Defective Intracortical Inhibition as a Marker of Impaired Neural Compensation in Amputees Undergoing Rehabilitation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Sociodemographic, Clinical, and Other Neurophysiological Variables
2.4. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Regression Models
3.1.1. Resting Motor Threshold (rMT) Models
3.1.2. Motor-Evoked Potential (MEP) Models
3.1.3. Short Intracortical Inhibition (SICI) Models
3.1.4. Intracortical Facilitation (ICF) Models
4. Discussion
4.1. ICF in the Non-Affected Hemisphere
4.2. SICI in Both Hemispheres
4.3. rMT in the Non-Affected Hemisphere
4.4. MEP Amplitudes in the Affected Hemisphere
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CI | Confidence interval |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| ESS | Epworth Sleepiness Scale |
| FIM | Functional Independence Measure |
| HAS | Hospital Anxiety Scale |
| HDS | Hospital Depression Scale |
| ICF | Intracortical facilitation |
| LLA | Lower-limb amputation |
| MEP | Motor-evoked potential |
| MoCA | Montreal Cognitive Assessment |
| OSAS | Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome |
| PLP | Phantom limb pain |
| PLS | Phantom limb sensation |
| RLP | Residual limb pain |
| rMT | Resting motor threshold |
| SICI | Short intracortical inhibition |
| TMS | Transcranial magnetic stimulation |
| VIF | Variance inflation factor |
References
- Hughes, W.; Goodall, R.; Salciccioli, J.D.; Marshall, D.C.; Davies, A.H.; Shalhoub, J. Editor’s Choice—Trends in Lower Extremity Amputation Incidence in European Union 15+ Countries 1990–2017. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2020, 60, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moxey, P.W.; Gogalniceanu, P.; Hinchliffe, R.J.; Loftus, I.M.; Jones, K.J.; Thompson, M.M.; Holt, P.J. Lower extremity amputations—A review of global variability in incidence. Diabet. Med. 2011, 28, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler-Graham, K.; MacKenzie, E.J.; Ephraim, P.L.; Travison, T.G.; Brookmeyer, R. Estimating the prevalence of limb loss in the United States: 2005 to 2050. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2008, 89, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortington, L.V.; Geertzen, J.H.; van Netten, J.J.; Postema, K.; Rommers, G.M.; Dijkstra, P.U. Short and long term mortality rates after a lower limb amputation. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2013, 46, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R.; van den Heuvel, W.J.; Arokiasamy, P. Factors affecting quality of life in lower limb amputees. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2011, 35, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devan, H.; Tumilty, S.; Smith, C. Physical activity and lower-back pain in persons with traumatic transfemoral amputation: A national cross-sectional survey. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2012, 49, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenkreis, P.; Pleger, B.; Cornelius, B.; Weyen, U.; Dertwinkel, R.; Zenz, M.; Malin, J.P.; Tegenthoff, M. Reorganization in the ipsilateral motor cortex of patients with lower limb amputation. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 349, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Corwell, B.; Yaseen, Z.; Hallett, M.; Cohen, L.G. Mechanisms of cortical reorganization in lower-limb amputees. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 3443–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flor, H. Phantom-limb pain: Characteristics, causes, and treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2002, 1, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.P.; Katz, J.; Davis, K.D. Stability of phantom limb phenomena after upper limb amputation: A longitudinal study. Neuroscience 2008, 156, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunduz, M.E.; Pinto, C.B.; Saleh Velez, F.G.; Duarte, D.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Lopes, F.; Fregni, F. Motor Cortex Reorganization in Limb Amputation: A Systematic Review of TMS Motor Mapping Studies. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Pinto, C.B.; Saleh Velez, F.G.; Duarte, D.; Gunduz, M.E.; Simis, M.; Lepesteur Gianlorenco, A.C.; Barouh, J.L.; Crandell, D.; Guidetti, M.; et al. Structural and functional motor cortex asymmetry in unilateral lower limb amputation with phantom limb pain. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 131, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardone, R.; Versace, V.; Sebastianelli, L.; Brigo, F.; Christova, M.; Scarano, G.I.; Saltuari, L.; Trinka, E.; Hauer, L.; Sellner, J. Transcranial magnetic stimulation in subjects with phantom pain and non-painful phantom sensations: A systematic review. Brain Res. Bull. 2019, 148, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, K.L.; Russell, H.G.; Schumacher, P.J.; Robinson-Freeman, K.E.; O’Conor, E.C.; Gibney, K.D.; Yambem, O.; Dykes, R.W.; Waters, R.S.; Tsao, J.W. A review of current theories and treatments for phantom limb pain. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2168–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeker, T.J.; Keaser, M.L.; Khan, S.A.; Gullapalli, R.P.; Seminowicz, D.A.; Greenspan, J.D. Non-invasive Motor Cortex Neuromodulation Reduces Secondary Hyperalgesia and Enhances Activation of the Descending Pain Modulatory Network. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musumeci, G.; D’Alonzo, M.; Ranieri, F.; Falato, E.; Capone, F.; Motolese, F.; Di Pino, G.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Pilato, F. Intracortical and interhemispheric excitability changes in arm amputees: A TMS study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2023, 156, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hordacre, B.; Bradnam, L.V.; Barr, C.; Patritti, B.L.; Crotty, M. Intracortical inhibition is modulated by phase of prosthetic rehabilitation in transtibial amputees. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schwenkreis, P.; Witscher, K.; Janssen, F.; Dertwinkel, R.; Zenz, M.; Malin, J.P.; Tegenthoff, M. Changes of cortical excitability in patients with upper limb amputation. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 293, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemann, U.; Hallett, M.; Cohen, L.G. Mechanisms of deafferentation-induced plasticity in human motor cortex. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 7000–7007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candido Santos, L.; Gushken, F.; Gadotti, G.M.; Dias, B.F.; Marinelli Pedrini, S.; Barreto, M.; Zippo, E.; Pinto, C.B.; Piza, P.V.T.; Fregni, F. Intracortical Inhibition in the Affected Hemisphere in Limb Amputation. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, V.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Gianlorenço, A.C.; Fregni, F. Neuropsychiatric drugs and a neurophysiological marker as predictors of health-related quality of life in patients with phantom limb pain. Pain Med. 2024, 25, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleeva, D.; Soghoyan, G.; Biktimirov, A.; Piliugin, N.; Matvienko, Y.; Sintsov, M.; Lebedev, M. Modulations in high-density EEG during the suppression of phantom-limb pain with neurostimulation in upper limb amputees. Cereb. Cortex 2024, 34, bhad504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussigmann, T.; Bardel, B.; Lefaucheur, J.P. Resting-state electroencephalography (EEG) biomarkers of chronic neuropathic pain. A systematic review. Neuroimage 2022, 258, 119351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacerda, G.J.M.; Costa, V.; Camargo, L.; Battistella, L.R.; Imamura, M.; Fregni, F. Neurophysiological Markers of Adaptation and Compensation Following Lower Limb Amputation: An Analysis of EEG Oscillations and Clinical Predictors from the DEFINE Cohort Study. Neurol. Int. 2025, 17, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Teixeira, P.E.P.; Martinez-Magallanes, D.; Neto, M.S.; Pichardo, E.A.; Camargo, L.; Lima, D.; Cardenas-Rojas, A.; Fregni, F. Brain compensatory mechanisms in depression and memory complaints in fibromyalgia: The role of theta oscillatory activity. Pain Med. 2024, 25, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simis, M.; Imamura, M.; Sampaio de Melo, P.; Marduy, A.; Battistella, L.; Fregni, F. Deficit of Inhibition as a Marker of Neuroplasticity (DEFINE Study) in Rehabilitation: A Longitudinal Cohort Study Protocol. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 695406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickham, P.P. Human experimentation: Code of ethics of the world medical association: Declaration of helsinki. Br. Med. J. 1964, 2, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botega, N.J.; Bio, M.R.; Zomignani, M.A.; Garcia, C., Jr.; Pereira, W.A. Mood disorders among inpatients in ambulatory and validation of the anxiety and depression scale HAD. Rev. Saude Publica. 1995, 29, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, M.W. Reliability and factor analysis of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep 1992, 15, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, E.N.; Gramegna, C.; Esposito, A.; Gazzaniga, V.; Zago, S.; Difonzo, T.; Maddaluno, O.; Appollonio, I.; Bolognini, N. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA): Updated norms and psychometric insights into adaptive testing from healthy individuals in Northern Italy. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2022, 34, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadassery, S.J.; Kong, K.H.; Ho, W.M.L.; Seneviratna, A. Interview Functional Independence Measure score: Self-reporting as a simpler alternative to multidisciplinary functional assessment. Singapore Med. J. 2019, 60, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groppa, S.; Oliviero, A.; Eisen, A.; Quartarone, A.; Cohen, L.G.; Mall, V.; Kaelin-Lang, A.; Mima, T.; Rossi, S.; Thickbroom, G.W.; et al. A practical guide to diagnostic transcranial magnetic stimulation: Report of an IFCN committee. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 123, 858–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacerda, G.J.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Barbosa, S.P.; Marques, L.M.; Battistella, L.; Fregni, F. A Neural Signature for Brain Compensation in Stroke with EEG and TMS: Insights from the DEFINE cohort study. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2024, 54, 102985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osbourne, J.W.; Waters, E. Four Assumptions of Multiple Regression That Researchers Should Always Test. Pract. Assess. Res. Eval. 2019, 8, 2002–2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kinjo, M.; Wada, M.; Nakajima, S.; Tsugawa, S.; Nakahara, T.; Blumberger, D.M.; Mimura, M.; Noda, Y. Transcranial magnetic stimulation neurophysiology of patients with major depressive disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2021, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, R.S.; Sanacora, G.; Krystal, J.H. Altered Connectivity in Depression: GABA and Glutamate Neurotransmitter Deficits and Reversal by Novel Treatments. Neuron 2019, 102, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, E.; Eichler, R.; Roux, L.; Fujisawa, S.; Rotstein, H.G.; Buzsáki, G. Inhibition-induced theta resonance in cortical circuits. Neuron 2013, 80, 1263–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, A.; Feurra, M.; Pellegrino, G.; Brittain, J.S. Investigating and Modulating Physiological and Pathological Brain Oscillations: The Role of Oscillatory Activity in Neural Plasticity. Neural. Plast. 2019, 2019, 9403195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, M.; Gianlorenço, A.C.; Lacerda, G.J.M.; Battistella, L.R.; Fregni, F. Pain Pressure Threshold as a Non-Linear Marker of Neural Adaptation in Amputees: Evidence from the DEFINE Cohort. NeuroSci 2025, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Sang, L.; Li, L.; Li, P.; Yin, X.; Qiu, M. Brain Functional Connectivity Plasticity Within and Beyond the Sensorimotor Network in Lower-Limb. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makin, T.R.; Flor, H. Brain (re) organisation following amputation: Implications for phantom limb pain. Neuroimage 2020, 218, 116943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, Y.H.; Sundman, M.; Ton That, V.; Green, J.; Trapani, C. Cortical excitability and plasticity in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis of transcranial magnetic stimulation studies. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 79, 101660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardone, R.; Golaszewski, S.; Frey, V.; Brigo, F.; Versace, V.; Sebastianelli, L.; Saltuari, L.; Höller, Y. Altered response to repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in patients with chronic primary insomnia. Sleep Med. 2020, 72, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, C.H.; Tang, X.W.; Cao, Y.; Cao, H.T.; Zhang, W.; Wu, J.F.; Zhu, Y.L.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wu, Y.; et al. Cortical excitability signatures for the degree of sleepiness in human. eLife 2021, 10, e65099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grippo, A.; Carrai, R.; Romagnoli, I.; Lanini, B.; Bianchi, R.; Gigliotti, F.; Scano, G. Cortical excitability in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: Transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Sleep 2005, 28, 1547–1553. [Google Scholar]



| Demographic and Clinical Variables | Median (IQR) or n (%) | Missing Data (n) |
|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD) | 47.0 (31–61) | None |
| Biological sex | None | |
| Male | 50 (84.75) | |
| Female | 9 (15.25) | |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean (SD) | 25.15 (22.75–28.62) | None |
| Race | None | |
| White | 20 (33.90) | |
| Non-White | 39 (66.10) | |
| Years of education, mean (SD) | 9.51 (3.87) | None |
| Marital status | None | |
| Single | 23 (38.98) | |
| Married | 24 (40.68) | |
| Divorced | 10 (16.95) | |
| Widowed | 2 (3.39) | |
| Amputation etiology | None | |
| Traumatic | 28 (47.46) | |
| Non-traumatic | 31 (52.54) | |
| Amputation side | None | |
| Right | 22 (37.29) | |
| Left | 37 (62.71) | |
| Amputation level, n (%) | ||
| Above the knee | 37 (62.71) | |
| Below the knee | 22 (37.29) | |
| Hand dominance | None | |
| Right | 54 (91.53) | |
| Left | 5 (8.47) | |
| Time since amputation | 18.00 (11.30–30.33) | None |
| Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) | 8.00 (6.00–12.00) | 3 |
| Phantom limb pain (PLP) | 1 | |
| yes | 29 (50) | |
| no | 29 (50) | |
| Phantom limb sensation (PLS) | 1 | |
| yes | 43 (74.14) | |
| no | 15 (49) | |
| Residual limb pain (RLP) | 2 | |
| yes | 12 (21.05) | |
| no | 45 (78.95) | |
| Hospital Anxiety Scale (HAS) | 3.00 (1.50–6.00) | 10 |
| Hospital Depression Scale (HDS) | 2.00 (0.00–4.00) | 10 |
| Functional Independence Measure (FIM) | 116 (114–118) | 10 |
| Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) | 23 (20–24) | 12 |
| Dependent Variables | Median (IQR) |
|---|---|
| Resting motor threshold (%) | |
| Non-affected hemisphere | 54.0 (46.5–60) |
| Affected hemisphere | 54.0 (49.0–63.0) |
| Motor-evoked potential (MEP), mV | |
| Non-affected hemisphere | 1.14 (0.98–1.37) |
| Affected hemisphere | 1.14 (0.95–1.36) |
| Short intracortical inhibition (SICI) ratio | |
| Non-affected hemisphere | 0.41 (0.24–0.64) |
| Affected hemisphere | 0.41 (0.17–0.66) |
| Intracortical facilitation (ICF) ratio | |
| Non-affected hemisphere | 1.41 (0.93–1.95) |
| Affected hemisphere | 1.51 (1.05–1.95) |
| Theta Oscillations | Median (IQR) |
|---|---|
| Frontal | 14.66 (10.90–20.26) |
| Central | 16.33 (11.78–20.85) |
| Parietal | 14.57 (11.05–18.78) |
| rMT, Non-Affected Hemisphere, n = 58 | Beta Coefficient | 95% CI | p-Value | VIF | R-Squared |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLP | 7.453 | [0.753, 14.154] | 0.030 | 1.125 | 0.311 |
| MoCA | −1.181 | [−2.202, −0.160] | 0.025 | 1.050 | |
| FIM | 0.740 | [−0.094, 1.573] | 0.080 | 1.144 | |
| Age | 0.173 | [−0.013, 0.360] | 0.068 | 1.063 |
| MEP, Affected Hemisphere, n = 46 | Beta Coefficient | 95% CI | p-Value | VIF | R-Squared |
| FIM | −0.026 | [−0.051, −0.001] | 0.044 | 1.057 | 0.344 |
| ESS | 0.026 | [0.003, 0.049] | 0.030 | 1.069 | |
| Race | 0.343 | [0.123, 0.564] | 0.003 | 1.089 | |
| Biological sex | −0.270 | [−0.558, 0.009] | 0.058 | 1.080 | |
| MEP, Non-Affected Hemisphere, n = 48 | |||||
| FIM | −0.034 | [−0.059, −0.009] | 0.008 | 1.077 | 0.228 |
| PLP | −0.188 | [−0.403, 0.027] | 0.085 | 1.186 | |
| Race | 0.185 | [−0.031, 0.400] | 0.003 | 1.137 | |
| Biological sex | −0.091 | [−0.377, 0.195] | 0.058 | 1.167 |
| SICI, Affected Hemisphere, n = 58 | Beta Coefficient | 95% CI | p-Value | VIF | R-Squared |
| PLP | −0.181 | [−0.011, −0.351] | 0.038 | 1.034 | 0.291 |
| Etiology | 0.297 | [0.108, 0.485] | 0.003 | 1.263 | |
| Race | −0.197 | [−0.375, −0.019] | 0.030 | 1.022 | |
| Biological sex | 0.005 | [−0.242, 0.251] | 0.970 | 1.140 | |
| Age | 0.002 | [−0.004, 0.007] | 0.521 | 1.143 | |
| SICI, Non-Affected Hemisphere, n = 37 | |||||
| Theta, frontal | 5.294 | [3.119, 7.468] | <0.001 | 1.048 | 0.434 |
| Biological sex | −0.463 | [−0.838, 0.113] | 0.130 | 1.029 | |
| Age | 0.001 | [−0.008, 0.010] | 0.796 | ||
| Theta, central | 5.383 | [3.449, 7.317] | <0.001 | 1.016 | 0.500 |
| Biological sex | −0.257 | [−0.699, 0.185] | 0.246 | 1.006 | |
| Age | 0.004 | [−0.007, 0.009] | 0.915 | 1.013 | |
| Theta, parietal | 5.116 | [3.146, 7.165] | <0.001 | 1.005 | 0.460 |
| Biological sex | −0.254 | [−0.713, 0.206] | 0.269 | 1.006 | |
| Age | −0.002 | [−0.011, 0.006] | 0.617 | 1.001 |
| ICF, Non-Affected Hemisphere, n = 49 | Beta Coefficient | 95% CI | p-Value | VIF | R-Squared |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
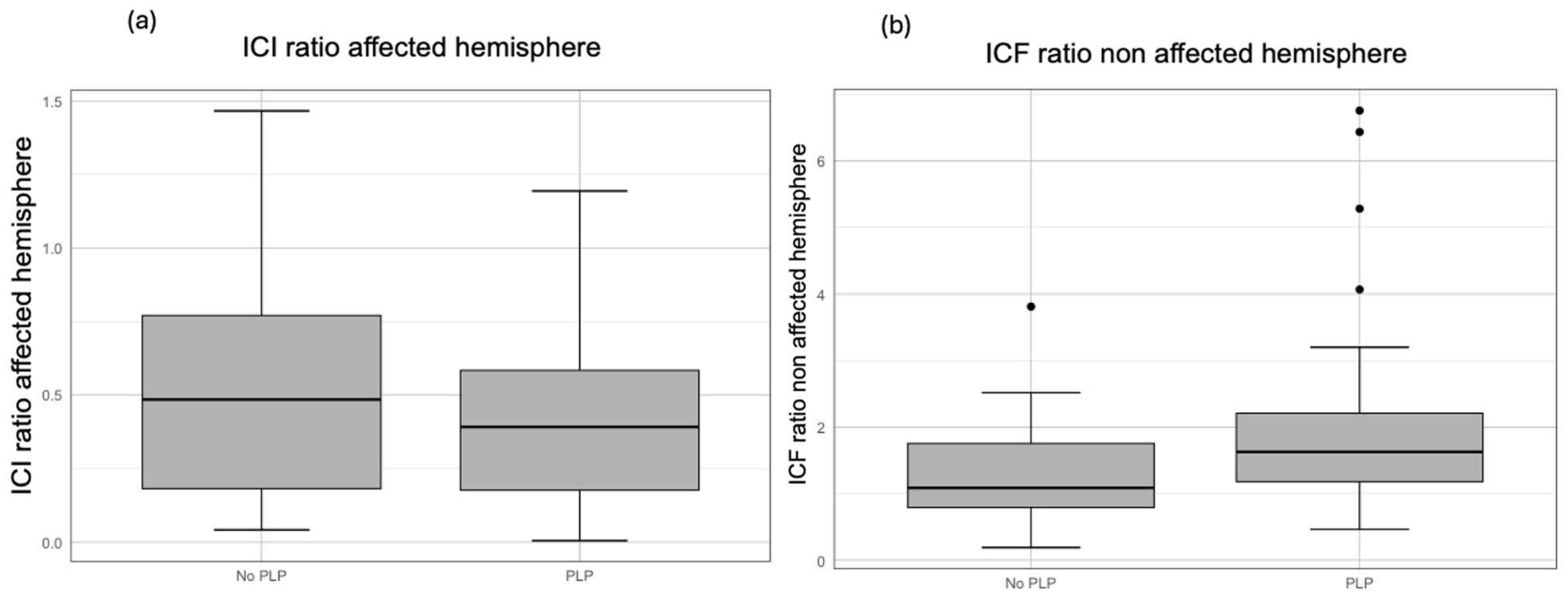
| PLP | 0.662 | [0.025, 1.298] | 0.042 | 1.034 | 0.254 |
| Etiology | 0.612 | [−0.093, 1.317] | 0.088 | 1.263 | |
| Race | −0.700 | [−1.365, −0.034] | 0.040 | 1.022 | |
| Age | 0.009 | [−0.011, 0.029] | 0.386 | 1.143 | |
| Biological sex | 0.292 | [−0.631, 1.215] | 0.529 | 1.140 | |
| Depression (HDS) | 0.204 | [0.077, 0.338] | 0.002 | 1.017 | 0.326 |
| Race | −1.019 | [−1.750, −0.288] | 0.007 | 1.021 | |
| Age | 0.014 | [−0.007, 0.036] | 0.185 | 1.008 | |
| Biological sex | 0.706 | [−0.294, 1.707] | 0.162 | 1.009 |
| TMS Parameters | Affected Hemisphere | Non-Affected Hemisphere |
|---|---|---|
| ↑ MT | ↑ PLP ↓ MoCA ↑ FIM | |
| ↑ MEP | ↓ FIM | ↓ FIM |
| ↑ ESS | ||
| ↑ SICI | ↓ PLP | ↑ Theta, frontal |
| ↑ Theta, central ↑ Theta, parietal | ||
| ↑ ICF | ↑ PLP ↑ Depression |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lacerda, G.J.M.; Camargo, L.; Silva, F.M.Q.; Imamura, M.; Battistella, L.R.; Fregni, F. Defective Intracortical Inhibition as a Marker of Impaired Neural Compensation in Amputees Undergoing Rehabilitation. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051015
Lacerda GJM, Camargo L, Silva FMQ, Imamura M, Battistella LR, Fregni F. Defective Intracortical Inhibition as a Marker of Impaired Neural Compensation in Amputees Undergoing Rehabilitation. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(5):1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051015
Chicago/Turabian StyleLacerda, Guilherme J. M., Lucas Camargo, Fernanda M. Q. Silva, Marta Imamura, Linamara R. Battistella, and Felipe Fregni. 2025. "Defective Intracortical Inhibition as a Marker of Impaired Neural Compensation in Amputees Undergoing Rehabilitation" Biomedicines 13, no. 5: 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051015
APA StyleLacerda, G. J. M., Camargo, L., Silva, F. M. Q., Imamura, M., Battistella, L. R., & Fregni, F. (2025). Defective Intracortical Inhibition as a Marker of Impaired Neural Compensation in Amputees Undergoing Rehabilitation. Biomedicines, 13(5), 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051015







