Amelioration of Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology in Zebrafish by Photobiomodulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Zebrafish Maintenance
2.2. Chemicals/Reagents
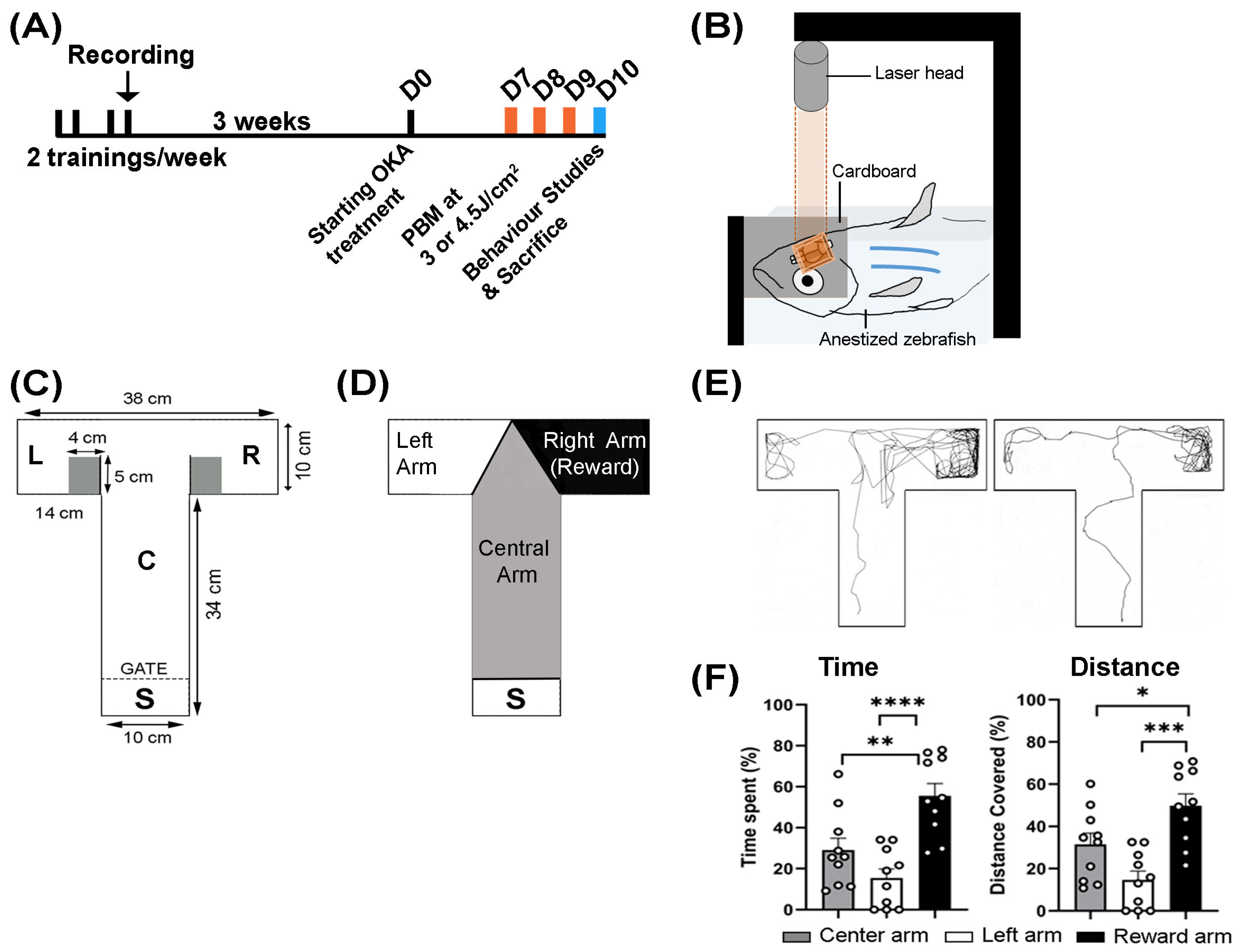
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Okadaic Acid Treatment
2.5. Photobiomodulation (PBM) Treatment
2.6. Behavioral Studies
2.7. Video Recording and Animal Tracking
2.8. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
2.9. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
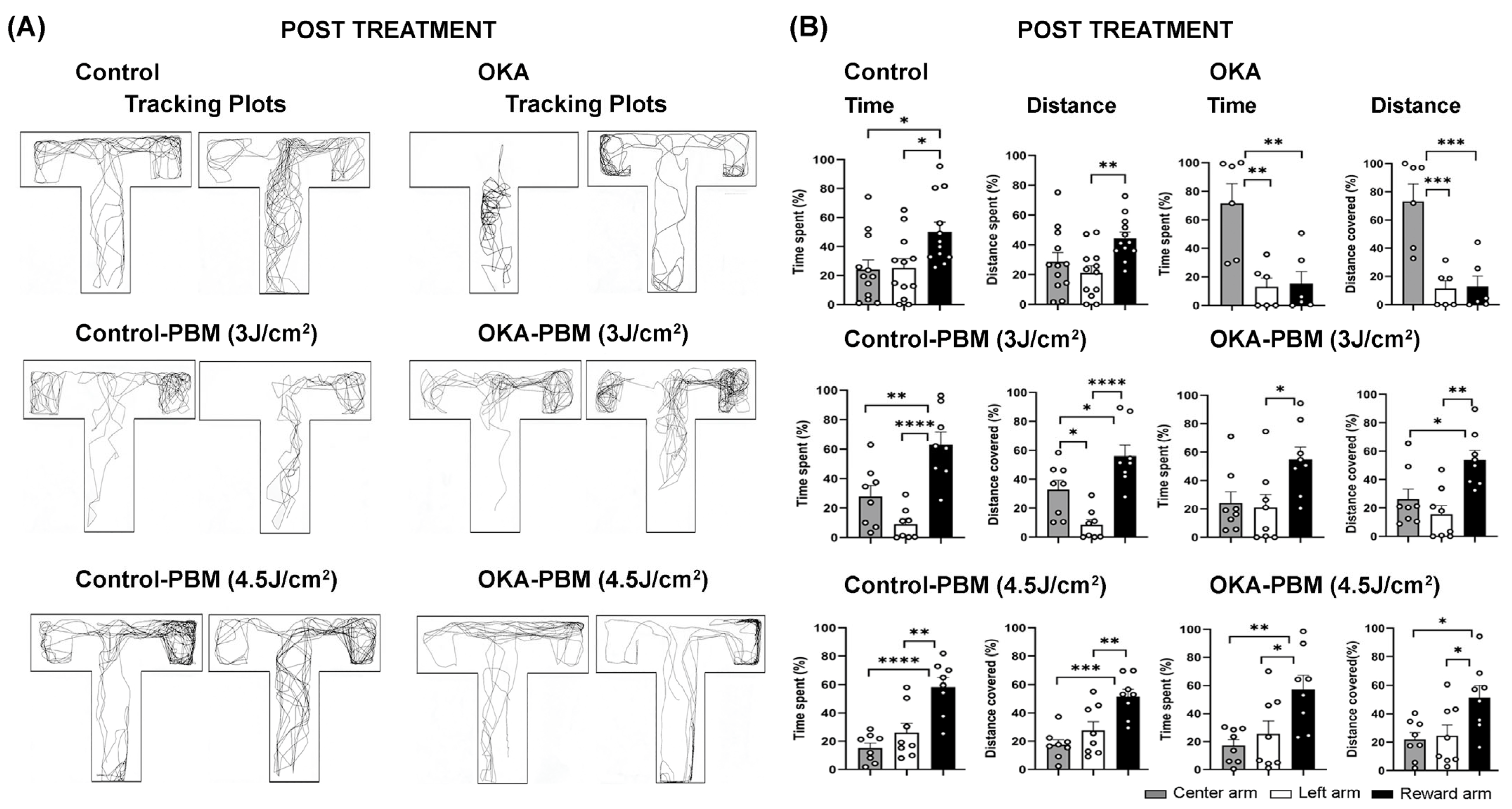
3.1. Behavioral Response to OKA and PBM Treatments
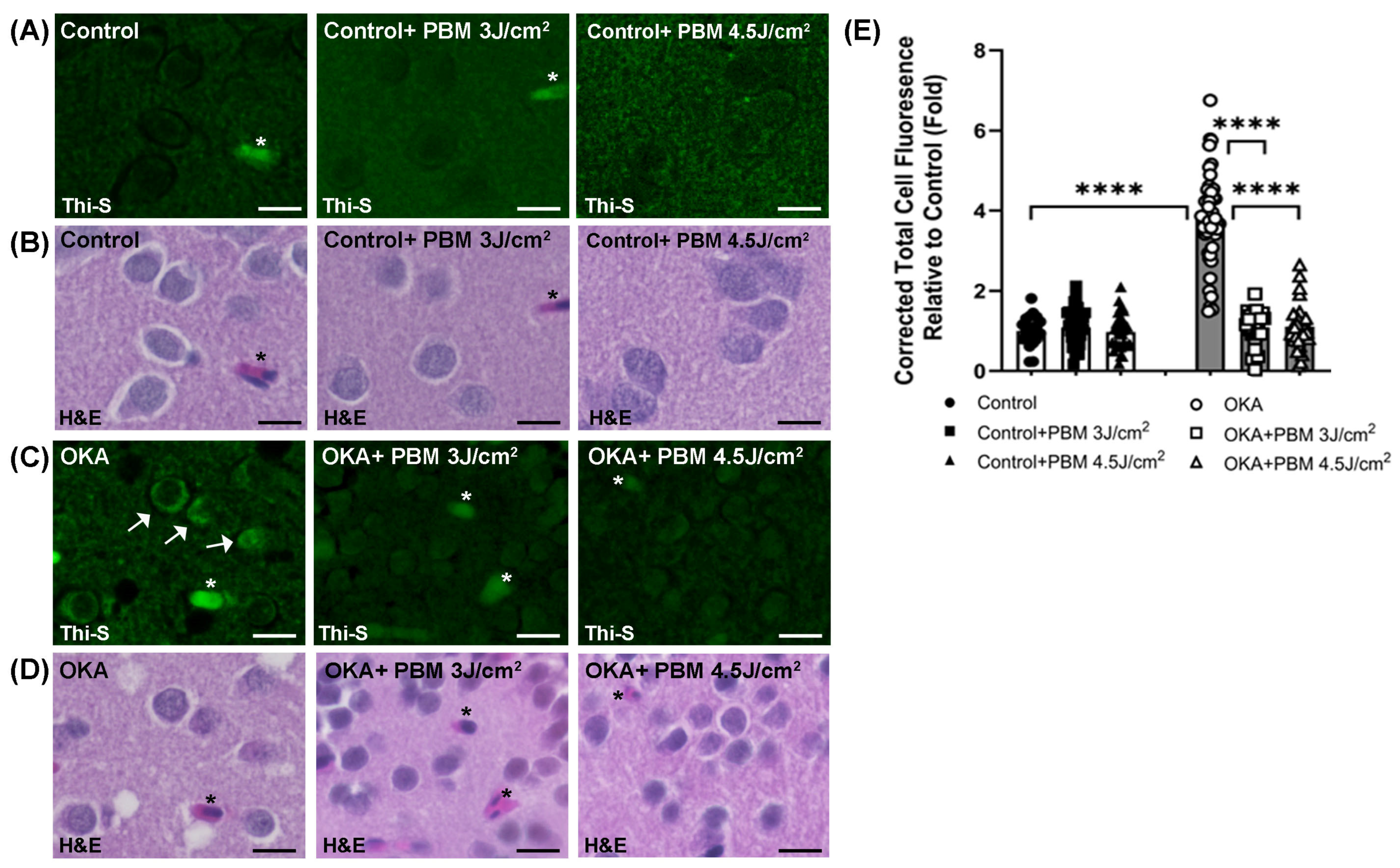
3.2. Effects of OKA and PBM Treatments on Intracellular Tau Aggregation
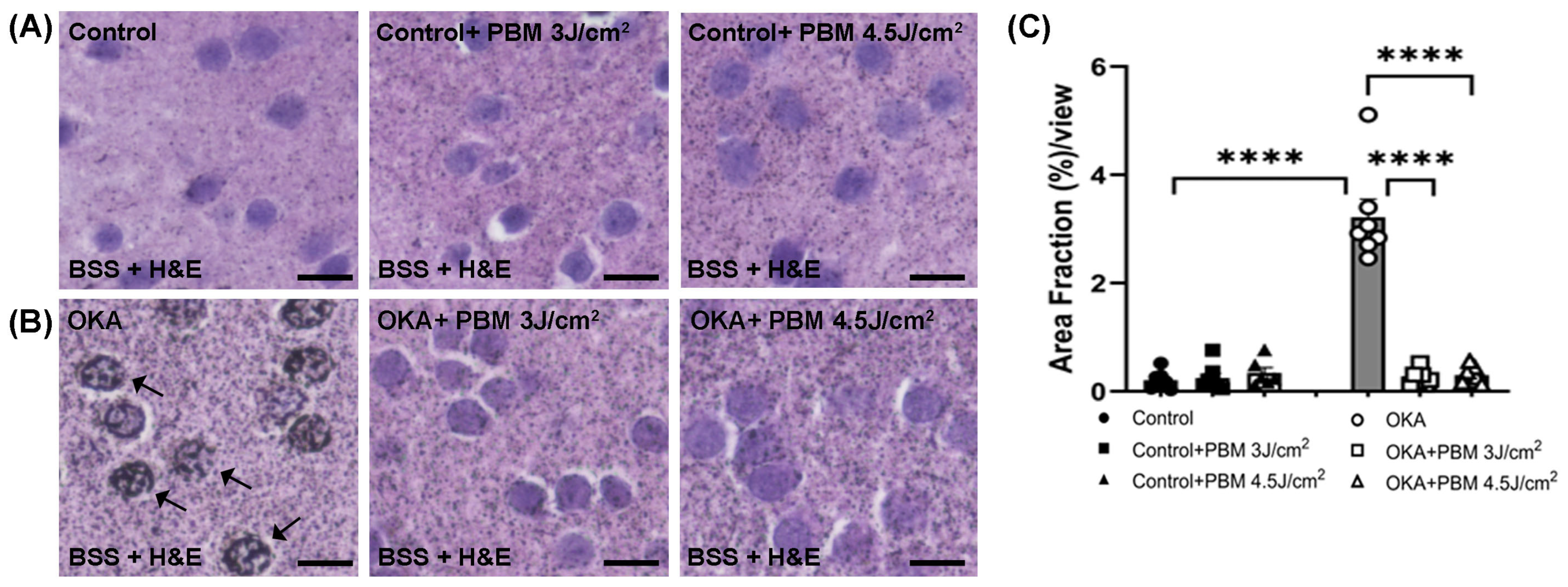
3.3. Effects of OKA and PBM Treatments on Brain Histology and Apoptosis
3.4. Effects of OKA and PBM Treatments on Neuroinflammation
3.5. Effects of OKA and PBM Treatments on Mitochondrial Biogenesis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Aβ | Amyloid beta |
| AD | Alzheimer’s Disease |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| BSS | Bielschowsky’s silver staining |
| CAT | Catalase |
| CCO | Cytochrome C Oxidase |
| CTCF | Corrected total cell fluorescence |
| dUTP | Deoxyuridine triphosphate |
| GSK-3β | Glycogen synthase 3β |
| IACUC | Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated Kinase |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| GFAP | Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| GSH | Reduced glutathione |
| IL-1β | Interleukin 1-beta |
| LLLT | Low-level laser therapy |
| MMP | Mitochondrial membrane potential |
| mTOR | Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin |
| NFTs | Neurofibrillary tangles |
| NIR | Near-infrared |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| OKA | Okadaic acid |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PGC-1α | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| PBM | Photobiomodulation |
| PKA | Protein kinase A |
| PKC | Protein kinase C |
| PP2A | Protein Phosphatase 2A |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RPL13a | Ribosomal protein L13a |
| RT-PCR | Real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| Sirt1 | Silent Information Regulator Transcript 1 |
| TFAM | Mitochondrial transcription factor A |
| Thi-S | Thioflavin-S |
| TNFα | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| TUNEL | Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP Nick-End Labeling |
References
- Kenyon, C.J. The genetics of ageing. Nature 2010, 464, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieschke, G.J.; Currie, P.D. Animal models of human disease: Zebrafish swim into view. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoriello, C.; Zon, L.I. Hooked! Modeling human disease in zebrafish. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2337–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacutu, R.; Craig, T.; Budovsky, A.; Wuttke, D.; Lehmann, G.; Taranukha, D.; Costa, J.; Fraifeld, V.E.; de Magalhães, J.P. Human Ageing Genomic Resources: Integrated databases and tools for the biology and genetics of ageing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D1027–D1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, M.J.; Zerulla, T.C.; Tierney, K.B. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a model for the study of aging and exercise: Physical ability and trainability decrease with age. Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 50, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, S.; Uchiyama, J.; Baughman, A.M.; Goto, T.; Lin, M.C.; Tsai, S.B. The zebrafish as a vertebrate model of functional aging and very gradual senescence. Exp. Gerontol. 2003, 38, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khor, E.S.; Noor, S.M.; Wong, P.F. Understanding the Role of ztor in Aging-related Diseases Using the Zebrafish Model. In Vivo 2019, 33, 1713–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.M., 3rd; Cookson, M.R.; Van Den Bosch, L.; Zetterberg, H.; Holtzman, D.M.; Dewachter, I. Hallmarks of neurodegenerative diseases. Cell 2023, 186, 693–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammon, K. Neurodegenerative disease: Brain windfall. Nature 2014, 515, 299–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Pozo, A.; Frosch, M.P.; Masliah, E.; Hyman, B.T. Neuropathological alterations in Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2011, 1, a006189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kril, J.J.; Patel, S.; Harding, A.J.; Halliday, G.M. Neuron loss from the hippocampus of Alzheimer’s disease exceeds extracellular neurofibrillary tangle formation. Acta Neuropathol. 2002, 103, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostinho, P.; Cunha, R.A.; Oliveira, C. Neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 2766–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurcau, M.C.; Andronie-Cioara, F.L.; Jurcau, A.; Marcu, F.; Tit, D.M.; Pascalau, N.; Nistor-Cseppento, D.C. The Link between Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Neuroinflammation in the Pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s Disease: Therapeutic Implications and Future Perspectives. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.T.; Uddin, M.S.; Mamun, A.A.; Jeandet, P.; Aleya, L.; Mansouri, R.A.; Ashraf, G.M.; Mathew, B.; Bin-Jumah, M.N.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Combination Drug Therapy for the Management of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullard, A. FDA approves third anti-amyloid antibody for Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2024, 23, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo-Pacheco, N.; Sarmiento-Blanco, S.; Vergara-Cadavid, G.; Castro-Leones, M.; Contreras-Puentes, N. Monoclonal therapy with lecanemab in the treatment of mild Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2025, 104, 102620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.H.; Chang, Y.T.; Tseng, H.S.; Kuo, C.Y.; Chen, J.H.; Chien, P.Y.; Chang, Y.J.; Hung, C.C. Comparisons of efficacy and safety of immunotherapies for Alzheimer’s disease treatment: A network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Clin. Med. 2025, 25, 100336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeremic, D.; Navarro-Lopez, J.D.; Jimenez-Diaz, L. Clinical Benefits and Risks of Antiamyloid Antibodies in Sporadic Alzheimer Disease: Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis With a Web Application. J. Med. Internet Res. 2025, 27, e68454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialojan, C.; Takai, A. Inhibitory effect of a marine-sponge toxin, okadaic acid, on protein phosphatases. Specificity and kinetics. Biochem. J. 1988, 256, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, P.K.; Rai, S.; Nath, C. Okadaic acid induced neurotoxicity: An emerging tool to study Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Neurotoxicology 2013, 37, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K.; Gong, C.X. Contributions of protein phosphatases PP1, PP2A, PP2B and PP5 to the regulation of tau phosphorylation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 22, 1942–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nada, S.E.; Williams, F.E.; Shah, Z.A. Development of a Novel and Robust Pharmacological Model of Okadaic Acid-induced Alzheimer’s Disease in Zebrafish. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2016, 15, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Simpkins, J.W. An okadaic acid-induced model of tauopathy and cognitive deficiency. Brain Res. 2010, 1359, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yamada, K.; Zou, L.B.; Nabeshima, T. Spatial memory deficit and neurodegeneration induced by the direct injection of okadaic acid into the hippocampus in rats. J. Neural Transm. 2001, 108, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, S.; Kannan, R.R. Zebrafish: An emerging real-time model system to study Alzheimer’s disease and neurospecific drug discovery. Cell Death Discov. 2018, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadra, M.; Kasem, N.; Haanaes, H.R.; Ellingsen, J.E.; Lyngstadaas, S.P. Enhancement of bone formation in rat calvarial bone defects using low-level laser therapy. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2004, 97, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, T.; Xuan, W.; Xu, T.; Dai, T.; Sharma, S.K.; Kharkwal, G.B.; Huang, Y.Y.; Wu, Q.; Whalen, M.J.; Sato, S.; et al. Comparison of therapeutic effects between pulsed and continuous wave 810-nm wavelength laser irradiation for traumatic brain injury in mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrnes, K.R.; Waynant, R.W.; Ilev, I.K.; Wu, X.; Barna, L.; Smith, K.; Heckert, R.; Gerst, H.; Anders, J.J. Light promotes regeneration and functional recovery and alters the immune response after spinal cord injury. Lasers Surg. Med. 2005, 36, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Dmitriev, A.E.; Cardoso, M.J.; Viers-Costello, A.G.; Borke, R.C.; Streeter, J.; Anders, J.J. 810 nm Wavelength light: An effective therapy for transected or contused rat spinal cord. Lasers Surg. Med. 2009, 41, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oron, A.; Oron, U.; Chen, J.; Eilam, A.; Zhang, C.; Sadeh, M.; Lampl, Y.; Streeter, J.; DeTaboada, L.; Chopp, M. Low-level laser therapy applied transcranially to rats after induction of stroke significantly reduces long-term neurological deficits. Stroke 2006, 37, 2620–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, D.; Houreld, N.; Abrahamse, H. Low level laser therapy (LLLT) as an effective therapeutic modality for delayed wound healing. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1056, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castano, A.P.; Dai, T.; Yaroslavsky, I.; Cohen, R.; Apruzzese, W.A.; Smotrich, M.H.; Hamblin, M.R. Low-level laser therapy for zymosan-induced arthritis in rats: Importance of illumination time. Lasers Surg. Med. 2007, 39, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, L.D.; Lu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, Q. Photobiomodulation Therapy Attenuates Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury in a Neonatal Rat Model. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 65, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Tucker, D.; Dong, Y.; Wu, C.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, T.C.; Zhang, Q. Photobiomodulation therapy promotes neurogenesis by improving post-stroke local microenvironment and stimulating neuroprogenitor cells. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 299, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobiela Ketz, A.; Byrnes, K.R.; Grunberg, N.E.; Kasper, C.E.; Osborne, L.; Pryor, B.; Tosini, N.L.; Wu, X.; Anders, J.J. Characterization of Macrophage/Microglial Activation and Effect of Photobiomodulation in the Spared Nerve Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain. Pain Med. 2017, 18, 932–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hamblin, M.R. Mechanisms and applications of the anti-inflammatory effects of photobiomodulation. AIMS Biophys. 2017, 4, 337–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passarella, S.; Karu, T. Absorption of monochromatic and narrow band radiation in the visible and near IR by both mitochondrial and non-mitochondrial photoacceptors results in photobiomodulation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2014, 140, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamblin, M.R. Mechanisms and Mitochondrial Redox Signaling in Photobiomodulation. Photochem. Photobiol. 2018, 94, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karu, T.I.; Pyatibrat, L.V.; Afanasyeva, N.I. A novel mitochondrial signaling pathway activated by visible-to-near infrared radiation. Photochem. Photobiol. 2004, 80, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; Huang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Lyu, P.J.; Hamblin, M.R. Photobiomodulation of human adipose-derived stem cells using 810 nm and 980 nm lasers operates via different mechanisms of action. Bba-Gen Subj. 2017, 1861, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.Y.; Lee, M.Y.; Chung, P.S.; Kim, S.; Choi, B.; Suh, M.W.; Rhee, C.K.; Jung, J.Y. Enhanced mitochondrial membrane potential and ATP synthesis by photobiomodulation increases viability of the auditory cell line after gentamicin-induced intrinsic apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.P.; Wang, J.J.; Yu, C.L.; Lan, C.C.; Chen, G.S.; Yu, H.S. Helium-neon laser irradiation stimulates cell proliferation through photostimulatory effects in mitochondria. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.K.; Kharkwal, G.B.; Sajo, M.; Huang, Y.Y.; De Taboada, L.; McCarthy, T.; Hamblin, M.R. Dose response effects of 810 nm laser light on mouse primary cortical neurons. Lasers Surg. Med. 2011, 43, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.H.; Byun, J.H.; Heo, C.Y.; Kim, E.H.; Choi, H.Y.; Pak, C.S. Effect of Low-Level Laser Therapy on Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2015, 39, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, B.; Genova, E.; Zhang, Q.; Su, Y.; Shi, X.; Isales, C.; Eroglu, A. Photobiomodulation has rejuvenating effects on aged bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lombaert, M.C.; Rick, E.L.; Krugner-Higby, L.A.; Wolman, M.A. Behavioral Characteristics of Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio) after MS222 Anesthesia for Fin Excision. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2017, 56, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gulyás, M.; Bencsik, N.; Pusztai, S.; Liliom, H.; Schlett, K. AnimalTracker: An ImageJ-Based Tracking API to Create a Customized Behaviour Analyser Program. Neuroinformatics 2016, 14, 479–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eroglu, B.; Moskophidis, D.; Mivechi, N.F. Loss of Hsp110 leads to age-dependent tau hyperphosphorylation and early accumulation of insoluble amyloid beta. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 30, 4626–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClelland, G.B.; Craig, P.M.; Dhekney, K.; Dipardo, S. Temperature- and exercise-induced gene expression and metabolic enzyme changes in skeletal muscle of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Physiol. 2006, 577, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azbazdar, Y.; Poyraz, Y.K.; Ozalp, O.; Nazli, D.; Ipekgil, D.; Cucun, G.; Ozhan, G. High-fat diet feeding triggers a regenerative response in the adult zebrafish brain. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 2486–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadifar, E.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Moghadam, M.S.; Shahrestanaki, A.H.; Van Doan, H.; Saad, A.H.; Aboubakr, M.; Abdelhiee, E.Y.; Fadl, S.E. The effect of Pediococcus acidilactici MA 18/5M on immune responses and mRNA levels of growth, antioxidant and immune-related genes in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquac. Rep. 2020, 17, 100374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Hao, Q.; Yang, Y.; Ringo, E.; Olsen, R.E.; Clarke, J.L.; Ran, C.; et al. Propionate induces intestinal oxidative stress via Sod2 propionylation in zebrafish. iScience 2021, 24, 102515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, A.; Nguyen, X.V.; Bing, G. Comparative analysis of an improved thioflavin-s stain, Gallyas silver stain, and immunohistochemistry for neurofibrillary tangle demonstration on the same sections. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2002, 50, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, C.; Nolan, A.L.; de Paula França Resende, E.; Miller, Z.; Ehrenberg, A.J.; Gorno-Tempini, M.L.; Rosen, H.J.; Kramer, J.H.; Spina, S.; Rabinovici, G.D.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease clinical variants show distinct regional patterns of neurofibrillary tangle accumulation. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 138, 597–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, J.; Gupta, N.; Agrawal, M.; Bala Bhaskar, A.S.; Lakshmana Rao, P.V. Modulation of ROS/MAPK signaling pathways by okadaic acid leads to cell death via, mitochondrial mediated caspase-dependent mechanism. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; Carson, M.J.; El Khoury, J.; Landreth, G.E.; Brosseron, F.; Feinstein, D.L.; Jacobs, A.H.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Vitorica, J.; Ransohoff, R.M.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.S.; Paris, D.; Mathura, V.; Quadros, A.N.; Crawford, F.C.; Mullan, M.J. Inflammatory cytokine levels correlate with amyloid load in transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2005, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khemka, V.K.; Ganguly, A.; Bagchi, D.; Ghosh, A.; Bir, A.; Biswas, A.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Chakrabarti, S. Raised serum proinflammatory cytokines in Alzheimer’s disease with depression. Aging Dis. 2014, 5, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.P.-H.; Huang, J.; Chan, K.W.Y.; Leung, W.K.; Goto, T.; Ho, Y.-S.; Chang, R.C.-C. IL-1β and TNF-α play an important role in modulating the risk of periodontitis and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, P.K.; Tota, S.; Rai, S.; Swarnkar, S.; Shukla, R.; Nath, C. A study on neuroinflammatory marker in brain areas of okadaic acid (ICV) induced memory impaired rats. Life Sci. 2012, 90, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, B.; Wang, X.; Su, B.; Lee, H.G.; Casadesus, G.; Perry, G.; Zhu, X. Impaired mitochondrial biogenesis contributes to mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2012, 120, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling, J.F.; Pilegaard, H. PGC-1alpha-mediated regulation of mitochondrial function and physiological implications. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 45, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, N.G.; Wang, J.; Wilhelmsson, H.; Oldfors, A.; Rustin, P.; Lewandoski, M.; Barsh, G.S.; Clayton, D.A. Mitochondrial transcription factor A is necessary for mtDNA maintenance and embryogenesis in mice. Nat. Genet. 1998, 18, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekstrand, M.I.; Falkenberg, M.; Rantanen, A.; Park, C.B.; Gaspari, M.; Hultenby, K.; Rustin, P.; Gustafsson, C.M.; Larsson, N.G. Mitochondrial transcription factor A regulates mtDNA copy number in mammals. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Haroutunian, V.; Katsel, P.; Cardozo, C.P.; Ho, L.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Pasinetti, G.M. PGC-1alpha expression decreases in the Alzheimer disease brain as a function of dementia. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsouri, L.; Parr, C.; Bogdanovic, N.; Willem, M.; Sastre, M. PPARγ co-activator-1α (PGC-1α) reduces amyloid-β generation through a PPARγ-dependent mechanism. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 25, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Guo, M.N.; Liu, Z.Z.; Ma, S.F.; Liu, W.J.; Qian, J.J.; Zhang, W.N. PGC-1α reduces Amyloid-β deposition in Alzheimer’s disease: Effect of increased VDR expression. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 744, 135598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, J.; Drori, S.; Uldry, M.; Silvaggi, J.M.; Rhee, J.; Jäger, S.; Handschin, C.; Zheng, K.; Lin, J.; Yang, W.; et al. Suppression of reactive oxygen species and neurodegeneration by the PGC-1 transcriptional coactivators. Cell 2006, 127, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhao, Y. SIRT1/PGC-1alpha Signaling Promotes Mitochondrial Functional Recovery and Reduces Apoptosis after Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Rats. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, C.; Tremblay, C.; Emond, V.; Lebbadi, M.; Salem, N., Jr.; Bennett, D.A.; Calon, F. Sirtuin 1 reduction parallels the accumulation of tau in Alzheimer disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 68, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehpour, F.; Ahmadian, N.; Rasta, S.H.; Farhoudi, M.; Karimi, P.; Sadigh-Eteghad, S. Transcranial low-level laser therapy improves brain mitochondrial function and cognitive impairment in D-galactose-induced aging mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 58, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.S.; Wu, C.S.; Yu, C.L.; Kao, Y.H.; Chiou, M.H. Helium-neon laser irradiation stimulates migration and proliferation in melanocytes and induces repigmentation in segmental-type vitiligo. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eduardo Fde, P.; Bueno, D.F.; de Freitas, P.M.; Marques, M.M.; Passos-Bueno, M.R.; Eduardo Cde, P.; Zatz, M. Stem cell proliferation under low intensity laser irradiation: A preliminary study. Lasers Surg. Med. 2008, 40, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gendron, D.J.; Hamblin, M.R. Applications of Photobiomodulation Therapy to Musculoskeletal Disorders and Osteoarthritis with Particular Relevance to Canada. Photobiomodul. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2019, 37, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, J.C. Biological effects of polychromatic light. Photochem. Photobiol. 2002, 76, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karu, T.I.; Kolyakov, S.F. Exact action spectra for cellular responses relevant to phototherapy. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2005, 23, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderhead, R.G. Photobiological Basics of Photomedicine: A Work of Art Still in Progress. Med. Lasers 2017, 6, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Xing, D.; Zhu, D.; Chen, Q. Low-power laser irradiation inhibiting Abeta25-35-induced PC12 cell apoptosis via PKC activation. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 22, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, S.; Xing, D. Inhibition of Abeta(25-35)-induced cell apoptosis by low-power-laser-irradiation (LPLI) through promoting Akt-dependent YAP cytoplasmic translocation. Cell. Signal. 2012, 24, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Dong, T.; Li, P.; Wu, M.X. Noninvasive low-level laser therapy for thrombocytopenia. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 349ra101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shen, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhang, D.; Xing, D. Activation of PKA/SIRT1 signaling pathway by photobiomodulation therapy reduces Abeta levels in Alzheimer’s disease models. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Guttenplan, K.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Bennett, F.C.; Bohlen, C.J.; Schirmer, L.; Bennett, M.L.; Munch, A.E.; Chung, W.S.; Peterson, T.C.; et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Yoo, I.D.; Lim, J.; Moon, J.S. Pathological phenotypes of astrocytes in Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, T.; Chen, X.; Li, L.; Feng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, L.; Zhang, C.; Yao, W. Microglia induce the transformation of A1/A2 reactive astrocytes via the CXCR7/PI3K/Akt pathway in chronic post-surgical pain. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wu, C.; Parker, E.; Li, Y.; Dong, Y.; Tucker, L.; Brann, D.W.; Lin, H.W.; Zhang, Q. Non-invasive photobiomodulation treatment in an Alzheimer Disease-like transgenic rat model. Theranostics 2022, 12, 2205–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Sharma, S.K.; Carroll, J.; Hamblin, M.R. Biphasic dose response in low level light therapy—An update. Dose Response 2011, 9, 602–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, K.; Klingseisen, A.; Sieger, D.; Priller, J. Zebrafish as a model organism for neurodegenerative disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 940484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, P.K.; Tota, S.; Rai, S.; Shukla, R.; Ali, S.; Najmi, A.K.; Nath, C. Okadaic acid induced neurotoxicity leads to central cholinergic dysfunction in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 690, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekar, N.; Dwivedi, S.; Tota, S.K.; Kamat, P.K.; Hanif, K.; Nath, C.; Shukla, R. Neuroprotective effect of curcumin on okadaic acid induced memory impairment in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 715, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, N.; Lu, W.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Lou, Y.; Kong, J. Vitamin D Attenuates Alzheimer-like Pathology Induced by Okadaic Acid. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, K.A.; Oyler, G.A.; Doolittle, G.M.; Vincent, I.; Lehman, R.A.; Kincaid, R.L.; Billingsley, M.L. Okadaic acid induces hyperphosphorylated forms of tau protein in human brain slices. Ann. Neurol. 1993, 33, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, P.K.; Rai, S.; Swarnkar, S.; Shukla, R.; Nath, C. Molecular and cellular mechanism of okadaic acid (OKA)-induced neurotoxicity: A novel tool for Alzheimer’s disease therapeutic application. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 50, 852–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, D.; Shah, Z.A.; Hensley, K.; Williams, F.E. Lanthionine ketimine-5-ethyl ester provides neuroprotection in a zebrafish model of okadaic acid-induced Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Int. 2018, 115, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topal, A.; Oğuş, H.; Sulukan, E.; Comaklı, S.; Ceyhun, S.B. Okadaic acid enhances NfKB, TLR-4, caspase 3, ERK ½, c-FOS, and 8-OHdG signaling pathways activation in brain tissues of zebrafish larvae. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 149, 109529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizil, C.; Kaslin, J.; Kroehne, V.; Brand, M. Adult neurogenesis and brain regeneration in zebrafish. Dev. Neurobiol. 2012, 72, 429–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosacak, M.I.; Papadimitriou, C.; Kizil, C. Regeneration, Plasticity, and Induced Molecular Programs in Adult Zebrafish Brain. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 769763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benn, J.; Cheng, S.; Keeling, S.; Smith, A.E.; Vaysburd, M.J.; Boken, D.; Miller, L.V.C.; Katsinelos, T.; Franco, C.; Dupre, E.; et al. Aggregate-selective removal of pathological tau by clustering-activated degraders. Science 2024, 385, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.V.C.; Papa, G.; Vaysburd, M.; Cheng, S.; Sweeney, P.W.; Smith, A.; Franco, C.; Katsinelos, T.; Huang, M.; Sanford, S.A.I.; et al. Co-opting templated aggregation to degrade pathogenic tau assemblies and improve motor function. Cell 2024, 187, 5967–5980 e5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, P.K.; Tota, S.; Shukla, R.; Ali, S.; Najmi, A.K.; Nath, C. Mitochondrial dysfunction: A crucial event in okadaic acid (ICV) induced memory impairment and apoptotic cell death in rat brain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2011, 100, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, D.; Williams, F.E. Utilizing zebrafish and okadaic acid to study Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1538–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colwill, R.M.; Raymond, M.P.; Ferreira, L.; Escudero, H. Visual discrimination learning in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav. Process. 2005, 70, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, F.E.; White, D.; Messer, W.S. A simple spatial alternation task for assessing memory function in zebrafish. Behav. Process. 2002, 58, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Name | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| PGC1α [49] | TGAGGAAAATGAGGCCAACT | AGCTTCTTCAGCAGGGAAGG |
| TFAM | CGAAAGATTGCCCAGCAGT | GTCGTTTTTCCTCCGCAAA |
| GFAP [50] | ACCCGTGACGGAGAGATCAT | GCCAGTGTCTGAGCCTCATT |
| IL1ß [51] | CGGGCAATATGAAGTCACC | GTCCACATCTCCAGCCTGA |
| RPL13a [50] | TCTGGAGGACTGTAAGAGGTATGC | AGACGCACAATCTTGAGAGCAG |
| Sirt1 [52] | CCAAACGAAAGAAACGCAAAGA | CACAGGAAACAGACACCCCAG |
| TNFα [51] | TAGAACAACCCAGCAAACTC | TCTCCTTCTTCAACATCCAA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eroglu, B.; Velez, D.; Jones, K.; Deak, F.; Eroglu, A. Amelioration of Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology in Zebrafish by Photobiomodulation. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 3121. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13123121
Eroglu B, Velez D, Jones K, Deak F, Eroglu A. Amelioration of Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology in Zebrafish by Photobiomodulation. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(12):3121. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13123121
Chicago/Turabian StyleEroglu, Binnur, Daniela Velez, Kimya Jones, Ferenc Deak, and Ali Eroglu. 2025. "Amelioration of Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology in Zebrafish by Photobiomodulation" Biomedicines 13, no. 12: 3121. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13123121
APA StyleEroglu, B., Velez, D., Jones, K., Deak, F., & Eroglu, A. (2025). Amelioration of Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology in Zebrafish by Photobiomodulation. Biomedicines, 13(12), 3121. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13123121




