Circular Nucleic Acids Act as an Oncogenic MicroRNA Sponge to Inhibit Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. RT-qPCR
2.3. Absolute Quantification of RNA Expression
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Extraction and Purification of circDNA
2.6. In Vitro RNA Transcription, Circularization, and Purification
2.7. Serum Stability Assay
2.8. Annexin V FITC Assay
2.9. Transwell Migration Assay
2.10. Measurement of Lipid Peroxidation
2.11. Detection of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
2.12. Xenograft Tumor Experiment
2.13. RayBio Mouse Inflammatory Antibody Array
3. Results
3.1. Screening of Oncogenic microRNAs and Target Tumor Suppressor Genes in HCC
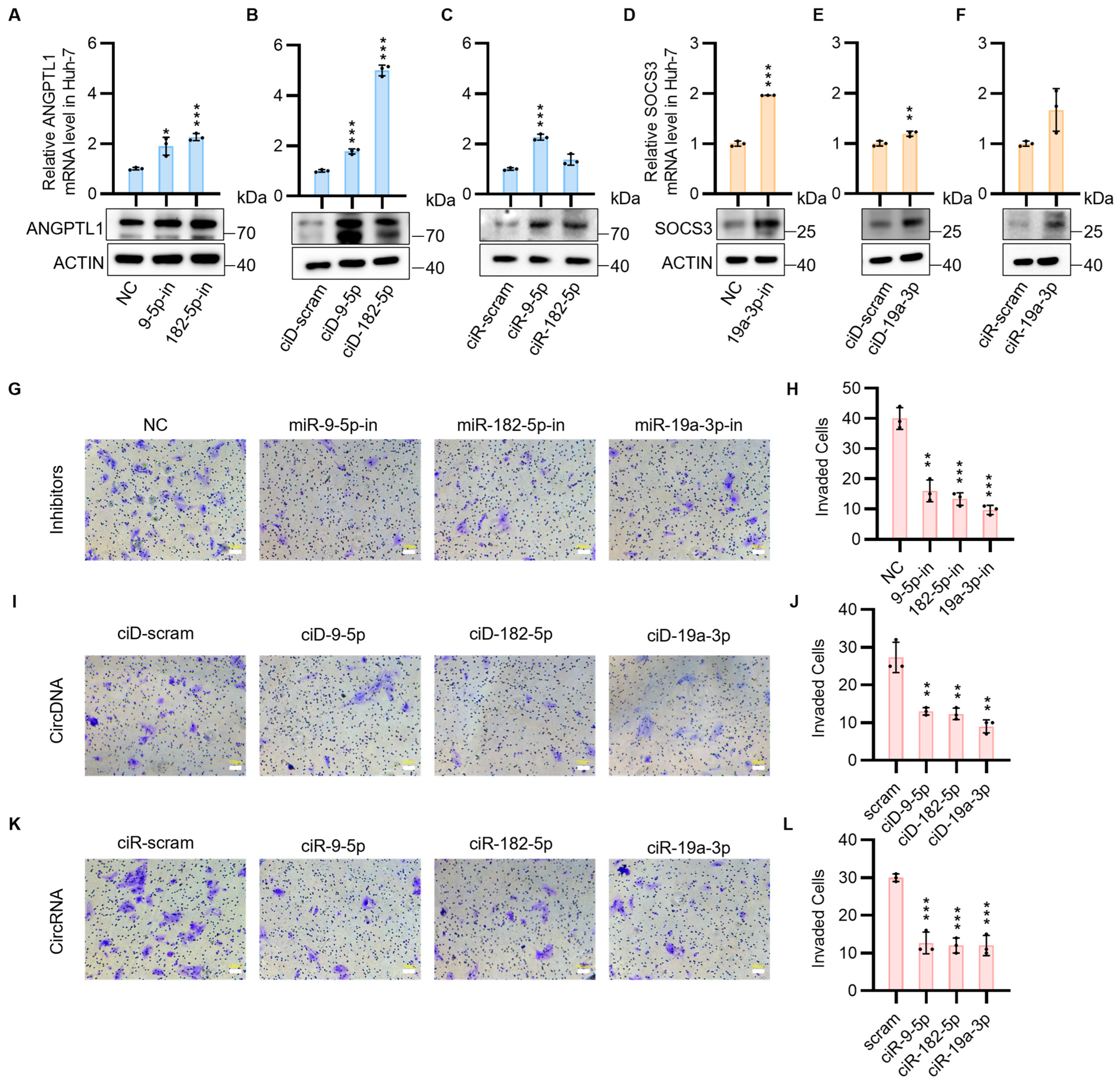
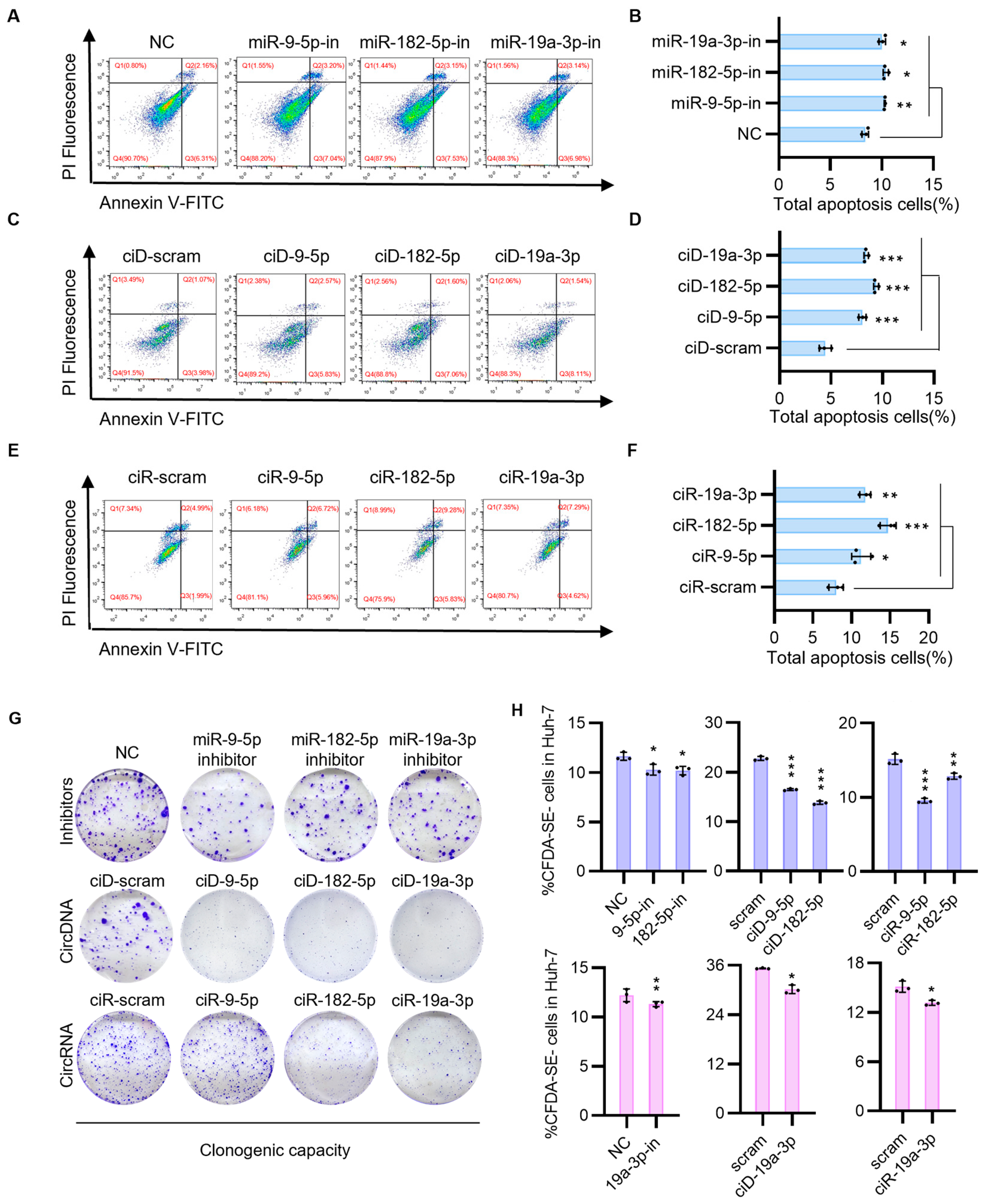
3.2. CircNAs Act as Competitive Inhibitors of OncomiRs, Derepressing ANGPTL1 and SOCS3 Expression to Suppress HCC Cell Proliferation and Migration While Promoting Apoptosis
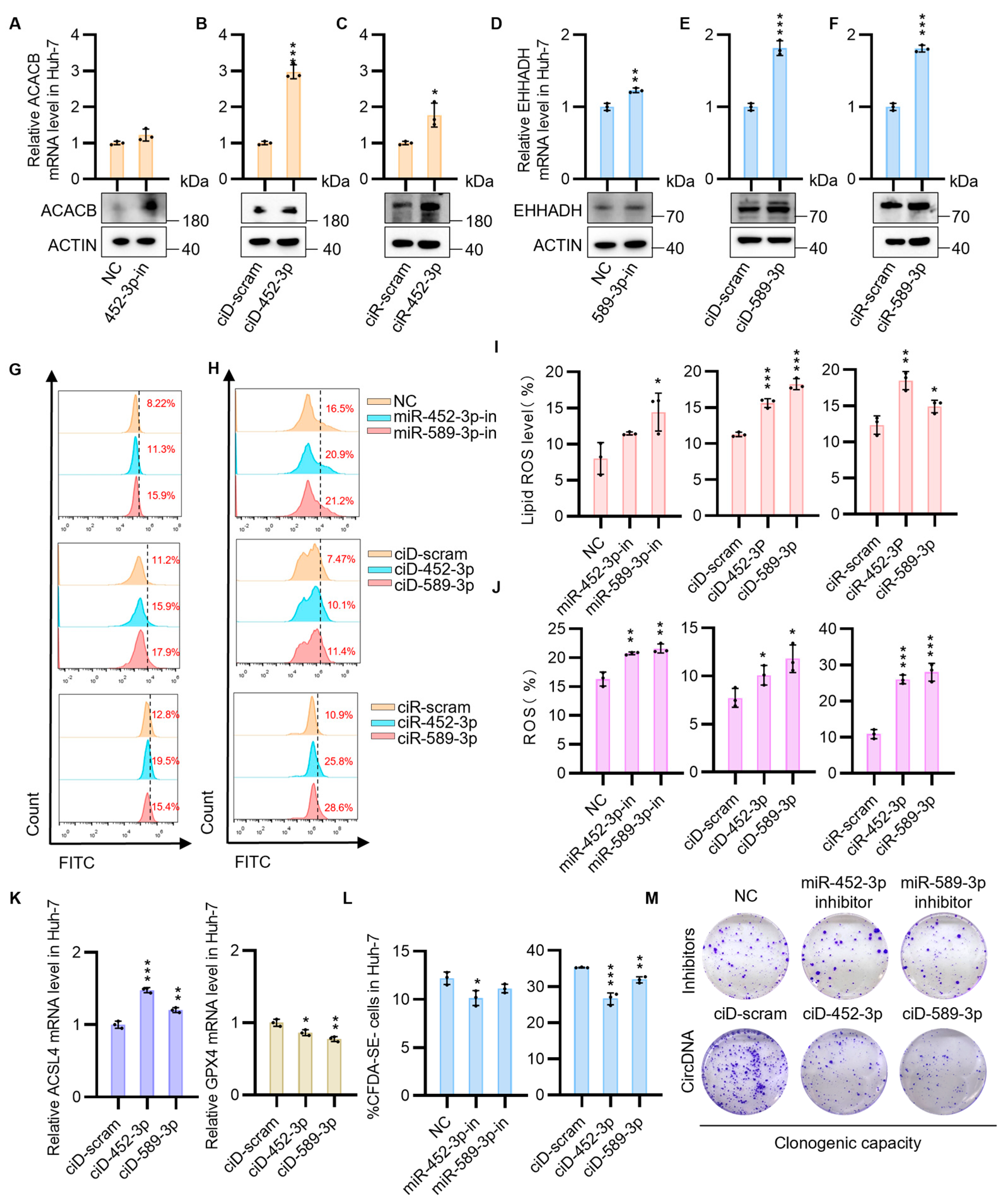
3.3. CircNAs Act as Competitive Inhibitors of OncomiRs, Derepressing ACACB and EHHADH Expression to Suppress Cell Proliferation While Promoting Ferroptosis in HCC Cells
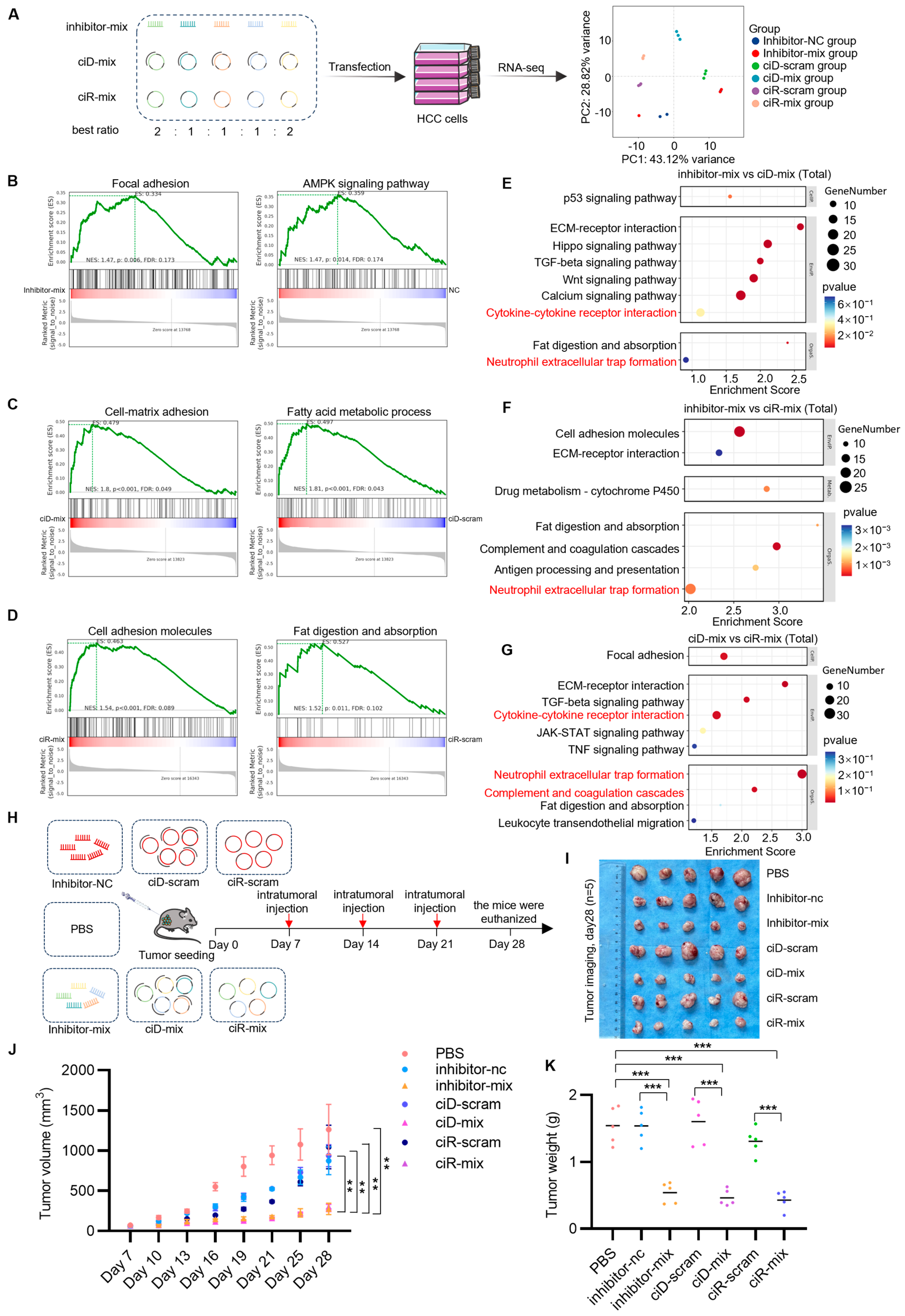
3.4. Manipulating Transcriptional Networks via OncomiR Sponge Molecules to Intensify Hepatocellular Carcinoma Regression and Immune Efficacy
3.5. OncomiR Sponge Molecular Drugs Elicit Inflammatory Factor Activation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singal, A.G.; Kanwal, F.; Llovet, J.M. Global trends in hepatocellular carcinoma epidemiology: Implications for screening, prevention and therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 864–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Lee, S.; Senavirathne, G.; Lai, E.C. microRNAs in action: Biogenesis, function and regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023, 24, 816–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.X.; Rothenberg, M.E. MicroRNA. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helwak, A.; Kudla, G.; Dudnakova, T.; Tollervey, D. Mapping the Human miRNA Interactome by CLASH Reveals Frequent Noncanonical Binding. Cell 2013, 153, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.W.; Ferland-McCollough, D.; Jackson, T.J.; Bushell, M. microRNAs in cancer management. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, e249–e258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.W.; Heegaard, N.H.H.; Ørum, H. MicroRNAs in Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1431–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenvang, J.; Silahtaroglu, A.N.; Lindow, M.; Elmen, J.; Kauppinen, S. The utility of LNA in microRNA-based cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2008, 18, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmén, J.; Lindow, M.; Silahtaroglu, A.; Bak, M.; Christensen, M.; Lind-Thomsen, A.; Hedtjärn, M.; Hansen, J.B.; Hansen, H.F.; Straarup, E.M.; et al. Antagonism of microRNA-122 in mice by systemically administered LNA-antimiR leads to up-regulation of a large set of predicted target mRNAs in the liver. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esau, C.C. Inhibition of microRNA with antisense oligonucleotides. Methods 2008, 44, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaman, D.; Chen, P.Y.; Fak, J.; Yalcin, A.; Pearce, M.; Unnerstall, U.; Marks, D.S.; Sander, C.; Tuschl, T.; Gaul, U. Antisense-Mediated Depletion Reveals Essential and Specific Functions of MicroRNAs in Drosophila Development. Cell 2005, 121, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esau, C.; Davis, S.; Murray, S.F.; Yu, X.X.; Pandey, S.K.; Pear, M.; Watts, L.; Booten, S.L.; Graham, M.; McKay, R.; et al. miR-122 regulation of lipid metabolism revealed by in vivo antisense targeting. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, S.; Lollo, B.; Freier, S.; Esau, C. Improved targeting of miRNA with antisense oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 2294–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ørom, U.A.; Kauppinen, S.; Lund, A.H. LNA-modified oligonucleotides mediate specific inhibition of microRNA function. Gene 2006, 372, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, R.S.; Watanabe, T.A.; Truong, L.; Freier, S.; Lesnik, E.A.; Sioufi, N.B.; Sasmor, H.; Manoharan, M.; Levin, A.A. Pharmacokinetic properties of 2’-O-(2-methoxyethyl)-modified oligonucleotide analogs in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 296, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bak, R.O.; Hollensen, A.K.; Primo, M.N.; Sørensen, C.D.; Mikkelsen, J.G. Potent microRNA suppression by RNA Pol II-transcribed ‘Tough Decoy’ inhibitors. RNA 2013, 19, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, B.; Li, N.; Chen, M.; Qiao, M.; Wang, N.; Cao, Y.; et al. Loss of circSRY reduces γH2AX level in germ cells and impairs mouse spermatogenesis. Life Sci. Alliance 2013, 6, e202201617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Abraham, J.M.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Ashktorab, H.; Smoot, D.T.; Cole, R.N.; Boronina, T.N.; et al. Synthetic Circular RNA Functions as a miR-21 Sponge to Suppress Gastric Carcinoma Cell Proliferation. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 13, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Chen, S.; Han, J.-X.; Tan, Q.; Wang, X.-R.; Wang, H.-Z.; Zhong, W.-L.; Qin, Y.; Qiao, K.-L.; Zhang, C.; et al. Derepression of co-silenced tumor suppressor genes by nanoparticle-loaded circular ssDNA reduces tumor malignancy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaao6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-X.; Guo, S.-K.; Nan, F.; Xu, Y.-F.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.-L. RNA circles with minimized immunogenicity as potent PKR inhibitors. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 420–434.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obi, P.; Chen, Y.G. The design and synthesis of circular RNAs. Methods 2021, 196, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, R.; Montecucco, A.; Ciarrocchi, G.; Biamonti, G. Functional characterization of the T4 DNA ligase: A new insight into the mechanism of action. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 2106–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, T.-C.; Tan, C.-T.; Chang, Y.-W.; Hong, C.-C.; Lee, W.-J.; Chen, M.-W.; Jeng, Y.-M.; Chiou, J.; Yu, P.; Chen, P.-S.; et al. Angiopoietin-like protein 1 suppresses SLUG to inhibit cancer cell motility. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Q.; Jiang, L.; Liu, M.; Yu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Fang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.-H.; Yuan, Y.-F.; et al. ANGPTL1 Interacts with Integrin α1β1 to Suppress HCC Angiogenesis and Metastasis by Inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 Signaling. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5831–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Lu, D.; Qu, D.; Li, Y.; Zhao, N.; Cui, G.; Li, X.; Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; Wei, M.; et al. The Role of ANGPTL Gene Family Members in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 1844352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, M. The Roles of ANGPTL Families in Cancer Progression. J. UOEH 2019, 41, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, Y.M.; Tawfiq, R.A.; Gibriel, A.A.; Ali, A.A.; Kassem, D.H.; Hammam, O.A.; Elmazar, M.M. Activation of FXR modulates SOCS3/Jak2/STAT3 signaling axis in a NASH-dependent hepatocellular carcinoma animal model. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 186, 114497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-K.; Li, C.; Zhang, R.-Y.; Wei, D.; Shang, Y.-K.; Yong, Y.-L.; Kong, L.-M.; Zheng, N.-S.; Liu, K.; Lu, M.; et al. EYA2 suppresses the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via SOCS3-mediated blockade of JAK/STAT signaling. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroso, J.A.B.; Ramos-Lobo, A.M.; Donato, J. SOCS3 as a future target to treat metabolic disorders. Horm. Athens Greece 2019, 18, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gan, L.; Zhou, Z.; Jin, W.; Sun, C. SOCS3 promotes inflammation and apoptosis via inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocyte. Immunobiology 2015, 220, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Zhu, S.; Chen, P.; Hou, W.; Wen, Q.; Liu, J.; Xie, Y.; Liu, J.; Klionsky, D.J.; Kroemer, G.; et al. AMPK-Mediated BECN1 Phosphorylation Promotes Ferroptosis by Directly Blocking System Xc- Activity. Curr. Biol. CB 2018, 28, 2388–2399.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Zandkarimi, F.; Zhang, Y.; Meena, J.K.; Kim, J.; Zhuang, L.; Tyagi, S.; Ma, L.; Westbrook, T.F.; Steinberg, G.R.; et al. Energy-stress-mediated AMPK activation inhibits ferroptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Li, M.; Jiang, F.; Yi, Q.; Yang, W. EHHADH is a key gene in fatty acid metabolism pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma: A transcriptomic analysis. J. South. Med. Univ. 2023, 43, 680–693. [Google Scholar]
- Bersuker, K.; Hendricks, J.M.; Li, Z.; Magtanong, L.; Ford, B.; Tang, P.H.; Roberts, M.A.; Tong, B.; Maimone, T.J.; Zoncu, R.; et al. The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature 2019, 575, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ding, C.; Chen, Y.; Hu, W.; Yu, C.; Peng, C.; Feng, X.; Cheng, Q.; Wu, W.; Lu, Y.; et al. ACSL4 reprograms fatty acid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma via c-Myc/SREBP1 pathway. Cancer Lett. 2021, 502, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.; Kanneganti, T.-D. Function and regulation of IL-1α in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Mayberry, C.L.; Lv, X.; Hu, F.; Khan, T.; Logan, N.A.; Wilson, J.J.; Sears, J.D.; Chaussabel, D.; Chang, C.-H. IL3-Driven T Cell-Basophil Crosstalk Enhances Antitumor Immunity. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2024, 12, 822–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbasi, A.; Siurala, M.; Su, L.L.; Tariveranmoshabad, M.; Picton, L.K.; Ravikumar, P.; Li, P.; Lin, J.-X.; Escuin-Ordinas, H.; Da, T.; et al. Potentiating adoptive cell therapy using synthetic IL-9 receptors. Nature 2022, 607, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Shen, J.; Xue, D.; Li, H.; Xu, L.; Cao, W.; Wang, W.; Fu, Y.-X.; Peng, H. Anti-PD-1 cis-delivery of low-affinity IL-12 activates intratumoral CD8+T cells for systemic antitumor responses. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hailemichael, Y.; Johnson, D.H.; Abdel-Wahab, N.; Foo, W.C.; Bentebibel, S.-E.; Daher, M.; Haymaker, C.; Wani, K.; Saberian, C.; Ogata, D.; et al. Interleukin-6 blockade abrogates immunotherapy toxicity and promotes tumor immunity. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 509–523.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusumi, A.; Kumagai, K. Interleukin 3 (IL-3). Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 1994, 21, 915–925. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Tang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, X.; Tang, S.; Tang, Y.; et al. CircIFNGR2 enhances proliferation and migration of CRC and induces cetuximab resistance by indirectly targeting KRAS via sponging to MiR-30b. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakawa, H.-O.; Tomari, Y. Life of RISC: Formation, action, and degradation of RNA-induced silencing complex. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, L.; Manos, P.D.; Ahfeldt, T.; Loh, Y.-H.; Li, H.; Lau, F.; Ebina, W.; Mandal, P.K.; Smith, Z.D.; Meissner, A.; et al. Highly efficient reprogramming to pluripotency and directed differentiation of human cells with synthetic modified mRNA. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 7, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uematsu, S.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors and Type I interferons. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 15319–15323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, H.; Ma, Z.; Barber, G.N. STING regulates intracellular DNA-mediated, type I interferon-dependent innate immunity. Nature 2009, 461, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Li, Y.; Diao, F.; Lei, C.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Tien, P.; et al. The adaptor protein MITA links virus-sensing receptors to IRF3 transcription factor activation. Immunity 2008, 29, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetson, D.B.; Medzhitov, R. Recognition of cytosolic DNA activates an IRF3-dependent innate immune response. Immunity 2006, 24, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paludan, S.R. Activation and regulation of DNA-driven immune responses. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2015, 79, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Sun, P.; Hu, G.; Yu, X.; Zhang, W.; Feng, X.; Yu, L.; Zhang, P. Circular Nucleic Acids Act as an Oncogenic MicroRNA Sponge to Inhibit Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051171
Zhang Q, Sun P, Hu G, Yu X, Zhang W, Feng X, Yu L, Zhang P. Circular Nucleic Acids Act as an Oncogenic MicroRNA Sponge to Inhibit Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(5):1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051171
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qianyi, Pengcheng Sun, Guang Hu, Xuanyao Yu, Wen Zhang, Xuan Feng, Lan Yu, and Pengfei Zhang. 2025. "Circular Nucleic Acids Act as an Oncogenic MicroRNA Sponge to Inhibit Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression" Biomedicines 13, no. 5: 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051171
APA StyleZhang, Q., Sun, P., Hu, G., Yu, X., Zhang, W., Feng, X., Yu, L., & Zhang, P. (2025). Circular Nucleic Acids Act as an Oncogenic MicroRNA Sponge to Inhibit Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression. Biomedicines, 13(5), 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051171





