Association Between Asthma and Gout: A Longitudinal Follow-Up Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Exposure (Gout)
2.3. Outcome (Asthma)
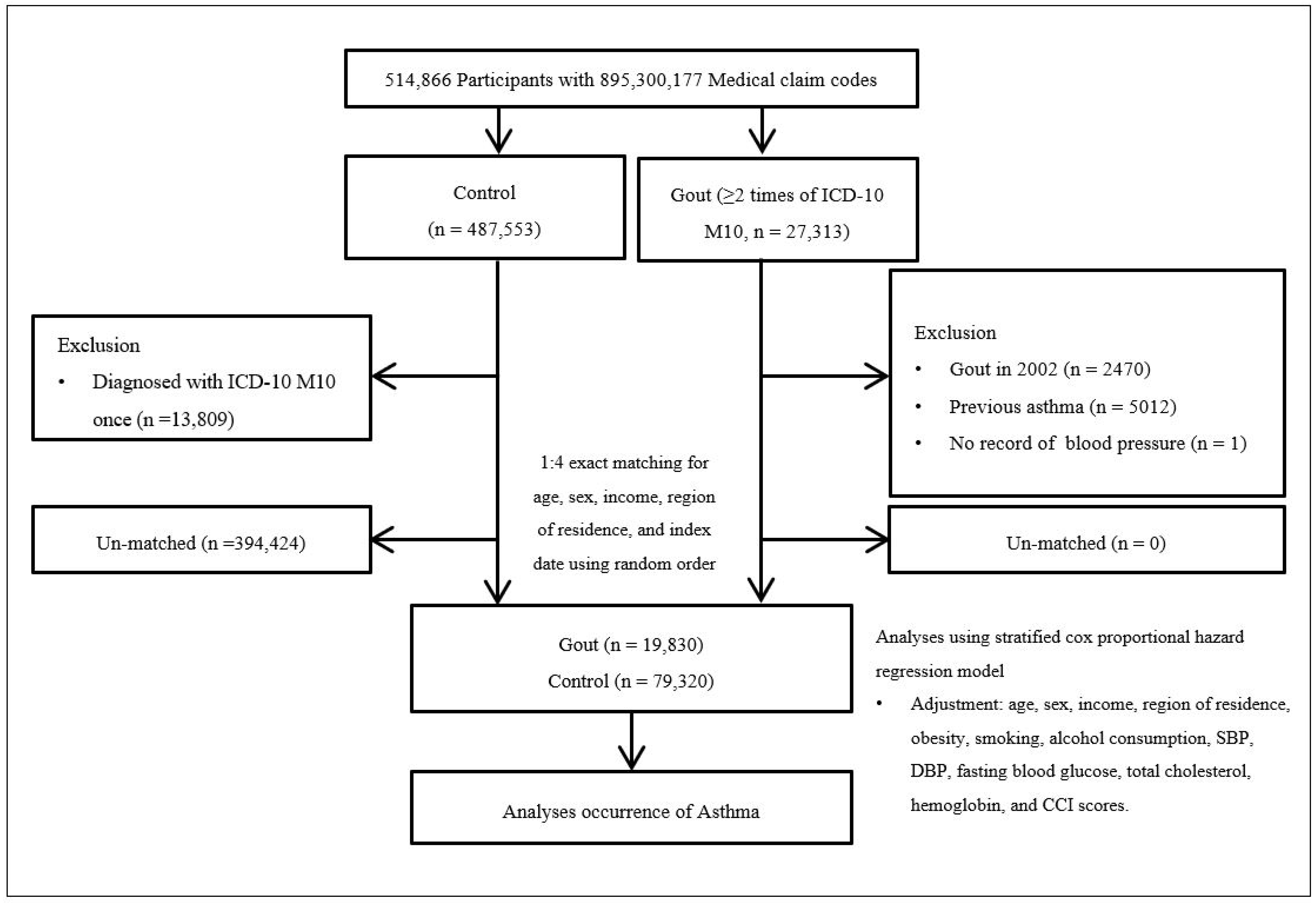
2.4. Participants Selection
2.5. Covariates
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martillo, M.A.; Nazzal, L.; Crittenden, D.B. The crystallization of monosodium urate. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2014, 16, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehlin, M.; Jacobsson, L.; Roddy, E. Global epidemiology of gout: Prevalence, incidence, treatment patterns and risk factors. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karis, E.; Crittenden, D.B.; Pillinger, M.H. Hyperuricemia, gout, and related comorbidities: Cause and effect on a two-way street. South Med. J. 2014, 107, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandratre, P.; Roddy, E.; Clarson, L.; Richardson, J.; Hider, S.; Mallen, C.D. Health-related quality of life in gout: A systematic review. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 2031–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mody, G.M. Rheumatology in Africa-challenges and opportunities. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.L.; Wang, T.W.; Chen, Y.C.; Hu, J.M.; Ku, P.M.; Hsieh, C.H.; Lee, C.H.; Kuo, F.C.; Lu, C.H.; Su, C.C.; et al. Gout as a risk factor for acute myocardial infarction: Evidence from competing risk model analysis. J. Investig. Med. 2021, 69, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.K.; Leigh, R.; McLaurin, K.K.; Kim, K.; Hultquist, M.; Molfino, N.A. A randomized, controlled trial to evaluate the effect of an anti-interleukin-9 monoclonal antibody in adults with uncontrolled asthma. Respir. Res. 2013, 14, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swed, S.; Sawaf, B.; Al-Obeidat, F.; Hafez, W.; Rakab, A.; Alibrahim, H.; Nasif, M.N.; Alghalyini, B.; Zia Zaidi, A.R.; Alshareef, L.; et al. Asthma prevalence among United States population insights from NHANES data analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, K.F.; Bandoli, G.; Chambers, C.D.; Schatz, M.; Palmsten, K. Asthma prevalence among women aged 18 to 44 in the United States: National health and nutrition examination survey 2001–2016. J. Asthma 2020, 57, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA): Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. Update 2014 and Online Appendix. Available online: http://www.ginasthma.org (accessed on 24 January 2025).
- Masoli, M.; Fabian, D.; Holt, S.; Beasley, R.; Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) Program. The global burden of asthma: Executive summary of the GINA dissemination committee report. Allergy 2004, 59, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet, J.; Bousquet, P.J.; Godard, P.; Daures, J.P. The public health implications of asthma. Bull. World Health Organ. 2005, 83, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wan, C.; Wen, F. An unexpected role for serum uric acid as a biomarker for severity of asthma exacerbation. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2014, 32, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Jia, Y.; Yi, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, O. High Serum Uric Acid Was a Risk Factor for Incident Asthma: An Open Cohort Study. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 2020, 13, 2337–2346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Xu, J.; Wen, Y.; Ramos-Rodriguez, A.; Jiang, C.; Fang, S.; Kagalwalla, M.; Ohri, N. Relationship Between Gout and Asthma: A National Database Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69 (Suppl. S10), 2085. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, K.; Iijima, K.; Elias, M.K.; Seno, S.; Tojima, I.; Kobayashi, T.; Kephart, G.M.; Kurabayashi, M.; Kita, H. Airway uric acid is a sensor of inhaled protease allergens and initiates type 2 immune responses in respiratory mucosa. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 4032–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulnaby, N.K.; Sayed, A.O.; Shalaby, N.M. Predictive value of serum uric acid in hospitalized adolescents and adults with acute asthma. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2016, 12, 1701–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Min, C.; Oh, D.J.; Choi, H.G. Tobacco Smoking and Alcohol Consumption Are Related to Benign Parotid Tumor: A Nested Case-Control Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 12, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Kwak, S.G.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.K.; Choe, J.Y.; Park, S.H. Prevalence and incidence of gout in Korea: Data from the national health claims database 2007–2015. Rheumatol. Int. 2017, 37, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.G.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; Hwang, Y.I.; Jang, S.H.; Jung, K.S. Association Between Asthma and Depression: A National Cohort Study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Wee, J.H.; Choi, H.G.; Park, J.Y.; Hwang, Y.I.; Jang, S.H.; Jung, K.S. Association Between Statin Medication and Asthma/Asthma Exacerbation in a National Health Screening Cohort. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 2783–2791. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Regional Office for the Western Pacific. The Asia-Pacific Perspective: Redefining Obesity and Its Treatment; Health Communications Australia: Sydney, Australia, 2000. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/206936 (accessed on 24 January 2025).
- Quan, H.; Li, B.; Couris, C.M.; Fushimi, K.; Graham, P.; Hider, P.; Januel, J.M.; Sundararajan, V. Updating and validating the Charlson comorbidity index and score for risk adjustment in hospital discharge abstracts using data from 6 countries. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 173, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sautin, Y.Y.; Johnson, R.J. Uric acid: The oxidant-antioxidant paradox. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2008, 27, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschvink, N.; Fiévez, L.; Bureau, F.; Degand, G.; Maghuin-Rogister, G.; Smith, N.; Art, T.; Lekeux, P. Adaptation to multiday ozone exposure is associated with a sustained increase of bronchoalveolar uric acid. Free Radic. Res. 2002, 36, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiropoulos, K.; Trakada, G.; Nikolaou, E.; Prodromakis, E.; Efremidis, G.; Pouli, A.; Koniavitou, A. Endothelin-1 levels in the pathophysiology of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and bronchial asthma. Respir. Med. 2003, 97, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romi, M.M.; Arfian, N.; Tranggono, U.; Setyaningsih, W.A.W.; Sari, D.C.R. Uric acid causes kidney injury through inducing fibroblast expansion, Endothelin-1 expression, and inflammation. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finsnes, F.; Lyberg, T.; Christensen, G.; Skjønsberg, O.H. Leukotriene antagonism reduces the generation of endothelin-1 and interferon-γ and inhibits eosinophilic airway inflammation. Respir. Med. 2002, 96, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Ye, X.; Escames, G.; Lei, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Jing, T.; Yao, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, Z.; et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Contributions to inflammation-related diseases. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2023, 28, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofani, E.; Semitekolou, M.; Morianos, I.; Samitas, K.; Xanthou, G. Targeting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Severe Asthma. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.R.; Wang, J.Q.; Li, J. Role of NLRP3 in the pathogenesis and treatment of gout arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1137822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, R.A.; Rathod, T.; Roddy, E.; Muller, S.; Hider, S.L.; Mallen, C.D. The association of gout with socioeconomic status in primary care: A cross-sectional observational study. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 2004–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozyrskyj, A.L.; Kendall, G.E.; Jacoby, P.; Sly, P.D.; Zubrick, S.R. Association between socioeconomic status and the development of asthma: Analyses of income trajectories. Am. J. Public Health 2010, 100, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.X.; Phipatanakul, W.; Gaffin, J.M. Environment and the development of severe asthma in inner city population. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 23, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, A.; Brickley, E.; Rodrigues, L.; Normansell, R.A.; Barreto, M.; Cooper, P.J. Urbanisation and asthma in low-income and middle-income countries: A systematic review of the urban-rural differences in asthma prevalence. Thorax 2019, 74, 1020–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Olejnik, A.E.; Kuźnar-Kamińska, B. Association of Obesity and Severe Asthma in Adults. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pleasants, R.A.; Croft, J.B.; Lugogo, N.; Ohar, J.; Heidari, K.; Strange, C.; Wheaton, A.G.; Mannino, D.M.; Kraft, M. Body mass index, respiratory conditions, asthma, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir. Med. 2015, 109, 851–859. [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Suzuki, K.; Koya, T.; Sakagami, T.; Youkou, A.; Kagamu, H.; Arakawa, M.; Gejyo, F.; Narita, I.; et al. Influence of underweight on asthma control. Allergol. Int. 2012, 61, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Total Participants | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gout | Control | SD | |
| Age (years old) (n, %) | 0.00 | ||
| 40–44 | 562 (2.83) | 2248 (2.83) | |
| 45–49 | 1937 (9.77) | 7748 (9.77) | |
| 50–54 | 3189 (16.08) | 12,756 (16.08) | |
| 55–59 | 4064 (20.49) | 16,256 (20.49) | |
| 60–64 | 3422 (17.26) | 13,688 (17.26) | |
| 65–69 | 2757 (13.90) | 11,028 (13.90) | |
| 70–74 | 1995 (10.06) | 7980 (10.06) | |
| 75–79 | 1192 (6.01) | 4768 (6.01) | |
| 80–84 | 553 (2.79) | 2212 (2.79) | |
| 85+ | 159 (0.80) | 636 (0.80) | |
| Sex (n, %) | 0.00 | ||
| Male | 16,169 (81.54) | 64,676 (81.54) | |
| Female | 3661 (18.46) | 14,644 (18.46) | |
| Income (n, %) | 0.00 | ||
| 1 (lowest) | 2814 (14.19) | 11,256 (14.19) | |
| 2 | 2425 (12.23) | 9700 (12.23) | |
| 3 | 3017 (15.21) | 12,068 (15.21) | |
| 4 | 4180 (21.08) | 16,720 (21.08) | |
| 5 (highest) | 7394 (37.29) | 29,576 (37.29) | |
| Residential area (n, %) | 0.00 | ||
| Urban | 8482 (42.77) | 33,928 (42.77) | |
| Rural | 11,348 (57.23) | 45,392 (57.23) | |
| Obesity (n, %) | 0.27 | ||
| Underweight | 258 (1.30) | 1856 (2.34) | |
| Normal | 4953 (24.98) | 27,572 (34.76) | |
| Overweight | 5459 (27.53) | 22,510 (28.38) | |
| Obese I | 8311 (41.91) | 25,480 (32.12) | |
| Obese II | 849 (4.28) | 1902 (2.40) | |
| Smoking status (n, %) | 0.03 | ||
| Non-smoker | 10,563 (53.27) | 42,084 (53.06) | |
| Past smoker | 2852 (14.38) | 10,343 (13.04) | |
| Current smoker | 6415 (32.35) | 26,893 (33.90) | |
| Alcohol consumption (n, %) | 0.11 | ||
| <1 time a week | 11,166 (56.31) | 49,094 (61.89) | |
| ≥1 time a week | 8664 (43.69) | 30,226 (38.11) | |
| SBP (n, %) | 0.16 | ||
| <120 mmHg | 4680 (23.60) | 22,430 (28.28) | |
| 120–139 mmHg | 9779 (49.31) | 39,685 (50.03) | |
| ≥140 mmHg | 5371 (27.09) | 17,205 (21.69) | |
| DBP (n, %) | 0.14 | ||
| <80 mm Hg | 7736 (39.01) | 35,233 (44.42) | |
| 80–89 mmHg | 7545 (38.05) | 29,407 (37.07) | |
| ≥90 mmHg | 4549 (22.94) | 14,680 (18.51) | |
| Fasting blood glucose (n, %) | 0.01 | ||
| <100 mg/dL | 11,172 (56.34) | 46,197 (58.24) | |
| 100–125 mg/dL | 6631 (33.44) | 24,412 (30.78) | |
| ≥126 mg/dL | 2027 (10.22) | 8711 (10.98) | |
| Total cholesterol (n, %) | 0.09 | ||
| <200 mg/dL | 10,546 (53.18) | 45,225 (57.02) | |
| 200–239 mg/dL | 6414 (32.34) | 24,911 (31.41) | |
| ≥240 mg/dL | 2870 (14.47) | 9184 (11.58) | |
| CCI score (n, %) | 0.10 | ||
| 0 | 11,085 (55.90) | 49,249 (62.09) | |
| 1 | 3341 (16.85) | 12,084 (15.23) | |
| ≥2 | 5404 (27.25) | 17,987 (22.68) | |
| Asthma (n, %) | 1898 (9.57) | 6668 (8.41) | 0.04 |
| Characteristics | Hazard Ratios for Asthma | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N of Event /N of Total (%) | Follow-Up Duration (PY) | IR per 1000 (PY) | IRD (95% CI) | Crude † | p-Value | Adjusted †‡ | p-Value | |
| Total participants | ||||||||
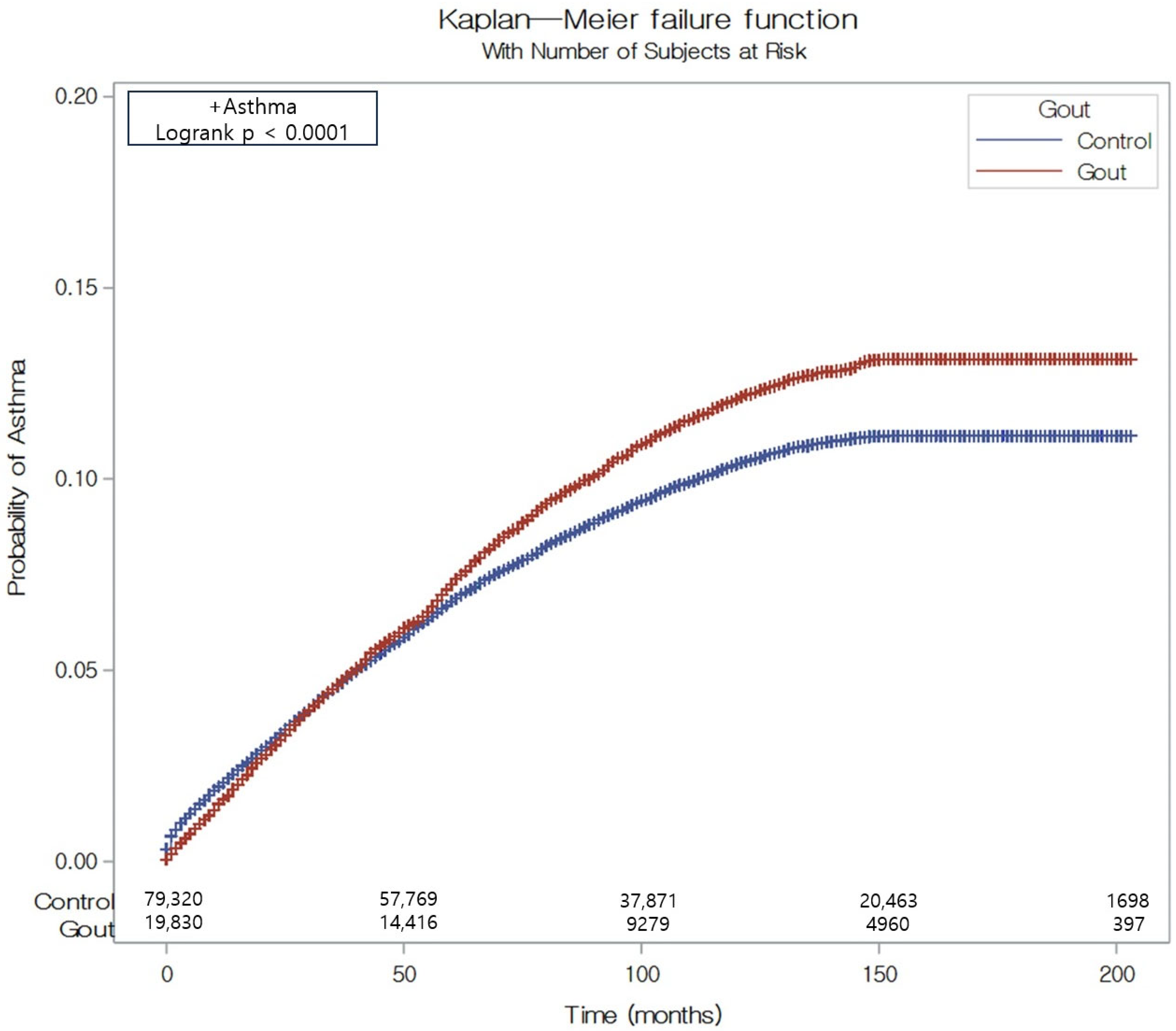
| Gout | 1898/19,830 (9.57) | 151,948 | 12.50 | 1.60 (1.04 to 2.22) | 1.14 (1.09 to 1.20) | <0.001 * | 1.11 (1.05 to 1.17) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 6668/79,320 (8.41) | 613,929 | 10.90 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Age < 60 years old | ||||||||
| Gout | 956/9752 (9.80) | 88,335 | 10.80 | 1.64 (−1.17 to 3.70) | 1.17 (1.09 to 1.26) | <0.001 * | 1.14 (1.06 to 1.23) | 0.001 * |
| Control | 3273/39,008 (8.39) | 357,449 | 9.16 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Age ≥ 60 years old | ||||||||
| Gout | 942/10,078 (9.35) | 63,613 | 14.80 | 1.60 (−2.19 to 4.70) | 1.11 (1.04 to 1.20) | 0.004 * | 1.08 (1.00 to 1.16) | 0.044 * |
| Control | 3395/40,312 (8.42) | 256,480 | 13.20 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Male | ||||||||
| Gout | 1460/16,169 (9.03) | 126,380 | 11.60 | 1.30 (−1.24 to 3.15) | 1.12 (1.06 to 1.19) | <0.001 * | 1.09 (1.03 to 1.16) | 0.003 * |
| Control | 5231/64,676 (8.09) | 509,329 | 10.30 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Female | ||||||||
| Gout | 438/3661 (11.96) | 25,568 | 17.10 | 3.40 (−1.94 to 8.31) | 1.23 (1.11 to 1.37) | <0.001 * | 1.18 (1.06 to 1.32) | 0.002 * |
| Control | 1437/14,644 (9.81) | 104,600 | 13.70 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Low income | ||||||||
| Gout | 856/8256 (10.37) | 60,685 | 14.10 | 2.60 (−0.84 to 5.67) | 1.21 (1.12 to 1.31) | <0.001 * | 1.17 (1.08 to 1.26) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 2850/33,024 (8.63) | 247,125 | 11.50 | 1 | 1 | |||
| High income | ||||||||
| Gout | 1042/11,574 (9.00) | 91,263 | 11.40 | 1.00 (−1.97 to 3.18) | 1.09 (1.02 to 1.17) | 0.012 * | 1.06 (0.99 to 1.14) | 0.096 |
| Control | 3818/46,296 (8.25) | 366,804 | 10.40 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Urban resident | ||||||||
| Gout | 777/8482 (9.16) | 66,014 | 11.80 | 1.40 (−2.22 to 3.87) | 1.13 (1.04 to 1.22) | 0.004 * | 1.08 (1.00 to 1.18) | 0.050 |
| Control | 2768/33,928 (8.16) | 265,760 | 10.40 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Rural resident | ||||||||
| Gout | 1121/11,348 (9.88) | 85,934 | 13.00 | 1.80 (−1.02 to 4.38) | 1.16 (1.08 to 1.24) | <0.001 * | 1.12 (1.05 to 1.20) | 0.001 * |
| Control | 3900/45,392 (8.59) | 348,169 | 11.20 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Underweight | ||||||||
| Gout | 18/258 (6.98) | 2031 | 8.86 | −1.54 (−18.15 to 15.13) | 0.87 (0.53 to 1.42) | 0.582 | 0.87 (0.53 to 1.43) | 0.581 |
| Control | 150/1856 (8.08) | 14,439 | 10.40 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Normal weight | ||||||||
| Gout | 471/4953 (9.51) | 37,937 | 12.40 | 1.80 (−1.13 to 6.69) | 1.16 (1.05 to 1.28) | 0.004 * | 1.12 (1.02 to 1.24) | 0.022 * |
| Control | 2294/27,572 (8.32) | 215,782 | 10.60 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Overweight | ||||||||
| Gout | 507/5459 (9.29) | 41,685 | 12.20 | 1.60 (−1.82 to 5.87) | 1.14 (1.03 to 1.26) | 0.010 * | 1.12 (1.01 to 1.23) | 0.029 * |
| Control | 1849/22,510 (8.21) | 174,584 | 10.60 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Obese | ||||||||
| Gout | 902/9160 (9.85) | 70,295 | 12.80 | 1.40 (−3.72 to 2.46) | 1.13 (1.04 to 1.22) | 0.002 * | 1.11 (1.02 to 1.19) | 0.011 * |
| Control | 2375/27,382 (8.67) | 209,124 | 11.40 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Non-smoker | ||||||||
| Gout | 1103/10,563 (10.44) | 81,566 | 13.50 | 1.70 (−3.72 to 1.83) | 1.15 (1.08 to 1.23) | <0.001 * | 0.88 (0.82 to 0.94) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 3796/42,084 (9.02) | 322,618 | 11.80 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Past/current smoker | ||||||||
| Gout | 795/9267 (8.58) | 70,382 | 11.30 | 1.44 (0.89 to 6.80) | 1.13 (1.04 to 1.22) | 0.003 * | 0.92 (0.85 to 0.99) | 0.035 * |
| Control | 2872/37,236 (7.71) | 291,311 | 9.86 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Alcohol consumption < 1 time a week | ||||||||
| Gout | 1133/11,166 (10.15) | 84,211 | 13.50 | 1.90 (−0.33 to 5.07) | 1.15 (1.08 to 1.23) | <0.001 * | 0.90 (0.84 to 0.96) | 0.002 * |
| Control | 4362/49,094 (8.88) | 376,998 | 11.60 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Alcohol consumption ≥ 1 time a week | ||||||||
| Gout | 765/8664 (8.83) | 67,737 | 11.30 | 1.57 (−2.72 to 3.38) | 1.16 (1.07 to 1.26) | 0.001 * | 0.88 (0.81 to 0.96) | 0.003 * |
| Control | 2306/30,226 (7.63) | 236,931 | 9.73 | 1 | 1 | |||
| SBP < 120 mmHg and DBP < 80 mmHg | ||||||||
| Gout | 1178/13,395 (8.79) | 96,419 | 12.20 | 1.50 (1.38 to 6.52) | 1.12 (1.05 to 1.20) | 0.001 * | 0.90 (0.84 to 0.96) | 0.002 * |
| Control | 4627/58,232 (7.95) | 431,427 | 10.70 | 1 | 1 | |||
| SBP ≥ 120 mmHg or DBP ≥ 80 mmHg | ||||||||
| Gout | 720/6435 (11.19) | 55,529 | 13.00 | 1.80 (−2.89 to 3.57) | 1.16 (1.06 to1.26) | 0.001 * | 0.89 (0.81 to 0.97) | 0.006 * |
| Control | 2041/21,088 (9.68) | 182,502 | 11.20 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Fasting blood glucose < 100 mg/dL | ||||||||
| Gout | 1183/11,172 (10.59) | 89,776 | 13.20 | 1.90 (−0.79 to 4.32) | 1.15 (1.08 to 1.23) | <0.001 * | 0.87 (0.81 to 0.93) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 4263/46,197 (9.23) | 376,575 | 11.30 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Fasting blood glucose ≥ 100 mg/dL | ||||||||
| Gout | 715/8658 (8.26) | 62,172 | 11.50 | 1.40 (−3.59 to 3.01) | 1.13 (1.04 to 1.23) | 0.003 * | 0.93 (0.85 to 1.01) | 0.090 |
| Control | 2405/33,123 (7.26) | 237,354 | 10.10 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Total cholesterol < 200 mg/dL | ||||||||
| Gout | 957/10,546 (9.07) | 77,783 | 12.30 | 1.60 (1.46 to 7.11) | 1.13 (1.05 to 1.21) | 0.001 * | 0.91 (0.84 to 0.98) | 0.008 * |
| Control | 3701/45,225 (8.18) | 344,446 | 10.70 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Total cholesterol ≥ 200 mg/dL | ||||||||
| Gout | 941/9284 (10.14) | 74,165 | 12.70 | 1.70 (−4.23 to 1.55) | 1.15 (1.07 to 1.24) | <0.001 * | 0.87 (0.81 to 0.94) | 0.001 * |
| Control | 2967/34,095 (8.70) | 269,483 | 11.00 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CCI score = 0 | ||||||||
| Gout | 818/11085 (7.38) | 82,647 | 9.90 | 0.86 (0.30 to 5.76) | 1.08 (1.00 to 1.17) | 0.041 * | 0.89 (0.82 to 0.96) | 0.003 * |
| Control | 3395/49249 (6.89) | 375,678 | 9.04 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CCI score = 1 | ||||||||
| Gout | 383/3341 (11.46) | 25,367 | 15.10 | 1.10 (−6.04 to 4.09) | 1.07 (0.96 to 1.20) | 0.219 | 0.87 (0.78 to 0.98) | 0.024 * |
| Control | 1278/12,084 (10.58) | 91,076 | 14.00 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CCI scores ≥ 2 | ||||||||
| Gout | 697/5404 (12.90) | 43,934 | 15.90 | 2.30 (−2.94 to 4.52) | 1.17 (1.07 to 1.27) | 0.001 * | 0.90 (0.82 to 0.98) | 0.014 * |
| Control | 1995/17,987 (11.09) | 147,175 | 13.60 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Characteristics | Hazard Ratios for Asthma | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N of Event /N of Total (%) | Follow-Up Duration (PY) | IR per 1000 (PY) | IRD (95% CI) | Crude † | p-Value | Adjusted †‡ | p-Value | |
| Total participants | ||||||||
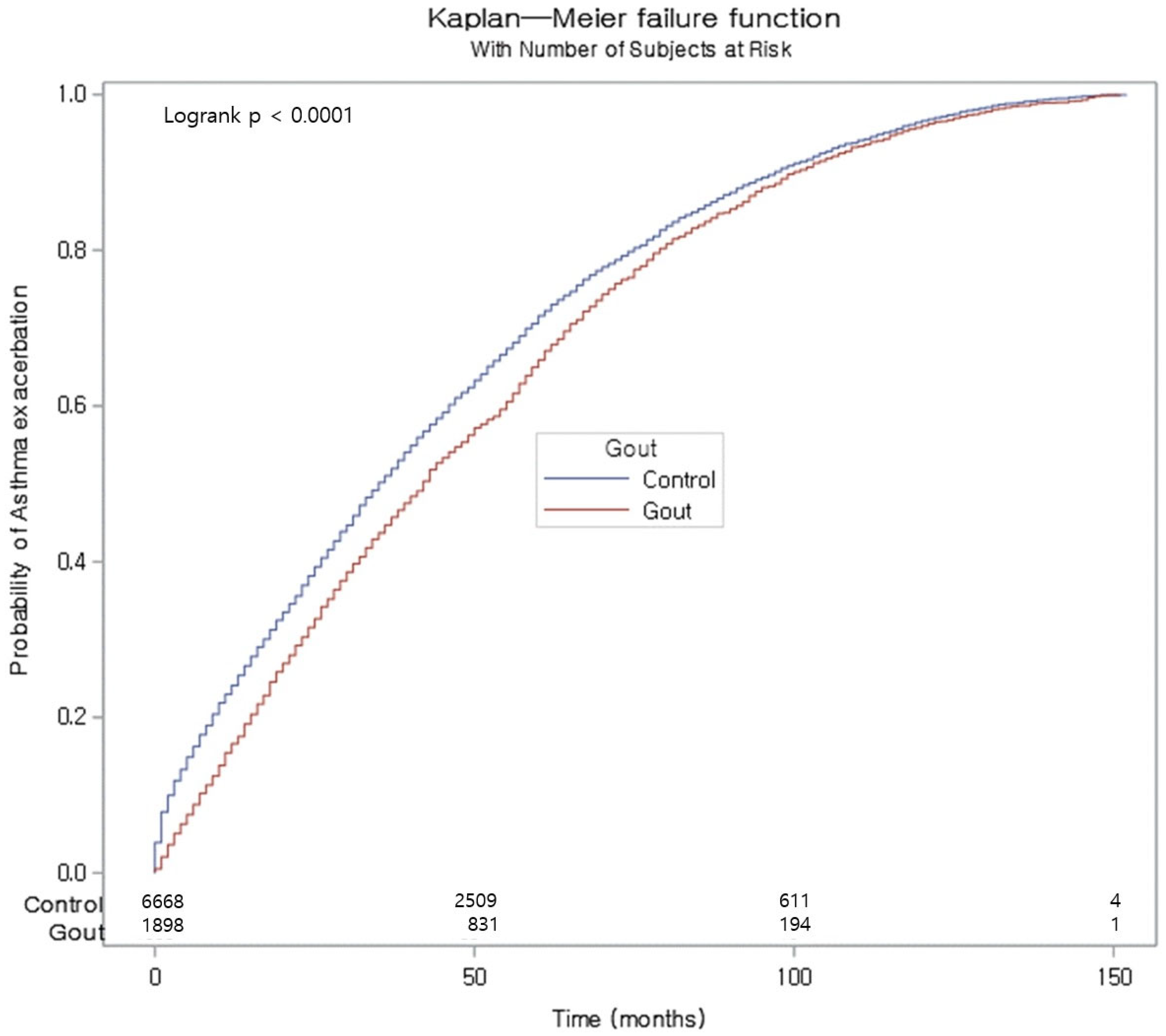
| Gout | 310/1898 (16.33) | 21,223 | 14.60 | 0.80 (−1.03 to 2.58) | 1.05 (0.93 to 1.19) | 0.437 | 0.99 (0.87 to 1.12) | 0.842 |
| Control | 1027/6668 (15.40) | 74,256 | 13.80 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Age < 60 years old | ||||||||
| Gout | 135/956 (14.12) | 11,329 | 11.90 | 1.90 (−0.23 to 4.05) | 1.18 (0.97 to 1.44) | 0.090 | 1.06 (0.87 to 1.30) | 0.547 |
| Control | 390/3273 (11.92) | 38,976 | 10.00 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Age ≥ 60 years old | ||||||||
| Gout | 175/942 (18.58) | 9894 | 17.70 | −0.40 (−3.36 to 2.62) | 0.97 (0.82 to 1.15) | 0.761 | 0.94 (0.79 to 1.11) | 0.437 |
| Control | 637/3395 (18.76) | 35,280 | 18.10 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Male | ||||||||
| Gout | 226/1460 (15.48) | 16,442 | 13.70 | 0.00 (−2.03 to 2.03) | 1.00 (0.86 to 1.16) | 0.970 | 0.96 (0.83 to 1.12) | 0.599 |
| Control | 801/5231 (15.31) | 58,266 | 13.70 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Female | ||||||||
| Gout | 84/438 (19.18) | 4781 | 17.60 | 3.50 (−0.51 to 7.38) | 1.23 (0.96 to 1.58) | 0.108 | 1.08 (0.84 to 1.40) | 0.531 |
| Control | 226/1437 (15.73) | 15,990 | 14.10 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Low income | ||||||||
| Gout | 157/856 (18.34) | 9384 | 16.70 | 1.20 (−1.67 to 4.13) | 1.08 (0.90 to 1.29) | 0.403 | 1.04 (0.87 to 1.25) | 0.656 |
| Control | 483/2850 (16.95) | 31,153 | 15.50 | 1 | 1 | |||
| High income | ||||||||
| Gout | 153/1042 (14.68) | 11,839 | 12.90 | 0.30 (−1.99 to 2.59) | 1.02 (0.85 to 1.21) | 0.872 | 0.93 (0.78 to 1.12) | 0.448 |
| Control | 544/3818 (14.25) | 43,103 | 12.60 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Urban resident | ||||||||
| Gout | 124/777 (15.96) | 8621 | 14.40 | 2.00 (−0.68 to 4.72) | 1.15 (0.94 to 1.40) | 0.184 | 1.10 (0.90 to 1.35) | 0.356 |
| Control | 385/2768 (13.91) | 31,147 | 12.40 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Rural resident | ||||||||
| Gout | 186/1121 (16.59) | 12,602 | 14.80 | −0.10 (−2.55 to 2.29) | 0.99 (0.84 to 1.17) | 0.929 | 0.93 (0.78 to 1.09) | 0.357 |
| Control | 642/3900 (16.46) | 43,109 | 14.90 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Underweight | ||||||||
| Gout | 7/18 (38.89) | 146 | 47.90 | 22.30 (−32.46 to 76.74) | 1.62 (0.72 to 3.62) | 0.243 | 2.85 (1.17 to 6.97) | 0.022 * |
| Control | 38/150 (25.33) | 1483 | 25.60 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Normal weight | ||||||||
| Gout | 91/471 (19.32) | 5039 | 18.10 | 4.50 (−4.70 to 13.40) | 1.29 (1.03 to 1.63) | 0.029 * | 1.18 (0.93 to 1.49) | 0.168 |
| Control | 350/2294 (15.26) | 25,741 | 13.60 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Overweight | ||||||||
| Gout | 79/507 (15.58) | 5666 | 13.90 | 0.90 (−8.79 to 8.79) | 1.07 (0.83 to 1.37) | 0.620 | 0.95 (0.74 to 1.23) | 0.719 |
| Control | 268/1849 (14.49) | 20,664 | 13.00 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Obese | ||||||||
| Gout | 133/902 (14.75) | 10,372 | 12.80 | −1.30 (−9.89 to 3.68) | 0.92 (0.76 to 1.12) | 0.421 | 0.88 (0.72 to 1.07) | 0.205 |
| Control | 371/2375 (15.62) | 26,368 | 14.10 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Non-smoker | ||||||||
| Gout | 191/1103 (17.32) | 12,368 | 15.40 | 2.60 (0.28 to 4.92) | 1.20 (1.01 to 1.41) | 0.034 * | 1.10 (0.94 to 1.31) | 0.241 |
| Control | 550/3796 (14.49) | 42,832 | 12.80 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Past/current smoker | ||||||||
| Gout | 119/795 (14.97) | 8855 | 13.40 | −1.80 (−4.61 to 1.13) | 0.88 (0.72 to 1.08) | 0.222 | 0.85 (0.69 to 1.04) | 0.118 |
| Control | 477/2872 (16.61) | 31,424 | 15.20 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Alcohol consumption <1 time a week | ||||||||
| Gout | 193/1133 (17.03) | 12,615 | 15.30 | 1.90 (−0.41 to 4.19) | 1.13 (0.96 to 1.33) | 0.136 | 1.05 (0.89 to 1.24) | 0.546 |
| Control | 656/4362 (15.04) | 48,929 | 13.40 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Alcohol consumption ≥ 1 time a week | ||||||||
| Gout | 117/765 (15.29) | 8608 | 13.60 | −1.00 (−3.99 to 1.88) | 0.93 (0.76 to 1.15) | 0.504 | 0.89 (0.72 to 1.09) | 0.263 |
| Control | 371/2306 (16.09) | 25,327 | 14.60 | 1 | 1 | |||
| SBP < 120 mmHg and DBP < 80 mmHg | ||||||||
| Gout | 54/358 (15.08) | 96,419 | 12.20 | 1.20 (−2.68 to 5.07) | 1.09 (0.81 to 1.47) | 0.567 | 1.03 (0.76 to 1.40) | 0.830 |
| Control | 217/1573 (13.80) | 431,427 | 10.70 | 1 | 1 | |||
| SBP ≥ 120 mmHg or DBP ≥ 80 mmHg | ||||||||
| Gout | 256/1540 (16.62) | 17,256 | 14.80 | 0.50 (−1.48 to 2.61) | 1.03 (0.90 to 1.19) | 0.638 | 0.98 (0.85 to 1.13) | 0.740 |
| Control | 810/5095 (15.90) | 56,776 | 14.30 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Fasting blood glucose < 100 mg/dL | ||||||||
| Gout | 196/1183 (16.57) | 13,391 | 14.60 | 0.70 (−1.54 to 3.01) | 1.05 (0.90 to 1.24) | 0.521 | 0.99 (0.84 to 1.17) | 0.922 |
| Control | 664/4263 (15.58) | 47,765 | 13.90 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Fasting blood glucose ≥ 100 mg/dL | ||||||||
| Gout | 114/715 (15.94) | 7832 | 14.60 | 0.90 (−2.12 to 3.82) | 1.05 (0.85 to 1.29) | 0.662 | 0.98 (0.80 to 1.22) | 0.878 |
| Control | 363/2405 (15.09) | 26,491 | 13.70 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Total cholesterol < 200 mg/dL | ||||||||
| Gout | 172/957 (17.97) | 10,486 | 16.40 | 2.20 (−0.38 to 4.81) | 1.14 (0.97 to 1.36) | 0.121 | 1.09 (0.91 to 1.29) | 0.346 |
| Control | 580/3701 (15.67) | 40,891 | 14.20 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Total cholesterol ≥ 200 mg/dL | ||||||||
| Gout | 138/941 (14.67) | 10,737 | 12.90 | −0.50 (−3.05 to 1.96) | 0.96 (0.79 to 1.16) | 0.672 | 0.89 (0.73 to 1.08) | 0.222 |
| Control | 447/2967 (15.07) | 33,365 | 13.40 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CCI score = 0 | ||||||||
| Gout | 65/818 (7.95) | 9766 | 6.66 | 0.34 (−6.79 to 6.02) | 1.05 (0.80 to 1.38) | 0.724 | 1.03 (0.78 to 1.36) | 0.814 |
| Control | 255/3395 (7.51) | 40,347 | 6.32 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CCI score = 1 | ||||||||
| Gout | 73/383 (19.06) | 4149 | 17.60 | −0.20 (−11.35 to 9.82) | 0.98 (0.75 to 1.27) | 0.880 | 0.96 (0.74 to 1.26) | 0.787 |
| Control | 244/1278 (19.09) | 13,731 | 17.80 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CCI scores ≥ 2 | ||||||||
| Gout | 172/697 (24.68) | 7308 | 23.50 | −2.70 (−11.87 to 4.88) | 0.90 (0.76 to 1.07) | 0.253 | 0.92 (0.77 to 1.10) | 0.352 |
| Control | 528/1995 (26.47) | 20,178 | 26.20 | 1 | 1 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.; Kim, T.J.; Kwon, M.J.; Wee, J.H.; Hong, S.K.; Choi, H.G.; Lee, J.S. Association Between Asthma and Gout: A Longitudinal Follow-Up Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040819
Kim H, Kim TJ, Kwon MJ, Wee JH, Hong SK, Choi HG, Lee JS. Association Between Asthma and Gout: A Longitudinal Follow-Up Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(4):819. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040819
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Heejin, Tae Jun Kim, Mi Jung Kwon, Jee Hye Wee, Sung Kwang Hong, Hyo Geun Choi, and Joong Seob Lee. 2025. "Association Between Asthma and Gout: A Longitudinal Follow-Up Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort" Biomedicines 13, no. 4: 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040819
APA StyleKim, H., Kim, T. J., Kwon, M. J., Wee, J. H., Hong, S. K., Choi, H. G., & Lee, J. S. (2025). Association Between Asthma and Gout: A Longitudinal Follow-Up Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort. Biomedicines, 13(4), 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040819






