Emerging Pharmacological Approaches for the Treatment of Arterial Hypertension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pathophysiology of Hypertension and General Approach to Treatment
3. Resistant Hypertension
4. Novel Strategies for RAAS Targeting (Figure 1)
4.1. Nonsteroidal MRAs
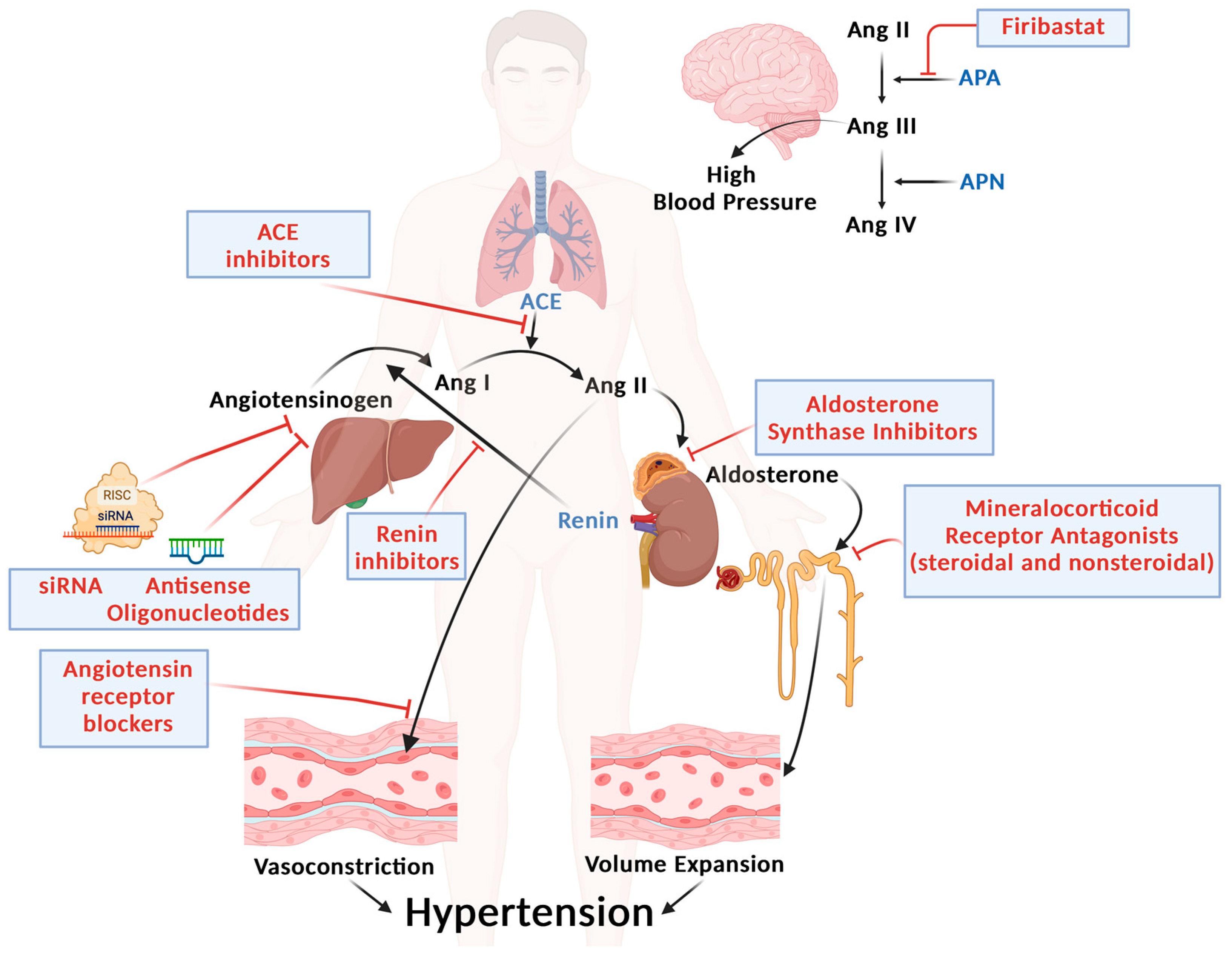
4.2. Aldosterone Synthase Inhibitors (ASIs)
4.3. Inhibition of Angiotensinogen
4.4. Aminopeptidase A (APA) Inhibitors
5. Other Drug Classes
5.1. Endothelin Receptor Antagonists (ERAs) (Figure 2, Panel A)
5.2. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist (GLP-1 RA)-Based Therapies (Figure 2, Panel B)
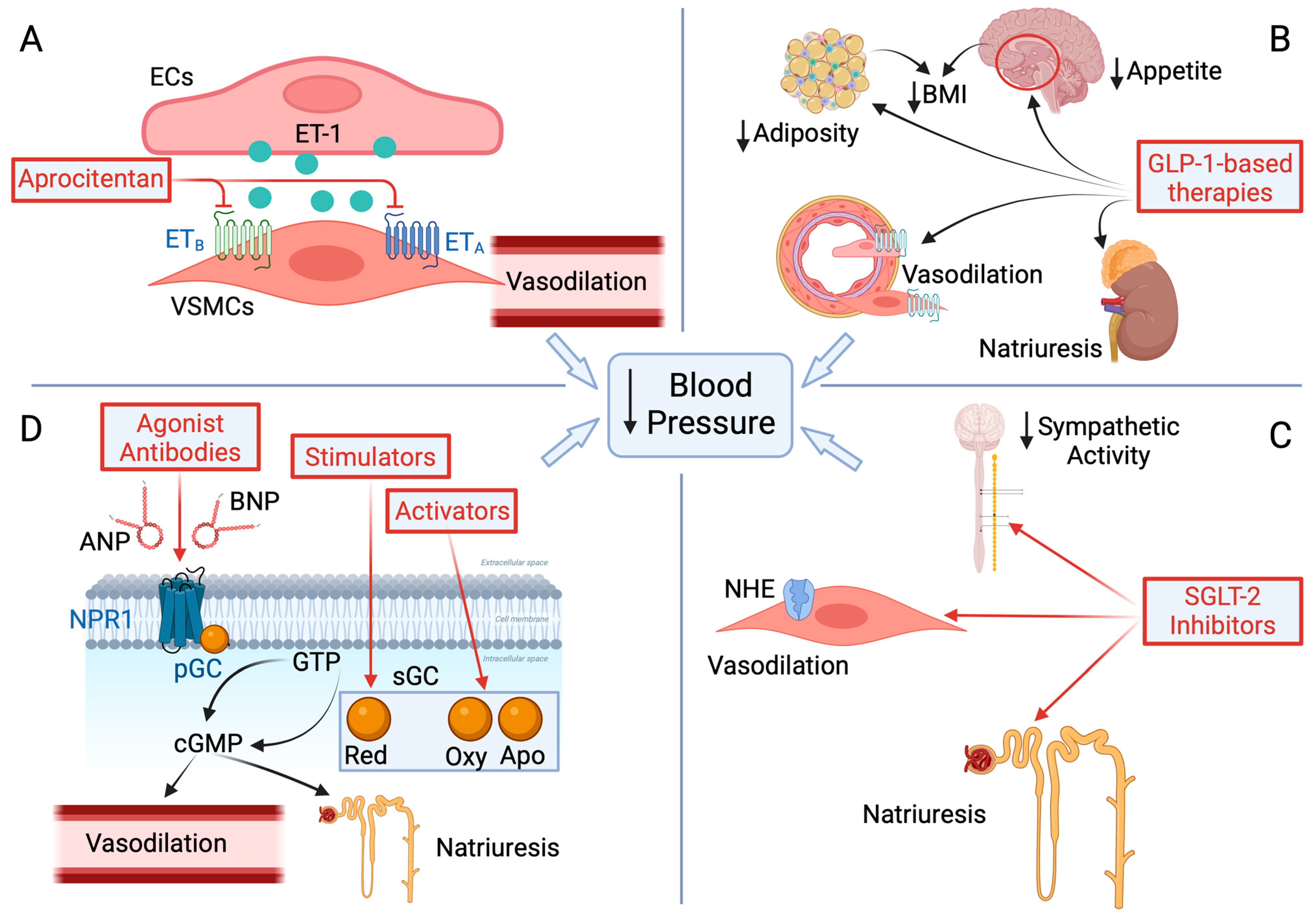
5.3. Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) Inhibitors (Figure 2, Panel C)
5.4. Natriuretic Peptide Receptor 1 (NPR1) and Soluble Guanylate Cyclase (sGC) Agonists (Figure 2, Panel D)
6. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Makki, A.; DiPette, D.; Whelton, P.K.; Murad, M.H.; Mustafa, R.A.; Acharya, S.; Beheiry, H.M.; Champagne, B.; Connell, K.; Cooney, M.T.; et al. Hypertension Pharmacological Treatment in Adults: A World Health Organization Guideline Executive Summary. Hypertension 2022, 79, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2017 Risk Factor Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1923–1994. [Google Scholar]
- Nolde, J.M.; Beaney, T.; Carnagarin, R.; Schutte, A.E.; Poulter, N.R.; Schlaich, M.P. Global Impact of Different Blood Pressure Thresholds in 4 021 690 Participants of the May Measurement Month Initiative. Hypertension 2022, 79, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acelajado, M.C.; Hughes, Z.H.; Oparil, S.; Calhoun, D.A. Treatment of Resistant and Refractory Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewster, U.C.; Setaro, J.F.; Perazella, M.A. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system: Cardiorenal effects and implications for renal and cardiovascular disease states. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2003, 326, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, T.; Borghi, C.; Charchar, F.; Khan, N.A.; Poulter, N.R.; Prabhakaran, D.; Ramirez, A.; Schlaich, M.; Stergiou, G.S.; Tomaszewski, M.; et al. 2020 International Society of Hypertension Global Hypertension Practice Guidelines. Hypertension 2020, 75, 1334–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, R.M.; Calhoun, D.A.; Bakris, G.L.; Brook, R.D.; Daugherty, S.L.; Dennison-Himmelfarb, C.R.; Egan, B.M.; Flack, J.M.; Gidding, S.S.; Judd, E.; et al. Resistant Hypertension: Detection, Evaluation, and Management: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2018, 72, e53–e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daugherty, S.L.; Powers, J.D.; Magid, D.J.; Tavel, H.M.; Masoudi, F.A.; Margolis, K.L.; O’Connor, P.J.; Selby, J.V.; Ho, P.M. Incidence and prognosis of resistant hypertension in hypertensive patients. Circulation 2012, 125, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, B.M.; Li, J. Role of aldosterone blockade in resistant hypertension. Semin. Nephrol. 2014, 34, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, E.K.; Calhoun, D.A.; Warnock, D.G. Pathophysiology and treatment of resistant hypertension: The role of aldosterone and amiloride-sensitive sodium channels. Semin. Nephrol. 2014, 34, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schrier, R.W. Aldosterone ‘escape’ vs. ‘breakthrough’. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2010, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, A.; Hundemer, G.L.; Nanba, K.; Parksook, W.W.; Brown, J.M. Primary Aldosteronism: State-of-the-Art Review. Am. J. Hypertens. 2022, 35, 967–988. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dahal, K.; Kunwar, S.; Rijal, J.; Alqatahni, F.; Panta, R.; Ishak, N.; Russell, R.P. The Effects of Aldosterone Antagonists in Patients with Resistant Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized and Nonrandomized Studies. Am. J. Hypertens. 2015, 28, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, H.; Dong, P.; Zhao, J. A meta-analysis of add-on use of spironolactone in patients with resistant hypertension. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 233, 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Good, D.W. Nongenomic actions of aldosterone on the renal tubule. Hypertension 2007, 49, 728–739. [Google Scholar]
- Barfacker, L.; Kuhl, A.; Hillisch, A.; Grosser, R.; Figueroa-Perez, S.; Heckroth, H.; Nitsche, A.; Ergüden, J.; Gielen-Haertwig, H.; Schlemmer, K.; et al. Discovery of BAY 94-8862: A nonsteroidal antagonist of the mineralocorticoid receptor for the treatment of cardiorenal diseases. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, 1385–1403. [Google Scholar]
- Bakris, G.L.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Pitt, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossing, P.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Schloemer, P.; Joseph, A.; et al. Effect of Finerenone on Chronic Kidney Disease Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar]
- Pitt, B.; Filippatos, G.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Bakris, G.L.; Rossing, P.; Joseph, A.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Schloemer, P.; et al. Cardiovascular Events with Finerenone in Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2252–2263. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, R.; Filippatos, G.; Pitt, B.; Anker, S.D.; Rossing, P.; Joseph, A.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Gebel, M.; Ruilope, L.M.; et al. Cardiovascular and kidney outcomes with finerenone in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: The FIDELITY pooled analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 474–484. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, R.; Rossignol, P.; Romero, A.; Garza, D.; Mayo, M.R.; Warren, S.; Ma, J.; White, W.B.; Williams, B. Patiromer versus placebo to enable spironolactone use in patients with resistant hypertension and chronic kidney disease (AMBER): A phase 2, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, R.; Pitt, B.; Palmer, B.F.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Burgess, E.; Filippatos, G.; Małyszko, J.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossignol, P.; Rossing, P.; et al. A comparative post hoc analysis of finerenone and spironolactone in resistant hypertension in moderate-to-advanced chronic kidney disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pitt, B.; Kober, L.; Ponikowski, P.; Gheorghiade, M.; Filippatos, G.; Krum, H.; Nowack, C.; Kolkhof, P.; Kim, S.-Y.; Zannad, F. Safety and tolerability of the novel non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist BAY 94-8862 in patients with chronic heart failure and mild or moderate chronic kidney disease: A randomized, double-blind trial. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 2453–2463. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, R.; Kolkhof, P.; Bakris, G.; Bauersachs, J.; Haller, H.; Wada, T.; Zannad, F. Steroidal and non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in cardiorenal medicine. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 152–161. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, S.; Itoh, H.; Rakugi, H.; Okuda, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Yamakawa, S. Double-Blind Randomized Phase 3 Study Comparing Esaxerenone (CS-3150) and Eplerenone in Patients With Essential Hypertension (ESAX-HTN Study). Hypertension 2020, 75, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Kario, K.; Ito, S.; Itoh, H.; Rakugi, H.; Okuda, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Yamakawa, S. Effect of the Nonsteroidal Mineralocorticoid Receptor Blocker, Esaxerenone, on Nocturnal Hypertension: A Post Hoc Analysis of the ESAX-HTN Study. Am. J. Hypertens. 2021, 34, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kario, K.; Ohbayashi, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Itabashi, N.; Kato, M.; Uchiyama, K.; Hirano, K.; Nakamura, N.; Miyamoto, T.; Nagashima, H.; et al. Home blood pressure-lowering effect of a non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor blocker, esaxerenone, versus trichlormethiazide for uncontrolled hypertension: The EXCITE-HT randomized controlled study. Hypertens. Res. 2024, 47, 2435–2446. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duggan, S. Esaxerenone: First Global Approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 477–481. [Google Scholar]
- Leopold, J.A.; Ingelfinger, J.R. Aldosterone and Treatment-Resistant Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 464–467. [Google Scholar]
- Laffin, L.J.; Rodman, D.; Luther, J.M.; Vaidya, A.; Weir, M.R.; Rajicic, N.; Slingsby, B.T.; Nissen, S.E.; Beasley, R.; Budoff, M.; et al. Aldosterone Synthase Inhibition With Lorundrostat for Uncontrolled Hypertension: The Target-HTN Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2023, 330, 1140–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, M.W.; Halvorsen, Y.D.; Marshall, W.; Pater, M.; Isaacsohn, J.; Pearce, C.; Murphy, B.; Alp, N.; Srivastava, A.; Bhatt, D.L.; et al. Phase 2 Trial of Baxdrostat for Treatment-Resistant Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 395–405. [Google Scholar]
- Tuttle, K.R.; Hauske, S.J.; Canziani, M.E.; Caramori, M.L.; Cherney, D.; Cronin, L.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Hugo, C.; Nangaku, M.; Rotter, R.C.; et al. Efficacy and safety of aldosterone synthase inhibition with and without empagliflozin for chronic kidney disease: A randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2024, 403, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnier, M.; Egan, B.M. Adherence in Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1124–1140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, H.; Siddiqui, M.; Judd, E.; Oparil, S.; Calhoun, D. Prevalence of pseudoresistant hypertension due to inaccurate blood pressure measurement. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2016, 10, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Cruz-Lopez, E.O.; Tu, H.C.; Zlatev, I.; Danser, A.H.J. Targeting Angiotensinogen With N-Acetylgalactosamine-Conjugated Small Interfering RNA to Reduce Blood Pressure. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2023, 43, 2256–2264. [Google Scholar]
- Bakris, G.L.; Saxena, M.; Gupta, A.; Chalhoub, F.; Lee, J.; Stiglitz, D.; Makarova, N.; Goyal, N.; Guo, W.; Zappe, D.; et al. RNA Interference With Zilebesiran for Mild to Moderate Hypertension: The KARDIA-1 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2024, 331, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Touyz, R.M. Silencing Angiotensinogen in Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 278–281. [Google Scholar]
- Addison, M.L.; Ranasinghe, P.; Webb, D.J. Novel Pharmacological Approaches in the Treatment of Hypertension: A Focus on RNA-Based Therapeutics. Hypertension 2023, 80, 2243–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Hodgkinson, C.P.; Pratt, R.E.; Dzau, V.J. CRISPR/Cas9 Mediated Deletion of the Angiotensinogen Gene Reduces Hypertension: A Potential for Cure? Hypertension 2021, 77, 1990–2000. [Google Scholar]
- Fink, G.D. Can Gene Targeting Be Used to Cure Hypertension? Hypertension 2021, 77, 2001–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.W.; Mizutani, S.; Harding, J.W. Focus on Brain Angiotensin III and Aminopeptidase A in the Control of Hypertension. Int. J. Hypertens. 2012, 2012, 124758. [Google Scholar]
- Reaux, A.; Fournie-Zaluski, M.C.; David, C.; Zini, S.; Roques, B.P.; Corvol, P.; Llorens-Cortes, C. Aminopeptidase A inhibitors as potential central antihypertensive agents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 13415–13420. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferdinand, K.C.; Balavoine, F.; Besse, B.; Black, H.R.; Desbrandes, S.; Dittrich, H.C.; Nesbitt, S.D.; On behalf of the NEW HOPE Investigators. Efficacy and Safety of Firibastat, A First-in-Class Brain Aminopeptidase A Inhibitor, in Hypertensive Overweight Patients of Multiple Ethnic Origins. Circulation 2019, 140, 138–146. [Google Scholar]
- Krum, H.; Viskoper, R.J.; Lacourciere, Y.; Budde, M.; Charlon, V. The effect of an endothelin-receptor antagonist, bosentan, on blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension. Bosentan Hypertension Investigators. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 784–790. [Google Scholar]
- Schiffrin, E.L. State-of-the-Art lecture. Role of endothelin-1 in hypertension. Hypertension 1999, 34, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cardillo, C.; Campia, U.; Iantorno, M.; Panza, J.A. Enhanced vascular activity of endogenous endothelin-1 in obese hypertensive patients. Hypertension 2004, 43, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weber, M.A.; Black, H.; Bakris, G.; Krum, H.; Linas, S.; Weiss, R.; Linseman, J.V.; Wiens, B.L.; Warren, M.S.; Lindholm, L.H. A selective endothelin-receptor antagonist to reduce blood pressure in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2009, 374, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar]
- Bakris, G.L.; Lindholm, L.H.; Black, H.R.; Krum, H.; Linas, S.; Linseman, J.V.; Arterburn, S.; Sager, P.; Weber, M. Divergent results using clinic and ambulatory blood pressures: Report of a darusentan-resistant hypertension trial. Hypertension 2010, 56, 824–830. [Google Scholar]
- Schlaich, M.P.; Bellet, M.; Weber, M.A.; Danaietash, P.; Bakris, G.L.; Flack, J.M.; Dreier, R.F.; Sassi-Sayadi, M.; Haskell, L.P.; Narkiewicz, K.; et al. Dual endothelin antagonist aprocitentan for resistant hypertension (PRECISION): A multicentre, blinded, randomised, parallel-group, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2022, 400, 1927–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadin, F.; Sud, K.; Munoz Estrella, A.; Moctezuma, S.; Wu, L.; Berookhim, J.; Lucas, C.H.; Patel, D.; Argulian, E. The prevalence and predictors of resistant hypertension in high-risk overweight and obese patients: A cross-sectional study based on the 2017 ACC/AHA guidelines. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2019, 21, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, J.E.; do Carmo, J.M.; da Silva, A.A.; Wang, Z.; Hall, M.E. Obesity-induced hypertension: Interaction of neurohumoral and renal mechanisms. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 991–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Michos, E.D.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Gulati, M. Role of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Achieving Weight Loss and Improving Cardiovascular Outcomes in People with Overweight and Obesity. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e029282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Silva, J.C.; Tavares, C.A.M.; Girardi, A.C.C. The blood pressure lowering effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: A mini-review of the potential mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2023, 69, 102355. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barboza, J.J.; Huaman, M.R.; Melgar, B.; Diaz-Arocutipa, C.; Valenzuela-Rodriguez, G.; Hernandez, A.V. Efficacy of Liraglutide in Non-Diabetic Obese Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, F.B.; Lumbang, G.N.O.; Gaid, D.R.M.; Cruz, L.L.A.; Magalong, J.V.; Bantayan, N.R.B.; Lara-Breitinger, K.M.; Gulati, M.; Bakris, G. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists modestly reduced blood pressure among patients with and without diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis and meta-regression. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 2209–2228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Aronne, L.J.; Ahmad, N.N.; Wharton, S.; Connery, L.; Alves, B.; Kiyosue, A.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Packer, M.; Zile, M.R.; Kramer, C.M.; Baum, S.J.; Litwin, S.E.; Menon, V.; Ge, J.; Weerakkody, G.J.; Ou, Y.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide for Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 427–437. [Google Scholar]
- Kario, K.; Hoshide, S.; Narita, K.; Okawara, Y.; Kanegae, H. Cardiovascular Prognosis in Drug-Resistant Hypertension Stratified by 24-Hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure: The JAMP Study. Hypertension 2021, 78, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra, A.; Grunstein, R.R.; Fietze, I.; Weaver, T.E.; Redline, S.; Azarbarzin, A.; Sands, S.A.; Schwab, R.J.; Dunn, J.P.; Chakladar, S.; et al. Tirzepatide for the Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kario, K.; Hoshide, S.; Mizuno, H.; Kabutoya, T.; Nishizawa, M.; Yoshida, T.; Yoshida, T.; Abe, H.; Katsuya, T.; Fujita, Y.; et al. Nighttime Blood Pressure Phenotype and Cardiovascular Prognosis: Practitioner-Based Nationwide JAMP Study. Circulation 2020, 142, 1810–1820. [Google Scholar]
- de Lemos, J.A.; Linetzky, B.; Le Roux, C.W.; Laffin, L.J.; Vongpatanasin, W.; Fan, L.; Hemmingway, A.; Ahmad, N.N.; Bunck, M.C.; Stefanski, A. Tirzepatide Reduces 24-h Ambulatory Blood Pressure in Adults with Body Mass Index ≥ 27 kg/m2: SURMOUNT-1 Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring Substudy. Hypertension 2024, 81, e41–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Kaplan, L.M.; Frias, J.P.; Wu, Q.; Du, Y.; Gurbuz, S.; Coskun, T.; Haupt, A.; Milicevic, Z.; Hartman, M.L. Triple-Hormone-Receptor Agonist Retatrutide for Obesity—A Phase 2 Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 514–526. [Google Scholar]
- Wharton, S.; Blevins, T.; Connery, L.; Rosenstock, J.; Raha, S.; Liu, R.; Ma, X.; Mather, K.J.; Haupt, A.; Robins, D.; et al. Daily Oral GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Orforglipron for Adults with Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frias, J.P.; Deenadayalan, S.; Erichsen, L.; Knop, F.K.; Lingvay, I.; Macura, S.; Mathieu, C.; Pedersen, S.D.; Davies, M. Efficacy and safety of co-administered once-weekly cagrilintide 2.4 mg with once-weekly semaglutide 2.4 mg in type 2 diabetes: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, active-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 720–730. [Google Scholar]
- Marx, N.; Husain, M.; Lehrke, M.; Verma, S.; Sattar, N. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists for the Reduction of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Circulation 2022, 146, 1882–1894. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.M.; Kang, Y.M.; Im, K.; Neuen, B.L.; Anker, S.D.; Bhatt, D.L.; Butler, J.; Cherney, D.Z.; Claggett, B.L.; Fletcher, R.A.; et al. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors and Major Adverse Cardiovascular Outcomes: A SMART-C Collaborative Meta-Analysis. Circulation 2024, 149, 1789–1801. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahwin, P.; Martinez, D. The relationship between SGLT2 and systemic blood pressure regulation. Hypertens. Res. 2024, 47, 2094–2103. [Google Scholar]
- Kario, K.; Ferdinand, K.C.; O’Keefe, J.H. Control of 24-h blood pressure with SGLT2 inhibitors to prevent cardiovascular disease. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 63, 249–262. [Google Scholar]
- Kario, K.; Ferdinand, K.C.; Vongpatanasin, W. Are SGLT2 Inhibitors New Hypertension Drugs? Circulation 2021, 143, 1750–1753. [Google Scholar]
- Ostrominski, J.W.; Vaduganathan, M.; Selvaraj, S.; Claggett, B.L.; Miao, Z.M.; Desai, A.S.; Jhund, P.S.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Lam, C.S.; Inzucchi, S.E.; et al. Dapagliflozin and Apparent Treatment-Resistant Hypertension in Heart Failure With Mildly Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction: The DELIVER Trial. Circulation 2023, 148, 1945–1957. [Google Scholar]
- An, J.; Sim, J.J.; Zhou, M.M.; Zhou, H.; Choi, S.K.; Brettler, J.W.; Ong-Su, A.L.; Reynolds, K. Blood Pressure Reduction and Changes in Antihypertensive Medication Use Among Patients with Hypertension Who Initiated Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2024, 26, 1318–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, N.; Jardine, M.J.; Oshima, M.; Hockham, C.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Schutte, A.E.; Arnott, C.; Chang, T.I.; et al. Blood Pressure Effects of Canagliflozin and Clinical Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease: Insights From the CREDENCE Trial. Circulation 2021, 143, 1735–1749. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Toyoda, M.; Hatori, N.; Kanaoka, T.; Wakui, H.; Sakai, H.; Furuki, T.; Chin, K.; Ito, S.; et al. Pretreatment body mass index affects achievement of target blood pressure with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. Hypertens. Res. 2024, 47, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vongpatanasin, W.; Addo, T. The Next Chapter of Renal Denervation After US Food and Drug Administration Approval. Circulation 2024, 149, 760–763. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dunn, M.E.; Kithcart, A.; Kim, J.H.; Ho, A.J.; Franklin, M.C.; Romero Hernandez, A.; de Hoon, J.; Botermans, W.; Meyer, J.; Jin, X.; et al. Agonist antibody to guanylate cyclase receptor NPR1 regulates vascular tone. Nature 2024, 633, 654–661. [Google Scholar]
- Sandner, P. From molecules to patients: Exploring the therapeutic role of soluble guanylate cyclase stimulators. Biol. Chem. 2018, 399, 679–690. [Google Scholar]
- Tawa, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Ohkita, M. Soluble guanylate cyclase stimulators and activators as potential antihypertensive drugs. Hypertens. Res. 2025, 48, 1458–1470. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schinzari, F.; Montenero, R.; Cardillo, C.; Tesauro, M. Emerging Pharmacological Approaches for the Treatment of Arterial Hypertension. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040790
Schinzari F, Montenero R, Cardillo C, Tesauro M. Emerging Pharmacological Approaches for the Treatment of Arterial Hypertension. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(4):790. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040790
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchinzari, Francesca, Rossella Montenero, Carmine Cardillo, and Manfredi Tesauro. 2025. "Emerging Pharmacological Approaches for the Treatment of Arterial Hypertension" Biomedicines 13, no. 4: 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040790
APA StyleSchinzari, F., Montenero, R., Cardillo, C., & Tesauro, M. (2025). Emerging Pharmacological Approaches for the Treatment of Arterial Hypertension. Biomedicines, 13(4), 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040790






