Synaptic Changes in Mice Lacking Alpha- and Gamma-Synucleins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
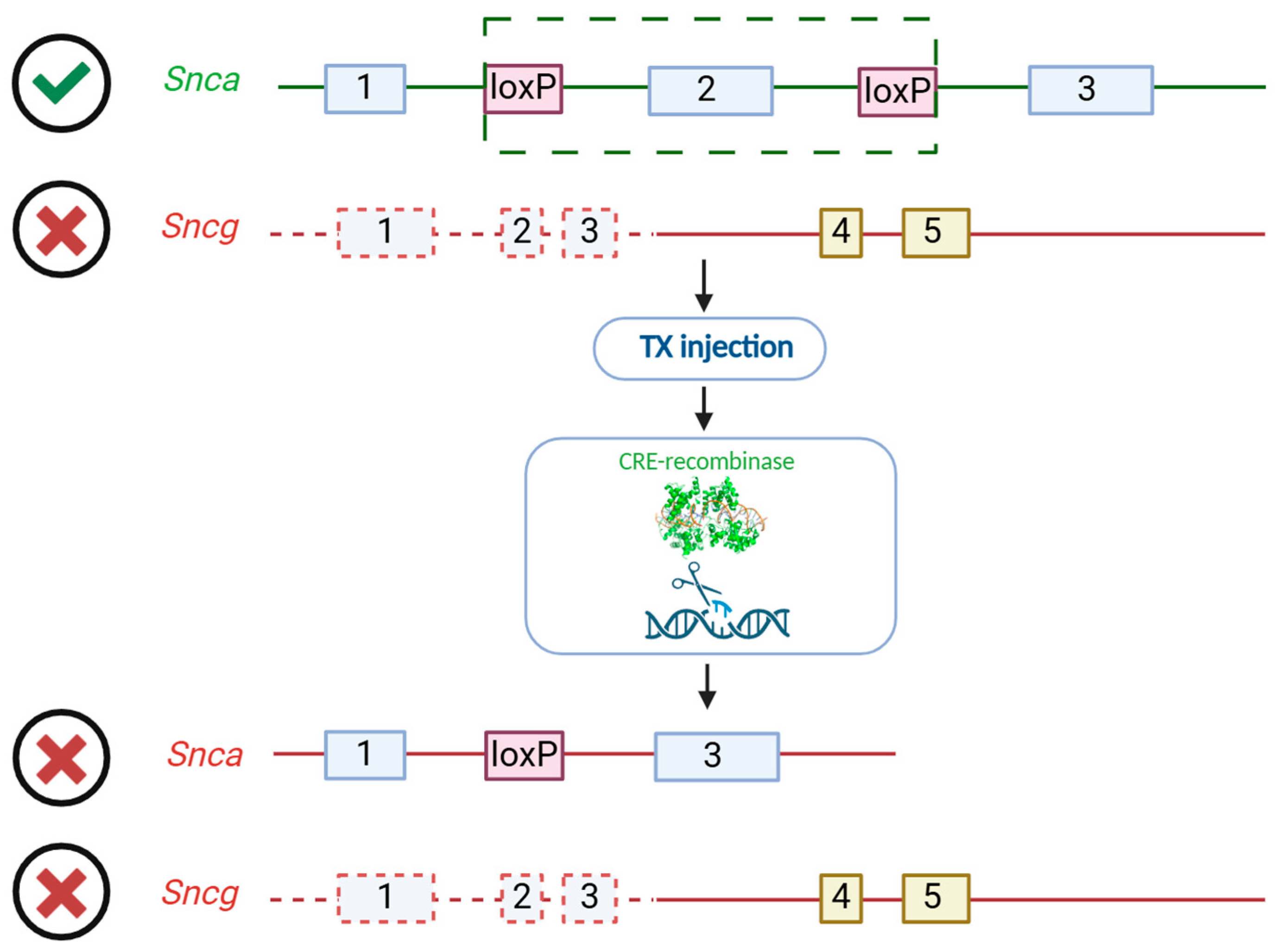
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Genotyping
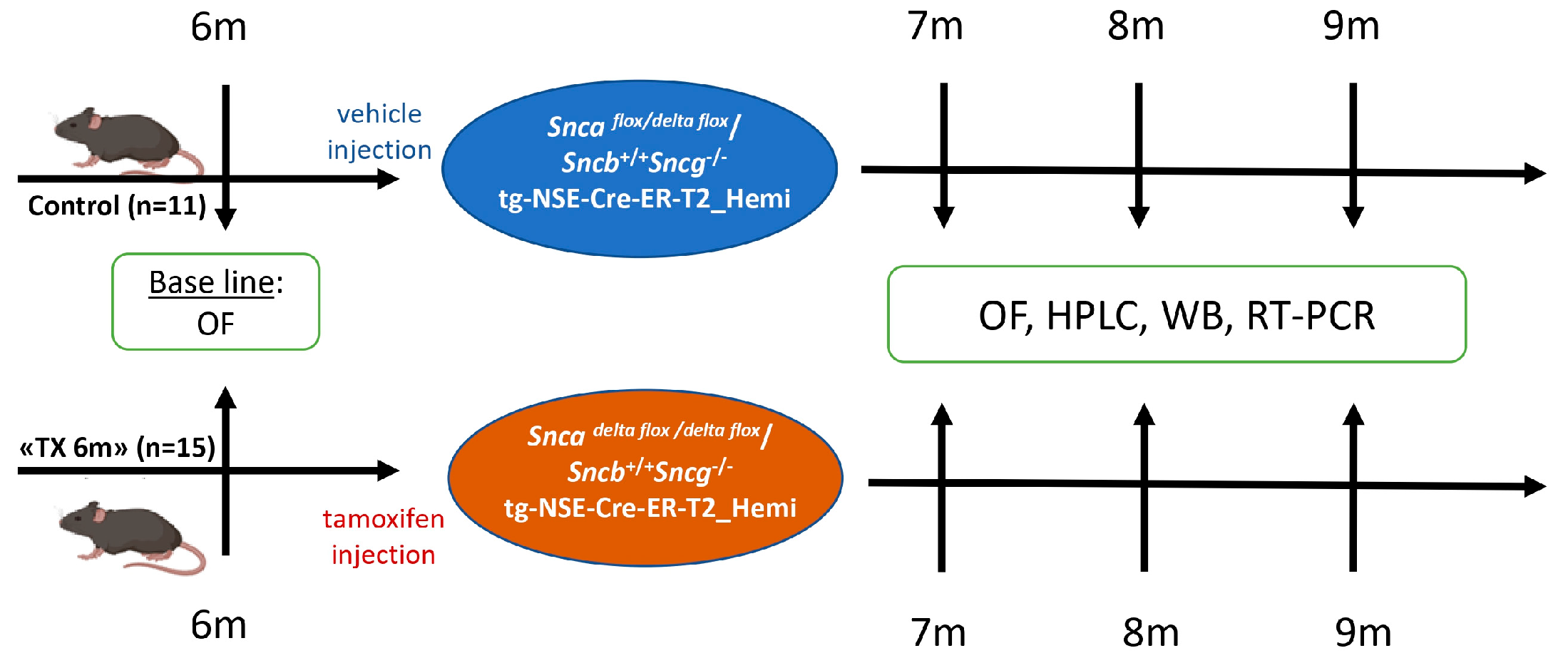
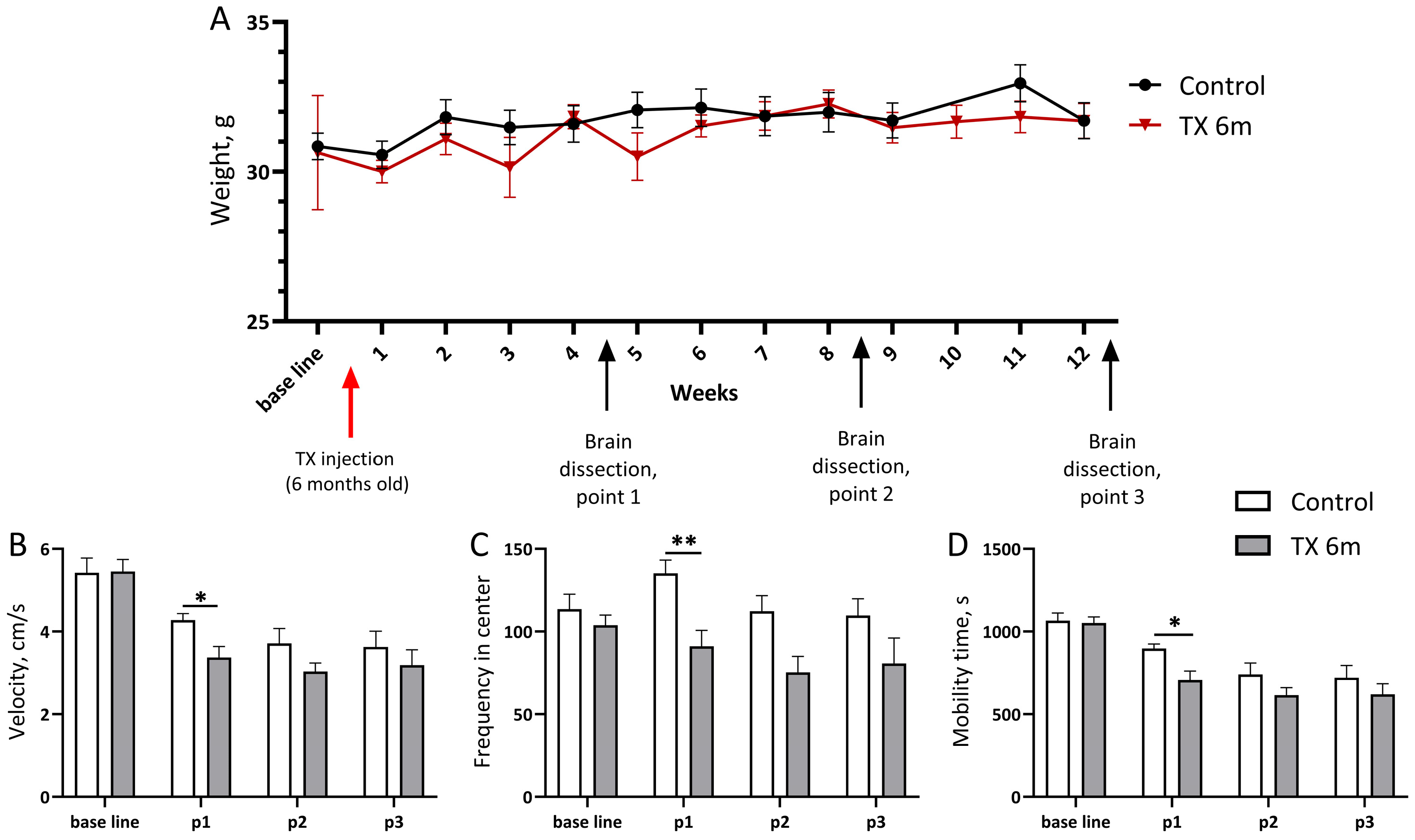
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Open Field Test
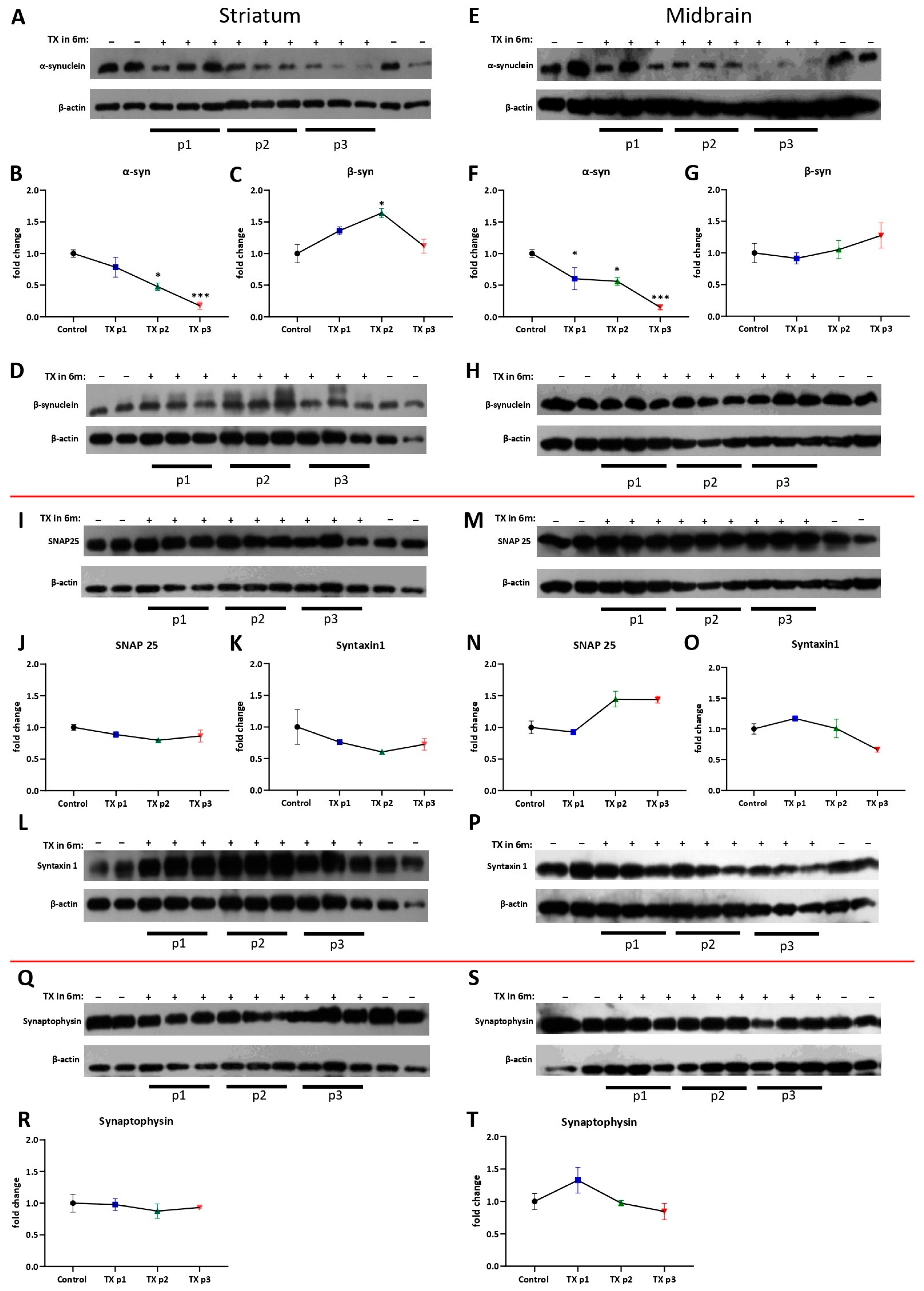
2.5. Protein Level Assay
Primary and Secondary Antibodies
2.6. Striatal Neurochemical Analysis by High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.7. Analysis of Gene Expression
2.8. Statistics
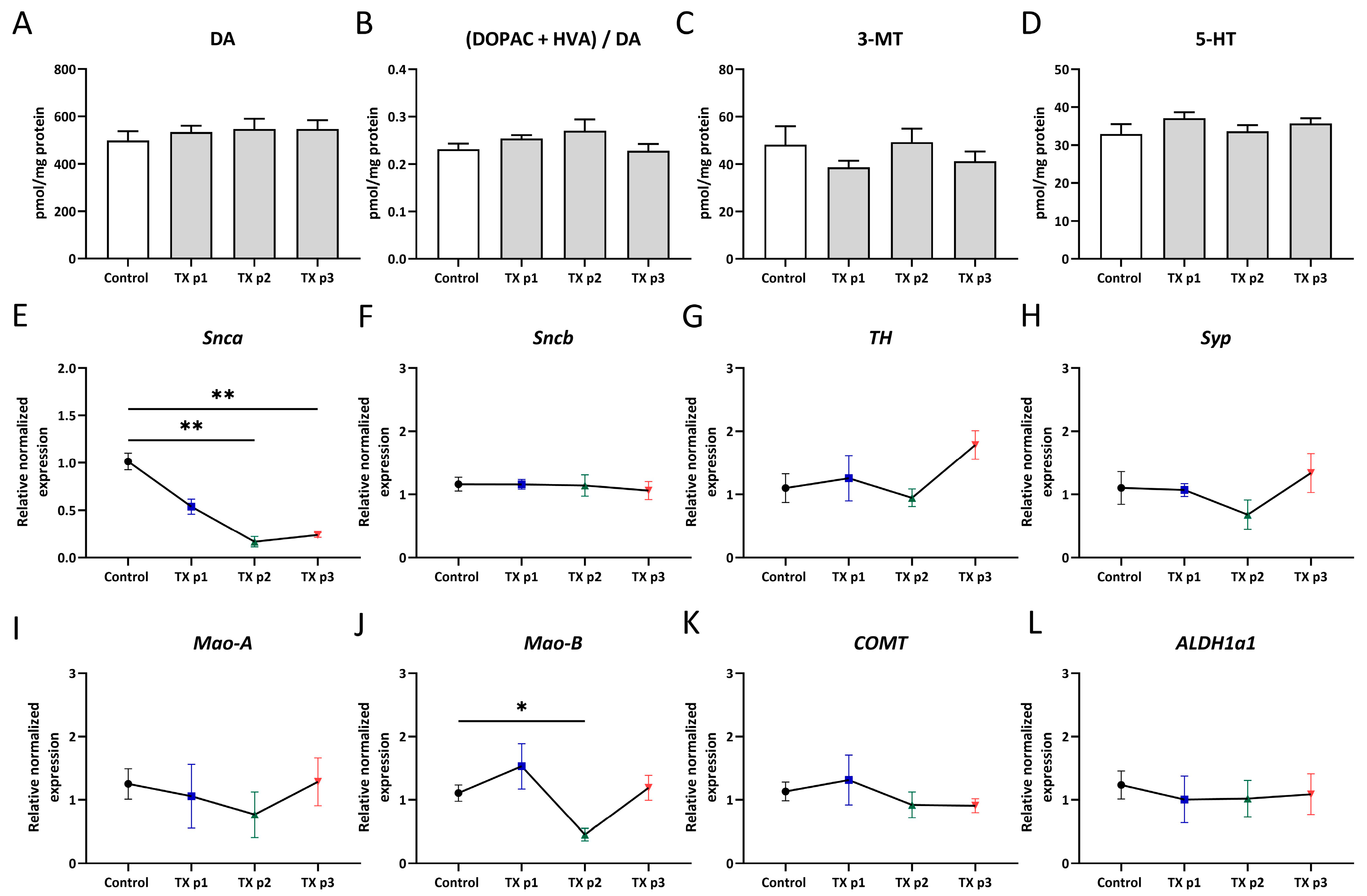
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PD | Parkinson disease |
| DA | dopamine |
| DA neurons | dopaminergic neurons |
| SN | substantia nigra |
| PFC | prefrontal cortex |
| VTA | ventral tegmental area |
| TH | tyrosine hydroxylase |
| L-DOPA | L-dihydroxyphenylalanine |
| AADC | aromatic amino acid decarboxylase |
| DAT | dopamine transporter |
| VMAT-2 | vesicular monoamine transporter 2 |
| Mao-A | monoamine oxidase-A |
| Mao-B | monoamine oxidase-B |
| ALDH | aldehyde dehydrogenase |
| GAPDH | glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| COMT | catechol-o-methyltransferase |
| HVA | homovanilic acid |
| DHBA | 3,4-dihydroxybenzylamine |
| DOPAL | 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde |
| DOPAC | 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid |
| 3-MT | 3-methoxytyramine |
| 5-HT | 5-hydroxytryptamine or serotonin |
| SNARE | soluble NSF attachment receptor |
| VAMP | vesicle-associated membrane protein |
| SNAP-25 | synaptosomal-associated protein, 25-kD |
| tSNAREs | target plasma membrane SNARE proteins |
| vSNAREs | vesicle membrane SNARE proteins |
| CSPα | cysteine string protein |
| NSE | neuro-specific enolase |
| ER-T2 | estrogen receptor T2 |
| OF | open field test |
| HPLC | high-performance liquid chromatography |
| WB | Western blotting |
| RT-PCR | real-time PCR |
| KO | knockout |
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
References
- Jankovic, J.; Tan, E.K. Parkinson’s Disease: Etiopathogenesis and Treatment. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.-S.; Liu, S.C.-H.; Wu, R.-M. Alpha-Synuclein and Cognitive Decline in Parkinson Disease. Life 2021, 11, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poewe, W.; Seppi, K.; Tanner, C.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Brundin, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schrag, A.-E.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson Disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Okun, M.S. Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson Disease: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virameteekul, S.; Revesz, T.; Jaunmuktane, Z.; Warner, T.T.; De Pablo-Fernández, E. Clinical Diagnostic Accuracy of Parkinson’s Disease: Where Do We Stand? Mov. Disord. 2023, 38, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overk, C.R.; Masliah, E. Pathogenesis of synaptic degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and lewy body disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 88, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellucci, A.; Zaltieri, M.; Navarria, L.; Grigoletto, J.; Missale, C.; Spano, P. From α-Synuclein to Synaptic Dysfunctions: New Insights into the Pathophysiology of Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Res. 2012, 1476, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, X.Y.; Cao, M. Dysfunction of Synaptic Endocytic Trafficking in Parkinson’s Disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 19, 2649–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagraoui, A.; Di Giovanni, G.; De Deurwaerdère, P. Neurobiological and Pharmacological Perspectives of D3 Receptors in Parkinson’s Disease. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gock, N.; Follett, J.; Rintoul, G.L.; Beischlag, T.V.; Lee, F.J.S. Endosomal Recycling and Dopamine Neurotransmission: Exploring the Links between the Retromer and Parkinson’s Disease. Synapse 2022, 76, e22224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.A.; Miller, D.R.; Annarumma, S.; Rusch, C.T.; Ramirez-Zamora, A.; Khoshbouei, H. Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia: A Historical Review of Parkinson’s Disease, Dopamine, and Modern Advancements in Research and Treatment. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 2892–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, S.; Peters, O.; Millership, S.; Ninkina, N.; Doig, N.; Connor-Robson, N.; Threlfell, S.; Kooner, G.; Deacon, R.M.; Bannerman, D.M.; et al. Functional Alterations to the Nigrostriatal System in Mice Lacking All Three Members of the Synuclein Family. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 7264–7274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabresi, P.; Picconi, B.; Tozzi, A.; Di Filippo, M. Dopamine-Mediated Regulation of Corticostriatal Synaptic Plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinta, S.J.; Andersen, J.K. Dopaminergic Neurons. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2005, 37, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.U.S.; Meli, N.; Blaess, S. The Development of the Mesoprefrontal Dopaminergic System in Health and Disease. Front. Neural Circuits 2021, 15, 746582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaro, A.; Huber, R.; Panksepp, J. Behavioral Functions of the Mesolimbic Dopaminergic System: An Affective Neuroethological Perspective. Brain Res. Rev. 2007, 56, 283–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzschentke, T.M. Pharmacology and Behavioral Pharmacology of the Mesocortical Dopamine System. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001, 63, 241–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, L.V.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet 2015, 386, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinoff, P.B.; Axelrod, J. Biochemistry of Catecholamines. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1971, 40, 465–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, B.; Sambo, D.; Khoshbouei, H. Alpha-Synuclein Modulates Dopamine Neurotransmission. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2017, 83–84, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Uéda, K.; Chan, P. α-Synuclein and Dopamine Metabolism. Mol. Neurobiol. 2005, 31, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninkina, N.; Millership, S.J.; Peters, O.M.; Connor-Robson, N.; Chaprov, K.; Kopylov, A.T.; Montoya, A.; Kramer, H.; Withers, D.J.; Buchman, V.L. β-Synuclein Potentiates Synaptic Vesicle Dopamine Uptake and Rescues Dopaminergic Neurons from MPTP-Induced Death in the Absence of Other Synucleins. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sulzer, D. Regulation of Striatal Dopamine Release by Presynaptic Auto- and Heteroreceptors. Basal Ganglia 2012, 2, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersch, S.M.; Yi, H.; Heilman, C.J.; Edwards, R.H.; Levey, A.I. Subcellular Localization and Molecular Topology of the Dopamine Transporter in the Striatum and Substantia Nigra. J. Comp. Neurol. 1997, 388, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, B.; Das, S.; Reith, M.E.; Kortagere, S. Overview of the Structure and Function of the Dopamine Transporter and Its Protein Interactions. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1150355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asanuma, M.; Miyazaki, I.; Murakami, S.; Diaz-Corrales, F.J.; Ogawa, N. Striatal Astrocytes Act as a Reservoir for L-DOPA. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oaks, A.W.; Sidhu, A. Synuclein Modulation of Monoamine Transporters. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiser, J.; Weindl, D.; Hiller, K. Complexity of Dopamine Metabolism. Cell Commun. Signal. 2013, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishijima, H.; Tomiyama, M. What Mechanisms Are Responsible for the Reuptake of Levodopa-Derived Dopamine in Parkinsonian Striatum? Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, F.; Gao, F.; Medvedeva, V.; Lee, P.; Bove, N.; Fleming, S.M.; Michaud, M.; Lemesre, V.; Patassini, S.; De La Rosa, K.; et al. Chronic Administration of Cholesterol Oximes in Mice Increases Transcription of Cytoprotective Genes and Improves Transcriptome Alterations Induced by Alpha-Synuclein Overexpression in Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Neurons. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 69, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, M.-H.; Sa, M.; Ju, Y.H.; Park, M.G.; Lee, C.J. Revisiting the Role of Astrocytic MAOB in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesi, M.; Santinami, A.; Ruffoli, R.; Conti, G.; Fornai, F. Novel Aspects of Dopamine Oxidative Metabolism (Confounding Outcomes Take Place of Certainties). Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2001, 89, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Männistö, P.T.; Kaakkola, S. Catechol-O-Methyltransferase (COMT): Biochemistry, Molecular Biology, Pharmacology, and Clinical Efficacy of the New Selective COMT Inhibitors. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999, 51, 593–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, V.; Sandler, M.; Owen, F.; Riley, G.J. Dopamine Is a Monoamine Oxidase B Substrate in Man. Nature 1977, 265, 80–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na An, H.; Heo, J.Y.; Lee, C.J.; Nam, M.H. The Pathological Role of Astrocytic MAOB in Parkinsonism Revealed by Genetic Ablation and Over-expression of MAOB. Exp. Neurobiol. 2021, 30, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, P.; Pintar, J.E.; Breakefield, X.O. Immunocytochemical demonstration of monoamine oxidase B in brain astrocytes and serotonergic neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 6385–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westlund, K.N.; Krakower, T.J.; Kwan, S.W.; Abell, C.W. Intracellular Distribution of Monoamine Oxidase A in Selected Regions of Rat and Monkey Brain and Spinal Cord. Brain Res. 1993, 612, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.S.; Ahn, E.H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Manfredsson, F.P.; Sandoval, I.M.; Dhakal, S.; Iuvone, P.M.; Cao, X.; Ye, K. α-Synuclein Stimulation of Monoamine Oxidase-B and Legumain Protease Mediates the Pathology of Parkinson’s Disease. EMBO J. 2018, 37, e98878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhof, T.C. The Synaptic Vesicle Cycle. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 27, 509–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khounlo, R.; Hawk, B.J.D.; Khu, T.-M.; Yoo, G.; Lee, N.K.; Pierson, J.; Shin, Y.-K. Membrane Binding of α-Synuclein Stimulates Expansion of SNARE-Dependent Fusion Pore. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 663431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, T.-Y.; Munson, M. SNARE Complex Assembly and Disassembly. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R397–R401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, M.A.; Xiao, W.; Macosko, J.C.; Chan, C.; Shin, Y.K.; Bennett, M.K. The Synaptic SNARE Complex Is a Parallel Four-Stranded Helical Bundle. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 5, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, S.; McMahon, H.T. Mechanisms of Membrane Fusion: Disparate Players and Common Principles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Su, Z.; McNew, J.A.; Shin, Y.-K. Hemifusion in SNARE-Mediated Membrane Fusion. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burré, J.; Sharma, M.; Tsetsenis, T.; Buchman, V.; Etherton, M.R.; Südhof, T.C. Alpha-Synuclein Promotes SNARE-Complex Assembly in Vivo and in Vitro. Science 2010, 329, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, L.; Bao, H.; Premi, S.; Das, U.; Chapman, E.R.; Roy, S. Functional Cooperation of α-Synuclein and VAMP2 in Synaptic Vesicle Recycling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 11113–11115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burré, J.; Sharma, M.; Südhof, T.C. α-Synuclein Assembles into Higher-Order Multimers upon Membrane Binding to Promote SNARE Complex Formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4274–E4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawk, B.J.D.; Khounlo, R.; Shin, Y.-K. Alpha-Synuclein Continues to Enhance SNARE-Dependent Vesicle Docking at Exorbitant Concentrations. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.; Kim, J.; Hawk, B.J.; Shin, Y.-K. α-Synuclein May Cross-Bridge v-SNARE and Acidic Phospholipids to Facilitate SNARE-Dependent Vesicle Docking. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 2039–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, T.; Bendor, J.; Toupin, C.; Thorn, K.; Edwards, R.H. α-Synuclein Promotes Dilation of the Exocytotic Fusion Pore. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Vivacqua, G.; Yu, S. The Role of Alpha-Synuclein in Neurotransmission and Synaptic Plasticity. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2011, 42, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.C.; Schmidt, O.; Ninkina, N.; Jones, P.A.; Sharkey, J.; Buchman, V.L. Developmental Loss and Resistance to MPTP Toxicity of Dopaminergic Neurones in Substantia Nigra Pars Compacta of Gamma-Synuclein, Alpha-Synuclein and Double Alpha/Gamma-Synuclein Null Mutant Mice. J. Neurochem. 2004, 89, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Gallardo, G.; Fernández-Chacón, R.; Schlüter, O.M.; Südhof, T.C. Alpha-Synuclein Cooperates with CSPalpha in Preventing Neurodegeneration. Cell 2005, 123, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaprov, K.D.; Lysikova, E.A.; Teterina, E.V.; Buchman, V.L. Kinetics of Alpha-Synuclein Depletion in Three Brain Regions Following Conditional Pan-Neuronal Inactivation of the Encoding Gene (Snca) by Tamoxifen-Induced Cre-Recombination in Adult Mice. Transgenic Res. 2021, 30, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninkina, N.; Tarasova, T.V.; Chaprov, K.D.; Roman, A.Y.; Kukharsky, M.S.; Kolik, L.G.; Ovchinnikov, R.; Ustyugov, A.A.; Durnev, A.D.; Buchman, V.L. Alterations in the Nigrostriatal System Following Conditional Inactivation of α-Synuclein in Neurons of Adult and Aging Mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2020, 91, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorobyov, V.; Deev, A.; Morozova, O.; Oganesyan, Z.; Krayushkina, A.M.; Ivanova, T.A.; Chaprov, K. Early Effects of Alpha-Synuclein Depletion by Pan-Neuronal Inactivation of Encoding Gene on Electroencephalogram Coherence between Different Brain Regions in Mice. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokhan, V.S.; Van’kin, G.I.; Bachurin, S.O.; Shamakina, I.Y. Differential Involvement of the Gamma-Synuclein in Cognitive Abilities on the Model of Knockout Mice. BMC Neurosci. 2013, 14, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kokhan, V.S.; Kokhan, T.Y.G.; Samsonova, A.N.; Fisenko, V.P.; Ustyugov, A.A.; Aliev, G. The Dopaminergic Dysfunction and Altered Working Memory Performance of Aging Mice Lacking Gamma-Synuclein Gene. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2018, 17, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallajosyula, J.K.; Kaur, D.; Chinta, S.J.; Rajagopalan, S.; Rane, A.; Nicholls, D.G.; Di Monte, D.A.; Macarthur, H.; Andersen, J.K. MAO-B Elevation in Mouse Brain Astrocytes Results in Parkinson’s Pathology. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeWitt, P.A. Clinical Trials of Neuroprotection in Parkinson’s Disease: Long-Term Selegiline and Alpha-Tocopherol Treatment. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 1994, 43, 171–181. [Google Scholar]
- Shoulson, I. An Interim Report of the Effect of Selegiline (L-Deprenyl) on the Progression of Disability in Early Parkinson’s Disease. The Parkinson Study Group. Eur. Neurol. 1992, 32 (Suppl. 1), 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakiuchi, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Sawai, T.; Arawaka, S. Effects of Selegiline on Neuronal Autophagy Involving α-Synuclein Secretion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 725, 150267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolato, M.; Godar, S.C.; Davarian, S.; Chen, K.; Shih, J.C. Behavioral Disinhibition and Reduced Anxiety-like Behaviors in Monoamine Oxidase B-Deficient Mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 2746–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillet, A.; Krack, P.; Lhommée, E.; Météreau, E.; Klinger, H.; Favre, E.; Le Bars, D.; Schmitt, E.; Bichon, A.; Pelissier, P.; et al. The Prominent Role of Serotonergic Degeneration in Apathy, Anxiety and Depression in de Novo Parkinson’s Disease. Brain 2016, 139 Pt 9, 2486–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, G.; Shin, Y.-K.; Lee, N.K. The Role of α-Synuclein in SNARE-Mediated Synaptic Vesicle Fusion. J. Mol. Biol. 2023, 435, 167775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene Name | Primer Name | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Snca | A_Int1For A_Int1Rev Cre_rev | 5′-TGC TGG GCA CAG TGT TGA TTG-3′ 5′-AAA GGC TGG GCT TCA AGC AG-3′ 5′-CAT GAG TAC TTG TGG CTC AC-3′ |
| Sncb | bsynUP bsynWT bsynKO | 5′AGGACACCACTGGCCCCGAGTCC-3′ 5′-GACGCACGTCCGCACGTCCACCC-3′ 5′-TGCCCCTGAAATGCTGCGCC-3′ |
| Sncg | SAUP GDN NeoB | 5′-AGT CCT GGC ACC TCT AAG CA-3′ 5′-GGG CTG ATG TGT GGC TAT CT-3′ 5′-GAA GAA CGA GAT CAG CAG CC-3′ |
| Gene Name | Gene | Direction | Primer Sequence | Product Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase | F R | CAC TGA GCA TCT CCC TCA CA GTG GGT GCA GCG AAC TTT AT | 111 |
| α-Synuclein | Alpha-synuclein | F R | CTG CCC TTG CCT CTT TCA TTG TGA ACA CAT CCA TGG CTA AAG A | 116 |
| β-Synuclein | Beta-synuclein | F R | CAA GGA AGG CGT CCT CTA TGT ATG CCT GCT CCT TGG TTT TCT | 89 |
| TH | tyrosine hydroxylase | F R | GCC TCC TCA CCT ATG CAC TC CCC AGA GAT GCA AGT CCA AT | 122 |
| Mao A | monoamine oxidase-A | F R | TCA CAG GCC ACA TGT TCG AC AAC TCT ATC CCG GGC TTC CA | 119 |
| Mao B | monoamine oxidase-B | F R | CCA CAT TGA CCA GAC AGG GG TCT TCA TGC CCA AAG CAG GT | 107 |
| COMT | catechol-o-methyltransferase | F R | ATC CCA GGA CCT TAT CCC CC GTG TCT GGA AGG TAG CGG TC | 99 |
| ALDH, A1 | aldehyde dehydrogenase | F R | GGC CTT CAC TGG ATC AAC AC GGG TGA CTC TCT TCA GAT TG | 77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krayushkina, A.M.; Morozova, O.; Khizeva, A.; Ivanova, T.A.; Ninkina, N.; Chaprov, K. Synaptic Changes in Mice Lacking Alpha- and Gamma-Synucleins. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2866. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13122866
Krayushkina AM, Morozova O, Khizeva A, Ivanova TA, Ninkina N, Chaprov K. Synaptic Changes in Mice Lacking Alpha- and Gamma-Synucleins. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(12):2866. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13122866
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrayushkina, Anastasia M., Olga Morozova, Anastasia Khizeva, Tamara A. Ivanova, Natalia Ninkina, and Kirill Chaprov. 2025. "Synaptic Changes in Mice Lacking Alpha- and Gamma-Synucleins" Biomedicines 13, no. 12: 2866. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13122866
APA StyleKrayushkina, A. M., Morozova, O., Khizeva, A., Ivanova, T. A., Ninkina, N., & Chaprov, K. (2025). Synaptic Changes in Mice Lacking Alpha- and Gamma-Synucleins. Biomedicines, 13(12), 2866. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13122866





