Notable Differences in Clinical Features and Inflammatory Gene Expression Between Genital Lichen Sclerosus and Lichen Planus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Patterns of LS and Lpg Are Distinct Across Age, Sex, Localization, and Comorbidities
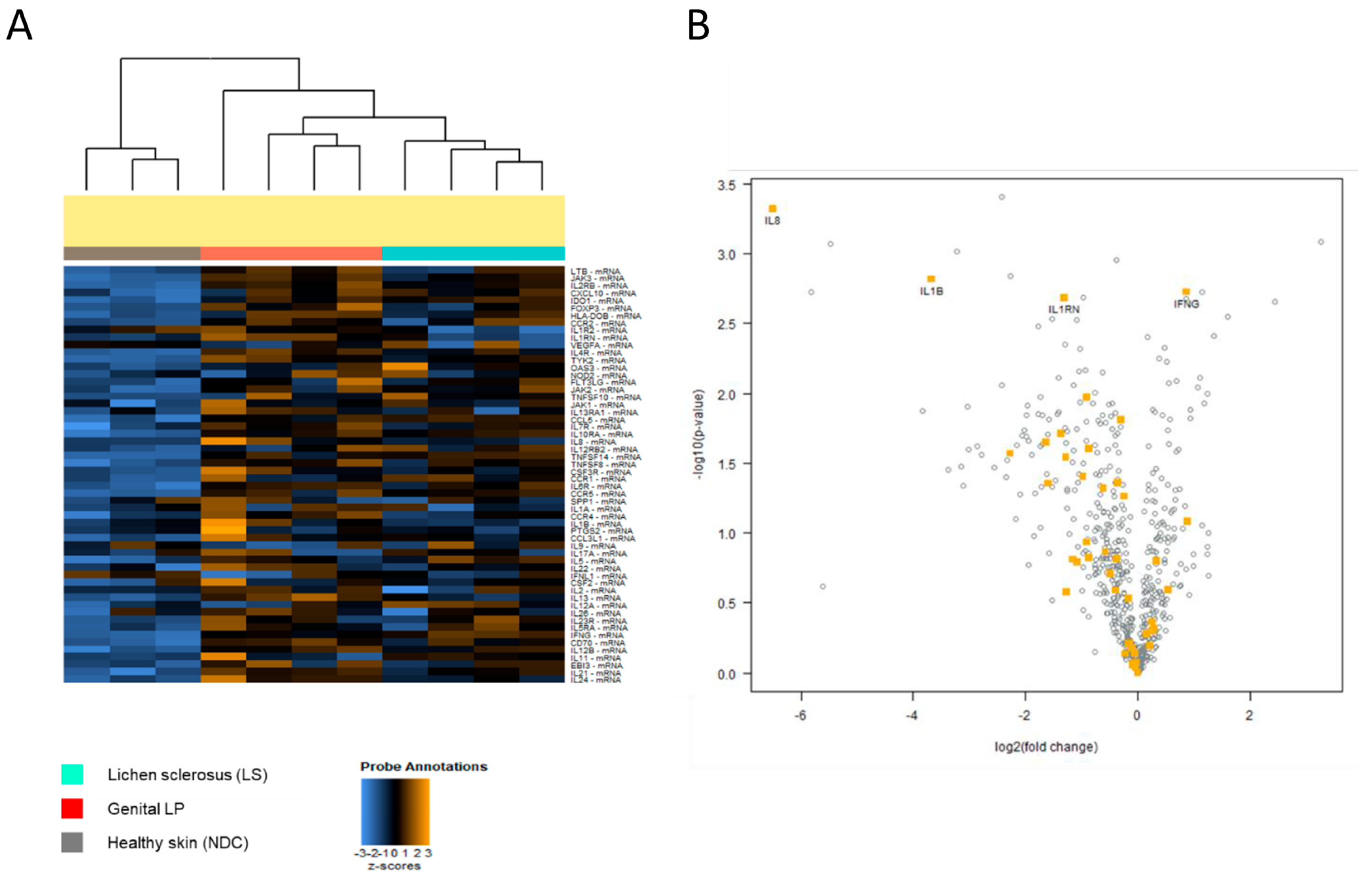
3.2. Inflammation-Related Genes Are Lower Expressed in LS Compared with Lpg
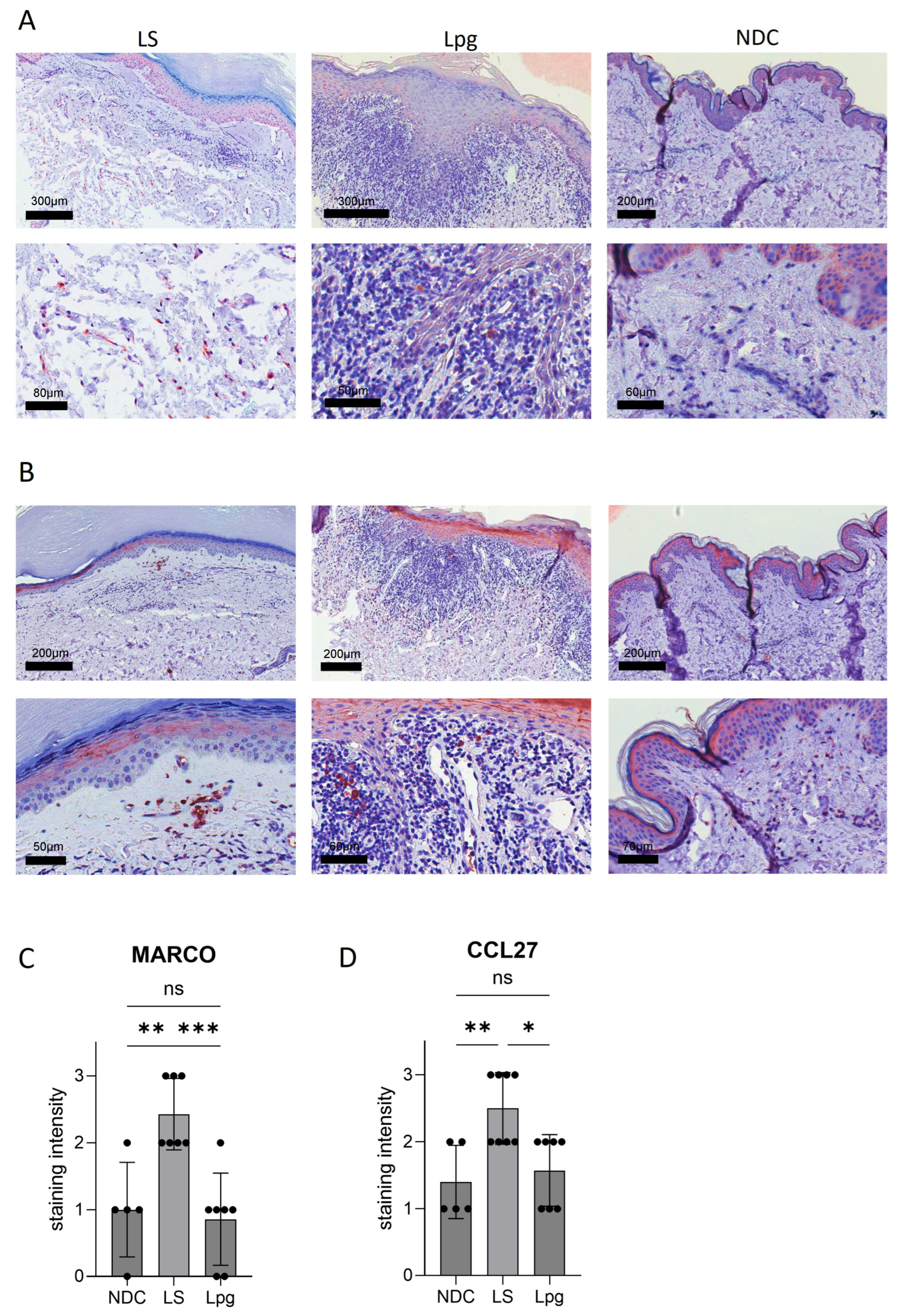
3.3. CCL27 and MARCO Are Strongly Upregulated in LS Compared with Lpg
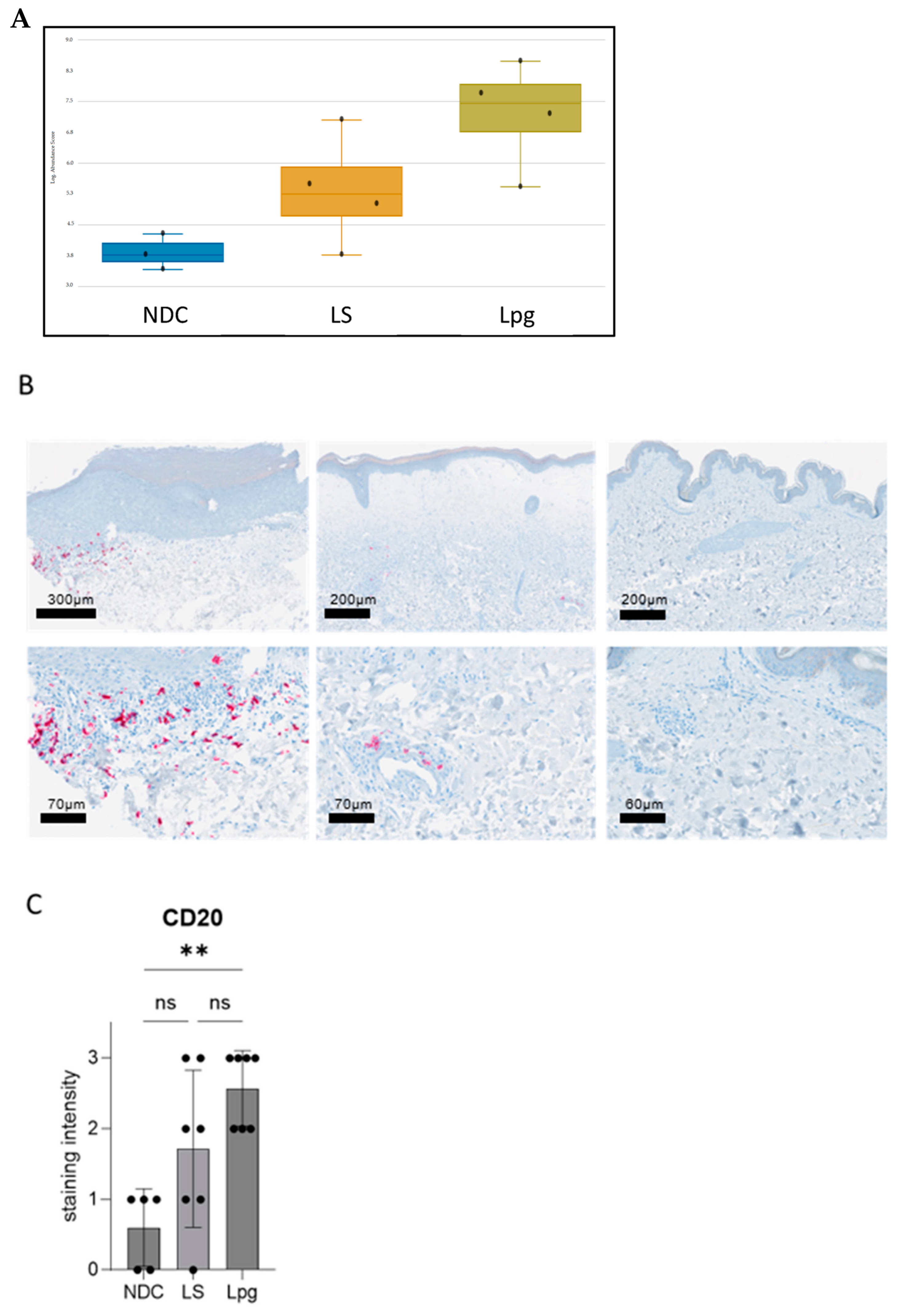
3.4. Higher Abundancy of B Cells in Lpg Compared with LS
3.5. Interleukin-1 Related-Mediated Signaling Pathway Is Specifically Upregulated in Lpg Compared with LS
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LS | Lichen sclerosus |
| Lpg | Lichen planus genitalis |
| LP | Lichen planus |
| GC | Glucocorticoids |
| NDC | Non-diseased controls |
| FFPE | Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| AEC | Aminoethyl carbazole |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IFN-γ | Interferon gamma |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| NK | Natural killer cell |
| BCR | B-cell receptor |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
References
- Kirtschig, G.; Kinberger, M.; Kreuter, A.; Simpson, R.; Gunthert, A.; van Hees, C.; Becker, K.; Ramakers, M.J.; Corazza, M.; Muller, S.; et al. EuroGuiderm guideline on lichen sclerosus—Introduction into lichen sclerosus. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38, 1850–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R. Lichen sclerosus. Dermatol. Clin. 2010, 28, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, T.; Fatima, R.; Sami, M. Extragenital lichen sclerosus: A comprehensive review. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2022, 63, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solimani, F.; Forchhammer, S.; Schloegl, A.; Ghoreschi, K.; Meier, K. Lichen planus—A clinical guide. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2021, 19, 864–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, A.S.J.; Suarez, O.A. Current treatment of lichen sclerosus and stricture. World J. Urol. 2020, 38, 3061–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fergus, K.B.; Lee, A.W.; Baradaran, N.; Cohen, A.J.; Stohr, B.A.; Erickson, B.A.; Mmonu, N.A.; Breyer, B.N. Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations, and Treatment of Lichen Sclerosus: A Systematic Review. Urology 2020, 135, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlou, A.; Santegoets, L.A.; van der Meijden, W.I.; Heijmans-Antonissen, C.; Swagemakers, S.M.; van der Spek, P.J.; Ewing, P.C.; van Beurden, M.; Helmerhorst, T.J.; Blok, L.J. An autoimmune phenotype in vulvar lichen sclerosus and lichen planus: A Th1 response and high levels of microRNA-155. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tziotzios, C.; Lee, J.Y.W.; Brier, T.; Saito, R.; Hsu, C.K.; Bhargava, K.; Stefanato, C.M.; Fenton, D.A.; McGrath, J.A. Lichen planus and lichenoid dermatoses: Clinical overview and molecular basis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 79, 789–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manousaridis, I.; Manousaridis, K.; Peitsch, W.K.; Schneider, S.W. Individualizing treatment and choice of medication in lichen planus: A step by step approach. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2013, 11, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, L.; Vogt, T. Lichen ruber planus: Better understanding, better treatment! Hautarzt 2018, 69, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshman, G. Lichen planus. Australas. J. Dermatol. 1998, 39, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Schiesser, B.; Zecha, C.; Zierold, S.; Kolm, I.; Rockel, M.; Frohlich, W.; Mittag, N.; Schmitt, C.; Kumbrink, J.; Hassel, J.C.; et al. Checkpoint inhibitor-induced lichen planus differs from spontaneous lichen planus on the clinical, histological, and gene expression level. JAAD Int. 2024, 15, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Bailey, A.; Kuleshov, M.V.; Clarke, D.J.B.; Evangelista, J.E.; Jenkins, S.L.; Lachmann, A.; Wojciechowicz, M.L.; Kropiwnicki, E.; Jagodnik, K.M.; et al. Gene Set Knowledge Discovery with Enrichr. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.Y.; Tan, C.M.; Kou, Y.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Meirelles, G.V.; Clark, N.R.; Ma’ayan, A. Enrichr: Interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W90–W97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noubiap, J.J.; Nansseu, J.R.; Lontchi-Yimagou, E.; Nkeck, J.R.; Nyaga, U.F.; Ngouo, A.T.; Tounouga, D.N.; Tianyi, F.L.; Foka, A.J.; Ndoadoumgue, A.L.; et al. Geographic distribution of metabolic syndrome and its components in the general adult population: A meta-analysis of global data from 28 million individuals. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 188, 109924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.B.; Hashim, M.J.; King, J.K.; Govender, R.D.; Mustafa, H.; Al Kaabi, J. Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes—Global Burden of Disease and Forecasted Trends. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, G.S.; Bynum, M.L.; Somers, E.C. Recent insights in the epidemiology of autoimmune diseases: Improved prevalence estimates and understanding of clustering of diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2009, 33, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirtschig, G.; Becker, K.; Gunthert, A.; Jasaitiene, D.; Cooper, S.; Chi, C.C.; Kreuter, A.; Rall, K.K.; Aberer, W.; Riechardt, S.; et al. Evidence-based (S3) Guideline on (anogenital) Lichen sclerosus. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, e1–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.J.; Wojnarowska, F. Lichen sclerosus. Lancet 1999, 353, 1777–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Lopez, F.R.; Vieira-Baptista, P. Lichen sclerosus in women: A review. Climacteric 2017, 20, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirtschig, G. Lichen Sclerosus-Presentation, Diagnosis and Management. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2016, 113, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubath, C.; Delacretaz, A.; Glatard, A.; Vollenweider, P.; Preisig, M.; Richard-Lepouriel, H.; Hasler, R.; Gamma, F.; Solida, A.; Thonney, J.; et al. Evaluation of Cardiometabolic Risk in a Large Psychiatric Cohort and Comparison With a Population-Based Sample in Switzerland. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2020, 81, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untaaveesup, S.; Kantagowit, P.; Leelakanok, N.; Chansate, P.; Eiumtrakul, W.; Pratchyapruit, W.; Sriphrapradang, C. The Association between Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Lichen Sclerosus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Chang, J.; Yang, K. Causal Association Between Diabetes, Body Mass Index and Lichen Sclerosus: A Bidirectional Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 17, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darlenski, R.; Mihaylova, V.; Handjieva-Darlenska, T. The Link Between Obesity and the Skin. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 855573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, D.A.; Papara, C.; Vorobyev, A.; Staiger, H.; Bieber, K.; Thaci, D.; Ludwig, R.J. Lichen sclerosus: The 2023 update. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1106318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.A.; Tan, X.; Macri, C.J.; Goldstein, A.T.; Fu, S.W. Lichen Sclerosus: An autoimmunopathogenic and genomic enigma with emerging genetic and immune targets. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Kraus, C.N.; Zhao, W.; Xu, J.; Suh, S.; Nguyen, Q.; Jia, Y.; Nair, A.; Oakes, M.; Tinoco, R.; et al. Single-cell and spatial transcriptomics of vulvar lichen sclerosus reveal multi-compartmental alterations in gene expression and signaling cross-talk. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E.; Tierno, R.; Azkargorta, M.; Elortza, F.; Alkhraisat, M.H. Effect of Health Status and Heat-Induced Inactivation on the Proteomic Profile of Plasma Rich in Growth Factors Obtained from Donors with Chronic Inflammatory Skin Conditions. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhang, L.; Shao, S. The application of MARCO for immune regulation and treatment. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Suarez-Farinas, M.; Zaba, L.C.; Nograles, K.E.; Pierson, K.C.; Mitsui, H.; Pensabene, C.A.; Kzhyshkowska, J.; Krueger, J.G.; Lowes, M.A. A subpopulation of CD163-positive macrophages is classically activated in psoriasis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 2412–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, N.; Fu, Y.; Hu, S.; Xia, M.; Yang, J. CCR10 and its ligands in regulation of epithelial immunity and diseases. Protein Cell 2012, 3, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homey, B.; Alenius, H.; Muller, A.; Soto, H.; Bowman, E.P.; Yuan, W.; McEvoy, L.; Lauerma, A.I.; Assmann, T.; Bunemann, E.; et al. CCL27-CCR10 interactions regulate T cell-mediated skin inflammation. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakinuma, T.; Saeki, H.; Tsunemi, Y.; Fujita, H.; Asano, N.; Mitsui, H.; Tada, Y.; Wakugawa, M.; Watanabe, T.; Torii, H.; et al. Increased serum cutaneous T cell-attracting chemokine (CCL27) levels in patients with atopic dermatitis and psoriasis vulgaris. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangavadivel, S.; Zelle-Rieser, C.; Olivier, A.; Postert, B.; Untergasser, G.; Kern, J.; Brunner, A.; Gunsilius, E.; Biedermann, R.; Hajek, R.; et al. CCR10/CCL27 crosstalk contributes to failure of proteasome-inhibitors in multiple myeloma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 78605–78618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitschke, L.; Carsetti, R.; Ocker, B.; Kohler, G.; Lamers, M.C. CD22 is a negative regulator of B-cell receptor signalling. Curr. Biol. 1997, 7, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clay, F.E.; Cork, M.J.; Tarlow, J.K.; Blakemore, A.I.; Harrington, C.I.; Lewis, F.; Duff, G.W. Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist gene polymorphism association with lichen sclerosus. Hum. Genet. 1994, 94, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Jin, J.; Fischer, H.; Mildner, M.; Gschwandtner, M.; Mlitz, V.; Eckhart, L.; Tschachler, E. The caspase-1 inhibitor CARD18 is specifically expressed during late differentiation of keratinocytes and its expression is lost in lichen planus. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 87, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, P.R.; Kurzrock, R. Anakinra-responsive lichen planus in a woman with Erdheim-Chester disease: A therapeutic enigma. Dermatol. Online J. 2014, 20, 21241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| LS | Lpg | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 142 | 32 | |
| Age/median | 14–93/62 | 20–78/53 | 0.00386 |
| Sex | |||
| Female | 78 (55%) | 10 (31%) | 0.01550 |
| Male | 64 (45%) | 22 (69%) | 0.01550 |
| Type of LS | |||
| Genital only | 125 (88%) | 17 (53%) | 0.00001 |
| Genital + extragenital | 17 (12%) | 15 (47%) | 0.00001 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Metabolic syndrome | 71 (50%) | 7 (22%) | 0.03852 |
| Hypertension | 37 (26%) | 3 (9%) | 0.04276 |
| Diabetes mellitus type 2 | 18 (13%) | 3 (9%) | 0.60457 |
| Dyslipoproteinemia | 14 (10%) | 1 (3%) | 0.22667 |
| Autoimmune diseases | 44 (31%) | 9 (28%) | 0.67583 |
| Hepatitis B/C infection | 7 (5%) | 2 (7%) | 0.76061 |
| Gene Name | Fold Change | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| CCL27 | 9.55125 | 0.00082 |
| MARCO | 5.4807 | 0.00220 |
| CFD | 3.05171 | 0.00281 |
| CXCL14 | 2.57319 | 0.00386 |
| GZMH | 2.35832 | 0.01011 |
| MST1R | 2.2628 | 0.01177 |
| CREB5 | 2.20201 | 0.00190 |
| C6 | 2.16129 | 0.00775 |
| NT5E | 2.10345 | 0.00904 |
| C2 | 1.91899 | 0.01316 |
| SIGLEC1 | 1.91526 | 0.01515 |
| IFNG | 1.83616 | 0.00189 |
| XCL2 | 1.80402 | 0.00209 |
| ITGA2 | 1.6683 | 0.04843 |
| CD160 | 1.65957 | 0.02528 |
| HLA-G | 1.62132 | 0.00811 |
| ITGAM | 1.6146 | 0.02613 |
| MRC1 | 1.5971 | 0.04956 |
| Term Name | Directed Global Significance Score | Global Significance Score | # of Genes in Term |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cytotoxicity | 1.7082 | 1.9881 | 10 |
| Complement | 1.643 | 1.7624 | 15 |
| Antigen processing | 1.0967 | 1.2809 | 22 |
| Transporter functions | 1.0753 | 1.7324 | 22 |
| Senescence | −0.3817 | 1.1772 | 12 |
| NK cell functions | −0.6734 | 1.9272 | 31 |
| Macrophage functions | −0.7495 | 2.1201 | 15 |
| Cell functions | −1.0654 | 1.8345 | 70 |
| Leukocyte functions | −1.1671 | 2.588 | 8 |
| Microglia functions | −1.1867 | 2.0073 | 5 |
| T-cell functions | −1.2103 | 1.7363 | 70 |
| Adhesion | −1.2587 | 2.0096 | 25 |
| Cell cycle | −1.3787 | 1.5133 | 13 |
| CT antigen | −1.4201 | 1.9419 | 27 |
| Regulation | −1.4338 | 2.0148 | 155 |
| Chemokines | −1.4812 | 2.1429 | 99 |
| TNF superfamily | −1.6006 | 1.8693 | 30 |
| TLR | −1.7065 | 2.1575 | 11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poffet, P.; Baghin, V.; Fröhlich, F.; Banzola, I.; Laube, J.; Mellett, M.; Heinzerling, L.; Meier-Schiesser, B. Notable Differences in Clinical Features and Inflammatory Gene Expression Between Genital Lichen Sclerosus and Lichen Planus. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2817. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112817
Poffet P, Baghin V, Fröhlich F, Banzola I, Laube J, Mellett M, Heinzerling L, Meier-Schiesser B. Notable Differences in Clinical Features and Inflammatory Gene Expression Between Genital Lichen Sclerosus and Lichen Planus. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(11):2817. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112817
Chicago/Turabian StylePoffet, Patrick, Veronika Baghin, Fabienne Fröhlich, Irina Banzola, Julia Laube, Mark Mellett, Lucie Heinzerling, and Barbara Meier-Schiesser. 2025. "Notable Differences in Clinical Features and Inflammatory Gene Expression Between Genital Lichen Sclerosus and Lichen Planus" Biomedicines 13, no. 11: 2817. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112817
APA StylePoffet, P., Baghin, V., Fröhlich, F., Banzola, I., Laube, J., Mellett, M., Heinzerling, L., & Meier-Schiesser, B. (2025). Notable Differences in Clinical Features and Inflammatory Gene Expression Between Genital Lichen Sclerosus and Lichen Planus. Biomedicines, 13(11), 2817. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112817






