The Effects of the Biological Agents Infliximab, Vedolizumab, and Ustekinumab on Intestinal Anastomosis: An Experimental Study in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethics
2.2. Experimental Protocol
2.2.1. Rat Experimental Model and Administration Protocol
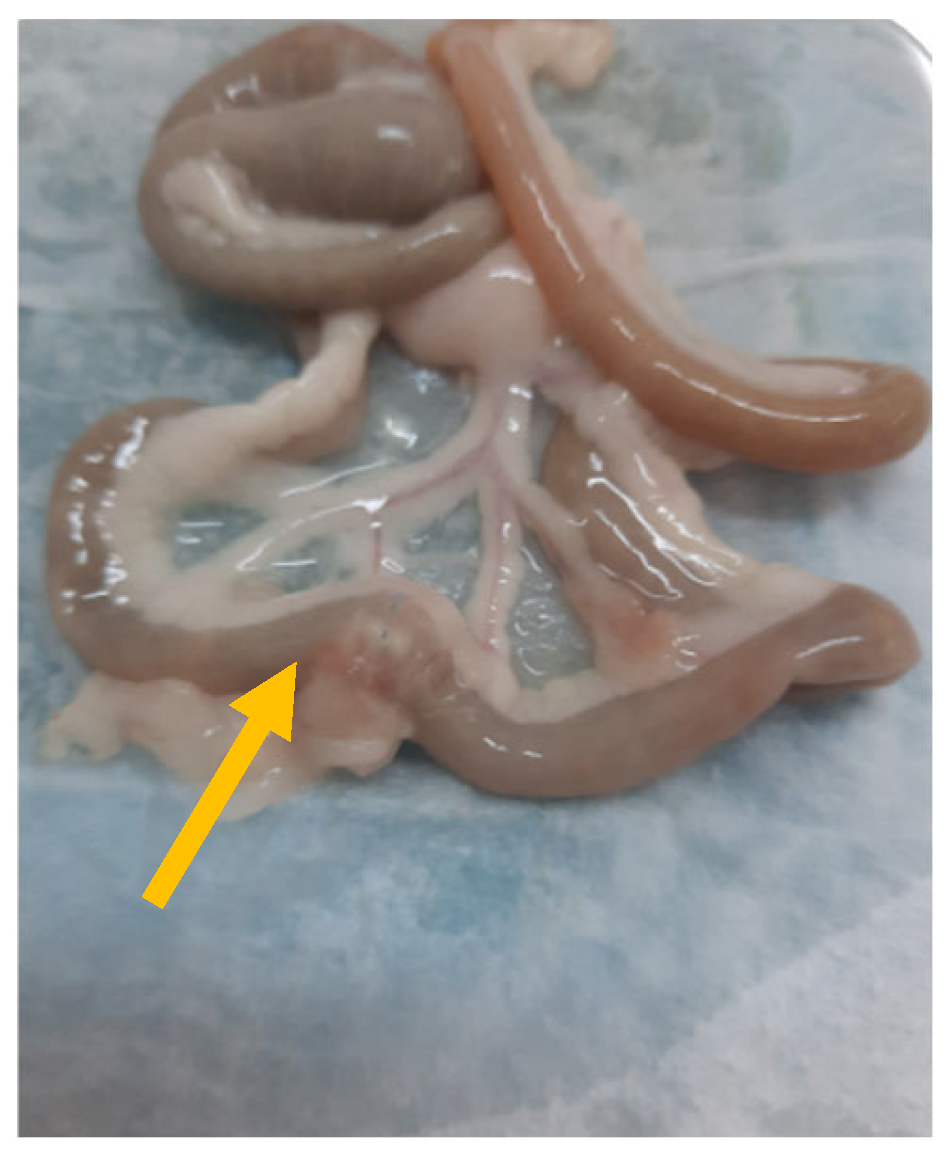
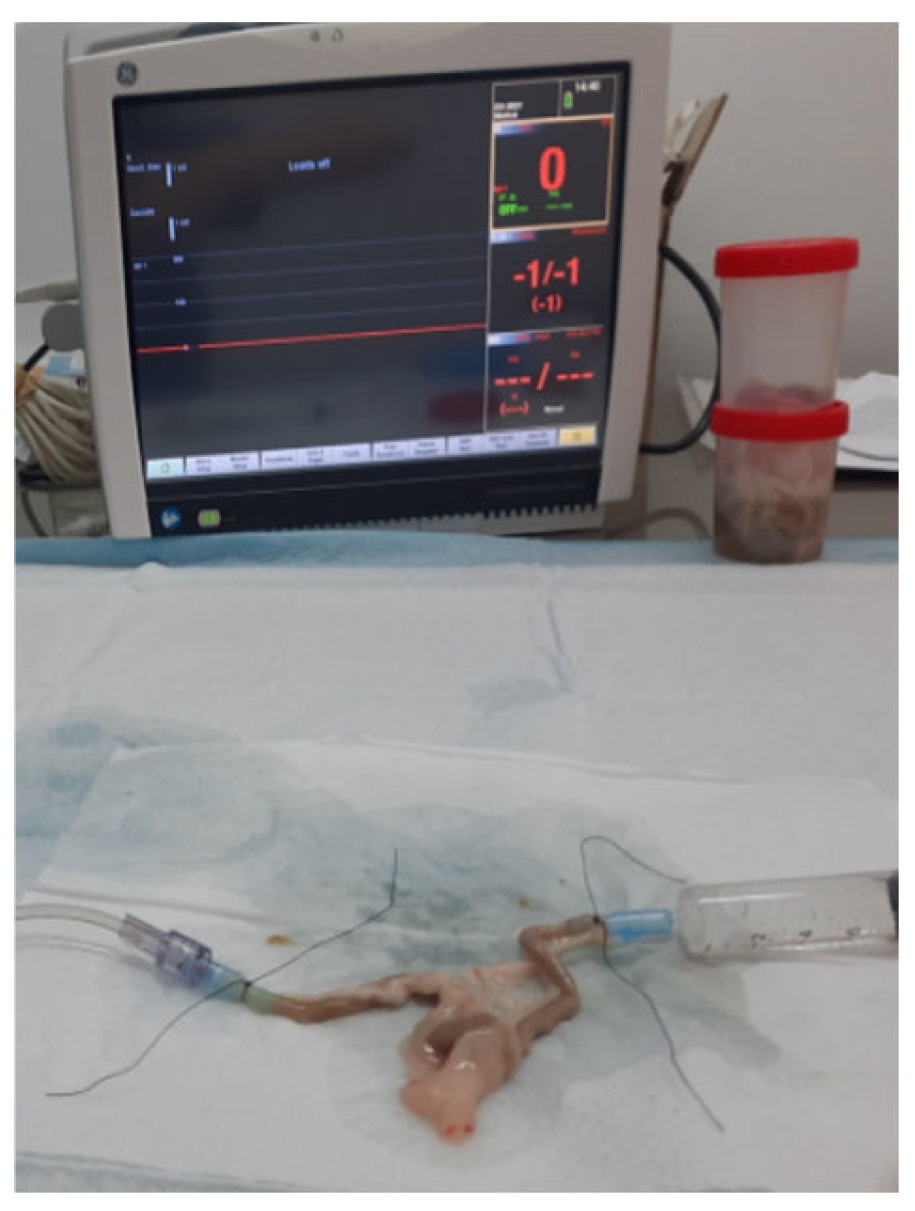
2.2.2. Bursting Pressure Measurement
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| POD | Postoperative day |
| BP | Bursting pressure |
| IBDs | Inflammatory bowel diseases |
| INFL | Infliximab |
| VDLZ | Vedolizumab |
| USTK | Ustekinumab |
References
- Lawson, M.M.; Thomas, A.G.; Akobeng, A.K. Tumour necrosis factor alpha blocking agents for induction of remission in ulcerative colitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 3, Cd005112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mor, I.J.; Vogel, J.D.; da Luz Moreira, A.; Shen, B.; Hammel, J.; Remzi, F.H. Infliximab in ulcerative colitis is associated with an increased risk of postoperative complications after restorative proctocolectomy. Dis. Colon Rectum 2008, 51, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poritz, L.S.; Rowe, W.A.; Koltun, W.A. Remicade does not abolish the need for surgery in fistulizing Crohn’s disease. Dis. Colon Rectum 2002, 45, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhofstad, M.H.; Lange, W.P.; van der Laak, J.A.; Verhofstad, A.A.; Hendriks, T. Microscopic analysis of anastomotic healing in the intestine of normal and diabetic rats. Dis. Colon Rectum 2001, 44, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inan, A.; Koca, C.; Sen, M. Effects of diclofenac sodium on bursting pressures of anastomoses and hydroxyproline contents of perianastomotic tissues in a laboratory study. Int. J. Surg. 2006, 4, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundmann, S.; Hoefer, I.; Ulusans, S.; van Royen, N.; Schirmer, S.H.; Ozaki, C.K.; Bode, C.; Piek, J.J.; Buschmann, I. Anti-tumor necrosis factor-{alpha} therapies attenuate adaptive arteriogenesis in the rabbit. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, H1497–H1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeuchi, D.; Onodera, H.; Aung, T.; Kan, S.; Kawamoto, K.; Imamura, M.; Maetani, S. Correlation of tensile strength with bursting pressure in the evaluation of intestinal anastomosis. Dig. Surg. 1999, 16, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhter, A.B.; Berchenko, G.N.; Nikolaev, A.V. Macrophage-fibroblast interaction and its possible role in regulating collagen metabolism during wound healing. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 1977, 83, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coquet-Reinier, B.; Berdah, S.V.; Grimaud, J.C.; Birnbaum, D.; Cougard, P.A.; Barthet, M.; Desjeux, A.; Moutardier, V.; Brunet, C. Preoperative infliximab treatment and postoperative complications after laparoscopic restorative proctocolectomy with ileal pouch-anal anastomosis: A case-matched study. Surg. Endosc. 2010, 24, 1866–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, C.C.Y.; Narula, A.; Lightner, A.L.; McKenna, N.P.; Colombel, J.F.; Narula, N. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: Preoperative Vedolizumab Treatment and Postoperative Complications in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2018, 12, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Jiang, K.; Hong, J.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, B. Association between vedolizumab and postoperative complications in IBD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2021, 36, 2081–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, R.; Mohan, B.P.; Ponnada, S.; Regueiro, M.; Lightner, A.L.; Click, B. Postoperative outcomes after preoperative ustekinumab exposure in patients with Crohn’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2021, 34, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, H.H.; Ma, C.; Kotze, P.G.; Seow, C.H.; Al-Farhan, H.; Al-Darmaki, A.K.; Pang, J.X.Q.; Fedorak, R.N.; Devlin, S.M.; Dieleman, L.A.; et al. Preoperative Ustekinumab Treatment Is Not Associated With Increased Postoperative Complications in Crohn’s Disease: A Canadian Multi-Centre Observational Cohort Study. J. Can. Assoc. Gastroenterol. 2018, 1, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaconstantinou, I.; Zeglinas, C.; Gazouli, M.; Nastos, K.; Yiallourou, A.; Lykoudis, P.; Evangelou, K.; Papalois, A.; Papaioannou, M.; Vlachogiannakos, J.; et al. Effect of infliximab on the healing of intestinal anastomosis. An experimental study in rats. Int. J. Surg. 2014, 12, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploug, T.; Andersen, K.; Hansen, K.; Hjelmborg, J.; Qvist, N. Influence of adalimumab treatment on anastomotic strength, degree of inflammation, and collagen formation: An experimental study on the small intestine of rabbits. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabau, M.; Eyal, A.; Kluger, Y.; Dayan, D. Bursting pressure in anastomotic healing in experimentally induced colitis in rats. Dis. Colon Rectum 1998, 41, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, D.E.; Horesh, N.; Lightner, A.L.; Ben-Horin, S.; Eliakim, R.; Koulaouzidis, A.; Kopylov, U. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis: Vedolizumab and Postoperative Complications in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 2327–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainsbury, M.L.; Chu, D.I.; Howard, L.A.; Coukos, J.A.; Farraye, F.A.; Stucchi, A.F.; Becker, J.M. Preoperative infliximab is not associated with an increased risk of short-term postoperative complications after restorative proctocolectomy and ileal pouch-anal anastomosis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2011, 15, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00065 (accessed on 30 November 2024).
- Chlumsky, V. Experimentelle Untersuchungen über die verschiedenen Methoden der Darmvereinigung. Beitr. Klein. Chir. 1899, 25, 539–600. [Google Scholar]
- Jiborn, H.; Ahonen, J.; Zederfeldt, B. Healing of experimental colonic anastomoses. I. Bursting strength of the colon after left colon resection and anastomosis. Am. J. Surg. 1978, 136, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Roy van Zuidewijn, D.B.; Hendriks, T.; Wobbes, T.; Klompmakers, A.A.; de Boer, H.H. Healing of experimental colonic anastomoses: Effect of antineoplastic agents. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 1987, 13, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wise, L.; McAlister, W.; Stein, T.; Schuck, P. Studies on the healing of anastomoses of small and large intestines. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1975, 141, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uzunlu, O.; Aydin, E.; Çomut, E.; Avcı, E.; Şenol, H. The comparison of the suture materials on intestinal anastomotic healing: An experimental study. Turk. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2023, 29, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaresma, A.B.; Yamamoto, T.; Kotze, P.G. Biologics and surgical outcomes in Crohn’s disease: Is there a direct relationship? Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820931738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterland, P.; Athanasiou, T.; Patel, H. Post-operative abdominal complications in Crohn’s disease in the biological era: Systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2016, 8, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, L.; An, P.; Zhou, B.; Liu, G. Meta-Analysis: The Influence of Preoperative Infliximab Use on Postoperative Complications of Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hussuna, A.; Krag, A.; Olaison, G.; Bendtsen, F.; Gluud, L.L. The effect of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha agents on postoperative anastomotic complications in Crohn’s disease: A systematic review. Dis. Colon Rectum 2013, 56, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaconstantinou, I.; Zeglinas, C.; Gazouli, M.; Nastos, K.; Yiallourou, A.; Papalois, A.; Tzathas, C. The impact of peri-operative anti-TNF treatment on anastomosis-related complications in Crohn’s disease patients. A critical review. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2014, 18, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poylin, V.Y.; Serrato, J.C.; Pastrana Del Valle, J.; Feuerstein, J.D. Vedolizumab does not increase perioperative surgical complications in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, cohort study. Intest. Res. 2022, 20, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novello, M.; Stocchi, L.; Holubar, S.; Shawki, S.; Lipman, J.; Gorgun, E.; Hull, T.; Steele, S.R. Surgical outcomes of patients treated with ustekinumab vs. vedolizumab in inflammatory bowel disease: A matched case analysis. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2019, 34, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightner, A.L.; Raffals, L.E.; Mathis, K.L.; Cima, R.R.; Tse, C.S.; Pemberton, J.H.; Dozois, E.J.; Loftus, E.V. Postoperative Outcomes in Vedolizumab-Treated Patients Undergoing Abdominal Operations for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2017, 11, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightner, A.L.; McKenna, N.P.; Tse, C.S.; Hyman, N.; Smith, R.; Ovsepyan, G.; Fleshner, P.; Crowell, K.; Koltun, W.; Ferrante, M.; et al. Postoperative Outcomes in Ustekinumab-Treated Patients Undergoing Abdominal Operations for Crohn’s Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2018, 12, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novello, M.; Stocchi, L.; Steele, S.R.; Holubar, S.D.; Duraes, L.C.; Kessler, H.; Shawki, S.; Hull, L.T. Case-matched Comparison of Postoperative Outcomes Following Surgery for Inflammatory Bowel Disease After Exposure to Vedolizumab vs Other Biologics. J. Crohns Colitis 2020, 14, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightner, A.L.; McKenna, N.P.; Alsughayer, A.; Harmsen, W.S.; Taparra, K.; Parker, M.E.; Raffals, L.E.; Loftus, E.V., Jr. Biologics and 30-Day Postoperative Complications After Abdominal Operations for Crohn’s Disease: Are There Differences in the Safety Profiles? Dis. Colon Rectum 2019, 62, 1352–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandivort, T.C.; Horton, D.B.; Johnson, S.B. Regulatory and strategic considerations for addressing immunogenicity and related responses in biopharmaceutical development programs. J. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2020, 4, 547–555. [Google Scholar]
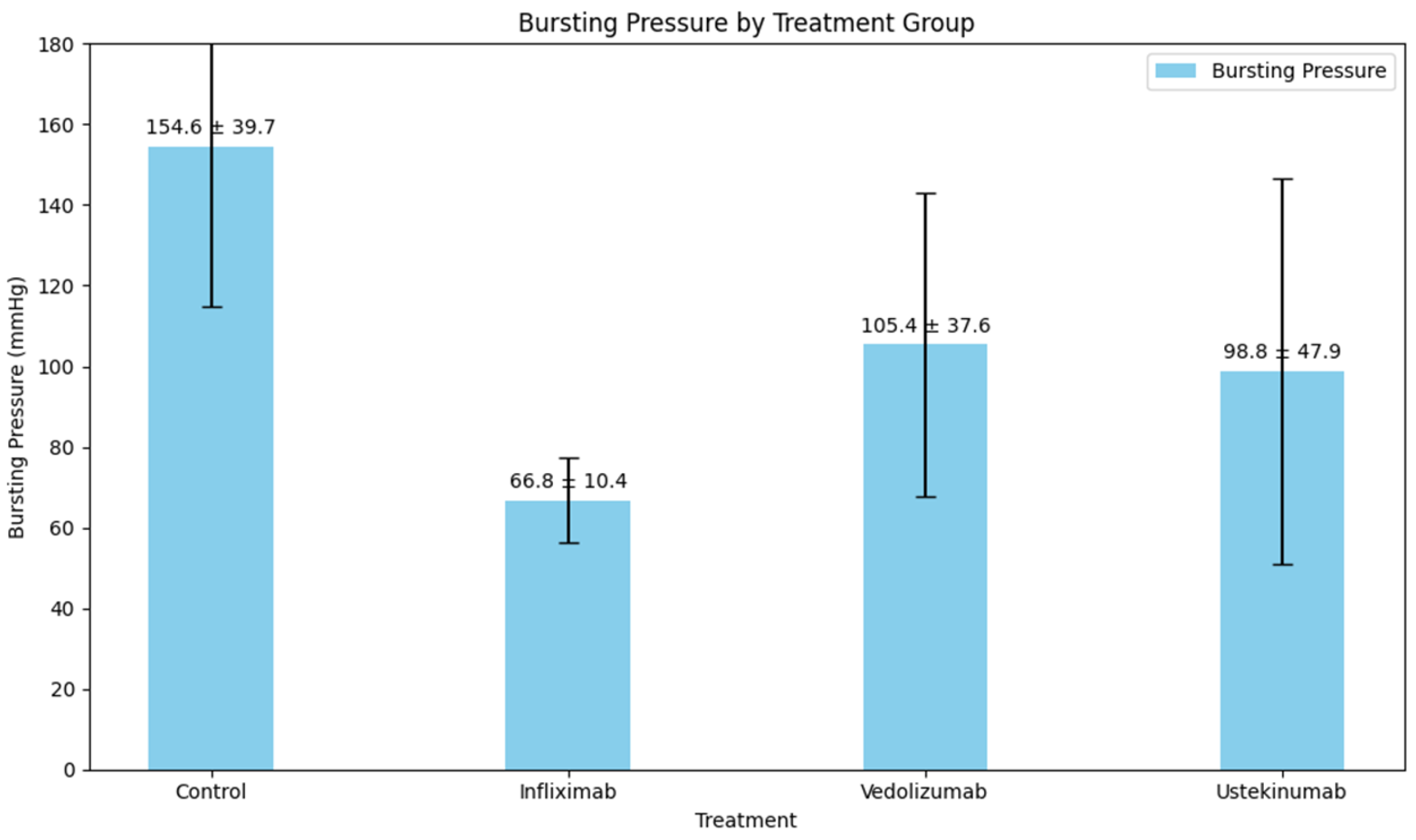

| Type of Comparison | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| One-way ANOVA | <0.001 | |
| Subgroup Analysis | Bursting Pressure (mmHg) [mean ± SD] | |
| Control vs. infliximab | 154.6 ± 39.7 vs. 66.8 ± 10.4 | <0.001 |
| Control vs. vedolizumab | 154.6 ± 39.7 vs. 105.4 ± 37.6 | <0.001 |
| Control vs. ustekinumab | 154.6 ± 39.7 vs. 98.8 ± 47.9 | 0.051 |
| Infliximab vs. vedolizumab | 66.8 ± 10.4 vs. 105.4 ± 37.6 | 1.000 |
| Infliximab vs. ustekinumab | 66.8 ± 10.4 vs. 98.8 ± 47.9 | 0.207 |
| Vedolizumab vs. ustekinumab | 105.4 ± 37.6 vs. 98.8 ± 47.9 | 0.365 |
| Event | Group | Observed | Not Observed | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mortality | Control | 0 | 10 | 0.021 |
| Infliximab | 0 | 10 | ||
| Vedolizumab | 0 | 10 | ||
| Ustekinumab | 3 | 7 | ||
| Anastomotic Leak | Control | 1 | 9 | 0.877 |
| Infliximab | 1 | 9 | ||
| Vedolizumab | 1 | 9 | ||
| Ustekinumab | 2 | 8 |
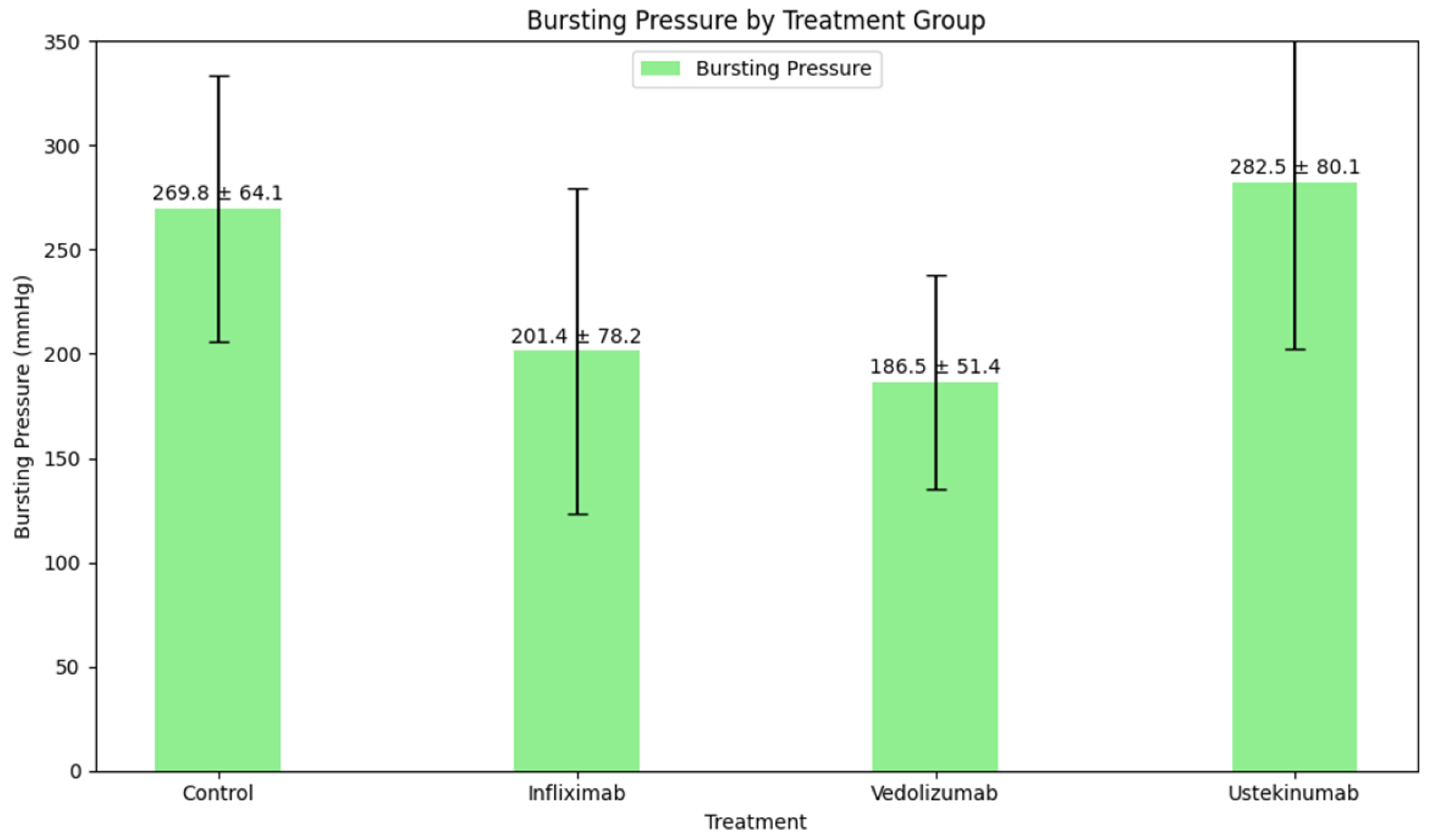
| Type of Comparison | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| One-way ANOVA | 0.008 | |
| Subgroup Analysis | Bursting Pressure (mmHg) [mean ± SD] | |
| Control vs. infliximab | 269.8 ± 64.1 vs. 201.4 ± 78.2 | 0.212 |
| Control vs. vedolizumab | 269.8 ± 64.1 vs. 186.5 ± 51.4 | 0.083 |
| Control vs. ustekinumab | 269.8 ± 64.1 vs. 282.5 ± 80.1 | 1.000 |
| Infliximab vs. vedolizumab | 201.4 ± 78.2 vs. 186.5 ± 51.4 | 1.000 |
| Infliximab vs. ustekinumab | 201.4 ± 78.2 vs. 282.5 ± 80.1 | 0.031 |
| Vedolizumab vs. ustekinumab | 186.5 ± 51.4 vs. 282.5 ± 80.1 | 0.031 |
| Event | Group | Observed | Not Observed | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mortality | Control | 0 | 10 | 0.380 |
| Infliximab | 0 | 10 | ||
| Vedolizumab | 1 | 9 | ||
| Ustekinumab | 0 | 10 | ||
| Anastomotic Leak | Control | 0 | 10 | N/A |
| Infliximab | 0 | 10 | ||
| Vedolizumab | 0 | 10 | ||
| Ustekinumab | 0 | 10 |
| Group | Dehiscence Pressure (mmHg) [mean ± SD] | p-Value * | p-Value # | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 3 | Day 7 | |||
| Control | 154.6 ± 39.7 | 269.8 ± 64.1 | 0.005 | 0.008 |
| Infliximab | 66.8 ± 10.4 | 201.4 ± 78.2 | 0.005 | 0.008 |
| Vedolizumab | 105.4 ± 37.6 | 186.5 ± 51.4 | 0.008 | 0.012 |
| Ustekinumab | 98.8 ± 47.9 | 282.5 ± 80.1 | 0.028 | 0.068 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Menni, A.; Tzikos, G.; Goulas, P.; Chatziantoniou, G.; Vouchara, A.; Apostolidis, A.S.; Ioannidis, A.; Germanidis, G.; Papazoglou, L.G.; Giouleme, O.; et al. The Effects of the Biological Agents Infliximab, Vedolizumab, and Ustekinumab on Intestinal Anastomosis: An Experimental Study in Rats. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051079
Menni A, Tzikos G, Goulas P, Chatziantoniou G, Vouchara A, Apostolidis AS, Ioannidis A, Germanidis G, Papazoglou LG, Giouleme O, et al. The Effects of the Biological Agents Infliximab, Vedolizumab, and Ustekinumab on Intestinal Anastomosis: An Experimental Study in Rats. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(5):1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051079
Chicago/Turabian StyleMenni, Alexandra, Georgios Tzikos, Patroklos Goulas, George Chatziantoniou, Angeliki Vouchara, Athanasios S. Apostolidis, Aristeidis Ioannidis, Georgios Germanidis, Lyssimachos G. Papazoglou, Olga Giouleme, and et al. 2025. "The Effects of the Biological Agents Infliximab, Vedolizumab, and Ustekinumab on Intestinal Anastomosis: An Experimental Study in Rats" Biomedicines 13, no. 5: 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051079
APA StyleMenni, A., Tzikos, G., Goulas, P., Chatziantoniou, G., Vouchara, A., Apostolidis, A. S., Ioannidis, A., Germanidis, G., Papazoglou, L. G., Giouleme, O., & Apostolidis, S. (2025). The Effects of the Biological Agents Infliximab, Vedolizumab, and Ustekinumab on Intestinal Anastomosis: An Experimental Study in Rats. Biomedicines, 13(5), 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051079






