Neutralization of Marinobufagenin Demonstrates Efficacy In Vitro and In Vivo in Models of Pre-Eclampsia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
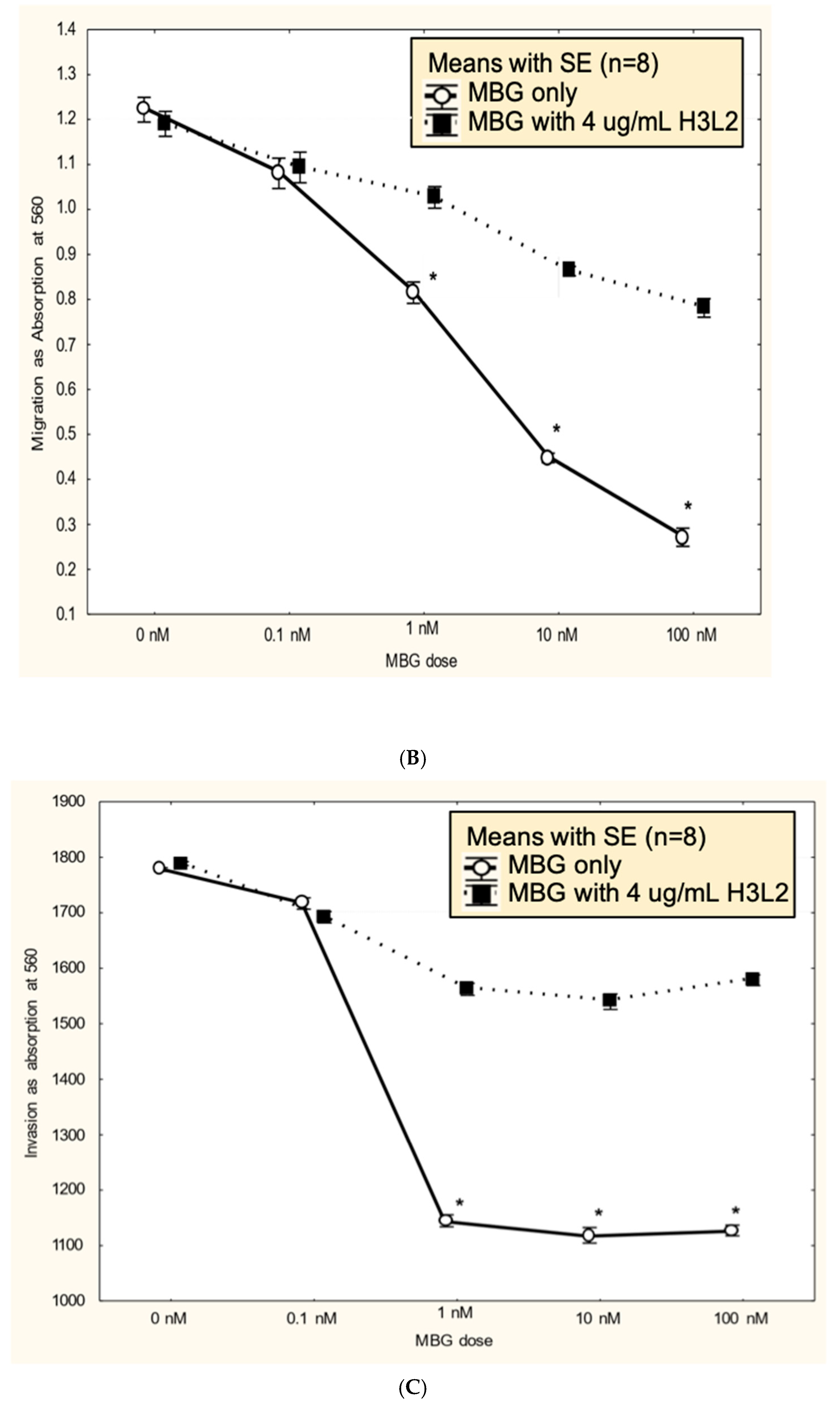
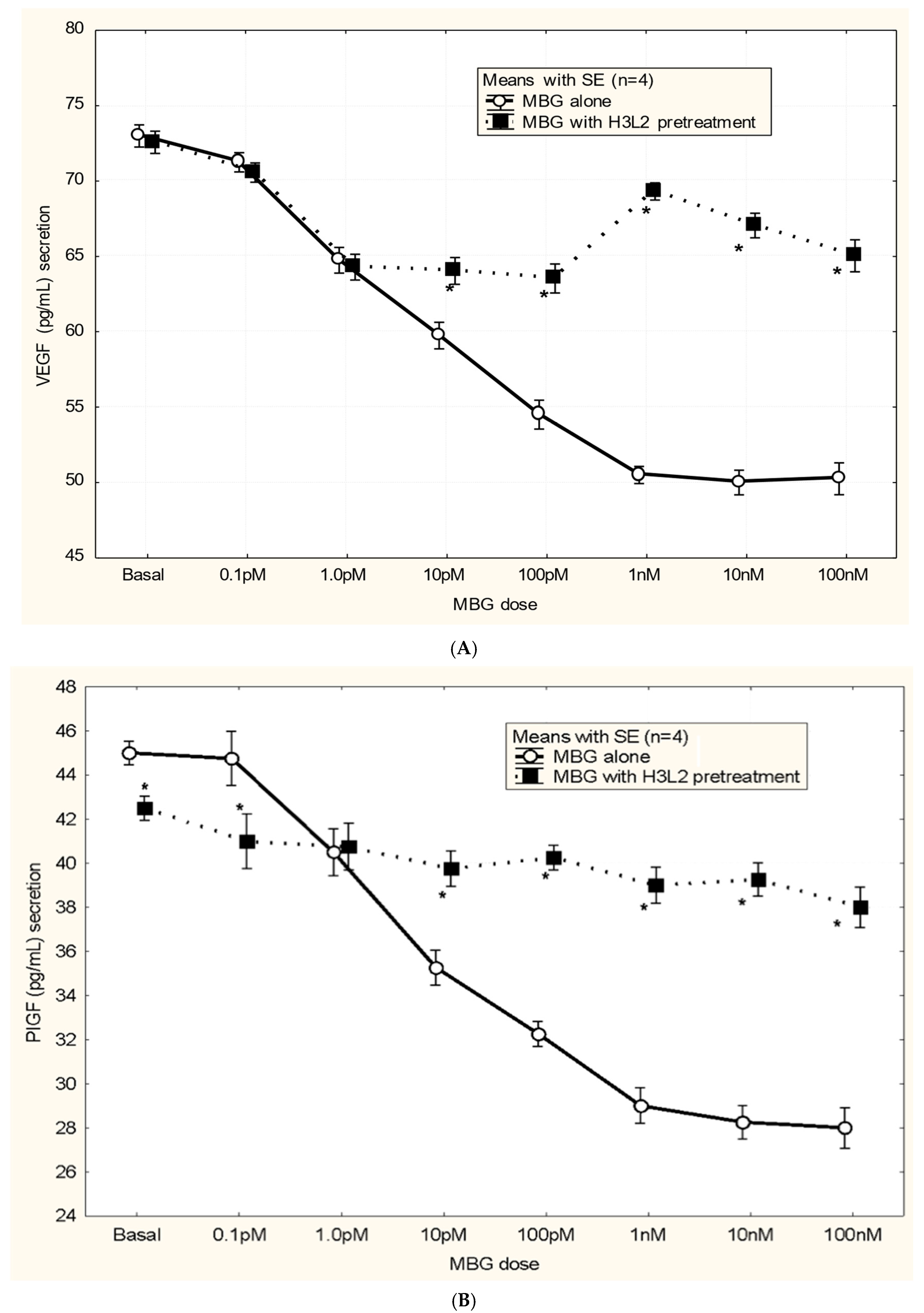
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions/Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- World Health Organization (2000) Maternal Mortality in 2000; Estimates Developed by WHO, UNICEF and UNFPA; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- von Dadelszen, P.; Magee, L.A. Pre-eclampsia: An Update. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2014, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steegers, E.A.; von Dadelszen, P.; Duvekot, J.J.; Pijnenborg, R. Pre-eclampsia. Lancet 2010, 376, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berg, C.; Mackay, A.; Qin, C.; Callaghan, W. Overview of maternal morbidity during hospitalization for labor and delivery in the United States: 1993 to 1997 and 2001 to 2005. Obstet. Anesthesia Dig. 2009, 30, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, A.B.; Saftlas, A.F.; Hsia, J.; Atrash, H.K. Secular trends in the rates of preeclampsia, eclampsia, and gestational hypertension, United States, 1987-2004. Am. J. Hypertens. 2008, 21, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pridjian, G.; Puschett, J.B. Preeclampsia, Part I: Clinical and pathophysiological considerations. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2002, 57, 598–618. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorova, O.V.; Agalakova, N.I.; Morrell, C.H.; Lakatta, E.G.; Bagrov, A.Y. ANP differentially modulates marinobufagenin-induced sodium pump inhibition in kidney and aorta. Hypertension 2006, 48, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoner, W.; Scheiner-Bobis, G. Endogenous and exogenous cardiac glycosides: Their roles in hypertension, salt metabolism, and cell growth. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2007, 293, C509–C536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorova, O.V.; I Tapilskaya, N.; Bzhelyansky, A.M.; Frolova, E.V.; Nikitina, E.R.; A Reznik, V.; A Kashkin, V.; Bagrov, A.Y. Interaction of Digibind with endogenous cardiotonic steroids from preeclamptic placentae. J. Hypertens. 2010, 28, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puschett, J.; Agunanne, E.; Uddin, M. Marinobufagenin, resibufogenin and preeclampsia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2010, 1802, 1246–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagrov, A.Y.; Roukoyatkina, N.I.; Pinaev, A.G.; Dmitrieva, R.I.; Fedorova, O.V. Effects of two endogenous NKA inhibitors, marinobufagenin and ouabain, on isolated rat aorta. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 274, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Nikitina, E.R.; Mikhailov, A.V.; Nikandrova, E.S.; Frolova, E.V.; Fadeev, A.V.; Shman, V.V.; Shilova, V.Y.; Tapilskaya, N.I.; Shapiro, J.I.; Fedorova, O.V.; et al. In preeclampsia endogenous cardiotonic steroids induce vascular fibrosis and impair relaxation of umbilical arteries. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Shapiro, J.I. Regulation of sodium pump endocytosis by cardiotonic steroids: Molecular mechanisms and physiological implications. Pathophysiology 2007, 14, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagrov, A.Y.; I Shapiro, J. Endogenous digitalis: Pathophysiologic roles and therapeutic applications. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 2008, 4, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agunanne, E.; Horvat, D.; Harrison, R.; Uddin, M.; Jones, R.; Kuehl, T.; Ghanem, D.; Berghman, L.; Lai, X.; Li, J.; et al. Marinobufagenin Levels in Preeclamptic Patients: A Preliminary Report. Am. J. Perinatol. 2011, 28, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averina, I.V.; Tapilskaya, N.I.; Reznik, V.A.; Frolova, E.V.; Fedorova, O.V.; Lakatta, E.G.; Bagrov, A.Y. Endogenous Na/K-ATPase inhibitors in patients with preeclampsia. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2006, 52, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lopatin, D.A.; Ailamazian, E.K.; Dmitrieva, R.I.; Shpen, V.M.; Fedorova, O.V.; Doris, P.A.; Bagrov, A.Y. Circulating bufodienolide and cardenolide sodium pump inhibitors in preeclampsia. J. Hypertens. 1999, 17, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.N.; Horvat, D.; Childs, E.W.; Puschett, J.B. Marinobufagenin causes endothelial cell monolayer hyperpermeability by altering apoptotic signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2009, 296, R1726–R1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrig, J.C.; Horvat, D.; Allen, S.R.; Jones, R.O.; Kuehl, T.J.; Uddin, M.N. Cardiotonic steroids induce anti-angiogenic and anti-proliferative profiles in first trimester extravillous cytotrophoblast cells. Placenta 2014, 35, 932–936. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, M.N.; Horvat, D.; Glaser, S.S.; Mitchell, B.M.; Puschett, J.B. Examination of the cellular mechanisms by which marinobufagenin inhibits cytotrophoblast function. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 17946–17953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagrov, A.Y.; Fedorova, O.V. Effects of two putative endogenous digitalis-like factors, marinobufagenin and ouabain, on the Na+,K+-pump in human mesenteric arteries. J. Hypertens. 1998, 16, 1953–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puschett, J.B. The role of excessive volume expansion in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Med. Hypotheses 2006, 67, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianosi-Irimie, M.; Vu, H.V.; Whitbred, J.M.; Pridjian, C.A.; Nadig, J.D.; Williams, M.Y.; Wrenn, D.C.; Pridjian, G.; Puschett, J.B. A rat model of preeclampsia. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2005, 8, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.V.; Ianosi-Irimie, M.R.; Pridjian, C.A.; Whitbred, J.M.; Durst, J.M.; Bagrov, A.Y.; Fedorova, O.V.; Pridjian, G.; Puschett, J.B. Involvement of marinobufagenin in a rat model of human preeclampsia. Am. J. Nephrol. 2005, 25, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agunanne, E.; Uddin, M.; Horvat, D.; Puschett, J. Contribution of angiogenic factors in a rat model of pre-eclampsia. Am. J. Nephrol. 2010, 32, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adair, C.; Buckalew, V.; Graves, S.; Lam, G.; Johnson, D.; Saade, G.; Lewis, D.; Robinson, C.; Danoff, T.; Chauhan, N.; et al. Digoxin Immune Fab Treatment for Severe Preeclampsia. Am. J. Perinatol. 2010, 27, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodlin, R.C. Antidigoxin Antibodies in Eclampsia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 318, 518–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorova, O.V.; Lakatta, E.G.; Bagrov, A.Y.; Melander, O. Plasma level of the endogenous sodium pump ligand marinobufagenin is related to the salt-sensitivity in men. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zazerskaya, I.E.; Ishkaraeva, V.V.; Frolova, E.V.; Solodovnikova, N.G.; Grigorova, Y.N.; David Adair, C.; Fedorova, O.V.; Bagrov, A.Y. Magnesium sulfate potentiates effect of DigiFab on marinobufagenin-induced Na/K-ATPase inhibition. Am. J. Hypertens. 2013, 26, 1269–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishkaraeva-Yakovleva, V.V.; Fedorova, O.V.; Solodovnikova, N.G.; Frolova, E.V.; Bzhelyansky, A.M.; Emelyanov, I.V.; Adair, C.D.; Zazerskaya, I.E.; Bagrov, A.Y. DigiFab interacts with endogenous cardiotonic steroids and reverses preeclampsia-induced Na/K-ATPase inhibition. Reprod. Sci. 2012, 19, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorova, O.V.; Simbirtsev, A.S.; Kolodkin, N.I.; Kotov, A.Y.; Agalakova, N.I.; Kashkin, V.A.; Tapilskaya, N.I.; Bzhelyansky, A.; Reznik, V.A.; Frolova, E.V.; et al. Monoclonal antibody to an endogenous bufadienolide, marinobufagenin, reverses preeclampsia-induced Na/K-ATPase inhibition and lowers blood pressure in NaCl-sensitive hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2008, 26, 2414–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, D.; Severson, J.; Uddin, M.; Mitchell, B.; Puschett, J. Resibufogenin prevents the manifestations of preeclampsia in an animal model of the syndrome. Hypertens. Pregnancy 2009, 27, 513–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.N.; Horvat, D.; DeMorrow, S.; Agunanne, E.; Puschett, J.B. Marinobufagenin is an upstream modulator of Gadd45a stress signaling in preeclampsia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2011, 1812, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorova, O.V.; Kolodkin, N.I.; Agalakova, N.I.; Namikas, A.R.; Bzhelyansky, A.; St-Louis, J.; Lakatta, E.G.; Bagrov, A.Y. Antibody to marinobufagenin lowers blood pressure in pregnant rats on a high NaCl intake. J. Hypertens. 2005, 23, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queen, C.; Schneider, W.P.; E Selick, H.; Payne, P.W.; Landolfi, N.F.; Duncan, J.F.; Avdalovic, N.M.; Levitt, M.; Junghans, R.P.; A Waldmann, T. A humanized antibody that binds to the interleukin 2 receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 10029–10033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.N.; Allen, S.R.; Jones, R.O.; Zawieja, D.C.; Kuehl, T.J. Pathogenesis of pre-eclampsia: Marinobufagenin and angiogenic imbalance as biomarkers of the syndrome. Transl. Res. 2012, 160, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keizer, R.J.; Huitema, A.D.R.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Beijnen, J.H. Clinical pharmacokinetics of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2010, 49, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puschett, J.B. Marinobufagenin predicts and resibufogenin prevents preeclampsia: A review of the evidence. Am. J. Perinatol. 2012, 29, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.J.; Vetteth, S.; Periyasamy, S.M.; Kanj, M.; Fedorova, L.; Khouri, S.; Kahaleh, M.B.; Xie, Z.; Malhotra, D.; Kolodkin, N.I.; et al. Central role for the cardiotonic steroid marinobufagenin in the pathogenesis of experimental uremic cardiomyopathy. Hypertension 2006, 47, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkareh, J.; Periyasamy, S.M.; Shidyak, A.; Vetteth, S.; Schroeder, J.; Raju, V.; Hariri, I.M.; El-Okdi, N.; Gupta, S.; Fedorova, L.; et al. Marinobufagenin induces increases in procollagen expression in a process involving protein kinase C and Fli-1: Implications for uremic cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2009, 296, F1219–F1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, S.W.; Williams, G.H. An Endogenous Ouabain-Like Factor Associated with Hypertensive Pregnant Women*. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1984, 59, 1070–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adair, D.; Buckalew, V.; Taylor, K.; Ernest, J.; Frye, A.H.; Evans, C.; Veille, J.-C. Elevated endoxin-like factor complicating a multif etal second trimester pregnancy: Treatment with digoxin-binding immunoglobulin. Am. J. Nephrol. 1996, 16, 529–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
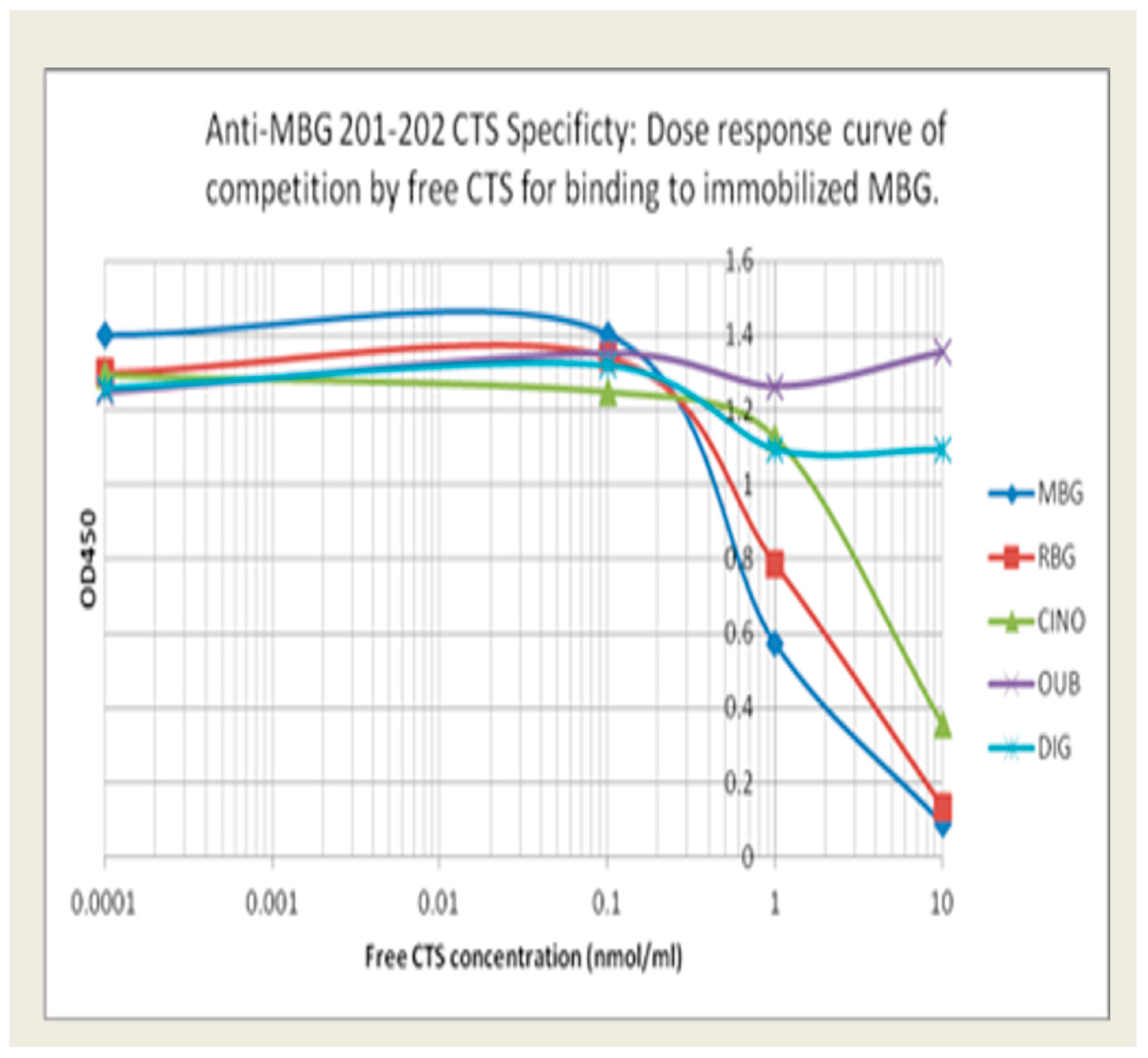




| Antibody | Antigen 1 (MBG-BSA) | Antigen 2 (MBG-KLH) | Relative CTS Specificity as % of MBG Binding (MBG-RBG-CINO-OUB-DIG) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 201–202 | 0.33 nM 1 | 0.20 nM 2 | 100-50-20-0-0 |
| 206–208 | 1.35 nM 3 | 0.20 nM 2 | 100-20-0-0-0 |
| 236–237 | 0.12 nM 2 | 0.14 nM 2 | 100-0-0-0-0 |
| Groups | Blood Pressure—Initial (mm Hg) * | Blood Pressure—Final (mm Hg) * | Urine Protein (mg/24 h) ** | No. of Pups | % Malformed Pups |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NP | 103 ± 5 | 98 ± 7 | 2.8 ± 1.1 | 14 ± 1.8 | 0 |
| PDS | 101 ± 8 | 141 ± 9 * | 5.7 ± 1.6 * | 10.2 ± 1.5 * | 16 * |
| NPM | 104 ± 4 | 137 ± 5 * | 6.4 ± 1.8 * | 9.5 ± 1.3 * | 18 * |
| PDS-3E9 | 102 ± 8 | 100.8 ± 8 | 3.1 ± 0.9 | 13.6 ± 2.1 | 0 |
| PDS-H3L2 | 104 ± 5 | 109.4 ± 11 | 3.5 ± 0.7 | 12.9 ± 3.2 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pantho, A.F.; Zaman, M.; Afroze, S.H.; Wages, J.M.; Yu, B.; Larrick, J.W.; Kuehl, T.J.; Vora, N.; Uddin, M.N. Neutralization of Marinobufagenin Demonstrates Efficacy In Vitro and In Vivo in Models of Pre-Eclampsia. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040782
Pantho AF, Zaman M, Afroze SH, Wages JM, Yu B, Larrick JW, Kuehl TJ, Vora N, Uddin MN. Neutralization of Marinobufagenin Demonstrates Efficacy In Vitro and In Vivo in Models of Pre-Eclampsia. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(4):782. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040782
Chicago/Turabian StylePantho, Ahmed F., Mehruba Zaman, Syeda H. Afroze, John M. Wages, Bo Yu, James W. Larrick, Thomas J. Kuehl, Niraj Vora, and Mohammad Nasir Uddin. 2025. "Neutralization of Marinobufagenin Demonstrates Efficacy In Vitro and In Vivo in Models of Pre-Eclampsia" Biomedicines 13, no. 4: 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040782
APA StylePantho, A. F., Zaman, M., Afroze, S. H., Wages, J. M., Yu, B., Larrick, J. W., Kuehl, T. J., Vora, N., & Uddin, M. N. (2025). Neutralization of Marinobufagenin Demonstrates Efficacy In Vitro and In Vivo in Models of Pre-Eclampsia. Biomedicines, 13(4), 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040782






