Protective Effects of Physalis angulata on Podocythopathies Through B-Cell-Activating Factor Inhibition in Doxorubicin-Induced Nephrotic Syndrome Rat Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Physalis angulata Extraction
2.3. Animal Model
2.4. Measurement of Proteinuria and Biochemical Markers
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. Immunoflourescence
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
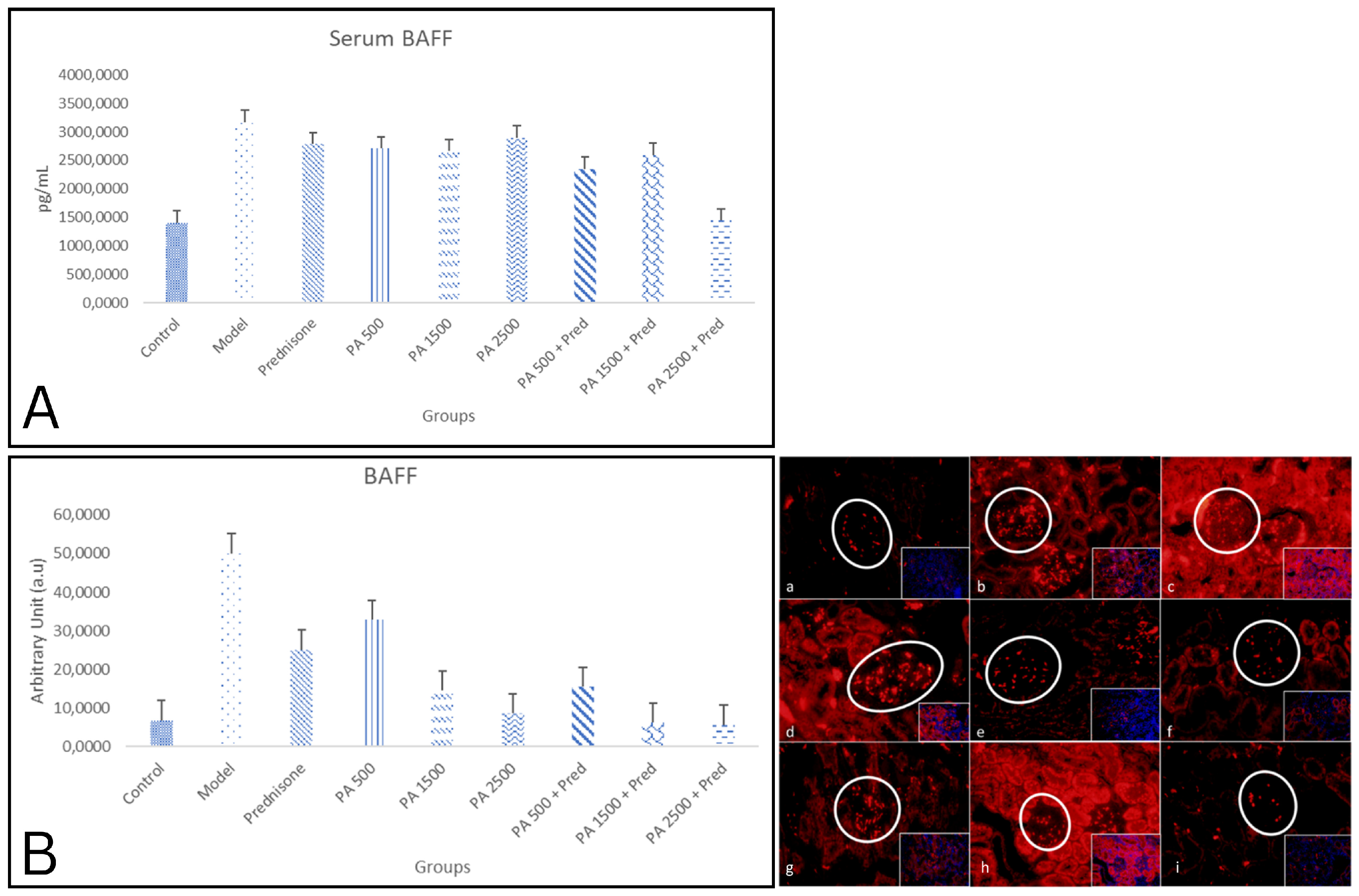
3.1. Serum and Kidney BAFF Levels
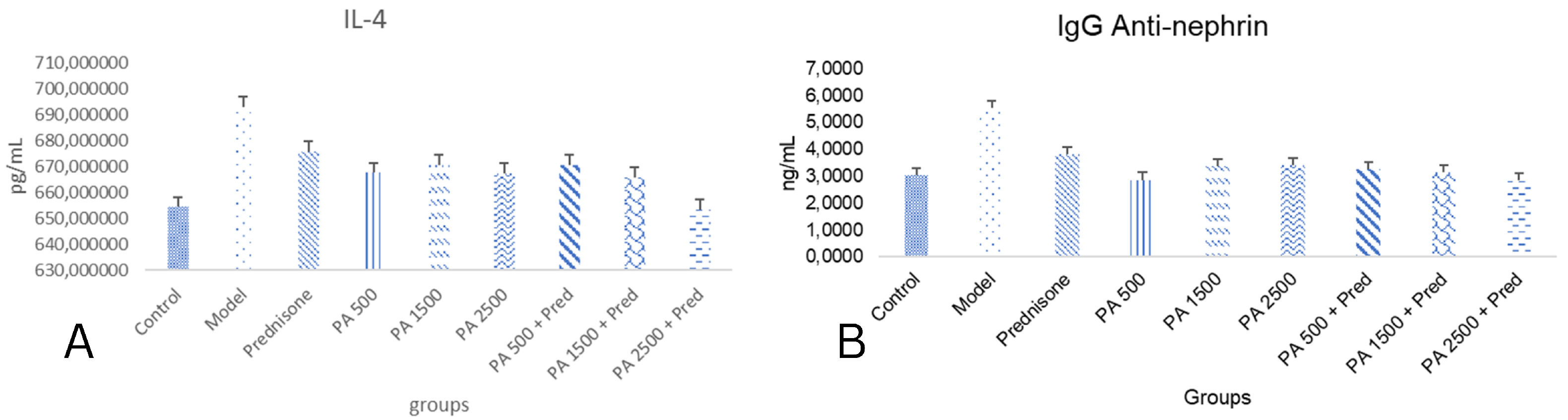
3.2. IL-4 and IgG Anti-Nephrin
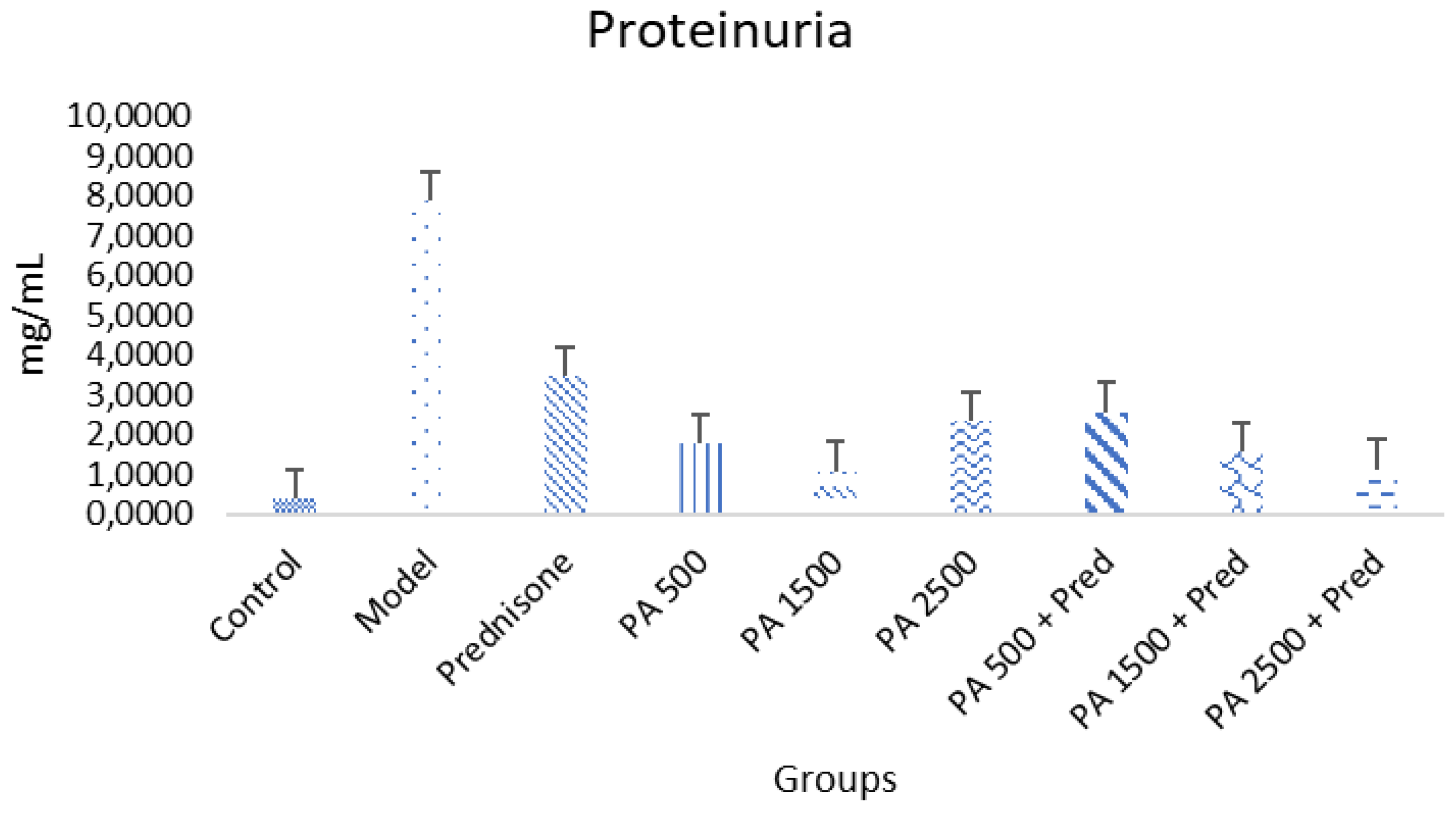
3.3. Reduction in Proteinuria
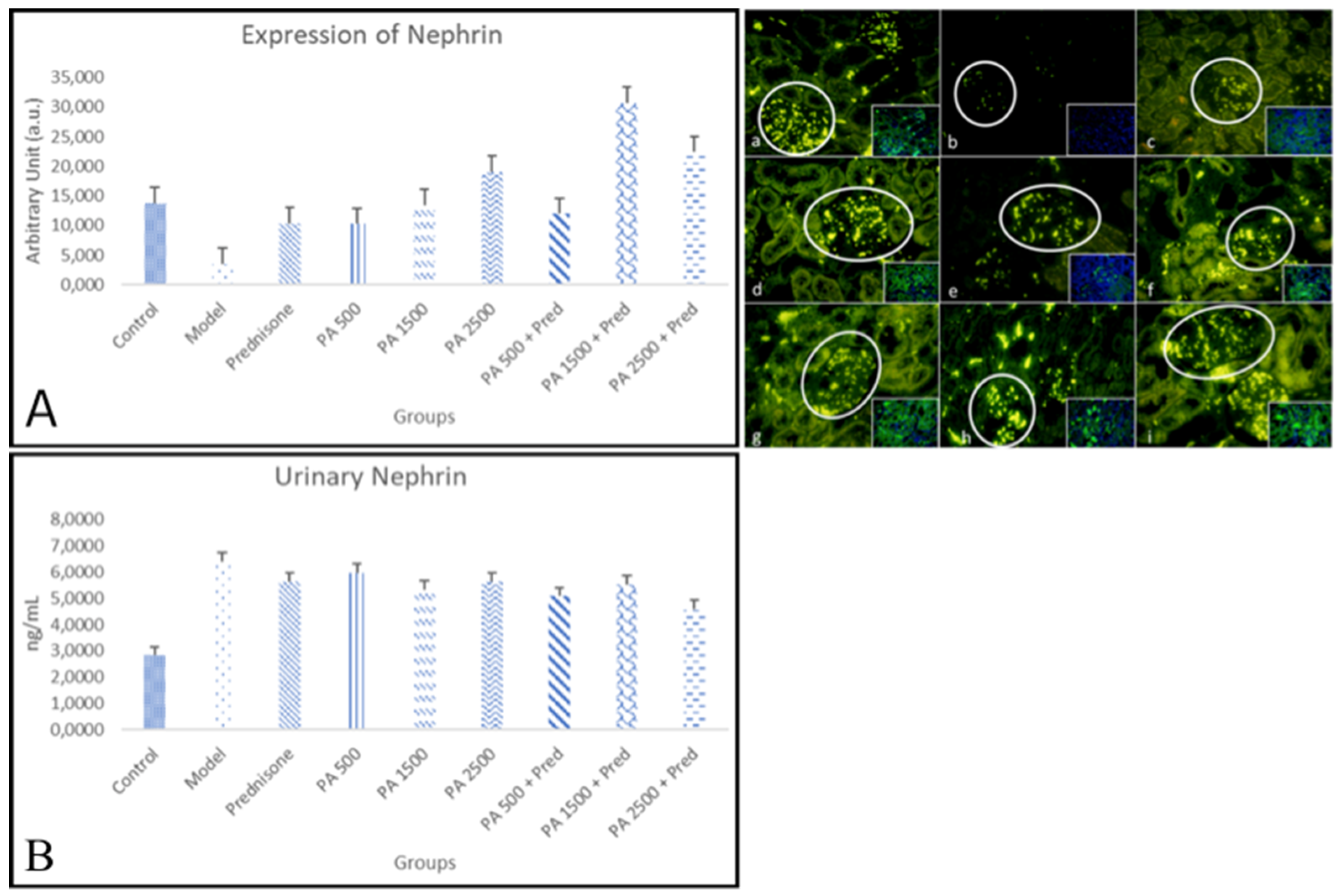
3.4. Podocytopathy Markers
3.4.1. Nephrin
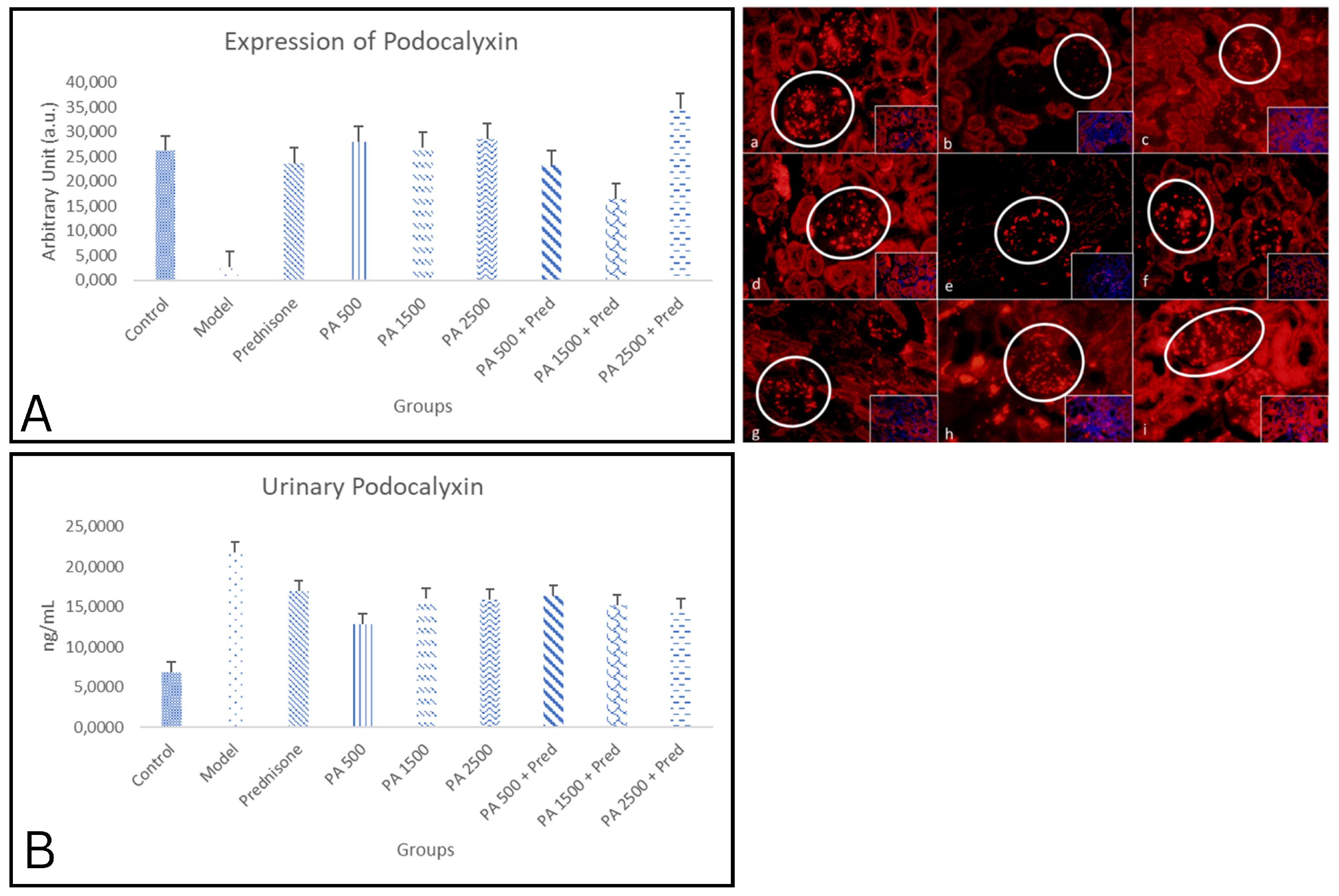
3.4.2. Podocalyxin
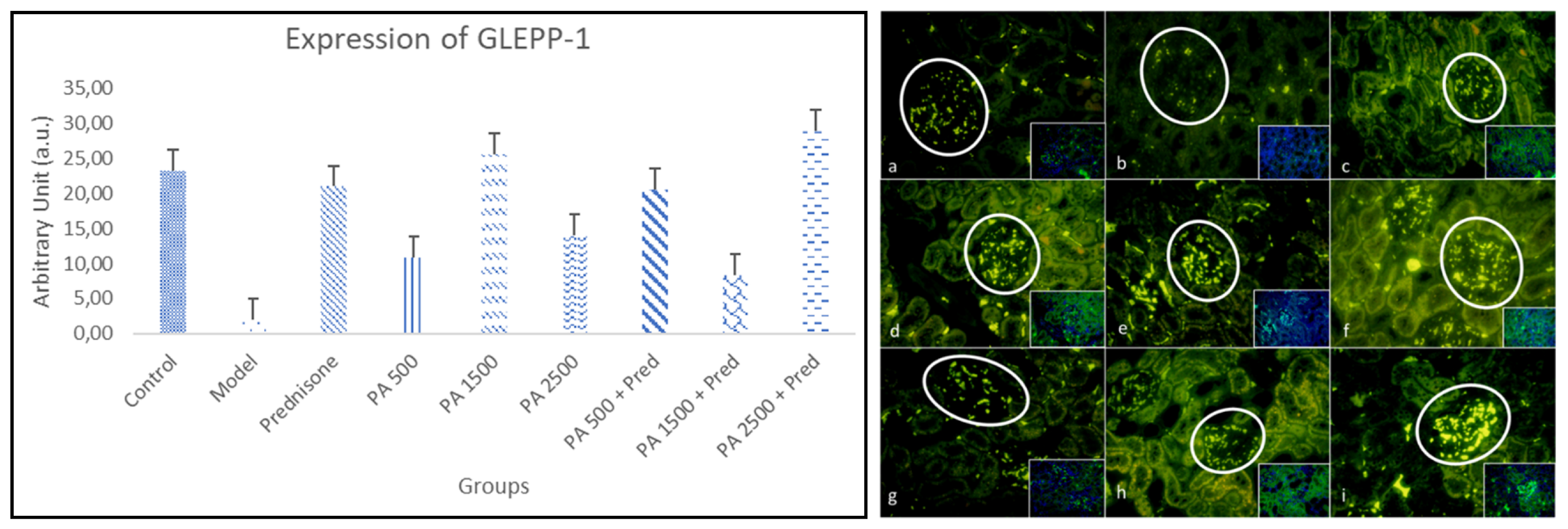
3.4.3. GLEPP-1
4. Discussion
4.1. Role of BAFF Inhibition
4.2. Effects of Physalis angulata in IL-4 and Anti-Nephrin IgG
4.3. Proteinuria
4.4. Protective Effects of Physalis angulata
4.4.1. Nephrin in Renal Tissue and Urine
4.4.2. Podocalyxin in Renal Tissue and Urine
4.4.3. GLEPP-1 in Renal Tissue
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BAFF | B-cell-activating factor |
| BCMA | Protein Maturation of B Cells |
| DAMPs | danger-associated molecular patterns |
| IL-4 | Interleukin-4 |
| GLEPP-1 | glomerular epithelial protein 1 |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| FSGS | Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis |
| PAMPs | pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| TACI | Transmembrane Activator and CAML Interactor |
References
- Tapia, C.; Bashir, K. Nephrotic Syndrome; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29262216/ (accessed on 9 August 2024).
- Maulana, M.G.; Fitriana, E.I.; Liana, P.; Lestari, H.I.; Dalilah. Risk Factors for Progressive Chronic Kidney Disease in Children with Idiopathic Nephrotic Syndrome at Dr. Mohammad Hoesin General Hospital Palembang. Open Access Indones. J. Med. Rev. 2023, 3, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forero-Delgadillo, J.; Ochoa, V.; Restrepo, J.M.; Torres-Canchala, L.; Nieto-Aristizábal, I.; Ruiz-Ordoñez, I.; Sánchez, A.; Barrera, M.C.; Jimenez, C.A.; Tobón, G.J. B-cell activating factor (BAFF) and its receptors’ expression in pediatric nephrotic syndrome is associated with worse prognosis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0277800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uwaezuoke, S.N. Childhood Idiopathic Nephrotic Syndrome as a Podocytopathy. In Glomerulonephritis and Nephrotic Syndrome; Intechopen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kopp, J.B.; Anders, H.J.; Susztak, K.; Podestà, M.A.; Remuzzi, G.; Hildebrandt, F.; Romagnani, P. Podocytopathies. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Smyth, B. From proteinuria to fibrosis: An update on pathophysiology and treatment options. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2021, 46, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesfine, B.B.; Vojisavljevic, D.; Kapoor, R.; Watson, D.; Kandasamy, Y.; Rudd, D. Urinary nephrin—A potential marker of early glomerular injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Nephrol. 2023, 37, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallipattu, S.K.; Kravets, I. The Role of Podocytes and Podocyte-Associated Biomarkers in Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease. J. Endocr. Soc. 2020, 4, bvaa029. [Google Scholar]
- Kostovska, I.; Trajkovska, T.; Topuzovska, S.; Cekovska, S.; Spasovski, G.; Kostovski, O.; Labudovic, D. Urinary nephrin is earlier, more sensitive and specific marker of diabetic nephropathy than microalbuminuria Urinarni nefrin je raniji, osetljiviji i specifičniji marker dijabetesne nefropatije nego mikroalbuminurija. J. Med. Biochem. 2019, 39, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Imaizumi, T.; Nakatochi, M.; Akiyama, S.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kurosawa, H.; Hirayama, Y.; Katsuno, T.; Tsuboi, N.; Hara, M.; Maruyama, S. Urinary podocalyxin as a biomarker to diagnose membranous nephropathy. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.W.; Davidson, A. BAFF inhibition in SLE—Is tolerance restored? Immunol. Rev. 2019, 292, 102–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivarelli, M.; Colucci, M.; Gargiulo, A.; Bettini, C.; Lo Russo, A.; Emma, F. Belimumab for the treatment of children with frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome: The BELNEPH study. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2022, 37, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheba, S.H.; Setiani, N.A.; Sutjiatmo, A.B.; Vikasari, S.N.; Sukandar, E.Y. Combination Effect of Cecendet (Physalisangulata L.) Extract and Methylprednisolone in Reducing Inflammation and Improving Renal Functions in Pristane-induced Lupus Rat Models. Maj. Kedokt. Bdg. 2019, 51, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meira, C.S.; Soares, J.W.C.; dos Reis, B.P.Z.C.; Pacheco, L.V.; Santos, I.P.; Silva, D.K.C.; de Lacerda, J.C.; Daltro, S.R.; Guimarães, E.T.; Soares, M.B. Therapeutic Applications of Physalins: Powerful Natural Weapons. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 864714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastuti, R.; Rosyidah, M. In Vitro Environmental Stresses for Enhancing Withanolides Production in Physalis angulata L. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 239, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugrahenny, D.; Permatasari, N.; Saifur Rohman, M. Physalis minima Leaves Extract Induces Re-Endothelialization in Deoxycorticosterone Acetate-Salt-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction in Rats. Res. J. Life Sci. 2017, 4, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugrahenny, D.; Permatasari, N.; Soeharto, S.; Rahayu, I.D.; Widodo, E.; Mintaroem, K.; Sujuti, H.; Ratnawati, R.; Mayangsari, E.; Irnandi, D.F.; et al. Physalis angulata Leaf Ethanol Extract Reduces Oxidative Stress and Improves Endothelial Progenitor Cells in L-NAME-Induced Hypertensive Rats. HAYATI J. Biosci. 2023, 30, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugrahenny, D.; Rudijanto, A.; Permatasari, N.; Wiyasa, I.W.A.; Widodo, M.A.; Mintaroem, K.; Widjajanto, E.; Mustofa, M. Physalis angulata leaf extract ameliorates L-N G-nitroarginine methyl ester (L-NAME)-induced preeclampsia symptoms in rats through improved endothelial progenitor cells and endothelial cells due to reduced antiangiogenic factor and oxidative stress. F1000Research 2022, 11, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Asanuma, K.; Hidaka, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Tanaka, E.; Takagi-Akiba, M.; Trejo, J.A.O.; Tomino, Y. Newly Identified Molecules Related to Podocyte Injury Induced by Adriamycin. Juntendo Med. J. 2015, 61, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutariya, B.; Saraf, M. α-asarone reduce proteinuria by restoring antioxidant enzymes activities and regulating necrosis factor κB signaling pathway in doxorubicin-induced nephrotic syndrome. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 98, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescovitz, M.D.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Krause-Steinrauf, H.; Becker, D.J.; Gitelman, S.E.; Goland, R.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Marks, J.B.; McGee, P.F.; Moran, A.M.; et al. Rituximab, B-Lymphocyte Depletion, and Preservation of Beta-Cell Function. Physiol. Behav. 2009, 361, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravani, P.; Bonanni, A.; Rossi, R.; Caridi, G.; Ghiggeri, G.M. Anti-CD20 antibodies for idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in children. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 11, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci, M.; Oniszczuk, J.; Vivarelli, M.; Audard, V. B-Cell Dysregulation in Idiopathic Nephrotic Syndrome: What We Know and What We Need to Discover. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 823204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardani, A.K.; Subandiyah, K. Peran B Cell Activating Factor (BAFF) pada Penatalaksanaan Sindrom Nefrotik: Sebuah Paradigma Baru. J. Klin. Ris. Kesehat. 2023, 3, 33–44. [Google Scholar]
- Dossier, C.; Jamin, A.; Deschênes, G. Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: The EBV hypothesis. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 81, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeletti, A.; Lugani, F.; La Porta, E.; Verrina, E.; Caridi, G.; Ghiggeri, G.M. Vaccines and nephrotic syndrome: Efficacy and safety. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2022, 38, 2915–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Ballesteros, F.J.; Oregon-Romero, E.; Franco-Topete, R.A.; Govea-Camacho, L.H.; Cruz, A.; Munoz-Valle, J.F.; Bustos-Rodríguez, F.J.; Pereira-Suárez, A.L.; Palafox-Sánchez, C.A. B-cell activating factor receptor expression is associated with germinal center B-cell maintenance. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 2053–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumric, M.; Zivkovic, P.M.; Kurir, T.T.; Vrdoljak, J.; Vilovic, M.; Martinovic, D.; Bratanic, A.; Lizatovic, I.K.; Bozic, J. Role of b-cell activating factor (Baff) in inflammatory bowel disease. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzzan, M.; Colombel, J.F.; Cerutti, A.; Treton, X.; Mehandru, S. B Cell-Activating Factor (BAFF)-Targeted B Cell Therapies in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 3407–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaly, S.; Rakaee, M.; Abdi, R.; Tsokos, G.C.; Fenton, K.A. Interplay of immune and kidney resident cells in the formation of tertiary lymphoid structures in lupus nephritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltagy, A.; Taleb, R.S.Z.; Allam, M.; Abd El-Kader, R.; Al-Girby, A.; Abdelati, A. Expression of B-cell activating factor (BAFF) in proliferative lupus nephritis, revisited. Alex. J. Med. 2024, 60, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnyana, I.K.; Yulinah, E.; Maeistuti, N.; Setiawan, F. Evaluation of Ethanolic Extracts of Mullaca (Physalis angulata L.) Herbs for Treatment of Lupus Disease in Mice Induced Pristane. Procedia Chem. 2014, 13, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angela, T.B.; Ekastuti, D.R.; Adnyane, I.K.M.; Satyaningtijas, A.S. The Potential of Ciplukan Leaf Extract (Physalis angulata L.) to Improve Kidney Function. Acta VETERINARIA Indones. 2023, 11, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kardani, A.K.; Fitri, L.E.; Samsu, N.; Subandiyah, K.; Endharti, A.T.; Nugrahenny, D.; Wibowo, S. Inhibition of B-cell activating factor activity using active compounds from Physalis angulata in the mechanism of nephrotic syndrome improvement: A computational approach. Narra J. 2024, 4, e859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colucci, M.; Carsetti, R.; Cascioli, S.; Serafinelli, J.; Emma, F.; Vivarelli, M. B cell phenotype in pediatric idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci, M.; Corpetti, G.; Emma, F.; Vivarelli, M. Immunology of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 33, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Rosales, M.; Palafox-Sánchez, C.A.; Franco-Topete, R.A.; Carrillo-Ballesteros, F.J.; Cruz, A.; Salazar-Camarena, D.C.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; Ramos-Solano, F. Renal Tissue Expression of BAFF and BAFF Receptors Is Associated with Proliferative Lupus Nephritis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.Y.; Shen, Y.; Chen, X.W.; Yan, Y.C.; Wu, F.X.; Dai, M.; Li, T.; Yang, C.-D. The characteristics and significance of locally infiltrating B Cells in lupus nephritis and their association with local BAFF expression. Int. J. Rheumatol. 2013, 2013, 954292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, M.J.; Monroe, J.G.; Chan, A.C. B-cell targeted therapies in human autoimmune diseases: An updated perspective. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 237, 264–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.H.J.; Chung, J.J.; Akilesh, S.; Koziell, A.; Jain, S.; Hodgin, J.B.; Miller, M.J.; Stappenbeck, T.S.; Miner, J.H.; Shaw, A.S. B cell-derived IL-4 acts on podocytes to induce proteinuria and foot process effacement. JCI Insight. 2017, 2, e81836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengifo-Salgado, E.; Vargas-Arana, G. Physalis angulata L. (Bolsa mullaca): A review of its traditional uses, chemistry and pharmacology. Bol. Latinoam. Caribe Plantas Med. Aromat. 2013, 12, 431–445. [Google Scholar]
- Eddy, A.A.; Symons, J.M. Nephrotic syndrome in childhood. Lancet 2003, 362, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noone, D.G.; Iijima, K.; Parekh, R. Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in children. Lancet 2018, 392, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downie, M.L.; Gallibois, C.; Parekh, R.S.; Noone, D.G. Nephrotic syndrome in infants and children: Pathophysiology and management. Paediatr. Int. Child. Health 2017, 37, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bökenkamp, A. Proteinuria—Take a closer look! Pediatr. Nephrol. 2020, 35, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davin, J.C. The glomerular permeability factors in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2016, 31, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gruijter, N.M.; Jebson, B.; Rosser, E.C. Cytokine production by human B cells: Role in health and autoimmune disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2022, 210, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Lu, G.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Guo, N.; Li, W. BAFF is involved in the pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy by activating the TRAF6/NF-KB signaling pathway in glomerular mesangial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 795–805. [Google Scholar]
- Colucci, M.; Carsetti, R.; Cascioli, S.; Casiraghi, F.; Perna, A.; Ravà, L.; Ruggiero, B.; Emma, F.; Vivarelli, M. B cell reconstitution after rituximab treatment in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 1811–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Venkatareddy, M.; Kalinowski, A.; Li, T.; Kukla, J.; Mollin, A.; Cara-Fuentes, G.; Patel, S.R.; Garg, P. Nephrin is necessary for podocyte recovery following injury in an adult mature glomerulus. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, A.J.B.; Keller, K.H.; Lerner, G.; Rosales, I.; Collins, A.B.; Sekulic, M.; Waikar, S.S.; Chandraker, A.; Riella, L.V.; Alexander, M.P. Discovery of Autoantibodies Targeting Nephrin in Minimal Change Disease Supports a Novel Autoimmune Etiology. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 33, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horinouchi, T. Anti-nephrin antibodies in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in Japanese children. Res. Sq. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostovska, I.; Trajkovska, K.T.; Topuzovska, S.; Cekovska, S.; Labudovic, D.; Kostovski, O.; Spasovski, G. Chapter One—Nephrinuria and podocytopathies. In Makowski GSBTA in CC; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 1–36. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0065242321000627 (accessed on 17 October 2024).
- Kostovska, I.; Trajkovska, K.T.; Cekovska, S.; Spasovski, G.; Labudovic, D. Nephrin and podocalyxin—New podocyte proteins for early detection of secondary nephropathies. BANTAO J. 2016, 14, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.; Naito, S.; Kawashima, N.; Ishigaki, N.; Sano, T.; Kamata, K.; Takeuchi, Y. New Anti-Nephrin Antibody Mediated Podocyte Injury Model Using a C57BL/6 Mouse Strain. Nephron 2018, 138, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendt, R.; Sobhani, A.; Diefenhardt, P.; Trappe, M.; Völker, L.A. An Updated Comprehensive Review on Diseases Associated with Nephrotic Syndromes. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, B.L.; Li, L. Clinical significance of determining urinary podocalyxin level in children with primary nephrotic syndrome. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 2012, 14, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stone, H.; Magella, B.; Bennett, M.R. The Search for Biomarkers to Aid in Diagnosis, Differentiation, and Prognosis of Childhood Idiopathic Nephrotic Syndrome. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacHado, J.R.; Rocha, L.P.; Neves, P.D.M.D.M.; Cobô, E.D.C.; Silva, M.V.; Castellano, L.R.; Corrêa, R.R.M.; Reis, M.A. An overview of molecular mechanism of nephrotic syndrome. Int. J. Nephrol. 2012, 2012, 937623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardani, A.K.; Fitri, L.E.; Samsu, N.; Subandiyah, K. Forging the Future: B Cell Activating Factor’s Impact on Nephrotic Syndrome. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 31, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kardani, A.K.; Fitri, L.E.; Samsu, N.; Subandiyah, K. Protective Effects of Physalis angulata on Podocythopathies Through B-Cell-Activating Factor Inhibition in Doxorubicin-Induced Nephrotic Syndrome Rat Model. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030719
Kardani AK, Fitri LE, Samsu N, Subandiyah K. Protective Effects of Physalis angulata on Podocythopathies Through B-Cell-Activating Factor Inhibition in Doxorubicin-Induced Nephrotic Syndrome Rat Model. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(3):719. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030719
Chicago/Turabian StyleKardani, Astrid K., Loeki E. Fitri, Nur Samsu, and Krisni Subandiyah. 2025. "Protective Effects of Physalis angulata on Podocythopathies Through B-Cell-Activating Factor Inhibition in Doxorubicin-Induced Nephrotic Syndrome Rat Model" Biomedicines 13, no. 3: 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030719
APA StyleKardani, A. K., Fitri, L. E., Samsu, N., & Subandiyah, K. (2025). Protective Effects of Physalis angulata on Podocythopathies Through B-Cell-Activating Factor Inhibition in Doxorubicin-Induced Nephrotic Syndrome Rat Model. Biomedicines, 13(3), 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030719





