Investigation of Serum Visfatin and Chemerin Levels in Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity Patients: Their Potential Role as Clinical and Biomarkers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Ethical Approval
2.3. Sample Collection and Biochemical Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
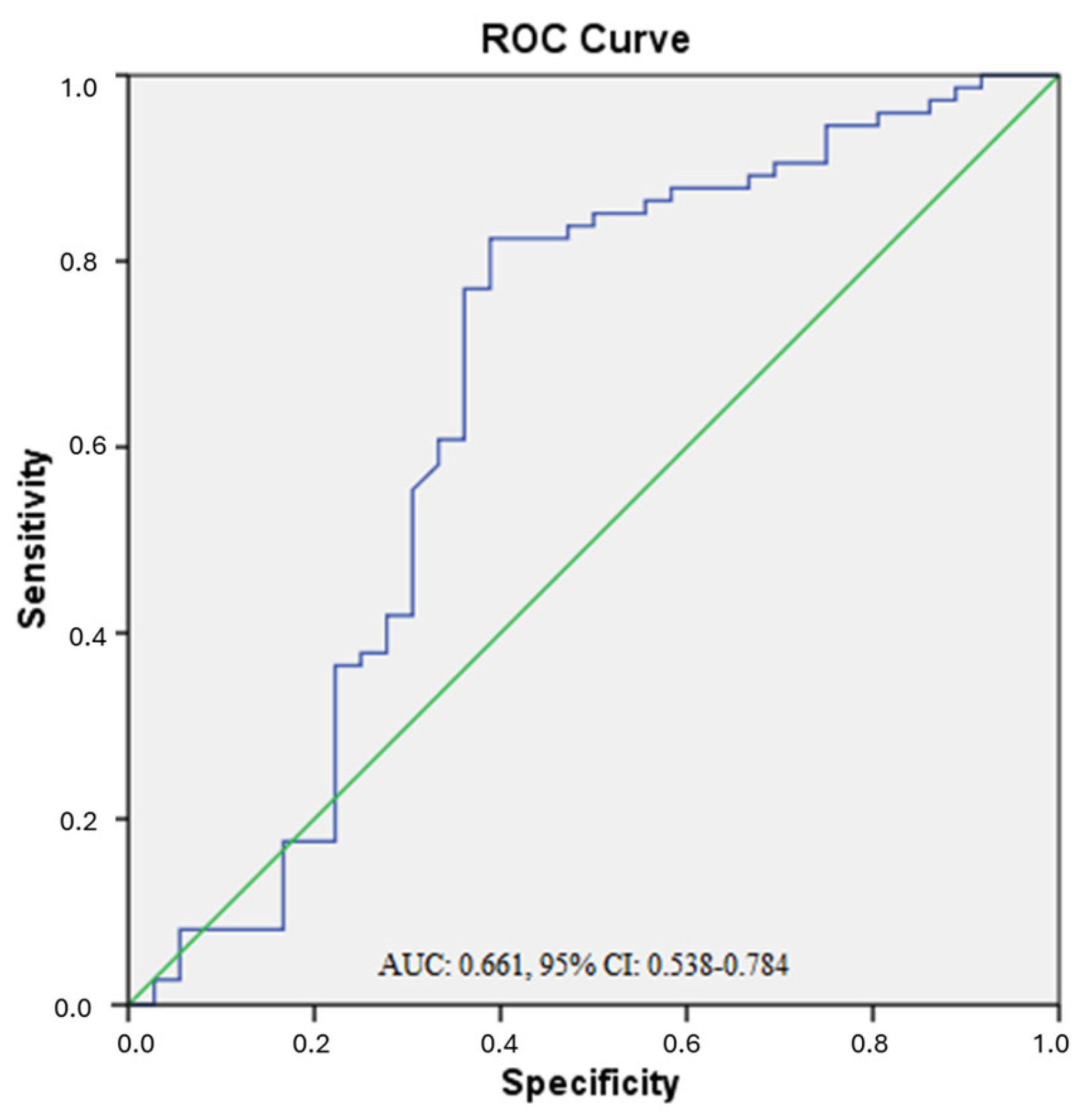
3.1. ROC Analysis
3.2. Biochemical Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADA | American Diabetes Association |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| HbA1c | Glycated hemoglobin |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance |
| NAMPT | Nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase |
| PBEF | pre-B cell colony enhancer factor |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| vWAT | Visceral white adipose tissue |
References
- Cheng, L.; Wang, J.; Dai, H.; Duan, Y.; An, Y.; Shi, L.; Lv, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Ma, Q.; et al. Brown and Beige Adipose Tissue: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Adipocyte 2021, 10, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruze, R.; Liu, T.; Zou, X.; Song, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, R.; Yin, X.; Xu, Q. Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Connections in Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Treatments. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1161521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsogiannos, P.; Kamble, P.G.; Pereira, M.J.; Sundbom, M.; Carlsson, P.O.; Eriksson, J.W.; Espes, D. Changes in Circulating Cytokines and Adipokines After RYGB in Patients with and without Type 2 Diabetes. Obesity 2021, 29, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wnuk, A.; Stangret, A.; Wątroba, M.; Płatek, A.E.; Skoda, M.; Cendrowski, K.; Sawicki, W.; Szukiewicz, D. Can Adipokine Visfatin Be a Novel Marker of Pregnancy-Related Disorders in Women with Obesity? Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e13022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-W.; Lee, M.; Oh, K.-J. Clinical Medicine Adipose Tissue-Derived Signatures for Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes: Adipokines, Batokines and MicroRNAs. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, Y.M.K.; Gaballa, M.R. Diabesity: An Overview of a Rising Epidemic. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckel, R.H.; Kahn, S.E.; Ferrannini, E.; Goldfine, A.B.; Nathan, D.M.; Schwartz, M.W.; Smith, R.J.; Smith, S.R. Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes: What Can Be Unified and What Needs to Be Individualized? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumvoll, M.; Goldstein, B.J.; Van Haeften, T.W. Type 2 Diabetes: Principles of Pathogenesis and Therapy. Lancet 2005, 365, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, A.; Hoffmann, L.S. Brown, Beige, and White: The New Color Code of Fat and Its Pharmacological Implications. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 55, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Gastaldelli, A.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Scherer, P.E. Why Does Obesity Cause Diabetes? Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, K.; Lehrke, M.; Parhofer, K.G.; Broedl, U.C. Adipokines and Insulin Resistance. Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.; Meadows, M.L.; Maxwell, L. Assessment of Salivary Adipokines Resistin, Visfatin, and Ghrelin as Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Biomarkers. Biochem. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 7463796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gennaro, G.; Palla, G.; Battini, L.; Simoncini, T.; Del Prato, S.; Bertolotto, A.; Bianchi, C. The Role of Adipokines in the Pathogenesis of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2019, 35, 737–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutaj, P.; Sibiak, R.; Jankowski, M.; Awdi, K.; Bryl, R.; Mozdziak, P.; Kempisty, B.; Wender-Ozegowska, E. The Role of the Adipokines in the Most Common Gestational Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, A.J.; Davenport, A.P.; Ohlstein, E.H. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology CIII: Chemerin Receptors CMKLR1 (Chemerin1) and GPR1 (Chemerin2) Nomenclature, Pharmacology, and Function. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 174–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekpe, L. Chemical Pathology of Chemerin and Its Link to Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 2, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, N.K. Kemerin. Gümüşhane Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilim. Derg. 2015, 4, 468–481. [Google Scholar]
- Ustebay, S.; Baykus, Y.; Deniz, R.; Ugur, K.; Yavuzkir, S.; Yardim, M.; Kalayci, M.; Çaglar, M.; Aydin, S. Chemerin and Dermcidin in Human Milk and Their Alteration in Gestational Diabetes. J. Hum. Lact. 2019, 35, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estienne, A.; Bongrani, A.; Reverchon, M.; Ramé, C.; Ducluzeau, P.-H.; Froment, P.; Dupont, J. Involvement of Novel Adipokines, Chemerin, Visfatin, Resistin and Apelin in Reproductive Functions in Normal and Pathological Conditions in Humans and Animal Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, H.; Ju, H.; Sun, M. Circulating Chemerin Levels and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulcelik, N.E.; Usman, A.; Gürlek, A. Role of Adipocytokines in Predicting the Development of Diabetes and Its Late Complications. Endocrine 2009, 36, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeghate, E. Visfatin: Structure, Function and Relation to Diabetes Mellitus and Other Dysfunctions. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 1851–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, J.; Klöting, N.; Kralisch, S.; Kovacs, P.; Fasshauer, M.; Schön, M.R.; Stumvoll, M.; Blüher, M. Plasma Visfatin Concentrations and Fat Depot-Specific mRNA Expression in Humans. Diabetes 2005, 54, 2911–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, F.; Liberale, L.; Bonaventura, A.; Vecchiè, A.; Casula, M.; Cea, M.; Monacelli, F.; Caffa, I.; Bruzzone, S.; Montecucco, F.; et al. Regulation and Function of Extracellular Nicotinamide Phosphoribosyltransferase/Visfatin. Compr. Physiol. 2017, 7, 603–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-P.; Chung, F.-M.; Chang, D.-M.; Tsai, J.C.-R.; Huang, H.-F.; Shin, S.-J.; Lee, Y.-J. Elevated Plasma Level of Visfatin/Pre-B Cell Colony-Enhancing Factor in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swets, J.A. Signal Detection Theory and ROC Analysis in Psychology and Diagnostics: Collected Papers; Psychology Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-1-315-80616-7. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, D.; Khanna, S.; Khanna, P.; Kahar, P.; Patel, B.M. Obesity: A Chronic Low-Grade Inflammation and Its Markers. Cureus 2022, 14, e22711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalla, M.M.I. Role of Visfatin in Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 10840–10851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recinella, L.; Orlando, G.; Ferrante, C.; Chiavaroli, A.; Brunetti, L.; Leone, S. Adipokines: New Potential Therapeutic Target for Obesity and Metabolic, Rheumatic, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 578966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yin, C.; Lan, X.; Wu, L.; Du, X.; Griffiths, H.R.; Gao, D. Adipokines, Hepatokines and Myokines: Focus on Their Role and Molecular Mechanisms in Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 873699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, M.A.; Tozcu, D.; Tekcan, A.; Capraz, M.; Demir, H.D. Serum Adiponectin and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors-γ Levels in Obese Patients with and without Prediabetes. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2024, 70, e20231000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Görkem, Ü.; Küçükler, F.K.; Toğrul, C.; Güngör, T. Are Adipokines Associated with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus? J. Turk. Ger. Gynecol. Assoc. 2016, 17, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnowihi, S.M.; Al Doghaither, H.A.; Osman, N.N. Serum Visfatin Concentration and Its Relationship with Sex Hormones in Obese Saudi Women. Int. J. Health Sci. 2020, 14, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hetta, H.F.; Ez-Eldeen, M.E.; Mohamed, G.A.; Gaber, M.A.; ElBadre, H.M.; Ahmed, E.A.; Abdellatief, R.B.; Abd-ElBaky, R.M.; Elkady, A.; Nafee, A.M.; et al. Visfatin Serum Levels in Obese Type 2 Diabetic Patients: Relation to Proinflammatory Cytokines and Insulin Resistance. Egypt. J. Immunol. 2018, 25, 141–151. [Google Scholar]
- Gul, O.O.; Cander, S.; Gul, B.; Açıkgoz, E.; Sarandol, E.; Ersoy, C. Evaluation of Insulin Resistance and Plasma Levels for Visfatin and Resistin in Obese and Non-Obese Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2015, 26, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léniz, A.; González, M.; Besné, I.; Carr-Ugarte, H.; Gómez-García, I.; Portillo, M.P. Role of Chemerin in the Control of Glucose Homeostasis. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2022, 541, 111504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.-L.; Ma, R.-M. Correlation of Serum Omentin-1 and Chemerin with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao = J. South. Med. Univ. 2016, 36, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, M.; Inomata, S.; Okimura, Y.; Iguchi, G.; Fukuoka, H.; Miyake, K.; Koga, D.; Akamatsu, S.; Kasuga, M.; Takahashi, Y. Decreased Serum Chemerin Levels in Male Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Sex Dimorphism. Endocr. J. 2013, 60, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozaoglu, K.; Segal, D.; Shields, K.A.; Cummings, N.; Curran, J.E.; Comuzzie, A.G.; Mahaney, M.C.; Rainwater, D.L.; VandeBerg, J.L.; MacCluer, J.W.; et al. Chemerin Is Associated with Metabolic Syndrome Phenotypes in a Mexican-American Population. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 3085–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Deeb, T.S.; Bakkar, S.M.; Eltoony, L.; Zakhary, M.M.; Kamel, A.A.; Nafee, A.M.; Hetta, H.F. The Adipokine Chemerin and Fetuin-A Serum Levels in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Relation to Obesity and Inflammatory Markers. Egypt. J. Immunol. 2018, 25, 191–202. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, S.S.; Eshki, A.; AlTassan, B.; Fatani, D.; Helmi, H.; AlSaif, S. Relationship of Serum Novel Adipokine Chemerin Levels with Body Composition, Insulin Resistance, Dyslipidemia and Diabesity in Saudi Women. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 1296–1302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mengliu, Y.; Gangyi, Y.; Jing, D.; Ying, L.; Haihong, Z.; Hua, L.; Boden, G.; Ling, L. Elevated Plasma Levels of Chemerin in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Hypertension. J. Investig. Med. 2010, 58, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wei, L.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, W. Relationship of serum Chemerin to obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2009, 89, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bozaoglu, K.; Bolton, K.; McMillan, J.; Zimmet, P.; Jowett, J.; Collier, G.; Walder, K.; Segal, D. Chemerin Is a Novel Adipokine Associated with Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 4687–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ademoglu, E. Higher Levels of Circulating Chemerin in Obese Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Acta Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, K.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Suh, Y.J.; Cho, S.G.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Hong, S.B.; et al. Effect of Lifestyle Modification on Serum Chemerin Concentration and Its Association with Insulin Sensitivity in Overweight and Obese Adults with Type 2 Diabetes. Clin. Endocrinol. 2014, 80, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherji, A.B.; Idowu, V.; Zhao, L.; Leung, L.L.K.; Shen, S.; Palaniappan, L.; Morser, J. Chemerin Levels in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes and a Normal Weight versus Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity: An Observational, Cross-Sectional Study. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gu, C.; Deng, M.; Yang, L.; Yang, W. Circulating Chemerin and Interleukin-6 in Children with Obesity: Possible Metabolic Risk Predictors. Transl. Pediatr. 2024, 13, 1760–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, A.A.; Parlee, S.D.; Sinal, C.J. Chemerin: A Potential Endocrine Link between Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Endocrine 2012, 42, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Controls (n: 36) | Non-Obese T2DM (n: 60) | Obese T2DM (n: 74) | p Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, F/M, (n/%) | 22/14 (61.1/38.9) | 19/41 (31.7/68.3) | 47/27 (63.5/36.5) | <0.001 |
| Age (years) | 44.47 ± 8.00 | 55.56 ± 9.67 | 54.02 ± 6.78 | 0.07 |
| Visfatin (ng/mL) | 30.25 ± 26.40 | 34.37 ± 26.48 | 33.00 ± 20.61 * | 0.01 |
| Chemerin (ng/mL) | 728.02 ± 557.95 | 690.09 ± 639.83 | 644.66 ± 591.01 | 0.42 |
| Height (cm) | 166.41 ± 10.58 | 164.93 ± 8.69 | 158.09 ± 9.31 | 0.13 |
| Weight (kg) | 68.83 ± 20.48 | 73.10 ± 11.20 | 89.71 ± 14.63 *# | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.80 ± 6.79 | 26.80 ± 2.80 | 35.96 ± 5.69 *# | <0.001 |
| Waist Circumference (cm) | 92.14 ± 10.36 | 93.93 ± 9.28 | 105.60 ± 9.44 *# | <0.001 |
| Smoking, Yes/No, (n/%) | 8/28 (22.2/77.8) | 9/51 (15.0/85.0) | 12/62 (16.2/83.8) | |
| Family History with DM, Yes/No, (n/%) | 16/10 (52.77/27.77) | 48/12 (76.66/16.66) | 62/12 (78.37/13.51) |
| Biochemical Parameters | Controls (n: 36) | Non- Obese T2DM (n: 60) | Obese T2DM (n: 74) | p Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c (%) | 5.5 ± 1.0 | 8.4 ± 1.9 * | 7.6 ± 2.3 * | <0.001 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 85.0 ± 15.7 | 192.1 ± 65.7 * | 174.8 ± 66.2 * | <0.001 |
| Biochemical Parameters | Non- Obese T2DM (n: 60) | Obese T2DM (n: 74) | p Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insulin (µIU/mL) | 8.8 ± 8.9 | 12.3 ± 11.6 † | 0.007 |
| HOMA-IR | 4.1 ± 4.2 | 5.1 ± 5.6 † | 0.029 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yilmaz, D.T.; Gul, M.A.; Capraz, M.; Demir, H.D.; Tekcan, A. Investigation of Serum Visfatin and Chemerin Levels in Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity Patients: Their Potential Role as Clinical and Biomarkers. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2619. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112619
Yilmaz DT, Gul MA, Capraz M, Demir HD, Tekcan A. Investigation of Serum Visfatin and Chemerin Levels in Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity Patients: Their Potential Role as Clinical and Biomarkers. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(11):2619. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112619
Chicago/Turabian StyleYilmaz, Duygu Tozcu, Mehmet Ali Gul, Mustafa Capraz, Hatice Dortok Demir, and Akin Tekcan. 2025. "Investigation of Serum Visfatin and Chemerin Levels in Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity Patients: Their Potential Role as Clinical and Biomarkers" Biomedicines 13, no. 11: 2619. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112619
APA StyleYilmaz, D. T., Gul, M. A., Capraz, M., Demir, H. D., & Tekcan, A. (2025). Investigation of Serum Visfatin and Chemerin Levels in Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity Patients: Their Potential Role as Clinical and Biomarkers. Biomedicines, 13(11), 2619. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112619







