, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenu, E.W.; van Driel, M.L.; Staines, D.R.; Ashton, K.J.; Ramos, S.B.; Keane, J.; Klimas, N.G.; Marshall-Gradisnik, S.M. Immunological Abnormalities as Potential Biomarkers in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proal, A.; Marshall, T. Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome in the Era of the Human Microbiome: Persistent Pathogens Drive Chronic Symptoms by Interfering With Host Metabolism, Gene Expression, and Immunity. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Fichtner, A.S.; Bruni, E.; Odak, I.; Sandrock, I.; Bubke, A.; Borchers, A.; Schultze-Florey, C.; Koenecke, C.; Förster, R.; et al. A Fetal Wave of Human Type 3 Effector Γδ Cells with Restricted TCR Diversity Persists into Adulthood. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabf0125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, T.; Karunakaran, M.M. Butyrophilins: Γδ T Cell Receptor Ligands, Immunomodulators and More. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 876493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Liu, M.; Lv, A.; Gao, Y.; Hu, H.; Lam, K.T.; Chan, G.C.; Yang, Y.; et al. Targeted Activation of Human Vγ9Vδ2-T Cells Controls Epstein-Barr Virus-Induced B Cell Lymphoproliferative Disease. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loebel, M.; Strohschein, K.; Giannini, C.; Koelsch, U.; Bauer, S.; Doebis, C.; Thomas, S.; Unterwalder, N.; von Baehr, V.; Reinke, P.; et al. Deficient EBV-Specific B- and T-Cell Response in Patients with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Oh, H.-M.; Lee, E.-J.; Lim, E.-J.; Son, C.-G. Evaluation of Viral Infection as an Etiology of ME/CFS: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidbury, B.A. Ross River Virus Immune Evasion Strategies and the Relevance to Post-Viral Fatigue, and Myalgic Encephalomyelitis Onset. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 662513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yu, Q.; Wu, C.; Sun, Z.; Wu, X.; Liu, R.; Zhang, H. Acupuncture of the Beishu Acupoint Participates in Regulatory Effects of Ginsenoside Rg1 on T Cell Subsets of Rats with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2020, 9, 3436–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, N.; Lerch, A.; Jason, L.A.; Sorenson, M.; Fletcher, M.A.; Herrington, J. A Comparison of Immune Functionality in Viral versus Non-Viral CFS Subtypes. J. Behav. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Corthay, A. How Do Regulatory T Cells Work? Scand. J. Immunol. 2009, 70, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, P.; Amrani, A.; Yamanouchi, J.; Han, B.; Thiessen, S.; Utsugi, T.; Verdaguer, J.; Santamaria, P. CD40 Ligation Releases Immature Dendritic Cells from the Control of Regulatory CD4+CD25+ T Cells. Immunity 2003, 19, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, W.; Ono, H.; Matsutani, T.; Nakamura, M.; Shin, I.; Amano, K.; Suzuki, R.; Yamamura, T. Skewing of the B Cell Receptor Repertoire in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 95, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylova, I.; DeRuyter, M.; Rummens, J.L.; Bosmans, E.; Maes, M. Decreased Expression of CD69 in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome in Relation to Inflammatory Markers: Evidence for a Severe Disorder in the Early Activation of T Lymphocytes and Natural Killer Cells. Neuroendocrinol. Lett. 2007, 28, 477–483. [Google Scholar]
- Huth, T.K.; Brenu, E.W.; Ramos, S.; Nguyen, T.; Broadley, S.; Staines, D.; Marshall-Gradisnik, S. Pilot Study of Natural Killer Cells in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis and Multiple Sclerosis. Scand. J. Immunol. 2015, 83, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasa-Dzelzkaleja, S.; Krumina, A.; Capenko, S.; Nora-Krukle, Z.; Gravelsina, S.; Vilmane, A.; Ievina, L.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Murovska, M.; VirA Project. The Persistent Viral Infections in the Development Severity of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroll, M.A. Allostatic Overload in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS). Med. Hypotheses 2013, 81, 506–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.V.; Buckland, M.; Murphy, G.; Taylor, N.; Vleck, V.; Mein, C.; Wozniak, E.; Smuk, M.; White, P.D. Cytokine Responses to Exercise and Activity in Patients with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: Case-Control Study. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 190, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, J.G.; Holmes, T.H.; Anderson, J.N.; Maecker, H.T.; Rosenberg-Hasson, Y.; Valencia, I.J.; Chu, L.; Younger, J.W.; Tato, C.M.; Davis, M.M. Cytokine Signature Associated with Disease Severity in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7150–E7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strawbridge, R.; Sartor, M.L.; Scott, F.; Cleare, A.J. Inflammatory Proteins Are Altered in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 107, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsjö, M.A.; Olsson, G.L.; Wicksell, R.K.; Alving, K.; Holmström, L.; Andreasson, A. The Role of Low-Grade Inflammation in ME/CFS (Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome)—Associations with Symptoms. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2020, 113, 104578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.; Maes, M. Increased Nuclear Factor-κB and Loss of P53 Are Key Mechanisms in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS). Med. Hypotheses 2012, 79, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.; Maes, M. Mitochondrial Dysfunctions in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Explained by Activated Immuno-Inflammatory, Oxidative and Nitrosative Stress Pathways. Metab. Brain Dis. 2013, 29, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, F.Y.; Li, M.; Breunis, H.; Timilshina, N.; Minden, M.D.; Alibhai, S.M.H. Correlation between Cytokine Levels and Changes in Fatigue and Quality of Life in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2013, 37, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedraz-Petrozzi, B.; Neumann, E.; Sammer, G. Pro-Inflammatory Markers and Fatigue in Patients with Depression: A Case-Control Study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, L.; Du, K.; Chen, J.; Ding, H.; Petersen, F.; Ye, S.; Lin, Z.; Yu, X. Serum Levels of CXCL5 Are Decreased and Correlate with Circulating Platelet Counts in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 27, e15089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.Y.; Zhang, M.J.; Liu, P.F.; Xiao, G.; Lyu, X.M. Correlation between serum CCL20 level and disease severity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2021, 55, 226–232. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Hong, X.; Du, H. Association Between Serum Chemokine Ligand 20 Levels and Disease Activity and Th1/Th2/Th17-Related Cytokine Levels in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2023, 43, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, Y.; Arangia, A.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; D’Amico, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cupi, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Fusco, R.; et al. Analysis of the Influence of IL-6 and the Activation of the Jak/Stat3 Pathway in Fibromyalgia. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, C.; Qu, Y.; Guo, J.; Shi, T.; Bo, W.; Sun, Z.; Asakawa, T. The Clinical Value of Cytokines in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).