Molecular Biomarkers and More Efficient Therapies for Sepsis
1. Introduction
2. Advances in Molecular Biomarkers
2.1. Proenkephalin as an Early Predictor of Mortality
2.2. Cell-Free DNA (cfDNA) Combined with SOFA in Severity Assessment
2.3. Ischemia-Modified Albumin (IMA) and Lactate in Mortality Prediction
2.4. Calprotectin in Early Diagnosis of Infections
2.5. LVV-Hemorphin-7 (LVV-H7) in Predicting Sepsis
3. Innovative Therapeutic Approaches
3.1. Seraph®-100 Hemoperfusion
3.2. Corticosteroids and Genomic Insights
3.3. Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators (SPMs)
4. Challenges and Opportunities
4.1. Heterogeneity in Sepsis
4.2. Integration of Artificial Intelligence
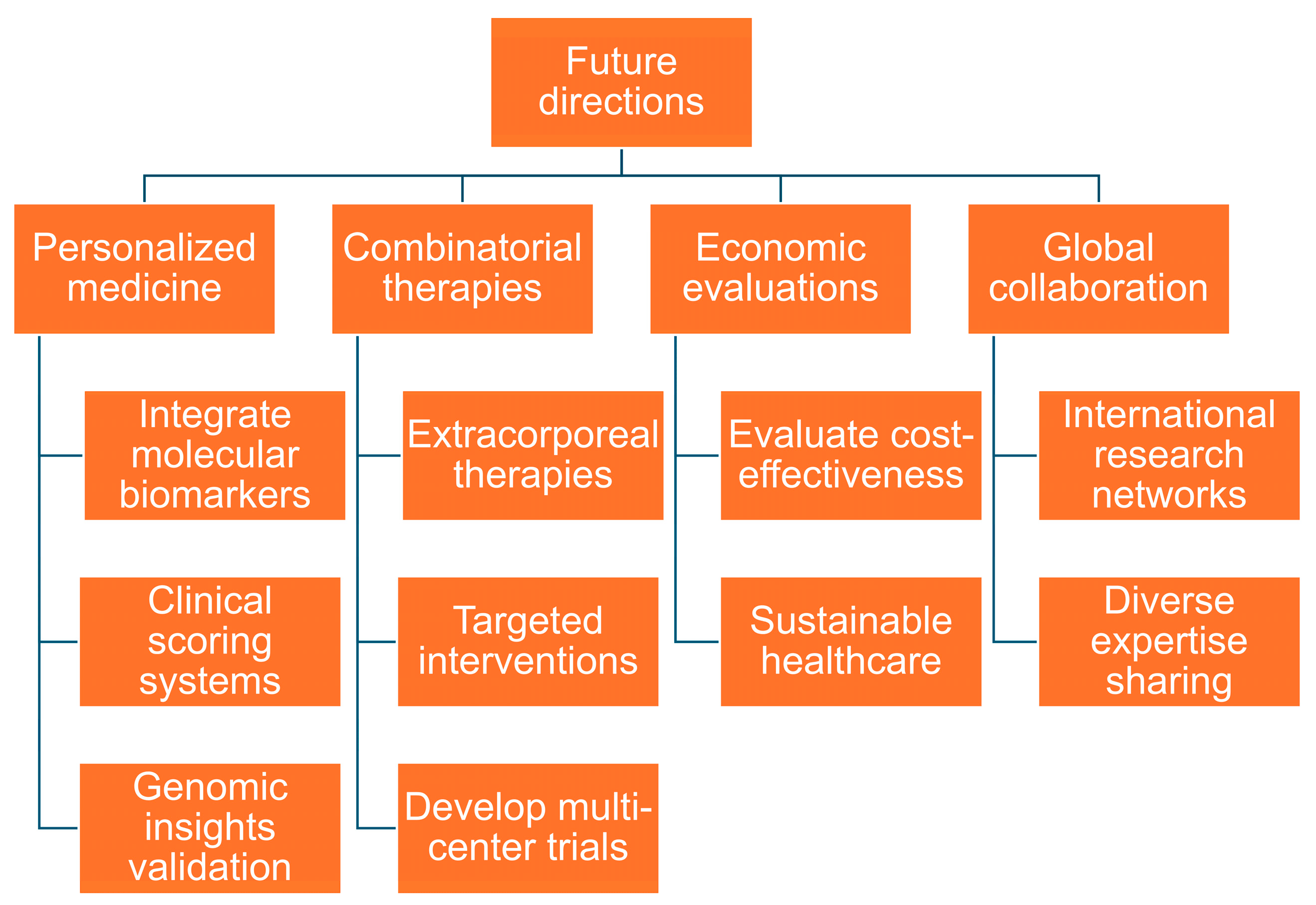
5. Future Directions
5.1. Personalized Medicine
5.2. Combinatorial Therapies
5.3. Economic Evaluations
5.4. Global Collaboration
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van den Berg, M.; van Beuningen, F.E.; ter Maaten, J.C.; Bouma, H.R. Hospital-related costs of sepsis around the world: A systematic review exploring the economic burden of sepsis. J. Crit. Care 2022, 71, 154096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoli, C.J.; Reynolds, M.A.; Sinha, M.; Gitlin, M.; Crouser, E. Epidemiology and Costs of Sepsis in the United States-An Analysis Based on Timing of Diagnosis and Severity Level. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 1889–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudd, K.E.; Kissoon, N.; Limmathurotsakul, D.; Bory, S.; Mutahunga, B.; Seymour, C.W.; Angus, D.C.; West, T.E. The global burden of sepsis: Barriers and potential solutions. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiersinga, W.J.; van der Poll, T. Immunopathophysiology of human sepsis. EBioMedicine 2022, 86, 104363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, A.; Mackraj, I.; Govender, T. Advances in sepsis diagnosis and management: A paradigm shift towards nanotechnology. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verras, C.; Bezati, S.; Bistola, V.; Ventoulis, I.; Matsiras, D.; Tsiodras, S.; Parissis, J.; Polyzogopoulou, E. Point-of-Care Serum Proenkephalin as an Early Predictor of Mortality in Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department with Septic Shock. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Miranda, F.S.; Claudio, L.; de Almeida, D.S.M.; Nunes, J.B.; Barauna, V.G.; Luiz, W.B.; Vassallo, P.F.; Campos, L.C.G. Cell-Free Nuclear and Mitochondrial DNA as Potential Biomarkers for Assessing Sepsis Severity. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, W.; Park, J.H.; Cho, H.; Moon, S.; Ahn, S. Ischemia-Modified Albumin, Lactate, and Combination for Predicting Mortality in Patients with Septic Shock in the Emergency Department. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havelka, A.; Larsson, A.O.; Mårtensson, J.; Bell, M.; Hultström, M.; Lipcsey, M.; Eriksson, M. Analysis of Calprotectin as an Early Marker of Infections Is Economically Advantageous in Intensive Care-Treated Patients. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.K.; Chung, H.W.; Chen, Y.T.; Chen, H.C.; Chen, I.H.; Su, W.L. Association of LVV-Hemorphin-7 with Sepsis and Shock: Roles of Cathepsin D and G in Hemoglobin Metabolism in a Prospective ICU Cohort Study. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacquaniti, A.; Smeriglio, A.; Campo, S.; La Camera, E.; Lanteri, G.; Giunta, E.; Monardo, P.; Trombetta, D. In Vitro Simulated Hemoperfusion on Seraph(®)-100 as a Promising Strategy to Counteract Sepsis. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, A. Recent Data about the Use of Corticosteroids in Sepsis-Review of Recent Literature. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovani, C.M.; Yin, K. Immunosuppression in Sepsis: Biomarkers and Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, A.; Wireko, F.W.; Gajic, O.; Odeyemi, Y.E. The Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio and Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients with Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cysneiros, A.; Galvão, T.; Domingues, N.; Jorge, P.; Bento, L.; Martin-Loeches, I. ARDS Mortality Prediction Model Using Evolving Clinical Data and Chest Radiograph Analysis. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhargava, A.; López-Espina, C.; Schmalz, L.; Khan, S.; Watson, G.L.; Urdiales, D.; Updike, L.; Kurtzman, N.; Dagan, A.; Doodlesack, A.; et al. FDA-Authorized AI/ML Tool for Sepsis Prediction: Development and Validation. NEJM AI 2024, 1, AIoa2400867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Burnham, K.L.; Charles, P.D.; Heilig, R.; Vendrell, I.; Whalley, J.; Torrance, H.D.; Antcliffe, D.B.; May, S.M.; Neville, M.J.; et al. High-throughput mass spectrometry maps the sepsis plasma proteome and differences in patient response. Sci. Transl. Med. 2024, 16, eadh0185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Chen, S.; Ding, R. Evaluation of the Molecular Mechanisms of Sepsis Using Proteomics. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 733537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Beeftink, T.; Guillen-Guio, B.; Lorenzo-Salazar, J.M.; Corrales, A.; Suarez-Pajes, E.; Feng, R.; Rubio-Rodríguez, L.A.; Paynton, M.L.; Cruz, R.; García-Laorden, M.I.; et al. A genome-wide association study of survival in patients with sepsis. Crit. Care 2022, 26, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umemura, Y.; Ogura, H.; Takuma, K.; Fujishima, S.; Abe, T.; Kushimoto, S.; Hifumi, T.; Hagiwara, A.; Shiraishi, A.; Otomo, Y.; et al. Current spectrum of causative pathogens in sepsis: A prospective nationwide cohort study in Japan. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 103, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calandra, T.; Cohen, J.; FRCP for the International Sepsis Forum Definition of Infection in the ICU Consensus Conference. The International Sepsis Forum Consensus Conference on Definitions of Infection in the Intensive Care Unit. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 33, 1538–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, C.; Jones, T.M.; Hamad, Y.; Pande, A.; Varon, J.; O’Brien, C.; Anderson, D.J.; Warren, D.K.; Dantes, R.B.; Epstein, L.; et al. Prevalence, Underlying Causes, and Preventability of Sepsis-Associated Mortality in US Acute Care Hospitals. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e187571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; Machado, F.R.; McIntyre, L.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 1181–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottari, G.; Ranieri, V.M.; Ince, C.; Pesenti, A.; Aucella, F.; Scandroglio, A.M.; Ronco, C.; Vincent, J.L. Use of extracorporeal blood purification therapies in sepsis: The current paradigm, available evidence, and future perspectives. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; Chawla, L.; Husain-Syed, F.; Kellum, J.A. Rationale for sequential extracorporeal therapy (SET) in sepsis. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Feng, Y.; Fu, P. Blood purification for sepsis: An overview. Precis. Clin. Med. 2021, 4, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.H.; Super, M.; Yung, C.W.; Cooper, R.M.; Domansky, K.; Graveline, A.R.; Mammoto, T.; Berthet, J.B.; Tobin, H.; Cartwright, M.J.; et al. An extracorporeal blood-cleansing device for sepsis therapy. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindal, E.W.; Armstead, B.E.; Monaghan, S.F.; Heffernan, D.S.; Ayala, A. Emerging therapeutic targets for sepsis. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2021, 25, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-y.; Ning, B.-t. Signaling pathways and intervention therapies in sepsis. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mer, M.; Schultz, M.J.; Adhikari, N.K. Core elements of general supportive care for patients with sepsis and septic shock in resource-limited settings. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 1690–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perner, A.; Rhodes, A.; Venkatesh, B.; Angus, D.C.; Martin-loeches, I.; Preiser, J.-C.; Vincent, J.-L.; Marshall, J.; Reinhart, K.; Joannidis, M.; et al. Sepsis: Frontiers in supportive care, organisation and research. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, B.; Lambden, S.; Fivez, T.; Gibot, S.; Derive, M.; Grouin, J.M.; Salcedo-Magguilli, M.; Lemarié, J.; De Schryver, N.; Jalkanen, V.; et al. Prospective evaluation of the efficacy, safety, and optimal biomarker enrichment strategy for nangibotide, a TREM-1 inhibitor, in patients with septic shock (ASTONISH): A double-blind, randomised, controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laterre, P.F.; Pickkers, P.; Marx, G.; Wittebole, X.; Meziani, F.; Dugernier, T.; Huberlant, V.; Schuerholz, T.; François, B.; Lascarrou, J.B.; et al. Safety and tolerability of non-neutralizing adrenomedullin antibody adrecizumab (HAM8101) in septic shock patients: The AdrenOSS-2 phase 2a biomarker-guided trial. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshar, M.; Arain, E.; Ye, C.; Gilbert, E.; Xie, M.; Lee, J.; Churpek, M.M.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.; Markossian, T.; Joyce, C. Patient Outcomes and Cost-Effectiveness of a Sepsis Care Quality Improvement Program in a Health System. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llitjos, J.F.; Carrol, E.D.; Osuchowski, M.F.; Bonneville, M.; Scicluna, B.P.; Payen, D.; Randolph, A.G.; Witte, S.; Rodriguez-Manzano, J.; François, B. Enhancing sepsis biomarker development: Key considerations from public and private perspectives. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, W.-L.; Chiu, S.-K.; Shen, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-T. Molecular Biomarkers and More Efficient Therapies for Sepsis. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020468
Su W-L, Chiu S-K, Shen C-H, Chen Y-T. Molecular Biomarkers and More Efficient Therapies for Sepsis. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(2):468. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020468
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Wen-Lin, Sheng-Kang Chiu, Chih-Hao Shen, and Yi-Ting Chen. 2025. "Molecular Biomarkers and More Efficient Therapies for Sepsis" Biomedicines 13, no. 2: 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020468
APA StyleSu, W.-L., Chiu, S.-K., Shen, C.-H., & Chen, Y.-T. (2025). Molecular Biomarkers and More Efficient Therapies for Sepsis. Biomedicines, 13(2), 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020468




