Isolated Monoclonal Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells Showed Differential Therapeutic Effects on Renal Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Monoclonal Isolation and Expansion of hUSCs
2.2. Identification Surface Markers of hUSCs Using Flow Cytometry
2.3. Quantitative Expression Analysis
2.4. Animals
2.5. Renal Unilateral Ischemic Reperfusion Injury Model
2.6. Transcriptome Sequencing of hUSCs
2.7. Transcriptome Sequencing of Mouse Kidneys
2.8. Masson’s Trichrome Staining and Quantitative Analysis of Renal Fibrosis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Culture and Characterization of Monoclonal Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells
3.2. Differentiating Renal Tissue Specificity Among Human Urine-Derived Stem Cell Monoclonal Clones
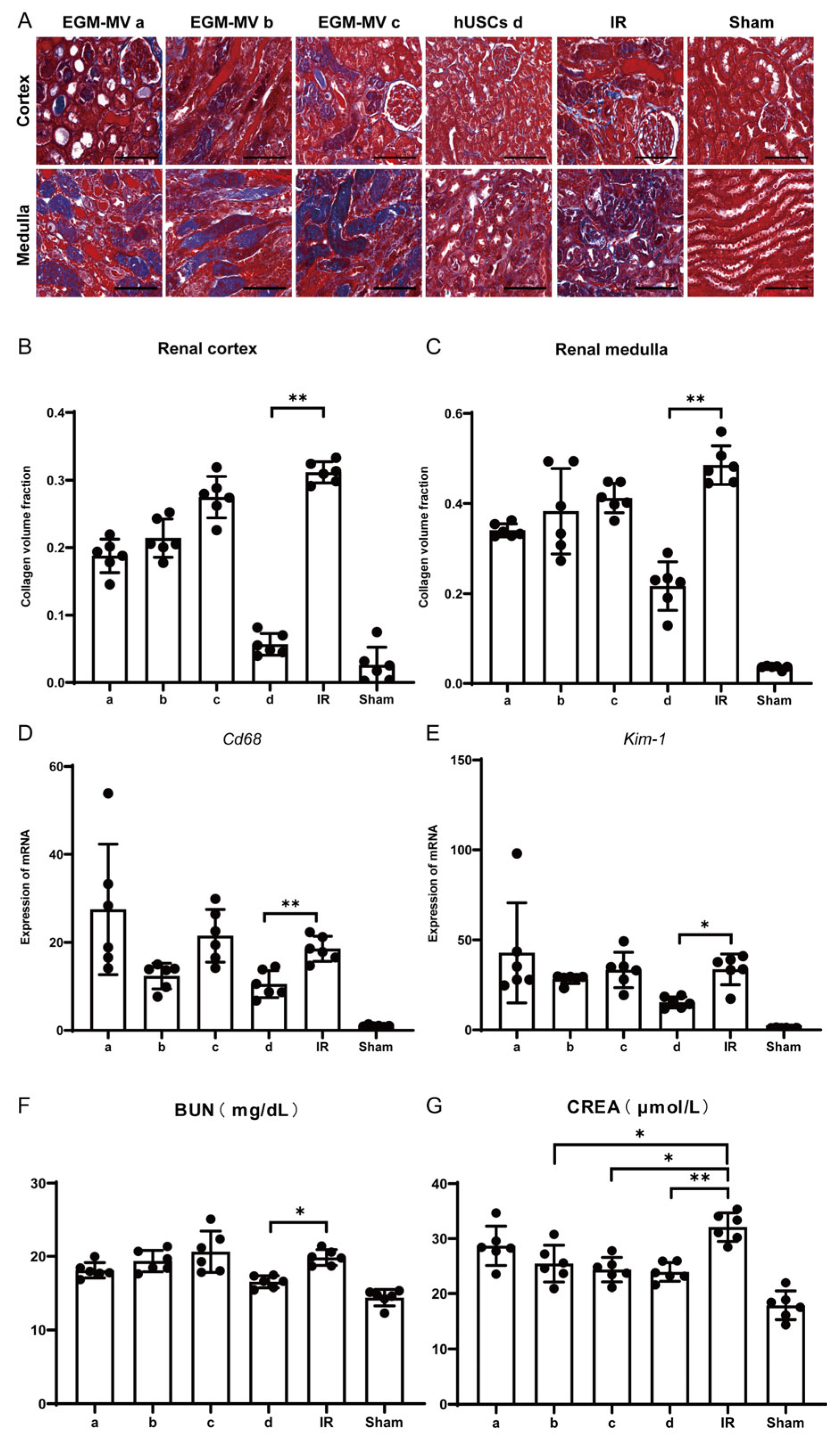
3.3. Therapeutic Efficacy of Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells on Renal Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in Mice
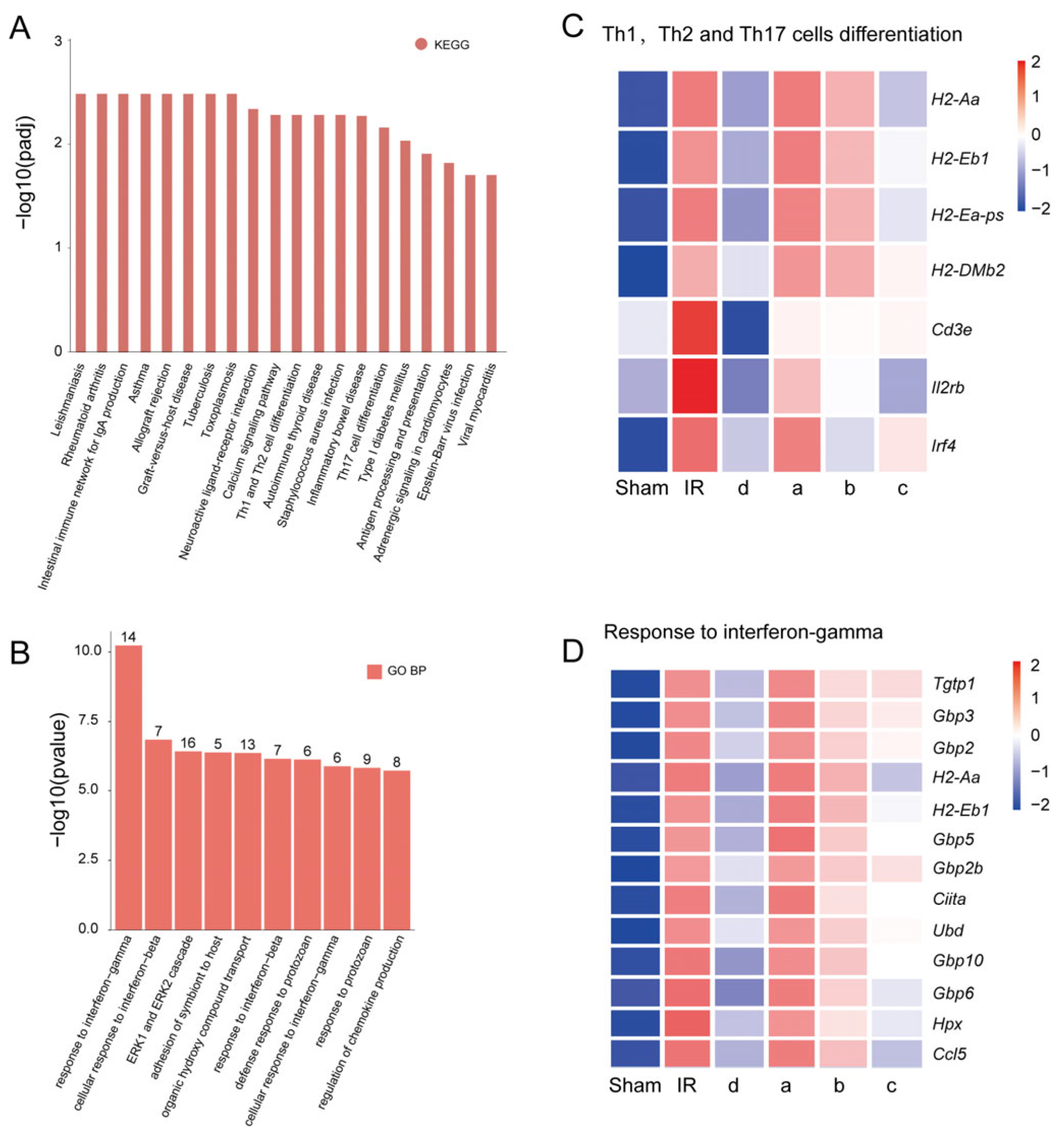
3.4. HUSC Cultured in Modified Culture Medium May Treat Renal Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury by Suppress Immune Response
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mousaei Ghasroldasht, M.; Seok, J.; Park, H.-S.; Liakath Ali, F.B.; Al-Hendy, A. Stem Cell Therapy: From Idea to Clinical Practice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, L.F.; Wolf, E.J.; Brindle, T.; Cernich, A.; Dean, W.K.; Dearth, C.L.; Grimm, M.; Kusiak, A.; Nitkin, R.; Potter, K.; et al. The convergence of regenerative medicine and rehabilitation: Federal perspectives. npj Regen. Med. 2018, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.H.; Chen, M.L.; Guo, Q.T.; Shen, L.J.; Liu, X.; Pan, J.B.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Xu, T.; Zhang, D.Y.; Wei, G.H. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome-derived miR-874-3p targeting RIPK1/PGAM5 attenuates kidney tubular epithelial cell damage. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2023, 28, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Tan, Y.W.; Li, Y.M.; Peng, Z.Y. Exosomes Highlight Future Directions in the Treatment of Acute Kidney Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandana, J.J.; Manrique, C.; Lacko, L.A.; Chen, S. Human pluripotent-stem-cell-derived organoids for drug discovery and evaluation. Cell Stem Cell 2023, 30, 571–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Qian, C.; Song, M.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, G.; Shen, Q.; Chen, W.; Wang, A.; Shen, S.; et al. Application Prospect of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells in Organoids and Cell Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.-Y.; Qian, Z.-P.; Lan, Q.; Xu, Y.-J.; Da, J.-J.; Yu, F.-X.; Zha, Y. Human pluripotent stem cell-derived kidney organoids: Current progress and challenges. World J. Stem Cells 2024, 16, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Li, S.; Li, K.; Zhou, P.; Mussano, F. Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Extracellular Vesicles: Therapeutic Potential in Organ Transplantation. Stem Cells Int. 2024, 2024, 2043550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.S.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, B.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, G.-B.; Kwon, T.G.; Chun, S.Y. Advanced Properties of Urine Derived Stem Cells Compared to Adipose Tissue Derived Stem Cells in Terms of Cell Proliferation, Immune Modulation and Multi Differentiation. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2015, 30, 1764–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, L.; Huang, Y.Z.; Huang, Y.; Parolini, O.; Zhong, Q.; Tian, X.; Deng, L. Comparison of the Proliferation and Differentiation Potential of Human Urine-, Placenta Decidua Basalis-, and Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 7131532, Erratum in Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 1651506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.Y.; Chun, S.Y.; Ha, Y.S.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, J.; Song, P.H.; Kim, H.T.; Yoo, E.S.; Kim, B.S.; Kwon, T.G. Potency of Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells for Renal Lineage Differentiation. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2017, 14, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, L.; Chen, G.-Q.; Zhu, L.; Feng, X.-L.; Gong, M.-J.; Hu, C.-C.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Li, M.; et al. Therapeutic potential of urine-derived stem cells in renal regeneration following acute kidney injury: A comparative analysis with mesenchymal stem cells. World J. Stem Cells 2024, 16, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.W.; Chun, S.Y.; Kim, B.S.; Ha, Y.S.; Lee, J.N.; Lee, E.H.; Kim, I.Y.; You, S.; Kwon, T.G. Locally transplanted human urine-induced nephron progenitor cells contribute to renal repair in mice kidney with diabetic nephropathy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 629, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y.-H.; Pan, S.-Y.; Yang, C.-H.; Lin, S.-L. Stem cells and kidney regeneration. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2014, 113, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Han, J.; Fang, J.; Li, R. The Beneficial Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Acute Kidney Injury: A Narrative Review. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2024, 19, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzinghi, B.; Melica, M.E.; Lasagni, L.; Romagnani, P.; Lazzeri, E. Renal progenitors derived from urine for personalized diagnosis of kidney diseases. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2024, 49, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdeyron, P.; Giraud, S.; Hauet, T.; Steichen, C. Urine-derived stem/progenitor cells: A focus on their characterization and potential. World J. Stem Cells 2020, 12, 1080–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.J.; Pi, J.K.; Hu, J.G.; Huang, Y.Z.; Gao, H.W.; Li, S.F.; Li-Ling, J.; Xie, H.Q. Identification and characterization of two morphologically distinct stem cell subpopulations from human urine samples. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Sun, F.; Shen, J.; Nasser, M.I.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Yin, G.; Wang, Y.; et al. A Comprehensive Review of the Therapeutic Value of Urine-Derived Stem Cells. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 781597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejoy, J.; Welch, R.C.; Qian, E.S.; Williams, F.M.; Gibson-Corley, K.N.; Wilson, M.H.; Paragas, N.; Woodard, L.E. Urine-derived stem cells display homing, incorporation, and regeneration in human organoid and mouse models of acute kidney injury. Mol. Ther. 2025, 33, 3307–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimann, J.G.; Riella, M.C.; Levin, N.W. International Society of Nephrology’s 0by25 initiative (zero preventable deaths from acute kidney injury by 2025): Focus on diagnosis of acute kidney injury in low-income countries. Clin. Kidney J. 2018, 11, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipponnet, C.; Aniort, J.; Garrouste, C.; Kemeny, J.-L.; Heng, A.-E. Ischemia reperfusion injury in kidney transplantation. Medicine 2018, 97, e13650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannon, R.B. Acute Kidney Injury in Kidney Transplants: New Insights. Nephron 2019, 143, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sávio-Silva, C.; Soinski-Sousa, P.E.; Balby-Rocha, M.T.A.; Lira, Á.d.O.; Rangel, É.B. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in acute kidney injury (AKI): Review and perspectives. Rev. Assoc. Médica Bras. 2020, 66, s45–s54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.-Y.; Wang, B.; Tang, T.-T.; Wen, Y.; Li, Z.-L.; Feng, S.-T.; Wu, M.; Liu, D.; Yin, D.; Ma, K.-L.; et al. Exosomal miR-125b-5p deriving from mesenchymal stem cells promotes tubular repair by suppression of p53 in ischemic acute kidney injury. Theranostics 2021, 11, 5248–5266, Erratum in Theranostics 2024, 14, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, H.; Abolmaali, S.S.; Heidari, R.; Valizadeh, H.; Tamaddon, A.M.; Azarpira, N. Integrin receptor-binding nanofibrous peptide hydrogel for combined mesenchymal stem cell therapy and nitric oxide delivery in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglia, M.; Merlotti, G.; Colombatto, A.; Bruno, S.; Stasi, A.; Franzin, R.; Castellano, G.; Grossini, E.; Fanelli, V.; Cantaluppi, V. Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Therapeutic Approach for Acute Kidney Injury. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 849891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhou, H.; Li, F. Role of extracellular vesicles in pathogenesis and therapy of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wu, J.; Bi, Q.; Wang, W. Exosomal lncRNA TUG1 derived from human urine-derived stem cells attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by interacting with SRSF1 to regulate ASCL4-mediated ferroptosis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcheque, J.; Bussolati, B.; Csete, M.; Perin, L. Concise Reviews: Stem Cells and Kidney Regeneration: An Update. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2019, 8, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Singh, S. Review on kidney diseases: Types, treatment and potential of stem cell therapy. Ren. Replace. Ther. 2023, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzeri, E.; Ronconi, E.; Angelotti, M.L.; Peired, A.; Mazzinghi, B.; Becherucci, F.; Conti, S.; Sansavini, G.; Sisti, A.; Ravaglia, F.; et al. Human Urine-Derived Renal Progenitors for Personalized Modeling of Genetic Kidney Disorders. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1961–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.F.; Jiang, Z.Z.; Liu, Y.M.; Niu, X.; Hu, B.; Guo, S.C.; Wang, N.S.; Wang, Y. Human urine-derived stem cells contribute to the repair of ischemic acute kidney injury in rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 5541–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavathuparambil Abdul Manaph, N.; Al-Hawwas, M.; Bobrovskaya, L.; Coates, P.T.; Zhou, X.F. Urine-derived cells for human cell therapy. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 189, Erratum in Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, G.; Zhu, L.; Sun, C.; An, Y. Urine-derived stem cells: Promising advancements and applications in regenerative medicine and beyond. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Lun, L.D.; Huang, Q.; Ning, Y.C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.N.; Yin, Z.W.; Zhang, Y.P.; Xia, L.H.; Yin, Z.; et al. Youthful systemic milieu alleviates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in elderly mice. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.S.; Koo, T.Y.; Lee, J.G.; Jang, J.Y.; Xu, Y.X.; Hwang, J.H.; Park, S.; Yan, J.J.; Ryu, J.H.; Ryu, Y.M.; et al. Anti-CD45RB Antibody Therapy Attenuates Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Inducing Regulatory B Cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 1870–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.T.; Shimbo, T.; Wijaya, E.; Ouchi, Y.; Takaki, E.; Yamamoto, R.; Kikuchi, Y.; Kaneda, Y.; Tamai, K. Chromatin accessibility identifies diversity in mesenchymal stem cells from different tissue origins. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, Z.; Lin, Y.Y.; Cheng, W.F.; Wang, X.Y.; Chen, Z.W.; Jiang, X.Y.; Li, S.B.; Zhang, X.C.; Yan, L.F.; Lin, X.; et al. Human urine-derived stem cells from different donor sources ameliorate diabetic nephropathy in mice by activating autophagy and restoring mitochondrial function of podocyte. Life Sci. 2025, 378, 123831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Ding, B.; Wan, M.; Chen, L.; Jackson, J.; Atala, A. Formation and optimization of three-dimensional organoids generated from urine-derived stem cells for renal function in vitro. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Jin, J.A.; So, H.J.; Lee, J.U.; Ji, M.J.; Kwon, E.J.; Han, P.S.; Lee, H.K.; Kang, T.W. In vivo safety and biodistribution profile of Klotho-enhanced human urine-derived stem cells for clinical application. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2023, 14, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huo, G.; Geng, J.; Liu, X.; Huang, G.; Xu, A. Isolated Monoclonal Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells Showed Differential Therapeutic Effects on Renal Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in Mice. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2911. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13122911
Huo G, Geng J, Liu X, Huang G, Xu A. Isolated Monoclonal Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells Showed Differential Therapeutic Effects on Renal Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in Mice. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(12):2911. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13122911
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuo, Guiyang, Jie Geng, Xuanhe Liu, Guangrui Huang, and Anlong Xu. 2025. "Isolated Monoclonal Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells Showed Differential Therapeutic Effects on Renal Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in Mice" Biomedicines 13, no. 12: 2911. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13122911
APA StyleHuo, G., Geng, J., Liu, X., Huang, G., & Xu, A. (2025). Isolated Monoclonal Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells Showed Differential Therapeutic Effects on Renal Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in Mice. Biomedicines, 13(12), 2911. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13122911




