Long-Term Alterations of Renal Microvasculature in Rats Following Maternal PM2.5 Exposure: Vitamin D Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
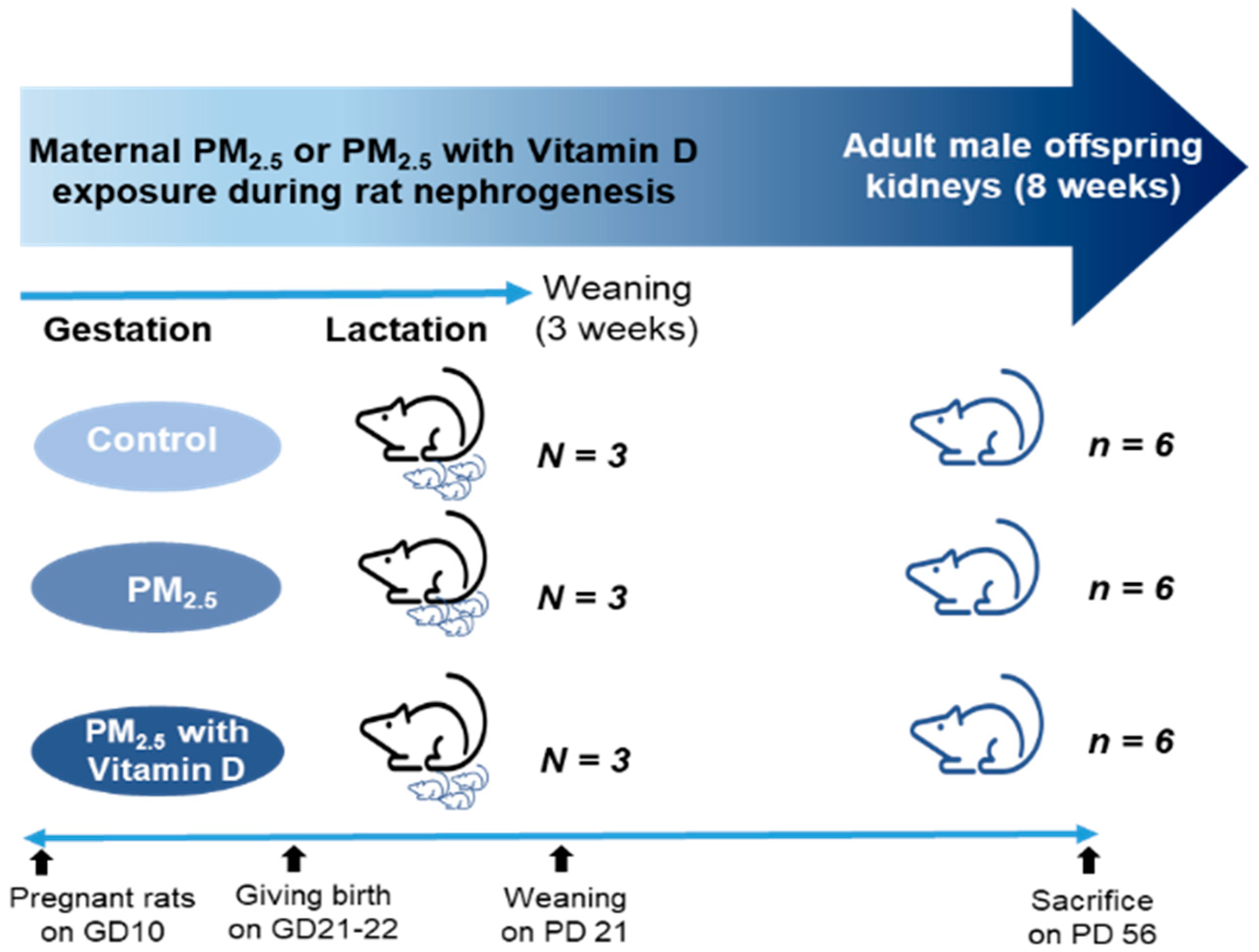
2.1. PM2.5 and Animal Preparation
2.2. Histological Examination
2.3. Western Blotting
2.4. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.5. Biochemical Analysis
2.6. Glomerular Counting
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
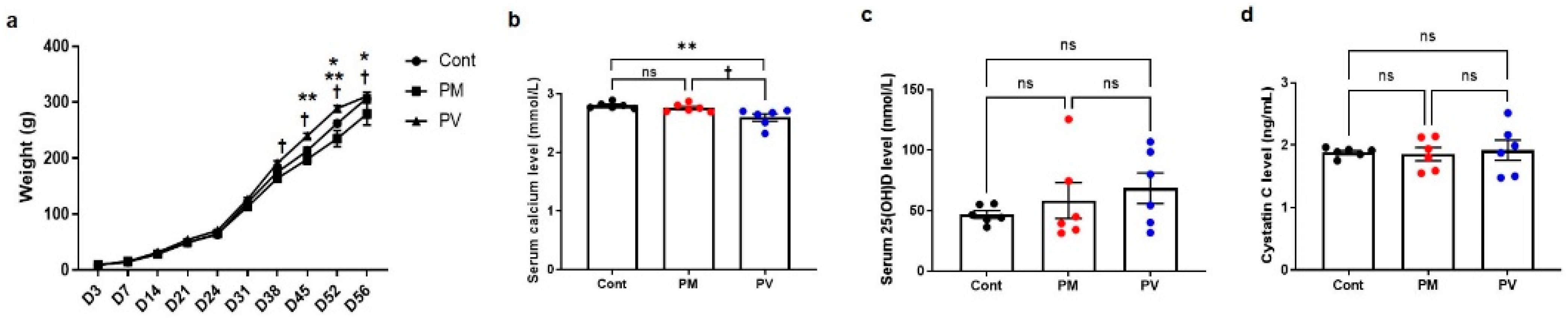
3.1. Body Weight Changes and Laboratory Data
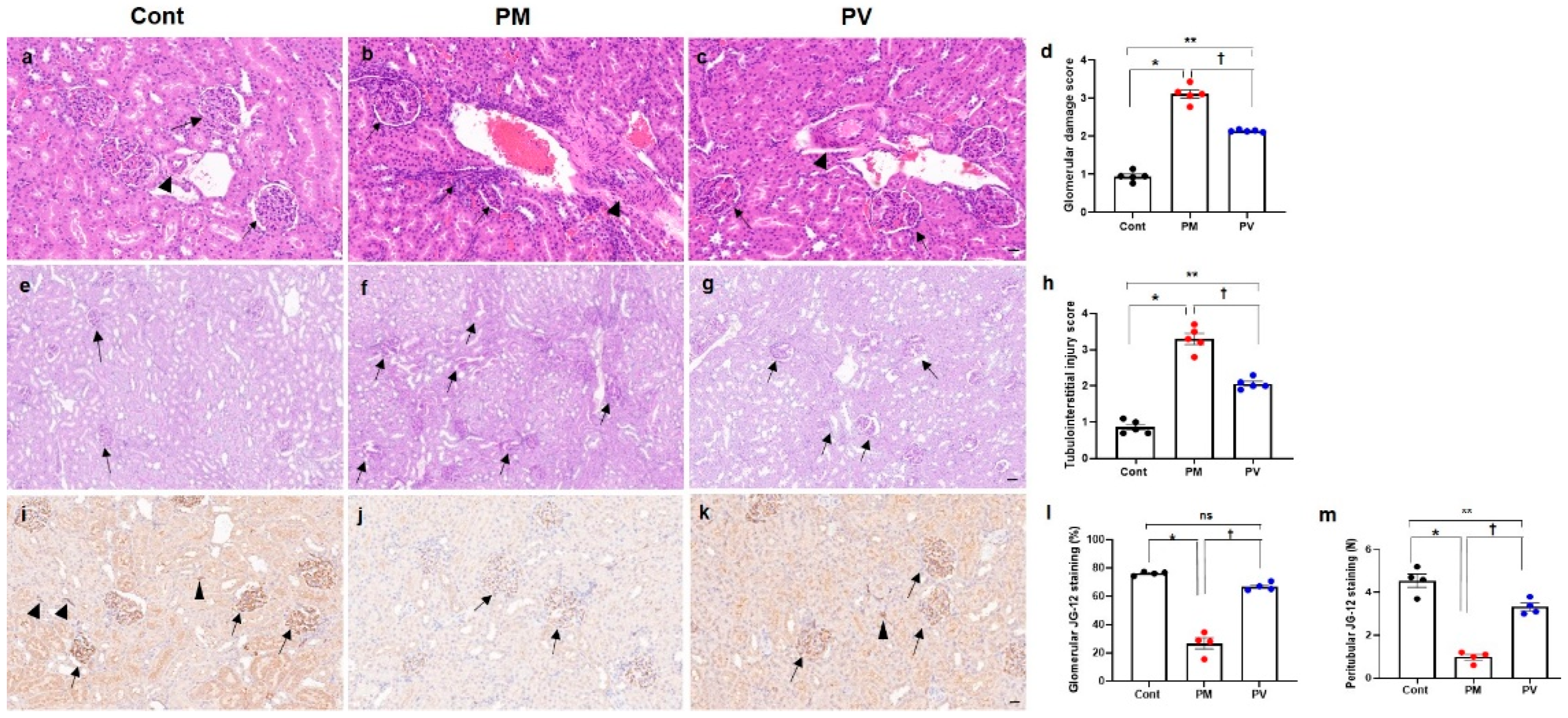
3.2. Renal Histological Alterations
3.3. Intrarenal Capillary JG12 Expression
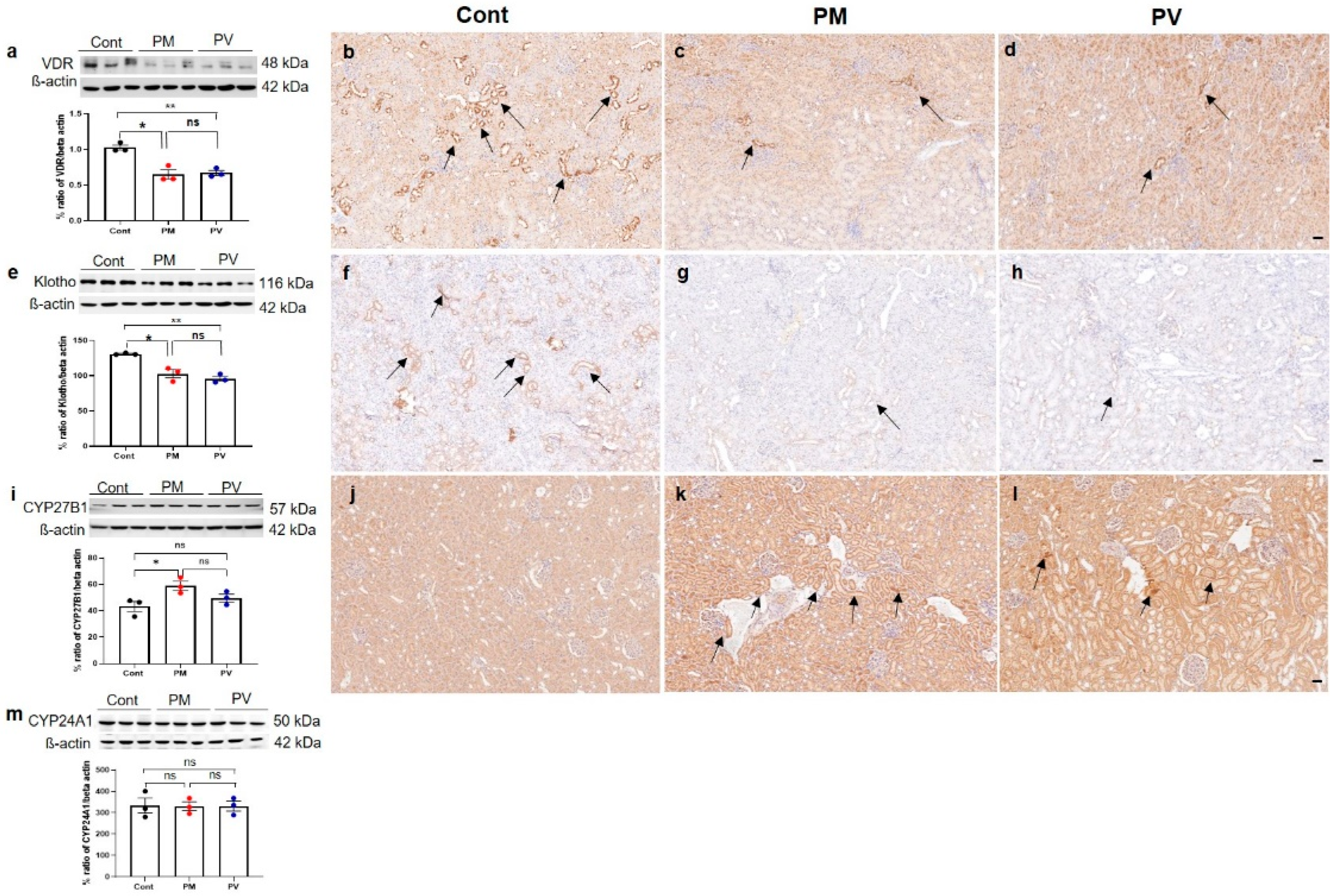
3.4. Intrarenal VDR, Klotho, CYP27B1, and CYP241A Expression
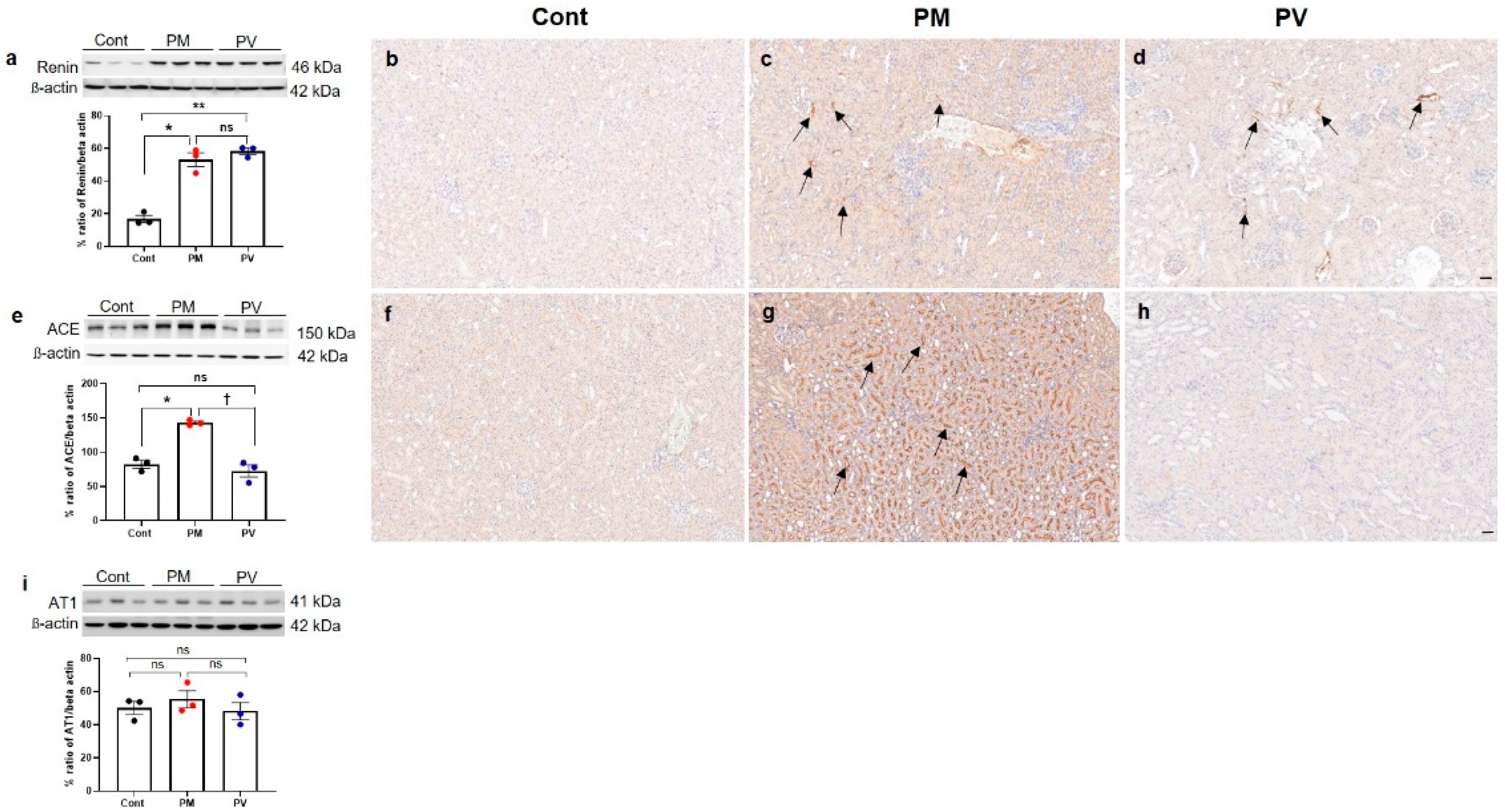
3.5. Intrarenal Renin, ACE, and AT1 Expression
3.6. Intrarenal VEGF-A, VEGFR2, and HIF-1α Expression
3.7. Intrarenal Ang-1, Ang-2, Tie-2 and TSP-1 Expression
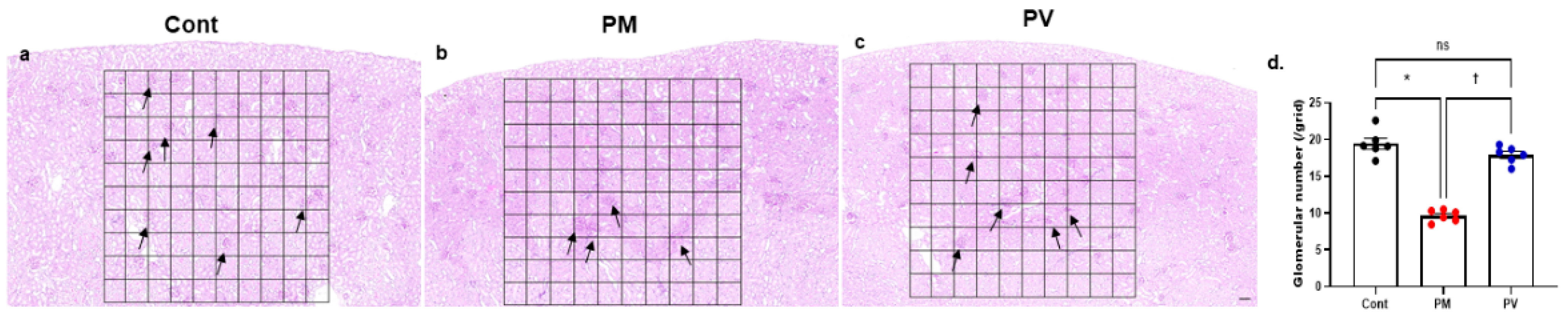
3.8. Glmerular Number
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ang | angiopoietin |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| CYP | cytochrome P 450 mixed-function oxidase |
| H&E | hematoxylin and eosin |
| PAS | periodic acid–Schiff |
| PM2.5 | fine particulate matter |
| RAS | renin-angiotensin system |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| VEGFR2 | vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 |
References
- Wathanavasin, W.; Banjongjit, A.; Phannajit, J.; Eiam-Ong, S.; Susantitaphong, P. Association of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) exposure and chronic kidney disease outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, M.F.; Surapaneni, A.; Stewart, J.D.; Liao, D.; Yanosky, J.D.; Whitsel, E.A.; Power, M.C.; Grams, M.E. Particulate Matter and Albuminuria, Glomerular Filtration Rate, and Incident CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 15, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meariman, J.K.; Zulli, H.; Perez, A.; Bajracharya, S.D.; Mohandas, R. Small vessel disease: Connections between the kidney and the heart. Am. Heart. J. Plus. 2023, 26, 100257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aztatzi-Aguilar, O.G.; Uribe-Ramírez, M.; Narváez-Morales, J.; De Vizcaya-Ruiz, A.; Barbier, O. Early kidney damage induced by subchronic exposure to PM2.5 in rats. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L.; Sun, X.; Wang, N.; Liu, X.; Yao, X.; Qiu, T.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; et al. The influence of PM2.5 exposure on kidney diseases. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2022, 41, 9603271211069982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Wang, R.; Yang, W.; Sun, L.; Xu, M.; Zhang, B.; Yang, L.; Shang, L.; Qi, C.; Chung, M.C. Associations among prenatal PM2.5, birth weight, and renal function. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Zhu, X.; Wei, X.; Long, M.; Jiang, L.; Li, C.; Jin, D.; Du, Y. Pro- and anti-fibrotic effects of vascular endothelial growth factor in chronic kidney diseases. Ren. Fail. 2022, 44, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J. How to delay the progression of chronic kidney disease: Focusing on medications. Child. Kidney Dis. 2024, 28, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhinand, C.S.; Raju, R.; Soumya, S.J.; Arya, P.S.; Sudhakaran, P.R. VEGF-A/VEGFR2 signaling network in endothelial cells relevant to angiogenesis. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2016, 10, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimke, H.; Sparks, M.A.; Thomson, B.R.; Frische, S.; Coffman, T.M.; Quaggin, S.E. Tubulovascular cross-talk by vascular endothelial growth factor a maintains peritubular microvasculature in kidney. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Mo, H.; Miao, J.; Zhou, D.; Tan, R.J.; Hou, F.F.; Liu, Y. Klotho Ameliorates Kidney Injury and Fibrosis and Normalizes Blood Pressure by Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin System. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 3211–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, I.S.; Shin, H.K.; Kim, J.C.; Lee, M.Y. Role of Klotho, an antiaging protein, in pulmonary fibrosis. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Maique, J.O.; Cleaver, O.; Moe, O.W.; Hu, M.C. VEGFR2 insufficiency enhances phosphotoxicity and undermines Klotho’s protection against peritubular capillary rarefaction and kidney fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2023, 324, F106–F123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusaba, T.; Okigaki, M.; Matui, A.; Murakami, M.; Ishikawa, K.; Kimura, T.; Sonomura, K.; Adachi, Y.; Shibuya, M.; Shirayama, T.; et al. Klotho is associated with VEGF receptor-2 and the transient receptor potential canonical-1 Ca2+ channel to maintain endothelial integrity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19308–19313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, A.B.; Copur, S.; Tanriover, C.; Yavuz, F.; Vehbi, S.; Gaipov, A.; Magagnoli, L.; Ciceri, P.; Cozzolino, M.; Kanbay, M. Angiopoietin as a Novel Prognostic Marker in Kidney Disease. Blood. Purif. 2024, 53, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potente, M.; Gerhardt, H.; Carmeliet, P. Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis. Cell 2011, 146, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnudi, L.; Benedetti, S.; Woolf, A.S.; Long, D.A. Vascular growth factors play critical roles in kidney glomeruli. Clin. Sci. 2015, 129, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, K.; Marcussen, N.; Pedersen, M.; Kjaersgaard, G.; Facemire, C.; Coffman, T.M.; Jensen, B.L. Angiotensin II promotes development of the renal microcirculation through AT1 receptors. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliers, D.; Gorin, Y.; Ghosh-Choudhury, G.; Abboud, H.E.; Kasinath, B.S. Angiotensin II stimulation of VEGF mRNA translation requires production of reactive oxygen species. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2006, 290, F927–F936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizkalla, B.; Forbes, J.M.; Cooper, M.E.; Cao, Z. Increased renal vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietins by angiotensin II infusion is mediated by both AT1 and AT2 receptors. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 3061–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira de Almeida, L.; Della Coletta Francescato, H.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J.; Jose Albuquerque de Paula, F.; Giovanni Alves da Silva, C.; Silva Costa, R.; Machado Coimbra, T. Imbalance of Pro- and Anti-Angiogenic Factors due to Maternal Vitamin D Deficiency Causes Renal Microvasculature Alterations Affecting the Adult Kidney Function. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deluque, A.L.; Oliveira, B.M.; Souza, C.S.; Maciel, A.L.D.; Francescato, H.D.C.; Giovanini, C.; de Almeida, L.F.; de Paula, F.J.A.; Costa, R.S.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J.; et al. Paricalcitol Improves the Angiopoietin/Tie-2 and VEGF/VEGFR2 Signaling Pathways in Adriamycin-Induced Nephropathy. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.N.; Tain, Y.L. Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System to Prevent Hypertension and Kidney Disease of Developmental Origins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigore, D.; Ojeda, N.B.; Robertson, E.B.; Dawson, A.S.; Huffman, C.A.; Bourassa, E.A.; Speth, R.C.; Brosnihan, K.B.; Alexander, B.T. Placental insufficiency results in temporal alterations in the renin angiotensin system in male hypertensive growth restricted offspring. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 293, R804–R811. [Google Scholar]
- Son, M.H.; Park, E.; Yim, H.E.; Nam, Y.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Choi, E.K.; Jeong, S.H.; Lee, J.H. Maternal exposure to airborne particulate matter during pregnancy and lactation induces kidney injury in rat dams and their male offspring: The role of vitamin D in pregnancy and beyond. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 43, 648–662. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, E.; Yim, H.E.; Nam, Y.J.; Jeong, S.H.; Kim, J.A.; Lee, J.H.; Son, M.H.; Yoo, K.H. Exposure to airborne particulate matter induces renal tubular cell injury in vitro: The role of vitamin D signaling and renin-angiotensin system. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10184. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Exposure Assessment Tools by Routes—Inhalation [Internet]. United States Environmental Protection Agency; 2022. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/expobox/exposure-assessment-tools-routes-inhalation#calculations (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Ojeda, N.B.; Intapad, S.; Alexander, B.T. Sex differences in the developmental programming of hypertension. Acta Physiol. 2014, 210, 307–316. [Google Scholar]
- Raij, L.; Azar, S.; Keane, W. Mesangial immune injury, hypertension, and progressive glomerular damage in Dahl rats. Kidney Int. 1984, 26, 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, L.; Hua, L.; Xu, H.; Li, C.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, J.; Ding, R. Maternal atmospheric particulate matter exposure and risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 317, 120704. [Google Scholar]
- Morales-Rubio, R.A.; Alvarado-Cruz, I.; Manzano-León, N.; Andrade-Oliva, M.D.; Uribe-Ramirez, M.; Quintanilla-Vega, B.; Osornio-Vargas, Á.; De Vizcaya-Ruiz, A. In utero exposure to ultrafine particles promotes placental stress-induced programming of renin-angiotensin system-related elements in the offspring results in altered blood pressure in adult mice. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2019, 16, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Odat, I.; Chen, H.; Chan, Y.L.; Amgad, S.; Wong, M.G.; Gill, A.; Pollock, C.; Saad, S. The impact of maternal cigarette smoke exposure in a rodent model on renal development in the offspring. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103443. [Google Scholar]
- Popham, K.; Kandasamy, Y. The impact of smoking and nicotine exposure during pregnancy on fetal nephrogenesis: A systematic review. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2023, 14, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chien, M.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Wang, J.H.; Shih, C.L.; Wu, P. Effects of vitamin D in pregnancy on maternal and offspring health-related outcomes: An umbrella review of systematic review and meta-analyses. Nutr. Diabetes 2024, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woods, L.L.; Rasch, R. Perinatal ANG II programs adult blood pressure, glomerular number, and renal function in rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, R1593–R1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, F.G.; Poppi, E.P.; Fanelli, C.; Malheiros, D.M.; Zatz, R.; Fujihara, C.K. AT1 blockade during lactation as a model of chronic nephropathy: Mechanisms of renal injury. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2008, 294, F1345–F1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, J.; Cho, H. Angiotensin receptor blocker induced fetopathy: Two case reports and literature review. Child. Kidney Dis. 2023, 27, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Xu, C. Physiology and Pathophysiology of the Intrarenal Renin-Angiotensin System: An Update. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar]
- Freundlich, M.; Quiroz, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Bravo, Y.; Weisinger, J.R.; Li, Y.C.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, B. Suppression of renin-angiotensin gene expression in the kidney by paricalcitol. Kidney Int. 2008, 74, 1394–1402. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, M.; Gong, J.; Liu, Y.; Xiang, R.; Tan, X. Loss of vitamin D receptor in chronic kidney disease: A potential mechanism linking inflammation to epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2012, 303, F1107–F1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Borst, M.H.; Vervloet, M.G.; ter Wee, P.M.; Navis, G. Cross talk between the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and vitamin D-FGF-23-klotho in chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1603–1609. [Google Scholar]
- de Almeida, L.F.; Francescato, H.D.C.; da Silva, C.G.A.; Costa, R.S.; Coimbra, T.M. Calcitriol reduces kidney development disorders in rats provoked by losartan administration during lactation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11472. [Google Scholar]
- Yim, H.E.; Kim, J.H.; Yoo, K.H.; Bae, I.S.; Hong, Y.S.; Lee, J.W. Spironolactone and enalapril differentially up-regulate the expression of VEGF and heme oxygenase-1 in the neonatal rat kidney. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 69, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, K.H.; Yim, H.E.; Bae, E.S.; Hong, Y.S. Capillary rarefaction and altered renal development: The imbalance between pro- and anti-angiogenic factors in response to angiotensin II inhibition in the developing rat kidney. J. Mol. Histol. 2018, 49, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinning, A.R.; Jensen, B.L.; Johnsen, I.; Chen, D.; Coffman, T.M.; Madsen, K. Vascular endothelial growth factor signaling is necessary for expansion of medullary microvessels during postnatal kidney development. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2016, 311, F586–F599. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.H.; Anderson, S.; Kim, Y.G.; Mazzalli, M.; Suga, S.; Jefferson, J.A.; Gordon, K.L.; Oyama, T.T.; Hughes, J.; Hugo, C.; et al. Impaired angiogenesis in the aging kidney: Vascular endothelial growth factor and thrombospondin-1 in renal disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2001, 37, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson-Cohen, C.; Katz, R.; Price, B.L.; Harju-Baker, S.; Mikacenic, C.; Himmelfarb, J.; Liles, W.C.; Wurfel, M.M. Association of markers of endothelial dysregulation Ang1 and Ang2 with acute kidney injury in critically ill patients. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Song, Q.; Su, X.; Shen, Y.; Yan, H.; Yu, Z.; Li, Z.; Yuan, J.; Huang, J.; Ni, Z.; et al. Serum angiopoietin-2/angiopoietin-1 ratio is associated with cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in peritoneal dialysis patients: A prospective cohort study. Ren. Fail. 2024, 46, 2380037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, Z. Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) and Chronic Kidney Disease. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 254, 183–215. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, E.; Yim, H.-E.; Son, M.-H.; Nam, Y.-J.; Lee, Y.-S.; Jeong, S.-H.; Lee, J.-H. Long-Term Alterations of Renal Microvasculature in Rats Following Maternal PM2.5 Exposure: Vitamin D Effects. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051166
Park E, Yim H-E, Son M-H, Nam Y-J, Lee Y-S, Jeong S-H, Lee J-H. Long-Term Alterations of Renal Microvasculature in Rats Following Maternal PM2.5 Exposure: Vitamin D Effects. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(5):1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051166
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Eujin, Hyung-Eun Yim, Min-Hwa Son, Yoon-Jeong Nam, Yu-Seon Lee, Sang-Hoon Jeong, and Ju-Han Lee. 2025. "Long-Term Alterations of Renal Microvasculature in Rats Following Maternal PM2.5 Exposure: Vitamin D Effects" Biomedicines 13, no. 5: 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051166
APA StylePark, E., Yim, H.-E., Son, M.-H., Nam, Y.-J., Lee, Y.-S., Jeong, S.-H., & Lee, J.-H. (2025). Long-Term Alterations of Renal Microvasculature in Rats Following Maternal PM2.5 Exposure: Vitamin D Effects. Biomedicines, 13(5), 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051166






