Keep an Eye on Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Technology: Secondary Findings and Differential Diagnosis in Inherited Retinal Dystrophies (IRDs)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Variants Potentially Modifying Phenotypes
3.2. Deletions Masked by Apparent Homozygosity
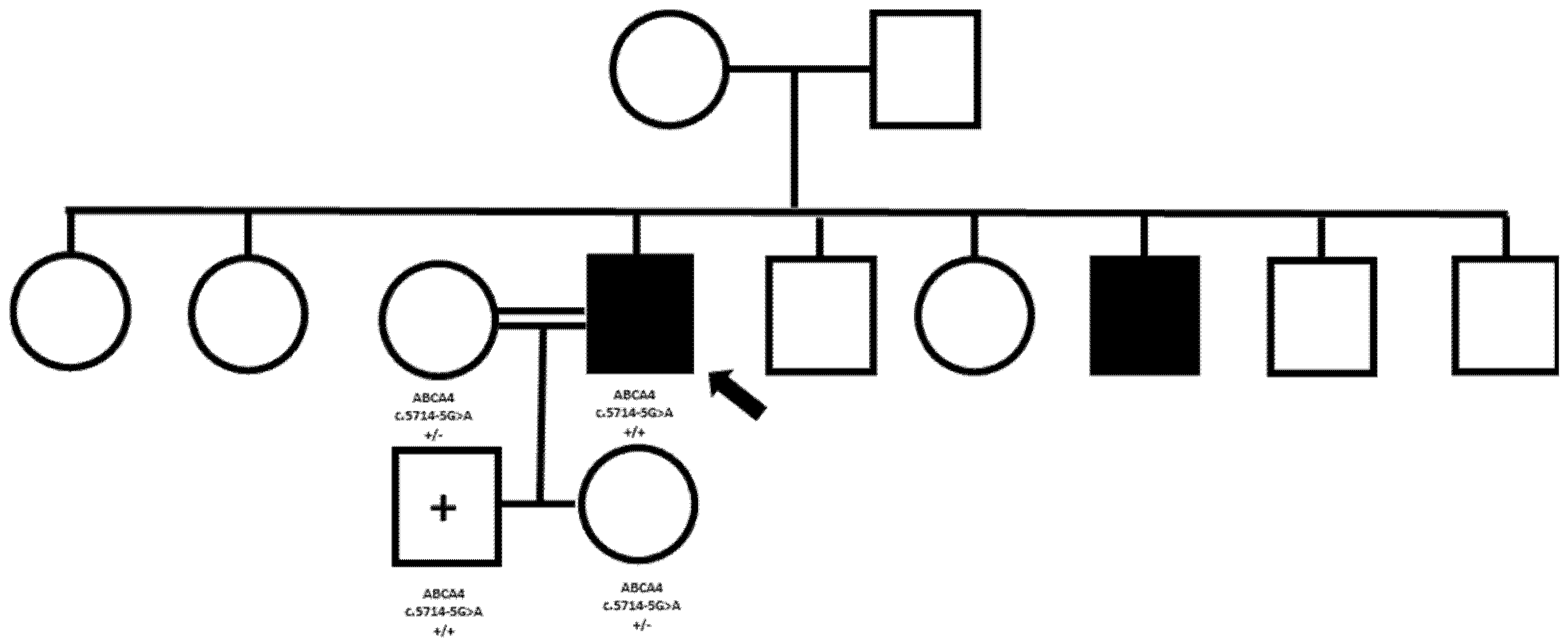
3.3. Pathogenic Variants Leading to Phenotypes Revisitation
3.4. Phenotypic Consequences of High Levels of Consanguinity and Unexpected Preclinical Diagnosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, K.; Garg, S. Navigating the current landscape of clinical genetic testing for inherited retinal dystrophies. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, M. Advances in retina genetics: Progress, potential, and challenges. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2025, 73 (Suppl. S1), S31–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ratra, D.; Ozdek, S.; Raviselvan, M.; Elchuri, S.; Sharma, T. Approach to inherited retinal diseases. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 70, 2305–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gopinath, C.; Rompicherla, R.; Mathias, G.P.; Patil, R.; Poornachandra, B.; Vinekar, A.; Mochi, T.B.; Braganza, S.; Shetty, K.B.; Kumaramanickavel, G.; et al. Inherited retinal disorders: A genotype-phenotype correlation in an Indian cohort and the importance of genetic testing and genetic counselling. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2023, 261, 2003–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontikos, N.; Arno, G.; Jurkute, N.; Schiff, E.; Ba-Abbad, R.; Malka, S.; Gimenez, A.; Georgiou, M.; Wright, G.; Armengol, M.; et al. Genetic Basis of Inherited Retinal Disease in a Molecularly Characterized Cohort of More Than 3000 Families from the United Kingdom. Ophthalmology 2020, 127, 1384–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chiang, J.; Pei, W.; Lamey, T.; McLaren, T.; A Thompson, J.; Montgomery, H.; De Roach, J. Progress and prospects of next-generation sequencing testing for inherited retinal dystrophy. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 15, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathi, M.; Thomas-Wilson, A.; Buchovecky, C.; Dharmadhikari, A.; Barua, S.; Lee, W.; Ruan, M.Z.C.; Soucy, M.; Ragi, S.; Tanaka, J.; et al. Clinical exome sequencing for inherited retinal degenerations at a tertiary care center. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espada-Musitu, D.; Manero-Azua, Á.; Vado, Y.; de Nanclares, G.P. Genetic counselling in the era of next generation sequencing. An. Pediatr. Engl. Ed. 2025, 102, 503712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisschuh, N.; Mayer, A.K.; Strom, T.M.; Kohl, S.; Glöckle, N.; Schubach, M.; Andreasson, S.; Bernd, A.; Birch, D.G.; Hamel, C.P.; et al. Mutation Detection in Patients with Retinal Dystrophies Using Targeted Next Generation Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0145951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sheck, L.H.N.; Esposti, S.D.; Mahroo, O.A.; Arno, G.; Pontikos, N.; Wright, G.; Webster, A.R.; Khan, K.N.; Michaelides, M. Panel-based genetic testing for inherited retinal disease screening 176 genes. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2021, 9, e1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bernardis, I.; Chiesi, L.; Tenedini, E.; Artuso, L.; Percesepe, A.; Artusi, V.; Simone, M.L.; Manfredini, R.; Camparini, M.; Rinaldi, C.; et al. Unravelling the Complexity of Inherited Retinal Dystrophies Molecular Testing: Added Value of Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 6341870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dockery, A.; Whelan, L.; Humphries, P.; Farrar, G.J. Next-Generation Sequencing Applications for Inherited Retinal Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jain, R.; Daigavane, S. Advances and Challenges in Gene Therapy for Inherited Retinal Dystrophies: A Comprehensive Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e69895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Russell, S.; Bennett, J.; A Wellman, J.; Chung, D.C.; Yu, Z.-F.; Tillman, A.; Wittes, J.; Pappas, J.; Elci, O.; McCague, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of voretigene neparvovec (AAV2-hRPE65v2) in patients with RPE65-mediated inherited retinal dystrophy: A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Leroy, B.P.; Fischer, M.D.; Flannery, J.G.; MacLaren, R.E.; Dalkara, D.; Scholl, H.P.; Chung, D.C.; Spera, C.; Viriato, D.; Banhazi, J. Gene Therapy for Inherited Retinal Disease: Long-Term Durability of Effect. Ophthalmic Res. 2023, 66, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittas, D.M.; Gavrilov, Z.; Ucambarlic, E.; Gandor, C.; Otify, D.Y.; Becirovic, E. CRISPR/Cas-Mediated Gene Activation as a Versatile Tool for Treatment of Inherited Retinal Dystrophies. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2025, 1468, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.Y.; Dhaliwal, J.K.; Sasitharan, A.; Kalevar, A. Cell Therapy for Retinal Degenerative Diseases: Progress and Prospects. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Becherucci, V.; Bacci, G.M.; Marziali, E.; Sodi, A.; Bambi, F.; Caputo, R. The New Era of Therapeutic Strategies for the Treatment of Retinitis Pigmentosa: A Narrative Review of Pathomolecular Mechanisms for the Development of Cell-Based Therapies. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nguyen, X.T.; Moekotte, L.; Plomp, A.S.; Bergen, A.A.; van Genderen, M.M.; Boon, C.J.F. Retinitis Pigmentosa: Current Clinical Management and Emerging Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pawar, Y.B.; Thool, A.R. Navigating the Genetic Landscape: A Comprehensive Review of Novel Therapeutic Strategies for Retinitis Pigmentosa Management. Cureus 2024, 16, e67046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Colombo, L.; Maltese, P.E.; Castori, M.; El Shamieh, S.; Zeitz, C.; Audo, I.; Zulian, A.; Marinelli, C.; Benedetti, S.; Costantini, A.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology in 591 Italian Probands With Nonsyndromic Retinitis Pigmentosa and Usher Syndrome. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bolz, H.J. Diagnostic Analyses of Retinal Dystrophy Genes: Current Status and Perspective. Klin. Monbl. Augenheilkd. 2021, 238, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surl, D.; Won, D.; Lee, S.-T.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, J.; Lim, H.T.; Chung, S.A.; Song, W.K.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.S.; et al. Clinician-Driven Reanalysis of Exome Sequencing Data From Patients With Inherited Retinal Diseases. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2414198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Black, G.C.; Sergouniotis, P.; Sodi, A.; Leroy, B.P.; Van Cauwenbergh, C.; Liskova, P.; Grønskov, K.; Klett, A.; Kohl, S.; Taurina, G.; et al. The need for widely available genomic testing in rare eye diseases: An ERN-EYE position statement. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Calzetti, G.; Schwarzwälder, K.; Ottonelli, G.; Kaminska, K.; Strauss, R.W.; De Baere, E.; Leroy, B.P.; Audo, I.; Zeitz, C.; Cursiefen, C.; et al. Genetic Testing of Patients with Inherited Retinal Diseases in the European Countries: An International Survey by the European Vision Institute. Ophthalmic Res. 2024, 67, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzàlez-Duarte, R.; de Castro-Miró, M.; Tuson, M.; Ramírez-Castañeda, V.; Gils, R.V.; Marfany, G. Scaling New Heights in the Genetic Diagnosis of Inherited Retinal Dystrophies. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1185, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méjécase, C.; Malka, S.; Guan, Z.; Slater, A.; Arno, G.; Moosajee, M. Practical guide to genetic screening for inherited eye diseases. Ther. Adv. Ophthalmol. 2020, 12, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Paudel, N.; Daly, A.; Waters, F.; Stratieva, P. Genetic Testing Experiences of People Living with Inherited Retinal Degenerations: Results of a Global Survey. Ophthalmic Res. 2024, 67, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela, M.D.; Bellingham, J.; Motta, F.; Jurkute, N.; Ellingford, J.M.; Quinodoz, M.; Oprych, K.; Niblock, M.; Janeschitz-Kriegl, L.; Kaminska, K.; et al. Multidisciplinary team directed analysis of whole genome sequencing reveals pathogenic non-coding variants in molecularly undiagnosed inherited retinal dystrophies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2023, 32, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Marques, J.P.; Soares, C.A.; Carvalho, A.L.; Estrela-Silva, S.; Santos, L.C.; Ramos, L.; Silva, E. Portuguese Society of Ophthalmology and Portuguese Society of Human Genetics Joint Clinical Practice Guidelines for Genetic Testing in Inherited Retinal Dystrophies. Clin. Genet. 2025, 107, 600–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, X.; Tao, T.; Zhao, L.; Li, G.; Yang, L. Molecular diagnosis based on comprehensive genetic testing in 800 Chinese families with non-syndromic inherited retinal dystrophies. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2021, 49, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindstrand, A.; Frangakis, S.; Carvalho, C.M.; Richardson, E.B.; McFadden, K.A.; Willer, J.R.; Pehlivan, D.; Liu, P.; Pediaditakis, I.L.; Sabo, A.; et al. Copy-Number Variation Contributes to the Mutational Load of Bardet-Biedl Syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 318–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, X.; Dai, H.; Li, G.; Jia, R.; Meng, X.; Yu, S.; Yang, L.; Hong, J. Screening copy number variations in 35 unsolved inherited retinal disease families. Hum. Genet. 2024, 143, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schulz, H.L.; Grassmann, F.; Kellner, U.; Spital, G.; Rüther, K.; Jägle, H.; Hufendiek, K.; Rating, P.; Huchzermeyer, C.; Baier, M.J.; et al. Mutation Spectrum of the ABCA4 Gene in 335 Stargardt Disease Patients From a Multicenter German Cohort-Impact of Selected Deep Intronic Variants and Common SNPs. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cehajic-Kapetanovic, J.; Birtel, J.; McClements, M.E.; Shanks, M.E.; Clouston, P.; Downes, S.M.; Issa, P.C.; MacLaren, R.E. Clinical and Molecular Characterization of PROM1-Related Retinal Degeneration. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e195752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Plagnol, V.; Curtis, J.; Epstein, M.; Mok, K.Y.; Stebbings, E.; Grigoriadou, S.; Wood, N.W.; Hambleton, S.; Burns, S.O.; Thrasher, A.J.; et al. A robust model for read count data in exome sequencing experiments and implications for copy number variant calling. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2747–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shibata, A.; Sugiura, K.; Suzuki, A.; Ichiki, T.; Akiyama, M. Apparent homozygosity due to compound heterozygosity of one point mutation and an overlapping exon deletion mutation in ABCA12: A genetic diagnostic pitfall. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 80, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Schil, K.; Naessens, S.; Van de Sompele, S.; Carron, M.; Aslanidis, A.; Van Cauwenbergh, C.; Mayer, A.K.; Van Heetvelde, M.; Bauwens, M.; Verdin, H.; et al. Mapping the genomic landscape of inherited retinal disease genes prioritizes genes prone to coding and noncoding copy-number variations. Genet. Med. 2018, 20, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bujakowska, K.M.; Fernandez-Godino, R.; Place, E.; Consugar, M.; Navarro-Gomez, D.; White, J.; Bedoukian, E.C.; Zhu, X.; Xie, H.M.; Gai, X.; et al. Copy-number variation is an important contributor to the genetic causality of inherited retinal degenerations. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Introne, W.J.; Huizing, M.; Malicdan, M.C.V.; O’Brien, K.J.; Gahl, W.A. Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., et al., Eds.; University of Washington, Seattle: Seattle, WA, USA, 2000; pp. 1993–2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1287/ (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Raimondi, R.; D’esposito, F.; Sorrentino, T.; Tsoutsanis, P.; De Rosa, F.P.; Stradiotto, E.; Barone, G.; Rizzato, A.; Allegrini, D.; Costagliola, C.; et al. How to Set Up Genetic Counselling for Inherited Macular Dystrophies: Focus on Genetic Characterization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Katsanis, N.; Ansley, S.J.; Badano, J.L.; Eichers, E.R.; Lewis, R.A.; Hoskins, B.E.; Scambler, P.J.; Davidson, W.S.; Beales, P.L.; Lupski, J.R. Triallelic inheritance in Bardet-Biedl syndrome, a Mendelian recessive disorder. Science 2001, 293, 2256–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichers, E.; Lewis, R.A.; Katsanis, N.; Lupski, J.R. Triallelic inheritance: A bridge between Mendelian and multifactorial traits. Ann. Med. 2004, 36, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beales, P.L.; Elcioglu, N.; Woolf, A.S.; Parker, D.; A Flinter, F. New criteria for improved diagnosis of Bardet-Biedl syndrome: Results of a population survey. J. Med. Genet. 1999, 36, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Green, J.S.; Parfrey, P.S.; Harnett, J.D.; Farid, N.R.; Cramer, B.C.; Johnson, G.; Heath, O.; McManamon, P.J.; O’Leary, E.; Pryse-Phillips, W. The cardinal manifestations of Bardet-Biedl syndrome, a form of Laurence-Moon-Biedl syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 321, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dollfus, H.; Lilien, M.R.; Maffei, P.; Verloes, A.; Muller, J.; Bacci, G.M.; Cetiner, M.; van den Akker, E.L.T.; Pechhacker, M.G.; Testa, F.; et al. Bardet-Biedl syndrome improved diagnosis criteria and management: Inter European Reference Networks consensus statement and recommendations. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2024, 32, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- RetNet. Available online: https://retnet.org/ (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- OMIM. Available online: https://www.omim.org/ (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Chen, J.; Smaoui, N.; Hammer, M.B.H.; Jiao, X.; Riazuddin, S.A.; Harper, S.; Katsanis, N.; Chaabouni, H.; Berson, E.L.; Hejtmancik, J.F. Molecular analysis of Bardet-Biedl syndrome families: Report of 21 novel mutations in 10 genes. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 5317–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Badano, J.L.; Katsanis, N. Beyond Mendel: An evolving view of human genetic disease transmission. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, J.S.; Georgiou, M.; Kalitzeos, A.; Moore, A.T.; Michaelides, M. Progressive cone and cone-rod dystrophies: Clinical features, molecular genetics and prospects for therapy. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 103, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tsang, S.H.; Sharma, T. Progressive Cone Dystrophy and Cone-Rod Dystrophy (XL, AD, and AR). Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1085, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolz, H.J. Genetische Diagnostik von Netzhautdystrophien: Revolutionierung durch neue Methoden der DNA-Sequenzierung [Genetic diagnostics of retinal dystrophies: Breakthrough with new methods of DNA sequencing]. Ophthalmologe 2018, 115, 1028–1034, In German. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiff, C.; Owczarek-Lipska, M.; Spital, G.; Röger, C.; Hinz, H.; Jüschke, C.; Thiele, H.; Altmüller, J.; Nürnberg, P.; Da Costa, R.; et al. The mutation p.E113K in the Schiff base counterion of rhodopsin is associated with two distinct retinal phenotypes within the same family. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Donato, L.; Alibrandi, S.; Scimone, C.; Rinaldi, C.; Dascola, A.; Calamuneri, A.; D’angelo, R.; Sidoti, A. The impact of modifier genes on cone-rod dystrophy heterogeneity: An explorative familial pilot study and a hypothesis on neurotransmission impairment. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0278857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dizhoor, A.M.; Lowe, D.G.; Olshevskaya, E.V.; Laura, R.P.; Hurley, J.B. The human photoreceptor membrane guanylyl cyclase, RetGC, is present in outer segments and is regulated by calcium and a soluble activator. Neuron 1994, 12, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzahem, T.A.; AlTheeb, A.; Ba-Abbad, R. PRPS1-associated retinopathy: A diagnostic odyssey. Ophthalmic Genet. 2024, 45, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, T.B.; Schultz, J.M.; Ahmed, Z.M.; Tsilou, E.T.; Brewer, C.C. Usher syndrome: Hearing loss with vision loss. Adv. Otorhinolaryngol. 2011, 70, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, E.; Märker, T.; Daser, A.; Frey-Mahn, G.; Beyer, V.; Farcas, R.; Schneider-Rätzke, B.; Kohlschmidt, N.; Grossmann, B.; Bauss, K.; et al. Homozygous disruption of PDZD7 by reciprocal translocation in a consanguineous family: A new member of the Usher syndrome protein interactome causing congenital hearing impairment. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Sheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Sun, X.; Jiang, C.; Qi, R.; Yuan, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, G.; et al. Distinct mutations with different inheritance mode caused similar retinal dystrophies in one family: A demonstration of the importance of genetic annotations in complicated pedigrees. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jones, K.D.; Wheaton, D.K.; Bowne, S.J.; Sullivan, L.S.; Birch, D.G.; Chen, R.; Daiger, S.P. Next-generation sequencing to solve complex inherited retinal dystrophy: A case series of multiple genes contributing to disease in extended families. Mol. Vis. 2017, 23, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zenteno, J.C.; García-Montaño, L.A.; Cruz-Aguilar, M.; Ronquillo, J.; Rodas-Serrano, A.; Aguilar-Castul, L.; Matsui, R.; Vencedor-Meraz, C.I.; Arce-González, R.; Graue-Wiechers, F.; et al. Extensive genic and allelic heterogeneity underlying inherited retinal dystrophies in Mexican patients molecularly analyzed by next-generation sequencing. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Di Iorio, E.; Adamo, G.G.; Sorrentino, U.; De Nadai, K.; Barbaro, V.; Mura, M.; Pellegrini, M.; Boaretto, F.; Tavolato, M.; Suppiej, A.; et al. Pseudodominant inheritance of retinitis pigmentosa in a family with mutations in the Eyes Shut Homolog (EYS) gene. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- D’esposito, F.; Cennamo, G.; de Crecchio, G.; Maltese, P.E.; Cecchin, S.; Bertelli, M.; Ziccardi, L.; Veneruso, P.E.; Magli, A.; Cennamo, G.; et al. Multimodal Imaging in Autosomal Dominant Cone-Rod Dystrophy Caused by Novel CRX Variant. Ophthalmic Res. 2018, 60, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Esposito, F.; Capobianco, M.; Gagliano, C.; Avitabile, A.; Gagliano, G.; Esposito, G.; Dammino, E.; Carotenuto, A.; Zeppieri, M. Keep an Eye on Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Technology: Secondary Findings and Differential Diagnosis in Inherited Retinal Dystrophies (IRDs). Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051117
D’Esposito F, Capobianco M, Gagliano C, Avitabile A, Gagliano G, Esposito G, Dammino E, Carotenuto A, Zeppieri M. Keep an Eye on Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Technology: Secondary Findings and Differential Diagnosis in Inherited Retinal Dystrophies (IRDs). Biomedicines. 2025; 13(5):1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051117
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Esposito, Fabiana, Matteo Capobianco, Caterina Gagliano, Alessandro Avitabile, Giuseppe Gagliano, Gabriella Esposito, Edoardo Dammino, Antonio Carotenuto, and Marco Zeppieri. 2025. "Keep an Eye on Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Technology: Secondary Findings and Differential Diagnosis in Inherited Retinal Dystrophies (IRDs)" Biomedicines 13, no. 5: 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051117
APA StyleD’Esposito, F., Capobianco, M., Gagliano, C., Avitabile, A., Gagliano, G., Esposito, G., Dammino, E., Carotenuto, A., & Zeppieri, M. (2025). Keep an Eye on Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Technology: Secondary Findings and Differential Diagnosis in Inherited Retinal Dystrophies (IRDs). Biomedicines, 13(5), 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051117








