The Role of Posturography in the Diagnosis of Temporomandibular Disorders and Their Impact on Body Posture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
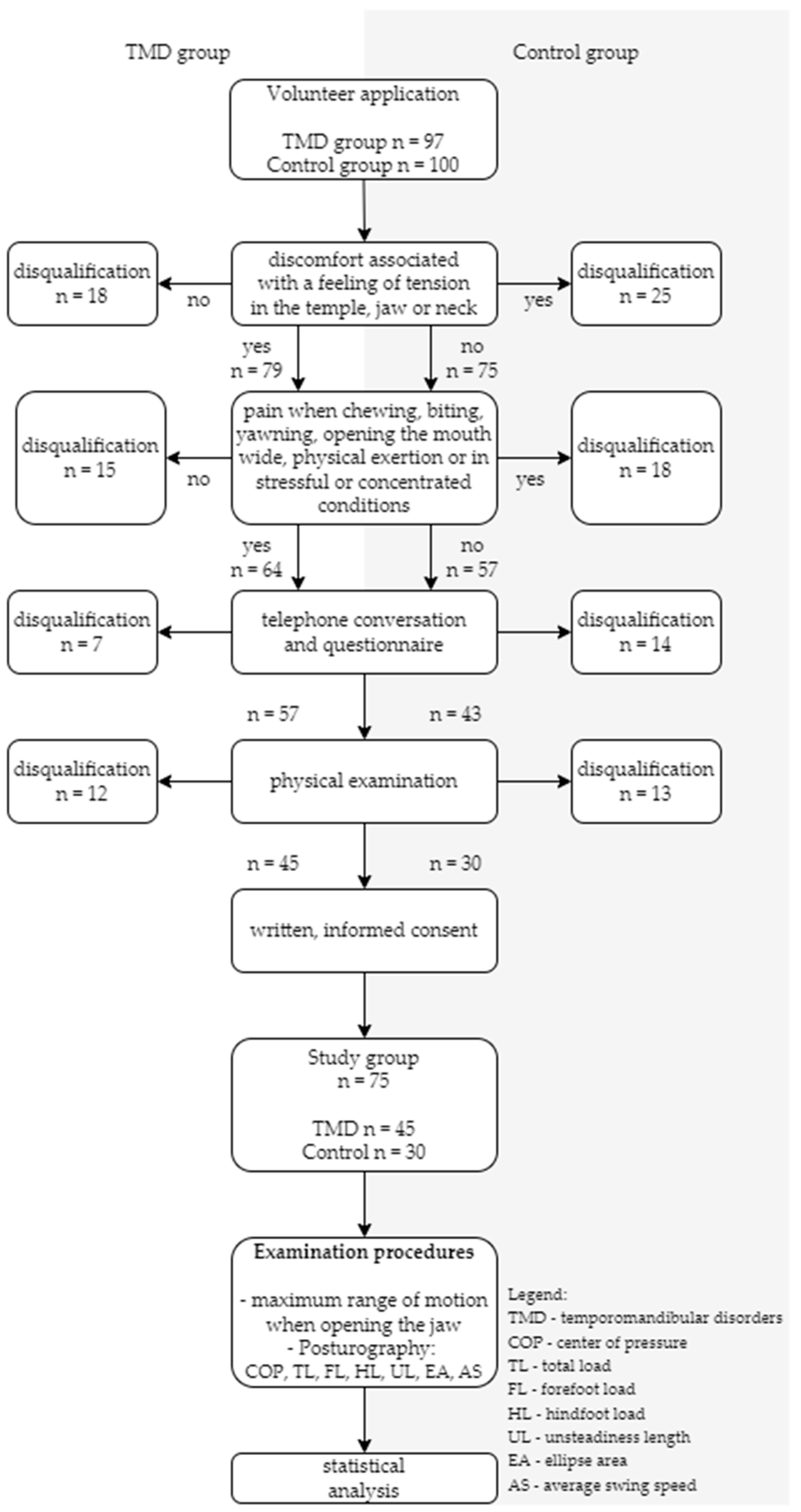
2.1. Volunteers
- Have you experienced discomfort related to tension in your temples, jaw, or neck in the last 30 days?
- Have you experienced pain during chewing, biting, yawning, opening your mouth wide, physical exertion, or under stressful or concentrated conditions in the last 30 days?
2.2. Research Procedure
2.2.1. Posturography
2.2.2. Limitation Concerning Reliability
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Group
3.2. Analysis of the Ellipse Area and Deflection Lengths
3.2.1. Ellipse Area Analysis
3.2.2. Unsteadiness Length Analysis
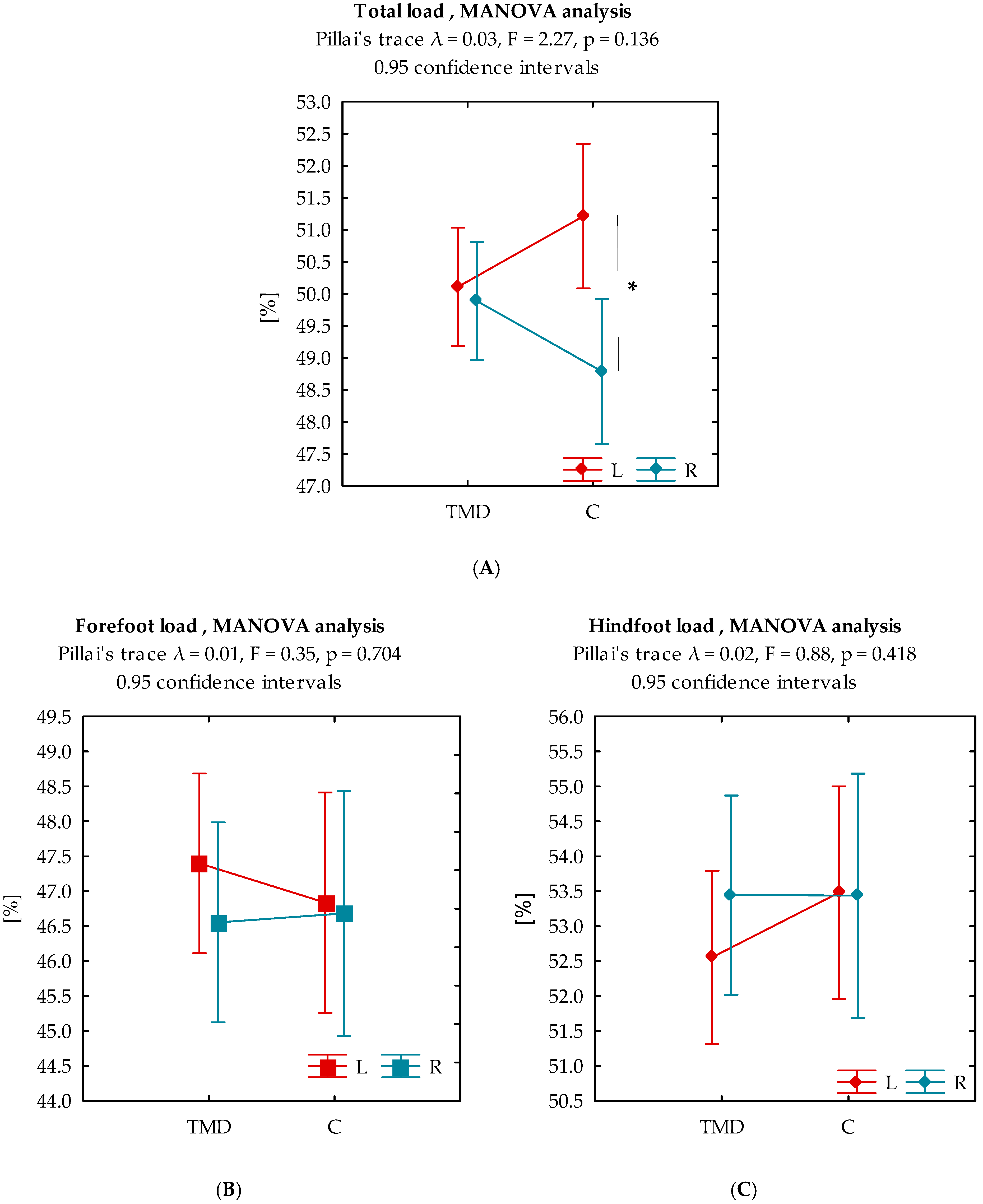
3.3. Analysis of Variance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reutimann, S.; Hill-Strathy, M.; Krewer, C.; Bergmann, J.; Müller, F.; Jahn, K.; Rauen, K. Influence of footwear on postural sway: A systematic review and meta-analysis on barefoot and shod bipedal static posturography in patients and healthy subjects. Gait Posture 2022, 92, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, J.E.; Carpenter, M.G.; van der Kooij, H.; Bloem, B.R. The clinical utility of posturography. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 2424–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, X.; Li, X.; Shi, B.; Tan, L. The preliminary study of the effects of individual musculoskeletally stable position in the treatment of temporomandibular disorders. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, M.; Freitas, S.M.S.F. Revision of posturography based on force plate for balance evaluation. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2010, 14, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlivaev, B.; Kurashvili, V.; Sinyuchkova, E.; Kuznetsov, A. The role of posturography on the initial stage of sports training. BIO Web Conf. 2020, 26, 00016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feletti, F.; Mucci, V.; Aliverti, A. Chapter 62—Posture analysis in extreme sports. In DHM and Posturography; Scataglini, S., Paul, G., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ângelo, D.F.; Faria-Teixeira, M.C.; Maffia, F.; Sanz, D.; Sarkis, M.; Marques, R.; Mota, B.; João, R.S.; Cardoso, H.J. Association of Malocclusion with Temporomandibular Disorders: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.-J.; Zhang, Q.-Q.; Zhang, F.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.-F. Biomechanical behavior of temporomandibular joint movements driven by mastication muscles. Int. J. Numer. Method Biomed. Eng. 2024, 40, e3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szyszka-Sommerfeld, L.; Sycińska-Dziarnowska, M.; Spagnuolo, G.; Woźniak, K. Surface electromyography in the assessment of masticatory muscle activity in patients with pain-related temporomandibular disorders: A systematic review. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1184036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- List, T.; Jensen, R.H. Temporomandibular disorders: Old ideas and new concepts. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffman, E.; Ohrbach, R.; Truelove, E.; Look, J.; Anderson, G.; Goulet, J.-P.; List, T.; Svensson, P.; Gonzalez, Y.; Lobbezoo, F.; et al. Diagnostic Criteria for Temporomandibular Disorders (DC/TMD) for Clinical and Research Applications: Recommendations of the International RDC/TMD Consortium Network* and Orofacial Pain Special Interest Group†. J. Oral Facial Pain Headache 2014, 28, 6–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Zhang, S.; Kan, H.; Zhang, Q. Relationship between cervical angle and temporomandibular disorders in young and middle-aged population. Cranio 2022, 42, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalçınkaya, E.; Cingi, C.; Bayar Muluk, N.; Ulusoy, S.; Hanci, D. Are temporomandibular disorders associated with habitual sleeping body posture or nasal septal deviation? Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 273, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Card, R.K.; Bordoni, B. Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Foot Muscles. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Szyszka-Sommerfeld, L.; Machoy, M.; Lipski, M.; Woźniak, K. Electromyography as a Means of Assessing Masticatory Muscle Activity in Patients with Pain-Related Temporomandibular Disorders. Pain Res. Manag. 2020, 2020, 9750915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yüzbaşıoğlu, Ü.; Kaynak, B.A.; Taş, S. Assessment of Cervical Joint Position Sense and Head Posture in Individuals With Myogenic Temporomandibular Dysfunctions and Identifying Related Factors: A Case-Control Study. J. Oral Rehabil. 2025, 52, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampe, T.; Fürstberger, L.; Kordsmeyer, T.L.; Penke, L.; Mahler, A.M.; Mäder, C.M.; Bürgers, R.; Krohn, S. Impact of occlusal stabilization splints on global body posture: A prospective clinical trial. Clin. Oral Investig. 2024, 28, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Paolo, C.; Papi, P.; Falisi, G.; Pompa, G.; Santilli, V.; Polimeni, A.; Fiorini, A. Subjects with temporomandibular joint disc displacement and body posture assessment via rasterstereography: A pilot case-control study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 8703–8712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stecco, C.; Vleeming, A.; De Caro, R. Functional Atlas of the Human Fascial System; Churchill Livingstone; Elsevier: Edinburgh, Scotland; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Day, J.A. (Ed.) Fascial Manipulation—Stecco Method: The Pratictioner’s Perspective; Handspring Publishing: Edinburgh, Scotland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nishino, L.K.; Rocha, G.D.; Souza TSAde Ribeiro Fde, A.Q.; Cóser, P.L. Protocol for static posturography with dynamic tests in individuals without vestibular complaints using the Horus system. Codas 2021, 33, e20190270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewko, J.; Kamińska, K.; Doroszkiewicz, H.; Talarska, D.; Sierakowska, M.; Krajewska-Kułak, E. The assessment of the risk of falling and functional mobility of the elderly in their living environment. Nurs. Probl. Probl. Pielęgniarstwa 2014, 22, 159–164. [Google Scholar]

| Item No. | Page No. | |
|---|---|---|
| Recommendation | ||
| Title and abstract | 1 | 1 |
| Introduction | ||
| Background/rationale | 2 | 1–2 |
| Objectives | 3 | 2 |
| Methods | ||
| Study design | 4 | 3 |
| Setting | 5 | 3–5 |
| Participants | 6 | 3–5 |
| Variables | 7 | 5–9 |
| Data sources/measurement | 8 | 3–5 |
| Bias | 9 | 4–5 |
| Study size | 10 | 5 |
| Quantitative variables | 11 | 5 |
| Statistical methods | 12 | 5 |
| Results | ||
| Participants | 13 | 3–5 |
| Descriptive data | 14 | 3–6 |
| Outcome data | 15 | 5–9 |
| Main results | 16 | 5–9 Supplementary material Table S1 |
| Other analyses | 17 | 5–10 |
| Discussion | ||
| Key results | 18 | 11 |
| Limitations | 19 | 12 |
| Interpretation | 20 | 12 |
| Generalisability | 21 | 11–12 |
| Other information | ||
| Funding | 22 | 14 |
| Study Group n = 75 ♀ = 61, ♂ = 14 | TMD n = 45 ♀ = 38, ♂ = 7 | Control Group n = 30 ♀ = 23, ♂ = 7 | TMD vs. C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD/IQR | Mean ± SD/IQR | Mean ± SD/IQR | U-M-W/Test-T | |
| age [years] | 27.00 [22.00–33.50] | 28.50 [23.00–34.75] | 26.00 [22.00–32.00] | −0.50 |
| weight [kg] | 71.00 [60.00–80.00] | 72.00 [68.25–80.00] | 68.00 [59.00–79.00] | −1.41 |
| height [m] | 1.69 [1.64–1.75] | 1.71 [1.65–1.80] | 1.69 [1.64–1.72] | −1.20 |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 24.69 [21.26–26.84] | 25.26 [22.72–26.64] | 23.44 [21.01–27.25] | −0.96 |
| MMO [cm] | 4.18 ± 0.76 | 3.98 ± 0.75 | 4.48 ± 0.70 | −2.85 ** |
| TL LF [%] | 50.55 ± 3.13 | 50.11 ± 2.63 | 51.21 ± 3.71 | −1.51 |
| TL RF [%] | 49.45 ± 3.13 | 49.89 ± 2.63 | 48.79 ± 3.71 | 1.51 |
| FL LF [%] | 47.18 ± 4.31 | 47.40 ± 4.08 | 46.84 ± 4.68 | 0.55 |
| FL RF [%] | 46.61 ± 4.78 | 46.56 ± 4.20 | 46.68 ± 5.62 | −0.11 |
| HL LF [%] | 52.93 ± 4.17 | 52.56 ± 4.05 | 53.48 ± 4.36 | −0.94 |
| HL RF [%] | 53.44 ± 4.77 | 53.44 ± 4.20 | 53.44 ± 5.59 | 0.01 |
| UL EO [mm] | 336.36 [304.39–387.56] | 328.36 [291.61–368.61] | 344.07 [317.62–404.14] | 1.47 |
| UL EC [mm] | 363.40 [308.38–427.41] | 330.86 [287.72–385.44] | 379.33 [315.40–440.63] | 1.55 |
| EA EO [mm2] | 54.82 [30.91–115.53] | 61.25 [41.80–145.92] | 47.66 [27.40–90.25] | −1.30 |
| EA EC [mm2] | 35.12 [17.64–57.19] | 38.91 [28.17–47.25] | 24.70 [15.78–59.50] | −1.09 |
| AS EO [mm/s] | 7.12 [6.54–8.28] | 6.95 [6.11–7.99] | 7.30 [6.70–8.65] | 1.53 |
| AS EC [mm/s] | 7.77 [6.62–8.87] | 7.72 [6.64–8.77] | 7.85 [6.62–8.87] | 0.21 |
| Ellipse Area | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMD | C | |||
| EO | EC | EO | EC | |
| EO | x | −2.658 ** | x | −2.129 * |
| EC | x | x | x | x |
| Unsteadiness length | ||||
| EO | EC | EO | EC | |
| EO | x | −27.947 *** | x | −20.302 *** |
| EC | x | x | x | x |
| Total Load | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMD | C | |||
| L | R | L | R | |
| L | x | −0.240 | x | −2.141 * |
| R | x | x | x | x |
| Forefoot load | ||||
| L | R | L | R | |
| L | x | −1.504 | x | −0.224 |
| R | x | x | x | x |
| Hindfoot load | ||||
| L | R | L | R | |
| L | x | 1.718 | x | −0.069 |
| R | x | x | x | x |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antczak, K.; Pluta, W.; Lubkowski, M.; Radecka, A.; Lubkowska, A. The Role of Posturography in the Diagnosis of Temporomandibular Disorders and Their Impact on Body Posture. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13122857
Antczak K, Pluta W, Lubkowski M, Radecka A, Lubkowska A. The Role of Posturography in the Diagnosis of Temporomandibular Disorders and Their Impact on Body Posture. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(12):2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13122857
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntczak, Krzysztof, Waldemar Pluta, Michał Lubkowski, Aleksandra Radecka, and Anna Lubkowska. 2025. "The Role of Posturography in the Diagnosis of Temporomandibular Disorders and Their Impact on Body Posture" Biomedicines 13, no. 12: 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13122857
APA StyleAntczak, K., Pluta, W., Lubkowski, M., Radecka, A., & Lubkowska, A. (2025). The Role of Posturography in the Diagnosis of Temporomandibular Disorders and Their Impact on Body Posture. Biomedicines, 13(12), 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13122857








